-
61 Intelligence
There is no mystery about it: the child who is familiar with books, ideas, conversation-the ways and means of the intellectual life-before he begins school, indeed, before he begins consciously to think, has a marked advantage. He is at home in the House of intellect just as the stableboy is at home among horses, or the child of actors on the stage. (Barzun, 1959, p. 142)It is... no exaggeration to say that sensory-motor intelligence is limited to desiring success or practical adaptation, whereas the function of verbal or conceptual thought is to know and state truth. (Piaget, 1954, p. 359)ntelligence has two parts, which we shall call the epistemological and the heuristic. The epistemological part is the representation of the world in such a form that the solution of problems follows from the facts expressed in the representation. The heuristic part is the mechanism that on the basis of the information solves the problem and decides what to do. (McCarthy & Hayes, 1969, p. 466)Many scientists implicitly assume that, among all animals, the behavior and intelligence of nonhuman primates are most like our own. Nonhuman primates have relatively larger brains and proportionally more neocortex than other species... and it now seems likely that humans, chimpanzees, and gorillas shared a common ancestor as recently as 5 to 7 million years ago.... This assumption about the unique status of primate intelligence is, however, just that: an assumption. The relations between intelligence and measures of brain size is poorly understood, and evolutionary affinity does not always ensure behavioral similarity. Moreover, the view that nonhuman primates are the animals most like ourselves coexists uneasily in our minds with the equally pervasive view that primates differ fundamentally from us because they lack language; lacking language, they also lack many of the capacities necessary for reasoning and abstract thought. (Cheney & Seyfarth, 1990, p. 4)Few constructs are asked to serve as many functions in psychology as is the construct of human intelligence.... Consider four of the main functions addressed in theory and research on intelligence, and how they differ from one another.1. Biological. This type of account looks at biological processes. To qualify as a useful biological construct, intelligence should be a biochemical or biophysical process or at least somehow a resultant of biochemical or biophysical processes.2. Cognitive approaches. This type of account looks at molar cognitive representations and processes. To qualify as a useful mental construct, intelligence should be specifiable as a set of mental representations and processes that are identifiable through experimental, mathematical, or computational means.3. Contextual approaches. To qualify as a useful contextual construct, intelligence should be a source of individual differences in accomplishments in "real-world" performances. It is not enough just to account for performance in the laboratory. On [sic] the contextual view, what a person does in the lab may not even remotely resemble what the person would do outside it. Moreover, different cultures may have different conceptions of intelligence, which affect what would count as intelligent in one cultural context versus another.4. Systems approaches. Systems approaches attempt to understand intelligence through the interaction of cognition with context. They attempt to establish a link between the two levels of analysis, and to analyze what forms this link takes. (Sternberg, 1994, pp. 263-264)High but not the highest intelligence, combined with the greatest degrees of persistence, will achieve greater eminence than the highest degree of intelligence with somewhat less persistence. (Cox, 1926, p. 187)There are no definitive criteria of intelligence, just as there are none for chairness; it is a fuzzy-edged concept to which many features are relevant. Two people may both be quite intelligent and yet have very few traits in common-they resemble the prototype along different dimensions.... [Intelligence] is a resemblance between two individuals, one real and the other prototypical. (Neisser, 1979, p. 185)Given the complementary strengths and weaknesses of the differential and information-processing approaches, it should be possible, at least in theory, to synthesise an approach that would capitalise upon the strength of each approach, and thereby share the weakness of neither. (Sternberg, 1977, p. 65)Historical dictionary of quotations in cognitive science > Intelligence
-
62 Memory
To what extent can we lump together what goes on when you try to recall: (1) your name; (2) how you kick a football; and (3) the present location of your car keys? If we use introspective evidence as a guide, the first seems an immediate automatic response. The second may require constructive internal replay prior to our being able to produce a verbal description. The third... quite likely involves complex operational responses under the control of some general strategy system. Is any unitary search process, with a single set of characteristics and inputoutput relations, likely to cover all these cases? (Reitman, 1970, p. 485)[Semantic memory] Is a mental thesaurus, organized knowledge a person possesses about words and other verbal symbols, their meanings and referents, about relations among them, and about rules, formulas, and algorithms for the manipulation of these symbols, concepts, and relations. Semantic memory does not register perceptible properties of inputs, but rather cognitive referents of input signals. (Tulving, 1972, p. 386)The mnemonic code, far from being fixed and unchangeable, is structured and restructured along with general development. Such a restructuring of the code takes place in close dependence on the schemes of intelligence. The clearest indication of this is the observation of different types of memory organisation in accordance with the age level of a child so that a longer interval of retention without any new presentation, far from causing a deterioration of memory, may actually improve it. (Piaget & Inhelder, 1973, p. 36)4) The Logic of Some Memory Theorization Is of Dubious Worth in the History of PsychologyIf a cue was effective in memory retrieval, then one could infer it was encoded; if a cue was not effective, then it was not encoded. The logic of this theorization is "heads I win, tails you lose" and is of dubious worth in the history of psychology. We might ask how long scientists will puzzle over questions with no answers. (Solso, 1974, p. 28)We have iconic, echoic, active, working, acoustic, articulatory, primary, secondary, episodic, semantic, short-term, intermediate-term, and longterm memories, and these memories contain tags, traces, images, attributes, markers, concepts, cognitive maps, natural-language mediators, kernel sentences, relational rules, nodes, associations, propositions, higher-order memory units, and features. (Eysenck, 1977, p. 4)The problem with the memory metaphor is that storage and retrieval of traces only deals [ sic] with old, previously articulated information. Memory traces can perhaps provide a basis for dealing with the "sameness" of the present experience with previous experiences, but the memory metaphor has no mechanisms for dealing with novel information. (Bransford, McCarrell, Franks & Nitsch, 1977, p. 434)7) The Results of a Hundred Years of the Psychological Study of Memory Are Somewhat DiscouragingThe results of a hundred years of the psychological study of memory are somewhat discouraging. We have established firm empirical generalisations, but most of them are so obvious that every ten-year-old knows them anyway. We have made discoveries, but they are only marginally about memory; in many cases we don't know what to do with them, and wear them out with endless experimental variations. We have an intellectually impressive group of theories, but history offers little confidence that they will provide any meaningful insight into natural behavior. (Neisser, 1978, pp. 12-13)A schema, then is a data structure for representing the generic concepts stored in memory. There are schemata representing our knowledge about all concepts; those underlying objects, situations, events, sequences of events, actions and sequences of actions. A schema contains, as part of its specification, the network of interrelations that is believed to normally hold among the constituents of the concept in question. A schema theory embodies a prototype theory of meaning. That is, inasmuch as a schema underlying a concept stored in memory corresponds to the mean ing of that concept, meanings are encoded in terms of the typical or normal situations or events that instantiate that concept. (Rumelhart, 1980, p. 34)Memory appears to be constrained by a structure, a "syntax," perhaps at quite a low level, but it is free to be variable, deviant, even erratic at a higher level....Like the information system of language, memory can be explained in part by the abstract rules which underlie it, but only in part. The rules provide a basic competence, but they do not fully determine performance. (Campbell, 1982, pp. 228, 229)When people think about the mind, they often liken it to a physical space, with memories and ideas as objects contained within that space. Thus, we speak of ideas being in the dark corners or dim recesses of our minds, and of holding ideas in mind. Ideas may be in the front or back of our minds, or they may be difficult to grasp. With respect to the processes involved in memory, we talk about storing memories, of searching or looking for lost memories, and sometimes of finding them. An examination of common parlance, therefore, suggests that there is general adherence to what might be called the spatial metaphor. The basic assumptions of this metaphor are that memories are treated as objects stored in specific locations within the mind, and the retrieval process involves a search through the mind in order to find specific memories....However, while the spatial metaphor has shown extraordinary longevity, there have been some interesting changes over time in the precise form of analogy used. In particular, technological advances have influenced theoretical conceptualisations.... The original Greek analogies were based on wax tablets and aviaries; these were superseded by analogies involving switchboards, gramophones, tape recorders, libraries, conveyor belts, and underground maps. Most recently, the workings of human memory have been compared to computer functioning... and it has been suggested that the various memory stores found in computers have their counterparts in the human memory system. (Eysenck, 1984, pp. 79-80)Primary memory [as proposed by William James] relates to information that remains in consciousness after it has been perceived, and thus forms part of the psychological present, whereas secondary memory contains information about events that have left consciousness, and are therefore part of the psychological past. (Eysenck, 1984, p. 86)Once psychologists began to study long-term memory per se, they realized it may be divided into two main categories.... Semantic memories have to do with our general knowledge about the working of the world. We know what cars do, what stoves do, what the laws of gravity are, and so on. Episodic memories are largely events that took place at a time and place in our personal history. Remembering specific events about our own actions, about our family, and about our individual past falls into this category. With amnesia or in aging, what dims... is our personal episodic memories, save for those that are especially dear or painful to us. Our knowledge of how the world works remains pretty much intact. (Gazzaniga, 1988, p. 42)The nature of memory... provides a natural starting point for an analysis of thinking. Memory is the repository of many of the beliefs and representations that enter into thinking, and the retrievability of these representations can limit the quality of our thought. (Smith, 1990, p. 1)Historical dictionary of quotations in cognitive science > Memory
-
63 disturbance
dɪsˈtə:bəns сущ.
1) нарушение внутреннего покоя а) беспокойство, нарушение тишины, одиночества б) беспокойство, тревога, опасение;
возбуждение Syn: agitation, excitement, discomposure
2) нарушение внешних установлений, порядка а) непорядок, беспорядок, нарушение порядка б) общественные волнения, беспорядки The election passed without any disturbance. ≈ Выборы прошли спокойно. Syn: agitation, tumult, uproar в) юр. нарушение чьих-л. прав г) вторжение в естественный ход вещей, нарушение его Syn: molestation ∙ atmospheric disturbance
3) а) неисправность, повреждение б) мед. расстройство, патологическое отклонение, патология, дисфункция circulatory disturbance disturbance in smell disturbance of sound perception disturbance in speech hearing disturbance of the function heart disturbance disturbance of cardiac function disturbance of the blood pressure disturbance of methabolism speech disturbance disturbance in speech vision disturbance
4) а) геол. дисклокация б) геол. перерыв геологического периода ∙ to cause, create, make a disturbance ≈ причинять беспокойство to quell, put down a disturbance ≈ подавлять беспокойство нарушение равновесия, покоя - ecological * нарушение экологической системы тж. pl волнения, беспорядки;
пертурбации, потрясения - political *s политическая смута - to make /to create, to cause/ a * вызвать беспорядки;
поднять шум, нарушить общественный порядок;
устроить беспорядки - there was a * at the back of the hall в задних рядах что-то происходило конфликт - the * between the North and the South конфликт между Севером и Югом волнение, тревога;
беспокойство;
нарушение душевного равновесия - emotional *s треволнения нарушение;
повреждение;
неисправность;
срыв (юридическое) воспрепятствование использованию права - * of franchise нарушение избирательного права, недопущение к выборам (медицина) расстройство;
патологическое отклонение - * of respiration расстройство дыхания - * of speech расстройство речи( техническое) нарушение режима( специальное) скачок (кривой) (радиотехника) помехи( физическое) (геология) возмущение, пертурбация - atmospheric *s возмущения в атмосфере (геология) дислокация( геология) перерыв (геологического периода) disturbance радио атмосферные помехи ~ беспокойство ~ волнение ~ (тж. pl) волнения;
беспорядки ~ воспрепятствование использованию права ~ геол. дисклокация ~ юр. нарушение (прав) ~ нарушение (тишины, покоя, порядка и т. п.) ~ нарушение ~ нарушение общественного порядка ~ нарушение пользования правом ~ нарушение равновесия ~ нарушение спокойного пользования правом ~ неисправность, повреждение ~ неисправность ~ перерыв (геологического периода) ~ повреждение ~ тревога, беспокойство ~ of market conditions колебания рыночной конъюнктуры ~ of market conditions неустойчивое состояние рынка ~ of mind расстройство рассудка mental ~ психическое расстройство public ~ народное волнениеБольшой англо-русский и русско-английский словарь > disturbance
-
64 purpose
'pə:pəs1) (the reason for doing something; the aim to which an action etc is directed: What is the purpose of your visit?) propósito,fin; razón2) (the use or function of an object: The purpose of this lever is to stop the machine in an emergency.) función, uso, utilidad3) (determination: a man of purpose.) determinación•- purposefully
- purposeless
- purposely
- purpose-built
- on purpose
- serve a purpose
- to no purpose
purpose n propósito / motivo / intenciónwhat is the purpose of your visit? ¿cuál es el motivo de su visita?on purpose a propósito / adredeI didn't do it on purpose, it was an accident no lo hice a propósito, fue un accidentetr['pɜːpəs]1 (aim, intention) propósito, intención nombre femenino, fin nombre masculino; (reason) razón nombre femenino, motivo■ what is the purpose of your visit? ¿cuál es el motivo de su visita?■ she went with the express purpose of causing a scene fue con el propósito expreso de montar una escena2 (use) uso, utilidad nombre femenino3 (determination) resolución nombre femenino\SMALLIDIOMATIC EXPRESSION/SMALLto no purpose inútilmente, en vanoto have a purpose in life tener una meta en la vidato have a sense of purpose tener una razón de serto serve a purpose servir de algo, servir para algoto serve no purpose no servir para nada, ser inútilon purpose a propósito, adrede, a postapurpose ['pərpəs] n1) intention: propósito m, intención fon purpose: a propósito, adrede2) function: función f3) resolution: resolución f, determinación fn.• centro s.m.• designio s.m.• efecto s.m.• empresa s.f.• fin s.m.• finalidad s.f.• intención s.f.• mira s.f.• objeto s.m.• propósito s.m.• proyecto s.m.• solución s.f.v.• proponer v.• proyectar v.'pɜːrpəs, 'pɜːpəs1) ca) (intention, reason) propósito m, intención fwhat was your purpose in doing it? — ¿qué pretendías or qué te proponías con eso?
I left the door open for a purpose — por algo or por alguna razón dejé la puerta abierta
for one's own purposes — por su (or mi etc) propio interés
the machine is good enough for our purposes — la máquina sirve para lo que nos proponemos hacer con ella
on purpose — a propósito, adrede, ex profeso, aposta (Esp fam)
b) ( use)to serve a (useful) purpose — servir* de algo
2) u ( resolution) determinación f['pɜːpǝs]to have a/no sense of purpose — tener*/no tener* una meta or un norte en la vida
1. N1) (=intention) propósito m, objetivo mshe has a purpose in life — tiene un objetivo or una meta or un norte en la vida
what was your purpose in going? — ¿con qué intención fuiste?
purpose of visit — (on official form) motivo del viaje
•
I put that there for a purpose — he puesto eso ahí a propósito or por una razón•
on purpose — a propósito, adredeintent 2.•
with the purpose of — con el fin de2) (=use) uso m, utilidad fwhat is the purpose of this tool? — ¿qué uso or utilidad tiene esta herramienta?
•
to good purpose — provechosamente•
it was all to no purpose — todo fue inútil or en vano•
you can adapt it to your own purposes — lo puede adaptar a sus necesidadesserve 1., 2)•
it serves no useful purpose — no tiene uso práctico, no tiene utilidad práctica3) (=determination) resolución f, determinación f•
to have a sense of purpose — tener un rumbo en la vidainfirm•
she has great strength of purpose — tiene muchísima resolución or determinación, es muy resuelta2.VT†to purpose doing sth/to do sth — proponerse or planear hacer algo
* * *['pɜːrpəs, 'pɜːpəs]1) ca) (intention, reason) propósito m, intención fwhat was your purpose in doing it? — ¿qué pretendías or qué te proponías con eso?
