-
1 service
I ['sɜːvɪs] 1. сущ.1) служба, занятие, работаmeritorious service — служба, достойная награды
to take smb. into one's service — нанимать кого-л. на службу
- community serviceto take service with smb. — поступать на службу к кому-л.
2)diplomatic service брит. / foreign service амер. — дипломатическая служба
б) = military service военная службаto be dismissed / discharged from the service — быть уволенным с военной службы
He died on active service. — Он погиб на фронте.
He saw service during the First World War. — Он служил в армии во время Первой мировой войны.
He did a year's military service. — Он отслужил в армии один год.
в) ( the Services) вооружённые силы (сухопутные войска, военно-воздушные силы и военно-морской флот)3)а) учреждение, подразделение; службаб) обслуживание, оказание услуг, сервисprofessional services — профессиональное обслуживание; услуги профессионала
to offer / give / provide service — предлагать услуги, обслуживать
4) сообщение, связь, движениеdaily service between New York City and Washington, DC — ежедневное сообщение между городами Нью-Йорк и Вашингтон
5) помощь, одолжение, услугаI am glad to be of service. — Рад оказать услугу.
I am entirely at your service. — Я полностью в вашем распоряжении.
Syn:help 2.6) воен. род войск7) сервиз8) юр. повестка, судебное извещение9) рел.; = religious service богослужениеmemorial service / service for the dead — заупокойная служба, панихида; богослужение в память о погибших; поминальная служба
- evening serviceto hold a service — служить службу, отправлять богослужение
- morning service
- noontime service
- sunrise service10) спорт.; = serve 2. подачаto break smb.'s service — отбить чью-л. подачу
11) мор. клетневание2. гл.1) обслуживатьAirports are so far from the cities they supposedly service. — Аэропорты находятся очень далеко от городов, которые они должны обслуживать.
Syn:serve 1.2)а) амер. проводить технический осмотр, ремонтировать (машины и т. п.)Your car will be serviced on Thursday. — Ваша машина будет отремонтирована в четверг.
3) фин. выплачивать проценты по долгу4) с.-х. случать ( животных)II ['sɜːvɪs] = service tree -
2 service
̈ɪˈsə:vɪs I
1. сущ.
1) служба, занятие, работа to press smb. into service ≈ заставлять кого-л. служить to take smb. into one's service ≈ нанимать кого-л. meritorious service service record
2) а) учреждение, подразделение (в компетенции которого находятся те или иные вопросы) б) служба obstetrical service ≈ служба родовспоможения
3) обслуживание, оказание услуг, сервис to do, perform, provide, render a service ≈ предлагать услуги, обслуживать to introduce, offer service ≈ предлагать услуги to suspend a service ≈ временно прекращать обслуживание service charge ≈ плата за операцию (общераспространенный сбор за банковские услуги) emergency service ≈ неотложная помощь, скорая помощь orientation service ≈ служба профориентации per-call service ≈ плата по числу звонков
4) сообщение, связь, движение;
рейсы (between;
from;
to) to introduce service ≈ вводить сообщение to offer, provide service ≈ обеспечивать сообщение to run on a regular service ≈ обеспечивать регулярное сообщение to suspend service ≈ временно прекращать сообщение human services ≈ сфера услуг
5) помощь, одолжение, услуга I am glad to be of service. ≈ Рад оказать услугу. at your service ≈ к вашим услугам Syn: help, use
1., benefit
1.
6) а) государственная служба Civil Service ≈ государственная (гражданская) служба National Service ≈ воинская или трудовая повинность( в Англии) civil service ≈ государственная служба consular service ≈ консульская служба diplomatic service ≈ дипломатическая служба foreign service ≈ дипломатическая служба intelligence service ≈ секретная служба, разведывательная служба secret service ≈ секретная служба, разведывательная служба, разведка б) военная служба
7) воен. род войск
8) сервиз coffee service ≈ кофейный сервиз dinner service ≈ обеденный сервиз tea service ≈ чайный сервиз
9) повестка, судебное извещение
10) мор. клетневание
11) спорт подача( мяча) to break smb.'s service ≈ отбить чью-л. подачу to hold one's service ≈ удерживать подачу to lose one's service ≈ проиграть подачу
12) церк. служба, месса to hold a service ≈ служить службу burial service marriage service memorial service prayer service religious service evening service morning service noontime service sunrise service
2. гл.
1) обслуживать, служить, быть полезным Syn: serve
2) а) амер. проводить технический осмотр, ремонтировать (машины и т. п.) She enjoyed her work, which consisted chiefly in running and servicing a powerful but tricky electric motor. ≈ Ей нравилась ее работа, которая заключалась в запуске и осуществлении текущего технического обеспечения электрического двигателя. б) заправлять горючим
3) выплачивать проценты по долгу
4) обеспечивать (чем-л.)
5) случать( животных) II = service-tree услужение - domestic * домашняя работа, обязанности слуги - to be in( smb.'s) * быть слугой, служить (у кого-л.) - to go into /to, out to/ * пойти в прислуги - to take * with smb. поступать к кому-л. в прислуги - to take smb. into one's * нанимать кого-л., брать в услужение кого-л. - last week the cook left our * на прошлой неделе от нас ушла кухарка работа - hard * тяжелая работа - to be out of * быть без работы /без места/ - to go out of * уйти с работы - to reward smb. for his good * награждать кого-л. за хорошую службу - to be on detached * быть в командировке - to send smb. off on special * послать кого-л. со специальным заданием - he gives good * он хорошо работает, он отличный работник рабочий стаж, срок службы - prolonged meritorious * выслуга лет - to have ten years * иметь десятилетний стаж работы государственная служба - the Civil S. государственная /гражданская/ служба - to be in the Civil S. быть на гражданской /на государственной/ службе - the diplomatic *, (американизм) Foreign S. дипломатическая служба - the consular * консульская служба - on His Majesty's S. (сокр. O.H.M.S.) на службе его величества (форма франкирования официальной переписки) учреждение (ведающее специальной отраслью работы) - information * информационная служба - reporting *s отдел официальных отчетов (ООН) - administrative *s административный отдел( секретариата ООН) ;
административные службы - typewriting * машинописное бюро служба - telegraph * телеграфная связь - communication * служба связи - railway *, * of trains железнодорожное сообщение - passenger * пассажирское сообщение - to restore normal train * восстановить регулярное движение поездов - to institute a new air * ввести новую линию воздушного сообщения - the telephone * is out of order телефонная связь нарушена - to operate regular *s from A. to B. установить регулярные рейсы между А. и Б. обслуживание, сервис - good * at a hotel хорошее обслуживание в гостинице - prompt * быстрое обслуживание - to give customers prompt * быстро обслуживать покупателей - medical * медицинское обслуживание - electric-light * обеспечение электроэнергией сфера услуг;
обслуживание населения;
служба быта, сервис - * workers работники, занятые в сфере обслуживания (продавцы, парикмахеры, официанты и т. п.) библиотечное обслуживание (тж. * to readers) - * catalogue служебный каталог - * fee плата за абонемент - * hours часы работы( библиотеки) военная служба - Selective S. (американизм) воинская повинность для отдельных граждан (по отбору) - active *, * with the colours действительная военная служба - to be called up for active * быть призванным на действительную военную службу - to do one's military * проходить военную службу - to be in the * служить в армии - length /period/ of * срок военной службы - fit for * годен к военной службе - to quit the * увольняться с военной службы - to be dismissed /discharged/ from the * быть уволенным с военной службы - to retire from * выйти в отставку - * ashore( морское) береговая служба - sea * служба на плавающих кораблях - examination * (морское) брандвахтенная /досмотровая/ служба - daily * (морское) служба корабельных нарядов( военное) вид вооруженных сил;
род войск - the three *s - the army, the navy, the aviation три рода войск: сухопутные войска, военно-морской флот и военно-воздушные силы - what branch of the * do you expect to enter? в какой род войск вы будете зачислены? услуга, одолжение;
помощь - to be at smb.'s * быть к чьим-л. услугам - I am at your * я к вашим услугам /в вашем распоряжении/ - to offer one's *s предлагать свои услуги - to be of * to smb. быть кому-л. полезным, пригодиться кому-л., сослужить кому-л. службу - glad to be of * to you рад быть вам полезным - to do /to render/ smb. a (great) * оказать кому-л. (большую) услугу - will you do me a *? окажите мне услугу - what good *s this pen has done me! эта ручка мне хорошо послужила! - you do yourself no * by such replies вы себе только вредите такими ответами - he didn't need the *s of an interpreter он не нуждался в услугах /в помощи/ переводчика - in gratitude for your valuable *s в благодарность за ваши неоценимые услуги - an exchange of friendly *s обмен дружескими услугами - the dictionary is of enormous * to students этот словарь оказывает большую помощь учащимся заслуга - great *s большие заслуги - prominent *s to the State выдающиеся заслуги перед государством - to exaggerate one's own *s преувеличивать собственные заслуги - for smb.'s past *s за прошлые заслуги сервиз - dinner * обеденный сервиз - a * of china фарфоровый сервиз прибор - toilet * туалетный прибор( церковное) богослужение, служба - morning * утренняя служба - burial * отпевание - marriage * венчание - baptismal * крестины - memorial * заупокойная служба, панихида - to attend a * присутствовать на богослужении - to conduct a * вести службу - are you going to *? ты идешь в церковь подача мяча (теннис) - your *! ваша подача! - strong * сильная подача - * ball мяч, вводимый в игру с подачи (юридическое) исполнение постановления суда;
вручение( повестки и т. п.) ;
судебное извещение - personal * личное оповещение - substituted * оповещение по почте - * of a writ копия распоряжения суда - * of attachment приведение в исполнение судебного постановления о взятии лица под стражу (сельскохозяйственное) случка - * period сервис-период (от отела до плодотворной случки) (морское) клетневание (техническое) эксплуатация - * instructions правила эксплуатации - * life эксплуатационный срок службы - a radio set with free 12 months * радиоприемник с гарантией на год > to have seen * быть в долгом употреблении, износиться > my overcoat has seen long * мое пальто уже износилось /отслужило свой век/ > his face has seen * по его лицу видно, что он не молод /что он видал виды/ военный;
относящийся к вооруженным силам - * age (group) призывной возраст - * aviation военная авиация - * call уставной /служебный/ сигнал - * certificate служебное удостоверение;
свидетельство - * chevron нашивка за шестимесячную службу на фронте - * families семьи военнослужащих - * number личный номер( военнослужащего) - * record послужной список - * ribbon орденская планка - * test испытания в войсках, войсковые испытания - * troops войска обслуживания;
тыловые части и подразделения - * uniform /dress/ повседневная форма одежды - * unit обслуживающая часть - * weapon боевое оружие служебный - * entrance служебный вход - * call служебный телефонный разговор( особ. международный) - * stair черный ход - * benefits выходное пособие;
(военное) льготы и привилегии военнослужащих - * conditions( техническое) условия эксплуатации /работы/ повседневный;
прочный, ноский( об одежде) обслуживающий - * trades профессии, относящиеся к сфере обслуживания обслуживать производить осмотр и текущий ремонт - to * a car обслуживать автомобиль заправлять( горючим) - to * a car with gasoline заправлять машину горючим (ботаника) рябина домашняя (Pyrus domestica) - wild * кустарник или невысокое дерево с горькими плодами account solicitation ~ бюро рассмотрения ходатайств о предоставлении кредитов advisory ~ консультативная служба (например, по вопросам трудоустройства, профессиональной ориентации и т. д.) aftersales ~ послепродажное обслуживание ambulance ~ служба "Скорой помощи";
"Скорая помощь" as a ~ в качестве услуги ~ услуга, одолжение;
at your service к вашим услугам;
to be of service быть полезным auxiliary ~ вспомогательная служба, дополнительная (побочная) служба bank transfer ~ банковские переводы bathing ~ банная служба ~ услуга, одолжение;
at your service к вашим услугам;
to be of service быть полезным bus ~ автобусное сообщение car hire ~ служба проката автомобилей care attendant ~s услуги по уходу за больными central care ~ центральная служба по уходу civic ~ служба общественных работ;
участие( безработных) в общественных работах и в общественных службах civil alternative ~ альтернативная воинская служба на объектах общественного характер cleaning ~ служба по очистке территорий и удалению мусора client ~ обслуживание клиентов client ~ обслуживание клиентуры combined ~ смешанные перевозки community ~ государственная служба community ~ общинная служба community ~ социальное обеспечение complimentary limousine ~ бесплатное обслуживание автомобильным транспортом compulsory military ~ воинская повинность;
обязательная воинская служба в течение установленного законом срока consultative ~ консультативная служба consumer ~ обслуживание потребителей courier ~ услуги курьера customer ~ вчт. обслуживание клиентов customer ~ обслуживание покупателя customer ~ предоставление услуг покупателю datel ~ вчт. система передачи по телефону кодированой информации dealing ~ обслуживание биржевых операций delayed ~ вчт. обслуживание с ожиданием diffusion ~ служба распространения direct debiting ~ банковские услуги по оформлению безналичных платежей divine ~ богослужение drop-in ~ служба помощи без предварительной записи (оказывает помощь алкоголикам, наркоманам, бездомным) educational ~ служба обучения (воспитания, переподготовки, переквалификации) elapsed ~ вчт. обслуживание выполненное до прерывания emergency call ~ телефонная служба скорой помощи employment ~ служба занятости employment ~ служба занятости;
служба трудоустройства employment ~ служба по трудоустройству employment ~ служба трудоустройства environmental ~ экологическая служба escort ~ служба сопровождения;
караульная служба exempt from military ~ освобожденный от военной службы extention ~ служба распространения знаний farm relief ~ служба содействия фермерским хозяйствам ferry ~ паромное сообщение ferry ~ служба морских перевозок financial ~ финансовая консультационная фирма financial ~ финансовое обслуживание free ~ бесплатная услуга freight ~ грузовые перевозки freight ~ предоставление транспортных услуг friendly visiting ~s бесплатные услуги на дому( оказываемые благотворительными организациями или отдельными лицами) goods ~ доставка товаров government ~ государственная служба gratuitions ~ бесплатная служба home-help ~ служба помощи по дому hourly ~ транс. почасовое обслуживание 24 hours social ~s круглосуточные социальные службы housing ~ жилищная служба information ~ вчт. информационная служба information ~ служба информации interpreter ~ служба перевода;
служба переводчиков investment management ~ служба управления портфелем ценных бумаг investment ~ обслуживание инвестирования joint ~ совместное обслуживание limousine ~ прокат автомобиля с водителем line ~ рейсовое плавание mail ~ почтовая связь maximum debt ~ максимальная сумма процентов по долгу minimum debt ~ минимальное обслуживание долга municipal health ~ муниципальная служба здравоохранения national health ~ государственная служба здравоохранения news ~ служба новостей night ~ ночная служба non-military ~ невоенная служба, альтернативная гражданская служба non-military ~ невоенная служба nonpreemptive ~ вчт. обслуживание без прерывания nonpreferential ~ вчт. обслуживание без приоритета order booking ~ приказ об обслуживании ordered ~ вчт. обслуживание в порядке поступления ordinary ~ обычная услуга ordinary ~ обычное обслуживание out-patient ~ амбулаторное обслуживание outside ~ обслуживание силами посторонней организации parcel bulk ~ перевозка мелкой партии бестарного груза personal ~ личное вручение судебного приказа pharmaceutical ~ фармацевтмческая служба;
фармацевтическое ослуживание phase ~ вчт. многофазное обслуживание phase-type ~ вчт. многофазное обслуживание placement ~ биржа труда placement ~ бюро трудоустройства placement ~ служба занятости police ~ полицейская служба postal ~ почтовая связь postal ~ почтовая служба preemptive ~ вчт. обслуживание с прерыванием premium ~ услуга, предоставляемая за дополнительную плату priority ~ вчт. обслуживание с приоритетом probationary ~ служба, исполняющая приговор о направлении на "испытание" property ~ услуги по управлению имуществом provide a ~ обеспечивать обслуживание provide a ~ оказывать услугу public employment ~ государственная служба занятости purchased ~ оплаченная услуга put into ~ вводить в эксплуатацию put into ~ включать в работу quantum ~ вчт. обслуживание порциями referral ~ справочная служба regular ~ регулярное сообщение regular ~ регулярные рейсы salvage ~ услуги по спасанию ~ церк. служба;
to say a service отправлять богослужение security ~ служба безопасности selection for ~ выбор на обслуживание self-drive car-hire ~ прокат легкового автомобиля без водителя ~ attr. служебный;
service record послужной список ~ by letter судебное извещение путем направления письма ~ by post судебное извещение по почте ~ in batches вчт. групповое обслуживание ~ in bulk групповое обслуживание ~ in cyclic order обслуживание в циклическом порядке ~ in random order обслуживание в случайном порядке ~ loss coefficient коэффициент простоя вследствие обслуживания ~ of court notice to pay debt вручение уведомления суда об уплате долга ~ of notice вручение извещения ~ of process повестка ~ of process процессуальное извещение, повестка ~ of process процессуальное извещение ~ of public lands эксплуатация государственных земель ~ of summons извещение, повестка о вызове в суд ~ on loan погашение долга ~ on loan уплата долга ~ attr. служебный;
service record послужной список ~ time expectation математическое ожидание времени обслуживания ~ with privileged interruptions вчт. обслуживание с прерыванием ~ with waiting вчт. обслуживание с ожиданием ~ without interruption вчт. обслуживание без прерывания service = service-tree service-tree: service-tree бот. рябина домашняя ~ воен. род войск;
the (fighting) services армия, флот и военная авиация services: services обслуживающие отрасли экономики ~ сфера услуг ~ услуги shuttle ~ движение туда и обратно( поездов, автобусов и т. п.), маятниковое движение single ~ вчт. обслуживание одиночных требований sitting ~ служба по присмотру за детьми на время отсутствия дома родителей social ~ социальная служба;
социальное обслуживание social ~ социальная услуга social ~s социальные службы (например, службы здравоохранения, профилактики заболеванй и предотвращения несчастных случаев) services: social ~ общественные учреждения social ~ социальные услуги substituted ~ субститут личного вручения судебного приказа ~ служба;
to take into one's service нанимать;
to take service (with smb.) поступать на службу (к кому-л.) ~ служба;
to take into one's service нанимать;
to take service (with smb.) поступать на службу (к кому-л.) training ~ служба профподготовки transport ~ транспортная линия transport ~ транспортное обслуживание unarmed ~ альтернативная служба (вместо военной) useful ~ вчт. срок полезного использования videotex ~ служба видеотексной связи voluntary ~ добровольная служба, добровольное оказание услуг warranty ~ вчт. гарантийная наработка welfare ~ служба социального обеспечения -
3 service level agreement
"An agreement between two or more parties describing the deliverables, support, and communication that each party will provide to the other." -
4 intermediary
1. сущ.эк. посредник (лицо, действующее в качестве связующего звена между участниками сделки, переговоров и т. п.; напр., финансовый институт, который выступает связующим звеном между поставщиком фондов (вкладчиком) и пользователем фондов (заемщиком), страховой брокер, выступающий связующим звеном между страхователем и страховщиком, и т. п.)through intermediary of smb. — при посредничестве кого-л.
Auction companies provide a service by acting as an intermediary between buyers and sellers. — Аукционные компании служат посредником между покупателями и продавцами.
Syn:See:financial intermediary, fiscal intermediary, insurance intermediary, information intermediary, labour market intermediary, market intermediary, marketing intermediary, reinsurance intermediary COMBS: agent 1), broker, intermediation, disintermediation, intermediate2. прил.1) общ. промежуточный, переходный (находящийся между чем-л. и чем-л. по характеристикам, месту расположения, времени появления и т. п.)intermediary form between corporate capitalism and socialism — промежуточная форма между корпоративным капитализмом и социализмом
2) эк. посреднический (выступающий связующим звеном между чем-л.)Syn:intermediate 2.
