-
1 guide note
English-German dictionary of Architecture and Construction > guide note
-
2 your
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (old and worn) mat[Swahili Word] mbachao[Swahili Plural] mibachao[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4[Derived Word] mbacha N, '-ako pron------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] -enu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] second person plural possessive pronoun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] wenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun classes 1,2,3,11/14[English Example] your child[Swahili Example] mtoto wenu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] yenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] your affairs[Swahili Example] mambo yenu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] lenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun class 5[English Example] your fruit[Swahili Example] tunda lenu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] chenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun class 7[English Example] your chair[Swahili Example] kiti chenu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] vyenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun class 8[English Example] your chairs[Swahili Example] viti vyenu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] zenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun class 10[English Example] your house[Swahili Example] nyumba zenu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] mwenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun class 18[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (plural)[Swahili Word] penu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun class 16[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] zako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun class 10[English Example] your wealth[Swahili Example] mali zako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] pako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun class 16[English Example] your place (rarely used)[Swahili Example] mahali pako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] vyako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun class 8[English Example] your things[Swahili Example] vitu vyako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] wako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun classes 1,2,3,11/14[English Example] your child[Swahili Example] mtoto wako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] lako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun class 5[English Example] your name[Swahili Example] jina lako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] mwako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun class 18[English Example] in your heart[Swahili Example] moyoni mwako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] yako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] your house[Swahili Example] nyumba yako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] chako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun class 7[English Example] yours in yours (each to his own)[Swahili Example] chako ni chako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your (singular)[Swahili Word] -ako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] second person singular possessive pronoun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your place[Swahili Word] kwako[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ako, noun class 15,17[English Example] I will come to your place[Swahili Example] Nitakuja kwako[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] your place[Swahili Word] kwenu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -enu, noun class 15,17[English Example] are you (plural) going to your place ?[Swahili Example] mnarudi kwenu ?[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------ -
3 her
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] -ake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] third person singular possessive pronoun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] -akwe[Swahili Plural] sing.[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] third person singular possessive pronoun (rarely used)------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] lake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 5[English Example] his/her name[Swahili Example] jina lake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] chake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 7[English Example] his/her thing[Swahili Example] kitu chake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] wake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] ake[English Example] her child[Swahili Example] mtoto wake[Note] noun class 1,2,3,11/14. See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] yake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] his/her country[Swahili Example] nchi yake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] vyake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 8[English Example] his/her things[Swahili Example] vitu vyake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] zake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 10[English Example] his/her houses[Swahili Example] nyumba zake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] mwake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 18[English Example] in his/her heart[Swahili Example] moyoni mwake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] pake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 16[English Example] his/her place (rarely used)[Swahili Example] pahali pake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] m[Part of Speech] verb object------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her[Swahili Word] mw[Part of Speech] verb object------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] her place[Swahili Word] kwake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun classes 15,17[English Example] I am going to his/her place[Swahili Example] ninaenda kwake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------ -
4 his
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] -ake[Part of Speech] pronoun[English Example] his chair, his chairs[Swahili Example] kiti chake, viti vyake[Note] third person singular possessive pronoun stem / also rarely: '-akwe------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] -akwe[Swahili Plural] sing.[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] third person singular possessive pronoun stem / also (usually): '-ake------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] lake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 5[English Example] his/her name[Swahili Example] jina lake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] chake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 7[English Example] his/her thing[Swahili Example] kitu chake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] wake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] ake[English Example] his child[Swahili Example] mtoto wake[Note] noun class 1,2,3,11/14. See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] yake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] his/her country[Swahili Example] nchi yake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] vyake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 8[English Example] his/her things[Swahili Example] vitu vyake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] zake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 10[English Example] his/her houses[Swahili Example] nyumba zake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] mwake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 18[English Example] in his/her heart[Swahili Example] moyoni mwake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his[Swahili Word] pake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun class 16[English Example] his/her place (rarely used)[Swahili Example] pahali pake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] his place[Swahili Word] kwake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ake, noun classes 15,17[English Example] I am going to his/her place[Swahili Example] ninaenda kwake[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------ -
5 my
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] -angu[Part of Speech] pronoun[English Example] my child, my house[Swahili Example] mtoto wangu, nyumba yangu[Note] first person singular possessive pronoun stem------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] wangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun classes 1,2,3,11/14[English Example] my child[Swahili Example] mtoto wangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] yangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] my friend, my mother[Swahili Example] rafiki yangu, Mama yangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] langu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun class 5[English Example] my name[Swahili Example] jina langu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] changu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun class 7[English Example] my chair[Swahili Example] kiti changu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] vyangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun class 8[English Example] my chairs[Swahili Example] viti vyangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] zangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun class 10[English Example] my friends[Swahili Example] rafiki zangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my place[Swahili Word] kwangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun classes 15, 17[English Example] welcome to my place[Swahili Example] karibu kwangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] pangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun class 16[English Example] my place (rarely used)[Swahili Example] mahali pangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] my[Swahili Word] mwangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu, noun class 18[English Example] in my heart[Swahili Example] moyoni mwangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] My![Swahili Word] kumbe[Part of Speech] interjection------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] My![Swahili Word] lo![Part of Speech] interjection------------------------------------------------------------ -
6 our
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] wetu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun classses 1,2,3,11/14[English Example] our child[Swahili Example] mtoto wetu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] -etu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] first person plural possessive pronoun stem------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] yetu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] our country[Swahili Example] nchi yetu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] letu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun class 5[English Example] our name[Swahili Example] jina letu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] chetu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun class 7[English Example] our bed[Swahili Example] kitanda chetu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] vyetu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun class 8[English Example] our things[Swahili Example] vitu vyetu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] zetu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun class 10[English Example] our countries[Swahili Example] nchi zetu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] mwetu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun class 18[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our[Swahili Word] petu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun class 16[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] our place[Swahili Word] kwetu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -etu, noun classes 15,17[English Example] welcome to our place[Swahili Example] karibu kwetu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------ -
7 their
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] -ao[Part of Speech] pronoun[English Example] their country, their countries[Swahili Example] nchi yao, nchi zao[Note] third person plural possessive pronoun stem------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] lao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun class 5[English Example] their shop[Swahili Example] duka lao[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] zao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun class 10[English Example] their work[Swahili Example] kazi zao[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] yao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] their shops[Swahili Example] maduka yao[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] chao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun class 8[English Example] their thing[Swahili Example] kitu chao[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] wao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun classes 1,2,3,11/14[English Example] their child[Swahili Example] mtoto wao[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] vyao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun class 8[English Example] their things[Swahili Example] vitu vyao[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] mwao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun class 18[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their[Swahili Word] pao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun class 16[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their (place)[Swahili Word] kwao[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -ao, noun classes 15 and 17[English Example] he is going back to their place[Swahili Example] anarudi kwao[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] their (sing)[Swahili Word] -ake[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] third person singular possessive pronoun See "his" or "her"------------------------------------------------------------ -
8 mine
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[English Plural] mines[Swahili Word] chimbo[Swahili Plural] machimbo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[Derived Word] chimba v------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[English Plural] mines[Swahili Word] chimbuko[Swahili Plural] machimbuko[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[Derived Word] chimba v------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[English Plural] mines[Swahili Word] kiwanda[Swahili Plural] viwanda[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 7/8------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[English Plural] mines[Swahili Word] mgodi[Swahili Plural] migodi[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[English Plural] mines[Swahili Word] mtego[Swahili Plural] mitego[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4[Derived Word] tega V[English Example] lay mines.[Swahili Example] fichia mtego[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[English Plural] mines[Swahili Word] shimo[Swahili Plural] mashimo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[English Example] gold mine[Swahili Example] shimo la dhahabu------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] -angu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] changu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu[English Example] this book is mine[Swahili Example] kitabu hiki ni changu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] miye[Part of Speech] pronoun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] zangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu noun class 10[English Example] my friends[Swahili Example] rafiki zangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] wangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu noun classes 1,2,3,11/14[English Example] my child[Swahili Example] mtoto wangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] kwangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu noun class 15,17[English Example] welcome to my place[Swahili Example] karibu kwangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] yangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu noun classes 4,6,9[English Example] my house, my Mother[Swahili Example] nyumba yangu, Mama yangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] langu[Swahili Plural] yangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu noun class 5[English Example] my name[Swahili Example] jina langu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] mwangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu noun class 18[English Example] in my heart[Swahili Example] moyoni mwangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine[Swahili Word] pangu[Part of Speech] pronoun[Derived Word] -angu noun class 16[English Example] my place (rarely used)[Swahili Example] mahali pangu[Note] See Swahili Noun Class Guide at www.yale.edu/swahili/nounclassguide.html------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mine worker[English Plural] mine workers[Swahili Word] mchimbaji wa madini[Swahili Plural] wachimbaji wa madini[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 1/2[Derived Word] chimba V------------------------------------------------------------ -
9 coherent system of units (of measurement)
когерентная система единиц физических величин
когерентная система единиц
Система единиц физических величин, состоящая из основных единиц и когерентных производных единиц.
Примечание. Кратные и дольные единицы от системных единиц не входят в когерентную систему.
[РМГ 29-99]EN
coherent system of units
system of units, based on a given system of quantities, in which the unit of measurement for each derived quantity is a coherent derived unit
NOTE 1 – A system of units can be coherent only with respect to a system of quantities and the adopted base units.
NOTE 2 – For a coherent system of units, numerical value equations have the same form, including numerical factors, as the corresponding quantity equations.
NOTE 3 – An example of coherent system of units is the set of coherent SI units with the relations between them.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.14
[IEV number 112-01-22]FR
système cohérent d'unités, m
système d'unités, fondé sur un système de grandeurs donné, dans lequel l'unité de mesure de chaque grandeur dérivée est une unité dérivée cohérente
NOTE 1 – Un système d'unités ne peut être cohérent que par rapport à un système de grandeurs et aux unités de base adoptées.
NOTE 2 – Pour un système cohérent d'unités, les équations aux valeurs numériques ont la même forme, y compris les facteurs numériques, que les équations aux grandeurs correspondantes.
NOTE 3 – Un exemple de système cohérent d’unités est l’ensemble des unités SI cohérentes muni des relations entre elles.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.14
[IEV number 112-01-22]
Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
- systéme coherent d´unités (de mesure)
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > coherent system of units (of measurement)
-
10 base unit (of measurement)
основная единица системы единиц физических величин
основная единица
Единица основной физической величины в данной системе единиц.
Пример. Основные единицы Международной системы единиц (СИ): метр (м), килограмм (кг), секунда.
[РМГ 29-99]EN
base unit
unit of measurement that is adopted by convention for a base quantity
NOTE 1 – In each coherent system of units, there is only one base unit for each base quantity. In the SI for example, the metre is the base unit of length. The centimetre and the kilometre are also units of length, but they are not base units in the SI. However, in the CGS systems, the centimetre is the base unit of length.
NOTE 2 – A base unit may also serve for a derived quantity of the same dimension. For example, rainfall, when defined as volume per area (areic volume), has the metre as a coherent derived unit in the SI. The ampere, base unit of electric current, is also the coherent derived unit of scalar magnetic potential.
NOTE 3 – For the quantity “number of entities”, the number one, symbol 1, can be regarded as a base unit in any system of units.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.10
[IEV number 112-01-18]FR
unité de base, f
unité de mesure adoptée par convention pour une grandeur de base
NOTE 1 – Dans chaque système cohérent d'unités, il y a une seule unité de base pour chaque grandeur de base. Dans le SI par exemple, le mètre est l'unité de base de longueur. Le centimètre et le kilomètre sont aussi des unités de longueur, mais ils ne sont pas des unités de base dans le SI. Cependant, dans les systèmes CGS, le centimètre est l'unité de base de longueur.
NOTE 2 – Une unité de base peut aussi servir pour une grandeur dérivée de même dimension. Par exemple, la hauteur de pluie, définie comme un volume surfacique (volume par aire) a le mètre comme unité dérivée cohérente dans le SI. L’ampère, unité de base de courant électrique, est aussi l’unité dérivée cohérente de potentiel magnétique scalaire.
NOTE 3 – Pour la grandeur « nombre d'entités », on peut considérer le nombre un, de symbole 1, comme une unité de base dans tout système d'unités.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.10
[IEV number 112-01-18]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > base unit (of measurement)
-
11 waveguide
акустико-эмиссионный волновод
Устройство, которое передает акустический сигнал АЭ от объекта испытаний к преобразователю, размещенному на расстоянии от объекта при АЭ контроле. Примером акустико-эмиссионного волновода может служить твердый провод или стержень, который акустически связан одним концом с контролируемым объектом, другим концом - с преобразователем.
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]Тематики
- виды (методы) и технология неразр. контроля
EN
волновод
Линия передачи, имеющая одну или несколько проводящих поверхностей, с поперечным сечением в виде замкнутого проводящего контура, охватывающего область распространения электромагнитной энергии
[ ГОСТ 18238-72]
волновод
Канал, по которому распространяется волна той или иной природы
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
волновод
-
[IEV number 151-12-34]EN
waveguide
line consisting of a system of material boundaries or structures for guiding electromagnetic waves
NOTE – A waveguide is usually intended to guide electromagnetic waves in other modes than TEM mode. Examples of construction are: metallic tube, dielectric rod, optical fibre, dielectric or semiconductor thin film, or mixed structure of conducting and dielectric materials.
Source: 704-02-06 MOD, 726-01-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-34]FR
guide d'ondes, m
ligne constituée d'un ensemble de surfaces limites ou de formes matérielles destiné à guider des ondes électromagnétiques
NOTE – Un guide d'ondes est généralement destiné à guider des ondes électromagnétiques dans des modes autres que le mode TEM. Des exemples de construction sont: tube métallique, tige diélectrique, fibre optique, couche mince diélectrique ou semiconductrice, assemblage de matériaux conducteurs et diélectriques.
Source: 704-02-06 MOD, 726-01-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-34]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
волновод
Зона пониженной скорости распространения сейсмических волн, совпадающая с астеносферой.
[ Словарь геологических терминов и понятий. Томский Государственный Университет]Тематики
- геология, геофизика
Обобщающие термины
EN
2.58 акустико-эмиссионный волновод (waveguide, acoustic emission): Устройство, которое передает акустический сигнал АЭ от объекта испытаний к преобразователю, размещенному на расстоянии от объекта при контроле АЭ.
Примечание - Примером акустико-эмиссионного волновода может служить твердый привод или стержень, который акустически связан одним концом с контролируемым объектом, другим концом - с преобразователем.
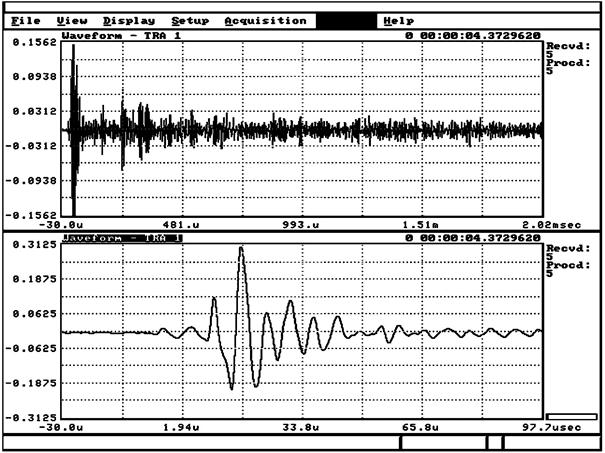
Рисунок 1 - Один и тот же пакет сигнала АЭ при различных временных развертках
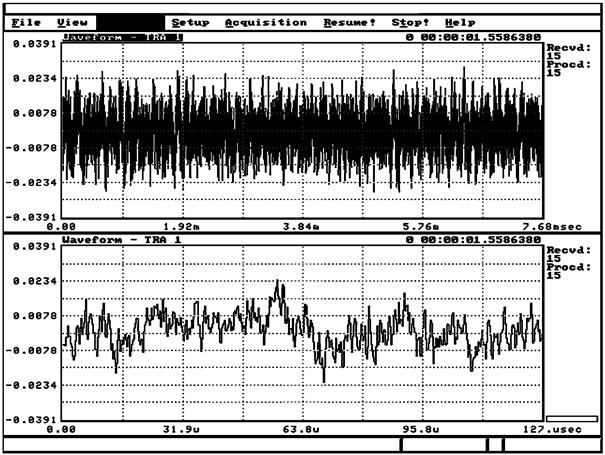
Рисунок 2 - Один и тот же непрерывный сигнал АЭ при различных временных развертках
<2>
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 12716-2009: Контроль неразрушающий. Акустическая эмиссия. Словарь оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > waveguide
-
12 wg
волновод
Линия передачи, имеющая одну или несколько проводящих поверхностей, с поперечным сечением в виде замкнутого проводящего контура, охватывающего область распространения электромагнитной энергии
[ ГОСТ 18238-72]
волновод
Канал, по которому распространяется волна той или иной природы
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
волновод
-
[IEV number 151-12-34]EN
waveguide
line consisting of a system of material boundaries or structures for guiding electromagnetic waves
NOTE – A waveguide is usually intended to guide electromagnetic waves in other modes than TEM mode. Examples of construction are: metallic tube, dielectric rod, optical fibre, dielectric or semiconductor thin film, or mixed structure of conducting and dielectric materials.
Source: 704-02-06 MOD, 726-01-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-34]FR
guide d'ondes, m
ligne constituée d'un ensemble de surfaces limites ou de formes matérielles destiné à guider des ondes électromagnétiques
NOTE – Un guide d'ondes est généralement destiné à guider des ondes électromagnétiques dans des modes autres que le mode TEM. Des exemples de construction sont: tube métallique, tige diélectrique, fibre optique, couche mince diélectrique ou semiconductrice, assemblage de matériaux conducteurs et diélectriques.
Source: 704-02-06 MOD, 726-01-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-34]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
рабочая группа
—
[[Англо-русский словарь сокращений транспортно-экспедиторских и коммерческих терминов и выражений ФИАТА]]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > wg
-
13 pipe
- труба бесшовная
- труба
- транспортная линия связи
- транспортировать по трубопроводу
- скважинная колонна труб
- оборудовать системой трубопроводов
- заглушка трубы
- гармошка
- волновод
волновод
Линия передачи, имеющая одну или несколько проводящих поверхностей, с поперечным сечением в виде замкнутого проводящего контура, охватывающего область распространения электромагнитной энергии
[ ГОСТ 18238-72]
волновод
Канал, по которому распространяется волна той или иной природы
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
волновод
-
[IEV number 151-12-34]EN
waveguide
line consisting of a system of material boundaries or structures for guiding electromagnetic waves
NOTE – A waveguide is usually intended to guide electromagnetic waves in other modes than TEM mode. Examples of construction are: metallic tube, dielectric rod, optical fibre, dielectric or semiconductor thin film, or mixed structure of conducting and dielectric materials.
Source: 704-02-06 MOD, 726-01-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-34]FR
guide d'ondes, m
ligne constituée d'un ensemble de surfaces limites ou de formes matérielles destiné à guider des ondes électromagnétiques
NOTE – Un guide d'ondes est généralement destiné à guider des ondes électromagnétiques dans des modes autres que le mode TEM. Des exemples de construction sont: tube métallique, tige diélectrique, fibre optique, couche mince diélectrique ou semiconductrice, assemblage de matériaux conducteurs et diélectriques.
Source: 704-02-06 MOD, 726-01-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-34]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
гармошка
Дефект поверхности листа в виде чередующихся вздутий, идущих поперек прокатки от торца по плоскости листа, образовавшихся при наличии полостей и рыхлости в осевой зоне слитка.
Примечания:
1. Между волнами гармошки могут возникать разрывы металла.
2. На микрошлифе в осевой зоне под гармошкой обнаруживается нарушение сплошности металла, частицы включений и зоны ликвации.