I left the door open for a purpose — por algo or por alguna razón dejé la puerta abierta
for one's own purposes — por su (or mi etc) propio interés
the machine is good enough for our purposes — la máquina sirve para lo que nos proponemos hacer con ella
on purpose — a propósito, adrede, ex profeso, aposta (Esp fam)
b) ( use)to serve a (useful) purpose — servir* de algo
2) u ( resolution) determinación fto have a/no sense of purpose — tener*/no tener* una meta or un norte en la vida
-
65 roll
I [rəʊl]1) (of paper, cloth) rotolo m.; (of banknotes) mazzetta f.; (of flesh) rotolo m., rotolino m.2) (bread) panino m.3) (register) registro m., elenco m.II [rəʊl]1) (rocking motion) dondolio m.2) sport (in gymnastics) capriola f.3) aer. mar. rollio m.4) gioc. (of dice) rotolio m., lancio m.5) (deep sound) (of drums) rullo m.; (of thunder) rombo m., rimbombo m., brontolio m.III 1. [rəʊl]1) (push) fare rotolare [ball, log]to roll sth. away — fare rotolare via qcs
to roll sth. into a ball — (of paper) appallottolare qcs.; (of dough, clay) fare una palla di qcs.; (of wool) avvolgere qcs. in gomitolo, raggomitolare qcs
4) (turn)6) gioc. lanciare, gettare [ dice]7) ling.2.to roll one's "r"s — arrotare le erre
1) (move) [ball, rock] rotolare; [person, animal] rotolarsito roll backwards — [ car] fare marcia indietro
to roll down — [ car] scendere da [ hill]; [ rock] rotolare giù per [ hill]
to roll into — [ train] entrare in [ station]
to roll off — [ car] precipitare o cadere da [ cliff]
4) (reverberate) [ thunder] rimbombare, brontolare; [ drum] rullare5) (function) [ camera] girare; [ press] mettersi in funzione•- roll in- roll off- roll on- roll out- roll up••to be rolling in it — colloq. nuotare nell'oro
to be X, Y and Z rolled into one — essere X, Y e Z riuniti, incorporati in una sola cosa, mescolati in un tutt'uno
* * *I 1. [rəul] noun1) (anything flat (eg a piece of paper, a carpet) rolled into the shape of a tube, wound round a tube etc: a roll of kitchen foil; a toilet-roll.)2) (a small piece of baked bread dough, used eg for sandwiches: a cheese roll.)3) (an act of rolling: Our dog loves a roll on the grass.)4) (a ship's action of rocking from side to side: She said that the roll of the ship made her feel ill.)5) (a long low sound: the roll of thunder.)6) (a thick mass of flesh: I'd like to get rid of these rolls of fat round my waist.)7) (a series of quick beats (on a drum).)2. verb1) (to move by turning over like a wheel or ball: The coin/pencil rolled under the table; He rolled the ball towards the puppy; The ball rolled away.)2) (to move on wheels, rollers etc: The children rolled the cart up the hill, then let it roll back down again.)3) (to form (a piece of paper, a carpet) into the shape of a tube by winding: to roll the carpet back.)4) ((of a person or animal in a lying position) to turn over: The doctor rolled the patient (over) on to his side; The dog rolled on to its back.)5) (to shape (clay etc) into a ball or cylinder by turning it about between the hands: He rolled the clay into a ball.)6) (to cover with something by rolling: When the little girl's dress caught fire, they rolled her in a blanket.)7) (to make (something) flat or flatter by rolling something heavy over it: to roll a lawn; to roll pastry (out).)8) ((of a ship) to rock from side to side while travelling forwards: The storm made the ship roll.)9) (to make a series of low sounds: The thunder rolled; The drums rolled.)10) (to move (one's eyes) round in a circle to express fear, surprise etc.)11) (to travel in a car etc: We were rolling along merrily when a tyre burst.)12) ((of waves, rivers etc) to move gently and steadily: The waves rolled in to the shore.)13) ((of time) to pass: Months rolled by.)•- roller- rolling
- roller-skate 3. verb(to move on roller-skates: You shouldn't roller-skate on the pavement.) (pattinare con i pattini a rotelle)- roll in
- roll up II(a list of names, eg of pupils in a school etc: There are nine hundred pupils on the roll.)* * *I [rəʊl]1) (of paper, cloth) rotolo m.; (of banknotes) mazzetta f.; (of flesh) rotolo m., rotolino m.2) (bread) panino m.3) (register) registro m., elenco m.II [rəʊl]1) (rocking motion) dondolio m.2) sport (in gymnastics) capriola f.3) aer. mar. rollio m.4) gioc. (of dice) rotolio m., lancio m.5) (deep sound) (of drums) rullo m.; (of thunder) rombo m., rimbombo m., brontolio m.III 1. [rəʊl]1) (push) fare rotolare [ball, log]to roll sth. away — fare rotolare via qcs
to roll sth. into a ball — (of paper) appallottolare qcs.; (of dough, clay) fare una palla di qcs.; (of wool) avvolgere qcs. in gomitolo, raggomitolare qcs
4) (turn)6) gioc. lanciare, gettare [ dice]7) ling.2.to roll one's "r"s — arrotare le erre
1) (move) [ball, rock] rotolare; [person, animal] rotolarsito roll backwards — [ car] fare marcia indietro
to roll down — [ car] scendere da [ hill]; [ rock] rotolare giù per [ hill]
to roll into — [ train] entrare in [ station]
to roll off — [ car] precipitare o cadere da [ cliff]
4) (reverberate) [ thunder] rimbombare, brontolare; [ drum] rullare5) (function) [ camera] girare; [ press] mettersi in funzione•- roll in- roll off- roll on- roll out- roll up••to be rolling in it — colloq. nuotare nell'oro
to be X, Y and Z rolled into one — essere X, Y e Z riuniti, incorporati in una sola cosa, mescolati in un tutt'uno
-
66 serve
1. transitive verb1) (work for) dienen (+ Dat.)2) (be useful to) dienlich sein (+ Dat.)this car served us well — dieses Auto hat uns gute Dienste getan
if my memory serves me right — wenn mich mein Gedächtnis nicht täuscht
3) (meet needs of) nutzen (+ Dat.)serve a/no purpose — einen Zweck erfüllen/keinen Zweck haben
serve its purpose or turn — seinen Zweck erfüllen
4) (go through period of) durchlaufen [Lehre]; absitzen, verbüßen [Haftstrafe]serve [one's] time — (undergo apprenticeship) seine Lehrzeit durchmachen; (undergo imprisonment) seine Zeit absitzen
6) (render obedience to) dienen (+ Dat.) [Gott, König, Land]7) (attend) bedienen8) (supply) versorgenserves three — (in recipe) für drei Personen od. Portionen
9) (provide with food) bedienen10) (make legal delivery of) zustellen12)2. intransitive verbserve[s] or it serves him right! — (coll.) [das] geschieht ihm recht!
1) (do service) dienenserve as chairman — das Amt des Vorsitzenden innehaben
serve on a jury — Geschworener/Geschworene sein
3) (be of use)serve to do something — dazu dienen, etwas zu tun
serve for or as — dienen als
4) (serve food)6) (Eccl.) ministrieren7) (Tennis etc.) aufschlagen3. nounit's your turn to serve — du hast Aufschlag
see academic.ru/66102/service">service 1. 8)Phrasal Verbs:- serve up* * *[sə:v] 1. verb1) (to work for a person etc eg as a servant: He served his master for forty years.) servieren2) (to distribute food etc or supply goods: She served the soup to the guests; Which shop assistant served you (with these goods)?) dienen3) (to be suitable for a purpose: This upturned bucket will serve as a seat.) dienen4) (to perform duties, eg as a member of the armed forces: He served (his country) as a soldier for twenty years; I served on the committee for five years.) dienen5) (to undergo (a prison sentence): He served (a sentence of) six years for armed robbery.) absitzen6) (in tennis and similar games, to start the play by throwing up the ball etc and hitting it: He served the ball into the net; Is it your turn to serve?) aufschlagen2. noun(act of serving (a ball).) der Aufschlag- server- serving
- it serves you right
- serve an apprenticeship
- serve out
- serve up* * *[sɜ:v, AM sɜ:rv]II. vt1. (in hotel, restaurant, shop)▪ to \serve sb jdn bedienenare you being \served, madam? werden Sie schon bedient, gnädige Frau?2. (present food, drink)what's a good wine to \serve with this dish? welchen Wein kann man zu diesem Gericht reichen?dinner is \served es ist angerichtetto \serve alcohol Alkohol ausschenkento \serve a meal ein Essen servieren3. (be enough for)▪ to \serve sb für jdn reichenall recipes will \serve 4 to 5 people alle Rezepte ergeben 4 bis 5 Portionen4. (work for)she \served the church faithfully for many years sie war jahrelang im Dienst der Kirche aktivto \serve sb's interests jds Interessen dienento \serve the public im Dienste der Öffentlichkeit stehen5. (complete due period)▪ to \serve sth etw ableistento \serve one's apprenticeship seine Lehrzeit absolvierento \serve five years as president eine fünfjährige Amtszeit als Präsident/Präsidentin durchlaufento \serve terms in office Amtszeiten durchlaufen6. (provide for)▪ to \serve sth etw versorgen7. (perform a function)to \serve a purpose einen Zweck erfüllenthis does not \serve any useful purpose das hat keinen praktischen Wertif my memory \serves me right wenn ich mich recht erinnere8. SPORTto \serve the ball Aufschlag haben; (in volleyball) Angabe habento \serve sb with papers jdm Papiere zustellen10.III. vi1. (provide food, drink) servieren\serve hot or cold kalt oder warm servieren2. (work for) dienen▪ to \serve as sth als etw fungierenshe \served as an interpreter sie fungierte als Dolmetscherinto \serve in the army in der Armee dienento \serve on a committee einem Ausschuss angehörento \serve on the council im Stadtrat sein, ÖSTERR, SCHWEIZ sitzento \serve on a jury Geschworene(r) f(m) sein3. (function)are these boxes sturdy enough to \serve as tables? sind diese Kisten stabil genug, um als Tische zu dienen?to \serve as a reminder/warning als Erinnerung/Mahnung dienenthis old penknife will \serve dieses alte Taschenmesser tut's fam* * *[sɜːv]1. vt1) (= work for) dienen (+dat); (= be of use) dienlich sein (+dat), nützen (+dat)he served his country/the company well — er hat sich um sein Land/die Firma verdient gemacht
he has served our cause faithfully — er hat sich um unsere Sache verdient gemacht, er hat unserer Sache treue Dienste geleistet
to serve sb's purpose — jds Zwecken (dat) dienen
it serves no useful purpose —
that will serve my needs — das ist genau (das), was ich brauche
this box has served us as a table — diese Kiste hat uns (dat) als Tisch gedient
2) (= work out) abdienen, ableisten; term of office durchlaufen; apprenticeship durchmachen; sentence verbüßen, absitzen (inf)3) (= supply) transport, gas etc versorgen4) (in shop) bedienento serve sb with 5 kilos of potatoes — jdm 5 kg Kartoffeln bringen or geben
I'm being served, thank you — danke, ich werde schon bedient or ich bekomme schon (inf)
5) (esp in restaurant) food, drink servieren; (= put on plate) aufgeben; guests bedienen; (waiter) bedienen, servieren (+dat); (= pour drink for) einschenken (+dat); wine etc einschenken; rations verteilen (to an +acc)dinner is served (butler) — das Essen or es ist aufgetragen; (host, hostess) darf ich zu Tisch bitten?
"serves three" (on packet etc) — "(ergibt) drei Portionen"
6) Mass, Communion ministrieren bei7) (TENNIS ETC) ball aufschlagento serve a summons on sb, to serve sb with a summons — jdn vor Gericht laden
the landlord served notice (to quit) on his tenants (esp Brit) — der Vermieter kündigte den Mietern
9) (old: treat) behandelnto serve sb ill — jdm einen schlechten Dienst erweisen, jdm übel mitspielen
(it) serves you right! (inf) — das geschieht dir( ganz) recht!
it serves him right for being so greedy (inf) — das geschieht ihm ganz recht, was muss er auch so gierig sein!
it would have served you right if... (inf) — es wäre dir ganz recht geschehen, wenn...
10) (stallion etc) decken2. vi1) (= do duty) dienento serve on the jury — Geschworene(r) mf sein
to serve on the council — Ratsmitglied nt sein
4)to serve as, to serve for — dienen als
it serves to show/explain... — das zeigt/erklärt...
these facts merely serve to prove my point — diese Fakten dienen lediglich dazu, mein Argument zu beweisen
3. n (TENNIS ETC)Aufschlag m* * *A v/iwith bei):serve under sb MIL unter jemandem dienen2. servieren, bedienen3. fungieren, amtieren ( beide:as als):serve on a committee einem Ausschuss angehören;serve on a jury als Geschworener fungieren4. dienen, nützen:it serves to do sth es dient dazu, etwas zu tun;it serves to show his cleverness daran kann man seine Klugheit erkennen5. genügen:it will serve das wird genügen oder den Zweck erfüllen;nothing serves but … hier hilft nichts als …6. günstig sein, passen:as occasion serves bei passender Gelegenheit7. dienen (as, for als):8. WIRTSCH bedienen:9. a) Tennis etc: aufschlagen, servieren:XY to serve Aufschlag XY;serve for the set (match) zum Satzgewinn (Matchgewinn) aufschlagen;serve to sb’s forehand ( into [ oder at] sb’s body) jemandem auf die Vorhand (auf den Körper) aufschlagenb) Volleyball: aufgeben10. KATH ministrierenB v/t3. seine Dienstzeit ( auch MIL) ableisten, seine Lehre machen, JUR (auch Eishockey etc) eine Strafe verbüßen, absitzen4. a) ein Amt innehaben, ausübenb) Dienst tun in (dat), ein Gebiet, einen Personenkreis betreuen, versorgenit serves no purpose es dient keinem Zweck;serve some private ends privaten Zwecken dienen“serves four” „ergibt vier Portionen“dinner is served! es ist serviert oder angerichtet!;serve sth up fig umg etwas auftischen9. MIL ein Geschütz etc bedienen10. versorgen ( with mit):11. umga) jemanden schändlich etc behandelnb) jemandem etwas zufügen:serve sb a trick jemandem einen Streich spielen;serve sb out es jemandem besorgen umg oder heimzahlen;(it) serves him right! (das) geschieht ihm ganz recht!12. befriedigen:serve one’s desire seiner Begierde frönen;serve the time sich der Zeit anpassen14. ZOOL eine Stute etc decken15. Tennis etc: den Ball aufschlagen:serve an ace ein Ass servieren17. TECH umwickeln* * *1. transitive verb1) (work for) dienen (+ Dat.)2) (be useful to) dienlich sein (+ Dat.)3) (meet needs of) nutzen (+ Dat.)serve a/no purpose — einen Zweck erfüllen/keinen Zweck haben
serve its purpose or turn — seinen Zweck erfüllen
4) (go through period of) durchlaufen [Lehre]; absitzen, verbüßen [Haftstrafe]serve [one's] time — (undergo apprenticeship) seine Lehrzeit durchmachen; (undergo imprisonment) seine Zeit absitzen
5) (dish up) servieren; (pour out) einschenken (to Dat.)6) (render obedience to) dienen (+ Dat.) [Gott, König, Land]7) (attend) bedienen8) (supply) versorgenserves three — (in recipe) für drei Personen od. Portionen
9) (provide with food) bedienen10) (make legal delivery of) zustellen11) (Tennis etc.) aufschlagen12)2. intransitive verbserve[s] or it serves him right! — (coll.) [das] geschieht ihm recht!