* * *
посредник, агент, брокер: финансовое учреждение, выступающее посредником между поставщиками и потребителями финансовых ресурсов; лицо, уполномоченное на совершение операций за счет клиента; примерами таких посредников являются банки, взаимные фонды, страховые компании, сберегательные институты, брокерские фирмы, кредитные союзы и т. д.; = financial intermediary.* * *посредник; финансовый посредник. . Словарь экономических терминов . -
5 Buckle, William
SUBJECT AREA: Mechanical, pneumatic and hydraulic engineering[br]b. 29 July 1794 Alnwick, Northumberland, Englandd. 30 September 1863 London, England[br]English mechanical engineer who introduced the first large screw-cutting lathe to Boulton, Watt \& Co.[br]William Buckle was the son of Thomas Buckle (1759–1849), a millwright who later assisted the 9th Earl of Dundonald (1749–1831) in his various inventions, principally machines for the manufacture of rope. Soon after the birth of William, the family moved from Alnwick to Hull, Yorkshire, where he received his education. The family again moved c.1808 to London, and William was apprenticed to Messrs Woolf \& Edwards, millwrights and engineers of Lambeth. During his apprenticeship he attended evening classes at a mechanical drawing school in Finsbury, which was then the only place of its kind in London.After completing his apprenticeship, he was sent by Messrs Humphrys to Memel in Prussia to establish steamboats on the rivers and lakes there under the patronage of the Prince of Hardenburg. After about four years he returned to Britain and was employed by Boulton, Watt \& Co. to install the engines in the first steam mail packet for the service between Dublin and Holyhead. He was responsible for the engines of the steamship Lightning when it was used on the visit of George IV to Ireland.About 1824 Buckle was engaged by Boulton, Watt \& Co. as Manager of the Soho Foundry, where he is credited with introducing the first large screw-cutting lathe. At Soho about 700 or 800 men were employed on a wide variety of engineering manufacture, including coining machinery for mints in many parts of the world, with some in 1826 for the Mint at the Soho Manufactory. In 1851, following the recommendations of a Royal Commission, the Royal Mint in London was reorganized and Buckle was asked to take the post of Assistant Coiner, the senior executive officer under the Deputy Master. This he accepted, retaining the post until the end of his life.At Soho, Buckle helped to establish a literary and scientific institution to provide evening classes for the apprentices and took part in the teaching. He was an original member of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, which was founded in Birmingham in January 1847, and a member of their Council from then until 1855. He contributed a number of papers in the early years, including a memoir of William Murdock whom he had known at Soho; he resigned from the Institution in 1856 after his move to London. He was an honorary member of the London Association of Foreman Engineers.[br]Bibliography1850, "Inventions and life of William Murdock", Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers 2 (October): 16–26.RTS -
6 near cash
!гос. фин. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.This paper provides background information on the framework for the planning and control of public expenditure in the UK which has been operated since the 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR). It sets out the different classifications of spending for budgeting purposes and why these distinctions have been adopted. It discusses how the public expenditure framework is designed to ensure both sound public finances and an outcome-focused approach to public expenditure.The UK's public spending framework is based on several key principles:"consistency with a long-term, prudent and transparent regime for managing the public finances as a whole;" "the judgement of success by policy outcomes rather than resource inputs;" "strong incentives for departments and their partners in service delivery to plan over several years and plan together where appropriate so as to deliver better public services with greater cost effectiveness; and"the proper costing and management of capital assets to provide the right incentives for public investment.The Government sets policy to meet two firm fiscal rules:"the Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending; and"the Sustainable Investment Rule states that net public debt as a proportion of GDP will be held over the economic cycle at a stable and prudent level. Other things being equal, net debt will be maintained below 40 per cent of GDP over the economic cycle.Achievement of the fiscal rules is assessed by reference to the national accounts, which are produced by the Office for National Statistics, acting as an independent agency. The Government sets its spending envelope to comply with these fiscal rules.Departmental Expenditure Limits ( DEL) and Annually Managed Expenditure (AME)"Departmental Expenditure Limit ( DEL) spending, which is planned and controlled on a three year basis in Spending Reviews; and"Annually Managed Expenditure ( AME), which is expenditure which cannot reasonably be subject to firm, multi-year limits in the same way as DEL. AME includes social security benefits, local authority self-financed expenditure, debt interest, and payments to EU institutions.More information about DEL and AME is set out below.In Spending Reviews, firm DEL plans are set for departments for three years. To ensure consistency with the Government's fiscal rules departments are set separate resource (current) and capital budgets. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.To encourage departments to plan over the medium term departments may carry forward unspent DEL provision from one year into the next and, subject to the normal tests for tautness and realism of plans, may be drawn down in future years. This end-year flexibility also removes any incentive for departments to use up their provision as the year end approaches with less regard to value for money. For the full benefits of this flexibility and of three year plans to feed through into improved public service delivery, end-year flexibility and three year budgets should be cascaded from departments to executive agencies and other budget holders.Three year budgets and end-year flexibility give those managing public services the stability to plan their operations on a sensible time scale. Further, the system means that departments cannot seek to bid up funds each year (before 1997, three year plans were set and reviewed in annual Public Expenditure Surveys). So the credibility of medium-term plans has been enhanced at both central and departmental level.Departments have certainty over the budgetary allocation over the medium term and these multi-year DEL plans are strictly enforced. Departments are expected to prioritise competing pressures and fund these within their overall annual limits, as set in Spending Reviews. So the DEL system provides a strong incentive to control costs and maximise value for money.There is a small centrally held DEL Reserve. Support from the Reserve is available only for genuinely unforeseeable contingencies which departments cannot be expected to manage within their DEL.AME typically consists of programmes which are large, volatile and demand-led, and which therefore cannot reasonably be subject to firm multi-year limits. The biggest single element is social security spending. Other items include tax credits, Local Authority Self Financed Expenditure, Scottish Executive spending financed by non-domestic rates, and spending financed from the proceeds of the National Lottery.AME is reviewed twice a year as part of the Budget and Pre-Budget Report process reflecting the close integration of the tax and benefit system, which was enhanced by the introduction of tax credits.AME is not subject to the same three year expenditure limits as DEL, but is still part of the overall envelope for public expenditure. Affordability is taken into account when policy decisions affecting AME are made. The Government has committed itself not to take policy measures which are likely to have the effect of increasing social security or other elements of AME without taking steps to ensure that the effects of those decisions can be accommodated prudently within the Government's fiscal rules.Given an overall envelope for public spending, forecasts of AME affect the level of resources available for DEL spending. Cautious estimates and the AME margin are built in to these AME forecasts and reduce the risk of overspending on AME.Together, DEL plus AME sum to Total Managed Expenditure (TME). TME is a measure drawn from national accounts. It represents the current and capital spending of the public sector. The public sector is made up of central government, local government and public corporations.Resource and Capital Budgets are set in terms of accruals information. Accruals information measures resources as they are consumed rather than when the cash is paid. So for example the Resource Budget includes a charge for depreciation, a measure of the consumption or wearing out of capital assets."Non cash charges in budgets do not impact directly on the fiscal framework. That may be because the national accounts use a different way of measuring the same thing, for example in the case of the depreciation of departmental assets. Or it may be that the national accounts measure something different: for example, resource budgets include a cost of capital charge reflecting the opportunity cost of holding capital; the national accounts include debt interest."Within the Resource Budget DEL, departments have separate controls on:"Near cash spending, the sub set of Resource Budgets which impacts directly on the Golden Rule; and"The amount of their Resource Budget DEL that departments may spend on running themselves (e.g. paying most civil servants’ salaries) is limited by Administration Budgets, which are set in Spending Reviews. Administration Budgets are used to ensure that as much money as practicable is available for front line services and programmes. These budgets also help to drive efficiency improvements in departments’ own activities. Administration Budgets exclude the costs of frontline services delivered directly by departments.The Budget preceding a Spending Review sets an overall envelope for public spending that is consistent with the fiscal rules for the period covered by the Spending Review. In the Spending Review, the Budget AME forecast for year one of the Spending Review period is updated, and AME forecasts are made for the later years of the Spending Review period.The 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review ( CSR), which was published in July 1998, was a comprehensive review of departmental aims and objectives alongside a zero-based analysis of each spending programme to determine the best way of delivering the Government's objectives. The 1998 CSR allocated substantial additional resources to the Government's key priorities, particularly education and health, for the three year period from 1999-2000 to 2001-02.Delivering better public services does not just depend on how much money the Government spends, but also on how well it spends it. Therefore the 1998 CSR introduced Public Service Agreements (PSAs). Each major government department was given its own PSA setting out clear targets for achievements in terms of public service improvements.The 1998 CSR also introduced the DEL/ AME framework for the control of public spending, and made other framework changes. Building on the investment and reforms delivered by the 1998 CSR, successive spending reviews in 2000, 2002 and 2004 have:"provided significant increase in resources for the Government’s priorities, in particular health and education, and cross-cutting themes such as raising productivity; extending opportunity; and building strong and secure communities;" "enabled the Government significantly to increase investment in public assets and address the legacy of under investment from past decades. Departmental Investment Strategies were introduced in SR2000. As a result there has been a steady increase in public sector net investment from less than ¾ of a per cent of GDP in 1997-98 to 2¼ per cent of GDP in 2005-06, providing better infrastructure across public services;" "introduced further refinements to the performance management framework. PSA targets have been reduced in number over successive spending reviews from around 300 to 110 to give greater focus to the Government’s highest priorities. The targets have become increasingly outcome-focused to deliver further improvements in key areas of public service delivery across Government. They have also been refined in line with the conclusions of the Devolving Decision Making Review to provide a framework which encourages greater devolution and local flexibility. Technical Notes were introduced in SR2000 explaining how performance against each PSA target will be measured; and"not only allocated near cash spending to departments, but also – since SR2002 - set Resource DEL plans for non cash spending.To identify what further investments and reforms are needed to equip the UK for the global challenges of the decade ahead, on 19 July 2005 the Chief Secretary to the Treasury announced that the Government intends to launch a second Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR) reporting in 2007.A decade on from the first CSR, the 2007 CSR will represent a long-term and fundamental review of government expenditure. It will cover departmental allocations for 2008-09, 2009-10 and 2010 11. Allocations for 2007-08 will be held to the agreed figures already announced by the 2004 Spending Review. To provide a rigorous analytical framework for these departmental allocations, the Government will be taking forward a programme of preparatory work over 2006 involving:"an assessment of what the sustained increases in spending and reforms to public service delivery have achieved since the first CSR. The assessment will inform the setting of new objectives for the decade ahead;" "an examination of the key long-term trends and challenges that will shape the next decade – including demographic and socio-economic change, globalisation, climate and environmental change, global insecurity and technological change – together with an assessment of how public services will need to respond;" "to release the resources needed to address these challenges, and to continue to secure maximum value for money from public spending over the CSR period, a set of zero-based reviews of departments’ baseline expenditure to assess its effectiveness in delivering the Government’s long-term objectives; together with"further development of the efficiency programme, building on the cross cutting areas identified in the Gershon Review, to embed and extend ongoing efficiency savings into departmental expenditure planning.The 2007 CSR also offers the opportunity to continue to refine the PSA framework so that it drives effective delivery and the attainment of ambitious national standards.Public Service Agreements (PSAs) were introduced in the 1998 CSR. They set out agreed targets detailing the outputs and outcomes departments are expected to deliver with the resources allocated to them. The new spending regime places a strong emphasis on outcome targets, for example in providing for better health and higher educational standards or service standards. The introduction in SR2004 of PSA ‘standards’ will ensure that high standards in priority areas are maintained.The Government monitors progress against PSA targets, and departments report in detail twice a year in their annual Departmental Reports (published in spring) and in their autumn performance reports. These reports provide Parliament and the public with regular updates on departments’ performance against their targets.Technical Notes explain how performance against each PSA target will be measured.To make the most of both new investment and existing assets, there needs to be a coherent long term strategy against which investment decisions are taken. Departmental Investment Strategies (DIS) set out each department's plans to deliver the scale and quality of capital stock needed to underpin its objectives. The DIS includes information about the department's existing capital stock and future plans for that stock, as well as plans for new investment. It also sets out the systems that the department has in place to ensure that it delivers its capital programmes effectively.This document was updated on 19 December 2005.Near-cash resource expenditure that has a related cash implication, even though the timing of the cash payment may be slightly different. For example, expenditure on gas or electricity supply is incurred as the fuel is used, though the cash payment might be made in arrears on aquarterly basis. Other examples of near-cash expenditure are: pay, rental.Net cash requirement the upper limit agreed by Parliament on the cash which a department may draw from theConsolidated Fund to finance the expenditure within the ambit of its Request forResources. It is equal to the agreed amount of net resources and net capital less non-cashitems and working capital.Non-cash cost costs where there is no cash transaction but which are included in a body’s accounts (or taken into account in charging for a service) to establish the true cost of all the resourcesused.Non-departmental a body which has a role in the processes of government, but is not a government public body, NDPBdepartment or part of one. NDPBs accordingly operate at arm’s length from governmentMinisters.Notional cost of a cost which is taken into account in setting fees and charges to improve comparability with insuranceprivate sector service providers.The charge takes account of the fact that public bodies donot generally pay an insurance premium to a commercial insurer.the independent body responsible for collecting and publishing official statistics about theUK’s society and economy. (At the time of going to print legislation was progressing tochange this body to the Statistics Board).Office of Government an office of the Treasury, with a status similar to that of an agency, which aims to maximise Commerce, OGCthe government’s purchasing power for routine items and combine professional expertiseto bear on capital projects.Office of the the government department responsible for discharging the Paymaster General’s statutoryPaymaster General,responsibilities to hold accounts and make payments for government departments and OPGother public bodies.Orange bookthe informal title for Management of Risks: Principles and Concepts, which is published by theTreasury for the guidance of public sector bodies.Office for NationalStatistics, ONS60Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————"GLOSSARYOverdraftan account with a negative balance.Parliament’s formal agreement to authorise an activity or expenditure.Prerogative powerspowers exercisable under the Royal Prerogative, ie powers which are unique to the Crown,as contrasted with common-law powers which may be available to the Crown on the samebasis as to natural persons.Primary legislationActs which have been passed by the Westminster Parliament and, where they haveappropriate powers, the Scottish Parliament and the Northern Ireland Assembly. Begin asBills until they have received Royal Assent.arrangements under which a public sector organisation contracts with a private sectorentity to construct a facility and provide associated services of a specified quality over asustained period. See annex 7.5.Proprietythe principle that patterns of resource consumption should respect Parliament’s intentions,conventions and control procedures, including any laid down by the PAC. See box 2.4.Public Accountssee Committee of Public Accounts.CommitteePublic corporationa trading body controlled by central government, local authority or other publiccorporation that has substantial day to day operating independence. See section 7.8.Public Dividend finance provided by government to public sector bodies as an equity stake; an alternative to Capital, PDCloan finance.Public Service sets out what the public can expect the government to deliver with its resources. EveryAgreement, PSAlarge government department has PSA(s) which specify deliverables as targets or aimsrelated to objectives.a structured arrangement between a public sector and a private sector organisation tosecure an outcome delivering good value for money for the public sector. It is classified tothe public or private sector according to which has more control.Rate of returnthe financial remuneration delivered by a particular project or enterprise, expressed as apercentage of the net assets employed.Regularitythe principle that resource consumption should accord with the relevant legislation, therelevant delegated authority and this document. See box 2.4.Request for the functional level into which departmental Estimates may be split. RfRs contain a number Resources, RfRof functions being carried out by the department in pursuit of one or more of thatdepartment’s objectives.Resource accountan accruals account produced in line with the Financial Reporting Manual (FReM).Resource accountingthe system under which budgets, Estimates and accounts are constructed in a similar wayto commercial audited accounts, so that both plans and records of expenditure allow in fullfor the goods and services which are to be, or have been, consumed – ie not just the cashexpended.Resource budgetthe means by which the government plans and controls the expenditure of resources tomeet its objectives.Restitutiona legal concept which allows money and property to be returned to its rightful owner. Ittypically operates where another person can be said to have been unjustly enriched byreceiving such monies.Return on capital the ratio of profit to capital employed of an accounting entity during an identified period.employed, ROCEVarious measures of profit and of capital employed may be used in calculating the ratio.Public Privatepartnership, PPPPrivate Finance Initiative, PFIParliamentaryauthority61Managing Public Money"————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARYRoyal charterthe document setting out the powers and constitution of a corporation established underprerogative power of the monarch acting on Privy Council advice.Second readingthe second formal time that a House of Parliament may debate a bill, although in practicethe first substantive debate on its content. If successful, it is deemed to denoteParliamentary approval of the principle of the proposed legislation.Secondary legislationlaws, including orders and regulations, which are made using powers in primary legislation.Normally used to set out technical and administrative provision in greater detail thanprimary legislation, they are subject to a less intense level of scrutiny in Parliament.European legislation is,however,often implemented in secondary legislation using powers inthe European Communities Act 1972.Service-level agreement between parties, setting out in detail the level of service to be performed.agreementWhere agreements are between central government bodies, they are not legally a contractbut have a similar function.Shareholder Executive a body created to improve the government’s performance as a shareholder in businesses.Spending reviewsets out the key improvements in public services that the public can expect over a givenperiod. It includes a thorough review of departmental aims and objectives to find the bestway of delivering the government’s objectives, and sets out the spending plans for the givenperiod.State aidstate support for a domestic body or company which could distort EU competition and sois not usually allowed. See annex 4.9.Statement of Excessa formal statement detailing departments’ overspends prepared by the Comptroller andAuditor General as a result of undertaking annual audits.Statement on Internal an annual statement that Accounting Officers are required to make as part of the accounts Control, SICon a range of risk and control issues.Subheadindividual elements of departmental expenditure identifiable in Estimates as single cells, forexample cell A1 being administration costs within a particular line of departmental spending.Supplyresources voted by Parliament in response to Estimates, for expenditure by governmentdepartments.Supply Estimatesa statement of the resources the government needs in the coming financial year, and forwhat purpose(s), by which Parliamentary authority is sought for the planned level ofexpenditure and income.Target rate of returnthe rate of return required of a project or enterprise over a given period, usually at least a year.Third sectorprivate sector bodies which do not act commercially,including charities,social and voluntaryorganisations and other not-for-profit collectives. See annex 7.7.Total Managed a Treasury budgeting term which covers all current and capital spending carried out by the Expenditure,TMEpublic sector (ie not just by central departments).Trading fundan organisation (either within a government department or forming one) which is largely orwholly financed from commercial revenue generated by its activities. Its Estimate shows itsnet impact, allowing its income from receipts to be devoted entirely to its business.Treasury Minutea formal administrative document drawn up by the Treasury, which may serve a wide varietyof purposes including seeking Parliamentary approval for the use of receipts asappropriations in aid, a remission of some or all of the principal of voted loans, andresponding on behalf of the government to reports by the Public Accounts Committee(PAC).62Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARY63Managing Public MoneyValue for moneythe process under which organisation’s procurement, projects and processes aresystematically evaluated and assessed to provide confidence about suitability, effectiveness,prudence,quality,value and avoidance of error and other waste,judged for the public sectoras a whole.Virementthe process through which funds are moved between subheads such that additionalexpenditure on one is met by savings on one or more others.Votethe process by which Parliament approves funds in response to supply Estimates.Voted expenditureprovision for expenditure that has been authorised by Parliament. Parliament ‘votes’authority for public expenditure through the Supply Estimates process. Most expenditureby central government departments is authorised in this way.Wider market activity activities undertaken by central government organisations outside their statutory duties,using spare capacity and aimed at generating a commercial profit. See annex 7.6.Windfallmonies received by a department which were not anticipated in the spending review.———————————————————————————————————————— -
7 Historical Portugal
Before Romans described western Iberia or Hispania as "Lusitania," ancient Iberians inhabited the land. Phoenician and Greek trading settlements grew up in the Tagus estuary area and nearby coasts. Beginning around 202 BCE, Romans invaded what is today southern Portugal. With Rome's defeat of Carthage, Romans proceeded to conquer and rule the western region north of the Tagus, which they named Roman "Lusitania." In the fourth century CE, as Rome's rule weakened, the area experienced yet another invasion—Germanic tribes, principally the Suevi, who eventually were Christianized. During the sixth century CE, the Suevi kingdom was superseded by yet another Germanic tribe—the Christian Visigoths.A major turning point in Portugal's history came in 711, as Muslim armies from North Africa, consisting of both Arab and Berber elements, invaded the Iberian Peninsula from across the Straits of Gibraltar. They entered what is now Portugal in 714, and proceeded to conquer most of the country except for the far north. For the next half a millennium, Islam and Muslim presence in Portugal left a significant mark upon the politics, government, language, and culture of the country.Islam, Reconquest, and Portugal Created, 714-1140The long frontier struggle between Muslim invaders and Christian communities in the north of the Iberian peninsula was called the Reconquista (Reconquest). It was during this struggle that the first dynasty of Portuguese kings (Burgundian) emerged and the independent monarchy of Portugal was established. Christian forces moved south from what is now the extreme north of Portugal and gradually defeated Muslim forces, besieging and capturing towns under Muslim sway. In the ninth century, as Christian forces slowly made their way southward, Christian elements were dominant only in the area between Minho province and the Douro River; this region became known as "territorium Portu-calense."In the 11th century, the advance of the Reconquest quickened as local Christian armies were reinforced by crusading knights from what is now France and England. Christian forces took Montemor (1034), at the Mondego River; Lamego (1058); Viseu (1058); and Coimbra (1064). In 1095, the king of Castile and Léon granted the country of "Portu-cale," what became northern Portugal, to a Burgundian count who had emigrated from France. This was the foundation of Portugal. In 1139, a descendant of this count, Afonso Henriques, proclaimed himself "King of Portugal." He was Portugal's first monarch, the "Founder," and the first of the Burgundian dynasty, which ruled until 1385.The emergence of Portugal in the 12th century as a separate monarchy in Iberia occurred before the Christian Reconquest of the peninsula. In the 1140s, the pope in Rome recognized Afonso Henriques as king of Portugal. In 1147, after a long, bloody siege, Muslim-occupied Lisbon fell to Afonso Henriques's army. Lisbon was the greatest prize of the 500-year war. Assisting this effort were English crusaders on their way to the Holy Land; the first bishop of Lisbon was an Englishman. When the Portuguese captured Faro and Silves in the Algarve province in 1248-50, the Reconquest of the extreme western portion of the Iberian peninsula was complete—significantly, more than two centuries before the Spanish crown completed the Reconquest of the eastern portion by capturing Granada in 1492.Consolidation and Independence of Burgundian Portugal, 1140-1385Two main themes of Portugal's early existence as a monarchy are the consolidation of control over the realm and the defeat of a Castil-ian threat from the east to its independence. At the end of this period came the birth of a new royal dynasty (Aviz), which prepared to carry the Christian Reconquest beyond continental Portugal across the straits of Gibraltar to North Africa. There was a variety of motives behind these developments. Portugal's independent existence was imperiled by threats from neighboring Iberian kingdoms to the north and east. Politics were dominated not only by efforts against the Muslims inPortugal (until 1250) and in nearby southern Spain (until 1492), but also by internecine warfare among the kingdoms of Castile, Léon, Aragon, and Portugal. A final comeback of Muslim forces was defeated at the battle of Salado (1340) by allied Castilian and Portuguese forces. In the emerging Kingdom of Portugal, the monarch gradually gained power over and neutralized the nobility and the Church.The historic and commonplace Portuguese saying "From Spain, neither a good wind nor a good marriage" was literally played out in diplomacy and war in the late 14th-century struggles for mastery in the peninsula. Larger, more populous Castile was pitted against smaller Portugal. Castile's Juan I intended to force a union between Castile and Portugal during this era of confusion and conflict. In late 1383, Portugal's King Fernando, the last king of the Burgundian dynasty, suddenly died prematurely at age 38, and the Master of Aviz, Portugal's most powerful nobleman, took up the cause of independence and resistance against Castile's invasion. The Master of Aviz, who became King João I of Portugal, was able to obtain foreign assistance. With the aid of English archers, Joao's armies defeated the Castilians in the crucial battle of Aljubarrota, on 14 August 1385, a victory that assured the independence of the Portuguese monarchy from its Castilian nemesis for several centuries.Aviz Dynasty and Portugal's First Overseas Empire, 1385-1580The results of the victory at Aljubarrota, much celebrated in Portugal's art and monuments, and the rise of the Aviz dynasty also helped to establish a new merchant class in Lisbon and Oporto, Portugal's second city. This group supported King João I's program of carrying the Reconquest to North Africa, since it was interested in expanding Portugal's foreign commerce and tapping into Muslim trade routes and resources in Africa. With the Reconquest against the Muslims completed in Portugal and the threat from Castile thwarted for the moment, the Aviz dynasty launched an era of overseas conquest, exploration, and trade. These efforts dominated Portugal's 15th and 16th centuries.The overseas empire and age of Discoveries began with Portugal's bold conquest in 1415 of the Moroccan city of Ceuta. One royal member of the 1415 expedition was young, 21-year-old Prince Henry, later known in history as "Prince Henry the Navigator." His part in the capture of Ceuta won Henry his knighthood and began Portugal's "Marvelous Century," during which the small kingdom was counted as a European and world power of consequence. Henry was the son of King João I and his English queen, Philippa of Lancaster, but he did not inherit the throne. Instead, he spent most of his life and his fortune, and that of the wealthy military Order of Christ, on various imperial ventures and on voyages of exploration down the African coast and into the Atlantic. While mythology has surrounded Henry's controversial role in the Discoveries, and this role has been exaggerated, there is no doubt that he played a vital part in the initiation of Portugal's first overseas empire and in encouraging exploration. He was naturally curious, had a sense of mission for Portugal, and was a strong leader. He also had wealth to expend; at least a third of the African voyages of the time were under his sponsorship. If Prince Henry himself knew little science, significant scientific advances in navigation were made in his day.What were Portugal's motives for this new imperial effort? The well-worn historical cliche of "God, Glory, and Gold" can only partly explain the motivation of a small kingdom with few natural resources and barely 1 million people, which was greatly outnumbered by the other powers it confronted. Among Portuguese objectives were the desire to exploit known North African trade routes and resources (gold, wheat, leather, weaponry, and other goods that were scarce in Iberia); the need to outflank the Muslim world in the Mediterranean by sailing around Africa, attacking Muslims en route; and the wish to ally with Christian kingdoms beyond Africa. This enterprise also involved a strategy of breaking the Venetian spice monopoly by trading directly with the East by means of discovering and exploiting a sea route around Africa to Asia. Besides the commercial motives, Portugal nurtured a strong crusading sense of Christian mission, and various classes in the kingdom saw an opportunity for fame and gain.By the time of Prince Henry's death in 1460, Portugal had gained control of the Atlantic archipelagos of the Azores and Madeiras, begun to colonize the Cape Verde Islands, failed to conquer the Canary Islands from Castile, captured various cities on Morocco's coast, and explored as far as Senegal, West Africa, down the African coast. By 1488, Bar-tolomeu Dias had rounded the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa and thereby discovered the way to the Indian Ocean.Portugal's largely coastal African empire and later its fragile Asian empire brought unexpected wealth but were purchased at a high price. Costs included wars of conquest and defense against rival powers, manning the far-flung navel and trade fleets and scattered castle-fortresses, and staffing its small but fierce armies, all of which entailed a loss of skills and population to maintain a scattered empire. Always short of capital, the monarchy became indebted to bankers. There were many defeats beginning in the 16th century at the hands of the larger imperial European monarchies (Spain, France, England, and Holland) and many attacks on Portugal and its strung-out empire. Typically, there was also the