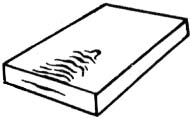
[ ГОСТ 21014-88]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
EN
DE
оборудовать системой трубопроводов
пускать по трубам
транспортировать по трубопроводу
подавать по трубопроводу
перекачивать по трубопроводу
трубопровод
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
- пускать по трубам
- транспортировать по трубопроводу
- подавать по трубопроводу
- перекачивать по трубопроводу
- трубопровод
EN
скважинная колонна труб
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
транспортировать по трубопроводу
перекачивать по трубопроводу
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
транспортная линия связи
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
EN
3.39 труба (pipe): Общее наименование обсадной, насосно-компрессорной трубы, трубы для потайных обсадных колонн и укороченной трубы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53366-2009: Трубы стальные, применяемые в качестве обсадных или насосно-компрессорных труб для скважин в нефтяной и газовой промышленности. Общие технические условия оригинал документа
3.65 труба бесшовная (Pipe, Seamless, SML): Труба, изготовленная в процессе горячей формовки, в результате которого получается трубное изделие без сварного шва.
Примечание - За горячей формовкой может следовать обработка или холодное экспандирование, позволяющее получить требуемые размеры.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54382-2011: Нефтяная и газовая промышленность. Подводные трубопроводные системы. Общие технические требования оригинал документа
3.2 труба (pipe): Отливка с равномерным каналом, с прямой осью, имеющая раструбные, охватываемые или фланцевые концы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 2531-2008: Трубы, фитинги, арматура и их соединения из чугуна с шаровидным графитом для водо- и газоснабжения. Технические условия оригинал документа
4.1.19 труба (pipe): Общее наименование обсадной, насосно-компрессорной трубы и укороченной трубы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 13680-2011: Трубы бесшовные обсадные, насосно-компрессорные и трубные заготовки для муфт из коррозионно-стойких высоколегированных сталей и сплавов для нефтяной и газовой промышленности. Технические условия оригинал документа
3.2 труба (pipe): Отливка с равномерным каналом, с прямой осью, имеющая раструбные, охватываемые или фланцевые концы.
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > pipe
-
14 electrical hazard
EN
electrical hazard
potential source of harm when electric energy is present in an electrical installation
NOTE – The ISO/IEC Guide 51:1990 gives as French equivalent “danger” for the English term “hazard”. In the draft revision of this guide, “hazard” is rendered in French by “phénomène dangereux”.
[IEV number 651-01-30]FR
danger électrique
source potentielle de dommage due à la présence d'énergie électrique dans une installation électrique
NOTE – Le Guide ISO/CEI 51:1990 donne comme équivalent pour le terme anglais "hazard" le terme français "danger". Dans le projet de révision de ce guide, "hazard" est rendu en français par "phénomène dangereux".
[IEV number 651-01-30]
4.3 Электрические опасности
Электрические опасности могут приводить к ожогам, травмам или смерти от поражения электрическим током и к ожогам. Они могут быть вызваны:- соприкосновением людей с токоведущими частями, находящимися при нормальной работе под напряжением (прямой контакт);
- соприкосновением людей с частями, попадающими под напряжение при неисправностях, особенно в результате повреждения электрической изоляции (непрямой контакт);
- приближением людей к токоведущим частям, находящимся под напряжением, особенно под высоким напряжением;
- несоответствием электрической изоляции предусмотренным условиям эксплуатации машины;
- контактом человека с деталями, заряженными статическим электричеством;
- тепловым излучением;
- выбросом расплавленных частиц или химических веществ при коротком замыкании или в случае перегрузок.
Электрические опасности также могут приводить к падениям людей (или предметов на людей) в результате шока, вызванного поражением электрическим током.
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 12100-1:2007]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > electrical hazard
-
15 derived unit (of measurement)
производная единица системы единиц физических величин
производная единица
Единица производной физической величины системы единиц, образованная в соответствии с уравнением, связывающим ее с основными единицами или с основными и уже определенными производными.
Примеры
1. 1 м/с - единица скорости, образованная из основных единиц СИ - метра и секунды.
2. 1 Н - единица силы, образованная из основных единиц СИ - килограмма, метра, и секунды.
[РМГ 29-99]EN
derived unit
unit of measurement for a derived quantity
NOTE 1 – Some derived units in the International System of Units (SI) have special names, e.g. hertz for frequency and joule for energy, but others have compound names, e.g. metre per second for speed. Compounds including units with special names are also used, e.g. volt per metre for the electric field strength, and newton metre for torque. See in particular ISO 31 and ISO/IEC 80000.
NOTE 2 – Derived units can also be expressed by using multiples and submultiples. For example, the metre per second, symbol m/s, and the centimetre per second, symbol cm/s, are derived units of speed in the SI. The kilometre per hour, symbol km/h, is a unit of speed outside the SI but accepted for use with the SI, because the unit hour is accepted for use with the SI. The knot, equal to one nautical mile per hour, is a unit of speed outside the SI, that is used by special interest groups.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.11
[IEV number 112-01-19]FR
unité dérivée, f
unité de mesure d'une grandeur dérivée
NOTE 1 – Certaines unités dérivées dans le SI ont des noms spéciaux, par exemple le hertz pour la fréquence et le joule pour l'énergie, tandis que d'autres ont des noms composés, par exemple le mètre par seconde pour la vitesse. Les unités ayant des noms spéciaux sont aussi utilisées dans des noms composés, par exemple le volt par mètre pour le champ électrique et le newton mètre pour le moment de torsion. Voir en particulier l'ISO 31 et l'ISO/CEI 80000.
NOTE 2 – On peut aussi exprimer les unités dérivées en utilisant des multiples et des sous-multiples. Par exemple, le mètre par seconde, symbole m/s, et le centimètre par seconde, symbole cm/s, sont des unités dérivées de vitesse dans le SI. Le kilomètre par heure, symbole km/h, est une unité de vitesse en dehors du SI mais en usage avec le SI, parce que l'heure est une unité en usage avec le SI. Le nœud, égal à un mille marin par heure, est une unité de vitesse en dehors du SI, qui répond aux besoins spécifiques de certains groupes d’utilisateurs.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.11
[IEV number 112-01-19]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > derived unit (of measurement)
-
16 CULTURE, LITERATURE, AND LANGUAGE
■ Bell, Aubrey F. G. The Oxford Book of Portuguese Verse: XIIth Century-XXth Century. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1925, 1952 (2nd edition, B. Vi-digal, ed.).■. Portuguese Literature. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1922, 1970 (2nd edition, B. Vidigal, ed.).■ Bleiberg, German, Maureen Ihrie, and Janet Pérez, eds. Dictionary of the Literature of the Iberian Peninsula, 2 vols. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1993.■ Castro, Francisco Lyon de, ed. História da literatura portuguesa, 7 vols. Lisbon: Alfa, 2001-02.■ Cidade, Hernani. Lições de Cultura e Literatura Portuguesa, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1960-62.■ Cook, Manuela. Portuguese: A Complete Course for Beginners. London: Hodder and Stoughton, 1996. Figueiredo, Fidelino. História literária de Portugal. Coimbra, 1944. Gentile, Georges Le. La Littérature Portugaise. Rev. ed. Paris, 1951. Kunoff, Hugo. Portuguese Literature from Its Origins to 1990: A Bibliography Based on the Collections at Indiana University. Metuchen, N.J.: Scarecrow Press, 1994.■ Longland, Jean. Contemporary Portuguese Poetry. A Bilingual Selection. Irvington-on-Hudson: Harvey House, 1966. Prado Coelho, Jacinto do. Dicionário das Literaturas Portuguesas, Galega e Brasileira, 3rd ed. Oporto, 1978. Rossi, Giuseppe C. Storia della letteratura portoghesa. Florence, 1953.■ Santos, João Camilo dos. "Portuguese Contemporary Literature." In Antônio Costa Pinto, ed., Modern Portugal, 218-42. Palo Alto, Calif.: SPOSS, 1998.■ Saraiva, Antônio José. História da cultura em Portugal, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1950-60.■. História da Literatura Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1990 ed.■, and Oscar Lopes. História da Literatura Portuguesa. Oporto and Coimbra, 1992 ed.■ Seguier, Jaime de, ed. Dicionário Prático Ilustrado. Oporto: Lello, 1961 and later eds.■ Simões, João Gaspar. História da poesia portuguesa, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1955-56 and later eds.■. História da poesia portuguesa do século XX. Lisbon, 1959 and later eds.■ Stern, Irwin, ed.-in-chief. Dictionary of Brazilian Literature. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1988.■ TRAVEL AND TOURIST GUIDES ON PORTUGAL■ Ballard, Sam, and Jane Ballard. Pousadas of Portugal: Unique Lodgings in State-owned Castles, Palaces, Mansions and Hotels. Boston: Harvard Common, 1986.■ Bridge, Ann, and Susan Lowndes Marques. The Selective Traveller in Portugal. London: Chatto & Windus, 1968.■ Ellingham, Mark, et al. Portugal: The Rough Guide. London: Rough Guides, 2008 ed.■ Hogg, Anthony. Travellers' Portugal. London: Solo Mio, 1983.■ Kite, Cynthia, and Ralph Kite. Portuguese Country Inns & Pousadas. New York: Warner Books; Karen Brown's Country Inn Series, 1988.■ Lowndes, Susan, ed. Fodor's Portugal 1991. New York: Fodor's, 1990.■ Proença Raúl, and Sant'anna Dionísio, eds. Guía De Portugal. I. Generalidades. Lisboa E, Arredores. Lisbon: Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian, 1924; 1983.■ Robertson, Ian. Portugal: Blue Guide. London: Benn; New York: Norton, 2000 and later eds.■ Stoop, Anne de. Living in Portugal. Paris and New York: Flammarion, 1995. Wright, David, and Patrick Swift. Minho and North Portugal: A Portrait and Guide. New York: Scribners, 1968.■. Lisbon: A Portrait and Guide. New York: Scribners, 1971.■. Algarve: A Portrait and Guide. New York: Scribners, 1973.■ HISTORY OF PORTUGAL Ancient and Medieval (2000 BCE-1415 CE)■ Alarção, Jorge de. Roman Portugal. Volume I: Introduction. Warminster, U.K., 1988.■ Almeida, Fortunato de. História de Portugal. Vol. I. Coimbra, 1922. Arnaut, Salvador Dias. A Crise Nacional dos fins do século XVI. Vol. 1. Coimbra, 1960.■ Baião, Antônio, Hernani Cidade, and Manuel Múrias, eds. História de Expansão Portuguesa no Mundo, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1937-40. Caetano, Marcello. Lições de História do Direito Português. Coimbra, 1962. Cortesão, Jaime. Os Factores Democráticos no Formação de Portugal. Lisbon, 1960.■ David, Pierre. Etudes Historiques sur la Galice et le Portugal du VI au XII siécle. Paris, 1947.■ Dias, Eduardo Mayone. Portugal's Secret Jews: The End of an Era. Rumford, R.I.: Peregrinação Publications, 1999. Diffie, Bailey W. Prelude to Empire: Portugal Overseas before Henry the Navigator. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1960. Dutra, Francis A. "Portugal: To 1279." Dictionary of the Middle Ages. Vol. X: 35-48. New York: Scribners, 1987.■. "Portugal: 1279-1481." Dictionary of the Middle Ages. Vol. X: 48-56. New York: Scribners, 1987. Gama Barros, Henrique de. História de Administração Pública em Portugal nos séculos XII à XV, 11 vols. Lisbon, 1945-51. Godinho, Vitorino Magalhães. A Economia dos Descobrimentos Henriquinos. Lisbon, 1962.■ Gonzaga de Azevedo, Luís. História de Portugal, 6 vols. Lisbon, 1939-44.■ Herculano, Alexandre. História de Portugal, 8 vols., 9th ed. Lisbon, 1940.■ Kennedy, Hugh. Muslim Spain and Portugal: A Political History of al-Anda-lus. London: Longman, 1996.■ Lencastre e Tavora, Luía Gonzaga. O Estudo da Sigilografia Medieval Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1990.■ Livermore, H. V. The Origins of Spain and Portugal. London: Allen & Unwin, 1971.■ Lopes, David. "Os Árabes nas obras de Alexandre Herculano." Boletim da Segunda Classe. Lisbon: Academia Real das Sciéncias, III (1909-10). MacKendrick, Paul. The Iberian Stones Speak. New York: Funk & Wagnalls, 1969.■ Martinez, Pedro Soares. História Diplomática De Portugal [chapter I, 114315]. Lisbon, 1986.■ Mattoso, José, ed. A Nobreza Medieval Portuguesa: A Família e o Poder. Lisbon: Estampa, 1981.■. Religião e cultura na Idade Média Portuguesa. Lisbon: Imprensa Nacional, 1982.■. Identificaçao de um país ( ensaio sobre as orígens de Portugal), 2 vols. Lisbon: Estampa, 1985.■. Novos Ensaios de História Medieval Portuguesa. Lisbon: Edit. Presença, 1988.■. Historia de Portugal. Vol. 2: A Monarquia Feudal ( 1096-1480). Lisbon: Estampa, 1993.■ Oliveira Marques, A. H. de. Hansa e Portugal na Idade Média. Lisbon, 1959.■. Introduçao à História da Agricultura em Portugal. Lisbon, 1968.■. Daily Life in Portugal in the Middle Ages. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1971.■. Ensaios de História Medieval Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1980.■. "Introduçao à História da Cidade Medieval Portuguesa." Bracara Augusta XXV, 92-93 (January-December 1981): 367-87.■. Guía do Estudante de História Medieval Portuguesa, 3rd ed. Lisbon, 1985.■. Portugal Na Crise Dos Séculos XIV e XV-Vol. IV of Serrão and Oliveira Marques, Nova História de Portugal. Lisbon, 1987.■ Peres, Damião de, ed. História de Portugal. Vols. I, II. Barcelos, 1928-29.■ Rau, Virginia. Subsídios para o estudo das Feiras Medievais Portuguesas. Lisbon, 1943.■. Sesma'rias Medievais Portuguesas. Lisbon, 1946.■ Ribeiro, Orlando. "Portugal, formação de." Dicionário da História de Portugal. Vol. III, 432-51. Lisbon, 1966.■ Rogers, Francis M. The Travels of the Infante Dom Pedro of Portugal. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1961.■ Russell, P. E. The English Intervention in Spain and Portugal in the Time of Edward III and Richard II. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1955.■ Savory, H. N. Spain and Portugal: The Prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula. New York: Thames and Hudson, 1968.■ Silva, Armando Coelho Ferreira. A Cultura Castreja no Noroeste de Portugal. Pacos de Ferreira, 1986.■ Varagnac, André. O Homem antes da Escrita ( Pre-história). Lisbon, 1963.■ Azevedo, J. Lúcio de. História de António de Vieira, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1918-20.■. Épocas de Portugal Económico. Lisbon, 1929.■ Borges de Macedo, Jorge. Problemas de História de Indústria Portuguesa no Século X VIII. Lisbon, 1963.■. "Pombal." Dicionário de História de Portugal. Vol. III, 415-23. Lisbon, 1968.■ Bovill, Edward W. The Battle of the Alcazar: An Account of the Defeat of Dom Sebastian at El-Ksar el-Kebir. London, 1952.■ Boxer, C. R. Four Centuries of Portuguese Expansion, 1415-1825: A Succinct Survey. Johannesburg, South Africa: Witwaterstrand University Press, 1961.■. The Portuguese Seaborne Empire 1415-1825. London: Hutchinson, 1969.■. João de Barros: Portuguese Humanist and Historian of Asia. New Delhi, India: Xavier Centre, 1981.■ Cheke, Marcus. Dictator of Portugal: A Life of the Marquis of Pombal, 16991782. London: Sidgwick & Jackson, 1938.■ Cunha, Luís da. Testamento Político. Lisbon, 1820.■ Davidson, Lillias C. Catherine of Bragança. London: John Murray, 1908.■ Dutra, Francis A. "Membership in the Order of Christ in the Seventeenth Century." The Americas 27 (1970): 3-25.■ Eberlein, H. D., and R. W. Ramsdell. The Practical Book of Italian, Spanish and Portuguese Furniture. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1927.■ Ericeira, Luís de Meneses [Count of]. História de Portugal Restaurado, 4 vols. Oporto, 1945.■ Fisher, H. E. S. "Anglo-Portuguese Trade, 1700-70." Economic History Review XVI, 2 (1963): 219-33.■ Francis, A. D. The Methuens and Portugal: 1691-1708. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1966.■ Hanson, Carl A. Economy and Society in Baroque Portugal, 1668-1703. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1981.■ Herculano, Alexandre. History of the Origin and Establishment of the Inquisition in Portugal. New York: AMS Press, 1968 reprint.■ Kendrick, T. D. The Lisbon Earthquake. London: Methuen, 1956.■ Livermore, H. V. "The Privileges of an Englishman in the Kingdom and Dominions of Portugal." Atlante 11 (1954): 57-77.■ Macauley, Neil. Dom Pedro: The Struggle for Liberty in Brazil and Portugal, 1798-1834. Durham, N.C.: Duke University Press, 1986.■ Macauley, Rose. They Went to Portugal. London: Jonathan Cape, 1946.■. They Went to Portugal, Too. London: Carcanet, 1990.■ Magalhães Godinho, Vitorino. Prix et Monnaies au Portugal. Paris, 1955.■. "Portugal and Her Empire." In New Cambridge Modern History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, Vol. V (1961): 384-97; Vol. VI (1961): 509-10.■. A Economia dos descobrimentos henri-quinos. Lisbon, 1962.■. Estructura da Antiga Sociedade Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1975.■ Mauro, Frédéric. Le Portugal et l'Atlantique au XVII siécle ( 1570-1670). Paris: SEVPEN, 1960.■ Maxwell, Kenneth. "Pombal and the Nationalization of the Luso-Brazilian Economy." Hispanic American Historical Review XLVIII (November 1968): 608-31.■. Conflicts and Conspiracies: Brazil and Portugal, 1750-1808. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1973.■ Norris, A. H., and R. W. Bremner. The Lines of Torres Vedras. Lisbon: British Historical Society of Portugal, 1980.■ Oliveira, Antônio de. A Vida Económica e Social de Coimbra de 1537 à 1640, 2 vols. Coimbra, 1971-72.■ Prestage, Edgar. The Royal Power and the Cortes in Portugal. Watford, U.K.: Voss & Michael, 1927.■. Portuguese Pioneers. London: Black, 1933.