1) (do service) dienenserve on a jury — Geschworener/Geschworene sein
2) (be employed; be soldier etc.) dienen3) (be of use)serve to do something — dazu dienen, etwas zu tun
serve for or as — dienen als
4) (serve food)5) (attend in shop etc.) bedienen6) (Eccl.) ministrieren7) (Tennis etc.) aufschlagen3. nounPhrasal Verbs:- serve up* * *n.Aufschlag (Tennis) m. v.aufschlagen (Tennis) v.bedienen v.dienen v.servieren v. -
67 BIOS
['baios] n. shkurtesë nga b asic i nput o utput s ystem ( BIOS) sistemi themelor për hyrje-dalje ( informatikë)What is BIOS?BIOS is an acronym for Basic Input/Output System. It is the boot firmware program on a PC, and controls the computer from the time you start it up until the operating system takes over. When you turn on a PC, the BIOS first conducts a basic hardware check, called a Power-On Self Test (POST), to determine whether all of the attachments are present and working. Then it loads the operating system into your computer's random access memory, or RAM.The BIOS also manages data flow between the computer's operating system and attached devices such as the hard disk, video card, keyboard, mouse, and printer.The BIOS stores the date, the time, and your system configuration information in a battery-powered, non-volatile memory chip, called a CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) after its manufacturing process.Although the BIOS is standardized and should rarely require updating, some older BIOS chips may not accommodate new hardware devices. Before the early 1990s, you couldn't update the BIOS without removing and replacing its ROM chip. Contemporary BIOS resides on memory chips such as flash chips or EEPROM (Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory), so that you can update the BIOS yourself if necessary.For detailed information about BIOS updates, visit:What is firmware?Firmware consists of programs installed semi-permanently into memory, using various types of programmable ROM chips, such as PROMS, EPROMs, EEPROMs, and flash chips.Firmware is non-volatile, and will remain in memory after you turn the system off.Often, the term firmware is used to refer specifically to boot firmware, which controls a computer from the time that it is turned on until the primary operating system has taken over. Boot firmware's main function is to initialize the hardware and then to boot (load and execute) the primary operating system. On PCs, the boot firmware is usually referred to as the BIOS.What is the difference between memory and disk storage?Memory and disk storage both refer to internal storage space in a computer.The term memory usually means RAM (Random Access Memory). To refer to hard drive storage, the terms disk space or storage are usually used.Typically, computers have much less memory than disk space, because RAM is much more expensive per megabyte than a hard disk. Today, a typical desktop computer might come with 512MB of RAM, and a 40 gigabyte hard disk.Virtual memory is disk space that has been designated to act like RAM.Computers also contain a small amount of ROM, or read-only memory, containing permanent or semi-permanent (firmware) instructions for checking hardware and starting up the computer. On a PC, this is called the BIOS.What is RAM?RAM stands for Random Access Memory. RAM provides space for your computer to read and write data to be accessed by the CPU (central processing unit). When people refer to a computer's memory, they usually mean its RAM.New computers typically come with at least 256 megabytes (MB) of RAM installed, and can be upgraded to 512MB or even a gigabyte or more.If you add more RAM to your computer, you reduce the number of times your CPU must read data from your hard disk. This usually allows your computer to work considerably faster, as RAM is many times faster than a hard disk.RAM is volatile, so data stored in RAM stays there only as long as your computer is running. As soon as you turn the computer off, the data stored in RAM disappears.When you turn your computer on again, your computer's boot firmware (called BIOS on a PC) uses instructions stored semi-permanently in ROM chips to read your operating system and related files from the disk and load them back into RAM.Note: On a PC, different parts of RAM may be more or less easily accessible to programs. For example, cache RAM is made up of very high-speed RAM chips which sit between the CPU and main RAM, storing (i.e., caching) memory accesses by the CPU. Cache RAM helps to alleviate the gap between the speed of a CPU's megahertz rating and the ability of RAM to respond and deliver data. It reduces how often the CPU must wait for data from main memory.What is ROM?ROM is an acronym for Read-Only Memory. It refers to computer memory chips containing permanent or semi-permanent data. Unlike RAM, ROM is non-volatile; even after you turn off your computer, the contents of ROM will remain.Almost every computer comes with a small amount of ROM containing the boot firmware. This consists of a few kilobytes of code that tell the computer what to do when it starts up, e.g., running hardware diagnostics and loading the operating system into RAM. On a PC, the boot firmware is called the BIOS.Originally, ROM was actually read-only. To update the programs in ROM, you had to remove and physically replace your ROM chips. Contemporary versions of ROM allow some limited rewriting, so you can usually upgrade firmware such as the BIOS by using installation software. Rewritable ROM chips include PROMs (programmable read-only memory), EPROMs (erasable read-only memory), EEPROMs (electrically erasable programmable read-only memory), and a common variation of EEPROMs called flash memory.What is an ACPI BIOS?ACPI is an acronym that stands for Advanced Configuration and Power Interface, a power management specification developed by Intel, Microsoft, and Toshiba. ACPI support is built into Windows 98 and later operating systems. ACPI is designed to allow the operating system to control the amount of power provided to each device or peripheral attached to the computer system. This provides much more stable and efficient power management and makes it possible for the operating system to turn off selected devices, such as a monitor or CD-ROM drive, when they are not in use.ACPI should help eliminate computer lockup on entering power saving or sleep mode. This will allow for improved power management, especially in portable computer systems where reducing power consumption is critical for extending battery life. ACPI also allows for the computer to be turned on and off by external devices, so that the touch of a mouse or the press of a key will "wake up" the computer. This new feature of ACPI, called OnNow, allows a computer to enter a sleep mode that uses very little power.In addition to providing power management, ACPI also evolves the existing Plug and Play BIOS (PnP BIOS) to make adding and configuring new hardware devices easier. This includes support for legacy non-PnP devices and improved support for combining older devices with ACPI hardware, allowing both to work in a more efficient manner in the same computer system. The end result of this is to make the BIOS more PnP compatible.What is CMOS?CMOS, short for Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor, is a low-power, low-heat semiconductor technology used in contemporary microchips, especially useful for battery-powered devices. The specific technology is explained in detail at:http://searchsmb.techtarget.com/sDefinition/0,,sid44_gci213860,00.htmlMost commonly, though, the term CMOS is used to refer to small battery-powered configuration chips on system boards of personal computers, where the BIOS stores the date, the time, and system configuration details.How do I enter the Setup program in my BIOS?Warning: Your BIOS Setup program is very powerful. An incorrect setting could cause your computer not to boot properly. You should make sure you understand what a setting does before you change it.You can usually run Setup by pressing a special function key or key combination soon after turning on the computer, during its power-on self test (POST), before the operating system loads (or before the operating system's splash screen shows). During POST, the BIOS usually displays a prompt such as:Press F2 to enter SetupMany newer computers display a brief screen, usually black and white, with the computer manufacturer's logo during POST.Entering the designated keystroke will take you into the BIOS Setup. Common keystrokes to enter the BIOS Setup are F1, F2, F10, and Del.On some computers, such as some Gateway or Compaq computers, graphics appear during the POST, and the BIOS information is hidden. You must press Esc to make these graphics disappear. Your monitor will then display the correct keystroke to enter.Note: If you press the key too early or too often, the BIOS may display an error message. To avoid this, wait about five seconds after turning the power on, and then press the key once or twice.What's the difference between BIOS and CMOS?Many people use the terms BIOS (basic input/output system) and CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) to refer to the same thing. Though they are related, they are distinct and separate components of a computer. The BIOS is the program that starts a computer up, and the CMOS is where the BIOS stores the date, time, and system configuration details it needs to start the computer.The BIOS is a small program that controls the computer from the time it powers on until the time the operating system takes over. The BIOS is firmware, which means it cannot store variable data.CMOS is a type of memory technology, but most people use the term to refer to the chip that stores variable data for startup. A computer's BIOS will initialize and control components like the floppy and hard drive controllers and the computer's hardware clock, but the specific parameters for startup and initializing components are stored in the CMOS. -
68 fault
- ток повреждения
- сверхток
- сброс
- сбой
- разлом
- повреждение (цепи, линии, устройства)
- повреждение (во взрывозащите)
- повреждение
- ошибка
- отказ
- ненормальный режим работы
- неисправность
- неисправное состояние
- нарушение
- короткое замыкание
- дизъюктивное нарушение
- дефект
- выход из строя
- аварийное сообщение
аварийное сообщение
-Параллельные тексты EN-RU
The system offers diagnostic and statistics functions and configurable warnings and faults, allowing better prediction of component maintenance, and provides data to continuously improve the entire system.
[Schneider Electric]Система (управления электродвигателем) предоставляет оператору различную диагностическую и статистическую информацию и позволяет сконфигурировать предупредительные и аварийные сообщения, что дает возможность лучше планировать техническое обслуживание и постоянно улучшать систему в целом.
[Перевод Интент]Various alarm notifications are available to indicate a compromised security state such as forced entry and door position.
[APC]Устройство может формировать различные аварийные сообщения о нарушении защиты, например, о несанкционированном проникновении или об изменении положения двери.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
EN
выход из строя
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]
выход системы из строя
вследствие отказа аппаратного или программного обеспечения либо средств связи
[Англо-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. © 1998-2007 гг., Э.М. Пройдаков, Л.А. Теплицкий. 13,8 тыс. статей.]
выход из строя
-
[Интент]Единичные выходы из строя в процессе испытаний элементов электронной техники (микросхем, электровакуумных и полупроводниковых приборов, конденсаторов, резисторов, кварцевых резонаторов и т.д.), а также ламп накаливания и предохранителей не могут служить основанием для прекращения испытаний, если это не вызвано недостатком конструкции прибора.
При повторных выходах из строя тех же элементов испытания следует считать неудовлетворительными.
[ ГОСТ 24314-80]При выходе из строя отдельно стоящих вентиляторов на двигателях мельниц, дымососов, мельничных вентиляторов, вентиляторов первичного воздуха и т.д. необходимо при первой возможности, но не позже чем его допускается заводской инструкцией, отключить двигатель 6 кВ для ремонта вентилятора охлаждения двигателя.
[РД 34.20.565]Судовая электрическая сеть, предназначенная для передачи электроэнергии при выходе из строя линий электропередачи силовой сети или исчезновении напряжения
[ ГОСТ 22652-77]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
дизъюктивное нарушение
Относительное перемещение частей пластов вдоль плоскости их разрыва (геол.)
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
короткое замыкание
Случайное или намеренное соединение резистором или импедансом со сравнительно низким сопротивлением двух или более точек в цепи, нормально находящихся под различным напряжением.
Случайное или намеренное низкоимпедансное или низкоомное соединение двух или более точек электрической цепи, нормально находящихся под разными электрическими потенциалами. (вариант компании Интент)
МЭК 60050(151-03-41) [2].
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
короткое замыкание
Случайный или преднамеренный проводящий путь между двумя или более проводящими частями, принуждающий различия электрических потенциалов между этими проводящими частями становиться равными или близкими к нулю.
Короткое замыкание обычно возникает в аварийном режиме электроустановки здания при повреждении изоляции токоведущих частей, находящихся под разными электрическими потенциалами, и возникновении между этими частями электрического контакта, имеющего пренебрежимо малое полное сопротивление. Короткое замыкание также может быть следствием ошибочных действий, совершаемых персоналом при монтаже и эксплуатации электроустановки здания, когда соединяют между собой проводящие части, которые в нормальном режиме находятся под разными электрическими потенциалами.
Короткое замыкание характеризуется током короткого замыкания, который, многократно превышая номинальный ток электрической цепи, может вызвать возгорание её элементов и явиться причиной пожара в здании. Поэтому в электроустановках зданий всегда проводят мероприятия, направленные на снижение вероятности возникновения короткого замыкания, а также выполняют защиту от короткого замыкания с помощью устройств защиты от сверхтока.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CA/view/27/]
короткое замыкание
Случайное или преднамеренное соединение двух или более проводящих частей, вызывающее снижение разности электрических потенциалов между этими частями до нуля или значения, близкого к нулю.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
короткое замыкание
КЗ
замыкание, при котором токи в ветвях электроустановки, примыкающих к месту его возникновения, резко возрастают, превышая наибольший допустимый ток продолжительного режима
[Методические указания по защите распределительных электрических сетей напряжением 0,4-10 кВ от грозовых перенапряжений]EN
short-circuit
accidental or intentional conductive path between two or more conductive parts forcing the electric potential differences between these conductive parts to be equal to or close to zero
Source: 151-03-41 MOD
[IEV number 195-04-11]FR
court-circuit
chemin conducteur accidentel ou intentionnel entre deux ou plusieurs parties conductrices forçant les différences de potentiel électriques entre ces parties conductrices à être nulles ou proches de zéro
Source: 151-03-41 MOD
[IEV number 195-04-11]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
A short-circuit is a low impedance connection between two conductors at different voltages.
[ABB]Короткое замыкание представляет собой низкоомное соединение двух проводников, находящихся под разными потенциалами.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- электробезопасность
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
- КЗ
EN
DE
FR
нарушение
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]EN
fault
Another term for offense.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]
Тематики
EN
неисправное состояние
Состояние объекта, при котором он не соответствует хотя бы одному из требований нормативно-технической и (или) конструкторской (проектной) документации.
[ ГОСТ 27.002-89]
[ОСТ 45.152-99]
неисправное состояние
неисправность
По ГОСТ 13377-75
[ ГОСТ 24166-80]
неисправное состояние
Состояние системы тревожной сигнализации, препятствующее реагированию системы на наличие опасности в соответствии с требованиями стандартов.
[ ГОСТ Р 50775-95]
[МЭК 839-1-1-88]Тематики
- надежность, основные понятия
- ремонт судов
- системы охраны и безопасности
- тех. обсл. и ремонт средств электросвязи
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
неисправность
отказ в работе
Состояние машины, характеризующееся неспособностью выполнять заданную функцию, исключая случаи проведения профилактического технического обслуживания, других запланированных действий или недостаток внешних ресурсов (например, отключение энергоснабжения).
Примечание 1
Неисправность часто является результатом повреждения самой машины, однако она может иметь место и без повреждения.
Примечание 2
На практике термины «неисправность», «отказ» и «повреждение» часто используются как синонимы.
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 12100-1:2007]
неисправность
Состояние оборудования, характеризуемое его неспособностью выполнять требуемую функцию, исключая профилактическое обслуживание или другие планово-предупредительные действия, а также исключая неспособность выполнять требуемую функцию из-за недостатка внешних ресурсов.
Примечание - Неисправность часто является следствием отказа самого оборудования, но может существовать и без предварительного отказа.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
неисправность
Состояние технического объекта (элемента), характеризуемое его неспособностью выполнять требуемую функцию, исключая периоды профилактического технического обслуживания или другие планово-предупредительные действия, или в результате недостатка внешних ресурсов.
Примечания
1 Неисправность является часто следствием отказа самого технического объекта, но может существовать и без предварительного отказа.
2 Английский термин «fault» и его определение идентичны данному в МЭК 60050-191 (МЭС 191-05-01) [1]. В машиностроении чаще применяют французский термин «defaut» или немецкий термин «Fehler», чем термины «panne» и «Fehlzusstand», которые употребляют с этим определением.