conflict that arose when a tenuously held world empire that rarely if ever paid its way demanded finance and manpower Portugal itself lacked.The first 80 years of the glorious imperial era, the golden age of Portugal's imperial power and world influence, was an African phase. During 1415-88, Portuguese navigators and explorers in small ships, some of them caravelas (caravels), explored the treacherous, disease-ridden coasts of Africa from Morocco to South Africa beyond the Cape of Good Hope. By the 1470s, the Portuguese had reached the Gulf of Guinea and, in the early 1480s, what is now Angola. Bartolomeu Dias's extraordinary voyage of 1487-88 to South Africa's coast and the edge of the Indian Ocean convinced Portugal that the best route to Asia's spices and Christians lay south, around the tip of southern Africa. Between 1488 and 1495, there was a hiatus caused in part by domestic conflict in Portugal, discussion of resources available for further conquests beyond Africa in Asia, and serious questions as to Portugal's capacity to reach beyond Africa. In 1495, King Manuel and his council decided to strike for Asia, whatever the consequences. In 1497-99, Vasco da Gama, under royal orders, made the epic two-year voyage that discovered the sea route to western India (Asia), outflanked Islam and Venice, and began Portugal's Asian empire. Within 50 years, Portugal had discovered and begun the exploitation of its largest colony, Brazil, and set up forts and trading posts from the Middle East (Aden and Ormuz), India (Calicut, Goa, etc.), Malacca, and Indonesia to Macau in China.By the 1550s, parts of its largely coastal, maritime trading post empire from Morocco to the Moluccas were under siege from various hostile forces, including Muslims, Christians, and Hindi. Although Moroccan forces expelled the Portuguese from the major coastal cities by 1550, the rival European monarchies of Castile (Spain), England, France, and later Holland began to seize portions of her undermanned, outgunned maritime empire.In 1580, Phillip II of Spain, whose mother was a Portuguese princess and who had a strong claim to the Portuguese throne, invaded Portugal, claimed the throne, and assumed control over the realm and, by extension, its African, Asian, and American empires. Phillip II filled the power vacuum that appeared in Portugal following the loss of most of Portugal's army and its young, headstrong King Sebastião in a disastrous war in Morocco. Sebastiao's death in battle (1578) and the lack of a natural heir to succeed him, as well as the weak leadership of the cardinal who briefly assumed control in Lisbon, led to a crisis that Spain's strong monarch exploited. As a result, Portugal lost its independence to Spain for a period of 60 years.Portugal under Spanish Rule, 1580-1640Despite the disastrous nature of Portugal's experience under Spanish rule, "The Babylonian Captivity" gave birth to modern Portuguese nationalism, its second overseas empire, and its modern alliance system with England. Although Spain allowed Portugal's weakened empire some autonomy, Spanish rule in Portugal became increasingly burdensome and unacceptable. Spain's ambitious imperial efforts in Europe and overseas had an impact on the Portuguese as Spain made greater and greater demands on its smaller neighbor for manpower and money. Portugal's culture underwent a controversial Castilianization, while its empire became hostage to Spain's fortunes. New rival powers England, France, and Holland attacked and took parts of Spain's empire and at the same time attacked Portugal's empire, as well as the mother country.Portugal's empire bore the consequences of being attacked by Spain's bitter enemies in what was a form of world war. Portuguese losses were heavy. By 1640, Portugal had lost most of its Moroccan cities as well as Ceylon, the Moluccas, and sections of India. With this, Portugal's Asian empire was gravely weakened. Only Goa, Damão, Diu, Bombay, Timor, and Macau remained and, in Brazil, Dutch forces occupied the northeast.On 1 December 1640, long commemorated as a national holiday, Portuguese rebels led by the duke of Braganza overthrew Spanish domination and took advantage of Spanish weakness following a more serious rebellion in Catalonia. Portugal regained independence from Spain, but at a price: dependence on foreign assistance to maintain its independence in the form of the renewal of the alliance with England.Restoration and Second Empire, 1640-1822Foreign affairs and empire dominated the restoration era and aftermath, and Portugal again briefly enjoyed greater European power and prestige. The Anglo-Portuguese Alliance was renewed and strengthened in treaties of 1642, 1654, and 1661, and Portugal's independence from Spain was underwritten by English pledges and armed assistance. In a Luso-Spanish treaty of 1668, Spain recognized Portugal's independence. Portugal's alliance with England was a marriage of convenience and necessity between two monarchies with important religious, cultural, and social differences. In return for legal, diplomatic, and trade privileges, as well as the use during war and peace of Portugal's great Lisbon harbor and colonial ports for England's navy, England pledged to protect Portugal and its scattered empire from any attack. The previously cited 17th-century alliance treaties were renewed later in the Treaty of Windsor, signed in London in 1899. On at least 10 different occasions after 1640, and during the next two centuries, England was central in helping prevent or repel foreign invasions of its ally, Portugal.Portugal's second empire (1640-1822) was largely Brazil-oriented. Portuguese colonization, exploitation of wealth, and emigration focused on Portuguese America, and imperial revenues came chiefly from Brazil. Between 1670 and 1740, Portugal's royalty and nobility grew wealthier on funds derived from Brazilian gold, diamonds, sugar, tobacco, and other crops, an enterprise supported by the Atlantic slave trade and the supply of African slave labor from West Africa and Angola. Visitors today can see where much of that wealth was invested: Portugal's rich legacy of monumental architecture. Meanwhile, the African slave trade took a toll in Angola and West Africa.In continental Portugal, absolutist monarchy dominated politics and government, and there was a struggle for position and power between the monarchy and other institutions, such as the Church and nobility. King José I's chief minister, usually known in history as the marquis of Pombal (ruled 1750-77), sharply suppressed the nobility and theChurch (including the Inquisition, now a weak institution) and expelled the Jesuits. Pombal also made an effort to reduce economic dependence on England, Portugal's oldest ally. But his successes did not last much beyond his disputed time in office.Beginning in the late 18th century, the European-wide impact of the French Revolution and the rise of Napoleon placed Portugal in a vulnerable position. With the monarchy ineffectively led by an insane queen (Maria I) and her indecisive regent son (João VI), Portugal again became the focus of foreign ambition and aggression. With England unable to provide decisive assistance in time, France—with Spain's consent—invaded Portugal in 1807. As Napoleon's army under General Junot entered Lisbon meeting no resistance, Portugal's royal family fled on a British fleet to Brazil, where it remained in exile until 1821. In the meantime, Portugal's overseas empire was again under threat. There was a power vacuum as the monarch was absent, foreign armies were present, and new political notions of liberalism and constitutional monarchy were exciting various groups of citizens.Again England came to the rescue, this time in the form of the armies of the duke of Wellington. Three successive French invasions of Portugal were defeated and expelled, and Wellington succeeded in carrying the war against Napoleon across the Portuguese frontier into Spain. The presence of the English army, the new French-born liberal ideas, and the political vacuum combined to create revolutionary conditions. The French invasions and the peninsular wars, where Portuguese armed forces played a key role, marked the beginning of a new era in politics.Liberalism and Constitutional Monarchy, 1822-1910During 1807-22, foreign invasions, war, and civil strife over conflicting political ideas gravely damaged Portugal's commerce, economy, and novice industry. The next terrible blow was the loss of Brazil in 1822, the jewel in the imperial crown. Portugal's very independence seemed to be at risk. In vain, Portugal sought to resist Brazilian independence by force, but in 1825 it formally acknowledged Brazilian independence by treaty.Portugal's slow recovery from the destructive French invasions and the "war of independence" was complicated by civil strife over the form of constitutional monarchy that best suited Portugal. After struggles over these issues between 1820 and 1834, Portugal settled somewhat uncertainly into a moderate constitutional monarchy whose constitution (Charter of 1826) lent it strong political powers to exert a moderating influence between the executive and legislative branches of the government. It also featured a new upper middle class based on land ownership and commerce; a Catholic Church that, although still important, lived with reduced privileges and property; a largely African (third) empire to which Lisbon and Oporto devoted increasing spiritual and material resources, starting with the liberal imperial plans of 1836 and 1851, and continuing with the work of institutions like the Lisbon Society of Geography (established 1875); and a mass of rural peasants whose bonds to the land weakened after 1850 and who began to immigrate in increasing numbers to Brazil and North America.Chronic military intervention in national politics began in 19th-century Portugal. Such intervention, usually commencing with coups or pronunciamentos (military revolts), was a shortcut to the spoils of political office and could reflect popular discontent as well as the power of personalities. An early example of this was the 1817 golpe (coup) attempt of General Gomes Freire against British military rule in Portugal before the return of King João VI from Brazil. Except for a more stable period from 1851 to 1880, military intervention in politics, or the threat thereof, became a feature of the constitutional monarchy's political life, and it continued into the First Republic and the subsequent Estado Novo.Beginning with the Regeneration period (1851-80), Portugal experienced greater political stability and economic progress. Military intervention in politics virtually ceased; industrialization and construction of railroads, roads, and bridges proceeded; two political parties (Regenerators and Historicals) worked out a system of rotation in power; and leading intellectuals sparked a cultural revival in several fields. In 19th-century literature, there was a new golden age led by such figures as Alexandre Herculano (historian), Eça de Queirós (novelist), Almeida Garrett (playwright and essayist), Antero de Quental (poet), and Joaquim Oliveira Martins (historian and social scientist). In its third overseas empire, Portugal attempted to replace the slave trade and slavery with legitimate economic activities; to reform the administration; and to expand Portuguese holdings beyond coastal footholds deep into the African hinterlands in West, West Central, and East Africa. After 1841, to some extent, and especially after 1870, colonial affairs, combined with intense nationalism, pressures for economic profit in Africa, sentiment for national revival, and the drift of European affairs would make or break Lisbon governments.Beginning with the political crisis that arose out of the "English Ultimatum" affair of January 1890, the monarchy became discredtted and identified with the poorly functioning government, political parties splintered, and republicanism found more supporters. Portugal participated in the "Scramble for Africa," expanding its African holdings, but failed to annex territory connecting Angola and Mozambique. A growing foreign debt and state bankruptcy as of the early 1890s damaged the constitutional monarchy's reputation, despite the efforts of King Carlos in diplomacy, the renewal of the alliance in the Windsor Treaty of 1899, and the successful if bloody colonial wars in the empire (1880-97). Republicanism proclaimed that Portugal's weak economy and poor society were due to two historic institutions: the monarchy and the Catholic Church. A republic, its stalwarts claimed, would bring greater individual liberty; efficient, if more decentralized government; and a stronger colonial program while stripping the Church of its role in both society and education.As the monarchy lost support and republicans became more aggressive, violence increased in politics. King Carlos I and his heir Luís were murdered in Lisbon by anarchist-republicans on 1 February 1908. Following a military and civil insurrection and fighting between monarchist and republican forces, on 5 October 1910, King Manuel II fled Portugal and a republic was proclaimed.First Parliamentary Republic, 1910-26Portugal's first attempt at republican government was the most unstable, turbulent parliamentary republic in the history of 20th-century Western Europe. During a little under 16 years of the republic, there were 45 governments, a number of legislatures that did not complete normal terms, military coups, and only one president who completed his four-year term in office. Portuguese society was poorly prepared for this political experiment. Among the deadly legacies of the monarchy were a huge public debt; a largely rural, apolitical, and illiterate peasant population; conflict over the causes of the country's misfortunes; and lack of experience with a pluralist, democratic system.The republic had some talented leadership but lacked popular, institutional, and economic support. The 1911 republican constitution established only a limited democracy, as only a small portion of the adult male citizenry was eligible to vote. In a country where the majority was Catholic, the republic passed harshly anticlerical laws, and its institutions and supporters persecuted both the Church and its adherents. During its brief disjointed life, the First Republic drafted important reform plans in economic, social, and educational affairs; actively promoted development in the empire; and pursued a liberal, generous foreign policy. Following British requests for Portugal's assistance in World War I, Portugal entered the war on the Allied side in March 1916 and sent armies to Flanders and Portuguese Africa. Portugal's intervention in that conflict, however, was too costly in many respects, and the ultimate failure of the republic in part may be ascribed to Portugal's World War I activities.Unfortunately for the republic, its time coincided with new threats to Portugal's African possessions: World War I, social and political demands from various classes that could not be reconciled, excessive military intervention in politics, and, in particular, the worst economic and financial crisis Portugal had experienced since the 16th and 17th centuries. After the original Portuguese Republican Party (PRP, also known as the "Democrats") splintered into three warring groups in 1912, no true multiparty system emerged. The Democrats, except for only one or two elections, held an iron monopoly of electoral power, and political corruption became a major issue. As extreme right-wing dictatorships elsewhere in Europe began to take power in Italy (1922), neighboring Spain (1923), and Greece (1925), what scant popular support remained for the republic collapsed. Backed by a right-wing coalition of landowners from Alentejo, clergy, Coimbra University faculty and students, Catholic organizations, and big business, career military officers led by General Gomes da Costa executed a coup on 28 May 1926, turned out the last republican government, and established a military government.The Estado Novo (New State), 1926-74During the military phase (1926-32) of the Estado Novo, professional military officers, largely from the army, governed and administered Portugal and held key cabinet posts, but soon discovered that the military possessed no magic formula that could readily solve the problems inherited from the First Republic. Especially during the years 1926-31, the military dictatorship, even with its political repression of republican activities and institutions (military censorship of the press, political police action, and closure of the republic's rowdy parliament), was characterized by similar weaknesses: personalism and factionalism; military coups and political instability, including civil strife and loss of life; state debt and bankruptcy; and a weak economy. "Barracks parliamentarism" was not an acceptable alternative even to the "Nightmare Republic."Led by General Óscar Carmona, who had replaced and sent into exile General Gomes da Costa, the military dictatorship turned to a civilian expert in finance and economics to break the budget impasse and bring coherence to the disorganized system. Appointed minister of finance on 27 April 1928, the Coimbra University Law School professor of economics Antônio de Oliveira Salazar (1889-1970) first reformed finance, helped balance the budget, and then turned to other concerns as he garnered extraordinary governing powers. In 1930, he was appointed interim head of another key ministry (Colonies) and within a few years had become, in effect, a civilian dictator who, with the military hierarchy's support, provided the government with coherence, a program, and a set of policies.For nearly 40 years after he was appointed the first civilian prime minister in 1932, Salazar's personality dominated the government. Unlike extreme right-wing dictators elsewhere in Europe, Salazar was directly appointed by the army but was never endorsed by a popular political party, street militia, or voter base. The scholarly, reclusive former Coimbra University professor built up what became known after 1932 as the Estado Novo ("New State"), which at the time of its overthrow by another military coup in 1974, was the longest surviving authoritarian regime in Western Europe. The system of Salazar and the largely academic and technocratic ruling group he gathered in his cabinets was based on the central bureaucracy of the state, which was supported by the president of the republic—always a senior career military officer, General Óscar Carmona (1928-51), General Craveiro Lopes (1951-58), and Admiral Américo Tómaz (1958-74)—and the complicity of various institutions. These included a rubber-stamp legislature called the National Assembly (1935-74) and a political police known under various names: PVDE (1932-45), PIDE (1945-69),and DGS (1969-74). Other defenders of the Estado Novo security were paramilitary organizations such as the National Republican Guard (GNR); the Portuguese Legion (PL); and the Portuguese Youth [Movement]. In addition to censorship of the media, theater, and books, there was political repression and a deliberate policy of depoliticization. All political parties except for the approved movement of regime loyalists, the União Nacional or (National Union), were banned.The most vigorous and more popular period of the New State was 1932-44, when the basic structures were established. Never monolithic or entirely the work of one person (Salazar), the New State was constructed with the assistance of several dozen top associates who were mainly academics from law schools, some technocrats with specialized skills, and a handful of trusted career military officers. The 1933 Constitution declared Portugal to be a "unitary, corporative Republic," and pressures to restore the monarchy were resisted. Although some of the regime's followers were fascists and pseudofascists, many more were conservative Catholics, integralists, nationalists, and monarchists of different varieties, and even some reactionary republicans. If the New State was authoritarian, it was not totalitarian and, unlike fascism in Benito Mussolini's Italy or Adolf Hitler's Germany, it usually employed the minimum of violence necessary to defeat what remained a largely fractious, incoherent opposition.With the tumultuous Second Republic and the subsequent civil war in nearby Spain, the regime felt threatened and reinforced its defenses. During what Salazar rightly perceived as a time of foreign policy crisis for Portugal (1936-45), he assumed control of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs. From there, he pursued four basic foreign policy objectives: supporting the Nationalist rebels of General Francisco Franco in the Spanish Civil War (1936-39) and concluding defense treaties with a triumphant Franco; ensuring that General Franco in an exhausted Spain did not enter World War II on the Axis side; maintaining Portuguese neutrality in World War II with a post-1942 tilt toward the Allies, including granting Britain and the United States use of bases in the Azores Islands; and preserving and protecting Portugal's Atlantic Islands and its extensive, if poor, overseas empire in Africa and Asia.During the middle years of the New State (1944-58), many key Salazar associates in government either died or resigned, and there was greater social unrest in the form of unprecedented strikes and clandestine Communist activities, intensified opposition, and new threatening international pressures on Portugal's overseas empire. During the earlier phase of the Cold War (1947-60), Portugal became a steadfast, if weak, member of the US-dominated North Atlantic Treaty Organization alliance and, in 1955, with American support, Portugal joined the United Nations (UN). Colonial affairs remained a central concern of the regime. As of 1939, Portugal was the third largest colonial power in the world and possessed territories in tropical Africa (Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau, and São Tomé and Príncipe Islands) and the remnants of its 16th-century empire in Asia (Goa, Damão, Diu, East Timor, and Macau). Beginning in the early 1950s, following the independence of India in 1947, Portugal resisted Indian pressures to decolonize Portuguese India and used police forces to discourage internal opposition in its Asian and African colonies.The later years of the New State (1958-68) witnessed the aging of the increasingly isolated but feared Salazar and new threats both at home and overseas. Although the regime easily overcame the brief oppositionist threat from rival presidential candidate General Humberto Delgado in the spring of 1958, new developments in the African and Asian empires imperiled the authoritarian system. In February 1961, oppositionists hijacked the Portuguese ocean liner Santa Maria and, in following weeks, African insurgents in northern Angola, although they failed to expel the Portuguese, gained worldwide media attention, discredited the New State, and began the 13-year colonial war. After thwarting a dissident military coup against his continued leadership, Salazar and his ruling group mobilized military repression in Angola and attempted to develop the African colonies at a faster pace in order to ensure Portuguese control. Meanwhile, the other European colonial powers (Britain, France, Belgium, and Spain) rapidly granted political independence to their African territories.At the time of Salazar's removal from power in September 1968, following a stroke, Portugal's efforts to maintain control over its colonies appeared to be successful. President Americo Tomás appointed Dr. Marcello Caetano as Salazar's successor as prime minister. While maintaining the New State's basic structures, and continuing the regime's essential colonial policy, Caetano attempted wider reforms in colonial administration and some devolution of power from Lisbon, as well as more freedom of expression in Lisbon. Still, a great deal of the budget was devoted to supporting the wars against the insurgencies in Africa. Meanwhile in Asia, Portuguese India had fallen when the Indian army invaded in December 1961. The loss of Goa was a psychological blow to the leadership of the New State, and of the Asian empire only East Timor and Macau remained.The Caetano years (1968-74) were but a hiatus between the waning Salazar era and a new regime. There was greater political freedom and rapid economic growth (5-6 percent annually to late 1973), but Caetano's government was unable to reform the old system thoroughly and refused to consider new methods either at home or in the empire. In the end, regime change came from junior officers of the professional military who organized the Armed Forces Movement (MFA) against the Caetano government. It was this group of several hundred officers, mainly in the army and navy, which engineered a largely bloodless coup in Lisbon on 25 April 1974. Their unexpected action brought down the 48-year-old New State and made possible the eventual establishment and consolidation of democratic governance in Portugal, as well as a reorientation of the country away from the Atlantic toward Europe.Revolution of Carnations, 1974-76Following successful military operations of the Armed Forces Movement against the Caetano government, Portugal experienced what became known as the "Revolution of Carnations." It so happened that during the rainy week of the military golpe, Lisbon flower shops were featuring carnations, and the revolutionaries and their supporters adopted the red carnation as the common symbol of the event, as well as of the new freedom from dictatorship. The MFA, whose leaders at first were mostly little-known majors and captains, proclaimed a three-fold program of change for the new Portugal: democracy; decolonization of the overseas empire, after ending the colonial wars; and developing a backward economy in the spirit of opportunity and equality. During the first 24 months after the coup, there was civil strife, some anarchy, and a power struggle. With the passing of the Estado Novo, public euphoria burst forth as the new provisional military government proclaimed the freedoms of speech, press, and assembly, and abolished censorship, the political police, the Portuguese Legion, Portuguese Youth, and other New State organizations, including the National Union. Scores of political parties were born and joined the senior political party, the Portuguese Community Party (PCP), and the Socialist Party (PS), founded shortly before the coup.Portugal's Revolution of Carnations went through several phases. There was an attempt to take control by radical leftists, including the PCP and its allies. This was thwarted by moderate officers in the army, as well as by the efforts of two political parties: the PS and the Social Democrats (PPD, later PSD). The first phase was from April to September 1974. Provisional president General Antonio Spínola, whose 1974 book Portugal and the Future had helped prepare public opinion for the coup, met irresistible leftist pressures. After Spinola's efforts to avoid rapid decolonization of the African empire failed, he resigned in September 1974. During the second phase, from September 1974 to March 1975, radical military officers gained control, but a coup attempt by General Spínola and his supporters in Lisbon in March 1975 failed and Spínola fled to Spain.In the third phase of the Revolution, March-November 1975, a strong leftist reaction followed. Farm workers occupied and "nationalized" 1.1 million hectares of farmland in the Alentejo province, and radical military officers in the provisional government ordered the nationalization of Portuguese banks (foreign banks were exempted), utilities, and major industries, or about 60 percent of the economic system. There were power struggles among various political parties — a total of 50 emerged—and in the streets there was civil strife among labor, military, and law enforcement groups. A constituent assembly, elected on 25 April 1975, in Portugal's first free elections since 1926, drafted a democratic constitution. The Council of the Revolution (CR), briefly a revolutionary military watchdog committee, was entrenched as part of the government under the constitution, until a later revision. During the chaotic year of 1975, about 30 persons were killed in political frays while unstable provisional governments came and went. On 25 November 1975, moderate military forces led by Colonel Ramalho Eanes, who later was twice elected president of the republic (1976 and 1981), defeated radical, leftist military groups' revolutionary conspiracies.In the meantime, Portugal's scattered overseas empire experienced a precipitous and unprepared decolonization. One by one, the former colonies were granted and accepted independence—Guinea-Bissau (September 1974), Cape Verde Islands (July 1975), and Mozambique (July 1975). Portugal offered to turn over Macau to the People's Republic of China, but the offer was refused then and later negotiations led to the establishment of a formal decolonization or hand-over date of 1999. But in two former colonies, the process of decolonization had tragic results.In Angola, decolonization negotiations were greatly complicated by the fact that there were three rival nationalist movements in a struggle for power. The January 1975 Alvor Agreement signed by Portugal and these three parties was not effectively implemented. A bloody civil war broke out in Angola in the spring of 1975 and, when Portuguese armed forces withdrew and declared that Angola was independent on 11 November 1975, the bloodshed only increased. Meanwhile, most of the white Portuguese settlers from Angola and Mozambique fled during the course of 1975. Together with African refugees, more than 600,000 of these retornados ("returned ones") went by ship and air to Portugal and thousands more to Namibia, South Africa, Brazil, Canada, and the United States.The second major decolonization disaster was in Portugal's colony of East Timor in the Indonesian archipelago. Portugal's capacity to supervise and control a peaceful transition to independence in this isolated, neglected colony was limited by the strength of giant Indonesia, distance from Lisbon, and Portugal's revolutionary disorder and inability to defend Timor. In early December 1975, before Portugal granted formal independence and as one party, FRETILIN, unilaterally declared East Timor's independence, Indonesia's armed forces invaded, conquered, and annexed East Timor. Indonesian occupation encountered East Timorese resistance, and a heavy loss of life followed. The East Timor question remained a contentious international issue in the UN, as well as in Lisbon and Jakarta, for more than 20 years following Indonesia's invasion and annexation of the former colony of Portugal. Major changes occurred, beginning in 1998, after Indonesia underwent a political revolution and allowed a referendum in East Timor to decide that territory's political future in August 1999. Most East Timorese chose independence, but Indonesian forces resisted that verdict untilUN intervention in September 1999. Following UN rule for several years, East Timor attained full independence on 20 May 2002.Consolidation of Democracy, 1976-2000After several free elections and record voter turnouts between 25 April 1975 and June 1976, civil war was averted and Portugal's second democratic republic began to stabilize. The MFA was dissolved, the military were returned to the barracks, and increasingly elected civilians took over the government of the country. The 1976 Constitution was revised several times beginning in 1982 and 1989, in order to reempha-size the principle of free enterprise in the economy while much of the large, nationalized sector was privatized. In June 1976, General Ram-alho Eanes was elected the first constitutional president of the republic (five-year term), and he appointed socialist leader Dr. Mário Soares as prime minister of the first constitutional government.From 1976 to 1985, Portugal's new system featured a weak economy and finances, labor unrest, and administrative and political instability. The difficult consolidation of democratic governance was eased in part by the strong currency and gold reserves inherited from the Estado Novo, but Lisbon seemed unable to cope with high unemployment, new debt, the complex impact of the refugees from Africa, world recession, and the agitation of political parties. Four major parties emerged from the maelstrom of 1974-75, except for the Communist Party, all newly founded. They were, from left to right, the Communists (PCP); the Socialists (PS), who managed to dominate governments and the legislature but not win a majority in the Assembly of the Republic; the Social Democrats (PSD); and the Christian Democrats (CDS). During this period, the annual growth rate was low (l-2 percent), and the nationalized sector of the economy stagnated.Enhanced economic growth, greater political stability, and more effective central government as of 1985, and especially 1987, were due to several developments. In 1977, Portugal applied for membership in the European Economic Community (EEC), now the European Union (EU) since 1993. In January 1986, with Spain, Portugal was granted membership, and economic and financial progress in the intervening years has been significantly influenced by the comparatively large investment, loans, technology, advice, and other assistance from the EEC. Low unemployment, high annual growth rates (5 percent), and moderate inflation have also been induced by the new political and administrative stability in Lisbon. Led by Prime Minister Cavaco Silva, an economist who was trained abroad, the PSD's strong organization, management, and electoral support since 1985 have assisted in encouraging economic recovery and development. In 1985, the PSD turned the PS out of office and won the general election, although they did not have an absolute majority of assembly seats. In 1986, Mário Soares was elected president of the republic, the first civilian to hold that office since the First Republic. In the elections of 1987 and 1991, however, the PSD was returned to power with clear majorities of over 50 percent of the vote.Although the PSD received 50.4 percent of the vote in the 1991 parliamentary elections and held a 42-seat majority in the Assembly of the Republic, the party began to lose public support following media revelations regarding corruption and complaints about Prime Minister Cavaco Silva's perceived arrogant leadership style. President Mário Soares voiced criticism of the PSD's seemingly untouchable majority and described a "tyranny of the majority." Economic growth slowed down. In the parliamentary elections of 1995 and the presidential election of 1996, the PSD's dominance ended for the time being. Prime Minister Antônio Guterres came to office when the PS won the October 1995 elections, and in the subsequent presidential contest, in January 1996, socialist Jorge Sampaio, the former mayor of Lisbon, was elected president of the republic, thus defeating Cavaco Silva's bid. Young and popular, Guterres moved the PS toward the center of the political spectrum. Under Guterres, the PS won the October 1999 parliamentary elections. The PS defeated the PSD but did not manage to win a clear, working majority of seats, and this made the PS dependent upon alliances with smaller parties, including the PCP.In the local elections in December 2001, the PSD's criticism of PS's heavy public spending allowed the PSD to take control of the key cities of Lisbon, Oporto, and Coimbra. Guterres resigned, and parliamentary elections were brought forward from 2004 to March 2002. The PSD won a narrow victory with 40 percent of the votes, and Jose Durão Barroso became prime minister. Having failed to win a majority of the seats in parliament forced the PSD to govern in coalition with the right-wing Popular Party (PP) led by Paulo Portas. Durão Barroso set about reducing government spending by cutting the budgets of local authorities, freezing civil service hiring, and reviving the economy by accelerating privatization of state-owned enterprises. These measures provoked a 24-hour strike by public-sector workers. Durão Barroso reacted with vows to press ahead with budget-cutting measures and imposed a wage freeze on all employees earning more than €1,000, which affected more than one-half of Portugal's work force.In June 2004, Durão Barroso was invited by Romano Prodi to succeed him as president of the European Commission. Durão Barroso accepted and resigned the prime ministership in July. Pedro