■. "The Mode of Government in Portugal during the Restoration [1640-68] Period." In Edgar Prestage, ed., Melange d'Etudes Portugaises Offerts a M. Georges Le Gentil, 265-70. Lisbon, 1949.■ Rabassa, Gregory. "Padre Antônio Vieira: Portugal's Amazing Polymath." Camões Centre Quarterly 2, 3-4 (Autumn and Winter 1990): 27-32. Rau, Virginia. D. Catarina de Bragança: Rainha de Inglaterra. Lisbon, 1944. Ricard, Robert. "Prophecy and Messianism in the Works of Antônio Vieira." The Americas 37 (1960): 357-88.■ Roche, T. W. E. Philippa: Dona Filipa of Portugal. London: Phillimore, 1971.■ Rogers, Francis M. The Travels of the Infante Dom Pedro of Portugal. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1961.■ Rooney, Peter T. "Hapsburg Fiscal Policies in Portugal, 1580-1640." Journal of European Economic History 23, 3 (1994): 545-62.■ Roth, Cecil. "The Religion of the Marranos." Jewish Quarterly Review 22 (1931): 1-33.■. A History of the Marranos. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society of America, 1932.■ Saraiva, Antônio José. Inquisição e Cristãos-Novos. Oporto, 1969.■. A Inquisição Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1969 and later eds.■ Schneider, Susan. O Marquês De Pombal E O Vinho Do Porto: Dependência e subdesenvolvimento em Portugal no século XVIII. Lisbon, 1980.■ Shaw, L. M. E. Trade, Inquisition and the English Nation in Portugal, 16401690. London: Carcancet, 1989.■ Shillington, V. M., and A. B. W. Chapman. The Commercial Relations of England and Portugal. London: Routledge, 1907.■ Sideri, Sandro. Trade and Power: Informal Colonialism in Anglo-Portuguese Relations. Rotterdam: Rotterdam University Press, 1970.■ Smith, John Athelstone [Conde de Carnota]. Marquis of Pombal, 2nd ed. London, 1872.■ Thomas, Gerturde Z. Richer Than Spices. New York: Knopf, 1965. Walford, A. R. The British Factory in Lisbon. Lisbon, 1940.■ Baptista, Jacinto. O Cinco de Outubro. Lisbon, 1965. Brandão, Raúl. Memórias, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1969 ed.■ Cabral, Manuel Villaverde. O desenvolvimento do capitalismo em Portugal no século XIX. Lisbon, 1981. Caetano, Marcello. História Breve das Constituções portuguesas. Lisbon, 1971 ed.■ Carnota, Conde da. Memoirs of Marshal, the Duke of Saldanha, with Selections from His Correspondence, 2 vols. London: John Murray, 1880. Carvalho, Joaquim de. Estudos sobre a cultura portuguesa do século XIX. Coimbra, 1955.■ Cheke, Marcus. Carlota Joaquina, Queen of Portugal. London: Sidgwick and Jackson, 1947.■ França, José-Augusto. Zé Provinho na Obra de Rafael Bordalo Pinheiro. Lisbon, 1975.■ Fuschini, Augusto. Liquidações políticas. Lisbon, 1896.■ Godinho, Vitorino Magalhães. Estrutura da Antiga Sociedade Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1975 ed.■ Hammond, Richard J. Portugal and Africa, 1815-1910: A Study in Uneconomic Imperialism. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, 1966.■ Homem, Amadeu Carvalho. A Propaganda Republicana ( 1870-1910). Coimbra, 1990.■ Livermore, H. V. Portugal: A Short History. Edinburgh, U.K.: Edinburgh University Press, 1973. Machado, Alvaro Manuel. A Geração de 70-uma revolução cultural e literária. Lisbon, 1986 ed.■ Martins, Joaquim Pedro de Oliveira. Portugal Contemporâneo, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1953 ed.■ Medina, João. Eça Político. Lisbon, 1974.■ Mônica, Maria Filomena. Fontes Pereira de Melo. Oporto: Ed. Afrontamento, 1999.■ Nobre, Eduardo. Paixoes Reais. Lisbon: Quimera, 2002.■ Pereira, Miriam Halpern. Livre Câmbio e Desenvolvimento Económico: Portugal na segunda metade do século XIX. Lisbon, 1971.■ Peres, Damião, ed. História de Portugal. Volume III. Barcelos, 1935 ed.■ Ramos, Rui. D.Carlos. 1863-1908. Lisbon: Circulo de Leitores, 2006.■. Liberal Reformism in Portugal. Oliveira Martins, the Movement for New Life and the Politics of the Constitutional Monarchy ( 1885-1908). Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1998.■ Rorick, David. Maria da Fonte: History and Myth. M.A. thesis, History Department, Sonoma State University, Sonoma, Calif., 1984.■ Sá, Vítor de. Perspectivas do Século XIX. Lisbon, 1964.■ Serrão, Joel. Sampaio Bruno: O homem e o pensamento. Lisbon, 1958.■. Temas Oitocentistas, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1959-62.■. "Liberalismo." In Joel Serrão, ed., Dicionário de História de Portugal. Vol. II, 732-41. Lisbon, 1965.■. Do Sebastianismo ao Socialismo. Lisbon, 1975 ed.■ Silbert, Albert. Do Portugal de Antiga Regime ao Portugal Oitocentista. Lisbon, 1972.■ Teles, Basílio. Do Ultimatum ao 31 de Janeiro. Lisbon, 1968 ed.■ Parliamentary, Republican Portugal (1910-26)■ Antunes, José Freire. A Cadeira do Sidónio Pais. Lisbon, 1980. Arriaga, Manuel de. Na primeira presidência da República Portugueza: Um rápido relatório. Lisbon, 1916.■ Bell, Aubrey, F. G. In Portugal. London, 1912.■. Portugal of the Portuguese. London: Pitman, 1915.■ Bragança-Cunha, V. de. Revolutionary Portugal, 1910-1936. London: Swift, 1937.■ Brandão, Raúl. Memórias, 3 vols. In Brandão, Obras Completas. Lisbon, 1969.■ Burity, Braz [Pseudonym of Joaquim Madureira]. A Forja da Lei. Coimbra, 1915.■ Cabral, Manuel V. Portugal Na Alvorada Do Século XX. Lisbon, 1979.■. 'The Aesthetics of Nationalism: Modernism and Authoritarianism in Early 20th-Century Portugal." Luso-Brazilian Review (Madison, Wisc.) 26, 1 (Summer 1989): 15-43. Campos, Ezequiel. Política. Oporto, 1924.■ Cardia, Sottomayor, ed. Seara Nova: Antologia. Pela Reforma da República (1, 2) 1921-1926, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1971-72.■ Carqueja, Bento. O Povo de Portugal. Oporto, 1916.■. O Futuro de Portugal: Portugal Apos À Guerra. Oporto, 1920.■ Cortesão, Jaime. "Memórias da Grande Guerra." In Obras Completas de Jaime Cortesão. Lisbon, 1969.■ Cunha Leal, Francisco. As Minhas Memórias, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1966-68.■ Derou, Jean. Les Relations Franco-Portugaises ( 1910-1926). Paris: Publications de la Sorbonne, 1986.■ Fazenda, Pedro. A Crise Política. Lisbon, 1926.■ Ferrão, Carlos. História De la República. Lisbon, 1976.■ Ferreira, David. "5 De Outubro de 1910." In Joel Serrão, ed., Dicionário de História De Portugal III (1968): 264-67. Ferreira Martins, Gen. Luís, ed. Portugal na Grande Guerra, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1945.■ Gomes da Costa, Gen. Manuel. Memórias. Lisbon, 1930. História Política da Primeira República Portuguesa ( 1910-1915), 2 vols. Lisbon, 1973.■ Lorenzo, Felix. Portugal ( cinco anos de republica). Madrid, 1915.■ Machado, Bernardino. Depois de 21 de Maio. Lisbon, 1922.■ Machado Santos, Antônio. 1907-1910: A revolução portugueza. Relatôrio.■ Lisbon, 1911. Madureira, Arnaldo. 0 28 De Maio. Lisbon, 1982.■ Magno, David. Livro da Guerra de Portugal na Flandres. Oporto, 1920.■. A Situação Portuguesa. Oporto, 1926.■ Marques Guedes, Armando. Cinco Meses no governo. Oporto, 1926.■ Martins, Rocha. Memórias sobre Sidónio Pais. Lisbon, 1921.■ Medeiros, Fernando. Nas Orígens Do A Sociedade E A Economia Portuguesas Salazarismo. Lisbon, 1978. Medina, João. "Oh! a República!...," Estudos sobre o Republicanismo e a Primeira República Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1990.■, ed. História Contemporânea De Portugal: Primeira República, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1986.■ Mônica, Maria Filomena. "Uma Aristocracia Operária: Os Chapeleiros (18701913)." Análise Social 60, 2nd series (1979). Montalvor, Luís de, ed. História de Regimen Republicano em Portugal, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1930-32.■ Oliveira, César. O Operariado E A República Democrática, 1910-1914. Oporto, 1972.■ Oliveira Marques, A. H. de. "The Portuguese 1920s: A General Survey." Iberian Studies 2 (1973): 32-40.■. História De la República Portuguesa: As Estruturas De Base, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1973-74.■. A Primeira República Portuguesa: Alguns aspectos estruturais. Lisbon, 1975 ed.■. O Terceiro Governo Afonso Costa— 1917. Lisbon, 1977.■. Pabôn, Jesus. La Revolución Portuguesa, 2 vols. Madrid, 1945-46; Portuguese edition: Lisbon, 1961. Paxeco, Oscar. Os Que Arrancaram Em 28 De Maio. Lisbon, 1937. Peres, Damião, ed. História De Portugal. Ediçao Monumental: Supplemento. Oporto, 1954.■ Pessoa, Fernando. A Memória do Presidente— Rei Sidónio Pais. Lisbon, 1928.■ Relvas, José. Memórias Políticas, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1977-78.■ Schwartzman, Kathleen C. "Lucros, investimentos e coligações políticas na I República." Análise Social XVIII, 72-71 (1982): 741-58.■. The Social Origins of Democratic Collapse: The First Portuguese Republic in the Global Economy. Lawrence: University of Kansas Press, 1989.■ Serrão, Joel. Liberalismo, socialismo e republicanismo. Lisbon, 1979.■ Silva, Antônio Maria da. O Meu Depoimento, 2 vols. Mem Martins, 1978-82.■ Teixeira, Nuno Severiano. O Poder e a guerra, 1914-1918. Lisbon: Estampa, 1996.■, and Antônio Costa Pinto, eds. A Primeira República Portuguesa: Entre O Liberalismo E O Autoritarismo. Lisbon: Ed. Colibri, 2000.■ Telo, Antônio José. Decadência E Queda Da I República Portuguesa, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1980-84.■ Torre (Gomez), Hipôlito dela, and J. Sanchez Cervello. Portugal En El Siglo XX. Madrid: Ediciones Istmo: Colecciôn La Historia en sus textos, 1992.■ Valente, Vasco Pulido. "A República e as classes trabalhadores (Outubro 1910-Agosto 1911)." Análise Social IX, 31 (1972): 293-316.■. O Poder e o Povo: A Revolução de 1910. Lisbon, 1974.■ Veríssimo Serrao, Joaquim. História De Portugal. Volume XI: A Primeira República ( 1910-1926): História Política, Religiosa, Militar e Ultramarina. Lisbon, 1989.■. História De Portugal Volume XII: História Diplomática, Social, Económica e Cultural. Lisbon, 1990.■ Vincent-Smith, John. "Britain and Portugal, 1910-1916." Ph.D. dissertation, History, University of London, 1971.■ Wheeler, Douglas L. "The Portuguese Revolution of 1910." Journal of Modern History 44 (June 1972): 172-94.■. Republican Portugal: A Political History, 1910-1926. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1978.■. "Nightmare Republic: Portugal, 1910-1926." History Today (London) 32 (September 1981): 5-10.■ Young, George. Portugal Old and Young: An Historical Study. Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1917.■ Afonso, Rui. Injustiça: O Caso Sousa Mendes. Lisbon: Caminho, 1990.■ Antunes, José Freire. Os Americanos E Portugal. Vol. 1. Os anos de Ricard Nixon, 1969-1974. Lisbon, 1986.■. Os Americanos e Portugal. 1961. Kennedy e Salazar: O Leão e a Raposa. Lisbon, 1991.■. Salazar/Caetano. Cartas Secretas. 1932-1968. Lisbon: Círculo de Leitores, 1993.■. Jorge Jardim: Agente Secreto. Lisbon: Bertrand, 1996.■. Portugal na guerra do petróleo: Os Açores E As Vitórias de Israel 1973. Lisbon: Edeline, 2000. Aquino, Acácio Tómas de. O Segredo das Prisões Atlânticas. Lisbon, 1978. Araquistain, Luis. "Dictatorship in Portugal." Foreign Affairs 7 (October 1928): 41-53.■ Assac, Jacques Ploncard. Salazar. Paris: La Table Ronde, 1967.■ Baklanoff, Eric N. "The Political Economy of Portugal's Old Regime: Growth and Change Preceding the 1974 Revolution." World Development 7, 8-9 (August-September 1979): 799-812.■ Barreno, Maria Isabel, Maria Teresa Horta, and Maria Velho da Costa. The Three Marias: New Portuguese Letters. New York: Doubleday, 1975.■ Blume, Norman. "SEDES: An Example of Opposition in a Conservative Authoritarian State." Government and Opposition 12 (Summer 1977): 351-66.■ Braga da Cruz, Manuel. A origem da democracia-cristã em Portugal e o Sala-zarismo. Lisbon, 1979.■. "Notas para uma caracterização política do salazarismo." In Gabinete de Investigações Sociais. Análise Social: A Formação de Portugal Contemporâneo: 1900-1980. Vol. I, 72-74 (April-December 1981): 773-94.■. "O Integralismo nas origens do Salazarismo." Análise Social XVIII (1982): 1409-19.■. "A Oposição Eleitoral ao Salazarismo." Revista de História das Ideias V (1983).■. Monárquicos e Republicanos no Estado Novo. Lisbon, 1986.■ Cabral, Manuel V. "Sobre o fascismo e o seu avento em Portugal." Análise Social XII, 48 (1976), 873-915.■ Caetano, Marcello. A Missão Dos Dirigentes. Lisbon, 1966, 4th ed.■. Depoimento. São Paulo, 1974.■. História Breve das Constituições Portugueses. Lisbon, 1974.■. As Minhas Memórias de Salazar. Lisbon, 1977.■ Campinos, Jorge. A Ditadura Militar, 1926-1933. Lisbon, 1975. Carrilho, Maria. Forças Armadas e Mudança Política em Portugal no Século XX. Lisbon, 1985.■, et al. Portugal na Segunda Guerra Mundial Contributos para uma reavaliação. Lisbon, 1989.■ Carvalho, Otelo Saraiva de. Alvorada em Abril. Lisbon, 1977.■ Castanheira, Jose Pedro and Valdemar Cruz. A Filha Rebelde. Lisbon: Temas & Debates, 2003.■ Costa Pinto, Antônio, et al. O Fascismo Em Portugal [Proceedings of Conference, Lisbon, March 1980]. Lisbon, 1982.■. 'The Radical Right and the Military Dictatorship in Portugal: The National May 28 League (1928-1933)." Luso-Brazilian Review 23, 1 (Summer 1986): 1-15.■. "O Salazarismo No Recente Investigação Sobre o Fascismo Europeu...." Análise Social XXV (1990): 695-713.■. As camisas azuis: Ideologias, elites e movimentos fascistas em Portugal, 1914-1945. Lisbon: Estampa, 1994.■. Salazar's Dictatorship and European Fascism: Problems of Interpretation. New York: Columbia University Press, 1995.■. The Blue Shirts: Portuguese Fascists and the New State. New York: Columbia University Press, 2000.■ Delgado, Humberto. The Memoirs of General Delgado. London: Cassell, 1964.■. Memórias De Humberto Delgado. Iva Delgado and Antônio de Figueiredo, eds. Lisbon: Dom Quixote, 1991.■ Duarte Silva, A. E., et al. Salazar E O Salazarismo. Lisbon, 1989.■ Egerton, F. C. C. Salazar, Rebuilder of Portugal. London: Hodder & Stoughton, 1943.■ Ferraz, Artur Ivens. A Asenção de Salazar: Memórias de Ivens Ferraz. Lisbon, 1988.■ Ferro, Antônio. Salazar: O Homem E A Sua Obra. Lisbon, 1933. English edition: Salazar: Portugal and Her Leader. London: Faber & Faber, 1939, and editions in other languages.■. Portugal: Breviário Da Pátria Para Os Ausentes. Lisbon, 1946.■ Figueiredo, Antônio. Portugal and Its Empire: The Truth. London: Gollancz, 1961.■. "The Case Against Portugal." In Philip Mason, ed., Angola: A Symposium. Views of a Revolt, 46-57. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1962.■. Portugal. Fifty Years of Dictatorship. Harmondsworth, U.K.: Penguin, 1975.■ Fox, Ralph. Portugal Now. London, 1937.■ Freitas do Amaral, Diogo. O Antigo Regime E A Revolução. Memórias Políticas ( 1941-1975). Lisbon: Bertrand, 1995.■ Fryer, Peter, and Patricia McGowan Pinheiro. Oldest Ally: A Portrait of Sala-zar's Portugal. London: Dobson, 1961.■ Gallagher, Tom. "Controlled Repression in Salazar's Portugal." Journal of Contemporary History 14, 3 (July 1979): 385-403.■. "The Mystery Train: Portugal's Military Dictatorship 1926-32." European Studies Review 11 (1981): 325-54.■. "From Hegemony to Opposition: The Ultraright Before and After 1974." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal, 81-103. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■. Portugal: A Twentieth Century Interpretation. Manchester, U.K.: Manchester University Press, 1983.■ Galvão, Henrique. Santa Maria: My Crusade for Portugal. London: Weiden-feld and Nicholson, 1961.■. Carta Aberta ao Dr. Salazar. Lisbon, 1975.■ Gamier, Christine. Vacances avec Salazar. Paris, 1952; American edition: Salazar in Portugal: An Intimate Portrait. New York, 1954. Georgel, Jacques. O Salazarismo. Lisbon, 1985.■ Gouveia, Fernando. Memórias de um Inspector da PIDE. Lisbon, 1979.■ Graham, Lawrence S. "Portugal: The Bureaucracy of Empire." LADAC Occasional Papers series 2, 9 (1973). Austin, Tex.: Institute of Latin American Studies.■. Portugal: The Decline and Collapse of an Authoritarian Order. Beverly Hills, Calif.: Sage, 1975.■. "The Military in Politics: The Politicization of the Portuguese Armed Forces." In L. S. Graham and H. M. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal, 221-56. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■, and Harry M. Makler, eds. Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■, and Douglas L. Wheeler, eds. In Search of Modern Portugal: The Revolution and Its Consequences. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■ Guyomard, George. La Dictature Militaire au Portugal. Paris, 1927.■ Janeiro, Helena Pinto. Salazar E Pétain. Relações Luso-Francesas Durante A II Guerra Mundial ( 1940-44). Lisbon: Cosmos, 1998.■ Kay, Hugh. "A Catholic View." In Philip Mason, ed., Angola: A Symposium. Views of a Revolt, 80-103. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1962.■. Salazar and Modern Portugal. New York: Hawthorne, 1970.■ Leeds, Elizabeth. "Labor Export, Development and the State: The Political Economy of Portuguese Emigration." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Political Science, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1984.■ Lewis, Paul H. "Salazar's Ministerial Elite, 1932-1968."Journal of Politics 40 (August 1987): 622-47.■ Lins, Alvaro. Missão em Portugal. Lisbon, 1974.■ Linz, Juan. "Foreword." In L. Graham and H. M. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents, xii-xi. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■ Lucena, Manuel. A evolução do sistema corporativo português, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1976.■. "The Evolution of Portuguese Corporatism under Salazar and Caetano." In L. Graham and H. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents, 47-88. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■ McCarthy, Mary. "Letter from Lisbon." The New Yorker XXX, 51 (February 5, 1955): 80-96.■ Magalhães Godinho, Vitorino. O Socialismo e o Futuro da Peninsula. Lisbon, 1969.■ Makler, Harry M. A " Elite" Industrial Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1969.■. "The Portuguese Industrial Elite and Its Corporative Relations." Economic Development and Cultural Change 24, 3 (April 1976): 495-526.■ Martins, Hermínio. "Opposition in Portugal." Government and Opposition 4 (Spring 1969): 250-63.■. "Portugal." In S. J. Woolf, ed., European Fascism, 302-36. New York: Vintage, 1969.