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 13849-1-2003]Тематики
EN
- abnormality
- abort
- abortion
- breakage
- breakdown
- bug
- defect
- disease
- disrepair
- disturbance
- fail
- failure
- failure occurrence
- fault
- faultiness
- fouling
- health problem
- layup
- malfunction
- problem
- shutdown
- trouble
DE
FR
ненормальный режим работы электротехнического изделия
Режим работы электротехнического изделия (электротехнического устройства, электрооборудования), при котором значение хотя бы одного из параметров режима выходит за пределы наибольшего или наименьшего рабочего значения.
[ ГОСТ 18311-80]
К ненормальным относятся режимы, связанные с отклонениями от допустимых значений величин тока, напряжения и частоты, опасные для оборудования или устойчивой работы энергосистемы.
Рассмотрим наиболее характерные ненормальные режимы.а) Перегрузка оборудования, вызванная увеличением тока сверх номинального значения. Номинальным называется максимальный ток, допускаемый для данного оборудования в течение неограниченного времени.
Если ток, проходящий по оборудованию, превышает номинальное значение, то за счет выделяемого им дополнительного тепла температура токоведущих частей и изоляции через некоторое время превосходит допустимую величину, что приводит к ускоренному износу изоляции и ее повреждению. Время, допустимое для прохождения повышенных токов, зависит от их величины. Характер этой зависимости показан на рис. 1-3 и определяется конструкцией оборудования и типом изоляционных материалов. Для предупреждения повреждения оборудования при его перегрузке необходимо принять меры к разгрузке или отключению оборудования.б) Качания в системах возникают при выходе из синхронизма работающих параллельно генераторов (или электростанций) А и В (рис. 1-2, б). При качаниях в каждой точке системы происходит периодическое изменение («качание») тока и напряжения. Ток во всех элементах сети, связывающих вышедшие из синхронизма генераторы А и В, колеблется от нуля до максимального значения, во много раз превышающего нормальную величину. Напряжение падает от нормального до некоторого минимального значения, имеющего разную величину в каждой точке сети. В точке С, называемой электрическим центром качаний, оно снижается до нуля, в остальных точках сети напряжение падает, но остается больше нуля, нарастая от центра качания С к источникам питания А и В. По характеру изменения тока и напряжения качания похожи на к. з. Возрастание тока вызывает нагревание оборудования, а уменьшение напряжения нарушает работу всех потребителей системы. Качание — очень опасный ненормальный режим, отражающийся на работе всей энергосистемы.
в) Повышение напряжения сверх допустимого значения возникает обычно на гидрогенераторах при внезапном отключении их нагрузки. Разгрузившийся гидрогенератор увеличивает частоту вращения, что вызывает возрастание э. д. с. статора до опасных для его изоляции значений. Защита в таких случаях должна снизить ток возбуждения генератора или отключить его.
Опасное для изоляции оборудования повышение напряжения может возникнуть также при одностороннем отключении или включении длинных линий электропередачи с большой емкостной проводимостью.
Кроме отмеченных ненормальных режимов, имеются и другие, ликвидация которых возможна при помощи релейной защиты.[Чернобровов Н. В. Релейная защита. Учебное пособие для техникумов]
Тематики
- изделие электротехническое
- релейная защита
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
отказ
Нарушение способности оборудования выполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечания
1. После отказа оборудование находится в неисправном состоянии.
2. «Отказ» является событием, в отличие от «неисправности», которая является состоянием.
3. Это понятие, как оно определено, не применяют коборудованиюобъекту, состоящему только из программных средств.
4. На практике термины «отказ» и «неисправность» часто используют как синонимы.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 13849-1-2003]
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
отказ
Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния объекта.
[ ГОСТ 27.002-89]
[ОСТ 45.153-99]
[СТО Газпром РД 2.5-141-2005]
[СО 34.21.307-2005]
отказ
Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния машины и (или) оборудования вследствие конструктивных нарушений при проектировании, несоблюдения установленного процесса производства или ремонта, невыполнения правил или инструкций по эксплуатации.
[Технический регламент о безопасности машин и оборудования]EN
failure
the termination of the ability of an item to perform a required function
NOTE 1 – After failure the item has a fault.
NOTE 2 – "Failure" is an event, as distinguished from "fault", which is a state.
NOTE 3 – This concept as defined does not apply to items consisting of software only.
[IEV number 191-04-01]
NOTE 4 - In practice, the terms fault and failure are often used synonymously
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
défaillance
cessation de l'aptitude d'une entité à accomplir une fonction requise
NOTE 1 – Après défaillance d'une entité, cette entité est en état de panne.
NOTE 2 – Une défaillance est un passage d'un état à un autre, par opposition à une panne, qui est un état.
NOTE 3 – La notion de défaillance, telle qu'elle est définie, ne s'applique pas à une entité constituée seulement de logiciel.
[IEV number 191-04-01]Тематики
- безопасность в целом
- безопасность гидротехнических сооружений
- безопасность машин и труда в целом
- газораспределение
- надежность средств электросвязи
- надежность, основные понятия
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
повреждение
Повреждение любого элемента, разделения, изоляции или соединения между элементами, не являющихся неповреждаемыми по МЭК 60079-11 [8], при проведении испытаний на искробезопасность.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-426-2006]
Тематики
EN
повреждение (цепи, линии, устройства)
-
[Интент]Тематики
- выключатель автоматический
- релейная защита
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
разлом
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
fault
A fracture or a zone of fractures along which there has been displacement of the sides relative to one another parallel to the fracture. (Source: BJGEO)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
сбой
Самоустраняющийся отказ или однократный отказ, устраняемый незначительным вмешательством оператора.
[ ГОСТ 27.002-89]
[ОСТ 45.153-99]
[СТО Газпром РД 2.5-141-2005]
сбой
Ненормальный режим, который может вызвать уменьшение или потерю способности функционального блока выполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечание
МЭС 191-05-01 определяет «сбой» как состояние, характеризуемое неспособностью выполнить необходимую функцию, исключая неспособности, возникающие во время профилактического ухода или других плановых мероприятий, либо в результате недостатка внешних ресурсов. Иллюстрация к этим двум точкам зрения показана на рисунке [ ИСО / МЭК 2382-14-01-10].
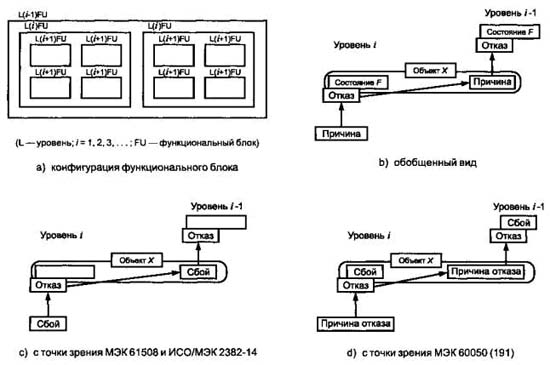
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61508-4-2007]Тематики
- газораспределение
- надежность средств электросвязи
- надежность, основные понятия
Обобщающие термины
EN
сброс
Разрывное нарушение, при котором сместитель падает в сторону опущенного крыла (висячее крыло опущено относительно лежачего).
[ Словарь геологических терминов и понятий. Томский Государственный Университет]Тематики
- геология, геофизика
Обобщающие термины
EN
сверхток
Любой ток, превышающий номинальный
МЭК 60050(441-11-06).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
[ ГОСТ Р 50345-99( МЭК 60898-95)]
сверхток
Электрический ток, превышающий номинальный электрический ток.
Сверхток представляет собой любой электрический ток, величина которого превышает номинальный ток какого-либо элемента электроустановки здания или используемого в ней электрооборудования, например: номинальный ток электрической цепи, допустимый длительный ток проводника, номинальный ток автоматического выключателя и т. д. В нормативной и правовой документации различают два основных вида сверхтока – ток перегрузки и ток короткого замыкания.
Появление сверхтока в каком-либо элементе электроустановки здания может привести к его перегреву, возгоранию и, как следствие, к возникновению пожара в здании. Поэтому в электроустановках зданий выполняют защиту от сверхтока.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%D1/view/59/]
сверхток
сверхток в электротехническом изделии
Ток, значение которого превосходит наибольшее рабочее значение тока электротехнического изделия (устройства).
[ ГОСТ 18311-80]
сверхток
Электрический ток, превышающий номинальный электрический ток.
Примечание - Для проводников номинальный ток считается равным длительному допустимому току.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Сверхток может оказывать или может не оказывать вредные воздействия в зависимости от его величины и продолжительности. Сверхтоки могут возникать в результате перегрузок в электроприемниках или при повреждениях, таких как короткие замыкания или замыканиях на землю
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]
сверхток
Любой ток, превышающий номинальное значение. Для проводов номинальным значением является допустимый ток.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]EN
overcurrent
electric current exceeding the rated electric current
NOTE – For conductors, the rated current is considered as equal to the current-carrying capacity
[IEV number 826-11-14]
over-current
<>current exceeding the rated current
<>[IEC 61095, ed. 2.0 (2009-02)]
over-current
electric current the value of which exceeds a specified limiting value
[IEV number 151-15-28]
[IEV number 442-01-20]FR
surintensité, f
courant électrique supérieur au courant électrique assigné
NOTE – Pour des conducteurs, on considère que le courant assigné est égal au courant admissible.
[IEV number 826-11-14]
surintensité
courant supérieur au courant assigné
[IEC 61095, ed. 2.0 (2009-02)]
[IEV number 442-01-20]
surintensité, f
courant électrique dont la valeur dépasse une valeur limite spécifiée
[IEV number 151-15-28]Параллельные тексты EN-RU The design of LV installations leads to basic protection devices being fitted for three types of faults:
-
overloads
-
short-circuits
-
insulation faults
Низковольтные электроустановки должны быть оснащены устройствами защиты трех типов:
-
от перегрузки;
-
от короткого замыкания;
- от токов утечки.
[Перевод Интент]
Примечание.
Слово fault в данном случае пришлось опустить, поскольку:
- его нельзя перевести как "неисправность", т. к. возникновение перегрузки ( overload) не является неисправностью;
- его нельзя перевести как "сверхток", т. к. ток утечки не является сверхтоком.The chosen switchgear must withstand and eliminate faults at optimised cost with respect to the necessary performance.
[Schneider Electric]Выбранная аппаратура распределения должна иметь такие характеристики, чтобы рентабельно выдерживать и ограничивать сверхтоки.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
ток повреждения
Ток, возникающий в результате пробоя или перекрытия изоляции.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
ток повреждения
Ток, который протекает через данную точку повреждения в результате повреждения изоляции.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]EN
fault current
current resulting from an insulation failure, the bridging of insulation or incorrect connection in an electrical circuit
[IEC 61439-1, ed. 2.0 (2011-08)]
fault current
current which flows across a given point of fault resulting from an insulation fault
[IEV number 826-11-11]FR
courant de défaut
courant résultant d'un défaut de l'isolation, du contournement de l’isolation ou d’un raccordement incorrect dans un circuit électrique
[IEC 61439-1, ed. 2.0 (2011-08)]
courant de défaut, m
courant s'écoulant en un point de défaut donné, consécutivement à un défaut de l'isolation
[IEV number 826-11-11]Тематики
EN
DE
- Fehlerstrom, m
FR
- courant de défaut, m
3.7.2 повреждение (fault): Повреждение любого элемента, разделения, изоляции или соединения между элементами, не являющимися по настоящему стандарту не повреждаемыми, от которых зависит искробезопасность цепи.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 52350.11-2005: Электрооборудование для взрывоопасных газовых сред. Часть 11. Искробезопасная электрическая цепь "I" оригинал документа
3.16 неисправность (fault): Состояние объекта, характеризующееся неспособностью исполнять требуемую функцию, исключая время профилактического технического обслуживания или других запланированных действий, или простои из-за недостатка внешних ресурсов
Примечание - Неисправность часто является результатом отказа объекта, но может существовать и без отказа.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51901.6-2005: Менеджмент риска. Программа повышения надежности оригинал документа
3.6 неисправность (fault): Состояние элемента, характеризующееся неспособностью исполнять требуемую функцию, исключая период технического обслуживания, ремонта или других запланированных действий, а также из-за недостатка внешних ресурсов.
Примечание - Неисправность часто является результатом отказа элемента, но может существовать и без предшествующего отказа.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51901.5-2005: Менеджмент риска. Руководство по применению методов анализа надежности оригинал документа
3.5 неисправность (fault): Состояние объекта, когда один из его элементов или группа элементов проявляют признаки деградации или нарушения работы, что может привести к отказу машины.
Примечания
1 Неисправность часто является следствием отказа, но может иметь место и при его отсутствии.
2 Состояние объекта не рассматривают как неисправное, если оно возникло вследствие запланированных процедур или нехватки внешних ресурсов.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 13379-2009: Контроль состояния и диагностика машин. Руководство по интерпретации данных и методам диагностирования оригинал документа
3.3 неисправность (fault): Состояние объекта, при котором он не способен выполнять требуемую функцию, за исключением такой неспособности при техническом обслуживании или других плановых мероприятиях или вследствие нехватки внешних ресурсов.
Примечания
1 Неисправность часто является следствием отказа объекта, но может иметь место и без него.
2 В настоящем стандарте термин «неисправность» используется наряду с термином «отказ» по историческим причинам.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51901.12-2007: Менеджмент риска. Метод анализа видов и последствий отказов оригинал документа
3.1.30 ошибка (fault): Разность между погрешностью весоизмерительного датчика и основной погрешностью весоизмерительного датчика (см. 3.1.34).
Источник: ГОСТ Р 8.726-2010: Государственная система обеспечения единства измерений. Датчики весоизмерительные. Общие технические требования. Методы испытаний оригинал документа
3.6 дефект (fault): Неисправность или ошибка в компоненте технического обеспечения, программного обеспечения или системы
[МЭК 61513, пункт 3.22]
Примечание 1 - Дефекты могут подразделяться на случайные, например, в результате ухудшения аппаратных средств из-за старения, и систематические, например, ошибки в программном обеспечении, которые вытекают из погрешностей проектирования.
Примечание 2 - Дефект (в особенности дефект проекта) может остаться необнаруженным в системе до тех пор, пока не окажется, что полученный результат не соответствует намеченной функции, то есть возникает отказ.
Примечание 3 - См. также «ошибка программного обеспечения» и «случайный дефект».
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62340-2011: Атомные станции. Системы контроля и управления, важные для безопасности. Требования по предотвращению отказов по общей причине оригинал документа
3.2 неисправность (fault): Состояние объекта, когда один из его элементов или группа элементов проявляет признаки деградации или нарушения работы, что может привести к отказу машины.
Примечание - Неисправность может привести к отказу.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 17359-2009: Контроль состояния и диагностика машин. Общее руководство по организации контроля состояния и диагностирования оригинал документа
3.17 дефект (fault): Неисправность или ошибка в компоненте технического обеспечения, программного обеспечения или системы.
[МЭК 61513, пункт 3.22]
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60880-2010: Атомные электростанции. Системы контроля и управления, важные для безопасности. Программное обеспечение компьютерных систем, выполняющих функции категории А оригинал документа
3.6.1 сбой (fault): Ненормальный режим, который может вызвать уменьшение или потерю способности функционального блока выполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечание - МЭС 191-05-01 определяет «сбой» как состояние, характеризуемое неспособностью выполнить необходимую функцию, исключая неспособности, возникающие во время профилактического ухода или других плановых мероприятий, либо в результате недостатка внешних ресурсов. Иллюстрация к этим двум точкам зрения показана на рисунке 4 [ИСО/МЭК 2382-14-01-10].