Santana Lopes, the leader of the PSD, became prime minister. Already unpopular at the time of Durão Barroso's resignation, the PSD-led government became increasingly unpopular under Santana Lopes. A month-long delay in the start of the school year and confusion over his plan to cut taxes and raise public-sector salaries, eroded confidence even more. By November, Santana Lopes's government was so unpopular that President Jorge Sampaio was obliged to dissolve parliament and hold new elections, two years ahead of schedule.Parliamentary elections were held on 20 February 2005. The PS, which had promised the electorate disciplined and transparent governance, educational reform, the alleviation of poverty, and a boost in employment, won 45 percent of the vote and the majority of the seats in parliament. The leader of the PS, José Sôcrates became prime minister on 12 March 2005. In the regularly scheduled presidential elections held on 6 January 2006, the former leader of the PSD and prime minister, Aníbal Cavaco Silva, won a narrow victory and became president on 9 March 2006. With a mass protest, public teachers' strike, and street demonstrations in March 2008, Portugal's media, educational, and social systems experienced more severe pressures. With the spreading global recession beginning in September 2008, Portugal's economic and financial systems became more troubled.Owing to its geographic location on the southwestern most edge of continental Europe, Portugal has been historically in but not of Europe. Almost from the beginning of its existence in the 12th century as an independent monarchy, Portugal turned its back on Europe and oriented itself toward the Atlantic Ocean. After carving out a Christian kingdom on the western portion of the Iberian peninsula, Portuguese kings gradually built and maintained a vast seaborne global empire that became central to the way Portugal understood its individuality as a nation-state. While the creation of this empire allows Portugal to claim an unusual number of "firsts" or distinctions in world and Western history, it also retarded Portugal's economic, social, and political development. It can be reasonably argued that the Revolution of 25 April 1974 was the most decisive event in Portugal's long history because it finally ended Portugal's oceanic mission and view of itself as an imperial power. After the 1974 Revolution, Portugal turned away from its global mission and vigorously reoriented itself toward Europe. Contemporary Portugal is now both in and of Europe.The turn toward Europe began immediately after 25 April 1974. Portugal granted independence to its African colonies in 1975. It was admitted to the European Council and took the first steps toward accession to the European Economic Community (EEC) in 1976. On 28 March 1977, the Portuguese government officially applied for EEC membership. Because of Portugal's economic and social backwardness, which would require vast sums of EEC money to overcome, negotiations for membership were long and difficult. Finally, a treaty of accession was signed on 12 June 1985. Portugal officially joined the EEC (the European Union [EU] since 1993) on 1 January 1986. Since becoming a full-fledged member of the EU, Portugal has been steadily overcoming the economic and social underdevelopment caused by its imperial past and is becoming more like the rest of Europe.Membership in the EU has speeded up the structural transformation of Portugal's economy, which actually began during the Estado Novo. Investments made by the Estado Novo in Portugal's economy began to shift employment out of the agricultural sector, which, in 1950, accounted for 50 percent of Portugal's economically active population. Today, only 10 percent of the economically active population is employed in the agricultural sector (the highest among EU member states); 30 percent in the industrial sector (also the highest among EU member states); and 60 percent in the service sector (the lowest among EU member states). The economically active population numbers about 5,000,000 employed, 56 percent of whom are women. Women workers are the majority of the workforce in the agricultural and service sectors (the highest among the EU member states). The expansion of the service sector has been primarily in health care and education. Portugal has had the lowest unemployment rates among EU member states, with the overall rate never being more than 10 percent of the active population. Since joining the EU, the number of employers increased from 2.6 percent to 5.8 percent of the active population; self-employed from 16 to 19 percent; and employees from 65 to 70 percent. Twenty-six percent of the employers are women. Unemployment tends to hit younger workers in industry and transportation, women employed in domestic service, workers on short-term contracts, and poorly educated workers. Salaried workers earn only 63 percent of the EU average, and hourly workers only one-third to one-half of that earned by their EU counterparts. Despite having had the second highest growth of gross national product (GNP) per inhabitant (after Ireland) among EU member states, the above data suggest that while much has been accomplished in terms of modernizing the Portuguese economy, much remains to be done to bring Portugal's economy up to the level of the "average" EU member state.Membership in the EU has also speeded up changes in Portuguese society. Over the last 30 years, coastalization and urbanization have intensified. Fully 50 percent of Portuguese live in the coastal urban conurbations of Lisbon, Oporto, Braga, Aveiro, Coimbra, Viseu, Évora, and Faro. The Portuguese population is one of the oldest among EU member states (17.3 percent are 65 years of age or older) thanks to a considerable increase in life expectancy at birth (77.87 years for the total population, 74.6 years for men, 81.36 years for women) and one of the lowest birthrates (10.59 births/1,000) in Europe. Family size averages 2.8 persons per household, with the strict nuclear family (one or two generations) in which both parents work being typical. Common law marriages, cohabitating couples, and single-parent households are more and more common. The divorce rate has also increased. "Youth Culture" has developed. The young have their own meeting places, leisure-time activities, and nightlife (bars, clubs, and discos).All Portuguese citizens, whether they have contributed or not, have a right to an old-age pension, invalidity benefits, widowed persons' pension, as well as payments for disabilities, children, unemployment, and large families. There is a national minimum wage (€385 per month), which is low by EU standards. The rapid aging of Portugal's population has changed the ratio of contributors to pensioners to 1.7, the lowest in the EU. This has created deficits in Portugal's social security fund.The adult literacy rate is about 92 percent. Illiteracy is still found among the elderly. Although universal compulsory education up to grade 9 was achieved in 1980, only 21.2 percent of the population aged 25-64 had undergone secondary education, compared to an EU average of 65.7 percent. Portugal's higher education system currently consists of 14 state universities and 14 private universities, 15 state polytechnic institutions, one Catholic university, and one military academy. All in all, Portugal spends a greater percentage of its state budget on education than most EU member states. Despite this high level of expenditure, the troubled Portuguese education system does not perform well. Early leaving and repetition rates are among the highest among EU member states.After the Revolution of 25 April 1974, Portugal created a National Health Service, which today consists of 221 hospitals and 512 medical centers employing 33,751 doctors and 41,799 nurses. Like its education system, Portugal's medical system is inefficient. There are long waiting lists for appointments with specialists and for surgical procedures.Structural changes in Portugal's economy and society mean that social life in Portugal is not too different from that in other EU member states. A mass consumption society has been created. Televisions, telephones, refrigerators, cars, music equipment, mobile phones, and personal computers are commonplace. Sixty percent of Portuguese households possess at least one automobile, and 65 percent of Portuguese own their own home. Portuguese citizens are more aware of their legal rights than ever before. This has resulted in a trebling of the number of legal proceeding since 1960 and an eight-fold increase in the number of lawyers. In general, Portuguese society has become more permissive and secular; the Catholic Church and the armed forces are much less influential than in the past. Portugal's population is also much more culturally, religiously, and ethnically diverse, a consequence of the coming to Portugal of hundreds of thousands of immigrants, mainly from former African colonies.Portuguese are becoming more cosmopolitan and sophisticated through the impact of world media, the Internet, and the World Wide Web. A prime case in point came in the summer and early fall of 1999, with the extraordinary events in East Timor and the massive Portuguese popular responses. An internationally monitored referendum in East Timor, Portugal's former colony in the Indonesian archipelago and under Indonesian occupation from late 1975 to summer 1999, resulted in a vote of 78.5 percent for rejecting integration with Indonesia and for independence. When Indonesian prointegration gangs, aided by the Indonesian military, responded to the referendum with widespread brutality and threatened to reverse the verdict of the referendum, there was a spontaneous popular outpouring of protest in the cities and towns of Portugal. An avalanche of Portuguese e-mail fell on leaders and groups in the UN and in certain countries around the world as Portugal's diplomats, perhaps to compensate for the weak initial response to Indonesian armed aggression in 1975, called for the protection of East Timor as an independent state and for UN intervention to thwart Indonesian action. Using global communications networks, the Portuguese were able to mobilize UN and world public opinion against Indonesian actions and aided the eventual independence of East Timor on 20 May 2002.From the Revolution of 25 April 1974 until the 1990s, Portugal had a large number of political parties, one of the largest Communist parties in western Europe, frequent elections, and endemic cabinet instability. Since the 1990s, the number of political parties has been dramatically reduced and cabinet stability increased. Gradually, the Portuguese electorate has concentrated around two larger parties, the right-of-center Social Democrats (PSD) and the left-of-center Socialist (PS). In the 1980s, these two parties together garnered 65 percent of the vote and 70 percent of the seats in parliament. In 2005, these percentages had risen to 74 percent and 85 percent, respectively. In effect, Portugal is currently a two-party dominant system in which the two largest parties — PS and PSD—alternate in and out of power, not unlike the rotation of the two main political parties (the Regenerators and the Historicals) during the last decades (1850s to 1880s) of the liberal constitutional monarchy. As Portugal's democracy has consolidated, turnout rates for the eligible electorate have declined. In the 1970s, turnout was 85 percent. In Portugal's most recent parliamentary election (2005), turnout had fallen to 65 percent of the eligible electorate.Portugal has benefited greatly from membership in the EU, and whatever doubts remain about the price paid for membership, no Portuguese government in the near future can afford to sever this connection. The vast majority of Portuguese citizens see membership in the EU as a "good thing" and strongly believe that Portugal has benefited from membership. Only the Communist Party opposed membership because it reduces national sovereignty, serves the interests of capitalists not workers, and suffers from a democratic deficit. Despite the high level of support for the EU, Portuguese voters are increasingly not voting in elections for the European Parliament, however. Turnout for European Parliament elections fell from 40 percent of the eligible electorate in the 1999 elections to 38 percent in the 2004 elections.In sum, Portugal's turn toward Europe has done much to overcome its backwardness. However, despite the economic, social, and political progress made since 1986, Portugal has a long way to go before it can claim to be on a par with the level found even in Spain, much less the rest of western Europe. As Portugal struggles to move from underde-velopment, especially in the rural areas away from the coast, it must keep in mind the perils of too rapid modern development, which could damage two of its most precious assets: its scenery and environment. The growth and future prosperity of the economy will depend on the degree to which the government and the private sector will remain stewards of clean air, soil, water, and other finite resources on which the tourism industry depends and on which Portugal's world image as a unique place to visit rests. Currently, Portugal is investing heavily in renewable energy from solar, wind, and wave power in order to account for about 50 percent of its electricity needs by 2010. Portugal opened the world's largest solar power plant and the world's first commercial wave power farm in 2006.An American documentary film on Portugal produced in the 1970s described this little country as having "a Past in Search of a Future." In the years after the Revolution of 25 April 1974, it could be said that Portugal is now living in "a Present in Search of a Future." Increasingly, that future lies in Europe as an active and productive member of the EU. -
8 support
поддержка; обеспечение; тыловое обеспечение; материально-техническое обеспечение; МТО; обслуживание; головной отряд ( авангарда) ; сторожевая застава; второй эшелон ( в обороне) ; тыловой отряд; поддерживать; обеспечивать; обслуживать;C3 support — обеспечение средствами оперативного управления и связи; обеспечение органов руководства, управления и связи
nuclear (weapons) logistical support — тыловое обеспечение [МТО] применения ЯО
nuclear (weapons) logistics support — тыловое обеспечение [МТО] применения ЯО
— chemical corps support— cryptologistics support— logistical support— munitions logistic support— transportation support -
9 follow the sun
следуй за солнцем
Методология использования служб Service Desk и групп поддержки по всему миру для предоставления непрерывающейся услуги в режиме 24×7. Телефонные обращения, инциденты, проблемы и запросы на обслуживание передаются между группами, находящимися в различных временных зонах.
[ http://www.dtln.ru/slovar-terminov]
следуй за солнцем
(ITIL Service Operation)
Методология использования службы поддержки пользователей и групп поддержки по всему миру для предоставления непрерывного обслуживания в режиме 24/7. Звонки, инциденты, проблемы и запросы на обслуживание передаются между группами, находящимися в различных временных зонах.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]EN
follow the sun
(ITIL Service Operation)
A methodology for using service desks and support groups around the world to provide seamless 24/7 service. Calls, incidents, problems and service requests are passed between groups in different time zones.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > follow the sun
-
10 Marconi, Marchese Guglielmo
[br]b. 25 April 1874 Bologna, Italyd. 20 July 1937 Rome, Italy[br]Italian radio pioneer whose inventiveness and business skills made radio communication a practical proposition.[br]Marconi was educated in physics at Leghorn and at Bologna University. An avid experimenter, he worked in his parents' attic and, almost certainly aware of the recent work of Hertz and others, soon improved the performance of coherers and spark-gap transmitters. He also discovered for himself the use of earthing and of elevated metal plates as aerials. In 1895 he succeeded in transmitting telegraphy over a distance of 2 km (1¼ miles), but the Italian Telegraph authority rejected his invention, so in 1896 he moved to England, where he filed the first of many patents. There he gained the support of the Chief Engineer of the Post Office, and by the following year he had achieved communication across the Bristol Channel.The British Post Office was also slow to take up his work, so in 1897 he formed the Wireless Telegraph \& Signal Company to work independently. In 1898 he sold some equipment to the British Army for use in the Boer War and established the first permanent radio link from the Isle of Wight to the mainland. In 1899 he achieved communication across the English Channel (a distance of more than 31 miles or 50 km), the construction of a wireless station at Spezia, Italy, and the equipping of two US ships to report progress in the America's Cup yacht race, a venture that led to the formation of the American Marconi Company. In 1900 he won a contract from the British Admiralty to sell equipment and to train operators. Realizing that his business would be much more successful if he could offer his customers a complete radio-communication service (known today as a "turnkey" deal), he floated a new company, the Marconi International Marine Communications Company, while the old company became the Marconi Wireless Telegraph Company.His greatest achievement occurred on 12 December 1901, when Morse telegraph signals from a transmitter at Poldhu in Cornwall were received at St John's, Newfoundland, a distance of some 2,100 miles (3,400 km), with the use of an aerial flown by a kite. As a result of this, Marconi's business prospered and he became internationally famous, receiving many honours for his endeavours, including the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1909. In 1904, radio was first used to provide a daily bulletin at sea, and in 1907 a transatlantic wireless telegraphy service was inaugurated. The rescue of 1,650 passengers from the shipwreck of SS Republic in 1909 was the first of many occasions when wireless was instrumental in saving lives at sea, most notable being those from the Titanic on its maiden voyage in April 1912; more lives would have been saved had there been sufficient lifeboats. Marconi was one of those who subsequently pressed for greater safety at sea. In 1910 he demonstrated the reception of long (8 km or 5 miles) waves from Ireland in Buenos Aires, but after the First World War he began to develop the use of short waves, which were more effectively reflected by the ionosphere. By 1918 the first link between England and Australia had been established, and in 1924 he was awarded a Post Office contract for short-wave communication between England and the various parts of the British Empire.With his achievements by then recognized by the Italian Government, in 1915 he was appointed Radio-Communications Adviser to the Italian armed forces, and in 1919 he was an Italian delegate to the Paris Peace Conference. From 1921 he lived on his yacht, the Elettra, and although he joined the Fascist Party in 1923, he later had reservations about Mussolini.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsNobel Prize for Physics (jointly with K.F. Braun) 1909. Russian Order of S t Anne. Commander of St Maurice and St Lazarus. Grand Cross of the Order of the Crown (i.e. Knight) of Italy 1902. Freedom of Rome 1903. Honorary DSc Oxford. Honorary LLD Glasgow. Chevalier of the Civil Order of Savoy 1905. Royal Society of Arts Albert Medal. Honorary knighthood (GCVO) 1914. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Medal of Honour 1920. Chairman, Royal Society of Arts 1924. Created Marquis (Marchese) 1929. Nominated to the Italian Senate 1929. President, Italian Academy 1930. Rector, University of St Andrews, Scotland, 1934.Bibliography1896, "Improvements in transmitting electrical impulses and in apparatus thereof", British patent no. 12,039.1 June 1898, British patent no. 12,326 (transformer or "jigger" resonant circuit).1901, British patent no. 7,777 (selective tuning).1904, British patent no. 763,772 ("four circuit" tuning arrangement).Further ReadingD.Marconi, 1962, My Father, Marconi.W.J.Baker, 1970, A History of the Marconi Company, London: Methuen.KFBiographical history of technology > Marconi, Marchese Guglielmo
-
11 machinery
машинное оборудование
термин " машинное оборудование" означает:
- сборочную единицу, состоящую из соединенных частей или компонентов, по крайней мере, одна из которых находится в движении, имеет соответствующие приводы, схему управления, цепь питания, и т.д., соединенные вместе с целью специального применения, в частности, для производства, обработки, перемещения или упаковки материала;
- группу машин, которые для достижения той же цели организованы и управляется таким образом, что они функционируют как единое целое;
- взаимозаменяемое оборудование, модифицирующее функции машины, которое отдельно поставляется на рынок и предназначено для установки на машине или на серии различных машин или на приводном устройстве самим оператором, при условии, что данное оборудование не является запасной частью или инструментом.
[Директива 98/37/ЕЭС по машинному оборудованию]EN
machinery
‘machinery’ means:
— an assembly of linked parts or components, at least one of which moves, with the appropriate
actuators, control and power circuits, etc., joined together for a specific application, in particular
for the processing, treatment, moving or packaging of a material,
— an assembly of machines which, in order to achieve the same end, are arranged and controlled so that they function as an integral whole,
— interchangeable equipment modifying the function of a machine, which is placed on the market for the purpose of being assembled with a machine or a series of different machines or with a tractor by the operator himself in so far as this equipment is not a spare part or a tool
[DIRECTIVE 98/37/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
3. The following are excluded from the scope of this Directive:
3. Из области применения данной Директивы исключаются:
— machinery whose only power source is directly applied manual effort, unless it is a machine used for lifting or lowering loads,
- машинное оборудование, для которых источником энергии является исключительно непосредственное применение ручной силы, за исключением механизмов для подъема и опускания грузов;
— machinery for medical use used in direct contact with patients,
- медицинские приборы;
— special equipment for use in fairgrounds and/or amusement parks,
- специальное оборудование для использования в аттракционах и/или парках для развлечений;
— steam boilers, tanks and pressure vessels,
- паровые котлы, резервуары и сосуды под давлением;
— machinery specially designed or put into service for nuclear purposes which, in the event of failure, may result in an emission of radioactivity,
- машинное оборудование, специально сконструированное или используемое в атомной отрасли, которые в случае аварии могут привести к выделению радиоактивных веществ;
— radioactive sources forming part of a machine,
- радиоактивные источники, составляющие часть машин;
— firearms,
- стрелковое оружие;
— storage tanks and pipelines for petrol, diesel fuel, inflammable liquids and dangerous substances,
- емкости для хранения или трубопроводы для бензина, дизельного топлива, огнеопасных жидкостей и опасных веществ;
— means of transport, i.e. vehicles and their trailers intended solely for transporting passengers by air or on road, rail or water networks, as well as means of transport in so far as such means are designed for transporting goods by air, on public road or rail networks or on water. Vehicles used in the mineral extraction industry shall not be excluded,
- транспортные средства, т.е. средства перевозки и их прицепы, предназначенные исключительно для перевозки пассажиров по воздуху, автодороге, железной дороге, или водными путями, а также транспортные средства, сконструированные для транспортировки грузов по воздуху, по общедоступным дорогам, железным дорогам или водным путям. Средства транспортировки, используемые в горнодобывающей промышленности, не исключаются из области применения настоящей Директивы;
— seagoing vessels and mobile offshore units together with equipment on board such vessels or units,
- морские суда и мобильные береговые агрегаты вместе с оборудованием на борту, такие как танки или установки;
— cableways, including funicular railways, for the public or private transportation of persons,
- канатные дороги, включая фуникулерные железные дороги для общественного или частного пользования, предназначенные для транспортировки людей;
— agricultural and forestry tractors, as defined in Article 1(1) of Directive 74/150/EEC (1),
(1) Council Directive 74/150/EEC of 4 March 1974 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States relating to the type-approval of wheeled agricultural or forestry tractors (OJ L 84, 28.3.1974, p. 10). Directive as last amended by Decision 95/1/EC, Euratom, ECSC (OJ L 1.1.1995, p. 1).-сельскохозяйственные и лесные тракторы, подпадающие под определение статьи 1 (1) Директивы Совета 74/150/ЕЭС(1);
(1) Директива Совета 74/150/ЕЭС от 4 марта 1974 г. по сближению законодательных актов Государств-членов, относящихся к одобрению типов колесных сельскохозяйственных или лесных тракторов (Официальный журнал Европейских сообществ № L 84, 28.3.1974 г., стр.10). Директива, измененная последний раз Решением 95/1/ЕЭС, Евроатом, ECSC (Официальный журнал Европейских сообществ № L 1/1/1995 г., стр 1)— machines specially designed and constructed for military or police purposes,
- машины, специально сконструированные и созданные для военных и полицейских целей;
— lifts which permanently serve specific levels of buildings and constructions, having a car moving between guides which are rigid and inclined at an angle of more than 15 degrees to the horizontal and designed for the transport of:
(i) persons;
(ii) persons and goods;
(iii) goods alone if the car is accessible, that is to say, a person may enter it without difficulty, and fitted with controls situated inside the car or within reach of a person inside,- лифты и подъемные устройства, постоянно обслуживающие определенные уровни зданий и конструкций, имеющие транспортную тележку, движущуюся между жесткими направляющими, которые имеют угол наклона более 15 градусов к горизонтальной поверхности и сконструированы для транспортировки:
(i) людей;
(ii) людей и имущества;
(iii) только имущества, в том случае, если кабина лифта открыта, т.е. человек может легко войти в такое транспортное средство и манипулировать средствами управления, находящимися внутри кабины или в пределах досягаемости для человека;— means of transport of persons using rack and pinion rail mounted vehicles,
- транспортные средства для перевозки людей, с использованием зубчатых или реечных рельс, по которым перемещается транспортные средства;
— mine winding gear,
- шахтные канатные подъемные устройства;
— theatre elevators,
- театральные подъемники;
— construction site hoists intended for lifting persons or persons and goods.
- строительные подъемники, предназначенные для подъема людей или людей и грузов.
4. Where, for machinery or safety components, the risks referred to in this Directive are wholly or partly covered by specific Community Directives, this Directive shall not apply, or shall cease to apply, in the case of such machinery or safety components and of such risks on the implementation of these specific Directives.
4. Когда для машинного оборудования и компонентов безопасности риски, определенные в настоящей Директиве, полностью или частично покрываются специальными Директивами Сообщества, настоящая Директива не применяется или прекращает свое действие, такое машинное оборудование и компоненты безопасности и такие риски подпадают под действие этих специальных Директив.
5. Where, for machinery, the risks are mainly of electrical origin, such machinery shall be covered exclusively by Directive 73/23/EEC (2).
(2) Council Directive 73/23/EEC of 19 February 1973 on the harmonisation of the laws of Member States relating to electrical equipment designed for use within certain voltage limits (OJ L 77, 26.3.1973, p. 29). Directive as last amended by Directive 93/68/EEC (OJ L 220, 30.8.1993, p. 1).5. Когда риски применения машинного оборудования связаны с электрическими источниками, то такое оборудование охватываются исключительно Директивой 73/23/ЕЭС(2).
(2) Директива Совета 73/23/ЕЭС/ от 19 февраля 1973 года о гармонизации законов Государств-Участников в отношении электрооборудования, предназначенного для использования в условиях определенных пределов напряжения (Официальный журнал Европейских сообществ № L 77, 26.03.1973, стр. 29). Директива с последней поправкой Директивой 93/68/ЕЭС (Официальный журнал Европейских сообществ № L 220, 30.08.1993, стр.1).Article 2
1. Member States shall take all appropriate measures to ensure that machinery or safety components covered by this Directive may be placed on the market and put into service only if they do not endanger the health or safety of persons and, where appropriate, domestic animals or property, when properly installed and maintained and used for their intended purpose.Статья 2
1. Государства - члены должны предпринимать все необходимые меры для обеспечения того, чтобы машинное оборудование или компоненты безопасности, попадающие под действие настоящей Директивы, поставлялись на рынок и вводились в эксплуатацию, только если они не составляют угрозу для здоровья и безопасности людей и домашних животных, или имуществу при условии надлежащей установки и обслуживания, а также использования по прямому назначению.2. This Directive shall not affect Member States’ entitlement to lay down, in due observance of the Treaty, such requirements as they may deem necessary to ensure that persons and in particular workers are protected when using the machinery or safety components in question, provided that this does not mean that the machinery or safety components are modified in a way not specified in the Directive.
2. Настоящая Директива не ограничивает права Государств - членов устанавливать при должном соблюдении Договора такие требования, которые они посчитают необходимыми для обеспечения защиты людей, особенно работников, при использовании машинного оборудования или компонентов безопасности, при условии, что модификация такого машинного оборудования и компонентов безопасности была произведена в соответствии с положениями настоящей Директивы.
3. At trade fairs, exhibitions, demonstrations, etc., Member States shall not prevent the showing of machinery or safety components which do not conform to the provisions of this Directive, provided that a visible sign clearly indicates that such machinery or safety components do not conform and that they are not for sale until they have been brought into conformity by the manufacturer or his authorised representative established in the Community. During demonstrations, adequate safety measures shall be taken to ensure the protection of persons.
3. На торговых ярмарках, выставках, демонстрациях и т.п. Государства - члены не должны препятствовать демонстрации машинного оборудования или компонентов безопасности, которые не соответствуют положениям настоящей Директивы, при условии, что видимый знак четко указывает, что такое машинное оборудование или компоненты безопасности не соответствуют данной Директиве, и что они не предназначаются для продажи до тех пор, пока изготовитель или его уполномоченный представитель в Сообществе не приведет их в полное соответствие с Директивой. Во время демонстраций должны приниматься адекватные меры для обеспечения безопасности граждан.
Article 3
Machinery and safety components covered by this Directive shall satisfy the essential health and safety requirements set out in Annex I.Статья 3
Машинное оборудование, а также компоненты безопасности, относящиеся к области действия настоящей Директивы, должны полностью удовлетворять основным требованиям по обеспечению здоровья и безопасности, изложенным в Приложении 1.Article 4
1. Member States shall not prohibit, restrict or impede the placing on the market and putting into service in their territory of machinery and safety components which comply with this Directive.Статья 4
1. Государства - члены не должны запрещать, ограничивать или препятствовать поставке на рынок машинного оборудования, а также компонентов безопасности, которые соответствуют
требованиям настоящей Директивы.2. Member States shall not prohibit, restrict or impede the placing on the market of machinery where the manufacturer or his authorised representative established in the Community declares in accordance with point B of Annex II that it is intended to be incorporated into machinery or assembled with other machinery to constitute machinery covered by this Directive, except where it can function independently.
‘Interchangeable equipment’, as referred to in the third indent of Article 1(2)(a), must in all cases bear the CE marking and be accompanied by the EC declaration of conformity referred to in Annex II, point A.2. Государства - члены не должны запрещать, ограничивать или препятствовать поставке на рынок машинного оборудования, если изготовитель или его уполномоченный представитель в Сообществе заявляет в соответствии с Приложением II B, что они предназначены для включения в машинное оборудование или компоноваться с другим оборудованием, так, что в соединении они составят машинное оборудование, отвечающее требованиям настоящей Директивы, за исключением тех случаев, когда они могут функционировать независимо.
"Взаимозаменяемое оборудование" в смысле третьего абзаца с черточкой в Статье 1 (2) (a) должно во всех случаях иметь маркировку "СЕ" и сопровождаться декларацией соответствия, определенной в Приложении II, пункте А.3. Member States may not prohibit, restrict or impede the placing on the market of safety components as defined in Article 1(2) where they are accompanied by an EC declaration of conformity by the manufacturer or his authorised representative established in the Community as referred to in Annex II, point C.
3. Государства - члены не имеют права запрещать, ограничивать или препятствовать распространению на рынке компонентов безопасности, определенных Статьей 1 (2), если эти компоненты сопровождаются декларацией соответствия ЕС, заявленной изготовителем или его уполномоченным представителем в Сообществе, как определено в Приложении II, пункте С.
Article 5
1. Member States shall regard the following as conforming to all the provisions of this Directive, including the procedures for checking the conformity provided for in Chapter II:
— machinery bearing the CE marking and accompanied by the EC declaration of conformity referred to in Annex II, point A,
— safety components accompanied by the EC declaration of conformity referred to in Annex II, point C.Статья 5
1. Государства - члены должны считать нижеследующее соответствующим всем положениям настоящей Директивы, включая процедуры проверки соответствия, предусмотренной в Главе II:
- машинное оборудование, имеющее маркировку "СЕ" и сопровождаемое декларацией соответствия ЕС, как указано в Приложении II, пункте A;
- компоненты безопасности, сопровождаемые декларацией соответствия ЕС, как указано в Приложении II, пункте C.
При отсутствии гармонизированных стандартов Государства - члены должны предпринимать любые меры, которые они сочтут необходимыми, для привлечения внимания заинтересованных сторон к существующим национальным техническим стандартам и спецификациям, которые считаются важными или относятся к выполнению основных требований по обеспечению здоровья и безопасности в соответствии с Приложением 1.2. Where a national standard transposing a harmonised standard, the reference for which has been published in the Official Journal of the European Communities, covers one or more of the essential safety requirements, machinery or safety components constructed in accordance with this standard shall be presumed to comply with the relevant essential requirements.
Member States shall publish the references of national standards transposing harmonised standards.2. В тех случаях, когда национальный стандарт, заменяющий гармонизированный стандарт, ссылка на который была опубликована в Официальном журнале Европейских сообществ, покрывает одно или несколько основных требований безопасности, машинное оборудование или компоненты безопасности, сконструированные в соответствии с таким стандартом, должны считаться соответствующими основным требованиям.