■. "Introduction: Tristes durées." In R. Feijô, H. Martins and J. de Pina-Cabral, eds., Death in Portugal: Studies in Portuguese Anthropology and Modern History. Oxford: Journal of the Anthropological Society of Oxford, 1983.■ Medina, João. Salazar em França. Lisbon, 1977.■. Salazar E Os Fascistas: Salazarismo e Nacional-Sindicalismo: A história dum conflito 1932/1935. Lisbon, 1978.■ Ministério dos Negôcios Estrangeiros, ed. Dez Anos de Política Externa ( 1936-1947): A Nação Portuguesa e a Segunda Guerra Mundial, 12 vols., and in progress. Lisbon, 1964.■ Mônica, Maria Filomena. Educação e Sociedade no Portugal de Salazar. Lisbon, 1978.■ Nogueira, Alberto Franco. Salazar, 6 vols. Coimbra and Oporto, 1978-85.■ Oliveira, César. Portugal e a II República de Espanha, 1931-l 936. Lisbon, 1985.■. Salazar E A Guerra Civil De Espanha, 2nd ed. Lisbon, 1988.■. Os Anos Decisivos: Portugal 1962-1985. Um testemunho. Lisbon: Presença, 1993.■ Oliveira Marques, A. H. de. A Maçonaria Portuguesa e o Estado Novo. Lisbon, 1975.■. History of Portugal; 1 in 2 vols. New York: Columbia University Press, 1976 ed.■. A Liga de Paris E A Ditadura Militar, 1927-1928. Lisbon, 1976.■. História de Portugal, 2 vols. Lisbon: 1980 and later eds.■, ed. A Literatura Clandestina Em Portugal, 1926-1932, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1990.■ Patriarca, Fátima. A Questaão Social no Salazarismo. Vol. 1. Lisbon: INCM, 1995.■. Sindicatos contra Salazar: A revolta do 18 de janeiro de 1934. Lisbon: Instituto de Ciências Sociais, 2000. Pattee, Richard. Portugal and the Portuguese World. Milwaukee, Wisc.: Bruce, 1957.■ Payne, Stanley G. A History of Spain and Portugal. Volume 2. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1973.■. "Salazarism: 'Fascism' or 'Bureaucratic Authoritarianism'?" In Estudos de história portuguesa: Homenagem à A. H. de Oliveira Marques. Lisbon, 1983.■ Pereira, José Pacheco. Conflitos sociais nos campos do sul de Portugal. Mem Martins, 1978.■. A Preparação Ideológica da Intervenção Militar de 28 de Maio de 1926. Oporto, 1978.■. "Problemas da história do P. C. P." In A. Costa Pinto et al., eds., O Fascismo Em Portugal [Proceedings of Conference, University of Lisbon, March 1980], 269-85. Lisbon, 1982.■ Pimentel, Irene Flunser. Judeus em Portugal durante a II Guerra Mundial. Em fuga de Hitler e do Holocausto. Lisbon: Esfera dos Livros, 2006.■ Pires, José Cardoso. Dinossauro Excelentíssimo. Lisbon, 1972.■ Porch, Douglas. The Portuguese Armed Forces and the Revolution. London: Croom Helm, 1977.■ Presidência do Conselho de Ministros. Comissão do Livro Negro Sobre o Regime Fascista ["Black Book" series]. Eleições No Regime Fascista. Lisbon, 1979.■. A Política De Informação No Regime Fascista, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1980.■. Livros Proibidos No Regime Fascista. Lisbon, 1981.■. Presos Políticos No Regime Fascista, 5 vols. Lisbon, 1981-87.■. Relatórios Para Oliveira Salazar, 1931-1939. Lisbon, 1981.■. Discriminação Política No Emprego No Regime Fascista. Lisbon, 1982.■. Proibição Da " Time" No Regime Fascista [ Time magazine July 23, 1946, with Dr. Salazar on cover]. Lisbon, 1982.■. Os Estudantes No Regime Fascista. Lisbon, 1983.■. Trabalho, Sindicatos E Greves No Regime Fascista. Lisbon, 1984.■. Correspondência Entre Mário De Figueiredo E Oliveira Salazar. Lisbon, 1986.■. Repressão Política E Social No Regime Fascista. Lisbon, 1986.■. Correspondência de Pedro Teotónio Pereira para Oliveira Salazar vol. 1 ( 1931-1939), 2 vols. Lisbon, 1987-89.■ Queiroga, Captain Fernando. Portugal Oprimido. Lisbon, 1974.■ Raby, David L. "Populism and the Portuguese Left: From Delgado to Otelo." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal, 61-80. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■. Fascism and Resistance in Portugal: Communists, Liberals and the Military Dissidents in the Opposition to Salazar, 1941-1974. Manchester, U.K.: Manchester University Press, 1988.■ Raby, Dawn Linda. "The Portuguese Presidential Election of 1949: A Successful Government Maneuver?" Luso-Brazilian Review 27, 1 (Summer 1990): 63-77.■ Rêgo, Raúl. Diário Político. Lisbon, 1969; 1974, 2nd ed.■. Horizontes Fechados. Oporto, 1970.■. Horizontes Fechados/ Páginas de Política, 3rd ed. Lisbon, 1974.■ Ribeiro, Aquilino. Volfrâmio. Lisbon, 1944.■. Quando os Lobos Uivam. Lisbon, 1958; English ed. Patricia McGowan■ Pinheiro, trans. London: Cape, 1963.■ Robinson, Richard A. H. Contemporary Portugal: A History. London and Boston: Allen & Unwin, 1979.■ Rocha, José Antônio De Oliveira. The Portuguese Administrative State. Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Political Science, University of South Carolina, 1986.■ Rosa, Frederico Delgado. Humberto Delgado. Biografia Do General Sem Medo. Lisbon: Esfera dos Livros, 2008. Rosas, Fernando. O Estado Novo Nos Anos Trinta: 1928-1938. Lisbon, 1986.■. O Salazarismo E A Aliança Luso-Britânica. Lisbon, 1988.■. Portugal Entre A Paz E A Guerra... 1939-1945. Lisbon, 1990.■. O Estado Novo ( 1926-1974). Vol. VII of José Mattoso, ed. Historia De■ Portugal. Lisbon: Edit. Estampa, 1994.■. and Pedro Aires Oliveira (eds.). A Transicao Falhada. O Marcelismo e o Fim do Estado Novo ( 1968-1974). Lisbon: Edit. Noticias, 2004.■ Rudel, Christian. Salazar. Paris: Mercure de France, 1969.■ Sá Carneiro, Francisco. Uma Tentativa de Participação política. Lisbon, 1971.■. A Liberalização bloqueada. Lisbon, 1972.■. Vale a Pena ser Deputado? Fundão, 1973.■ Salazar, Antônio de Oliveira. Discursos E Notas Políticas. [Speeches, Broadcasts, Notes and Statements, 1928-1966, 6 vols. Coimbra, 1935-1966]. Several editions.■. Doctrine and Action: Internal and Foreign Policy of the New Portugal, I928-1939. Robert Edgar Broughton, trans. London: Faber & Faber, 1939.■. "Realities and Trends of Portugal's Policies." International Affairs XXXIX, 2 (April 1963): 169-83.■. The Road for the Future [Speeches, statements of policy made during 1928-62]. Lisbon, 1963.■. Entrevistas: 1960-1966 [interviews]. Coimbra, 1967.■. Salazar: Pensamento e doutrina política. Textos anthológicos. [Anthology of speeches, writings, interviews granted, 1914-68]. Mendo C. Henriques and Gonçalo de Sampaio e Melo, eds. Lisbon, 1989.■ Santana, Emilio. Historia de um Atentado. O atentado contra Salazar. Lisbon, 1976.■ Schmitter, Philippe C. Corporatism and Public Policy in Authoritarian Portugal. London: Sage, 1975.■. "Liberation by Golpe: Retrospective Thoughts on the Demise of Authoritarian Rule in Portugal." Armed Forces and Society 2 (Nov. 1975): 5-33.■. "The Impact and Meaning of Elections in Authoritarian Portugal, 1933-74." In G. Hermet et al., eds., Elections Without Choice. Basingstoke, U.K.: Macmillan, 1978.■. "'The 'Regime d'exception' That Became the Rule: Forty-Eight Years of Authoritarian Domination in Portugal." In L. S. Graham and H. M. Mak-ler, eds., Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents, 3-46. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■, and Gerhard Lehmbruch, eds. Trends towards Corporatist Intermediation. Beverly Hills, Calif.: Sage, 1979.■ Shelton, Richard L. "Development of the Communist Party of Portugal, 1921-1976." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of History, St. Louis University, 1984.■ Silva, José. Memórias de um operário. Vol. 2. Oporto, 1971. Soares, Mário. Escritos Políticos. Lisbon, 1969.■. Portugal Bailloné. Paris, 1972; Portuguese edition: Portugal Amordaçado, Lisbon, 1974; English edition: Portugal's Struggle for Liberty. Translated by Mary Gawsworth. London: Allen & Unwin, 1975.■ Spínola, Antônio de. Portugal e o Futuro. Lisbon, 1974; English edition: Johannesburg: Perskor, 1974.■ Teixeira, Luis [Sampaio]. Perfil de Salazar. Lisbon, 1938.■ Teixeira, Nuno Severiano. "From Neutrality to Alignment: Portugal in the Foundation of the Atlantic Pact." EUI: Working Papers in History. Florence, Italy: European University Institute, 1991.■ Telo, Antônio José. Portugal na Segunda Guerra. Lisbon, 1987.■. A Neutralidade Portuguesa e o Ouro Nazi. Lisbon: Quetzal, 2000.■ Teotônio Pereira, Pedro. Memórias, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1972-73.■ Vasco, Nuno. Vigiados e perseguidos. Lisbon, 1977.■ Veríssimo, Serrão. Marcelo Caetano: Confidencias No Exílio. Lisbon, 1985. Vintras, R. E. The Portuguese Connection: The Secret History of the Azores Base. London: Bachman & Turner, 1974. West, S. George. The New Corporative State of Portugal [Inaugural lecture, King's College, London, Feb. 1937]. London: New Temple Press, 1937. Wheeler, Douglas L. "Thaw in Portugal." Foreign Affairs 48, 4 (July 1970): 769-81.■. "Days of Wine and Carnations: The Portuguese Revolution of [April 25] 1974." Bulletin. New Hampshire Council on World Affairs XX (July 1974): 1-10.■. "Antônio de Oliveira Salazar (1889-1970)." In Jacques Frémontier, ed., Les Hommes d'Siecle XX: Les Dictateurs. Paris: Mazenod, 1978.■. "The Military and the Portuguese Dictatorship, 1926- 1974." In S. Graham and H. M. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents, 191-219. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■. "In the Service of Order: The Portuguese Dictatorship's Political Police (PVDE; PIDE) and the British, German and Spanish Intelligence [Services]." Journal of Contemporary History 24, 2 (January 1983): 1-25.■. Republican Portugal: A Political History, 1910-1926. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1978. Portuguese edition: História Política de Portugal, 1910-l926. Mem Martins, 1985.■. "The Price of Neutrality: Portugal, the Wolfram Question, and World War II." Luso-Brazilian Review [two part article] 12, 1-2 (Summer 1986; Winter 1986): 107-27.■. A Ditadura Militar Portuguesa, 1926-1933. Mem Martins, 1988.■. "The Third Pig: From Theory to Grubby Fact in Reassessing the Estado Novo." In B. F. Taggie and R. W. Clement, eds., Iberia & the Mediterranean, 145-68. Warrensburg: Central Missouri State Press, 1989.■. "And Who Is My Neighbor? A World War II Hero of Conscience for Portugal." Luso-Brazilian Review 26, 1 (Summer 1989): 119-39.■. "Antônio de Oliveira Salazar (1889-1970)." In Research Guide to European Historical Biography. Vol. 3. Washington, D.C.: Beacham, 1992.■. "'Estado Presente de tranquilidade,' posto em causa: Portugal observado e analisado no contexto internacional de 1958-59." In Iva Delgado, Carlos Pacheco, and Telmo Faria, eds., Humberto Delgado: As eleições de 58, 448-71. Lisbon: Vega, 1998.■, and René Pélissier. Angola. New York: Praeger and London: Pall Mall, 1971; reprinted: Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1977.■ Wiarda, Howard J. "Toward a Framework for the Study of Political Change in Iberic-Latin Tradition: The Corporative Model." World Politics 25 (January 1973): 206-35.■. Corporatism and Development: The Portuguese Experience. Amherst: University of Massachusetts Press, 1977.■. "The Corporatist Tradition and the Corporative System in Portugal." In L. S. Graham and H. M. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal. The Revolution and Its Antecedents, 89-122. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■ Afonso, Rui. Um Homem Bom. Aristides De Sousa Mendes O " Wallenberg Portugues." Lisbon: Caminho, 1995.■. Injustica-o Caso Sousa Mendes. Lisbon: Caminho, 1990.■ Agudo, Manuel Ros. La Guerra Secreta de Franco ( 1939-1945). Barcelona, 2002.■ Anon., Fugindo a Hitler e a Salazar e ao Holocausto-Refugiados em Portugal entre 1933-1945. Lisbon: Soc. Tipografica, 1994.■ Barreiros, Jose Antonio. A Lusitania Dos Espioes. Lisbon: Hugin, 1995.■. O Espiao Alemao Em Goa. Operacao Long Shanks, 1943. Lisbon, 2001.■ Beevor, J. G. SOE. Recollections and Reflections 1940-45. London, 1981. Bloch, Michael. Operation Willi: The Plot to Kidnap the Duke of Windsor July 1940. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1984. Carrilho, Maria et. al., Portugal Na Segunda Guerra Mundial. Contributos para uma reavaliacao. Lisbon: Dom Quixote, 1989. Cole, Robert. Britain and the War of Words in Neutral Europe, 1939-45. New York: St. Martin's, 1990. Colvin, Ian. Flight 777. London: Evans, 1957. Dias, Mariana Tavares. Lisboa nos Anos 40. Lisbon: Quimera, 1997. Eizenstadt, Stuart E. Coord. U.S. and Allied Efforts to Recover and Restore Gold and Other Assets Stolen or Hidden by Germany during World War II. New York, 2001.■ Fralon, Jose-Alain. A Good Man in Evil Times. The Story of Aristides De Sousa Mendes: The Man Who Saved the Lives of Countless Refugees in World War II. New York: Carroll & Graf, 2001.■ Giraudoux, Jean. Portugal. Paris: Grasset, 1958.■ Johns, Philip. Within Two Cloaks. Missions With SIS and SOE. London, 1979.■ Koestler, Arthur. Arrival and Departure. London, 1943.■ Leitz, Christian. Sympathy for the Devil: Neutral Portugal and Nazi Germany in World War II. New York, 2001.■ Louca, Antonio. Hitler e Salazar. Comercio em tempos de Guerra 1940-1944. Lisbon, 2000.■ Luca, Antonio. "Portugal's Double Game: Between the Nazis and the Allies." In Avi Beker, ed., The Plunder of Jewish Property during the Holocaust. Confronting European History. New York, 2001. MacIntyre, Ben. Agent Zigzag. New York: Harmony, 2007. Martins, Maria Joao. O Paraiso Triste. O Quotidiano em Lisboa durante a II Grande Guerra. Lisbon: Vega, 1994. Masterman, J.C. The Double-Cross System in the War of 1939 to 1945. New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 1972. Muggeridge, Malcolm. Chronicles of Wasted Time. Chronicle 2: The Infernal Grove. New York: William Morrow, 1974.■ Nery, Julia. O Consul. Lisbon: Dom Quixote, 1991.■ Pimentel, Irene Flunser. Judeus em Portugal na Segunda Guerra Mundial. Lisbon, 2006.■ Popov, Dusko. Spy/ Counterspy. London, 1974.■ Prokosch, Frederick. The Conspirators. New York, 1943.■ Remarque, Erich Maria. The Night in Lisbon. New York, 1966.■ Ribeiro, Aquilino. Volfarmio Romance. Lisbon: Bertrand, 1943.■ Rosas, Fernando. Portugal entre a Paz e a Guerra. Lisbon: Estampa, 1990.■ Saint-Exupery, Antoine. Wartime Writings, 1939-1944. New York: Harcourt, Brace, 1986.■ Teixeira, Nuno Severiano, ed. Portugal E A Guerra. Historia das Intervencoes militares portuguesas nos grandes conflitos mundiais seculos XIX e XX. Lisbon: Colibri, 1998.■ Telo, Antonio Jose. Propagandal E Guerra Secreta Em Portugal 1939-45. Lisbon, 1990.■. Portugal na Segunda Guerra ( 1941-1945), 2 vols. Lisbon, 1991.■. A neutralidade portuguesa e o ouro nazi. Lisbon, 2000.■ Vintras, R.E. The Portuguese Connection: The Secret History of the Azores Base. London: Bachman and Turner, 1974. Wheeler, Douglas L. "The Age Old Business of Espionage." 1987 World Book Year Book. Chicago, 1987.■. "'In the Service of Order.' The Portuguese Political Police and the British, Germany and Spanish Intelligence [Services]." Journal of Contemporary History 36: no. 3 (Jan. 1983), 1-25.■. "And Who is My Neighbor? A World War II Hero of Conscience for Portugal." Luso-Brazilian Review 23 (no. 2) (Summer 1989), 119-39.■. "The Price of Neutrality: Portugal, the Wolfram Question, and World War II." Luso-Brazilian Review (Madison, WI), 23 (nos.1, 2) (Summer, 1986; Winter, 1986). 97-111; 108-127.■. "Last of the Great Air Mysteries of the War [World War II]." Bridport and Lyme Regis Gazette (Dorset, U.K.), June 5, 2003, 24-25.■. "Leslie Howard Helped Win World War II," St. Louis Post-Dispatch (St. Louis, Mo.), April 3, 5, 2005.■ Wilson, Robert. A Small Death in Lisbon. London, 2000.■. The Company Of Strangers. San Diego, 2002.■ Wylie, Neville. "An Amateur Learns His Job? Special Operations Executive in Portugal, 1940-42." Journal of Contemporary History. 36: no. 3 (2001), 441-57.■ Ferreira Martins, General. Historia do Exercito Portugues. Lisbon: Inquerito, 1945.■ Kaulza de Arriaga, General. Guerra e Politica. Em nome da verdade. Os anos decisivos. Lisbon: Referendo, 1987.■ Medeiros Ferreira, Jose. O Comportamento Politico dos Militares, Forcas Armadas e Regimes Politicos em Portugal no seculo XX. Lisbon: Estampa, 1992.■ Pereira Marques, Fernando. Exercito e Sociedade em Portugal. No Declinio do Antigo Regime e advento do Liberalismo. Lisbon: Regra do Jogo, 1981.■ Porch, Douglas. The Portuguese Armed Forces and the Revolution. London: Croom Helm, 1977.■ Ribeiro Dos Santos, Antonio Pedro. O Estado E A Order Publica. As Institui-coes Militares Portuguesas. Lisbon: Instituto Superior De Ciencias Sociais E Politicas, 1999.■ Saraiva de Carvalho, Otelo. Alvorada em Abril. Amadora (Portugal): Bertrand, 1977.■ Selvagem, Carlos. Portugal Militar. Compendio de Historia Militar e Naval de Portugal. Lisbon: Imprensa Nacional, 1931.■ Spinola, Antonio de. Portugal e o Futuro. Lisbon: Arcadia, 1974.■. Pais Sem Rumo. Contributo para a historia de uma Revolucao. Lisbon: Scire, 1978.■ Teixeira, Nuno Severiano. Portugal e a Guerra. Historia das intervencoes militares portuguesas nos grandes conflitos mundiais do seculo XX. Lisbon: Ed. Colibri, 1999.■. Coord., Nova Historia Militar de Portugal, 5 vols. Lisbon: Circulo de Leitores, 2003-.■ Valente, Vasco Pulido. O Poder e o Povo. A Revolucao de 1910. Lisbon: Moraes, 1976, 1982.■ Wheeler, Douglas L. Republican Portugal: A Political History ( 1910-1926). Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1978, 1998.■. A Ditadura Militar Portuguesa ( 1926-1933). Mem Martins: Europa- America, 1988.■. "The Military and the Portuguese Dictatorship, 1926-1974: "The Honor of the Army." In Lawrence S. Graham and Harry M. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents. 191-219. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■ Aguiar, Joaquim. "Hidden Fluidity in an Ultra-Stable Party System." In E. de Sousa Ferreira and W. C. Opello, Jr., eds., Conflict and Change in Portugal, 1974-1984, 101-27. Lisbon, 1985.■ Braga da Cruz, Manuel, ed. Sistema Eleitoral Portugües: Debate Político e Parlamentar. Lisbon: Imprensa Nacional/ Casa da Moeda, 1998.■, ed. "Portugal Político 25 Anos Depois." In Análise Social XXXV, 154/155 (Summer, 2000): 1-404.■ Bruneau, Thomas C., and Alex Macleod. Politics in Contemporary Portugal: Parties and the Consolidation of Democracy. Boulder, Colo.: Rienner, 1986.