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61508-4-2007: Функциональная безопасность систем электрических, электронных, программируемых электронных, связанных с безопасностью. Часть 4. Термины и определения оригинал документа
3.22 дефект (fault): Дефект в аппаратуре, программном обеспечении или в компоненте системы (см. рисунок 3).
Примечание 1 -Дефекты могут быть результатом случайных отказов, которые возникают, например, из-за деградации аппаратуры в результате старения; возможны систематические дефекты, например, в результате дефектов в программном обеспечении, возникающих из-за ошибок при проектировании.
Примечание 2 - Дефект (особенно дефекты, связанные с проектированием) может оставаться незамеченным, пока сохраняются условия, при которых он не отражается на выполнении функции, т.е. пока не произойдет отказ.
Примечание 3 - См. также «дефект программного обеспечения».
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61513-2011: Атомные станции. Системы контроля и управления, важные для безопасности. Общие требования оригинал документа
4.10.1 ошибка (fault): Разность между погрешностью показаний и погрешностью прибора.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ЕН 1434-1-2011: Теплосчетчики. Часть 1. Общие требования
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > fault
-
69 black start
- холодный старт источника бесперебойного питания
- пуск электростанции из полностью обесточенного состояния
- пуск агрегатов после полного погашения электростанции
- пуск (электростанции) из полностью обесточенного состояния
- запуск из полностью обесточенного состояния
- автономный пуск электростанции
автономный пуск электростанции
(без электропитания от постороннего источника)
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
запуск из полностью обесточенного состояния
—
[Англо-русский глосcарий энергетических терминов ERRA]EN
black start
A point on the system, such as a transmission line, through which all electricity must pass to get to its intended buyers. If there is limited capacity at this point, some priorities must be developed to decide whose power gets through. It also must be decided if the owner of the bottleneck may, or must, build additional facilities to relieve the constraint.
[Англо-русский глосcарий энергетических терминов ERRA]Тематики
EN
пуск (электростанции) из полностью обесточенного состояния
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
пуск агрегатов после полного погашения электростанции
—
[В.А.Семенов. Англо-русский словарь по релейной защите]Тематики
EN
пуск электростанции из полностью обесточенного состояния
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
холодный старт ИБП
Способность ИБП включаться и обеспечивать питанием критичную нагрузку при отсутствии входного напряжения в питающей сети, получая электроэнергию от аккумуляторной батареи.
[ http://www.radistr.ru/misc/document423.phtml]EN
black start
cold start
The ability to turn a UPS on from batteries, without mains.
[ http://www.upsonnet.com/UPS-Glossary/]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Battery-start function when utility power is not present.
[Delta Electronics]Способность ИБП включаться и обеспечивать питанием нагрузку при отсутствии напряжения питающей сети, получая электроэнергию от батареи.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > black start
-
70 SF
- функция коммутации
- функция безопасности ядерного реактора
- с автоматической подачей
- растворимая фракция
- пропадание (потеря) сигнала
- показатель серьёзности (отказа, события)
- показатель источника
- площадь оребрённой поверхности
- плавкий предохранитель
- относительное число неудачных сканирований
- одноволоконный
- коэффициент расширения спектра
- конкретные результаты
- безопасный сбой
безопасный сбой
—
[Е.С.Алексеев, А.А.Мячев. Англо-русский толковый словарь по системотехнике ЭВМ. Москва 1993]Тематики
EN
коэффициент расширения спектра
Показатель, характеризующий степень избыточности расширенной полосы частот относительно спектра информационного сигнала. Численно определяется как отношение ширины полосы частот в радиоканале к скорости передачи информации.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
одноволоконный
(МСЭ-Т L.13).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
относительное число неудачных сканирований
Показывает вероятность того, что в зоне обслуживания сети WiMAX нет ни одной доступной абонентской станции.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]Тематики
EN
плавкий предохранитель
Коммутационный аппарат, который посредством плавления одного или нескольких своих специально спроектированных и калиброванных элементов размыкает цепь, в которую он включен, и отключает ток, когда он превышает заданную величину в течение достаточного времени. Плавкий предохранитель содержит все части, образующие укомплектованный аппарат.
МЭК 60050(441-18-01).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
плавкий предохранитель
Аппарат, который вследствие расплавления одного или нескольких специально спроектированных и рассчитанных элементов размыкает цепь, в которую он включен, отключая ток, превышающий заданное значение в течение достаточно продолжительного времени. В состав плавкого предохранителя входят все части, образующие аппарат в комплекте
[ ГОСТ Р 50339. 0-2003 ( МЭК 60269-1-98)]
предохранитель
Коммутационный электрический аппарат, предназначенный для отключения защищаемой цепи посредством разрушения специально предусмотренных для этого токоведущих частей под действием тока, превышающего определенную величину.
[ ГОСТ 17703-72]
предохранитель
Устройство для разрыва электрических цепей при силе тока, превышающей допустимое значение
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
fuse
a device that by the fusing of one or more of its specially designed and proportioned components, opens the circuit in which it is inserted by breaking the current when this exceeds a given value for a sufficient time. The fuse comprises all the parts that form the complete device
[IEV number 441-18-01 ]FR
fusible
coupe-circuit à fusibles
appareil dont la fonction est d'ouvrir par la fusion d'un ou de plusieurs de ses éléments conçus et calibrés à cet effet le circuit dans lequel il est inséré en coupant le courant lorsque celui-ci dépasse pendant un temps suffisant une valeur donnée. Le fusible comprend toutes les parties qui constituent l'appareil complet
[IEV number 441-18-01 ]Настоящий стандарт распространяется на плавкие предохранители на номинальный ток от 2 до 2500 А, номинальное напряжение переменного тока до 1000 В и постоянного тока до 1200 В, устанавливаемые в комплектные устройства и предназначенные для защиты при перегрузках и коротких замыканиях силовых и вспомогательных цепей электроустановок промышленных предприятий, общественных и жилых зданий, изготовляемые для нужд народного хозяйства и экспорта и номинальное напряжение до 3000 В для защиты полупроводниковых устройств.
3.2.14. Предохранители должны быть сконструированы таким образом, чтобы отключать электрическую цепь при токах отключения в пределах: от условного тока плавления — для предохранителей с плавкими вставками типов g и gR или от наименьшего тока отключения, установленного в стандартах или технических условиях на предохранители конкретных серий и типов, для предохранителей с плавкими вставками типов а и aR — до наибольшего тока отключения
[ ГОСТ 17242-86]... токи, при которых проводят испытания, предназначенные для проверки способности данного плавкого предохранителя срабатывать удовлетворительно в диапазоне малых сверхтоков.
[ ГОСТ Р 50339.0-2003]... Если неисправность заканчивается срабатыванием плавкого предохранителя или если плавкий предохранитель не срабатывает примерно в течение 1 с, то...
[ ГОСТ Р 52319-2005]ЭЛЕКТРИЧЕСКИЕ ПАРАМЕТРЫ И ХАРАКТЕНИСТИКИ ПРЕДОХРАНИТЕЛЕЙ
(взято из ГОСТ 17242-86)-
Для держателя (или основания) предохранителя:
- номинальное напряжение;
- номинальный ток;
- род тока и номинальная частота для переменного тока;
- допустимые потери мощности;
- число полюсов, если их более одного.
-
Для плавкой вставки:
- номинальное напряжение;
- номинальный ток;
- род тока и номинальная частота для переменного тока;
- потери мощности;
- время-токовые характеристики с указанием коэффициентов K1 и K2 для плавких вставок типа а;
- перегрузочная способность;
- диапазон токов отключения;
- наибольшая отключающая способность;
- наименьший ток отключения для плавких вставок типа а;
- характеристика пропускаемого тока;
- характеристики интегралов Джоуля;
- перенапряжение и характеристика перенапряжения для плавких вставок типов aR и gR;
- условия селективности (при необходимости);
- электрическое сопротивление плавкой вставки в холодном состоянии (допускается указать в рабочих чертежах, утвержденных в установленном порядке).
-
Для предохранителя:
- степень защиты по ГОСТ 14255—69;
- номинальное напряжение, номинальный ток и коммутационная способность свободных контактов (при их наличии).
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Check to make sure that fuse F1 on power supply module V is not fused.
If the fuse is defective, it should not be replaced without determining the cause of failure.
If a fuse is replaced without eliminating the problem, there is the danger that the damage will spread.
[Schneider Electric]Убедитесь в исправности предохранителя F1 в модуле питания V.
Если предохранитель оказался неисправным, то прежде чем заменить его необходимо установить причину возникновения неисправности.
Замена предохранителя без выяснения причины его срабатывания может привести к повторению срабатывания.
[Перевод Интент]High voltage system may embrace a fuse.
Note that a fuse may not be manually adjusted as the circuit breaker relay does so the fuse choice for the appropriate purpose/circuit adaptation is deemed most important.
[LS Industrial Systems]Высоковольтная система < электропитания> может содержать предохранители.
Обратите внимание! Предохранитель нельзя настроить, как это можно сделать с расцепителем автоматического выключателя. Поэтому предохранитель необходимо выбрать так, чтобы он как можно точнее соотвествовал конкретным условиям защиты аппарата или участка цепи.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- защищать при перегрузках и коротких замыканиях
- отключать электрическую цепь
- срабатывание предохранителя
Синонимы
EN
- cutoff
- electric fuse
- fu
- fuse
- fuse switch
- fusible cutout
- fusible plug
- fusible switch
- plug fuse
- protective fuse
- safety cutoff
- safety fuse
- safety plug
- SF
- thermal fuse
DE
FR
площадь оребрённой поверхности
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
показатель источника
(напр. излучения)
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
показатель серьёзности (отказа, события)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
пропадание (потеря) сигнала
Сигнал, указывающий, что соответствующие данные пропали в том смысле, что стало активным состояние дефекта перекрестной наводки (не являющееся дефектом ухудшения). (МСЭ-T G.806).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
с автоматической подачей
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
функция безопасности ядерного реактора
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
функция коммутации
(МСЭ-Т Х.145).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > SF
-
71 probability
[͵prɒbəʹbılıtı] n1. вероятностьcalculus /calculation/ of probability - мат. теория вероятностей
conditional /transition(al)/ probability - мат. условная вероятность
probability function - мат. вероятностная функция
there is every probability of success - можно почти не сомневаться в успехе
what are the probabilities? - насколько это вероятно?
the probability is that he won't come - скорее всего, он не придёт
there is a strong probability that... - весьма /очень даже/ вероятно, что...
2. правдоподобность; правдоподобиеreports devoid of all probability - сообщения, лишённые всякого правдоподобия
-
72 capacity
kə'pæsətiplural - capacities; noun1) (ability to hold, contain etc: This tank has a capacity of 300 gallons.) capacidad2) (ability: his capacity for remembering facts.) capacidad3) (position: in his capacity as a leader.) calidadcapacity n capacidadtr[kə'pæsɪtɪ]noun (pl capacities)1 (maximum content - of container) capacidad nombre femenino, cabida; (- of theatre) aforo, capacidad nombre femenino, cabida3 (position, role) calidad nombre femenino\SMALLIDIOMATIC EXPRESSION/SMALLin a personal capacity a título personalto be filled to capacity estar al completoto work at full capacity trabajar a pleno rendimientocapacity crowd / capacity audience lleno completo, lleno totalcapacity [kə'pæsət̬i] adj: completo, totala capacity crowd: un lleno completo1) room, space: capacidad f, cabida f, espacio m2) capability: habilidad f, competencia f3) function, role: calidad f, función fin his capacity as ambassador: en su calidad de embajadoradj.• lleno, -a adj.• máximo, -a adj.n.• alcance s.m.• buque s.m.• cabida s.f.• calidad s.f.• capacidad s.f.• dimensión s.f.• espaciosidad s.f.• extensión s.f.• facultad s.m.• porte s.m.• potencia s.f.• vaso s.m.kə'pæsəti1) u ca) ( maximum content) capacidad f; (before n)a capacity crowd — un lleno completo or total
b) ( output) capacidad fto operate at full capacity — funcionar al límite de capacidad or a pleno rendimiento
2) u ( ability) capacidad fcapacity to + INF — capacidad para + inf
3) c ( role) calidad f[kǝ'pæsɪtɪ]1. N1) [of container etc] capacidad f ; (=seating capacity) cabida f, aforo m ; (Aut) cilindrada f ; (=carrying capacity) capacidad f de cargawhat is the capacity of this hall? — ¿cuántos caben en esta sala?
2) (=position) calidad fin what capacity were you there? — ¿en calidad de qué estabas allí?