Государства - члены должны публиковать ссылки на национальные стандарты, заменяющие гармонизированные стандарты.3. Member States shall ensure that appropriate measures are taken to enable the social partners to have an influence at national level on the process of preparing and monitoring the harmonised standards.
3. Государства - члены должны обеспечивать принятие необходимых мер для того, чтобы их социальные партнеры получали возможность влиять на национальном уровне на процессы подготовки и отслеживания гармонизированных стандартов.
Article 6
1. Where a Member State or the Commission considers that the harmonised standards referred to in Article 5(2) do not entirely satisfy the essential requirements referred to in Article 3, the Commission or the Member State concerned shall bring the matter before the committee set up under Directive 83/189/EEC, giving the reasons therefor. The committee shall deliver an opinion without delay.
Upon receipt of the committee’s opinion, the Commission shall inform the Member States whether or not it is necessary to withdraw those standards from the published information referred to in Article 5(2).Статья 6
1. В случае, если Государство - член или Комиссия считают, что гармонизированные стандарты, рассмотренные в Статье 5 (2), не полностью соответствуют основным требованиям, определенным в Статье 3, Комиссия или заинтересованное Государство - член должны поставить этот вопрос на рассмотрение комитета, созданного в соответствии с Директивой 83/189/ЕЭС, обосновав причины такого обращения. Комитет должен безотлагательно вынести решение.
После получения такого решения комитета Комиссия должна информировать Государства – члены, необходимо или нет отозвать эти стандарты из опубликованной информации, определенной в Статье 5 (2).2. A standing committee shall be set up, consisting of representatives appointed by the Member States and chaired by a representative of the Commission.
The standing committee shall draw up its own rules of procedure.
Any matter relating to the implementation and practical application of this Directive may be brought before the standing committee, in accordance with the following procedure:
The representative of the Commission shall submit to the committee a draft of the measures to be taken. The committee shall deliver its opinion on the draft, within a time limit which the chairman may lay down according to the urgency of the matter, if necessary by taking a vote.
The opinion shall be recorded in the minutes; in addition, each Member State shall have the right to ask to have its position recorded in the minutes.
The Commission shall take the utmost account of the opinion delivered by the committee.
It shall inform the committee of the manner in which its opinion has been taken into account.2. Должен быть создан постоянно действующий комитет, состоящий из представителей, назначенных Государствами – членами, и возглавляемый представителем Комиссии.
Постоянно действующий комитет будет сам устанавливать порядок действий и процедуры.
Любой вопрос, относящийся к выполнению и практическому применению настоящей Директивы, может быть поставлен на рассмотрение постоянно действующего комитета, в соответствии со следующими правилами:
Представитель Комиссии должен представить комитету проект предполагаемых к принятию мер. Комитет должен выразить свое мнение по проекту за время, установленное председателем в соответствии со срочностью вопроса, при необходимости определяемого путем голосования.
Это мнение должно быть зафиксировано в протоколе; кроме того, каждое Государство - член имеет право потребовать отразить свою позицию в протоколе. Комиссия должна максимально учитывать мнение, вынесенное комитетом.
Она должна проинформировать комитет, каким образом было учтено его мнение.Article 7
1. Where a Member State ascertains that:
— machinery bearing the CE marking, or
— safety components accompanied by the EC declaration of conformity, used in accordance with their intended purpose are liable to endanger the safety of persons, and, where appropriate, domestic animals or property, it shall take all appropriate measures to withdraw such machinery or safety components from the market, to prohibit the placing on the market, putting into service or use thereof, or to restrict free movement thereof.
Member States shall immediately inform the Commission of any such measure, indicating the reason for its decision and, in particular, whether non-conformity is due to:
(a) failure to satisfy the essential requirements referred to in Article 3;
(b) incorrect application of the standards referred to in Article 5(2);
(c) shortcomings in the standards themselves referred to in Article 5(2).Статья 7
1. Если Государство - член устанавливает, что:
- машинное оборудование, имеющее маркировку "СЕ", либо
- компоненты безопасности, сопровождаемые декларацией соответствия ЕС, используемые в соответствии с их назначением, могут нести угрозу безопасности людям, и, если это имеет место, домашним животным или собственности, оно должно принять все необходимые меры для изъятия такого машинного оборудования, либо компонентов безопасности с рынка, запретить их поставку на рынок, ввод в эксплуатацию или использование, либо ограничить их свободное обращение.
Государства - члены должны немедленно информировать Комиссию о любых подобных мерах, указать причины такого решения и, в особенности, информировать о том, явилось ли это несоответствие результатом:
a) неспособности удовлетворить основным требованиям, определенным в Статье 3;
b) неправильного применения стандартов, определенных в Статье 5 (п.2);
c) недостатков самих стандартов, определенных в Статье 5 (п. 2).2. The Commission shall enter into consultation with the parties concerned without delay. Where the Commission considers, after this consultation, that the measure is justified, it shall immediately so inform the Member State which took the initiative and the other Member States. Where the Commission considers, after this consultation, that the action is unjustified, it shall immediately so inform the Member State which took the initiative and the manufacturer or his authorised representative established within the Community.
Where the decision referred to in paragraph 1 is based on a shortcoming in the standards, and where the Member State at the origin of the decision maintains its position, the Commission shall immediately inform the committee in order to initiate the procedures referred to in Article 6(1).2. Комиссия должна безотлагательно провести консультацию с заинтересованными сторонами. В случае, если после проведения такой консультации, Комиссия полагает, что такая мера обоснована, она должна немедленно информировать об этом Государство - член, которое выдвинуло эту инициативу, а также остальные Государства - члены. Если Комиссия после проведения такой консультации полагает, что действия не были обоснованными, она немедленно извещает об этом Государство - член, проявившее инициативу, и изготовителя, либо его уполномоченного представителя в Сообществе.
Если решение, указанное в параграфе 1, основано на недостатках в стандартах, и если Государство - член на основании такого решения сохраняет свои позиции, то Комиссия должна немедленно информировать комитет для того, чтобы начать процедуры, описанные в Статье 6 (п. 1).3. Where:
— machinery which does not comply bears the CE marking,
— a safety component which does not comply is accompanied by an EC declaration of conformity,
the competent Member State shall take appropriate action against whom so ever has affixed the marking or drawn up the declaration and shall so inform the Commission and other Member States.3. Если:
- машинное оборудование, не соответствующие требованиям, имеют маркировку "СЕ",
- компоненты безопасности, не соответствующие требованиям, имеют декларацию соответствия ЕС,
компетентное Государство - член должно начать соответствующие действия против любого, кто поставил маркировку, или составил декларацию, и должно проинформировать об этом Комиссию и другие Государства - члены.4. The Commission shall ensure that Member States are kept informed of the progress and outcome of this procedure.
4. Комиссия должна обеспечить, чтобы Государства – члены были постоянно информированы о ходе и результатах данной процедуры.
CHAPTER II
CONFORMITY ASSESSMENT PROCEDURES
Article 8
1. The manufacturer or his authorised representative established in the Community must, in order to certify that machinery and safety components are in conformity with this Directive, draw up for all machinery or safety components manufactured an EC declaration of conformity based on the model given in Annex II, point A or C as appropriate.
In addition, for machinery alone, the manufacturer or his authorised representatives established in the Community must affix to the machine the CE marking.Глава II
Процедуры оценки соответствия
Статья 8
1. Для подтверждения того, что машинное оборудование, а также компоненты безопасности соответствуют положениям настоящей Директивы, изготовитель или его уполномоченный представитель в Сообществе должен составить декларацию ЕС о соответствии на произведенное машинное оборудование и компоненты безопасности по образцу, приведенному в Приложении II, соответственно пунктам A или C.
Корме того, на машинное оборудование изготовитель или его уполномоченный представитель в Сообществе должен нанести маркировку "СЕ" в соответствии со Статьей 10.2. Before placing on the market, the manufacturer, or his authorised representative established in the Community, shall:
(a) if the machinery is not referred to in Annex IV, draw up the file provided for in Annex V;
(b) if the machinery is referred to in Annex IV and its manufacturer does not comply, or only partly complies, with the standards referred to in Article 5(2) or if there are no such standards, submit an example of the machinery for the EC type-examination referred to in Annex VI;
(c) if the machinery is referred to in Annex IV and is manufactured in accordance with the standards referred to in Article 5(2):
— either draw up the file referred to in Annex VI and forward it to a notified body, which will acknowledge receipt of the file as soon as possible and keep it,
— submit the file referred to in Annex VI to the notified body, which will simply verify that the standards referred to in Article 5(2) have been correctly applied and will draw up a certificate of adequacy for the file,
— or submit the example of the machinery for the EC type-examination referred to in Annex VI.2. Перед поставкой на рынок изготовитель или его уполномоченный представитель в Сообществе должен:
(a) в случае, если машинное оборудование не указано в Приложении IV, составить документацию, предусмотренную Приложением V;
(b) если машинное оборудование указано в Приложении IV, и их изготовитель не выполняет, либо выполняет лишь частично требования стандартов, упомянутых в Статье 5 (2), либо, если таких стандартов не существует, то представить образец машинного оборудования для его испытания ЕС, определенного в Приложении VI;
(c) если машинное оборудование указано в Приложении IV и изготовлено в соответствии со стандартами, определенными в Статье 5 (п. 2):
- либо составить документацию, указанную в Приложении VI, и передать ее нотифицированному органу, который подтверждает получение документации в возможно короткие сроки, а также сохраняет ее;
- представить документацию, указанную в Приложении VI, нотифицированному органу, который просто проверит, что стандарты, упомянутые в Статье 5 (2), были применены правильно и составит сертификат соответствия по этой документации;
- либо представить образец машинного оборудования для испытания ЕС типового образца, определенного в Приложении VI.3. Where the first indent of paragraph 2(c) of this Article applies, the provisions of the first sentence of paragraphs 5 and 7 of Annex VI shall also apply.
Where the second indent of paragraph 2(c) of this Article applies, the provisions of paragraphs 5, 6 and 7 of Annex VI shall also apply.3. В тех случаях, когда может быть применен первый абзац параграфа 2 (с) этой Статьи должны также применяться положения первого предложения параграфов 5 и 7 Приложения VI.
В тех случаях, когда может быть применен второй абзац пункта 2 (с), должны также применяться положения параграфов 5, 6 и 7 Приложения VI.4. Where paragraph 2(a) and the first and second indents of paragraph 2(c) apply, the EC declaration of conformity shall solely state conformity with the essential requirements of the Directive.
Where paragraph 2(b) and the third indent of paragraph 2(c) apply, the EC declaration of conformity shall state conformity with the example that underwent EC type-examination.4. В тех случаях, когда применяется параграф 2 (а) и первый и второй абзацы параграфа 2 (c), декларация ЕС о соответствии должна удостоверить соответствие основным требованиям настоящей Директивы.
В случае, когда применяется параграф 2 (b) и третий абзац параграфа 2 (c), декларация ЕС о соответствии должна удостоверить соответствие образцу, прошедшему испытание ЕС типового образца.5. Safety components shall be subject to the certification procedures applicable to machinery pursuant to paragraphs 2, 3 and 4. Furthermore, during EC type-examination, the notified body shall verify the suitability of the safety component for fulfilling the safety functions declared by the manufacturer.
5.Компоненты безопасности должны подвергаться процедурам сертификации, применимым к машинному оборудованию в соответствии с параграфами 2, 3, 4. Более того, во время испытания ЕС типового образца нотифицированный орган должен проверить пригодность компонентов безопасности для выполнения тех функций безопасности, которые заявлены изготовителем.
6. (a) Where the machinery is subject to other Directives concerning other aspects and which also provide for the affixing of the CE marking, the latter shall indicate that the machinery is also presumed to conform to the provisions of those other Directives.
(b) However, where one or more of those Directives allow the manufacturer, during a transitional period, to choose which arrangements to apply, the CE marking shall indicate conformity only to the Directives applied by the manufacturer. In this case, particulars of the Directives applied, as published in the Official Journal of the European Communities, must be given in the documents, notices or instructions required by the directives and accompanying such machinery.6. (a) В тех случаях, когда машинное оборудование подпадает под действие Директив по другим аспектам, которые также предусматривают нанесение маркировки "СЕ", последняя указывает, что такое машинное оборудование соответствуют положениям этих прочих директив.
(b) Тем не менее, когда одна или несколько таких Директив позволяют изготовителям в течение переходного периода выбирать, какие из положений применить, маркировка "СЕ" будет указывать на соответствие только тем Директивам, которые применялись изготовителем. В этом случае подробная информация о примененных Директивах, опубликованных в Официальном журнале Европейских сообществ, должен приводиться в документах, аннотациях или инструкциях, требуемых в соответствии с Директивами, и сопровождать такое машинное оборудование.7. Where neither the manufacturer nor his authorised representative established in the Community fulfils the obligations of paragraphs 1 to 6, these obligations shall fall to any person placing the machinery or safety component on the market in the Community. The same obligations shall apply to any person assembling machinery or parts thereof or safety components of various origins or constructing machinery or safety components for his own use.
7. Если ни изготовитель, ни его уполномоченный представитель в Сообществе не выполнят своих обязательств по предыдущим параграфам, то эти обязательства должны быть выполнены любыми лицами, поставляющими машинное оборудование или компоненты безопасности на рынок Сообщества. Такие же обязательства возлагаются на любые лица, осуществляющие сборку машинного оборудования, либо его частей или компонентов безопасности различного происхождения, либо создающие машинное оборудование или компоненты безопасности для собственного пользования.
8. The obligations referred to in paragraph 7 shall not apply to persons who assemble with a machine or tractor interchangeable equipment as provided for in Article 1, provided that the parts are compatible and each of the constituent parts of the assembled machine bears the CE marking and is accompanied by the EC declaration of conformity.
8. Обязательства, изложенные в параграфе 7, не применяются к лицам, которые собирают с машиной, механизмом или транспортным средством взаимозаменяемое оборудование, указанное в Статье 1, при условии, что эти части совместимы, и каждая из частей машины в сборе имеет маркировку "СЕ" и Декларацию ЕС о соответствии.
Article 9
1. Member States shall notify the Commission and the other Member States of the approved bodies which they have appointed to carry out the procedures referred to in Article 8 together with the specific tasks which these bodies have been appointed to carry out and the identification numbers assigned to them beforehand by the Commission.
The Commission shall publish in the Official Journal of the European Communities a list of the notified bodies and their identification numbers and the tasks for which they have been notified. The Commission shall ensure that this list is kept up to date.Статья 9
1. Государства - члены должны уведомить Комиссию и другие Государства - члены об утвержденных органах, которые назначаются для выполнения процедур, описанных в Статье 8, также как и для различных особых задач, которые этим органам предназначено выполнять, и об идентификационных номерах, предварительно присвоенных им Комиссией.В Официальном журнале Европейских сообществ Комиссия должна публиковать список таких нотифицированных органов и их идентификационные номера, а также задачи, для решения которых они предназначены. Комиссия должна обеспечить своевременность обновления списка.
2. Member States shall apply the criteria laid down in Annex VII in assessing the bodies to be indicated in such notification. Bodies meeting the assessment criteria laid down in the relevant harmonised standards shall be presumed to fulfil those criteria.
2. Государства - члены должны применять критерии, изложенные в Приложении VII, для определения органов, которые будут указаны в таких назначениях. Органы, удовлетворяющие критериям, изложенным в соответствующих гармонизированных стандартах, считаются соответствующими критериям.
3. A Member State which has approved a body must withdraw its notification if it finds that the body no longer meets the criteria referred to in Annex VII. It shall immediately inform the Commission and the other Member States accordingly.
3. Государство - член, утвердившее такой орган, должно отменить его назначение, если оно обнаружит, что он больше не соответствует критериям, изложенным в Приложении VII. Государство - член должно немедленно известить об этом Комиссию и другие Государства - члены.
CHAPTER III
CE MARKING
Article 10
1. The CE conformity marking shall consist of the initials ‘CE’. The form of the marking to be used is shown in Annex III.ГЛАВА III
МАРКИРОВКА "СЕ"
Статья 10
1. Маркировка "СЕ" состоит из заглавных букв "СЕ". Форма маркировки, которая будет использоваться, указана в Приложении III.2. The CE marking shall be affixed to machinery distinctly and visibly in accordance with point 1.7.3 of Annex I.
2. Маркировка "СЕ" должна наноситься на машинное оборудование четко, на видном месте в соответствии с пунктом 1.7.3. Приложения I.
3. The affixing of markings on the machinery which are likely to deceive third parties as to the meaning and form of the CE marking shall be prohibited. Any other marking may be affixed to the machinery provided that the visibility and legibility of the CE marking is not thereby reduced.
3. Нанесение маркировок на машинное оборудование таким образом, что это может ввести в заблуждение относительно значения и формы маркировки "СЕ", запрещено. Любые другие маркировки могут быть нанесены на машинное оборудование таким образом, чтобы не мешать видимости и различимости маркировки "СЕ".
4. Without prejudice to Article 7:
(a) where a Member State establishes that the CE marking has been affixed unduly, the manufacturer or his authorised representative established within the Community shall be obliged to make the product conform as regards the provisions concerning the CE marking and to end the infringement under the conditions imposed by the Member State;
(b) where non-conformity continues, the Member State must take all appropriate measures to restrict or prohibit the placing on the market of the product in question or to ensure that it is withdrawn from the market in accordance with the procedure laid down in Article 7.4. Без ограничения применения Статьи 7:
(a) если Государство - член устанавливает, что маркировка "СЕ" была нанесена неправильно, изготовитель или его уполномоченный представитель в Сообществе будет обязан привести продукцию в соответствии с положениями, касающимися маркировки "СЕ" и положить конец нарушениям на условиях, установленных Государством - членом;
(b) если такое несоответствие будет продолжаться, то Государство - член должно принять все соответствующие меры для ограничения или запрещения поставки на рынок такой продукции, либо обеспечить изъятие ее с рынка в соответствии с процедурами, изложенными в Статье 7.CHAPTER IV
FINAL PROVISIONS
Article 11
Any decision taken pursuant to this Directive which restricts the placing on the market and putting into service of machinery or a safety component shall state the exact grounds on which it is based. Such a decision shall be notified as soon as possible to the party concerned, who shall at the same time be informed of the legal remedies available to him under the laws in force in the Member State concerned and of the time limits to which such remedies are subject.ГЛАВА IV
ЗАКЛЮЧИТЕЛЬНЫЕ ПОЛОЖЕНИЯ
Статья 11
Любое решение, принятое в исполнение настоящей Директивы, ограничивающее поставку на рынок и ввод в эксплуатацию машинного оборудования или компонентов безопасности, должно указывать точные причины, на которых оно основано. Такое решение должно быть по возможности быстро доведено до сведения заинтересованных сторон, их также следует проинформировать о законных мерах, которые могут быть предприняты по действующему законодательству в соответствующем Государстве - члене и о сроках, в которые данные меры применяются.Article 12
The Commission will take the necessary steps to have information on all the relevant decisions relating to the management of this Directive made available.Статья 12
Комиссия предпримет все необходимые шаги для получения информации по всем соответствующим решениям, касающимся применения и распространения настоящей Директивы.Article 13
1. Member States shall communicate to the Commission the texts of the provisions of national law which they adopt in the field governed by this Directive.
2. The Commission shall, before 1 January 1994, examine the progress made in the standardisation work relating to this Directive and propose any appropriate measures.Статья 13
1. Государства - члены должны передать Комиссии тексты положений национальных законодательных актов, принимаемых в сфере, определяемой настоящей Директивой.
2. Комиссия должна до 1 января 1994 г. изучить развитие работ по стандартизации, относящиеся к области действия настоящей Директивы и предложить любые целесообразные меры.Тематики
EN
машины
оборудование
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]
машины
Машина представляет собой аппарат, использующий или применяющий механическую энергию, состоящий из нескольких частей — каждая со своими определенными функциями, которые вместе выполняют некоторые виды работ. Для целей анализа это понятие включает отдельные машины или наборы машин. См. Машины и оборудование (МСО)
[ http://slovar-lopatnikov.ru/]Тематики
- экономика
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
машины и оборудование
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]
машины и оборудование
МСО
Часть основных фондов компании (предприятия), которая включает устройства, преобразующие энергию, материалы и информацию. В аналитической и оценочной практике в общее понятие М. и о. включаются отдельно оцениваемые установки, машины, оборудование и транспортные средства, подразделяемые на виды, а каждый вид – на марки (последним термином для краткости можно обозначать разные модели и модификации машины). Разные марки машин одного вида используются для одних и тех же целей: они способны производить одну и ту же продукцию, выполнять одни и те же работы или оказывать одни и те же услуги ( в противном случае их надо относить в другому виду машин), а следовательно, «взаимозаменяемы» и являются товарами, конкурирующими между собой на рынке Рынок машин каждого вида делится на первичный (новые М..) и вторичный (бывшие в эксплуатации), для которых применяются разные оценочные приемы и инструменты.. М.и о. являются главным объектом инвестирования при разработке и реализации инвестиционного проекта, и, соответственно, одним из основных элементов оценки инвестиционных проектов. Важно, что в отличие от ценных бумаг, акций, М.и о. являются объектами реальных инвестиций, а не финансовых инвестиций.
[ http://slovar-lopatnikov.ru/]EN
machinery
A group of parts or machines arranged to perform a useful function. (Source: MGH)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
механизм
Совокупность подвижно соединённых звеньев, совершающих под действием приложенных сил заранее определённые целесообразные движения
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
машины, механизмы
Совокупность связанных между собой частей и устройств, как минимум одно из которых движется, имеет соответствующий привод, органы управления и энергетические узлы, соединенные вместе для определенного применения, например для обработки, переработки, производства, транспортирования или упаковки материалов.
Термины «машина» и «механизм» также распространяются на совокупность машин, которые размещаются и управляются таким образом, чтобы функционировать как единое целое.
Примечание
В приложении А приведено общее схематическое изображение машины.
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 12100-1:2007]EN
DE
FR
оборудование
оборудование
Совокупность связанных между собой частей или устройств, из которых по крайней мере одно движется, а также элементы привода, управления и энергетические узлы, которые предназначены для определенного применения, в частности для обработки, производства, перемещения или упаковки материала. К термину «оборудование» относят также машину и совокупность машин, которые так устроены и управляемы, что они функционируют как единое целое для достижения одной и той же цели.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
-
[IEV number 151-11-25 ]
оборудование
Оснащение, материалы, приспособления, устройства, механизмы, приборы, инструменты и другие принадлежности, используемые в качестве частей электрической установки или в соединении с ней.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]EN
equipment
single apparatus or set of devices or apparatuses, or the set of main devices of an installation, or all devices necessary to perform a specific task
NOTE – Examples of equipment are a power transformer, the equipment of a substation, measuring equipment.
[IEV number 151-11-25 ]
equipment
material, fittings, devices, components, appliances, fixtures, apparatus, and the like used as part of, or in connection with, the electrical equipment of machines
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
équipement, m
matériel, m
appareil unique ou ensemble de dispositifs ou appareils, ou ensemble des dispositifs principaux d'une installation, ou ensemble des dispositifs nécessaires à l'accomplissement d'une tâche particulière
NOTE – Des exemples d’équipement ou de matériel sont un transformateur de puissance, l’équipement d’une sous-station, un équipement de mesure.
[IEV number 151-11-25]Тематики
EN
- accessories
- apparatus
- appliance
- assets
- environment
- equipment
- facility
- fitment
- fixing
- gear
- H/W
- hardware
- hardware environment
- HW
- installation
- instrument
- instrumentation
- layout
- machinery
- outfit
- paraphernalia
- plant
- plant stock
- product
- provisions
- rig
- rigging
- set-up
- stock-in-trade
- tackle
- technical equipment
- technique
DE
FR
- machine
- matériel, m
- équipement, m
организационный аппарат
—
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
3.26 машины (machinery): Устройство, состоящее из соединенных между собой частей или компонентов, по крайней мере, один из которых движется, с соответствующими исполнительными механизмами, силовыми цепями и цепями управления и т.д., объединенных вместе в целях конкретного применения, в частности, для обработки, переработки, перемещения или упаковки материала (материал означает эквивалент вещества или изделия).
Термин «машины» одновременно означает совокупность машин и механизмов, которые для достижения одной и той же цели установлены и управляются таким образом, что они функционируют как единое целое.
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > machinery
-
12 Ip
- точка [место] идентификации
- степень защиты (обеспечиваемая оболочкой)
- сетевой протокол Интернета
- протокол управления передачей (в информационных технологиях)
- протокол управления передачей (в электросвязи)
- протокол управления передачей (в вычислительных сетях)
- протокол Интернета
- промежуточное давление
- поставщик информации
- показатель производительности
- обработка изображения
- начальная перестановка (в DES-алгоритме)
- межперсональный
- исходная точка
- источник информации (в видеотексных системах)
- Интернет-протокол
- Интернет протокол
- интеллектуальная собственность
- Институт нефти (США)
- включающая способность при коротком замыкании, Ip
включающая способность при коротком замыкании, Ip
-Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- выключатель автоматический
- выключатель, переключатель
EN
Интернет-протокол
Межсетевой протокол пакетной передачи, который: - работает с 32-битовыми адресами, обеспечивает адресацию и маршрутизацию пакетов в сети; - работает без установления соединения, не обеспечивает сохранение порядка следования пакетов, не гарантирует доставку пакетов.
[ ГОСТ Р 54456-2011]Тематики
- телевидение, радиовещание, видео
EN
интеллектуальная собственность
Владение чем-либо (авторскими правами, патентом, художественной разработкой), что является продуктом творческой или умственной деятельности правообладателя.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]
интеллектуальная собственность
ИС
Нематериальные активы в виде товарных знаков, знаков обслуживания, совокупности элементов оформления товара, фирменных наименований, доменных имен и авторских прав.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]
интеллектуальная собственность
Совокупность исключительных прав на результаты интеллектуальной деятельности, а также на приравненные к ним средства индивидуализации. И.с. – это собирательное понятие, охватывающее права на: результаты интеллектуальной (творческой) деятельности в области литературы, искусства, науки и техники, а также в других областях творчества; средства индивидуализации участников гражданского оборота товаров или услуг; защиту от недобросовестной конкуренции. Использование результатов интеллектуальной деятельности и средств индивидуализации, которые являются объектом исключительных прав (интеллектуальной собственности) гражданина или юридического лица, осуществляется только с согласия правообладателя на основе лицензионных и авторских договоров. См. также Промышленная собственность.