■ Bruneau, Thomas C., ed. Political Parties and Democracy in Portugal. Boulder, Colo.: Westview, 1997. Carlucci, Frank. "Confiei no Povo Portugues." Visao (Lisbon), April 10, 1997, 46-47.■. "The View from the U.S. Embassy." In Hans Binnendijk, ed., Authoritarian Regimes in Transition. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Dept. of State, Foreign Service Institute, Center for the Study of Foreign Affairs, 1987.■ Coelho, Mário Baptista, ed. Portugal. O Sistema Política a Constitucional, 1974-87. Lisbon: Instituto de Ciências Sociais, UNL, 1989.■ Costa Pinto, Antonio. "Settling Accounts with the Past in a Troubled Transition to Democracy: The Portuguese Case." In Alexandra Barahona De Brito, Carmen Gonzalez-Enriquez, and Paloma Aguilar, eds., The Politics of Memory: Transitional Justice in Democratizing Societies, 65-91. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2001.■ Cruzeiro, Maria Manuela. Costa Gomes-o Ultimo Marechal. Lisbon: Edit. Noticias, 1998.■ Domingos, Emídio Da Veiga. Portugal Político. Análise das Instituiçoes. Lisbon, 1989.■ Goldey, David. "Elections and the Consolidation of Portuguese Democracy: 1974-1983." Electoral Studies 2, 3 (1983): 229-40.■ Graham, Lawrence S. "Institutionalizing Democracy: Governance in Post-1974 Portugal." In Ali Farazmand, ed., Handbook of Comparative and Development Public Administration, 81-90. New York: Dekker, 1991.■, and Douglas L. Wheeler, eds. In Search of Modern Portugal: The Revolution and Its Consequences. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■ Gunther, Richard. "Spain and Portugal." In G. A. Dorfman and P. J. Duignan, eds., Politics in Western Europe, 186-236. Stanford, Calif.: Hoover Institution Press, 1988.■ Magone, José Maria. European Portugal: The Difficult Road to Sustainable Democracy. Basingstoke, U.K.: Macmillan, 1997.■ Maxwell, Kenneth. The Making of Portuguese Democracy. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995.■, ed. Portugal in the 1980s: Dilemmas of Democratic Consolidation. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1986.■ Maxwell, Kenneth R., and Scott C. Monje, eds. Portugal: The Constitution and the Consolidation of Democracy, 1976-1989. New York: Camões Center, RIIC, Camões Center Special Report No. 2, Columbia University, 1991.■ Opello, Walter C., Jr. "The New Parliament in Portugal." Legislative Studies Quarterly, 3 (May 1978): 309-334.■. "Local Government and Political Culture in a Portuguese Rural County." Comparative Politics 13 (April 1981): 271-89.■. "Portugal's Administrative Elite: Social Origins and Political Attitudes." West European Politics 6 (Jan. 1983): 63-74.■. Portugal's Political Development: A Comparative Approach. Boulder, Colo.: Westview, 1985.■ Pinto Balsemão, Francisco. "The Constitution and Politics: Options for the Future." In K. Maxwell, ed., Portugal in the 1980s, 197-232. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1986.■ Sartori, Giovanni. "Portugal." In Sartori, G, ed., Parties and Party Systems. Vol. 1, 131-45. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1976. Secretary of State for Mass Communications. Constitution of the Portuguese Republic [1976]. Lisbon, 1977.■ Aguiar, Joaquim. A Ilusão do poder: Analise do Sistema Partidário, 19761982. Lisbon, 1983. Almeida, Diniz de. Orígens e Evolução do Movimento dos Capitães. Lisbon, 1977.■. Ascensao, Apogeu e Queda do MFA, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1979.■ Alves, Márcio Moreira. Les Soldats Socialistes du Portugal. Paris: Gallimard, 1975.■ Antunes, José Freire. Sá Carneiro: Um Meteoro Nos Anos Setenta. Lisbon, 1982.■. O Segredo do 25 de Novembro. Mem Martins, 1983.■ Arouca, Manuel. Os Filhos Da Costa Do Sol. Mem Martins, 1989. Audibert, Pierre, and Daniel Brignon. Portugal: Les nouveaux centurions. Paris, 1974.■ Baptista, Jacinto. Caminhos para uma revolução. Lisbon, 1975. Barreto, Antônio. Memórias da Reforma Agrária. Mem Martins: Europa-Amé-rica, 1983.■, and C. V. Preto, eds. A Situação Social em Portugal, 1960-1996. Lisbon: Instituto de Ciências Sociais, 1996.■ Bermeo, Nancy Gina. "Worker Management in Industry: Reconciling Representative Government and Industrial Democracy in a Polarized Society." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal, 181-98. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■. The Revolution within the Revolution: Workers' Control in Rural Portugal. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1986.■ Braeckman, Colette. Portugal: Revolution surveilée. Brussels: Rossei, 1975.■ Braga da Cruz, Manuel. "O Presidente da República na génese e evolução do sistema de governor portugües." Análise social XXIX, 125-26 (1994): 237-65.■, coord. "Portugal Político 25 Anos Depois." Análise Social XXXV, 154/155 (Summer 2000): 1-404. Bruneau, Thomas C. "Popular Support for Democracy in Post-revolutionary Portugal: Results from a Survey." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal, 21-42. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■. Politics and Nationhood: Post-Revolutionary Portugal. New York: Praeger, 1984.■. "Portugal Fifteen Years after the April Revolution." Field Staff Reports ( 1989-90/ No. 1, Europe), 3-11. Indianapolis, Ind.: Universities Field Staff International, 1990.■, and Alex Macleod. Politics in Contemporary Portugal: Parties and the Consolidation of Democracy. Boulder, Colo.: Rienner, 1986.■ Carvalho, Ortelo Saraiva de. Cinco Meses Mudaram Portugal. Lisbon, 1975.■. Alvorada em Abril. Lisbon, 1977.■ Cid, Augusto. PREC-Processo Revolucionário Eventualmente Chocante. Viseu, 1977.■ Costa Lobo, Marina, and Pedro C. Magalhaes. "From 'Third Wave' to 'Third Way': Europe and the Portuguese Socialists (1975-1999)," Journal of Southern Europe and the Balkans 3, no. 1 (2001), 25-35.■ Costa Pinto, Antônio, ed. Modern Portugal. Palo Alto, Calif.: SPOSS, 1998.■, and Nuno Severiano Teixeira, eds. Southern Europe and the Making of the European Union. New York: Columbia Univ. Press, 2002.■ Cunhal, Alvaro. A Revolução Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1975.■ Dias, Eduardo Mayone. Portugal's Secret Jews: The End of an Era. Rumford, R.I.: Peregrinação Publications, 1999.■ Downs, Charles. "Comissões de Moradores and Urban Struggles in Revolutionary Portugal." International Journal of Urban and Regional Research 4 (1986): 267-94.■. Revolution at the Grassroots: Community Organizations in the Portuguese Revolution. Albany: State University of New York Press, 1989.■ Dufour, Jean-Marc. Prague sur Tage. Paris, 1975.■ Durão Barroso, José. Le systémepolitiqueportugais face à l'intégration euro-péenne. Lisbon, 1983.■ Eisfeid, Rainer. "Portugal: What Role/What Future?" In K. Maxwell, ed., Portugal Ten Years after the Revolution. New York: RIIC, Columbia University, 1984.■. Sozialistischer Pluralismus in Europa: Ansãtze und Scheitern am Beispiel Portugal. Cologne: Verlag Wissenchaft ünd Politik, 1985.■. "Portugal and Western Europe." In K. Maxwell, ed., Portugal in the 1980s, 29-62. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1986.■ Farinha, Luis. "Regresso a Europa. Uma opcao feliz." Historia. XXIX; 95, III series (March 2007), 23-33.■ Faye, Jean-Pierre, ed. Portugal: The Revolution in the Labyrinth. Nottingham, U.K.: Spokesman, 1976. Ferreira, Hugo Gil, and Michael W. Marshall. Portugal's Revolution: Ten Years On. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1986. Figueira, João Costa. Cavaco Silva: Homem de Estado. Lisbon, 1987. Filoche, Gérard. Printemps Portugais. Paris: Editions Action, 1984. Frémontier, Jacques. Os Pontos nos ii. Lisbon, 1976. Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian. 25 de Abril-10 anos depois. Lisbon, 1984. Futscher Pereira, Bernardo. "Portugal and Spain." In K. Maxwell, ed. Portugal in the 1980s, 63-87. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1986.■ Gama, Jaime. Política Externa Portuguesa 1983-85: Ministério dos Negôcios Estrangeiros. Lisbon, 1986.■. "Preface." In J. Calvet de Magalhães, A. de Vasconcelos, and J. Ramos Silva, eds., Portugal: An Atlantic Paradox, 9-11. Lisbon, 1990. Gaspar, Jorge, and Nuno Vitorino. As Eleições De 25 De Abril: Geografia E Imagem Dos Partidos. Lisbon, 1976.■. "10 Anos de Democracia: Reflexos na geografia política." In E. de Sousa Ferreira and W. C. Opelio, Jr., eds., Conflict and Change in Portugal 1974-1984/ Conflitos e Mudanças em Portugal, 1974-1984, 135-55. Lisbon, 1985.■, et al. As Eleições para assembleia da república, 1979-1983: Estudos de geografia eleitoral. Lisbon, 1984. Gaspar, Jorge, and Nuno Vitorino, eds. Portugal em mapas e em números. Lisbon, 1981.■ Giaccone, Fausto. Una Storia Portoghese/ Uma História Portuguesa. Palermo: Randazzo Focus, 1987.■ Gladdish, Ken. "Portugal: An Open Verdict." In Geoffrey Pridham, ed. Securing Democracy: Political Parties and Democratic Consolidation in Southern Europe, 104-25. London and New York: Routledge, 1990.■ Graham, Lawrence S. The Decline and Collapse of an Authoritarian Order. Beverly Hills, Calif.: Sage, 1975.■, and Harry M. Makler, eds. Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■, and Douglas L. Wheeler, eds. In Search of Modern Portugal: The Revolution and Its Consequences. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■ Grayson, George W. "Portugal and the Armed Forces Movement." Orbis XIX, 2 (Summer 1975): 335-78.■ Green, Gil. Portugal's Revolution. New York: International, 1976.■ Hammond, John L. Building Popular Power: Workers' and Neighborhood Movements in the Portuguese Revolution. New York: Monthly Review Press, 1988.■ Harsgor, Michael. Naissance d'un Nouveau Portugal. Paris: Ed. du Seuil, 1975.■. Portugal in Revolution. Washington, D.C.: CSIS and Sage, 1976.■ Harvey, Robert. Portugal, Birth of a Democracy. London: Macmillan, 1978.■ Herr, Richard, ed. Portugal: The Long Road to Democracy and Europe. Berkeley, Calif.: International and Area Studies, 1992.■ Insight Team of the Sunday [London] Times. Insight on Portugal: The Year of the Captains. London: Deutsch, 1975.■ Janitschek, Hans. Mario Soares: Portrait of a Hero. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1985.■ Keefe, Eugene K., et al. Area Handbook for Portugal, 1st ed. Washington, D.C.: Foreign Area Studies of American University, 1977. Kramer, Jane. "A Reporter at Large: The Portuguese Revolution." The New Yorker (Dec. 15, 1975): 92-131.■ Lauré, Jason, and Ettagal Lauré. Jovem Portugal: After the Revolution. New York: Straus, Farrar and Giroux, 1977.■ Livermore, H. V. A New History of Portugal. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1976.■ Lourenço, Eduardo. Os Militares e O Poder. Lisbon, 1975.■. O Fascismo Nunca Existiu. Lisbon, 1976.■. "Identidade e Memôria: o caso português." In E. de Sousa Ferreira and W. C. Opello, Jr., eds., Conflict and Change in Portugal, 1974-l 984, 17-22. Lisbon, 1985.■ Lucena, Manuel. Evolução e Instituições: A Extinção dos Grémios da Lavoura Alentejanos. Mem Martins, 1984.■. "A herança de duas revoluções." In M. Baptista Coelho, ed., Portugal: O Sistema Político e Constitucional, 1974-87, 505-55. Lisbon, 1989.■ Macedo, Jorge Braga de, and S. Serfaty. Portugal since the Revolution: Economic and Political Perspectives. New York: Praeger, 1981.■ Magone, José M. European Portugal: The Difficult Road to Sustainable Democracy. New York: St. Martin's, 1997. Mailer, Phil. Portugal: The Impossible Revolution. London: Solidarity, 1977. Manta, João Abel. Cartoons/ 1969-1975. Lisbon, 1975.■ Manuel, Paul C. Uncertain Outcome: The Politics of Portugal's Transition to Democracy. Lanham, Md. and London: University Press of America, 1994.■ Mateus, Rui. Contos Proibidos. Memorias de Um PS Desconhecido, 3rd ed. Lisbon: Dom Quixote, 1996.■ Maxwell, Kenneth. "Portugal under Pressure." The New York Review of Books (May 2, 1974).■. "The Hidden Revolution in Portugal." The New York Review of Books (April 17, 1975).■. "The Thorns of the Portuguese Revolution." Foreign Affairs 54, 2 (Jan. 1976): 250-70.■. "The Communists and the Portuguese Revolution." Dissent 27, 2 (Spring 1980): 194-206.■. Portugal in the 1980s: Dilemmas of Democratic Consolidation. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1986.■. The Making of Portuguese Democracy. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995.■, ed. "Portugal: Toward the Twenty-First Century." Camoes Center Quarterly 5, 3-4 (Fall 1995): 6-55.■, ed. The Press and the Rebirth of Iberian Democracy. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1983.■. Portugal Ten Years after the Revolution: Reports of Three Columbia University-Gulbenkian Workshops. New York: Research Institute on International Change, Columbia University, 1984.■ Maxwell, Kenneth, and Michael H. Haltzel, eds. Portugal: Ancient Country, Young Democracy. Washington, D.C.: Wilson Center Press, 1990.■ Medeiros Ferreira, José. Ensaio Histórico sobre a revolução do 25 de Abril. Lisbon, 1983.■ Medina, João, ed. Portugal De Abril: Do 25 Aos Nossos Dias. In Medina, ed., História Contemporãnea De Portugal. Lisbon, 1985. Merten, Peter. Anarchismus ünd Arbeiterkãmpf in Portugal. Hamburg: Libertare, 1981.■ Miranda, Jorge. Constituição e Democracia. Lisbon, 1976.■. A Constituição de 1976. Lisbon, 1978.■ Morrison, Rodney J. Portugal: Revolutionary Change in an Open Economy. Boston: Auburn House, 1981.■ Mujal-Leôn, Eusebio. "The PCP [Portuguese Communist Party] and the Portuguese Revolution." Problems of Communism 26 (Jan.- Feb. 1977): 21-41.■ Neves, Mário. Missão em Moscovo. Lisbon, 1986.■ Oliveira, César. M. F. A. e Revolução Socialista. Lisbon, 1975.■. Os Anos Decisivos: Portugal 1962-1985. Um testemunho. Lisbon: Presença, 1993.■ Opello, Waiter C., Jr. Portugal's Political Development: A Comparative Approach. Boulder, Colo.: Westview, 1985.■. Portugal: From Monarchy to Pluralist Democracy. Boulder, Colo.: Westview, 1991.■ Pell, Senator Claiborne H. Portugal ( Including the Azores and Spain) in Search of New Directions: Report to the Committee on Foreign Relations, U.S. Senate. Washington, D.C.: Government Printing Office, 1976.■ Pereira, J. Pacheco. "A Case of Orthodoxy: The Communist Party of Portugal." In Waller and Fenema, eds., Communist Parties in Western Europe: Adaptation or Decline? Oxford: Basil Blackwell, 1988.■ Pilmott, Ben. "Socialism in Portugal: Was It a Revolution?" Government and Opposition 7 (Summer 1977).■. "Were the Soldiers Revolutionary? The Armed Forces Movement in Portugal, 1973-1976." Iberian Studies 7, 1 (1978): 13-21.■, and Jean Seaton. "Political Power and the Portuguese Media." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal, 43-57. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■ Porch, Douglas. The Portuguese Armed Forces and the Revolution. London: Croom Helm and Stanford, Calif.: Hoover Institution Press, 1977.■ Pouchin, Dominique. Portugal, quelle révolution? Paris, 1976.■ Pulido Valente, Vasco. "E Viva Otelo." In Pulido Valente, V., ed., O País das Maravilhas, 451-54. Lisbon, 1979 [anthology of articles from weekly Lisbon paper, Expresso].■. Estudos Sobre a Crise Nacional. Lisbon, 1980.■ Rebelo de Sousa, Marcelo. O Sistema de Governo Português antes e depois da Revisão Constitucional, 3rd ed. Lisbon, 1981. Rêgo, Raúl. Militares, Clérigos e Paisanos. Lisbon, 1981. Robinson, Richard A. H. Contemporary Portugal: A History. London: Allen & Unwin, 1979.■ Rodrigues, Avelino, Cesário Borga, and Mário Cardoso. O Movemento dos Capitães e o 25 de Abril. Lisbon, 1974.■. Portugal Depois De Abril. Lisbon, 1976.■ Ruas, H. B., ed. A Revolução das Flores. Lisbon, 1975.■ Rudel, Christian. La Liberte couleur d'oeillet. Paris: Fayard, 1980.■ Sa, Tiago Moreira de. Os Americanos na Revolucao Portuguesa ( 1974-1976). Lisbon: Edit. Noticias, 2004.■ Sá Carneiro, Francisco. Por Uma Social-Democracia Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1975.■ Sanches Osôrio, Helena. Um Só Rosto. Uma Só Fé. Conversas Com Adelino Da Palma Carlos. Lisbon, 1988. Sanches Osôrio, J. The Betrayal of the 25th of April in Portugal. Madrid: Sedmay, 1975.■ Schmitter, Philippe C. "Liberation by Golpe: Retrospective Thoughts on the Demise of Authoritarian Rule in Portugal." Armed Forces and Society 2 (1974): 5-33.■. "An Introduction to Southern European Transitions from Authoritarian Rule: Italy, Greece, Portugal, Spain and Turkey." In G. O'Donnell,■ P. C. Schmitter, and L. Whitehead, eds., Transitions from Authoritarian Rule, 3-10. Baltimore, Md.: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1986.■ Silva, Fernando Dioga da. "Uma Administração Envelhecido." Revista da Ad-ministraçao Pública 2 (Oct.-Dec. 1979).■ Simões, Martinho, ed. Relatório Do 25 De Novembro: Texto Integral, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1976.■ Soares, Isabel, ed. Mário Soares: O homem e o político. Lisbon, 1976. Soares, Mário. Democratização e Descolonização: Dez meses no Governo Provisório. Lisbon, 1975. Sobel, Lester A., ed. Portuguese Revolution, 1974-1976. New York: Facts on File, Inc., 1976.■ Spínola, Antônio de. Portugal e o Futuro. Lisbon, 1974.■. País Sem Rumo: Contributo para a História de uma Revolução. Lisbon, 1978.■ Story, Jonathan. "Portugal's Revolution of Carnations: Patterns of Change and Continuity." International Affairs 52 (July 1976): 417-34. Sweezey, Paul. "Class Struggles in Portugal." Monthly Review 27, 4 (Sept. 1975): 1-26.■ Szulc, Tad. "Lisbon and Washington: Behind Portugal's Revolution." Foreign Policy 21 (Winter 1975-76): 3-62. Tavares de Almeida, Antônio. Balsemão: O retrato. Lisbon, 1981. "Vasco." Desenhos Políticos. Lisbon, 1974.■ Vasconcelos, Alvaro. "Portugal in Atlantic-Mediterranean Security." In Douglas T. Stuart, ed., Politics and Security in the Southern Region of the Atlantic Alliance, 117-36. London: Macmillan, 1988.■ Wheeler, Douglas L. "Golpes militares e golpes literários. A literatura do golpe de 25 de Abril de 1974 em contexto histôrico." Penélope. Fazer E Desfazer A História, 19-20 (1998): 191-212.■. "Tributo ao Historiador dos Historiadores. Memorias de A.H.de Oliveira Marques (1933-2007)," Historia XXIX, 95, III series (March 2007), 18-22.■ Wiarda, Howard J. Transcending Corporatism? The Portuguese Corporative System and the Revolution of 1974. Columbia: Institute of International Studies, University of South Carolina, 1976.