I've worked for them in various capacities — he trabajado para ellos desempeñando distintas funciones
3) (=ability) capacidad fher capacities — su capacidad or aptitud
her capacity for research — su capacidad or aptitud para la investigación
to work at full capacity — [machine, factory] funcionar a pleno rendimiento
2.CPDcapacity audience N — lleno m
capacity booking N — reserva f total
capacity crowd N — = capacity audience
* * *[kə'pæsəti]1) u ca) ( maximum content) capacidad f; (before n)a capacity crowd — un lleno completo or total
b) ( output) capacidad fto operate at full capacity — funcionar al límite de capacidad or a pleno rendimiento
2) u ( ability) capacidad fcapacity to + INF — capacidad para + inf
3) c ( role) calidad f -
73 facility
fə'siləti
1. noun1) (ease or quickness: She showed great facility in learning languages.) facilidad2) (a skill: He has a great facility for always being right.) facilidad
2. noun plural(facilities the means to do something: There are facilities for cooking.)tr[fə'sɪlɪtɪ]noun (pl facilities)1 facilidad nombre femenino2 (means) facilidades nombre femenino plural1) ease: facilidad f2) center, complex: centro m, complejo m3) facilities nplamenities: comodidades fpl, servicios mpln.• facilidad s.f.fə'sɪləti1) facilities pla) ( amenities)sports facilities — instalaciones fpl deportivas
facilities for the disabled — instalaciones fpl para minusválidos
b) ( Fin)credit facilities — crédito m, facilidades fpl de pago
2) ( building) (AmE) complejo m, centro m3) u ( ability) (frml) facilidad f[fǝ'sɪlɪtɪ]N1) (=equipment, place) instalación fthe hotel's facilities are open to non-residents — las instalaciones del hotel están abiertas a los no residentes
recreational facilities — instalaciones fpl recreativas
sports facilities — instalaciones fpl deportivas
2) (=service, provision) servicio mthe company offers day-care facilities for children — la empresa ofrece un servicio de guardería para los niños
toilet facilities — servicios mpl, aseos mpl
transport facilities — servicios mpl de transporte
3) (Econ)credit facilities — facilidades fpl (de pago), crédito m
overdraft facility — crédito m al descubierto
4) (=function) función f5) (=centre) centro ma medical facility — un centro médico, un punto de asistencia médica
6) (=talent, ease) facilidad fhe had a facility for languages — tenía facilidad para los idiomas, se le daban bien los idiomas
7) (=ability) habilidad f, facultad f ; (=capacity) capacidad fhumans have lost the facility to use their sense of smell — los humanos han perdido la habilidad or la facultad de utilizar el olfato
the new model has the facility to reproduce speech — el nuevo modelo tiene la capacidad de or es capaz de reproducir el habla
* * *[fə'sɪləti]1) facilities pla) ( amenities)sports facilities — instalaciones fpl deportivas
facilities for the disabled — instalaciones fpl para minusválidos
b) ( Fin)credit facilities — crédito m, facilidades fpl de pago
2) ( building) (AmE) complejo m, centro m3) u ( ability) (frml) facilidad f -
74 formal
'fo:məl1) (done etc according to a fixed and accepted way: a formal letter.) formal, oficial2) (suitable or correct for occasions when things are done according to a fixed and accepted way: You must wear formal dress.) de etiqueta, de ceremonia3) ((of behaviour, attitude etc) not relaxed and friendly: formal behaviour.) formal4) ((of language) exactly correct by grammatical etc rules but not conversational: Her English was very formal.) formal5) ((of designs etc) precise and following a fixed pattern rather than occuring naturally: formal gardens.) ordenado, simétrico•- formally- formality
formal adj1. formal / oficial2. de etiqueta
formal adjetivo 1 ( en general) formal; ‹promesa/oferta› firm 2 ‹ persona› ( cumplidora) reliable, dependable; ( responsable) responsible
formal adjetivo
1 formal
2 (serio, educado) serious, serious-minded (cumplidor) reliable, dependable ' formal' also found in these entries: Spanish: aunque - bastante - ceremoniosa - ceremonioso - cita - denuncia - el - etiqueta - formalismo - mayoría - participación - permitirse - baño - cena - conferencia - escolarizar - gala - novio - plática - querer - traje - vestir English: absent - accustom - afford - audience - awaken - businesslike - dear - dependable - deserve - dinner - enjoy - far - fear - formal - intend - luncheon - mention - possess - propose - representation - responsible - serious - shall - should - sober - sober-minded - solid - speech - staid - unreliable - well-behaved - whom - affair - business - evening - formality - grand - grievance - prim - solemn - steady - you - your - yours - yourself - yourselvestr['fɔːməl]1 (official) formal, oficial2 (correct) formal; (traditional) tradicional3 (dress, dinner) de etiqueta4 (visit) de cumplido5 (person, language) ceremonioso,-a, formalista6 (ordered) formal, ordenado,-aformal ['fɔrməl] adj1) ceremonious: formal, de etiqueta, ceremonioso2) official: formal, oficial, de formaformal n1) ball: baile m formal, baile m de etiquetaadj.• ceremonioso, -a adj.• de cumplido adj.• de etiqueta adj.• etiquetero, -a adj.• formal adj.'fɔːrməl, 'fɔːməl1) ( ceremonial) <reception/dinner> formalformal dress — traje m de etiqueta
a formal call — una visita oficial or de protocolo
2) (official, conventional) formal3)a) <manner/person> ceremonioso; <style/language> formalb) ( symmetrical) < garden> de diseño formal['fɔːmǝl]1.ADJ [person] (=correct) correcto; (=reliable, stiff) formal; (=solemn) [greeting, language, occasion, announcement] solemne; [dress] de etiqueta; [visit] de cumplido; (Pol) [visit] oficial; [function] protocolario; [garden] simétrico; (=official) [evidence] documental; [acceptance] por escritoin English, "residence" is a formal term — en inglés, "residence" es un término formal
don't be so formal! — ¡no te andes con tantos cumplidos!
formal clothes — ropa f formal, ropa f de etiqueta
formal training — formación f profesional
2.CPDformal dress N — (=smart clothes) ropa f formal, ropa f de etiqueta; (=evening dress) traje m de noche
29% of companies now require employees to wear formal dress at all times — el 29% de las empresas exigen que sus empleados lleven ropa formal en todo momento
* * *['fɔːrməl, 'fɔːməl]1) ( ceremonial) <reception/dinner> formalformal dress — traje m de etiqueta
a formal call — una visita oficial or de protocolo
2) (official, conventional) formal3)a) <manner/person> ceremonioso; <style/language> formalb) ( symmetrical) < garden> de diseño formal -
75 male
meilnoun, adjective1) ((a person, animal etc) of the sex having testes or an organ or organs performing a similar function; not (of) the sex which carries the young until birth etc: the male of the species; the male rabbit.) macho, varón2) ((a plant) having flowers with stamens which can fertilize female flowers.) machomale1 adj1. macho2. varónmale2 n1. macho2. varón / hombretr[meɪl]1 (animal, plant) macho; (person, child) varón; (sex, hormone, character, organ) masculino,-a2 (manly) varonil, viril3 SMALLTECHNICAL/SMALL (screw, plug) macho\SMALLIDIOMATIC EXPRESSION/SMALLmale chauvinist pig falócrata nombre masculinomale nurse enfermeromale voice choir coro masculinomale ['meɪl] adj1) : macho2) masculine: masculinomale n: macho m (de animales o plantas), varón m (de personas)adj.• macho, -a adj.• masculino, -a adj.• varonil adj.• varón adj.n.• macho s.m.• varón s.m.
I meɪl1)a) <animal/plant> macho; <hormone/sex> masculinomale doctor — médico m, doctor m
male model — modelo m (masculino)
male nurse — enfermero m
2) ( Mech Eng) <plug/thread> macho
II
[meɪl]1.N (=animal, plant) macho m ; (=person) varón m2. ADJ1) [rat, spider, plant] macho; [baby, child] varón; [friend, worker, colleague] del sexo masculino; [population, hormone, sex, attitude, behaviour] masculino; [voice] de hombre, masculino2) (Tech) [plug] macho3.CPDmale chauvinism N — machismo m
male chauvinist N — machista m
the male member N — euph el miembro viril, el miembro masculino
male menopause N — menopausia f masculina, andropausia f
male model N — modelo m del sexo masculino
male nurse N — enfermero m
male prostitute N — prostituto m
supremacistmale voice choir N — coro m masculino or de hombres
* * *
I [meɪl]1)a) <animal/plant> macho; <hormone/sex> masculinomale doctor — médico m, doctor m
male model — modelo m (masculino)
male nurse — enfermero m
2) ( Mech Eng) <plug/thread> macho
II
-
76 take
(to take or keep (someone) as a hostage: The police were unable to attack the terrorists because they were holding three people hostage.) tomar/coger a alguien como rehéntake vb1. cogertake your umbrella, it's raining coge el paraguas, que está lloviendo2. llevarcould you take this to the post office? ¿podrías llevar esto a la oficina de correos?3. llevarsesomeone's taken my bicycle! ¡alguien se ha llevado mi bicicleta!4. tomar5. llevar / tardar / durarto take place tener lugar / ocurrirtr[teɪk]1 SMALLCINEMA/SMALL toma1 (carry, bring) llevar■ take your umbrella, it might rain lleva el paraguas, puede que llueva2 (drive, escort) llevar■ shall I take you to the station? ¿quieres que te lleve a la estación?3 (remove) llevarse, quitar, coger■ who's taken my pencil? ¿quién ha cogido mi lápiz?4 (hold, grasp) tomar, coger■ do you want me to take your suitcase? ¿quieres que te coja la maleta?5 (accept - money etc) aceptar, coger; (- criticism, advice, responsibility) aceptar, asumir; (- patients, clients) aceptar■ do you take cheques? ¿aceptáis cheques?6 (win prize, competition) ganar; (earn) ganar, hacer■ how much have we taken today? ¿cuánto hemos hecho hoy de caja?7 (medicine, drugs) tomar■ have you ever taken drugs? ¿has tomado drogas alguna vez?■ do you take sugar? ¿te pones azúcar?8 (subject) estudiar; (course of study) seguir, cursar9 (teach) dar clase a10 (bus, train, etc) tomar, coger11 (capture) tomar, capturar; (in board games) comer12 (time) tardar, llevar■ how long does it take to get to Madrid? ¿cuánto se tarda en llegar a Madrid?13 (hold, contain) tener cabida, acoger■ how many people does your car take? ¿cuántas personas caben en tu coche?14 (size of clothes) usar, gastar; (size of shoes) calzar■ what size do you take? ¿qué talla usas?, ¿cuál es tu talla?■ what size shoe does he take? ¿qué número calza?15 (measurement, temperature, etc) tomar; (write down) anotar16 (need, require) requerir, necesitar17 (buy) quedarse con, llevar(se)18 (bear) aguantar, soportar19 (react) tomarse; (interpret) interpretar■ she took it the wrong way lo interpretó mal, se lo tomó a mal20 (perform, adopt) tomar, adoptar; (exercise) hacer■ she takes the view that... opina que...21 (have) tomar(se)22 (suppose) suponer■ I take it that... supongo que...23 (consider) considerar, mirar24 SMALLLINGUISTICS/SMALL regir25 (rent) alquilar2 (fish) picar3 (in draughts etc) comer\SMALLIDIOMATIC EXPRESSION/SMALLnot to take no for an answer no aceptar una respuesta negativatake it from me escucha lo que te digotake it or leave it lo tomas o lo dejastake my word for it créemeto be hard to take ser difícil de aceptarto be on the take dejarse sobornarto have what it takes tener lo que hace faltato take five descansar cinco minutosto take it out of somebody dejar a uno sin ganas de nadato take somebody out of himself hacer que alguien se olvide de sus propias penasto take something as read dar algo por sentado,-a1) capture: capturar, apresar2) grasp: tomar, agarrarto take the bull by the horns: tomar al toro por los cuernos3) catch: tomar, agarrartaken by surprise: tomado por sorpresa4) captivate: encantar, fascinar5) ingest: tomar, ingerirtake two pills: tome dos píldoras6) remove: sacar, extraertake an orange: saca una naranja7) : tomar, coger (un tren, un autobús, etc.)8) need, require: tomar, requirirthese things take time: estas cosas toman tiempo9) bring, carry: llevar, sacar, cargartake them with you: llévalos contigotake the trash out: saca la basura10) bear, endure: soportar, aguantar (dolores, etc.)11) accept: aceptar (un cheque, etc.), seguir (consejos), asumir (la responsabilidad)12) suppose: suponerI take it that...: supongo que...to take a walk: dar un paseoto take a class: tomar una claseto take place happen: tener lugar, suceder, ocurrirtake vi: agarrar (dícese de un tinte), prender (dícese de una vacuna)take n1) proceeds: recaudación f, ingresos mpl, ganancias fpl2) : toma f (de un rodaje o una grabación)n.• taquilla s.f.• toma (Film) s.f.• toma s.f. (time)expr.• tardar expr.v.(§ p.,p.p.: took, taken) = aceptar v.• asir v.• calzar v.• cautivar v.• coger v.• ganar v.• llevar v.• quedarse con v.• tener v.(§pres: tengo, tienes...tenemos) pret: tuv-fut/c: tendr-•)• tomar v.
I
1. teɪk2) (carry, lead, drive) llevarshall I take the chairs inside/upstairs? — ¿llevo las sillas adentro/arriba?, ¿meto/subo las sillas?
I'll take you up/down to the third floor — subo/bajo contigo al tercer piso, te llevo al tercer piso
to take the dog (out) for a walk — sacar* el perro a pasear
this path takes you to the main road — este camino lleva or por este camino se llega a la carretera
3)a) \<\<train/plane/bus/taxi\>\> tomar, coger* (esp Esp)are you taking the car? — ¿vas a ir en coche?
we took the elevator (AmE) o (BrE) lift to the restaurant — tomamos or (esp Esp) cogimos el ascensor para subir/bajar al restaurante
b) \<\<road/turning\>\> tomar, agarrar (esp AmL), coger* (esp Esp)c) \<\<bend\>\> tomar, coger* (esp Esp); \<\<fence\>\> saltar4)a) (grasp, seize) tomar, agarrar (esp AmL), coger* (esp Esp)he took her by the hand — la tomó or (esp AmL) la agarró or (esp Esp) la cogió de la mano
b) ( take charge of)may I take your coat? — ¿me permite el abrigo?
would you mind taking the baby for a moment? — ¿me tienes al niño un momento?
c) ( occupy)take a seat — siéntese, tome asiento (frml)
5) (remove, steal) llevarse6) ( catch)he was taken completely unawares — lo agarró or (esp Esp) lo cogió completamente desprevenido
to be taken ill — caer* enfermo
7)a) ( capture) \<\<town/fortress/position\>\> tomar; \<\<pawn/piece\>\> comerb) ( win) \<\<prize/title\>\> llevarse, hacerse* con; \<\<game/set\>\> ganarc) ( receive as profit) hacer*, sacar*8) \<\<medicine/drugs\>\> tomarhave you taken your tablets? — ¿te has tomado las pastillas?
9)a) (buy, order) llevar(se)I'll take 12 ounces — déme or (Esp tb) póngame 12 onzas
b) ( buy regularly) comprarwe take The Globe — nosotros compramos or leemos The Globe
c) ( rent) \<\<cottage/apartment\>\> alquilar, coger* (Esp)10)a) ( acquire) \<\<lover\>\> buscarse*to take a wife/husband — casarse
b) ( sexually) (liter) \<\<woman\>\> poseer*11) ( of time) \<\<job/task\>\> llevar; \<\<process\>\> tardar; \<\<person\>\> tardar, demorar(se) (AmL)it took longer than expected — llevó or tomó más tiempo de lo que se creía
the letter took a week to arrive — la carta tardó or (AmL tb) se demoró una semana en llegar
12) ( need)it takes courage to do a thing like that — hay que tener or hace falta or se necesita valor para hacer algo así
to have (got) what it takes — (colloq) tener* lo que hay que tener or lo que hace falta
13)a) ( wear)what size shoes do you take? — ¿qué número calzas?
she takes a 14 — usa la talla or (RPl) el talle 14
b) ( Auto)c) ( Ling) construirse* con, regir*14) ( accept) \<\<money/bribes/job\>\> aceptardo you take checks? — ¿aceptan cheques?
take it or leave it — (set phrase) lo tomas o lo dejas
take that, you scoundrel! — (dated) toma, canalla!
15)a) (hold, accommodate)the tank takes/will take 42 liters — el tanque tiene una capacidad de 42 litros
b) (admit, receive) \<\<patients/pupils\>\> admitir, tomar, coger* (Esp)we don't take telephone reservations o (BrE) bookings — no aceptamos reservas por teléfono
16)a) (withstand, suffer) \<\<strain/weight\>\> aguantar; \<\<beating/blow\>\> recibirb) (tolerate, endure) aguantarI can't take it any longer! — no puedo más!, ya no aguanto más!
he can't take a joke — no sabe aceptar or no se le puede hacer una broma
c) ( bear)how is he taking it? — ¿qué tal lo lleva?
17)a) (understand, interpret) tomarseshe took it the wrong way — se lo tomó a mal, lo interpretó mal
to take something as read/understood — dar* algo por hecho/entendido
I take it that you didn't like him much — por lo que veo no te cayó muy bien; see also take for
b) ( consider) (in imperative) mirartake Japan, for example — mira el caso del Japón, por ejemplo
18)a) \<\<steps/measures\>\> tomar; \<\<exercise\>\> hacer*to take a walk/a step forward — dar* un paseo/un paso adelante
b) (supervise, deal with)would you take that call, please? — ¿puede atender esa llamada por favor?