[ http://slovar-lopatnikov.ru/]EN
intellectual property (IP)
Intangible assets such as trademarks, service marks, trade dress, trade names, domain names and copyrights.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]Тематики
Синонимы
- ИС
EN
интернет-протокол
Протокол сетевого уровня из стека TCP/IP для сетевой связи без установления соединения. Протокол обеспечивает адресацию, указание типа обслуживания пакетов ToS (type-of-service), фрагментацию, сборку и защиту передачи. Определен в RFC 791 (МСЭ-Т T.808, RFC 791).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]
интернет-протокол
Стандартный протокол, определяющий дейтаграмму, которая обеспечивает базу для доставки пакетов без установления соединения.
[ ГОСТ Р 54325-2011 (IEC/TS 61850-2:2003)]Тематики
- релейная защита
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
источник информации (в видеотексных системах)
—
[Е.С.Алексеев, А.А.Мячев. Англо-русский толковый словарь по системотехнике ЭВМ. Москва 1993]Тематики
EN
источник информации (в видеотексных системах)
—
[Е.С.Алексеев, А.А.Мячев. Англо-русский толковый словарь по системотехнике ЭВМ. Москва 1993]Тематики
EN
межперсональный
(МСЭ-Т F.400/ Х.400).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
начальная перестановка (в DES-алгоритме)
НП
—
[[http://www.rfcmd.ru/glossword/1.8/index.php?a=index&d=23]]Тематики
Синонимы
- НП
EN
обработка изображения
Процесс создания, редактирования и хранения изображений с помощью компьютера.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]Тематики
EN
показатель производительности
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
поставщик информации
контент-провайдер
Организация, служба или частное лицо, оказывающие различного рода информационные услуги, например, осуществляющие информационное наполнение веб-сайтов, выступающие в качестве источника информации общего пользования (сводки погоды и т.п.) или предоставляющие специального вида данные (о ближайшей аптеке, заторах дорожного движения) в сетях мобильной связи.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
промежуточное давление
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
протокол Интернета
Протокол сетевого уровня из стека TCP/IP для сетевой связи без установления соединения. Протокол обеспечивает адресацию, указание типа обслуживания пакетов ToS (type-of-service), фрагментацию, сборку и защиту передачи. Определен в RFC 791.
[ http://www.lexikon.ru/sputnik.html]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
протокол управления передачей
протокол Internet
Известен также как стек протоколов Internet (Internet Protocol Suite). Данный стек протоколов используется в семействе сетей Internet и для объединения гетерогенных сетей. Стек протоколов TCP/IP был разработан в ARPA как часть операционной системы UNIX, а впоследствии был адаптирован в качестве сетевого стандарта для различных сред.
[ http://www.lexikon.ru/dict/net/index.html]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
протокол управления передачей
межсетевой протокол
Платформонезависимый набор протоколов для коммуникации в глобальных вычислительных сетях.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
протокол управления передачей
протокол интернета
стек TCP/IP
межсетевой протокол
IP
Сетевые протоколы, обеспечивающие взаимодействие в межсоединенных подсетях (включая Интернет и интранет), состоящих из компьютеров с различной архитектурой и разными операционными системами.
(МСЭ-Т J.280).
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
Синонимы
- IP
- межсетевой протокол
- протокол интернета
- стек TCP/IP
EN
сетевой протокол Интернета
Основной сетевой протокол (L3) интернет-сетей, обеспечивающий адресацию узлов сети и маршрутизацию пакетов к адресату.
Основной протокол, обеспечивающий коммуникации в Internet. IP-адрес представляет собой цифровой адрес, состоящий из четырех чисел, разделенных точками. Каждый IP-адрес однозначно определяет компьютер в сети Internet. Для более легкого доступа к компьютеру обычно используют его доменное имя [http://www.webxpert.ru/slovar.html].
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]Тематики
EN
точка [место] идентификации
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
степень защиты
Способ защиты, обеспечиваемый оболочкой от доступа к опасным частям, попадания внешних твердых предметов и (или) воды и проверяемый стандартными методами испытаний.
[ ГОСТ 14254-96( МЭК 529-89)]
степень защиты, обеспечиваемая оболочкой (IP)
Числовые обозначения после кода IP, которые в соответствии с МЭК 60529 [12] характеризуют оболочку электрооборудования, обеспечивающую:
- защиту персонала от прикасания или доступа к находящимся под напряжением или движущимся частям (за исключением гладких вращающихся валов и т.п.), расположенным внутри оболочки;
- защиту электрооборудования от проникания в него твердых посторонних тел и,
- если указано в обозначении, защиту электрооборудования от вредного проникания воды.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-426-2006]EN
degree of protection of enclosure
IP (abbreviation)
numerical classification according to IEC 60529 preceded by the symbol IP applied to the enclosure of electrical apparatus to provide:
– protection of persons against contact with, or approach to, live parts and against contact with moving parts (other than smooth rotating shafts and the like) inside the enclosure,
– protection of the electrical apparatus against ingress of solid foreign objects, and
– where indicated by the classification, protection of the electrical apparatus against harmful ingress of water
[IEV number 426-04-02 ]FR
degré de protection procuré par une enveloppe
IP (abréviation)
classification numérique selon la CEI 60529, précédée du symbole IP, appliquée à une enveloppe de matériel électrique pour apporter:
– une protection des personnes contre tout contact ou proximité avec des parties actives et contre tout contact avec une pièce mobile (autre que les roulements en faible rotation) à l'intérieur d'une enveloppe
– une protection du matériel électrique contre la pénétration de corps solide étrangers, et
– selon l’indication donnée par la classification, une protection du matériel électrique contre la pénétration dangereuse de l’eau
[IEV number 426-04-02 ]Элементы кода IP и их обозначения по ГОСТ 14254-96( МЭК 529-89)
Цифры кода IP
Значение для защиты оборудования от проникновения внешних твердых предметов
Значение для защиты людей от доступа к опасным частям
Первая характеристическая цифра
0
Нет защиты
Нет защиты
1
диаметром ≥ 50 мм
тыльной стороной руки
2
диаметром ≥ 12,5 мм
пальцем
3
диаметром ≥ 2,5 мм
инструментом
4
диаметром ≥ 1,0 мм
проволокой
5
пылезащищенное
проволокой
6
пыленепроницаемое
проволокой
От вредного воздействия в результате проникновения воды
Вторая характеристическая цифра
0
Нет защиты
-
1
Вертикальное каплепадение
2
Каплепадение (номинальный угол 15°)
3
Дождевание
4
Сплошное обрызгивание
5
Действие струи
6
Сильное действие струи
7
Временное непродолжительное погружение
8
Длительное погружение
Дополнительная буква (при необходимости)
-
От доступа к опасным частям
A
тыльной стороной руки
B
пальцем
C
инструментом
проволокой
Вспомогательная буква (при необходимости)
Вспомогательная информация относящаяся к:
-
H
высоковольтным аппаратам
M
состоянию движения во время испытаний защиты от воды
S
состоянию неподвижности во время испытаний защиты от воды
W
Требования в части стойкости оболочек и электрооборудования в целом к климатическим, механическим внешним воздействующим факторам (ВВФ) и специальным средам (кроме проникновения внешних твердых предметов и воды) установлены вне рамок настоящего стандарта.
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
The code IP indicates the degrees of protection provided by an enclosure against access to hazardous parts, ingress of solid foreign objects and ingress of water.
The degree of protection of an enclosure is identified, in compliance with the specifications of the Standard IEC 60529, by the code letters IP (International Protection) followed by two numerals and two additional letters.
The first characteristic numeral indicates the degree of protection against ingress of solid foreign objects and against contact of persons with hazardous live parts inside the enclosure.
The second characteristic numeral indicates the degree of protection against ingress of water with harmful effects.
[ABB]Код IP обозначает степень защиты, обеспечиваемую оболочкой от попадания внутрь твердых посторонних предметов и воды.
Степень защиты оболочки обозначается в соответствии со стандартом МЭК 60529 буквенным обозначением IP (International Protection, т. е. Международная защита) после которого следуют две цифры, к которым в некоторых случаях добавляются еще две буквы.
Первая характеристическая цифра обозначает степень защиты от проникновения твердых посторонних предметов и от контакта людей с находящимися внутри оболочки опасными токоведущими частями.
Вторая характеристическая цифра обозначает степень защиты оболочки с точки зрения вредного воздействия, оказываемого проникновением воды.
[Перевод Интент]The protection of enclosures against ingress of dirt or against the ingress of water is defined in IEC529 (BSEN60529:1991). Conversely, an enclosure which protects equipment against ingress of particles will also protect a person from potential hazards within that enclosure, and this degree of protection is also defined as a standard.
The degrees of protection are most commonly expressed as ‘IP’ followed by two numbers, e.g. IP65, where the numbers define the degree of protection. The first digit shows the extent to which the equipment is protected against particles, or to which persons are protected from enclosed hazards. The second digit indicates the extent of protection against water.
The wording in the table is not exactly as used in the standards document, but the dimensions are accurateIP Degree of Protection according to EN/IEC 60529
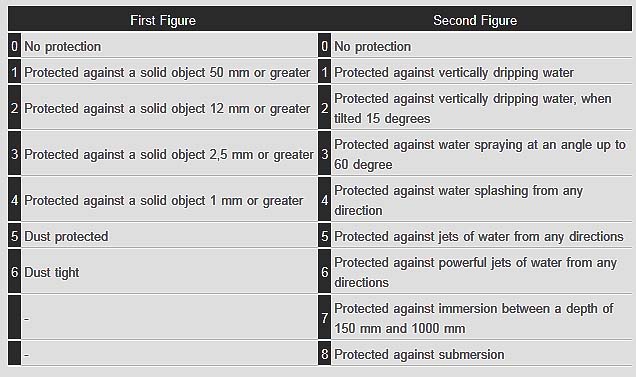
Correlations between IP (IEC) and NEMA 250 standards
IP10 -> NEMA 1
IP11 -> NEMA 2
IP54 -> NEMA 3 R
IP52 -> NEMA 5-12-12 K
IP54 -> NEMA 3-3 S
IP56 -> NEMA 4-4 X
IP67 -> NEMA 6-6 P[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/ip-protection-degree-iec-60529-explained]
Тематики
- безопасность машин и труда в целом
- электробезопасность
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- степень защиты
- степень защиты, обеспечиваемая оболочкой
- степень защиты, обеспечиваемая оболочкой (код IP)
EN
- amount of protection
- degree of protection IP
- degree of protection of an enclosure
- degree of protection of enclosure
- degree of protection provided by enclosure
- enclosure rating
- ingress protection rating
- IP
- IP degree of protection,
- IP rating
- IP Sealing Specification
- IP security
- IPSec
- level of protection
- mechanical rating
- protection
- protection index
- protection rating
DE
- IP-Schutzgrad, m
- Schutzart des Gehäuses, f
FR
3.1.12 Интернет протокол (Internet Protocol; IP): Межсетевой протокол пакетной передачи, работает с 32 битовыми адресами, обеспечивает адресацию и маршрутизацию пакетов в сети; работает без установления соединения, не обеспечивает сохранение порядка следования пакетов, не гарантирует доставку пакетов.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53531-2009: Телевидение вещательное цифровое. Требования к защите информации от несанкционированного доступа в сетях кабельного и наземного телевизионного вещания. Основные параметры. Технические требования оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Ip
-
13 Глава 4. Клич охотника в бумажных джунглях
...А сверху в гамаке висит администратор,задумчиво сплетая пальцы ног.М. ЩербаковМы все время предупреждаем: изучайте наш предмет, но используйте приобретенные знания осторожно. В официальной обстановке можно сильно вляпаться. На работе, например, говорить так же свободно, как дома или в баре, не принято. Планка дозволенного там искусственно завышена. Называть вещи своими именами (а как тут не выругаешься!) нельзя. Отсюда проистекает целая система эвфемизмов, часто называемая офисным жаргоном.Отчасти те же корни - у жаргона политического, но там еще много всяких наслоений.Главная особенность официальной речи во всех странах состоит в том, что любую гадость называют вполне приличным словом, да еще и оптимистично звучащим. Бессмертный классик Джордж Оруэлл определил это абсолютно всем в англоязычном мире известным термином doublespeak (помните - "война - это мир", ит.п.). С другой стороны, некоторые совершенно нормальные слова недопустимы и являются офисными табу (прямо как у диких племен).Вот в качестве экзотического образца слова, которые не рекомендуется произносить, а тем более писать (слышали от эксперта, работающего неподалеку от места, где Милошевича судят - сказать точнее не имеем права): invalidity (несостоятельность); infringement of rights (нарушение прав); violates a patent (нарушение патента). Догадались почему? Это вам потом в случае суда по патентным делам легко могут припомнить. Мол, сам же говорил...Впрочем, пример не совсем чист: он связан не просто с официальной речью, а с юридическим английским. Это та еще песня, в любой стране. Поди разберись! Приводимый ниже отрывок объясняет, почему американцам приходится нанимать юристов для урегулирования, казалось бы, пустяковых дел. Создана ли эта запутанность юристами специально? Ответить не можем. Вот вам определение слова "задница" из настоящего подзаконного акта, запрещающего нудизм (anti-nudity ordinance) (Действует в районе Санкт-Августин (St. Augustin, Fla. County) во Флориде (источник — A. and T. Condon. Legal Lunacy. — Putnam, N.Y. 1992)):"Buttocks: The area to the rear of the human body (sometimes referred to as the gluteus maximus) which lies between two imaginary lines running parallel to the ground when a person is standing, the first or top of such line being one- half inch below the top of the vertical cleavage of the nates (i.e., the prominance formed by the muscles running from the back of the hip to the back of the leg) and the second or bottom line being one-half inch above the lowest point of the curvature of the fleshy protuberance (sometimes referred to as the gluteal fold), and between two imaginary lines, one on each side of the body (the `outside lines'), which outside lines are perpendicular to the ground and to the horizontal lines described above and which perpendicular outside lines pass through the outermost point(s) at which each nate meets the outer side of the leg...." Не напоминает некоторые справочники?В принципе, лексикон офисного сленга делится на две группы - buzzwords (клише) и слова, проходящие по ведомству PC (political correctness). Последние используют, чтобы застраховаться от судебных исков за воображаемые обиды на расовой, религиозной, половой, возрастной и какой угодно другой (лишь бы юрист пробивной попался) основе. В качестве незаменимого пособия рекомендуем (лучше в оригинале!) книги Скотта Адамса (Scott Adams) про Дилберта. Он, например, детально поясняет, почему надо говорить resources (ресурсы), когда вы ведете речь о болванах (dolts), составляющих ваш коллектив (team members). Или с какой целью произносится associate (партнер), когда вы имеете в виду неумеху (pud) и неудачника (loser), с которым приходится работать. Очень циничный автор, но его серии карикатур многие обитатели cubicles (офисных кабинок) держат у себя на стенах. Это - мелкая фронда, безопасная, так как ни один начальник не признает, что это именно его Адамс изобразил.Картинок из Адамса мы без его разрешения приводить не будем, но пример настенного офисного юмора дадим (см. рис. (Итак, американцы шутят. Думаете, это что? Поздравление с днем рождения от товарищей по работе. Типичный поздравительный плакат из тех, что вывешиваются в офисе. Шутить со смертью — старая европейская традиция, отсюда и колядки, и Хэллоуин)).Buzzwords не сложны, вот несколько типичных, которые вы легко переведете сами (так лучше запомнится!). Собрание обязано иметь mission или purpose. Руководство должно обеспечивать leadership и motivation. Служащим следует быть proactive. Везде надо искать synergy. Естественная речь и мотивировки выглядят unprofessional. Цель работника - career advancement. В коллективе требуется исполнять роль team player и стремиться вырасти до team leader. Teamwork - непременное требование к служащим. Business as usual - почему-то всегда плохо, даже если этот бизнес приносит хороший и постоянный доход. Никогда не позволяйте, чтобы на людях вырвалось простецкое duh! Если вы не понимаете, почему diversity - это всегда сама по себе ценность, вас надо послать на diversity sensitivity training. На работе вы осуществляете total quality management и reengineering, проявляя self-motivation. Вы регулярно составляете status reports. То, о чем вы, как и все, мечтаете - job security (но в природе этого не существует).Еще несколько полезных ходовых офисных слов переведем:family = team (семья = команда - так называют родной коллектив); stakeholders (акционеры); stewardship (обслуживание, в каком-то смысле даже служение); leverage (рычаг, средство для достижения цели); solutions (решения: "we sell solutions" означает примерно - мы продаем не сосискоделательную машину, а комплексное решение всех ваших сосисочных проблем); revisit (пересмотреть), 24/7 (круглосуточно, без остановки); benchmark (лучший образец в данной области; benchmarking - сравнение с этим образцом); result-driven (ориентированный на результат); empower (передать полномочия), mindset (отношение); ballpark (ориентировочный: ballpark figure - примерная цифра).В мире мудрых мыслей (Скотта Адамса):Уолли: Stupidity is like nuclear power; it can be used for good or evil. (Глупость - как ядерная энергия, ее можно употребить и в добро, и во зло.)Дилберт: And you don't want to get any on you. (И вам совсем не надо, чтобы ее на вас испытывали.)А вот примеры клишированных мотивационных фраз и лозунгов, заимствованных нами из реальной жизни (слышали их неоднократно). При этих звуках у нормального американского служащего сама собой немедленно складывается фига в кармане (это мы на русский с их языка жестов переводим, на самом деле американцы складывают "middle finger").• Work smarter, not harder (так они говорят, когда предлагается объем работы, который не то что за 8, а и за 10 часов не сделать).• It's a new paradigm (американские менеджеры любят слово "парадигма" особой любовью - они его новым смыслом наполнили, лучше всего определяемым словом bullshit).• It's an opportunity, not a problem (ну, уволили тебя - значит, открываются горизонты новой карьеры, например, в Макдоналдсе).• You're a valued member of the team! (Ну, да...).• Nobody can do the things you can do! (Кто же, если не ты...).• You are helping make the world a better place! (Поэтому торг о зарплате здесь неуместен).• We are in a competitive business. (Так что затяните пояса и не нойте).• We make a difference! (Страшно распространенное выражение. Почему-то всегда подразумевается, что все изменения к лучшему. Нас всегда подмывает при виде этой фразы подрисовать физиономию аятоллы Хомейни).Усвоив и осмыслив приведенные выше выражения, вы сможете легко составлять собственные девизы. Вот, для примера, наш лозунг для американского офиса: Our mission is unprofessional proactive synergy! (В переводе на неофисный русский: "Сговоримся и подсидим коллегу!")Коротенький комментарий, связанный с переменами, синергизмом и названиями компаний.В мире мудрых мыслей (Скотта Адамса):Когда компании сливаются, они всегда заявляют о гигантском синергизме (leveraging synergy), причем взаимоусиление достигается всегда одним путем - массовыми увольнениями. Вот примеры возможных слияний, с соответствующим синергическим изменением профиля и названий:◦ Coca-Cola (напитки) + Head (спортивные товары) = Coke Head.◦ Bayer (аспирин) + AST (компьютеры) = Bayer AST.◦ Hertz (прокат машин) + A.B.Dick (оборудование офисов) = Hertz Dick.Переведите сами, используя наш словарь, какой смысл, на слух, имеют "синергические" названия.Шутка, но так и на практике бывает. Вот в Сиэтле давным-давно слились газеты "Seattle Post" и "Seattle Intelligencer". И знаете, как сейчас называется их главная городская газета? "Seattle Post-Inteligencer", что звучит как "Сиэтл после разума", выживший из ума, значит. Но настолько примелькалось, что не замечается.Еще несколько примеров штампованных офисных фраз. Больше половины - из свежей коллекции Кена Патрика (Ken Patrick). Он назвал это "Biz-Speak 101", то есть начальный курс деловой речи. Эти выражения сейчас в ходу ВСЕ. Не будем навязывать своих циничных комментариев. Да, bullshit. Нужно просто выучить и пользоваться.• World class (мирового уровня).• Think outside the box; Push the envelope (призыв к оригинальному мышлению).• Hands-on (непосредственно вовлеченный в дело).• Paradigm shift (смена критериев, приоритетов).• State of the art (современного уровня).• Real world solution (реальное решение).• Win-win situation (все в выигрыше).• (The ball is) In your court (ваша очередь).• Going forward (в будущем).• Strategic alliance (стратегический союз - например, меча и орала - тьфу, сорвалась рука, обещали же не острить).• Bricks and mortar (производящие, промышленные компании - в отличие от интернетных, которые после массового краха прозвали internet bubbles - интернетные пузыри).• Value-added (добавочная ценность продукта).• Step up to the plate (начать работать над чем-то).• Run up to the pole (попробовать).• Get to the bottom line (деньги, стоимость чего-то).• Stop the bleeding (сокращать расходы).• On the bubble (что-то нехорошее происходит, например, с компанией, "жареным запахло").• Best and brightest (лучшие служащие).• Exceeding customer expectation (больше, чем ждет потребитель).• On the same page (все друг друга понимают).• Strategic fit (важное дополнение).• Core competencies (основная область деятельности компании).• Best practice (соответствует лучшим стандартам).• Out of the loop (не в курсе).• Fast track (скоростное продвижение).• Knowledge base (базирующийся на современной технологии).• In the end of the day (в конце концов).• Touch base (обсудить).• Client focused (ориентированный на потребителя).• Game plan (стратегия).А теперь - самостоятельные упражнения.1. Переведите на нормальный язык: "Going forward, let's think outside the box and run it up the pole".2. Определите, к какому из вышеприведенных выражений подходит используемый тем же К. Патриком термин brownnosers (последнее слово есть в нашем словаре).Официальный сленг и административные клише хорошо освоены сметливыми проходимцами, которые, естественно, стараются, чтобы их пирамиды выглядели так же солидно, как пирамида Хеопса. Сколько приходит по почте мусора (junk mail), похожего на вид на официальные документы! Дело дошло до того, что Почтовое ведомство США (U.S.Postal Service) издало специальную памятку со списком слов-приманок (buzz phrases), характерных для жуликов, заманивающих свои жертвы (suckers) через газетные объявления и по почте.• Anybody can do it (это может каждый).• Quick and easy (быстро и легко).• Big, fast profits (большая, быстрая прибыль).• No experience needed (опыта не требуется).• Work in the comfort of your home (работа с комфортом у себя дома).• Work in your spare time (работа в свободное время).• No risk (никакого риска).• Fill a great demand (соответствует большому спросу).• Nothing illegal (ничего противозаконного).• Secret plan for success (секретный план успеха).• Tested in Europe (испытано в Европе).• Developed after years of secret research (создано в результате многолетних секретных исследований).• Proven to provide immediate positive results (проверенный способ получения немедленного положительного результата).Теперь вы официально предупреждены: если видите подобную фразу - весьма вероятно, что вас хотят надуть. Отечественные "бизнесмены" все это перенимают в последние годы очень быстро, и со многими обсуждаемыми терминами наш читатель наверняка уже встречался.Реальный пример американского почтового жульничества представлен на рис.