■. The Transition to Democracy in Spain and Portugal. Washington, D.C.: American Enterprise Institute for Public Policy Research, 1989. Wise, Audrey. Eyewitness in Revolutionary Portugal. With a Preface by Judith Hart, MP. London: Spokesman, 1975.■ PHYSICAL FEATURES: GEOGRAPHY, GEOLOGY, FAUNA, AND FLORA■ Birot, Pierre. Le Portugal: Étude de géographie régionale. Paris, 1950.■ Embleton, Clifford. Geomorphology of Europe. London: Macmillan, 1984.■ Girão, Aristides de Amorim. Divisão regional, divisão agrícola e divisão administrativa. Coimbra, 1932.■. Condições geográficos e históricas de autonomia política de Portugal. Coimbra, 1935.■. Atlas de Portugal, 2nd ed. Coimbra, 1958.■ Ribeiro, Orlando. Portugal, O Mediterrâneo e o Altântico. Coimbra, 1945 and later eds.■. Portugal. Volume V of Geografia de Espana y Portugal. Barcelona, 1955.■. Ensaios de Geografia Humana e regio nal. Lisbon, 1970.■. A geografia e a divisão regional do país. Lisbon, 1970.■ Stanislawski, Dan. The Individuality of Portugal. Austin: The University of Texas Press, 1959.■. Portugal's Other Kingdom: The Algarve. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1963.■ Taylor, Albert William. Wild Flowers of Spain and Portugal. London: Chatto & Windus, 1972.■ Way, Ruth, and Margaret Simmons. A Geography of Spain and Portugal. London: Methuen, 1962.■ ARCHAEOLOGY AND PREHISTORY■ "Actas do Colóquio Inter-Universitário do Noroeste Peninsular (Porto-Baião, 1988), vol. II, Proto-História, romanização e Idade Média." In Trabalhos de antropologia e etnologia. 28, 3-4 (1988).■ Alarcão, Jorge de, ed. "Do Paleolítico va arte visigótica." Vol. 1, História da■ Arte em Portugal. Lisbon: Alfa, 1986.■. Roman Portugal, 3 vols. Warminister, U.K.: Aris & Phillips, 1988.■. Portugal Das Orígens A Romanização. Vol. I. In J. Serrão and A. H. de Oliveira Marques, eds. Nova História de Portugal. Lisbon: Presença, 1990. Anderson, James M., and M. S. Lea. Portugal 1001 Sights: An Archaeological and Historical Guide. Calgary, Alberta: University of Calgary and Robert Hale, 1994.■ Balmuth, Miriam S., Antonio Gilman, and Lourdes Prados-Torreira, eds. Encounters and Transformations: The Archaeology of Iberia in Transition. Monographs in Mediterranean Archaeology, no. 7. Sheffield, U.K.: Sheffield Academic Press, 1997.■ Beirão, C. M. M. Une civilization protohistorique du Sud au Portugal ( 1er Age du Fer). Paris: D. Boccard, 1986.■ Cardoso, João Luís, Santinho A. Cunha, and Delberto Aguiar. O Homem Pre-Histórico no Concelho de Oeiras. Oeiras, Portugal: Estudos Arquelógicos de Oeiras, 1991.■ Harrison, Richard J. The Bell Beaker Cultures of Spain and Portugal. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1977.■ Mangas, Júlio, ed. Hispania epigraphica. Madrid, 1989.■ Maloney, Stephanie J. "The Villa of Toerre de Palma, Portugal: Archaeology and Preservation." Portuguese Studies Review VIII, 1 (Fall-Winter, 1999-2000): 14-28.■ Savory, H. N. Spain and Portugal: The Prehistory of the Iberian Peninsula. London, 1968.■ Silva, A. C. F. A cultura castreja no Noroeste de Portugal. Paços de Ferreira:■ Museu da Citânia de Sanfins, 1986. Straus, L. G. Iberia before the Iberians. Albuquerque, N.M., 1992.■ FOREIGN TRAVELERS AND RESIDENTS' ACCOUNTS■ Andersen, Hans Christian. A Visit to Portugal 1866. London: Peter Owen, 1972.■ Beckford, William. Italy, with Sketches of Spain and Portugal. Paris: Baudry's European Library, 1834.■ Boyd Alexander, ed. London: Hart-Davies, 1954.■. Recollections of an Excursion to the Monasteries of Alcoboca and Batalha. Fontwell, U.K.: Centaur Press, 1972.■ Bell, Aubrey F. G. In Portugal. London: Bodley Head, 1912.■ Borrow, George. The Bible in Spain, 2 vols. London: Constable, 1923 ed.■ Chaves, Castelo Branco. Os livros de viagens em Portugal no século XVIII e a sua projecção europeia. Lisbon, 1977.■ Costigan, Arthur William. Sketches of Society and Manners in Portugal. London: T. Vernon, 1787.■ Crawfurd, Oswald. Portugal Old and New. London: Kegan, Paul, 1880.■. Round the Calendar in Portugal. London: Chapman & Hall, 1890.■ Darymple, William. Travels through Spain and Portugal in 1774. London: J. Almon, 1777.■ Dumouriez, Charles Francois Duperrier. An Account of Portugal as It Appeared in 1766. London: C. Law, 1797.■ Fielding, Henry. Jonathan Wild and the Journal of a Voyage to Lisbon. London: J. M. Dent, 1932.■ Fullerton, Alice. To Portugal for Pleasure. London: Grafton, 1945.■ Gibbons, John. I Gathered No Moss. London: Robert Hale, 1939.■ Gordon, Jan, and Cora Gordon. Portuguese Somersault. London: Harrap, 1934.■ Hewitt, Richard. A Cottage in Portugal. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1996.■ Huggett, Frank. South of Lisbon: Winter Travels in Southern Portugal. London: Gollancz, 1960.■ Hume, Martin. Through Portugal. London: Richards, 1907.■ Hyland, Paul. Backwards Out of the Big World: A Voyage into Portugal. Hammersmith, U.K.: HarperCollins, 1996.■ Jackson, Catherine Charlotte, Lady. Fair Lusitania. London: Bentley, 1874.■ Kelly, Marie Node. This Delicious Land Portugal. London: Hutchinson, 1956.■ Kempner, Mary Jean. Invitation to Portugal. New York: Athenaeum, 1969.■ Kingston, William H. G. Lusitanian Sketches of the Pen and Pencil. 2 vol. London: Parker, 1845.■ Landmann, George. Historical, Military and Picturesque Observations on Portugal. 2 vol. London: Cadell and Davies, 1818.■ Latouche, John [Pseudonym of Oswald Crawfurd]. Travels in Portugal. London: Ward, Lock & Taylor, ca. 1874.■ Link, Henry Frederick. Travels in Portugal and France and Spain. London: Longman & Rees, 1801.■ Macauley, Rose. They Went to Portugal. London: Jonathan Cape, 1946.■. They Went to Portugal, Too. Manchester: Carcanet Books, 1990.■ Merle, Iris. Portuguese Panorama. London: Ouzel, 1958.■ Murphy, J. C. Travels in Portugal. London: 1795.■ Proper, Datus C. The Last Old Place: A Search through Portugal. New York: Simon & Schuster, 1992.■ Quillinan, Dorothy [Wordsworth]. Journal of a Few Months in Portugal with Glimpses of the South of Spain. 2 vol. London: Moxon, 1847. Sitwell, Sacheverell. Portugal and Madeira. London: Batsford, 1954. Smith, Karine R. Until Tomorrow: Azores and Portugal. Snohomish, Wash.: Snohomish Publishing, 1978. Southey, Robert. Journals of a Residence in Portugal, 1800-1801 and a Visit to France, 1838. London and New York: Oxford Univ. Press, 1912. Thomas, Gordon Kent. Lord Byron's Iberian Pilgrimage. Provo, Utah: Brigham Young University Press, 1983. Twiss, Richard. Travels through Portugal and Spain in 1772-1773. London, 1775.■ Watson, Gilbert. Sunshine and Sentiment in Portugal. London: Arnold, 1904. Wheeler, Douglas L. "A[n American] Fulbrighter in Lisbon, Portugal, 196162." Portuguese Studies Review 1 (1991): 9-16.■ PORTUGUESE CARTOGRAPHY, DISCOVERIES, AND NAVIGATION■ Albuquerque, Luís de. Curso de História de Naútica. Coimbra, 1972.■. Introdução a história dos descobrimentos, 3rd ed. Mem Martins, 1983.■. Os Descobrimentos Portugueses. Lisbon: Alfa, 1983.■. Portuguese Books on Nautical Science from Pedro Nunes to 1650. Lisbon, 1984.■. Os Descobrimentos Portugueses. Lisbon, 1985.■ Boorstin, Daniel. The Discoverers. New York: Random House, 1983. Boxer, C. R. The Portuguese Seaborne Empire, 1415-1825. London: Hutchinson, 1969.■ Brazão, Eduardo. La découverte de Terre-Neuve. Montreal: Les Presses de l'Université, 1964.■. "Les Corte-Real et le Nouveau Monde." Revue d'histoire d'Amérique Française 19, 1 (1965): 335-49. Cortesão, Armando, and Avelino Teixeira de Mota. Cartografia Portuguesa Antiga. Lisbon, 1960.■. Portugalia Monumenta Cartográfica, 6 vols. Lisbon, 1960-62.■. História da Cartografia Portuguesa, 2 vols. Coimbra, 1969-70.■ Cortesão, Jaime. L'expansion des portugais dans l'historie de la civilisation. Brussels, 1930.■. Os descobrimentos portugueses, 2 vols. V. Magalhães Godinho and Joel Serrão, eds. Lisbon, 1960.■. A expansão dos Portugueses no período henriquinho. Lisbon, 1965.■. Descobrimentos precolombanos dos portugueses. Lisbon, 1966.■ Costa, Abel Fontoura da. A Marinharia dos Descobrimentos, 3rd ed. Lisbon, 1960.■ Costa Brochado, Idalino F. Descobrimento do Atlântico. Lisbon, 1958. English ed., 1959-60.■ Coutinho, Admiral Gago. A naútica dos descobrimentos, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1951-52.■ Crone, G. R. Maps and Their Makers. New York: Capricorn Books, 1966.■ Dias, José S. da Silva. Os descobrimentos e a problemática cultural do Século XVI, 2nd ed. Lisbon, 1982.■ Disney, Anthony, and Emily Booth, eds. Vasco Da Gama and the Linking of Europe and Asia. New Delhi: Oxford University Press, 2000.■ Godinho, Vitorino Magalhães, ed. Documentos sobre a expansão portuguesa [ to 1460], 3 vols. Lisbon, 1945-54.■ Guedes, Max, and Gerald Lombardi, eds. Portugal. Brazil: The Age of Atlantic Discoveries. Lisbon: Bertrand; Milan: Ricci; Brazilian Culture Foundation, 1990. [Catalogue of New York Public Library Exhibit, Summer 1990]■ Harley, J. B., and David Woodward. The History of Cartography. Volume 1: Cartography in Prehistoric, Ancient and Medieval Europe and Mediterranean. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1987.■ Leite, Duarte. História dos Descobrimentos: Colectânea de esparsos, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1958-61.■ Ley, Charles. Portuguese Voyages, 1498-1663. London: Dent, 1953.■ Marques, J. Martins da Silva. Descobrimentos portugueses, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1944-71.■ Martyn, John R. C., ed. Pedro Nunes ( 1502-1578): His Lost Algebra and Other Discoveries. John R. C. Martyn, trans. New York: Peter Lang, 1996.■ Morison, Samuel Eliot. The European Discovery of America: The Northern Voyages, A. D. 500-1600. New York: Oxford University Press, 1971.■. Portuguese Voyages to America in the Fifteenth Century. Cambridge: Harvard University Press, 1974.■ Mota, Avelino Teixeira da. Mar, Além-Mar-Estudos e Ensaios de História e Geografia. Lisbon, 1972.■ Nemésio, Vitorino. Vida e Obra do Infante D. Henrique. Lisbon, 1959.■ Parry, J. H. The Discovery of the Sea. New York: Dial, 1974.■ Penrose, Boies. Travel and Discovery in the Renaissance, 1420-1620. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1952.■ Peres, Damião. História dos Descobrimentos Portugueses. Oporto, 1943.■ Prestage, Edgar. The Portuguese Pioneers. London, 1933; New York: Barnes & Noble, 1967.■ Rogers, Francis M. Precision Astrolabe: Portuguese Navigators and Transoceanic Aviation. Lisbon, 1971.■ Seary, E. R. "The Portuguese Element in the Place Names of Newfoundland." In Luís Albuquerque, ed., Vice-Almirante A. Teixeira da Mota: In Memo-riam. Vol. II, 359-64. Lisbon: Academia da Marinha, 1989.■ Subrahmanyam, Sanjay. The Career and Legend of Vasco Da Gama. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1997.■ Velho, Alvaro. Roteiro ( Navigator's Route) da Primeira Viagem de Vasco da Gama ( 1497-1499). Lisbon, 1960.■ Winius, George, ed. Portugal, the Pathfinder: Journeys from the Medieval toward the Modern World 1300-ca. 1600. Madison, Wisc.: Hispanic Seminary of Medieval Studies, 1995.■ PORTUGAL AND HER OVERSEAS EMPIRES (1415-1975)■ Abshire, David M., and Michael A. Samuels, eds. Portuguese Africa: A Handbook. New York: Praeger, 1969.■ Afonso, Aniceto, and Carlos de Matos Gomes. Guerra Colonial. Lisbon: Noticias, 2001.■ Albuquerque, J. Moushino de. Moçambique. Lisbon, 1898.■ Alden, Dauril. The Making of an Enterprise: The Society of Jesus in Portugal, Its Empire & Beyond. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, 1995.■ Alexandre, Valentim. Orígens do Colonialismo Português Moderno ( 18221891). Lisbon: Sá da Costa, 1979.■, and Jill Dias, eds. "O Império Africano 1825-1890. Volume X." In J.■ Serrão and A. H. de Oliveira Marques, eds., Nova História Da Expansão Portuguesa. Lisbon: Estampa, 1998.■ Ames, Glen J. "The Carreira da India, 1668-1682: Maritime Enterprise and the Quest for Stability in Portugal's Asian Empire." Journal of European Economic History 20, 1 (1991): 7-28.■. Renascent Empire? The House of Braganza and the Quest for Stability in Portuguese Monsoon Asia, ca. 1640-1683. Amsterdam: Amsterdam Univ.Press, 2000.■. Vasco da Gama. Renaissance Crusader. New York: Pearson/Longman, 2005.■ Antunes, José Freire. O Império com Pés de Barro: Colonizaçao e Descolonização: As Ideologias em Portugal. Lisbon: D. Quixote, 1980.■. O Factor Africano 1890-1990. Lisbon: Bertrand, 1990.■. A Guerra De Africa 1961-1974, 2 vols. Lisbon: Círculo de Leitores, 1995-96.■. Jorge Jardim: Agente Secreto 1919-1982. Lisbon: Bertrand, 1996.■ Axelson, Eric A. South-East Africa, 1488-1530. London: Longmans, 1940.■. "Prince Henry and the Discovery of the Sea Route to India." Geographical Journal (U.K.) 127, 2 (June 1961): 145-58.■. Portugal and the Scramble for Africa, 1875-1891. Johannesburg: Witwaterstrand University Press, 1967.■. Portuguese in South-East Africa, 1488-1699. Cape Town: Struik, 1973.■. Congo to Cape: Early Portuguese Explorers. New York: Harper & Row, 1974.■ Azevedo, Mário. Historical Dictionary of Mozambique, 2nd ed. Lanham, Md.: Scarecrow Press, 2003.■ Baião, António, Hernãni Cidade, and Manuel Murias, eds. História da Expansão Portuguesa no Mundo, 4 vols. Lisbon, 1937-40.■ Bender, Gerald J. "The Limits of Counterinsurgency [in the Angolan War, 1961-72]." Comparative Politics (1972): 331-60.■. Angola under the Portuguese: The Myth Versus Reality. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1978.■ Bhíla, H. H. K. Trade and Politics in a Shona Kingdom: The Manyika and Their Portuguese and African Neighbours, 1875-1902. Harlow, U.K.: Longman, 1990.■ Birmingham, David. The Portuguese Conquest of Angola. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1965.■. Trade and Conflict in Angola. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1966.■. Frontline Nationalism in Angola & Mozambique. London: James Currey, 1992.■. Portugal and Africa. New York: St. Martins, 1999.■ Bottineau, Yves. Le Portugal Et Sa Vocation Maritime. Paris: Boccard, 1977. Boxer, C. R. Fidalgos in the Far East— Fact and Fancy in the History of Macau. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1948. ———. The Christian Century in Japan. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1951.■ ———. Salvador de Sá and the Struggle for Brazil and Angola, 1602-1688. London, 1952.■ ———. Four Centuries of Portuguese Expansion, 1415-1825: A Succinct Survey. Johannesburg: Witwaterstrand University Press, 1961.■ ———. The Golden Age of Brazil, 1695-1750. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1962.■ ———. Race Relations in the Portuguese Colonial Empire, 1415-1825. Oxford:■ Clarendon Press, 1963. ———. Portuguese Society in the Tropics. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1965.■ ———. The Portuguese Seaborne Empire 1415-1825. London: Hutchi nson, 1969.■ ———, and Carlos de Azevedo, eds. Fort Jesus and the Portuguese in Mombasa. London: Hollis and Carter, 1960.■ Broadhead, Susan H. Historical Dictionary of Angola, 2nd ed. Metuchen, N.J.: Scarecrow Press, 1992.■ Burton, Richard. Goa and the Blue Mountains. London: Bentley, 1851.■ Cabral, Luís. Crónica da Libertação. Lisbon, 1984.■ Caetano, Marcello. Colonizing Traditions, Principles and Methods of the Portuguese. Lisbon, 1951.■ ———. Portugal E A Internacionalização Dos Problemas Africanos, 3rd ed. Lisbon, 1965.■ Cann, John P. Counterinsurgency in Africa: The Portuguese Way of War, 1961-1974. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1997. Castelo, Claudia. " O modo portugues de estar no mundo." O luso-tropicalismo e a ideologia colonial portuguesa ( 1931-1961). Oporto: Afrontamento, 1998. Castro, Armando. O Sistema Colonial Português em Africa ( meados do Século XX). Lisbon, 1978.■ Chaliand, Gerard. "The Independence of Guinea-Bissau and the Heritage of [Amilcar] Cabral." In Revolution in the Third World. Harmondsworth, U.K.: Penguin, 1978.■ Chilcote, Ronald H. Portuguese Africa. Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice-Hall, 1967.■ Clarence-Smith, Gervase. Slaves, Peasants and Capitalists in Southern Angola 1840-1926. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1979.■ ———. The Third Portuguese Empire 1825-1975: A Study in Economic Imperialism. Manchester, U.K.: Manchester University Press, 1985.■ Coates, Timothy J. Convicts and Orphans: Forced and State-Sponsored Colonizers in the Portuguese Empire, 1550-1720. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, 2001.■ Davies, Shann. Macau. Singapore: Times Editions, 1986.■ Dias, C. Malheiro, ed. História da colonização portuguesa no Brasil, 3 vols. Oporto, 1921-24.■ Diffie, Bailey W., and George Winius. Foundations of the Portuguese Empire, 1415-1580. Minneapolis: Minnesota University Press, 1977.■ Disney, Anthony R. Twilight of the Pepper Empire: Portuguese Trade in Southwest India in the Early Seventeenth Century. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1978.■ ———, and Emily Booth, eds. Vasco Da Gama and the Linking of Europe and Asia. New Delhi: Oxford University Press, 2000.■ Duffy, James. Shipwreck and Empire: Being an Account of Portuguese Maritime Disaster in a Century of Decline. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1955.■ ———. Portuguese Africa. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1959. ———. Portugal in Africa. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1962.■. "The Portuguese Territories." In Colin Legum, ed., Africa: A Handbook to the Continent. New York: Holmes & Meier, 1967. ———. A Question of Slavery. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1967. Felgas, Hélio. História do Congo Português. Carmona, Angola, 1958. ———. Guerra em Angola. Lisbon, 1961.■ Galvão, Henrique, and Carlos Selvagam. O Império Ultramarino Português, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1953.■ Gleijeses, Piero. Conflicting Missions: Havana, Washington and Africa, 19591976. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2002.■ Godinho, Vitorino Magalhães. "Portugal and Her Empire." In The New Cambridge Modern History. Vol. V (1961): 384-97; Vol. VI (1963): 509-TO.■ Grenfell, F. James. História da Igreja Baptista em Angola, 1879-1975. Queluz, Portugal: Núcleo, 1998.