19) ( Educ)a) ( teach) (BrE) darle* clase ab) ( learn) \<\<subject\>\> estudiar, hacer*; \<\<course\>\> hacer*to take an exam — hacer* or dar* or (CS) rendir* or (Méx) tomar un examen, examinarse (Esp)
20)a) ( record) tomarwe took regular readings — tomamos nota de la temperatura (or presión etc) a intervalos regulares
b) ( write down) \<\<notes\>\> tomar21) ( adopt)he takes the view that... — opina que..., es de la opinión de que...
she took an instant dislike to him — le tomó antipatía inmediatamente; see also liking a), offense 2) b), shape I 1) a)
2.
vi1)a) \<\<seed\>\> germinar; \<\<cutting\>\> prenderb) \<\<dye\>\> agarrar (esp AmL), coger* (esp Esp)2) ( receive) recibirall you do is take, take, take — no piensas más que en ti
•Phrasal Verbs:- take for- take in- take off- take on- take out- take to- take up
II
1) ( Cin) toma f2)a) ( earnings) ingresos mpl, recaudación fb) ( share) parte f; ( commission) comisión f[teɪk] (vb: pt took) (pp taken)1. VT1) (=remove) llevarse; (=steal) robar, llevarsewho took my beer? — ¿quién se ha llevado mi cerveza?
someone's taken my handbag — alguien se ha llevado mi bolso, alguien me ha robado el bolso
•
I picked up the letter but he took it from me — cogí la carta pero él me la quitó2) (=take hold of, seize) tomar, coger, agarrar (LAm)let me take your case/coat — permíteme tu maleta/abrigo
I'll take the blue one, please — me llevaré el azul
•
the devil take it! — ¡maldición! †•
take five! * — ¡hagan una pausa!, ¡descansen un rato!•
take your partners for a waltz — saquen a su pareja a bailar un vals•
please take a seat — tome asiento, por favoris this seat taken? — ¿está ocupado este asiento?
•
it took me by surprise — me cogió desprevenido, me pilló or agarró desprevenido (LAm)•
take ten! — (US) * ¡hagan una pausa!, ¡descansen un rato!•
to take a wife — † casarse, contraer matrimonio3) (=lead, transport) llevarher work took her to Bonn — su trabajó la destinó or llevó a Bonn
•
he took me home in his car — me llevó a casa en su coche•
they took me over the factory — me mostraron la fábrica, me acompañaron en una visita a la fábrica4) [+ bus, taxi] (=travel by) ir en; (at specified time) coger, tomar (esp LAm); [+ road, short cut] ir porwe took the five o'clock train — cogimos or tomamos el tren de las cinco
take the first on the right — vaya por or tome la primera calle a la derecha
5) (=capture) [+ person] coger, agarrar (LAm); [+ town, city] tomar; (Chess) comer6) (=obtain, win) [+ prize] ganar, llevarse; [+ 1st place] conseguir, obtener; [+ trick] ganar, hacerwe took £500 today — (Brit) (Comm) hoy hemos ganado 500 libras
7) (=accept, receive) [+ money] aceptar; [+ advice] seguir; [+ news, blow] tomar, recibir; [+ responsibility] asumir; [+ bet] aceptar, hacertake my advice, tell her the truth — sigue mi consejo or hazme caso y dile la verdad
what will you take for it? — ¿cuál es tu mejor precio?
•
London took a battering in 1941 — Londres recibió una paliza en 1941, Londres sufrió terriblemente en 1941•
will you take a cheque? — ¿aceptaría un cheque?•
you must take us as you find us — nos vas a tener que aceptar tal cual•
take it from me! — ¡escucha lo que te digo!you can take it from me that... — puedes tener la seguridad de que...
•
losing is hard to take — es difícil aceptar la derrota•
it's £50, take it or leave it! — son 50 libras, lo toma o lo dejawhisky? I can take it or leave it — ¿el whisky? ni me va ni me viene
•
I won't take no for an answer — no hay pero que valga•
he took a lot of punishment — (fig) le dieron muy duro•
take that! — ¡toma!8) (=rent) alquilar, tomar; (=buy regularly) [+ newspaper] comprar, leer9) (=have room or capacity for) tener cabida para; (=support weight of) aguantara car that takes five passengers — un coche con cabida para or donde caben cinco personas
can you take two more? — ¿puedes llevar dos más?, ¿caben otros dos?
10) (=wear) [+ clothes size] gastar, usar (LAm); [+ shoe size] calzarwhat size do you take? — (clothes) ¿qué talla usas?; (shoes) ¿qué número calzas?
11) (=call for, require) necesitar, requeririt takes a lot of courage — exige or requiere gran valor
•
it takes two to make a quarrel — uno solo no puede reñir•
she's got what it takes — tiene lo que hace falta12) (of time)•
I'll just iron this, it won't take long — voy a planchar esto, no tardaré or no me llevará mucho tiempotake your time! — ¡despacio!
13) (=conduct) [+ meeting, church service] presidir; (=teach) [+ course, class] enseñar; [+ pupils] tomar; (=study) [+ course] hacer; [+ subject] dar, estudiar; (=undergo) [+ exam, test] presentarse a, pasarwhat are you taking next year? — ¿qué vas a hacer or estudiar el año que viene?
•
to take a degree in — licenciarse en14) (=record) [+ sb's name, address] anotar, apuntar; [+ measurements] tomar15) (=understand, assume)I take it that... — supongo que..., me imagino que...
am I to take it that you refused? — ¿he de suponer que te negaste?
how old do you take him to be? — ¿cuántos años le das?
•
I took him for a doctor — lo tenía por médico, creí que era médicowhat do you take me for? — ¿por quién me has tomado?
•
I don't quite know how to take that — no sé muy bien cómo tomarme eso16) (=consider) [+ case, example] tomarnow take Ireland, for example — tomemos, por ejemplo, el caso de Irlanda, pongamos como ejemplo Irlanda
let us take the example of a family with three children — tomemos el ejemplo de una familia con tres hijos
take John, he never complains — por ejemplo John, él nunca se queja
taking one thing with another... — considerándolo todo junto..., considerándolo en conjunto...
17) (=put up with, endure) [+ treatment, climate] aguantar, soportarwe can take it — lo aguantamos or soportamos todo
•
I can't take any more! — ¡no aguanto más!, ¡no soporto más!•
I won't take any nonsense! — ¡no quiero oír más tonterías!18) (=eat) comer; (=drink) tomarwill you take sth before you go? — ¿quieres tomar algo antes de irte?
•
he took no food for four days — estuvo cuatro días sin comer•
he takes sugar in his tea — toma or pone azúcar en el té•
to take tea (with sb) — † tomar té (con algn)19) (=negotiate) [+ bend] tomar; [+ fence] saltar, saltar por encima de20) (=acquire)•
to be taken ill — ponerse enfermo, enfermar•
he took great pleasure in teasing her — se regodeaba tomándole el pelo•
I do not take any satisfaction in knowing that... — no experimento satisfacción alguna sabiendo que...21) (Ling) [+ case] regir22)• to be taken with sth/sb (=attracted) —
I'm not at all taken with the idea — la idea no me gusta nada or no me hace gracia
23) † liter (=have sexual intercourse with) tener relaciones sexuales con24) (as function verb) [+ decision, holiday] tomar; [+ step, walk] dar; [+ trip] hacer; [+ opportunity] aprovechar2. VI1) (=be effective) [dye] coger, agarrar (LAm); [vaccination, fire] prender; [glue] pegar2) (Bot) [cutting] arraigar3) (=receive)giveshe's all take, take, take — ella mucho dame, dame, pero luego no da nada
3. N1) (Cine) toma f3)- be on the take4) (=share) parte f ; (=commission) comisión f, tajada * f5) * (=opinion) opinión fwhat's your take on the new government? — ¿qué piensas de or qué opinión te merece el nuevo gobierno?
- take in- take off- take on- take out- take to- take upTAKE Both t ardar and llevar can be used to translate take with {time}. ► Use tar dar (en + ((infinitive))) to describe how long someone or something will take to do something. The subject of tardar is the person or thing that has to complete the activity or undergo the process:
How long do letters take to get to Spain? ¿Cuánto (tiempo) tardan las cartas en llegar a España?
How much longer will it take you to do it? ¿Cuánto más vas a tardar en hacerlo?
It'll take us three hours to get to Douglas if we walk Tardaremos tres horas en llegar a Douglas si vamos andando ► Use lle var to describe how long an activity, task or process takes to complete. The subject of llevar is the activity or task:
The tests will take at least a month Las pruebas llevarán por lo menos un mes
How long will it take? ¿Cuánto tiempo llevará? ► Compare the different focus in the alternative translations of the following example:
It'll take me two more days to finish this job Me llevará dos días más terminar este trabajo, Tardaré dos días más en terminar este trabajo For further uses and examples, see main entry* * *
I
1. [teɪk]2) (carry, lead, drive) llevarshall I take the chairs inside/upstairs? — ¿llevo las sillas adentro/arriba?, ¿meto/subo las sillas?
I'll take you up/down to the third floor — subo/bajo contigo al tercer piso, te llevo al tercer piso
to take the dog (out) for a walk — sacar* el perro a pasear
this path takes you to the main road — este camino lleva or por este camino se llega a la carretera
3)a) \<\<train/plane/bus/taxi\>\> tomar, coger* (esp Esp)are you taking the car? — ¿vas a ir en coche?
we took the elevator (AmE) o (BrE) lift to the restaurant — tomamos or (esp Esp) cogimos el ascensor para subir/bajar al restaurante
b) \<\<road/turning\>\> tomar, agarrar (esp AmL), coger* (esp Esp)c) \<\<bend\>\> tomar, coger* (esp Esp); \<\<fence\>\> saltar4)a) (grasp, seize) tomar, agarrar (esp AmL), coger* (esp Esp)he took her by the hand — la tomó or (esp AmL) la agarró or (esp Esp) la cogió de la mano
b) ( take charge of)may I take your coat? — ¿me permite el abrigo?
would you mind taking the baby for a moment? — ¿me tienes al niño un momento?
c) ( occupy)take a seat — siéntese, tome asiento (frml)
5) (remove, steal) llevarse6) ( catch)he was taken completely unawares — lo agarró or (esp Esp) lo cogió completamente desprevenido
to be taken ill — caer* enfermo
7)a) ( capture) \<\<town/fortress/position\>\> tomar; \<\<pawn/piece\>\> comerb) ( win) \<\<prize/title\>\> llevarse, hacerse* con; \<\<game/set\>\> ganarc) ( receive as profit) hacer*, sacar*8) \<\<medicine/drugs\>\> tomarhave you taken your tablets? — ¿te has tomado las pastillas?
9)a) (buy, order) llevar(se)I'll take 12 ounces — déme or (Esp tb) póngame 12 onzas
b) ( buy regularly) comprarwe take The Globe — nosotros compramos or leemos The Globe
c) ( rent) \<\<cottage/apartment\>\> alquilar, coger* (Esp)10)a) ( acquire) \<\<lover\>\> buscarse*to take a wife/husband — casarse
b) ( sexually) (liter) \<\<woman\>\> poseer*11) ( of time) \<\<job/task\>\> llevar; \<\<process\>\> tardar; \<\<person\>\> tardar, demorar(se) (AmL)it took longer than expected — llevó or tomó más tiempo de lo que se creía
the letter took a week to arrive — la carta tardó or (AmL tb) se demoró una semana en llegar
12) ( need)it takes courage to do a thing like that — hay que tener or hace falta or se necesita valor para hacer algo así
to have (got) what it takes — (colloq) tener* lo que hay que tener or lo que hace falta
13)a) ( wear)what size shoes do you take? — ¿qué número calzas?
she takes a 14 — usa la talla or (RPl) el talle 14
b) ( Auto)c) ( Ling) construirse* con, regir*14) ( accept) \<\<money/bribes/job\>\> aceptardo you take checks? — ¿aceptan cheques?
take it or leave it — (set phrase) lo tomas o lo dejas
take that, you scoundrel! — (dated) toma, canalla!
15)a) (hold, accommodate)the tank takes/will take 42 liters — el tanque tiene una capacidad de 42 litros
b) (admit, receive) \<\<patients/pupils\>\> admitir, tomar, coger* (Esp)we don't take telephone reservations o (BrE) bookings — no aceptamos reservas por teléfono
16)a) (withstand, suffer) \<\<strain/weight\>\> aguantar; \<\<beating/blow\>\> recibirb) (tolerate, endure) aguantarI can't take it any longer! — no puedo más!, ya no aguanto más!
he can't take a joke — no sabe aceptar or no se le puede hacer una broma
c) ( bear)how is he taking it? — ¿qué tal lo lleva?
17)a) (understand, interpret) tomarseshe took it the wrong way — se lo tomó a mal, lo interpretó mal
to take something as read/understood — dar* algo por hecho/entendido
I take it that you didn't like him much — por lo que veo no te cayó muy bien; see also take for
b) ( consider) (in imperative) mirartake Japan, for example — mira el caso del Japón, por ejemplo
18)a) \<\<steps/measures\>\> tomar; \<\<exercise\>\> hacer*to take a walk/a step forward — dar* un paseo/un paso adelante
b) (supervise, deal with)would you take that call, please? — ¿puede atender esa llamada por favor?
19) ( Educ)a) ( teach) (BrE) darle* clase ab) ( learn) \<\<subject\>\> estudiar, hacer*; \<\<course\>\> hacer*to take an exam — hacer* or dar* or (CS) rendir* or (Méx) tomar un examen, examinarse (Esp)
20)a) ( record) tomarwe took regular readings — tomamos nota de la temperatura (or presión etc) a intervalos regulares
b) ( write down) \<\<notes\>\> tomar21) ( adopt)he takes the view that... — opina que..., es de la opinión de que...
she took an instant dislike to him — le tomó antipatía inmediatamente; see also liking a), offense 2) b), shape I 1) a)
2.
vi1)a) \<\<seed\>\> germinar; \<\<cutting\>\> prenderb) \<\<dye\>\> agarrar (esp AmL), coger* (esp Esp)2) ( receive) recibirall you do is take, take, take — no piensas más que en ti
•Phrasal Verbs:- take for- take in- take off- take on- take out- take to- take up
II
1) ( Cin) toma f2)a) ( earnings) ingresos mpl, recaudación fb) ( share) parte f; ( commission) comisión f -
77 action
noun1) (doing something) Handeln, dastake action — Schritte od. etwas unternehmen
put a plan into action — einen Plan in die Tat umsetzen
be/be put out of action — außer Betrieb sein/gesetzt werden
a film full of action — ein Film mit viel Handlung
2) (effect)3) (act) Tat, diewhere the action is — (coll.) wo was los ist (ugs.)