(Итак, американцы шутят. Думаете, это что? Поздравление с днем рождения от товарищей по работе. Типичный поздравительный плакат из тех, что вывешиваются в офисе. Шутить со смертью — старая европейская традиция, отсюда и колядки, и Хэллоуин)).Buzzwords не сложны, вот несколько типичных, которые вы легко переведете сами (так лучше запомнится!). Собрание обязано иметь mission или purpose. Руководство должно обеспечивать leadership и motivation. Служащим следует быть proactive. Везде надо искать synergy. Естественная речь и мотивировки выглядят unprofessional. Цель работника - career advancement. В коллективе требуется исполнять роль team player и стремиться вырасти до team leader. Teamwork - непременное требование к служащим. Business as usual - почему-то всегда плохо, даже если этот бизнес приносит хороший и постоянный доход. Никогда не позволяйте, чтобы на людях вырвалось простецкое duh! Если вы не понимаете, почему diversity - это всегда сама по себе ценность, вас надо послать на diversity sensitivity training. На работе вы осуществляете total quality management и reengineering, проявляя self-motivation. Вы регулярно составляете status reports. То, о чем вы, как и все, мечтаете - job security (но в природе этого не существует).Еще несколько полезных ходовых офисных слов переведем:family = team (семья = команда - так называют родной коллектив); stakeholders (акционеры); stewardship (обслуживание, в каком-то смысле даже служение); leverage (рычаг, средство для достижения цели); solutions (решения: "we sell solutions" означает примерно - мы продаем не сосискоделательную машину, а комплексное решение всех ваших сосисочных проблем); revisit (пересмотреть), 24/7 (круглосуточно, без остановки); benchmark (лучший образец в данной области; benchmarking - сравнение с этим образцом); result-driven (ориентированный на результат); empower (передать полномочия), mindset (отношение); ballpark (ориентировочный: ballpark figure - примерная цифра).В мире мудрых мыслей (Скотта Адамса):Уолли: Stupidity is like nuclear power; it can be used for good or evil. (Глупость - как ядерная энергия, ее можно употребить и в добро, и во зло.)Дилберт: And you don't want to get any on you. (И вам совсем не надо, чтобы ее на вас испытывали.)А вот примеры клишированных мотивационных фраз и лозунгов, заимствованных нами из реальной жизни (слышали их неоднократно). При этих звуках у нормального американского служащего сама собой немедленно складывается фига в кармане (это мы на русский с их языка жестов переводим, на самом деле американцы складывают "middle finger").• Work smarter, not harder (так они говорят, когда предлагается объем работы, который не то что за 8, а и за 10 часов не сделать).• It's a new paradigm (американские менеджеры любят слово "парадигма" особой любовью - они его новым смыслом наполнили, лучше всего определяемым словом bullshit).• It's an opportunity, not a problem (ну, уволили тебя - значит, открываются горизонты новой карьеры, например, в Макдоналдсе).• You're a valued member of the team! (Ну, да...).• Nobody can do the things you can do! (Кто же, если не ты...).• You are helping make the world a better place! (Поэтому торг о зарплате здесь неуместен).• We are in a competitive business. (Так что затяните пояса и не нойте).• We make a difference! (Страшно распространенное выражение. Почему-то всегда подразумевается, что все изменения к лучшему. Нас всегда подмывает при виде этой фразы подрисовать физиономию аятоллы Хомейни).Усвоив и осмыслив приведенные выше выражения, вы сможете легко составлять собственные девизы. Вот, для примера, наш лозунг для американского офиса: Our mission is unprofessional proactive synergy! (В переводе на неофисный русский: "Сговоримся и подсидим коллегу!")Коротенький комментарий, связанный с переменами, синергизмом и названиями компаний.В мире мудрых мыслей (Скотта Адамса):Когда компании сливаются, они всегда заявляют о гигантском синергизме (leveraging synergy), причем взаимоусиление достигается всегда одним путем - массовыми увольнениями. Вот примеры возможных слияний, с соответствующим синергическим изменением профиля и названий:◦ Coca-Cola (напитки) + Head (спортивные товары) = Coke Head.◦ Bayer (аспирин) + AST (компьютеры) = Bayer AST.◦ Hertz (прокат машин) + A.B.Dick (оборудование офисов) = Hertz Dick.Переведите сами, используя наш словарь, какой смысл, на слух, имеют "синергические" названия.Шутка, но так и на практике бывает. Вот в Сиэтле давным-давно слились газеты "Seattle Post" и "Seattle Intelligencer". И знаете, как сейчас называется их главная городская газета? "Seattle Post-Inteligencer", что звучит как "Сиэтл после разума", выживший из ума, значит. Но настолько примелькалось, что не замечается.Еще несколько примеров штампованных офисных фраз. Больше половины - из свежей коллекции Кена Патрика (Ken Patrick). Он назвал это "Biz-Speak 101", то есть начальный курс деловой речи. Эти выражения сейчас в ходу ВСЕ. Не будем навязывать своих циничных комментариев. Да, bullshit. Нужно просто выучить и пользоваться.• World class (мирового уровня).• Think outside the box; Push the envelope (призыв к оригинальному мышлению).• Hands-on (непосредственно вовлеченный в дело).• Paradigm shift (смена критериев, приоритетов).• State of the art (современного уровня).• Real world solution (реальное решение).• Win-win situation (все в выигрыше).• (The ball is) In your court (ваша очередь).• Going forward (в будущем).• Strategic alliance (стратегический союз - например, меча и орала - тьфу, сорвалась рука, обещали же не острить).• Bricks and mortar (производящие, промышленные компании - в отличие от интернетных, которые после массового краха прозвали internet bubbles - интернетные пузыри).• Value-added (добавочная ценность продукта).• Step up to the plate (начать работать над чем-то).• Run up to the pole (попробовать).• Get to the bottom line (деньги, стоимость чего-то).• Stop the bleeding (сокращать расходы).• On the bubble (что-то нехорошее происходит, например, с компанией, "жареным запахло").• Best and brightest (лучшие служащие).• Exceeding customer expectation (больше, чем ждет потребитель).• On the same page (все друг друга понимают).• Strategic fit (важное дополнение).• Core competencies (основная область деятельности компании).• Best practice (соответствует лучшим стандартам).• Out of the loop (не в курсе).• Fast track (скоростное продвижение).• Knowledge base (базирующийся на современной технологии).• In the end of the day (в конце концов).• Touch base (обсудить).• Client focused (ориентированный на потребителя).• Game plan (стратегия).А теперь - самостоятельные упражнения.1. Переведите на нормальный язык: "Going forward, let's think outside the box and run it up the pole".2. Определите, к какому из вышеприведенных выражений подходит используемый тем же К. Патриком термин brownnosers (последнее слово есть в нашем словаре).Официальный сленг и административные клише хорошо освоены сметливыми проходимцами, которые, естественно, стараются, чтобы их пирамиды выглядели так же солидно, как пирамида Хеопса. Сколько приходит по почте мусора (junk mail), похожего на вид на официальные документы! Дело дошло до того, что Почтовое ведомство США (U.S.Postal Service) издало специальную памятку со списком слов-приманок (buzz phrases), характерных для жуликов, заманивающих свои жертвы (suckers) через газетные объявления и по почте.• Anybody can do it (это может каждый).• Quick and easy (быстро и легко).• Big, fast profits (большая, быстрая прибыль).• No experience needed (опыта не требуется).• Work in the comfort of your home (работа с комфортом у себя дома).• Work in your spare time (работа в свободное время).• No risk (никакого риска).• Fill a great demand (соответствует большому спросу).• Nothing illegal (ничего противозаконного).• Secret plan for success (секретный план успеха).• Tested in Europe (испытано в Европе).• Developed after years of secret research (создано в результате многолетних секретных исследований).• Proven to provide immediate positive results (проверенный способ получения немедленного положительного результата).Теперь вы официально предупреждены: если видите подобную фразу - весьма вероятно, что вас хотят надуть. Отечественные "бизнесмены" все это перенимают в последние годы очень быстро, и со многими обсуждаемыми терминами наш читатель наверняка уже встречался.Реальный пример американского почтового жульничества представлен на рис. ("Витамин О", отсутствующий в природе (но не все покупатели об этом знают)). Рекламируемый "Витамин О" (проверьте - такого нет ни в одном медицинском справочнике) - всего-навсего разбавленная перекись водорода (по $25 за маленькую бутылочку!).PC-терминология связана с борьбой политических лоббистов, и приоритеты там часто меняются. В принципе, стандартного английского, в плане чисто языковом, чтобы никого не обидеть вам хватит. Думается, сейчас русскому читателю уже не требуется объяснять, что надо говорить African-American и Chairperson. В этом плане вам всегда сделают скидку как приезжему. Вас ведь тоже будут бояться обидеть. Проблема скорее может быть в другом - в характерном для жителей России восприятии действительности, в системе ценностей, которая в цивилизованной части англоязычного мира несколько иная. То, что у нас нормально и даже смешно, там зачастую оскорбление. И наоборот (см. рис.
("Витамин О", отсутствующий в природе (но не все покупатели об этом знают)). Рекламируемый "Витамин О" (проверьте - такого нет ни в одном медицинском справочнике) - всего-навсего разбавленная перекись водорода (по $25 за маленькую бутылочку!).PC-терминология связана с борьбой политических лоббистов, и приоритеты там часто меняются. В принципе, стандартного английского, в плане чисто языковом, чтобы никого не обидеть вам хватит. Думается, сейчас русскому читателю уже не требуется объяснять, что надо говорить African-American и Chairperson. В этом плане вам всегда сделают скидку как приезжему. Вас ведь тоже будут бояться обидеть. Проблема скорее может быть в другом - в характерном для жителей России восприятии действительности, в системе ценностей, которая в цивилизованной части англоязычного мира несколько иная. То, что у нас нормально и даже смешно, там зачастую оскорбление. И наоборот (см. рис. (Итак, американцы шутят. Думаете, это что? Поздравление с днем рождения от товарищей по работе. Типичный поздравительный плакат из тех, что вывешиваются в офисе. Шутить со смертью — старая европейская традиция, отсюда и колядки, и Хэллоуин)). Но это не тема для книги про язык. Обещаем - мы еще напишем другую, под названием "Политическая проституция. Учебное пособие с упражнениями". А пока дадим лишь несколько примеров распространенных PC-выражений. Многие из них сейчас и на русском очень узнаваемы (прямое, неполиткорректное значение дано в скобках).• Pregnancy termination - прерывание беременности (аборт).• Non-discriminating sexual orientation - недифференцированной сексуальной ориентации (бисексуал).• Affirmative action - позитивные защитные действия (расовые квоты).• Native American - урожденный американец (индеец).• Conscientious objector - возражающий против призыва по соображениям совести (дезертир).• Pro-choice - за выбор (сторонник абортов).• Pro-life - за жизнь (противник абортов).• African-American - афро-американец (негр). От места рождения не зависит. Например, среди наших хороших знакомых есть афро-американцы - уроженцы Теннеси, Тринидада и Голландии, а вот уроженец Уганды, коричневый беженец времен Иди Амина, в эту категорию не попадет.• Caucasian - представитель европейской расы (белый). Да, в Америке и мы с вами называемся кавказцами и рассматриваемся как потомки рабовладельцев, в качестве которых всем должны. Насчет нашего происхождения из крепостных крестьян там не знают, а объясняешь - не верят.• Non-traditional partners (sexual orientation) - нетрадиционные партнерство, сексуальная ориентация (геи и лесбиянки).• Secular humanist - нерелигиозный гуманист (атеист).• Family Planning Center - центр планирования семьи (абортарий).• Political Action Committee - комитет политического содействия (группа лоббистов).• Challenged - имеющий проблемы (инвалид). Относится к любому физическому отклонению: mentally challenged - придурки, vertically challenged - коротышки ит.п.• Minorities - меньшинства (не белые). От фактической численности не зависит: 38 миллионов латиносов в Америке тоже minorities.• Afrocentrist - афроцентрист (черный расист).• Dead white men - мертвые белые мужчины (белые расисты/сексисты - классики). Подразумевается, что, скажем, Шекспир сознательно принижал женщин - в лице Дездемоны и негров - в лице Отелло.• Animal rights movement - движение за права животных (нео-луддиты - экстремисты, пытающиеся остановить развитие биотехнологии и медицинских исследований. Это они под покровом ночи лабораторных крыс освобождают).• Multi-culturalism - мультикультурализм (идея, что культуры всех народов абсолютно равны и должны быть представлены в учебных программах в равной пропорции, скажем, столько же французской, сколько монгольской).• Sexism - сексизм (половая дискриминация). В этом нехорошем деле замешаны все мужчины, проявляющие любым образом отношение к женщине как женщине. Да и все женщины, относящиеся к мужчинам иначе, чем к своим подружкам, - тоже сексистки.• Ageism - агеизм (дискриминация по возрасту). Сюда относят любые замечания насчет старших.• Eurocentrism - евроцентризм. Предпочтение европейской цивилизации (культуры, демократии, ит.д.). Воспринимается как тяжелая болезнь.• Lookism - любые суждения о внешнем виде человека (обругать - дискриминация, похвалить - сексизм). До нас термин "смотризм" пока не дошел.• Senior Citizens - старшие граждане (старичье, пенсионеры).• Compassionate Conservatives - мягкосердечные консерваторы (реакционеры). Просто PR-специалисты для старых злобных реакционеров новую упаковку изготовили.РС - предмет постоянных насмешек американских сатириков, да и не сатириков тоже. И впрямь, богатейшее ведь поле. Довольно распространенная шутка - переписывать классические истории и песенки в политически корректном и актуальном духе. Приведем типичный образец - он простой, переведите сами как упражнение. Справа - оригинал, всем с детства известный стишок из классического собрания "Матушки Гусыни". Подчеркнуты слова, которые стоит запомнить.
(Итак, американцы шутят. Думаете, это что? Поздравление с днем рождения от товарищей по работе. Типичный поздравительный плакат из тех, что вывешиваются в офисе. Шутить со смертью — старая европейская традиция, отсюда и колядки, и Хэллоуин)). Но это не тема для книги про язык. Обещаем - мы еще напишем другую, под названием "Политическая проституция. Учебное пособие с упражнениями". А пока дадим лишь несколько примеров распространенных PC-выражений. Многие из них сейчас и на русском очень узнаваемы (прямое, неполиткорректное значение дано в скобках).• Pregnancy termination - прерывание беременности (аборт).• Non-discriminating sexual orientation - недифференцированной сексуальной ориентации (бисексуал).• Affirmative action - позитивные защитные действия (расовые квоты).• Native American - урожденный американец (индеец).• Conscientious objector - возражающий против призыва по соображениям совести (дезертир).• Pro-choice - за выбор (сторонник абортов).• Pro-life - за жизнь (противник абортов).• African-American - афро-американец (негр). От места рождения не зависит. Например, среди наших хороших знакомых есть афро-американцы - уроженцы Теннеси, Тринидада и Голландии, а вот уроженец Уганды, коричневый беженец времен Иди Амина, в эту категорию не попадет.• Caucasian - представитель европейской расы (белый). Да, в Америке и мы с вами называемся кавказцами и рассматриваемся как потомки рабовладельцев, в качестве которых всем должны. Насчет нашего происхождения из крепостных крестьян там не знают, а объясняешь - не верят.• Non-traditional partners (sexual orientation) - нетрадиционные партнерство, сексуальная ориентация (геи и лесбиянки).• Secular humanist - нерелигиозный гуманист (атеист).• Family Planning Center - центр планирования семьи (абортарий).• Political Action Committee - комитет политического содействия (группа лоббистов).• Challenged - имеющий проблемы (инвалид). Относится к любому физическому отклонению: mentally challenged - придурки, vertically challenged - коротышки ит.п.• Minorities - меньшинства (не белые). От фактической численности не зависит: 38 миллионов латиносов в Америке тоже minorities.• Afrocentrist - афроцентрист (черный расист).• Dead white men - мертвые белые мужчины (белые расисты/сексисты - классики). Подразумевается, что, скажем, Шекспир сознательно принижал женщин - в лице Дездемоны и негров - в лице Отелло.• Animal rights movement - движение за права животных (нео-луддиты - экстремисты, пытающиеся остановить развитие биотехнологии и медицинских исследований. Это они под покровом ночи лабораторных крыс освобождают).• Multi-culturalism - мультикультурализм (идея, что культуры всех народов абсолютно равны и должны быть представлены в учебных программах в равной пропорции, скажем, столько же французской, сколько монгольской).• Sexism - сексизм (половая дискриминация). В этом нехорошем деле замешаны все мужчины, проявляющие любым образом отношение к женщине как женщине. Да и все женщины, относящиеся к мужчинам иначе, чем к своим подружкам, - тоже сексистки.• Ageism - агеизм (дискриминация по возрасту). Сюда относят любые замечания насчет старших.• Eurocentrism - евроцентризм. Предпочтение европейской цивилизации (культуры, демократии, ит.д.). Воспринимается как тяжелая болезнь.• Lookism - любые суждения о внешнем виде человека (обругать - дискриминация, похвалить - сексизм). До нас термин "смотризм" пока не дошел.• Senior Citizens - старшие граждане (старичье, пенсионеры).• Compassionate Conservatives - мягкосердечные консерваторы (реакционеры). Просто PR-специалисты для старых злобных реакционеров новую упаковку изготовили.РС - предмет постоянных насмешек американских сатириков, да и не сатириков тоже. И впрямь, богатейшее ведь поле. Довольно распространенная шутка - переписывать классические истории и песенки в политически корректном и актуальном духе. Приведем типичный образец - он простой, переведите сами как упражнение. Справа - оригинал, всем с детства известный стишок из классического собрания "Матушки Гусыни". Подчеркнуты слова, которые стоит запомнить. (таблица №1)Еще образчик американского самоприкола по поводу PC мы нашли на сувенирных магнитиках. Вы уже знаете про связь мата и юмора, так вот, там дан "перевод" фраз с сугубо официального языка на совершенно матерный. На кухонный холодильник такое повесить можно - но не в офис. Вот несколько примеров (на русский переводим не дословно, это вы сами легко сделаете, используя наш словарь, а подходяще по экспрессии и колориту).
(таблица №1)Еще образчик американского самоприкола по поводу PC мы нашли на сувенирных магнитиках. Вы уже знаете про связь мата и юмора, так вот, там дан "перевод" фраз с сугубо официального языка на совершенно матерный. На кухонный холодильник такое повесить можно - но не в офис. Вот несколько примеров (на русский переводим не дословно, это вы сами легко сделаете, используя наш словарь, а подходяще по экспрессии и колориту). (таблица №2)В заключение - несколько слов о специфическом партийном языке. У маргинальных политических групп он весьма оригинален. В поддержку русских коммунистов-интернационалистов (и для развлечения остальных читателей) приведем здесь подлинные левые американские мысли. Даем без комментариев и перевода цитату из "Словаря Анархиста" - брошюрки без выходных данных, подобранной нами в одном из троцкистских центров Канады. (Внимание! Опечаток тут нет, так писать у них принято, с ККК внутри и сша строчными буквами.)"Black": a political designation to refer not only to Afro-Amerikkkans, but, to people of color who are engaged in revolutionary struggle in the u.s. and all over the world. It should not be taken to mean the domination of Afro-Amerikkkans or the exclusion of other people of color from black revolutionary organizations.Black Collaborator: those few blacks brought into the capitalist system at all levels, including such high levels as black capitalist, project directors, administrators, etc., who have enough of a stake in the operation of the system to cooperate in pacification programs against their black brothers and sisters. The "House Niggers".Black Panther Party: an above ground community based armed self-defense organization whose job it was to defend the community by force of arms in "legal" posture and mode, unlike the clandestine Black Liberation Army. The Black Panther Party also served the community through community based survival programs such as free breakfast for children, free health care, liberation schools for political education, etc.Black Revolutionary Power: the taking of state power by black amerikkkans (Afro-Amerikkkans) in order to revolutionize the entire country on the basis of their enriched concept of man/woman.Bourgeoisie: the rich and the super rich. The ruling elite who own and manage the means of production, ex: Rockefeller, Mellon, Dupont, etc. They are the real rulers in a capitalist society who dictate and has everyone else eitherworking for them to maintain status-quo, or those who may slave for them in order to survive."Мы дали здесь лишь краткое представление об офисном сленге и терминологии администраторов, юристов, мошенников и политиков (как вам компания?). Хотите стать Большим администратором (юристом ит.д.) - изучайте это дело подробнее.
(таблица №2)В заключение - несколько слов о специфическом партийном языке. У маргинальных политических групп он весьма оригинален. В поддержку русских коммунистов-интернационалистов (и для развлечения остальных читателей) приведем здесь подлинные левые американские мысли. Даем без комментариев и перевода цитату из "Словаря Анархиста" - брошюрки без выходных данных, подобранной нами в одном из троцкистских центров Канады. (Внимание! Опечаток тут нет, так писать у них принято, с ККК внутри и сша строчными буквами.)"Black": a political designation to refer not only to Afro-Amerikkkans, but, to people of color who are engaged in revolutionary struggle in the u.s. and all over the world. It should not be taken to mean the domination of Afro-Amerikkkans or the exclusion of other people of color from black revolutionary organizations.Black Collaborator: those few blacks brought into the capitalist system at all levels, including such high levels as black capitalist, project directors, administrators, etc., who have enough of a stake in the operation of the system to cooperate in pacification programs against their black brothers and sisters. The "House Niggers".Black Panther Party: an above ground community based armed self-defense organization whose job it was to defend the community by force of arms in "legal" posture and mode, unlike the clandestine Black Liberation Army. The Black Panther Party also served the community through community based survival programs such as free breakfast for children, free health care, liberation schools for political education, etc.Black Revolutionary Power: the taking of state power by black amerikkkans (Afro-Amerikkkans) in order to revolutionize the entire country on the basis of their enriched concept of man/woman.Bourgeoisie: the rich and the super rich. The ruling elite who own and manage the means of production, ex: Rockefeller, Mellon, Dupont, etc. They are the real rulers in a capitalist society who dictate and has everyone else eitherworking for them to maintain status-quo, or those who may slave for them in order to survive."Мы дали здесь лишь краткое представление об офисном сленге и терминологии администраторов, юристов, мошенников и политиков (как вам компания?). Хотите стать Большим администратором (юристом ит.д.) - изучайте это дело подробнее.American slang. English-Russian dictionary > Глава 4. Клич охотника в бумажных джунглях
-
14 Bulleid, Oliver Vaughan Snell
[br]b. 19 September 1882 Invercargill, New Zealandd. 25 April 1970 Malta[br]New Zealand (naturalized British) locomotive engineer noted for original experimental work in the 1940s and 1950s.[br]Bulleid's father died in 1889 and mother and son returned to the UK from New Zealand; Bulleid himself became a premium apprentice under H.A. Ivatt at Doncaster Works, Great Northern Railway (GNR). After working in France and for the Board of Trade, Bulleid returned to the GNR in 1912 as Personal Assistant to Chief Mechanical Engineer H.N. Gresley. After a break for war service, he returned as Assistant to Gresley on the latter's appointment as Chief Mechanical Engineer of the London \& North Eastern Railway in 1923. He was closely associated with Gresley during the late 1920s and early 1930s.In 1937 Bulleid was appointed Chief Mechanical Engineer of the Southern Railway (SR). Concentration of resources on electrification had left the Southern short of up-to-date steam locomotives, which Bulleid proceeded to provide. His first design, the "Merchant Navy" class 4–6– 2, appeared in 1941 with chain-driven valve gear enclosed in an oil-bath, and other novel features. A powerful "austerity" 0−6−0 appeared in 1942, shorn of all inessentials to meet wartime conditions, and a mixed-traffic 4−6−2 in 1945. All were largely successful.Under Bulleid's supervision, three large, mixed-traffic, electric locomotives were built for the Southern's 660 volt DC system and incorporated flywheel-driven generators to overcome the problem of interruptions in the live rail. Three main-line diesel-electric locomotives were completed after nationalization of the SR in 1948. All were carried on bogies, as was Bulleid's last steam locomotive design for the SR, the "Leader" class 0−6−6−0 originally intended to meet a requirement for a large, passenger tank locomotive. The first was completed after nationalization of the SR, but the project never went beyond trials. Marginally more successful was a double-deck, electric, suburban, multiple-unit train completed in 1949, with alternate high and low compartments to increase train capacity but not length. The main disadvantage was the slow entry and exit by passengers, and the type was not perpetuated, although the prototype train ran in service until 1971.In 1951 Bulleid moved to Coras Iompair Éireann, the Irish national transport undertaking, as Chief Mechanical Engineer. There he initiated a large-scale plan for dieselization of the railway system in 1953, the first such plan in the British Isles. Simultaneously he developed, with limited success, a steam locomotive intended to burn peat briquettes: to burn peat, the only native fuel, had been a long-unfulfilled ambition of railway engineers in Ireland. Bulleid retired in 1958.[br]BibliographyBulleid took out six patents between 1941 and 1956, covering inter alia valve gear, boilers, brake apparatus and wagon underframes.Further ReadingH.A.V.Bulleid, 1977, Bulleid of the Southern, Shepperton: Ian Allan (a good biography written by the subject's son).C.Fryer, 1990, Experiments with Steam, Wellingborough: Patrick Stephens (provides details of the austerity 0–6–0, the "Leader" locomotive and the peat-burning locomotive: see Chs 19, 20 and 21 respectively).PJGRBiographical history of technology > Bulleid, Oliver Vaughan Snell
-
15 Tottenville
геогр. Тоттенвиль (район Нью-Йорка)Heading west brings us into the hood as Tottenville. It is everything between Arthur Kill, Richmond Valley Rd, Raritan Bay, and Page Ave. This hood is mostly residential. Originally, it was home to the Unami Indians until it was settled in 1678 by Christopher Billop and called it Bently after the ship he had used to come the new world. Around this time, the area was an important point for ferry service to Philadelphia. Durring the American Revolution, the Billop family had been Tories and were loyal to the British and lost their property when the war ended. In 1776, Benjamin Franklin, John Adams, and Edward Rutledge had a confrence with Admiral Lord Richard Howe to make a settlement, but it failed. Durring the 1800's factories were built here to provide jobs. In 1860, the B&O RR built a terminating station here and called it Tottenville, after the family who had lived here. Around 1900, Tottenville became known for shipbuilding, and the factories became obsolete. Houses were built in the Victorian style durring the 1920's and 1930's, though most developement came after the 1960's. For those who don't know, Tottenville is literally they southernmost point in the state of NY, though technically it's NYC. Unfortunately, this is the last of the NYC hoods, and I hope that many of you have enjoyed them when I had started them hence this will be the end. You can get here by taking the SIR to the Nassau, Atlantic, and Tottenville Stations. Here is what you will find in Tottenville. (From a forum)
Англо-русский универсальный дополнительный практический переводческий словарь И. Мостицкого > Tottenville
-
16 put on
1) (to switch on (a light etc): Put the light on!) allumer2) (to dress oneself in: Which shoes are you going to put on?) mettre3) (to add or increase: The car put on speed; I've put on weight.) prendre4) (to present or produce (a play etc): They're putting on `Hamlet' next week.) présenter5) (to provide (eg transport): They always put on extra buses between 8.00 and 9.00 a.m.) mettre en service6) (to make a false show of; to pretend: She said she felt ill, but she was just putting it on.) simuler7) (to bet (money) on: I've put a pound on that horse to win.) miser sur -
17 set