■ Hammond, Richard J. "Economic Imperialism: Sidelights on a Stereotype." Journal of Economic History XXI, 4 (1961): 582-98.■ ———. Portugal and Africa, 1815-1910: A Study in Uneconomic Imperialism. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, 1966.■ Hanson, Carl. Portugal and the Wider World 1147-1497. New Orleans, La.: University Press of the South, 2001.■ Harris, Marvin. Portugal's African Wards. New York: American Committee on Africa, 1957.■ ———. "Portugal's Contribution to the Underdevelopment of Africa and Brazil." In Ronald H. Chilcote, ed., Protest & Resistance in Angola & Brazil: Comparative Studies, 209-23. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1972.■ Henderson, Lawrence W. Angola: Five Centuries of Conflict. Ithaca, N.Y.: Cornell University Press, 1979. ———. A Igreja Em Angola. Lisbon: Edit. Além-Mar, 1990. Heywood, Linda. Contested Power in Angola 1840s to the Present. Rochester, N.Y.: University of Rochester Press, 2000.■ Hilton, Anne. The Kingdom of Kongo. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1985.■ Hower, Alfred, and Richard Preto-Rodas, eds. Empire in Transition: The Portuguese World in the Time of Camões. Gainesville: University Presses of Florida, 1985.■ Isaacman, Allen. "The Prazos da Coroa 1752-1830: A Functional Analysis of the Political System." STUDIA (Lisbon) 26 (1969): 149-78.■. Mozambique: The Africanization of a European Institution: The Zambezi Prazos, 1750-1902. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1972.■ ———. The Tradition of Resistance in Mozambique: Anti-Colonial Activity in the Zambesi Valley 1850-1921. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1976.■ James, Martin. Historical Dictionary of Angola, 3rd ed. Lanham, Md.: Scarecrow Press, 2004.■ Jardim, Jorge. Sanctions Double-Cross: Oil to Rhodesia. Lisbon, 1978. Johnson, Harold, and Maria Beatriz Nizza da Silva. O Império Luso-Brasileiro 1500-1620. Volume VI. In J. Serrão and A. H. de Oliveira Marques, eds. Nova História Da Expansão Portuguesa. Lisbon: Estampa, 1992. Joliffe, Jill. East Timor: Nationalism & Colonialism. University of Queensland Press, 1978.■ Kea, Ray A. Settlements, Trade and Politics in the Seventeenth Century Gold Coast. Baltimore, Md.: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1982.■ Kohen, Arnold. From the Place of the Dead. The Epic Struggles of Bishop Belo of East Timor. New York: St Martins, 1999.■ Livingstone, Charles, and David Livingstone. Narrative of an Expedition to the Zambezi and Its Tributaries. New York: 1866.■ Livingstone, David. Missionary Travels and Researches in South Africa. London, 1857.■ Lobban, Richard, and Joshua Forrest. Historical Dictionary of the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, 3rd ed. Lanham, Md.: Scarecrow Press, 1996. Lobban, Richard, and Marilyn Halter. Historical Dictionary of Cape Verde, 3rd ed. Lanham, Md.: Scarecrow Press, 1993. Martino, Antonio M. Joao de Azevedo Coutinho. Marinheiro e soldado de Portugal. Lisbon: Colibri, 2002. Martins, Rocha. História das Colónias Portuguesas. Lisbon, 1933. Marvaud, Angel. Le Portugal et Ses Colonies. Paris, 1912. Mason, Philip, ed. Angola: A Symposium; Views of a Revolt. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1961. Melo, João de, ed. Os Anos Da Guerra 1961-1975: Os Portugueses em Africa, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1988. Miller, Joseph C. Way of Death: Merchant Capitalism and the Angolan Slave Trade, 1730-1830. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1988.■ Ministry of Foreign Affairs. Portugal. Vinte Anos de Defesa do Estado Português de India. Lisbon, 1967.■. Portugal Replies in the United Nations. Lisbon, 1970.■ Mondlane, Eduardo. The Struggle for Mozambique. Harmondsworth, U.K.: Penguin, 1969.■ Moreira, Adriano. Política Ultramarina. Lisbon, 1956.■. Portugal's Stand in Africa. New York: University Publishers, 1962.■, and Jose Carlos Venancio. Eds. Luso-Tropicalismo. Uma Teoria Social em Questao. Lisbon: Vega, 2000.■ Múrias, Manuel, ed. História da expansão portuguesa no mundo, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1937-42.■. Short History of Portuguese Colonization. Lisbon, 1940.■ Newitt, Malyn. Portuguese Settlement on the Zambesi: Exploration, Land Tenure and Colonial Rule in East Africa. New York: Holmes & Meier, 1973.■. Portugal in Africa: The Last Hundred Years. London: Longmans, 1981.■. A History of Mozambique. London: Hurst, 1995.■. A History ofPortuguese Overseas Expansion, 1400-1668. London: Routledge, 2005.■. História De Portugal. 1933-1974: II Suplemento. Oporto, 1981.■. Salazar. Vol. V: A Resistência ( 1958-1964). Oporto, 1981.■ Nowell, Charles E. "Portugal and the Partition of Africa." Journal of Modern History XIX, 1 (1947): 1-17.■ Nunes, Antonio Lopes Pires. Angola 1961. Da Baixa do Cassange a Nambu-angongo. Lisbon: Prefacio, 2005.■ Okuma, Thomas. Angola in Ferment: The Background and Prospects of Angolan Nationalism. Boston: Beacon, 1962.■ Pattee, Richard. Portugal and the Portuguese World. Milwaukee, Wise.: Bruce, 1957.■ Pélissier, René. Les Guerres Grises: Resistance Et Revoltes en Angola ( 18451941). Orgeval: Pélissier, 1977.■. Naissance Du Mozambique: Tome 1, Tome 2, Resistance Et Revoltes Anticoloniales ( 1854-1981), 2 vols. Orgeval: Pélissier, 1984.■. História de Moçambique. Vol. II. Lisbon, 1988.■. Naissance de la Guinée: Portugais et Africains en Senegambie ( 1841-1936). Orgeval: Pélissier, 1989.■ Pires, Adelino Serras, and Fiona Claire Capstick. The Winds of Havoc: A Memoir of Adventure and Destruction in Deepest Africa. New York: St. Martin's, 2001.■ Prestage, Edgar. The Portuguese Pioneers. London: Black, 1933.■ Ranger, T. [Terence] O. "Revolt in Portuguese East Africa: The Makombe Rising of 1917." St. Anthony's Papers. Carbondale: Southern Illinois University Press, 15 (1963).■ Remy. Goa, Rome of the Orient. Trans. from the French by Lancelot Sheppard. London, 1957.■ Ribeiro, General Goncalves. A Vertigem da Descolonizacao. Da Agonia do Exodo a Cidadania Plena. Lisbon: Inquerito, 2002. Ricard, Robert. Etudes sur l'Histoire des Portugais au Maroc. Coimbra, 1955.■ Richards, J. M. Goa. London: Hurst, 1982.■ Rodney, Walter. A History of the Upper Guinea Coast, 1545-1800. New York: Oxford University Press, 1970. Rodrigues, José Honório. Africa e Brasil: Outro Horizonte. Rio de Janeiro, 1961.■ Rogers, Francis M. "Valentim Fernandes, Rodrigo de Santaella, and the Recognition of the Antilles as "Opposite India." Boletim da Sociedade de Geografia de Lisboa series 75 (July-September 1957): 279-309.■. The Obedience of a King of Portugal. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1958.■. The Quest for Eastern Christians: Travels and Rumors in the Age of Discovery. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1962.■ Russell-Wood, A. J. Fidalgos and Philanthropists: The Santa Casa da Mi-sericordia of Bahia, 1550-1755. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1968.■. "Colonial Brazil." In David W. Cohen and Jack Greene, eds., Neither Slave nor Free, 84-133. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1972.■. "Local Government in Portuguese America: A Study in Cultural Divergence." Comparative Studies in Society and History 16 (1974): 187-231.■. From Colony to Nation: Essays on the Independence of Brazil. Baltimore, Md.: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1975.■. World on the Move: The Portuguese in Africa, Asia & America, 1415-1808. New York: St. Martins, 1993.■ Salazar, António de Oliveira. Goa and the Indian Union. Lisbon, 1954.■. "Portugal, Goa and the Indian Union." Foreign Affairs (New York) 34, 3 (April, 1956): 418-31.■. "Realities and Trends of Portugal's Policies." International Affairs (London) XXXIX, 2 (April 1963): 169-83.■ Saldanha, C. F. A Short History of Goa. Goa, 1957.■ Sanceau, Elaine. Indies Adventure: The Amazing Career of Afonso de Albuquerque. London: Blackie, 1936.■. Portugal in Quest of Prester John. London: Hutchinson, 1943.■. The Land of Prester John. New York: Knopf, 1944.■. Henry the Navigator. New York: Norton, 1947.■. The Perfect Prince: Dom João II. Oporto, 1959.■. Good Hope, the Voyage of Vasco da Gama. Lisbon, 1967.■. Knight of the Renaissance: A Biography of Dom João de Castro. London: Hutchinson, n.d.■ Schubert, Benedict. A Guerra e as Igrejas: Angola, 1961-1991. Basel, Switzerland: Schlettwein, 2000 [orig. ed. in German, Lucerne, Exodus Pub., 1997].■ Schwartz, Stuart G. Sovereignty and Society in Colonial Brazil. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1973.■ Serra, Carlos, ed. História de Moçambique, 2 vols. Maputo, Mozambique: Tempo, 1982-83.■ Silva, Botelho da, ed. and comp. " Dossier" Goa. ( General Manuel) Vassalo e Silva. A Recusa do Sacrifício Inútil. Lisbon, 1975.■ Silva, Maria Beatriz Nizza da, ed. O Império Luso-Brasileiro 1750-1822. Volume VIII. In J. Serrão and A. H. de Oliveira Marques, eds., Nova História Da Expansão Portuguesa. Lisbon: Estampa, 1986.■ Silva Cunha J. M. da. Questões Ultramarinos e Internacionais. Lisbon, 1960.■ Silva Rego, A. da. História das missões do padroado português do Oriente: India ( 1500-1542). 1 vol. Lisbon, 1949.■. Portuguese Colonization in the Sixteenth Century: A Study of Royal Ordinances. Johannesburg: Witwaterstrand University Press, 1957.■. O Ultramar Português No Século XIX ( 1834-1910). Lisbon, 1966.■ Sousa Dias, Gastão. Os Portugueses em Angola. Lisbon, 1959.■ Sykes, John. Portugal and Africa: The People and the War. London: Hutchinson, 1971.■ Telo, António José. Lourenço Marques na Política Externa Portuguesa. Lisbon: Cosmos, 1991.■. Economia E Império No Portugal Contemporânea. Lisbon: Cosmos, 1994.■. Os Açores e o Controlo do Atlântico. Lisbon: Asa, 1993.■ Vail, Leroy, and Landeg White. Capitalism and Colonialism in Mozambique: A Study of Quelimane District. Minneapolis: Minnesota University Press, 1980.■ Veen, Ernst van. Defeat or Decay? An Inquiry into the Portuguese Decline in Asia 1580-1645. Leiden: University of Leiden, 2000.■ Verlinden, Charles. "Italian Influence on Iberian Colonization." Hispanic American Historical Review 33 (1953): 99-211.■. The Beginnings of Modern Colonization. Ithaca, N.Y.: Cornell University Press, 1970.■ Vogel, Charles. Le Portugal et Ses Colonies. Paris, 1860.■ Vogt, John. Portuguese Rule on the Gold Coast 1469-1682. Athens: University of Georgia Press, 1979.■ Wheeler, Douglas L. "The Portuguese in Angola. 1836-1891: A Study in Expansion and Administration." Ph.D. dissertation, Boston University, Department of History, 1963.■. "Anti-Imperialism Traditions in Portugal, Yesterday and Today." Boston University Graduate Journal XII, 2 (Spring 1964): 125-37.■. 'The Portuguese and Mozambique: The Past against the Future." In John A. Davis and James K. Baker, eds., Southern Africa in Transition. 180-96. New York: Praeger, 1966.■. "Gungunhana." In Norman R. Bennett, ed., Leadership in Eastern Africa, Six Political Biographies, 165-220. Boston: Boston University Press, 1968.■. "Gungunyane the Negotiator." Journal of African History IX, 4 (1968): 585-602.■. "Nineteenth-Century African Protest in Angola: Prince Nicolas of Kongo (1830?-1860)." African Historical Studies (Boston) I (1968): 40-59.■. "The Portuguese Army in Angola." Journal of Modern African Studies (Cambridge U.K.), 7, 3 (Oct. 1969): 425-39.■. "Thaw in Portugal." Foreign Affairs 48, 4 (July 1970): 769-81.■. "Portugal in Angola: A Living Colonialism?" In C. Potholm and R. Dale, eds., Southern Africa in Perspective, 172-82. New York: Free Press, 1972.■. "The First Portuguese Colonial Movement, 1835-1875." Iberian Studies (Keele, U.K.) I, 1 (Spring 1975): 25-27.■. "Rebels and Rebellions in Angola, 1672-1892." In Mark Karp, ed., African Dimensions: Essays in Honor of William O. Brown, 81-93. Boston: Boston University Press, 1975.■. "African Elements in Portugal's Armies in Africa (1961-1974)." Armed Forces and Society (Chicago) 2, 2 (Feb. 1976): 233-50.■. "Portuguese Colonial Governors in Africa, 1870-1974." In L. H. Gann and Peter Duignan, eds., African Proconsuls: European Governors in Africa, 415-26. New York: Free Press, 1978; and "J. Mousinho de Albuquerque (1855-1902)" and "J. Norton de Matos (1867-1955)": 427-44; 445-63.■. "The Portuguese Withdrawal from Africa, 1974-1975; The Angolan Case." In John Seiler, ed., Southern Africa Since the Portuguese Coup, 3-21. Boulder, Colo.: Westview, 1980.■. "The Portuguese Exploration Expeditions and Expansion in Angola, 1877-1883." In Academia de Marinha and Instituto de Investigação Científica Tropical, eds., Vice Almirante A. Teixeira Da Mota: In Memoriam. Volume I, 267-76. Lisbon, 1987.■. "'Aqui é Portugal!': The Politics of the Colonial Idea during the Estado Novo, 1926-1974." In Pavilhão de Portugal, EXPO'98 and Instituto de História Contemporânea, eds., Portugal No Transição Do Milênio: Colóquio Internacional, 375-105. Lisbon: Fim de Século, 1998.■. The Empire Time Forgot: Writing a History of the Portuguese Overseas Empire, 1808-1975. Oporto: Universidade Fernando Pessoa, 1998.■. "Filho Do Porto, Filho Do Império: Antônio Francisco Da Silva Porto (1817-1890) and the Politics of Motivation in Portugal's First and Second Scrambles for Africa (1836-1861; 1875-1891)." Revista da UFP [Universidade Fernando Pessoa] 4 (Dec. 1999): 225-54.■. "'Mais leis do que mosquitos': A Primeira República Portuguesa e o Império Ultramarino (1910-1926)." In Nuno Severiano Teixeira and Antó-nio Costa Pinto, eds., A Primeira República Portuguesa Entre O Liberalismo E O Autoritarismo, 133-68. Lisbon: University Nova de Lisboa, 2000.■. "Spiritual Peoples at Odds: Portugal, India and the Goa Question, 1947-61." In Anthony Disney and Emily Booth, eds., Vasco Da Gama and the Linking of Europe and Asia, 452-70. New Delhi: Oxford University Press, 2000.■. "Portugal, Africa and the future." In Stewart Lloyd-Jones and Antonio Costa Pinto, eds., The Last Empire: Thirty Years of Portuguese Decolonization, 113-25. Bristol, U.K.: Intellect, 2003.■. "The Forced Labor 'System' in Angola, 1903-1947: Reassessing Origins and Persistence in the Context of Colonial Consolidation, Economic Growth and Reform Failures." In CEAUP, Centro de Estudos Africanos da Universidade do Porto, ed., Trabalho forcado africano-experiencias coloniais comparadas, 367-393. Oporto: CEAUP, 2006.■. "As Raizes Do Nacionalismo Angolano: Publicacoes De Protesto Dos Assimilados, 1870-1940." In Nuno Vidal and Justino Pinto De Andrade, eds., O Processo De Transicao Para O Multipartidarismo Em Angola, 73-92. Lisbon: Ed. Firmamento, 2006.■, and René Pélissier. Angola. London: Pall Mall and New York: Praeger, 1971; reprinted, Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1977; Portuguese lang. edition, Lisbon: Tinta-da-China, 2009. Whiteway, R. W. The Rise of the Portuguese Power in India, 1497-1550. London: Constable, 1899.■ Winius, George D. The Fatal History of Portuguese Ceylon: Transition to Dutch Rule. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1971.■. "The Portuguese Asian 'Decadência' Revisited." In Alfred Hower and Richard Preto-Rodas, eds., Empire in Transition, 106-17. Gainesville: University Presses of Florida, 1980.■. The Black Legend of Portuguese India. New Delhi: New Concept, 1985.■ Alves, Marcial. Os Portugueses no Mundo. Lisbon, 1983.■ Anderson, Grace M., and David Higgs, eds. A Future to Inherit: Portuguese Communities in Canada. Toronto: McClelland and Stewart, 1976. Arroteia, Jorge Carvalho. A emigração Portuguesa-suas origens e distribuição. Lisbon, 1983.■ Brettell, Caroline B. "Nineteenth- and Twentieth-Century Portuguese Emigration: A Bibliography." Portuguese Studies Newsletter 3 (Fall-Winter, 1977-78).■. "Emigrar Para Voltar: A Portuguese Ideology of Return Migration." Papers in Anthropology 20 (1979): 1-20.■. We Have Already Cried Many Tears: The Stories of Three Portuguese Migrant Women. Cambridge, Mass.: Schenkman Publishing Co., 1982.■. Men Who Migrate, Women Who Wait: Population and History in a Portuguese Parish. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1986.■ Carvalho, Eduardo de. Os portugueses na Nova Inglaterra. Rio de Janeiro, 1931.■ Caspari, Andrea. "The Return Orientation among Portuguese Migrants in France." In E. de Sousa Ferreira and W. C. Opello, Jr., eds., Conflict and Change in Portugal, 1974-1984, 193-203. Lisbon, 1985.■ Dias, Eduardo Mayone, ed. Portugueses na América do Norte. Baden: Peregrinação, 1983.■ Fagundes, Francisco Cota. Hard Knocks: An Azorean-American Odyssey.■ [Memoir]. Providence, R.I.: Gávea-Brown, 2000. Felix, John Henry, and Peter F. Senecal. The Portuguese in Hawaii. Honolulu, Hawaii: Authors' edition, 1978. Fernandes, Ferreira. Os Primos da América. Lisbon: Relógio D'Agua, 1991. Ferreira, Eduardo de Sousa. As orígens e formas de emigração. Lisbon, 1976. Freitas, J. F. Portuguese-American Memories. Honolulu, Hawaii, 1930.■ Giles, Wenona. "Motherhood and Wage Labour in London, England: Portuguese Migrant Women and the Politics of Gender." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology. University of Toronto, 1987.■ Higgs, David, ed. Portuguese Migration in Global Perspective. Ontario: Multicultural Historical Society of Ontario, 1990.■ Klimt, Andrea. "Portuguese Migrants in Germany: Class, Ethnicity and Gender." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology. Stanford University, 1987.■ Lavigne, Gules. Les ethniques et la ville: L'aventure des immigrants portugais à Montreal. Montreal: Preamble, 1987.■ Leder, Hans Howard. Cultural Persistence in a Portuguese-American Community. New York: Arno Press, 1980.■ Lewis, J. R., and A. M. Williams. "Emigrants and Retornados: A Comparative Analysis of the Economic Impact of Return Migration in the Região Centro." In E. D. Sousa Ferreira and W. C. Opello, Jr., eds., Conflict and Change in Portugal, 1974-1984, 227-50. Lisbon, 1985.■ McCabe, Marsha L., and Joseph D. Thomas, eds. Portuguese Spinner: An American Story; Stories of History, Culture and Life from Portuguese Americans in Southeastern New England. New Bedford, Mass.: Spinner, 1998.■ Marques, D., and J. Medeiros. Portuguese Immigrants: 25 Years in Canada. Toronto: West End YMCA, 1989.