5) (legal process) [Gerichts]verfahren, dasbring an action against somebody — eine Klage od. ein Verfahren gegen jemanden anstrengen
he died in action — er ist [im Kampf] gefallen
7) (movement) Bewegung, die* * *['ækʃən]1) (something done: Action, not talking, is necessary if we are to defeat the enemy; Take action immediately; The firemen are ready to go into action.) das Handeln2) (movement: Tennis needs a good wrist action.) die Bewegung3) (a legal case: He brought an action for divorce against his wife.) Klage4) (the events (of a play, film etc): The action of the play takes place on an island.) die Handlung5) (a battle; fighting: He was killed in action; Our troops fought an action against the enemy.) das Gefecht•- academic.ru/116764/in_action">in action- out of action* * *ac·tion[ˈækʃən]nwhat we need is \action wir brauchen Tatenwe need firm \action wir müssen entschlossen vorgehenonly decisive \action will stop the crisis from escalating nur ein entschlossenes Vorgehen wird eine Eskalation der Krise verhindernso, what's the plan of \action? wie sieht also der Plan aus?come on lazy things, let's see some \action [around here]! ( fam) auf, ihr Faulpelze, legt euch ins Zeug! famwhat [kind of] \action is necessary to reduce unemployment? wie kann man die Arbeitslosigkeit senken?course of \action Vorgehensweise fcould you tell me what the best course of \action is? wie soll ich Ihrer Meinung nach am besten vorgehen?freedom of \action Handlungsfreiheit fa man/woman of \action ein Mann/eine Frau der Tatprompt \action promptes Handelnto be out of \action außer Gefecht seinto come into \action in die Tat umgesetzt werdento put sth into \action etw in die Tat umsetzento put sb out of \action jdn außer Gefecht setzento take \action handeln, etwas unternehmenno \action was taken es wurde nichts unternommenwe must take \action to deal with the problem wir müssen etwas unternehmen, um mit dem Problem fertig zu werdenin \action in Aktionyou're responsible for your own \actions now du bist jetzt selbst für das, was du tust, verantwortlichyour \action in releasing the caged animals was highly irresponsible es war höchst unverantwortlich von Ihnen, die eingesperrten Tiere freizulassenthe [main] \action die [Haupt]handlunglights, camera, \action! Beleuchtung, Kamera und Action!his films have a lot of \action and not much dialogue seine Filme sind voller Action und arm an Dialogento be missing in \action vermisst seinto be in \action im Einsatz seinto be destroyed by enemy \action durch Feindeinwirkung zerstört werdento go into \action ins Gefecht ziehento be killed in \action fallento see \action im Einsatz sein7. no pllet's go where the \action is lass uns hingehen, wo was los ist famI'll say the words and you can mime the \actions ich spreche den Text und du kannst die Bewegungen dazu machenthe fibres are broken down by chemical \action die Fasern werden durch chemische Vorgänge zersetztto be out of \action außer Betrieb seinto put sth out of \action etw außer Betrieb setzenin \action in Betriebhe's got a very awkward bowling \action er verfügt über einen eigenartigen Wurfstilclass \action Gruppenklage fcourt \action Prozess m\action for damages Schadenersatzklage f\action in personam/rem obligatorische/dingliche Klage fachspr\action in tort Schadenersatzklage fto bring an \action [for sth] against sb gegen jdn Klage [wegen einer S. gen] erheben, jdn [wegen einer S. gen] verklagento bring an \action for damages against sb jdn auf Schadenersatz verklagento take [industrial] \action streiken15.▶ the wheels of bureaucracy creaked into \action esp BRIT ( hum) die Mühlen der Bürokratie setzten sich langsam in Bewegung* * *['kSən]nto take action — etwas or Schritte unternehmen
have you taken any action on his letter? — haben Sie auf seinen Brief hin irgendetwas or irgendwelche Schritte unternommen?
course of action — Vorgehen nt
"action" (on office tray) — "zur Bearbeitung"
no further action — keine weiteren Maßnahmen; (label on file etc) abgeschlossen
the action of the play/novel takes place... — das Stück/der Roman spielt...
2) (= deed) Tat fhis first action was to phone me to suit the action to the word — als Erstes rief er mich an dem Wort die Tat folgen lassen, sein Wort in die Tat umsetzen
3)he's been out of action since he broke his leg — er ist nicht mehr in Aktion gewesen or war nicht mehr einsatzfähig, seit er sich das Bein gebrochen hat
he needs prodding into action — man muss ihm immer erst einen Stoß geben
there's no action in this film — in dem Film passiert nichts, dem Film fehlt die Action (inf)
to go where the action is (inf) — hingehen, wo was los ist (inf)
that's where the action is (inf) — da ist was los (inf)
5) (MIL) (= fighting) Aktionen pl; (= battle) Kampf m, Gefecht nt6) (= way of operating) (of machine) Arbeitsweise f; (of piano etc) Mechanik f; (of watch, gun) Mechanismus m; (= way of moving) (of athlete etc) Bewegung f; (of horse) Aktion f7) (ESP CHEM, PHYS: effect) Wirkung f (on auf +acc)9) (FIN inf)a piece or slice of the action — ein Stück nt aus dem Kuchen (sl)
* * *action [ˈækʃn] s1. a) Handeln, Handlung f, Maßnahme(n) f(pl), Tat f, Aktion f:man of action Mann m der Tat;full of action aktiv;bring into action ins Spiel bringen, einsetzen;call into action auf den Plan rufen;come into action in Aktion treten;put into action in die Tat umsetzen;see sb in action jemanden in Aktion sehen;actions speak louder than words Taten zählen mehr als Worte;take action Maßnahmen treffen, Schritte unternehmen, handeln;we must take action before it is too late wir müssen etwas unternehmen, bevor es zu spät ist;the police took no action die Polizei griff nicht ein;take action against vorgehen gegen ( → 12);course of action Handlungs-, Vorgehensweise f;for further action zur weiteren Veranlassungb) Handlung f, engS. Action f:there is no action in this play in diesem Stück tut sich oder passiert nichts;where the action is sl wo sich alles abspielt; wo was los ist; if you are interested in good food, Paris is where the action is musst du unbedingt nach Paris fahren2. auch PHYSIOL, TECH Tätigkeit f, Funktion f, Gang m (einer Maschine), Funktionieren n (eines Mechanismus):action of the heart Herztätigkeit, -funktion;action (of the bowels) Stuhlgang m;in action TECH in Betrieb, im Einsatz;put in action in Gang oder in Betrieb setzen;be out of action außer Betrieb sein ( → 13);put out of action außer Betrieb setzen ( → 13)3. a) TECH Mechanismus m, Werk nb) Arbeitsweise fa) (Ein)Wirkung f, Wirksamkeit f, Einfluss m:the action of this acid on metal die Einwirkung dieser Säure auf Metall;action of presence Kontaktwirkungb) Vorgang m, Prozess m5. Handlung f (eines Dramas etc):the action of the play takes place in das Stück spielt in (dat);the action takes place in London Ort der Handlung ist London6. KUNSTa) Bewegung f, Aktion f:b) Stellung f, Haltung f (einer Figur auf einem Bild)7. Bewegung f, Gangart f (eines Pferdes)8. Vortrag(sweise) m(f), Ausdruck m (eines Schauspielers)9. fig Benehmen n, Führung f, Haltung f10. SOZIOL Umwelteinflüsse pl11. WIRTSCH Preisbewegung f, Konjunktur(verlauf) f(m)12. JUR Klage f, Prozess m, (Rechts-, Gerichts)Verfahren n:action for annulment Nichtigkeitsklage;action for damages Schadenersatzklage;bring ( oder file, institute) an action against sb, take action against sb jemanden verklagen, gegen jemanden Klage erheben oder ein Gerichtsverfahren einleiten ( → 1); → debt 2, detinue, trespass B 5, trover 213. MIL Gefecht n, Gefechts-, Kampfhandlung f, Unternehmen n, Einsatz m:killed (missing, wounded) in action gefallen (vermisst, verwundet);go into action eingreifen;be out of action außer Gefecht sein (a. fig)( → 2);he saw action er war im Einsatz oder an der Front14. POL etc USa) Beschluss m, Entscheidung fb) Maßnahme(n) f(pl)15. MUS, TECHa) (Spiel)Mechanik fb) Traktur f (der Orgel)* * *noun1) (doing something) Handeln, dastake action — Schritte od. etwas unternehmen
be/be put out of action — außer Betrieb sein/gesetzt werden
2) (effect)3) (act) Tat, diewhere the action is — (coll.) wo was los ist (ugs.)
5) (legal process) [Gerichts]verfahren, dasbring an action against somebody — eine Klage od. ein Verfahren gegen jemanden anstrengen
he died in action — er ist [im Kampf] gefallen
7) (movement) Bewegung, die* * *n.Akt -e m.Aktion -en f.Arbeitsgang m.Gang ¨-e m.Handlung -en f.Prozess -e m.Tat -en f.Wirkung -en f. -
78 correlation
noun[Wechsel]beziehung, die; Korrelation, die (bes. Math., Naturw.); (connection) Zusammenhang, der* * *cor·re·la·tion[ˌkɒrəˈleɪʃən, AM ˌkɔ:r-]nthere's a strong \correlation between... es besteht ein enger Zusammenhang zwischen...there's little \correlation between wealth and happiness Reichtum und Glück haben wenig miteinander zu tun* * *["kɒrI'leISən]n(= correspondence) Beziehung f; (= close relationship) enger or direkter Zusammenhang; (MATH, STATISTICS) Korrelation f* * *1. Korrelation f, Wechselbeziehung f, -wirkung f, gegenseitige Abhängigkeit, Zusammenhang m:* * *noun[Wechsel]beziehung, die; Korrelation, die (bes. Math., Naturw.); (connection) Zusammenhang, der* * *n.Korrelation f.Wechselbeziehung f.Übereinstimmung f. -
79 set
[set] 1. present participle - setting; verb1) (to put or place: She set the tray down on the table.) setja, leggja2) (to put plates, knives, forks etc on (a table) for a meal: Please would you set the table for me?) leggja á borð3) (to settle or arrange (a date, limit, price etc): It's difficult to set a price on a book when you don't know its value.) ákveða, áætla4) (to give a person (a task etc) to do: The witch set the prince three tasks; The teacher set a test for her pupils; He should set the others a good example.) setja/leggja fyrir5) (to cause to start doing something: His behaviour set people talking.) koma af stað6) ((of the sun etc) to disappear below the horizon: It gets cooler when the sun sets.) setjast7) (to become firm or solid: Has the concrete set?) harðna8) (to adjust (eg a clock or its alarm) so that it is ready to perform its function: He set the alarm for 7.00 a.m.) stilla (á)9) (to arrange (hair) in waves or curls.) leggja hár10) (to fix in the surface of something, eg jewels in a ring.) greypa, setja í umgjörð11) (to put (broken bones) into the correct position for healing: They set his broken arm.) setja beinbrot2. adjective1) (fixed or arranged previously: There is a set procedure for doing this.) fastur, fyrirskipaður2) ((often with on) ready, intending or determined (to do something): He is set on going.) staðráðinn3) (deliberate: He had the set intention of hurting her.) yfirlagður4) (stiff; fixed: He had a set smile on his face.) stífur, stirðnaður5) (not changing or developing: set ideas.) ósveigjanlegur6) ((with with) having something set in it: a gold ring set with diamonds.) settur (e-u)3. noun1) (a group of things used or belonging together: a set of carving tools; a complete set of (the novels of) Jane Austen.) samstæða, sett2) (an apparatus for receiving radio or television signals: a television/radio set.) -tæki3) (a group of people: the musical set.) klíka, lið4) (the process of setting hair: a shampoo and set.) lagning5) (scenery for a play or film: There was a very impressive set in the final act.) leik-/sviðsmynd6) (a group of six or more games in tennis: She won the first set and lost the next two.) sett, hrina•- setting- setback
- set phrase
- set-square
- setting-lotion
- set-to
- set-up
- all set
- set about
- set someone against someone
- set against someone
- set someone against
- set against
- set aside
- set back
- set down
- set in
- set off
- set something or someone on someone
- set on someone
- set something or someone on
- set on
- set out
- set to
- set up
- set up camp
- set up house
- set up shop
- set upon -
80 set
alakulás, megmerevedett, kötött, szerviz, játszma to set: megállapodik, erősít, vmilyen állapotba juttat* * *[set] 1. present participle - setting; verb1) (to put or place: She set the tray down on the table.) (le)tesz2) (to put plates, knives, forks etc on (a table) for a meal: Please would you set the table for me?) megterít3) (to settle or arrange (a date, limit, price etc): It's difficult to set a price on a book when you don't know its value.) megállapít4) (to give a person (a task etc) to do: The witch set the prince three tasks; The teacher set a test for her pupils; He should set the others a good example.) kitűz, felad5) (to cause to start doing something: His behaviour set people talking.) késztet6) ((of the sun etc) to disappear below the horizon: It gets cooler when the sun sets.) lenyugszik (égitest)7) (to become firm or solid: Has the concrete set?) megköt8) (to adjust (eg a clock or its alarm) so that it is ready to perform its function: He set the alarm for 7.00 a.m.) beállít9) (to arrange (hair) in waves or curls.) berak (hajat)10) (to fix in the surface of something, eg jewels in a ring.) vmibe foglal (drágakövet)11) (to put (broken bones) into the correct position for healing: They set his broken arm.) helyre rak2. adjective1) (fixed or arranged previously: There is a set procedure for doing this.) kötött; meghatározott; kötelező2) ((often with on) ready, intending or determined (to do something): He is set on going.) eltökélt3) (deliberate: He had the set intention of hurting her.) megfontolt4) (stiff; fixed: He had a set smile on his face.) merev5) (not changing or developing: set ideas.) megmerevedett6) ((with with) having something set in it: a gold ring set with diamonds.) kirakva3. noun1) (a group of things used or belonging together: a set of carving tools; a complete set of (the novels of) Jane Austen.) készlet, sorozat2) (an apparatus for receiving radio or television signals: a television/radio set.) készülék3) (a group of people: the musical set.) csoport4) (the process of setting hair: a shampoo and set.) berakás (hajé)5) (scenery for a play or film: There was a very impressive set in the final act.) díszlet6) (a group of six or more games in tennis: She won the first set and lost the next two.) játszma•- setting- setback
- set phrase
- set-square
- setting-lotion
- set-to
- set-up
- all set
- set about
- set someone against someone
- set against someone
- set someone against
- set against
- set aside
- set back
- set down
- set in
- set off
- set something or someone on someone
- set on someone
- set something or someone on
- set on
- set out
- set to
- set up
- set up camp
- set up house
- set up shop
- set upon
См. также в других словарях:
function — function, functionalism Although the use of the concepts of function and functionalism is usually associated with the work of Talcott Parsons in modern sociology, there is a long tradition of functional explanation in studying societies, and a… … Dictionary of sociology
Function — Func tion, n. [L. functio, fr. fungi to perform, execute, akin to Skr. bhuj to enjoy, have the use of: cf. F. fonction. Cf. {Defunct}.] 1. The act of executing or performing any duty, office, or calling; performance. In the function of his public … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
function — 1. The noun has a number of technical meanings in mathematics and information technology, and has acquired general meanings that caused Fowler (1926) to categorize it as a popularized technicality. As a noun, it is often used somewhat… … Modern English usage
Function overloading — or method overloading is a feature found in various programming languages such as Ada, C#, VB.NET, C++, D and Java that allows the creation of several methods with the same name which differ from each other in terms of the type of the input and… … Wikipedia
there — [ ðer ] function word *** There can be used in the following ways: as a pronoun (to introduce the subject of the sentence): There s a spider in the bath. as an adverb: Wait there until I get back. as an interjection: There, that didn t hurt so… … Usage of the words and phrases in modern English
Function (mathematics) — f(x) redirects here. For the band, see f(x) (band). Graph of example function, In mathematics, a function associates one quantity, the a … Wikipedia
Function point — A function point is a unit of measurement to express the amount of business functionality an information system provides to a user. Function points are the units of measure used by the IFPUG Functional Size Measurement Method. The IFPUG FSM… … Wikipedia
Function problem — In computational complexity theory, a function problem is a problem other than a decision problem, that is, a problem requiring a more complex answer than just YES or NO.Notable examples include the travelling salesman problem, which asks for the … Wikipedia
Function object — A function object, also called a functor or functional, is a computer programming construct allowing an object to be invoked or called as if it were an ordinary function, usually with the same syntax.Function objects are unrelated to functors in… … Wikipedia
function — /fungk sheuhn/, n. 1. the kind of action or activity proper to a person, thing, or institution; the purpose for which something is designed or exists; role. 2. any ceremonious public or social gathering or occasion. 3. a factor related to or… … Universalium
Function composition — For function composition in computer science, see function composition (computer science). g ∘ f, the composition of f and g. For example, (g ∘ f)(c) = #. In mathematics, function composition is the application of one function to the resul … Wikipedia