set [set]jeu ⇒ 1 (a) série ⇒ 1 (a) ensemble ⇒ 1 (a), 1 (c) cercle ⇒ 1 (b) appareil ⇒ 1 (d) poste ⇒ 1 (d) set ⇒ 1 (e) fixe ⇒ 2 (a) arrêté ⇒ 2 (b) figé ⇒ 2 (b) résolu ⇒ 2 (c) prêt ⇒ 2 (d) mettre ⇒ 3 (a), 3 (c), 3 (d) poser ⇒ 3 (a), 3 (c), 3 (e), 3 (i) situer ⇒ 3 (b) régler ⇒ 3 (c) fixer ⇒ 3 (f), 3 (i) établir ⇒ 3 (f) faire prendre ⇒ 3 (h) se coucher ⇒ 4 (a) prendre ⇒ 4 (b)1 noun(a) (of tools, keys, golf clubs, sails) jeu m; (of numbers, names, instructions, stamps, weights) série f; (of books) collection f; (of furniture) ensemble m; (of cutlery, dishes, glasses) service m; (of lingerie) parure f; (of wheels) train m; (of facts, conditions, characteristics, data) ensemble m; (of events, decisions, questions) série f, suite f; Typography (of proofs, characters) jeu m; Computing (of characters, instructions) jeu m, ensemble m;∎ a set of matching luggage un ensemble de valises assorties;∎ a set of table/bed linen une parure de table/de lit;∎ a set of sheets une parure de lit;∎ badminton/chess set jeu m de badminton/d'échecs;∎ they're playing with Damian's train set ils jouent avec le train électrique de Damian;∎ the cups/the chairs are sold in sets of six les tasses/les chaises sont vendues par six;∎ I can't break up the set je ne peux pas les dépareiller;∎ they make a set ils vont ensemble;∎ to collect the (whole) set rassembler toute la collection, faire la collection;∎ he made me a duplicate set (of keys) il m'a fait un double des clés; (of contact lenses) il m'en a fait une autre paire;∎ a full set of the encyclopedia une encyclopédie complète;∎ a full set of Tolstoy's works les œuvres complètes de Tolstoï;∎ they've detected two sets of fingerprints ils ont relevé deux séries d'empreintes digitales ou les empreintes digitales de deux personnes;∎ given another set of circumstances, things might have turned out differently dans d'autres circonstances, les choses auraient pu se passer différemment;∎ the first set of reforms la première série ou le premier train de réformes;∎ they ran a whole set of tests on me ils m'ont fait subir toute une série d'examens(b) (social group) cercle m, milieu m;∎ he's not in our set il n'appartient pas à notre cercle;∎ we don't go around in the same set nous ne fréquentons pas le même milieu ou monde;∎ the riding/yachting set le monde ou milieu de l'équitation/du yachting;∎ the literary set les milieux mpl littéraires;∎ the Markham set Markham et ses amis(c) Mathematics ensemble m∎ a colour TV set un poste de télévision ou un téléviseur couleur∎ first set to Miss Williams set Williams∎ on (the) set Cinema & Television sur le plateau; Theatre sur scène(g) (part of performance → by singer, group)∎ he'll be playing two sets tonight il va jouer à deux reprises ce soir;∎ her second set was livelier la deuxième partie de son spectacle a été plus animée(i) (for hair) mise f en plis;∎ to have a set se faire faire une mise en plis∎ I could tell he was angry by the set of his jaw rien qu'à la façon dont il serrait les mâchoires, j'ai compris qu'il était en colère(k) (direction → of wind, current) direction f;∎ suddenly the set of the wind changed le vent a tourné soudainement∎ tomato/tulip sets tomates fpl/tulipes fpl à repiquer(n) (clutch of eggs) couvée f(q) (of badger) terrier m(a) (specified, prescribed → rule, price, quantity, sum, wage) fixe;∎ meals are at set times les repas sont servis à heures fixes;∎ there are no set rules for raising children il n'y a pas de règles toutes faites pour l'éducation des enfants;∎ the tasks must be done in the set order les tâches doivent être accomplies dans l'ordre prescrit;∎ with no set purpose sans but précis∎ her day followed a set routine sa journée se déroulait selon un rituel immuable;∎ he has a set way of doing it il a sa méthode pour le faire;∎ to be set in one's ways avoir ses (petites) habitudes;∎ to become set in one's views devenir rigide dans ses opinions(c) (intent, resolute) résolu, déterminé;∎ to be set on or upon sth vouloir qch à tout prix;∎ I'm (dead) set on finishing it tonight je suis (absolument) déterminé à le finir ce soir;∎ he's dead set against it il s'y oppose formellement(d) (ready, in position) prêt;∎ are you (all) set to go? êtes-vous prêt à partir?∎ he seems well set to win il semble être sur la bonne voie ou être bien parti pour gagner;∎ house prices are set to rise steeply les prix de l'immobilier vont vraisemblablement monter en flèche∎ one of our set books is 'Oliver Twist' un des ouvrages au programme est 'Oliver Twist'(a) (put in specified place or position) mettre, poser;∎ he set his cases down on the platform il posa ses valises sur le quai;∎ she set the steaming bowl before him elle plaça le bol fumant devant lui;∎ to set a proposal before the board présenter un projet au conseil d'administration;∎ to set sb on his/her feet again remettre qn sur pied;∎ to set a match to sth mettre le feu à qch;∎ to set sb ashore débarquer qn(b) (usu passive) (locate, situate → building, story) situer;∎ the house is set in large grounds la maison est située dans un grand parc;∎ his eyes are set too close together ses yeux sont trop rapprochés;∎ the story is set in Tokyo l'histoire se passe ou se déroule à Tokyo;∎ her novels are set in the 18th century ses romans se passent au XVIIIème siècle∎ I set my watch to New York time j'ai réglé ma montre à l'heure de New York;∎ set your watches an hour ahead avancez vos montres d'une heure;∎ he's so punctual you can set your watch by him! il est si ponctuel qu'on peut régler sa montre sur lui!;∎ I've set the alarm for six j'ai mis le réveil à (sonner pour) six heures;∎ how do I set the margins? comment est-ce que je fais pour placer les marges?;∎ set the timer for one hour mettez le minuteur sur une heure;∎ first set the control knob to the desired temperature mettez tout d'abord le bouton de réglage sur la température voulue;∎ the lever was set in the off position le levier était sur "arrêt"∎ the handles are set into the drawers les poignées sont encastrées dans les tiroirs;∎ there was a peephole set in the door il y avait un judas dans la porte;∎ to set a stake in the ground enfoncer ou planter un pieu dans la terre;∎ metal bars had been set in the concrete des barres en métal avaient été fixées dans le béton;∎ the brooch was set with pearls la broche était sertie de perles;∎ the ruby was set in a simple ring le rubis était monté sur un simple anneau;∎ Medicine to set a bone réduire une fracture;∎ figurative his face was set in a frown son visage était figé dans une grimace renfrognée;∎ she set her jaw and refused to budge elle serra les dents et refusa de bouger;∎ we had set ourselves to resist nous étions déterminés à résister(e) (lay, prepare in advance → trap) poser, tendre;∎ to set the table mettre le couvert ou la table;∎ to set the table for two mettre deux couverts;∎ set an extra place at table rajoutez un couvert(f) (establish → date, price, schedule, terms) fixer, déterminer; (→ rule, guideline, objective, target) établir; (→ mood, precedent) créer;∎ they still haven't set a date for the party ils n'ont toujours pas fixé de date pour la réception;∎ you've set yourself a tough deadline or a tough deadline for yourself vous vous êtes fixé un délai très court;∎ it's up to them to set their own production targets c'est à eux d'établir ou de fixer leurs propres objectifs de production;∎ a deficit ceiling has been set un plafonnement du déficit a été imposé ou fixé ou décidé;∎ to set a value on sth décider de la valeur de qch;∎ figurative they set a high value on creativity ils accordent une grande valeur à la créativité;∎ the price was set at £500 le prix a été fixé à 500 livres;∎ the judge set bail at $1,000 le juge a fixé la caution à 1000 dollars;∎ how are exchange rates set? comment les taux de change sont-ils déterminés?;∎ to set an age limit at… fixer une limite d'âge à…;∎ to set a new fashion or trend lancer une nouvelle mode;∎ to set a new world record établir un nouveau record mondial;∎ to set the tone for or of sth donner le ton de qch∎ to set sth alight or on fire mettre le feu à qch;∎ it sets my nerves on edge ça me crispe;∎ also figurative she set me in the right direction elle m'a mis sur la bonne voie;∎ to set sb against sb monter qn contre qn;∎ he/the incident set the taxman on my trail il/l'incident a mis le fisc sur ma piste;∎ to set the dogs on sb lâcher les chiens sur qn;∎ the incident set the family against him l'incident a monté la famille contre lui;∎ it will set the country on the road to economic recovery cela va mettre le pays sur la voie de la reprise économique;∎ his failure set him thinking son échec lui a donné à réfléchir;∎ the scandal will set the whole town talking le scandale va faire jaser toute la ville;∎ to set the dog barking faire aboyer le chien;∎ the wind set the leaves dancing le vent a fait frissonner les feuilles;∎ to set a machine going mettre une machine en marche(h) (solidify → yoghurt, jelly, concrete) faire prendre;∎ pectin will help to set the jam la pectine aidera à épaissir la confiture∎ the strikers' demands set the management a difficult problem les exigences des grévistes posent un problème difficile à la direction;∎ I set them to work tidying the garden je les ai mis au désherbage du jardin;∎ I've set myself the task of writing to them regularly je me suis fixé la tâche de leur écrire régulièrement∎ she set the class a maths exercise, she set a maths exercise for the class elle a donné un exercice de maths à la classe;∎ who sets the test questions? qui choisit les questions de l'épreuve?∎ to set sb's hair faire une mise en plis à qn;∎ and I've just had my hair set! et je viens de me faire faire une mise en plis!;∎ I set my own hair je me fais moi-même mes mises en plis∎ to set type composer∎ to set sth to music mettre qch en musique(a) (sun, moon, stars) se coucher;∎ we saw the sun setting nous avons vu le coucher du soleil(b) (become firm → glue, cement, plaster, jelly, yoghurt) prendre;∎ her features had set in an expression of determination ses traits s'étaient durcis en une expression de très forte détermination∎ he set to work il s'est mis au travail(e) (plant, tree) prendre racine(g) (wind, tide)∎ the wind looks set fair to the east on dirait un vent d'ouest►► Theatre, Cinema & Television set designer décorateur(trice) m,f;Grammar set expression expression f figée;set figures (in skating) figures fpl imposées;set meal, set menu meal menu m;Grammar set phrase expression f figée;(b) (fireworks) pièce f (de feu) d'artifice(c) (of scenery) élément m de décorSport set point (in tennis) balle f de set;Technology set screw vis f de réglage;Sport set scrum (in rugby) mêlée f fermée;set square équerre f (à dessiner);set task tâche f assignée;∎ to give sb a set task to do assigner à qn une tâche bien précise;Mathematics set theory théorie f des ensembles(a) (start → task) se mettre à;∎ she set about changing the tyre elle s'est mise à changer le pneu;∎ I didn't know how to set about it je ne savais pas comment m'y prendre;∎ how does one set about getting a visa? comment fait-on pour obtenir un visa?∎ he set about the mugger with his umbrella il s'en est pris à son agresseur à coups de parapluie∎ to set sth against sth comparer qch à qch;∎ to set the benefits against the costs évaluer les bénéfices par rapport aux coûts;∎ we must set the government's promises against its achievements nous devons examiner les promesses du gouvernement à la lumière de ses actions∎ some of these expenses can be set against tax certaines de ces dépenses peuvent être déduites des impôts(c) (friends, family) monter contre;∎ religious differences have set family against family les différences religieuses ont monté les familles les unes contre les autres;∎ to set oneself or one's face against sth s'opposer résolument à qch∎ to set the clock ahead avancer l'horloge;∎ we're setting the clocks ahead tonight on change d'heure cette nuit(a) (place separately → object) mettre à part ou de côté;∎ there was one deck chair set slightly apart from the others il y avait une chaise longue un peu à l'écart des autres;∎ they set themselves apart ils faisaient bande à part∎ her talent sets her apart from the other students son talent la distingue des autres étudiants(a) (put down → knitting, book) poser;∎ could you set aside what you're working on for a while? pouvez-vous laisser ce que vous êtes en train de faire un moment?(b) (reserve, keep → time, place) réserver; (→ money) mettre de côté; (→ arable land) mettre en friche;∎ I've set tomorrow aside for house hunting j'ai réservé la journée de demain pour chercher une maison;∎ the room is set aside for meetings la pièce est réservée aux réunions;∎ can you set the book aside for me? pourriez-vous me mettre ce livre de côté?;∎ chop the onions and set them aside coupez les oignons et réservez-les(c) (overlook, disregard) mettre de côté, oublier, passer sur;∎ they set their differences aside in order to work together ils ont mis de côté leurs différences pour travailler ensemble(d) (reject → dogma, proposal, offer) rejeter∎ the building is set back slightly from the road l'immeuble est un peu en retrait par rapport à la route(b) (delay → plans, progress) retarder;∎ his illness set him back a month in his work sa maladie l'a retardé d'un mois dans son travail;∎ the news may set him or his recovery back la nouvelle risque de retarder sa guérison;∎ this decision will set the economy back ten years cette décision va faire revenir l'économie dix ans en arrière∎ the trip will set her back a bit le voyage va lui coûter cher(a) (tray, bag etc) poser∎ the bus sets you down in front of the station le bus vous dépose devant la gare(c) (note, record) noter, inscrire;∎ try and set your thoughts down on paper essayez de mettre vos pensées par écrit(d) (establish → rule, condition) établir, fixer;∎ the government has set down a margin for pay increases le gouvernement a fixé une fourchette pour les augmentations de salaire;∎ permissible levels of pollution are set down in the regulations les taux de pollution tolérés sont fixés dans les réglementations;∎ to set sth down in writing coucher qch par écrit;∎ it is clearly set down that drivers must be insured il est clairement signalé ou indiqué que tout conducteur doit être assuréformal (expound → plan, objections) exposer, présenter;∎ the recommendations are set forth in the last chapter les recommandations sont détaillées ou énumérées dans le dernier chapitreliterary partir, se mettre en route➲ set in∎ if infection sets in si la plaie s'infecte;∎ the bad weather has set in for the winter le mauvais temps s'est installé pour tout l'hiver;➲ set off(b) (reaction, process, war) déclencher, provoquer;∎ their offer set off another round of talks leur proposition a déclenché une autre série de négociations;∎ it set her off on a long tirade against bureaucracy cela eut pour effet de la lancer dans une longue tirade contre la bureaucratie;∎ to set sb off laughing faire rire qn;∎ this answer set them off (laughing) cette réponse a déclenché les rires;∎ one look at his face set me off again en le voyant, mon fou rire a repris de plus belle;∎ if you say anything it'll only set him off (crying) again si tu dis quoi que ce soit, il va se remettre à pleurer;∎ the smallest amount of pollen will set her off la moindre dose de pollen lui déclenche une réaction allergique;∎ don't mention Maradona or you'll set him off again surtout ne prononce pas le nom de Maradona sinon il va recommencer;∎ someone mentioned the war and of course that set Uncle Arthur off quelqu'un prononça le mot guerre, et évidemment, oncle Arthur embraya aussitôt sur le sujet;∎ figurative to set sb off on the wrong track mettre qn sur une fausse piste∎ the vase sets off the flowers beautifully le vase met vraiment les fleurs en valeur∎ some of these expenses can be set off against tax certaines de ces dépenses peuvent être déduites des impôtspartir, se mettre en route;∎ he set off at a run il est parti en courant;∎ I set off to explore the town je suis parti explorer la ville;∎ after lunch, we set off again après le déjeuner, nous avons repris la route➲ set on(attack) attaquer, s'en prendre à∎ to set the police on the tracks of a thief mettre la police aux trousses d'un voleur;∎ to set sb on his/her way mettre qn sur les rails∎ to set a dog on sb lâcher un chien sur qn➲ set out∎ the shopping centre is very well set out le centre commercial est très bien conçu(b) (present → ideas) exposer, présenter;∎ the information is set out in the table below ces données sont présentées dans le tableau ci-dessous∎ just as he was setting out au moment de son départ;∎ to set out for school partir pour l'école;∎ to set out again repartir;∎ to set out in pursuit/in search of sb se mettre à la poursuite/à la recherche de qn(b) (undertake course of action) entreprendre;∎ he has trouble finishing what he sets out to do il a du mal à terminer ce qu'il entreprend;∎ I can't remember now what I set out to do je ne me souviens plus de ce que je voulais faire à l'origine;∎ they all set out with the intention of changing the world au début, ils veulent tous changer le monde;∎ she didn't deliberately set out to annoy you il n'était pas dans ses intentions de vous froisser;∎ his theory sets out to prove that… sa théorie a pour objet de prouver que…(a) (begin work) commencer, s'y mettre;∎ we set to with a will nous nous y sommes mis avec ardeur(b) familiar (two people → start arguing) avoir une prise de bec; (→ start fighting) en venir aux mains➲ set up(a) (install → equipment, computer) installer; (→ roadblock) installer, disposer; (→ experiment) préparer;∎ everything's set up for the show tout est préparé ou prêt pour le spectacle;∎ set the chairs up in a circle mettez ou disposez les chaises en cercle;∎ he set the chessboard up il a disposé les pièces sur l'échiquier;∎ the equation sets up a relation between the two variables l'équation établit un rapport entre les deux variables;∎ the system wasn't set up to handle so many users le système n'était pas conçu pour gérer autant d'usagers;∎ he set the situation up so she couldn't refuse il a arrangé la situation de telle manière qu'elle ne pouvait pas refuser(b) (erect, build → tent, furniture kit, crane, flagpole) monter; (→ shed, shelter) construire; (→ monument, statue) ériger;∎ to set up camp installer ou dresser le camp(c) (start up, institute → business, scholarship) créer; (→ hospital, school) fonder; (→ committee, task force) constituer; (→ system of government, republic) instaurer; (→ programme, review process, system) mettre en place; (→ inquiry) ouvrir; (→ dinner, meeting, appointment) organiser;∎ to set up house or home s'installer;∎ they set up house together ils se sont mis en ménage;∎ to set up a dialogue entamer le dialogue;∎ you'll be in charge of setting up training programmes vous serez responsable de la mise en place des programmes de formation;∎ the medical system set up after the war le système médical mis en place après la guerre(d) (financially, in business → person) installer, établir;∎ he set his son up in a dry-cleaning business il a acheté à son fils une entreprise de nettoyage à sec;∎ she could finally set herself up as an accountant elle pourrait enfin s'installer comme comptable;∎ the money would set him up for life l'argent le mettrait à l'abri du besoin pour le restant de ses jours;∎ the army set him up as a dictator l'armée l'installa comme dictateur∎ we're well set up with supplies nous sommes bien approvisionnés;∎ she can set you up with a guide/the necessary papers elle peut vous procurer un guide/les papiers qu'il vous faut;∎ I can set you up with a girlfriend of mine je peux te présenter à ou te faire rencontrer une de mes copines(f) (restore energy to) remonter, remettre sur pied;∎ have a brandy, that'll set you up prends un cognac, ça va te remonter∎ she claims she was set up elle prétend qu'elle est victime d'un coup monté;∎ he was set up as the fall guy on a fait de lui le bouc émissaire□, il a joué le rôle de bouc émissaire□s'installer, s'établir;∎ he's setting up in the fast-food business il se lance dans la restauration rapide;(physically or verbally) attaquer, s'en prendre à -
18 Gutenberg, Johann Gensfleisch zum
SUBJECT AREA: Paper and printing[br]b. c. 1394–9 Mainz, Germanyd. 3 February 1468 Mainz, Germany[br]German inventor of printing with movable type.[br]Few biographical details are known of Johann Gensfleisch zum Gutenberg, yet it has been said that he was responsible for Germany's most notable contribution to civilization. He was a goldsmith by trade, of a patrician family of the city of Mainz. He seems to have begun experiments on printing while a political exile in Strasbourg c. 1440. He returned to Mainz between 1444 and 1448 and continued his experiments, until by 1450 he had perfected his invention sufficiently to justify raising capital for its commercial exploitation.Circumstances were propitious for the invention of printing at that time. Rises in literacy and prosperity had led to the formation of a social class with the time and resources to develop a taste for reading, and the demand for reading matter had outstripped the ability of the scribes to satisfy it. The various technologies required were well established, and finally the flourishing textile industry was producing enough waste material, rag, to make paper, the only satisfactory and cheap medium for printing. There were others working along similar lines, but it was Gutenberg who achieved the successful adaptation and combination of technologies to arrive at a process by which many identical copies of a text could be produced in a wide variety of forms, of which the book was the most important. Gutenberg did make several technical innovations, however. The two-piece adjustable mould for casting types of varying width, from T to "M", was ingenious. Then he had to devise an oil-based ink suitable for inking metal type, derived from the painting materials developed by contemporary Flemish artists. Finally, probably after many experiments, he arrived at a metal alloy of distinctive composition suitable for casting type.In 1450 Gutenberg borrowed 800 guldens from Johannes Fust, a lawyer of Mainz, and two years later Fust advanced a further 800 guldens, securing for himself a partnership in Gutenberg's business. But in 1455 Fust foreclosed and the bulk of Gutenberg's equipment passed to Peter Schöffer, who was in the service of Fust and later married his daughter. Like most early printers, Gutenberg seems not to have appreciated, or at any rate to have been able to provide for, the great dilemma of the publishing trade, namely the outlay of considerable capital in advance of each publication and the slowness of the return. Gutenberg probably retained only the type for the 42- and 36-line bibles and possibly the Catholicon of 1460, an encyclopedic work compiled in the thirteenth century and whose production pointed the way to printing's role as a means of spreading knowledge. The work concluded with a short descriptive piece, or colophon, which is probably by Gutenberg himself and is the only output of his mind that we have; it manages to omit the names of both author and printer.Gutenberg seems to have abandoned printing after 1460, perhaps due to failing eyesight as well as for financial reasons, and he suffered further loss in the sack of Mainz in 1462. He received a kind of pension from the Archbishop in 1465, and on his death was buried in the Franciscan church in Mainz. The only major work to have issued for certain from Gutenberg's workshop is the great 42-line bible, begun in 1452 and completed by August 1456. The quality of this Graaf piece of printing is a tribute to Gutenberg's ability as a printer, and the soundness of his invention is borne out by the survival of the process as he left it to the world, unchanged for over three hundred years save in minor details.[br]Further ReadingA.Ruppel, 1967, Johannes Gutenberg: sein Leben und sein Werk, 3rd edn, Nieuwkoop: B.de Graaf (the standard biography), A.M.L.de Lamartine, 1960, Gutenberg, inventeur de l'imprimerie, Tallone.Scholderer, 1963, Gutenberg, Inventor of Printing, London: British Museum.S.H.Steinberg, 1974, Five Hundred Years of Printing 3rd edn, London: Penguin (provides briefer details).LRDBiographical history of technology > Gutenberg, Johann Gensfleisch zum
-
19 Edge Transport server role
An Exchange Server 2007 and 2010 server role that provides anti-spam and antivirus protection and applies messaging security policies to messages in transport between organizations by using a series of agents that act on messages as they are processed by the message transport components. This server role is deployed in the perimeter network outside the Active Directory directory service forest. Computers that have the Edge Transport server role installed handle all Internet-facing mail flow and provide Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) relay and smart host services for the Exchange organization.English-Arabic terms dictionary > Edge Transport server role
-
20 UPS
- услуга уровня пользователя
- система надёжного электроснабжения
- одинаковый размер частиц
- источник непрерывного энергоснабжения
- источник бесперебойного питания
источник бесперебойного питания
ИБП
Сочетание преобразователей, переключателей и устройств хранения электроэнергии (например, аккумуляторных батарей), образующее систему электропитания для поддержания непрерывности питания нагрузки в случае отказа источника энергоснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 62040-1-1-2009]
источник бесперебойного питания
ИБП
Устройство, поддерживающее заданное качество выходного напряжения при наличии нарушения питающей сети за счет использования энергии аккумуляторных батарей (исчезновение напряжения, искажения формы, отклонения от диапазона входных значений и т. д.). ИБП с двойным преобразованием класса VFI-SS-111 обеспечивают защиту от любых нарушений питающей сети.
[ http://www.radistr.ru/misc/document423.phtml с изменениями]
источник бесперебойного питания
UPS
Автоматическое устройство, устанавливаемое между источником энергии и оборудованием, обеспечивающее питание оборудования за счет энергии аккумуляторных батарей при отключении основного электроснабжения, защищающее оборудование от колебаний напряжения и электромагнитных шумов.
[РД 01.120.00-КТН-228-06]EN
uninterruptible power supply
UPS
An Electronic device connected between the Utility Power and electric consumers, comprising generally of filters, Rectifier, Battery, DC/AC Inverter, Transfer Switch and associated circuits.
The UPS is intended to provide clean undisturbed stabilized AC voltage, within strict amplitude and frequency limits, to protect the consumer from any Utility Power disturbances and irregularities, including outages for a limited time dictated by the capacity of the Battery Bank. The term UPS refers generally to AC Static systems, Other types include DC and Rotary UPS.
[ http://www.upsonnet.com/UPS-Glossary/]Исходная базовая идея у всех ИБП одинакова и основана на использовании резервного питания от аккумуляторов. Если напряжение в электрической сети исчезло, необходимо достаточно быстро переключить нагрузку на питание от встроенного аккумулятора, и наоборот, если напряжение восстановилось, снова переключить на питание от сети.
Время автономной работы от аккумулятора должно быть достаточным для безопасного завершения работы компьютера без потери информации.
В настоящее время сложилась общепринятая классификация ИБП по двум основным показателям - мощности и типу ИБП.
Классификация ИБП по мощности носит упрощенный характер и отражает в основном конструктивное исполнение ИБП:- ИБП малой мощности от 250 до 3000 ВА выпускаются в настольном или стоечном исполнении,
- ИБП средней мощности от 3000 до 30 000 ВА обычно изготавливаются в напольном исполнении,
- ИБП большой мощности от 40 до нескольких сотен кВА имеют напольное исполнение и размещаются в специальных электромашинных помещениях.
Существуют две топологии ИБП:
- off-line (резервные) ИБП,
- on-line ИБП.
[ http://www.tcs.ru/reviews/?id=345 с изменениями]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
источник непрерывного энергоснабжения
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
одинаковый размер частиц
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
система надёжного электроснабжения
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
услуга уровня пользователя
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > UPS
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
Service-oriented modeling — cite book |last=Bell |first=Michael|title=Service Oriented Modeling: Service Analysis, Design, and Architecture|year= 2008 |publisher=Wiley Sons|isbn=978 0 470 14111 3 |chapter=Introduction to Service Oriented Modeling] is a software development… … Wikipedia
Service (economics) — A service is the non material equivalent of a good. A service provision is an economic activity that does not result in ownership, and this is what differentiates it from providing physical goods. It is claimed to be a process that creates… … Wikipedia
service — ▪ I. service ser‧vice 1 [ˈsɜːvs ǁ ˈsɜːr ] noun 1. [countable usually plural] COMMERCE business that involves selling help and advice, or delivering goods etc for customers, rather than manufacturing goods: • He charged a £600,000 fee for… … Financial and business terms
Service delivery platform — The term Service Delivery Platform (SDP) usually refers to a set of components that provide a service’s delivery architecture (such as service creation, session control protocols) for a type of service. There is no standard definition of SDP in… … Wikipedia
service — {{Roman}}I.{{/Roman}} noun 1 system that provides sth the public needs ADJECTIVE ▪ efficient, excellent, good, valuable ▪ adequate ▪ bad, inadequate … Collocations dictionary
service — n. work done for others 1) to do, offer, perform, provide, render a service 2) custom; meritorious; public; yeoman ( loyal ) service 3) professional; social (BE) services (a fee for professional services) 4) service to (she received an award for… … Combinatory dictionary
service — [[t]sɜ͟ː(r)vɪs[/t]] ♦ services, servicing, serviced (For meaning 14, services is both the singular and the plural form.) 1) N COUNT: usu with supp A service is something that the public needs, such as transport, communications facilities,… … English dictionary
Service Improvement Plan — The Service Improvement Plan (SIP) is a program mandated by the Canadian Radio television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) to provide a defined level of basic telephone service to all Canadians, other than those so isolated that it is… … Wikipedia
Service-oriented architecture — (SOA) is a method for systems development and integration where functionality is grouped around business processes and packaged as interoperable services . SOA also describes IT infrastructure which allows different applications to exchange data… … Wikipedia
Service-oriented architecture implementation framework — Service oriented architectures (SOA) are based on the notion of software services, which are high level software components that include web services. Implementation of an SOA requires tools as well as run time infrastructure software. This is… … Wikipedia
Service Oriented Programming — (SOP) is a programming paradigm that uses services as the unit of computer work, to design and implement integrated business applications and mission critical software programs. Services can represent steps of business processes and thus one of… … Wikipedia