■ Martins, J. Oliveira. Fomento Rural e emigração Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1956.■ Mira, Manuel. The Forgotten Portuguese: The Melungeons and Other Groups; The Portuguese Making of America. Franklin, N.C.: Portuguese-American Historical Research Foundation, 1998.■ Nazareth, J. Manuel. "Familia e Emigração em Portugal." Economia e Sociedade (Lisbon) 23 (1977): 31-50.■ Nunes, Maria Luisa. A Portuguese Colonial in America: Belmira Nunes Lopes; The Autobiography of a Cape Verdean-American. Pittsburgh, Penn.: Latin American Literary Review Press, 1982.■ Oliver, Lawrence. Never Backward: The Autobiography of Lawrence Oliver; A Portuguese-American. San Diego, 1972.■ Pap, Leo. The Portuguese-Americans. Boston: Twayne, 1981.■ Pereira, Miriam Halpern. A Política Portuguesa de Emigraçao, 1850 a 1930. Lisbon: Regra do Jogo, 1981.■ Pereira da Rosa, Victor M., and Salvato V. Trigo. "Elementos para uma Caracterização da Família Imigrante Portuguesa na Africa do Sul." Economia e Sociologia 41 (1986): 61-71.■. Azorean Emigration: A Preliminary Overview. Oporto: Fernando Pessoa University, 1994.■. Portugueses e Moçambicanos no Apartheid: Da Ficção à Realidade. Lisbon, 1986.■ Purves, James. "Portuguese in Bermuda." Bermuda Historical Quarterly 3 (1946): 133-42.■ Ribeiro, F. G. Cassola. Emigração Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1986.■ Rocha-Trinidade, Maria Beatriz da. "La Sociologie des Migrations au Portugal." Current Sociology 32, 2 (Summer 1984): 175-98.■. "Towards Reintegration of Emigrants." In E. de Sousa Ferreira and Guy Clausse, eds., Closing the Migratory Cycle: The Case of Portugal, 183-94. Saarbrücken: Breitenbach, 1985.■. "Emigração." In Dicionario Illustrado Da História De Portugal ( 1985): 205-7.■. A Emigração. Lisbon, 1986.■. "Espaços de herança cultural portuguesa-gentes, factos, políticas." Analise Social (Lisbon) XXIV (1988): 313-51.■ Rocha-Trinidade, Maria Beatriz da, and Jorge Arroteia. Bibliografia da Emigração Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1984.■ Rogers, Francis M. Americans of Portuguese Descent: A Lesson in Differentiation. Beverly Hills, Calif.: Sage, 1974.■. Testemunhos sobre a Emigração Portuguesa: Antologia. Lisbon, 1976.■ Silva, F. Emídio da. A Emigração Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1917.■ Silva, Manuela, et al. Retorno, Emigração e Desenvolvimento Regional em Portugal. Lisbon, 1984.■ Simões, Mário Pinto. O Emigrante Português: Processos de Adaptação ( o exemplo da Suiça). Oporto, 1985.■ Simões, Nuno. O Brasil e a Emigração Portuguesa. Coimbra, 1934.■ Sousa Ferreira, Eduardo de, and Guy Clausse, eds. Closing the Migratory Cycle: The Case of Portugal. Saarbrucken: Verlag Breitenbach, 1986.■ Teixeira, Carlos, and Victor M. Pereira da Rosa, eds. The Portuguese in Canada: From the Sea to the City. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2000.■ Vicente, António Luís. Os Portuguese Nos Estados Unidos Da América: Política De Comunidades E Comunidade Política. Lisbon: FLAD, 1998.■ Viera, David, et al. Portuguese in the United States: A Bibliography ( Supplement to the 1976 Leo Pap Bibliography). Essay Number 6 in Essays in Portuguese Studies. Durham, N.H.: International Conference Group on Portugal, 1989.■ Williams, Jerry. And Yet They Come: Portuguese Immigration from the Azores to the United States. New York: Center for Migration Studies, 1982.■ Portugal's Atlantic Islands (Azores, Madeiras)■ Biddle, Anthony J. Drexel. The Madeira Islands, 2 vols. London: Hurst and Blackett, 1900.■ Bryans, Robin. Madeira, Pearl of the Atlantic. London: Robert Hale, 1959.■. The Azores. London: Faber & Faber, 1963.■ Cooke, Rupert Croft. Madeira. London: Putnam, 1961.■ Cossart, Noel. Madeira— the Island Vineyard. London: Christie's, 1984.■ Da Silva, Fernando Augusto, and Carlos Azevedo de Menezes. Elucidário Madeirense, 3 vols. Funchal, 1940.■ Duncan, T. Bentley. Atlantic Islands in the Seventeenth Century: Madeira, the Azores and the Cape Verdes in Seventeenth-Century Commerce andNavigation. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1972.■ Guill, James H. A History of the Azores Islands. Menlo Park, Calif.: Author's Edition, 1972.■ Instituto Histórico Da Ilha Terceira [Azores]. Os Açores E O Atlântico ( Séculos XIV-XVII) [Proceedings of International Colloquium, August 1983]. Angra do Heroismo, Terceira Island, Azores, 1984.■ Koebel, William Henry. Madeira Old and New. London: Griffiths, 1909.■ Mee, Jules. Histoire de la découverte des Iles Açores. Ghent, 1901.■ Peres, Damião. A Madeira sob os donatórios-Séculos XV e XVI. Funchal, 1914.■ Rogers, Francis M. Atlantic Islanders of the Azores and Madeiras. North Quincy, Mass.: Christopher House, 1979.■ Serpa, Caetano Valadão. A Gente Dos Açores. Identificaçao-Emigraçio E Religiosidade: Séculos XVI-XX. Lisbon: 1978.■ Silva, J. Donald. "With Columbus in Madeira." Portuguese Studies Review (Durham, NH) I, 1 (Spring-Summer 1991).■ Wheeler, Douglas L. "The Azores and the United States (1787-1987): Two Hundred Years of Shared History." Boletim do Instituto Histórico da Ilha Terceira XLV (1988): 55-71.■ Almada, José de. A Aliança Inglesa, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1947.■. Para a história da aliança luso-britânica. Lisbon, 1955.■ Atkinson, William C. British Contributions to Portuguese and Brazilian Studies. London: British Council, 1974.■ Bourne, Kenneth. The Foreign Policy of Victorian England 1830-1902. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1970.■ British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC). 600 Years of Anglo-Portuguese Alliance. London: BBC, 1973.■ British Community Council of London. Souvenir Brochure Commemorating the 600th Anniversary of the Anglo-Portuguese Treaty of Alliance and Friendship, 1373-1973. Lisbon, 1973.■ Cabral, Manuel Villaverde. Portugal na Alvorada do Século XX. Lisbon, 1979.■ Caetano, Marcello "Aliança Inglesa." Enciclopédia Luso-Brasileira da Cultura. Vol. 1 (1963): 1270-1271.■. "L'alliance Anglo-Portuguese: Histoire et situation actuelle." Chronique de politique etrangére (Paris) XX, 6 (1967): 695-708.■. Portugal e a Internacionalização dos Problemas Africanos. Lisbon, 1971.■ Castro, Armando. A dominação inglesa em Portugal. Estudo seguido de Antologia Textos dos Sécs. XVIII e XIX. Oporto: Afrontamento, 1972.■. "Portugal." In O. De Raeymaeker et al. Small Powers in Alignment, 27-96. Leuven, Belgium: Leuven University Press, 1974.■ Cunha Leal, Francisco. Portugal e Inglaterra. Corunna, 1932.■ Davidson, Basil. "The Oldest Alliance Faces a Crisis." In Philip Masonm, ed., Angola: A Symposium. Views of a Revolt, 138-60. London: Oxford University Press, 1962.■ Duff, Katherine. "The War and the Neutrals." In Arnold and Veronica Toyn-bee, eds., Survey of International Affairs. London: Chatham House, 1956.■ Duffy, James. A Question of Slavery. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1967.■ Epstein, John. "The Anglo-Portuguese Alliance, 1373-1973." World Survey (London) 54 (June 1973): p. 18.■ Ferreira, José Medeiros. Estudos de Estratégia e Relações Internacionais. Lisbon, 1981.■ Ferreira Martins, General L. O Poder Militar Da Gran-Bretanha E A Aliança Anglo-Lusa. Coimbra, 1939.■. A Cooperaçio Anglo-Portuguesa na Grande Guerra de 1914-18. Lisbon, 1942.■ Francis, A. D. The Methuens and Portugal 1691-1700. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1966.■. Portugal 1715-1808. London: Tamesis, 1985.■ Freitas, A. Barjona de. A Questão Ingleza. Lisbon, 1891.■ Gonçalves, Caetano. A Aliança Luso-Britânica e o Domínio Colonial Português. Lisbon, 1917.■ Guedes, Armando Marques. A Aliança Inglesa: Notas de História diplomática, 1383-1943. Lisbon, 1943. Halpern Pereira, Miriam. Revoluçio, finanças, dependência externa. Lisbon, 1979.■ Howorth, A. H. D'Araujo Scott. A Aliança Luso-Britânica E A Segunda Guerra Mundial. Lisbon, 1956.■ Kay, Hugh. Salazar and Modern Portugal. New York: Hawthorne, 1970.■ Lawrence, L. Nehru Seizes Goa. New York: Pageant, 1963.■ Livermore, H. V. "The Anglo-Portuguese Alliance: Historical Perspective." 600 Years of Anglo-Portuguese Alliance, 7-15. Lisbon: BBC, 1973.■ Macedo, Jorge Borges de. História Diplomática Portuguesa-Constantes e Linhas de Força. Lisbon, 1987.■ Manoel, J. de Câmara. Portugal e Inglatterra. Lisbon, 1909.■ Martinez, Pedro S. História Diplomática de Portugal. Lisbon, 1986.■ Medlicott, W. N. The Economic Blockade, Vol. II. London: His Majesty's Stationery Office, 1952.■ Oliveira, Pedro Aires. Os Despojos Da Alianca. A Gra-Bretanha e a questao colonial portuguesa 1945-1975. Lisbon: Tinta-da-China, 2007. Ortigão, Ramalho. John Bull. Lisbon, 1887.■ Prestage, Edgar. Diplomatic Relations of Portugal with France, England and Holland from 1646 to 1668. Watford, U.K.: Voss & Michael, 1925.■. Chapters in Anglo-Portuguese Relations. London: Voss & Michael, 1935.■ Russell, Peter E. The English Intervention in Spain and Portugal in the Time of Edward III and Richard II. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1955. Sarmento, J. E. Morães. The Anglo-Portuguese Alliance and Coast Defense. London, 1908.■ Serrão, Joel. "O Ultimatum (January 1890)." Dicionário de História de Portugal. Vol. IV (1971): 219-24.■ Shafaat, Ahmed Khan, ed. Anglo-Portuguese Negotiations Relating to Bombay, 1660-1667. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1922.■ Sideri, Sandro. Trade and Power: Informal Colonialism in Anglo-Portuguese Relations. Rotterdam: Rotterdam University Press, 1970.■ Sousa, Carlos Hermenegildo de. A Aliança Anglo-Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1943.■ Stone, Glyn A. "The Official British Attitude to the Anglo-Portuguese Alliance, 1910-45." Journal of Contemporary History (London) 10, 4 (Oct. 1975): 729-46.■. The Oldest Ally: Britain and the Portuguese Connection, 1936-1941. Woodbridge, U.K.: Royal Historical Society and Boydell Press, 1994. Teixeira, Nuno Severiano. O Ultimatum Inglês: Política Externa no Portugal do 1890. Lisbon, 1990.■ Teles, Basilio. Do Ultimatum ao 30 de Janeiro. Oporto, 1905.■ Vicente, António Pedro. "Um testemunho de 1796 sobre a Situação de Portugal face ao domínio inglês." In Arquivos do Centro Cultural Portugües, IV. Paris, 1972.■ Vieira de Castro, Luís. D. Carlos I. ( Elementos de História Diplomática), 2nd ed. Lisbon, 1941.■ Vincent-Smith, John. "Britain, Portugal and the First World War." European Studies Review 4, 3 (1974).■. "The Portuguese Economy and the Anglo-Portuguese Commercial Treaty of 1916." Iberian Studies (Keele, U.K.) III, 2 (Autumn 1974): 49-54.■. As Relações Políticas Luso-Britânicas 1910-1916. Lisbon, 1975.■. "The Portuguese Republic and Britain, 1910-14." Journal of Contemporary History 10, 4 (Oct. 1975): 707-27.■ Vintras, R. E. The Portuguese Connection: A Secret History of the Azores Base. London: Bachman & Turner, 1974. Viriato [Pseud]. A Aliança lnglesa. Lisbon, 1914.■ Walford, A. R. The British Factory in Lisbon and Its Closing Stages Ensuring upon the Treaty of 1810. Lisbon, 1940.■ Wheeler, Douglas L. "The Portuguese in Angola, 1836-1891: A Study in Expansion and Administration." Ph.D. dissertation, History Department, Boston University, 1963.■. "19th Century: Anglo-Portuguese Alliance and the Scramble for Africa." In BBC, 600 Years of Anglo-Portuguese Alliance, 40-43. London: BBC, 1973.■. "The Price of Neutrality: Portugal, the Wolfram Question and World War II." Luso-Brazilian Review (Madison, Wisc.) 34, 1, 2 (Summer 1986; Winter 1986): 107-27; 97-111.■ Wordsworth, William. William Wordsworth's Convention of Cintra: A Facsimile of the 1809 Tract [Introduction by Gordon Kent Thomas]. Provo, Utah: Brigham Young University Press, 1983.■ Young, George. Portugal Old and Young. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1917.■ ANTHROPOLOGY, SOCIOLOGY, RURAL AND URBAN SOCIETY■ Almeida, Miguel Vale de. The Hegemonic Male: Masculinity in a Portuguese Town. Oxford: Berghan, 1996.■ Black, Richard. Crisis and Change in Rural Europe: Agricultural Development in the Portuguese Mountains. Aldershot, U.K.: Avebury and Ashgate, 1992.■ Brettell, Caroline B. Men Who Migrate, Women Who Wait: Population and History in a Portuguese Parish. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1986.■. "The Absence of Men." Natural History 96, 2 (Feb. 1987): 52-61.■. "The Portuguese." In Encyclopedia of World Cultures. New Haven, Conn.: Human Relations Area Files, 1990.■. "The Priest and His People: The Contractual Basis for Religious Practice in Rural Portugal." In Ellen Badone, ed., Religious Orthodoxy and Popular Faith in European Society, 55-75. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1990.■ Brogger, Jan. Pre-bureaucratic Europeans: A Study of a Portuguese Fishing Community. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1989. Cabral, Manuel Villaverde. "Portuguese Perspectives." Sociologia Ruralis [Journal of European Rural Sociology] XXIV, 1 (1986); number devoted to rural Portugal today. Chaney, Rick. Regional Emigration and Remittances in Developing Countries: The Portuguese Experience. New York: Praeger, 1986. Cole, Sally. Women of the Praia: Work and Lives in a Portuguese Colonial Community. Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1991. Cutileiro, José. A Portuguese Rural Society. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1971.■ Deschamps, Paul. Portugal: La Vie Sociale Actuelle. Paris, 1935.■. Histoire Sociale du Portugal. Paris, 1959.■ Dias, Jorge. Rio do Onor-comunitarismo agropastoral. Oporto, 1953.■. Ensaios Etnológicos. Lisbon, 1961.■. The Portuguese Contribution to Cultural Anthropology. Johannesburg: Witwaterstrand University Press, 1964.■. Vilarinho Da Furna: Uma Aldeia Comunitária. Rev. ed. Lisbon, 1981.■ Downs, Charles. Os Moradores à Conquista da Cidade. Lisbon, 1978.■. "Community Organization, Political Change and Urban Policy: Portugal. 1974-1976." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Sociology. University of California, 1980.■. "Residents' Commissions and Urban Struggles in Revolutionary Portugal." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal: The Revolution and Its Consequences. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■ Dracklé, Dorlé. Macht und Ohnmacht: Der Kampf num die Agarreform im Alentejo ( Portugal). Gottingen, Germany: Edit. Re, 1991.■ Espírito Santo, Moise. Communidade Rural ao Norte do Tejo. Lisbon, 1980.■ Feijó, Rui, H. Martins, and João de Pina Cabral, eds. Death in Portugal. Oxford: Journal of the Anthropological Society of Oxford, 1983.■ Feijó, Rui Graça. "State, Nation and Regional Diversity in Portugal: An Overview." In Richard Herr and John H. Polt, eds., Iberian Identity: Essays on the Nature of Identity in Portugal and Spain, 37-47. Berkeley: Institute of International Studies, University of California, 1989.■ Feio, Mariano. Les Bas Alentejo et l'Algarve. Lisbon, 1949.■ Ferreira de Almeida, João. Classes sociais nos campos. Lisbon, 1986.■ Fonseca, Ramiro da. O Livro da Saúde e da Doença. Lisbon, 1979.■ Gallop, Rodney. Portugal: A Book of Folk-Ways. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1936. Reprinted, 1961.■ Hoefgen, Lynn. "The Integration of Returnees from the Colonies into Portugal's Social and Economic Life." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology, University of Florida, 1985.■ Ingerson, Alice Elizabeth. "Corporatism and Class Consciousness in Northwestern Portugal." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology. Johns Hopkins University, 1984.■ Jenkins, Robin. The Road to Alto. London: Pluto Press, 1979.■ Lawrence, Denise. "Menstrual Politics: Women and Pigs in Rural Portugal." In T. Buckley and A. Gottlieb, eds., Blood Magic: The Anthropology of Menstruation, 117-36. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1988.■. "Suburbanization of House Form and Gender Relations in a Rural Portuguese Agro-Town." Architecture and Behavior 4, 3 (1988): 197-212.■ Martins, Hermínio. "Portugal." In Margaret S. Archer and Salvador Giner, eds., Contemporary Europe: Class, Status and Power. New York: St. Martins, 1971.■ Mattoso, José. Identificação de um país. Lisbon, 1985.■ Merten, Peter. Anarchismüs und Arbeiterkãmpf in Portugal. Hamburg: Libera-tare Association, 1981.■ Monteiro, Paulo. Terra que ja foi terra: Análise Sociológica de nove lugares agro-pastorais da Serra da Lousã. Lisbon, 1985.■ Nataf, Daniel. "Social Cleavages and Regime Formation in Contemporary Portugal." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Political Science, UCLA, 1987.■ Nazareth, J. Manuel. "Familia e Emigração em Portugal: Ensaio Exploratório." Economia e Socialismo 23 (1977): 31-50.■ O'Neill, Brian Juan. "Dying and Inheriting in Rural Tras-os-Montes." Journal of the Anthropological Society of Oxford 14 (1983): 44-74.■. Social Inequality in a Portuguese Hamlet: Land, Late Marriage, and Inheritance, 1870-1978. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1987.■ Pacheco, Helder. Tradições Populares de Portugal. Lisbon, 1985.■ Pardoe, Julia. Traits and Traditions of Portugal, 2 vols. London, 1832.■ Pereira Neto, João Baptista. "Social Evolution in Portugal since 1945." In Raymond S. Sayers, ed., Portugal and Brazil in Transition, 212-27. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1968.■ Pina-Cabral, João de. Sons of Adam, Daughters of Eve: The Peasant World-View of the Alto Minho. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1986.■. "Sociocultural Differentiation and Regional Identity in Portugal." In■ R. Herr and J. H. Polt, eds., Iberian Identity, 3-18. Berkeley: Institute of International Studies, 1989.■ Poinard, Michel. La Retour des Traveilleurs Portugais. Paris: La Documentation Francaise, 1979.■ Reed, Robert Roy. "Managing the Revolution: Revolutionary Promise and Political Reality in Rural Portugal." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology, Indiana University, 1988.■ Riegelhaupt, Joyce F. "In the Shadow of the City: Integration of a Portuguese Village" [São João das Lampas, nr, Cascais]. Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Anthropology, Columbia University, 1964.■. "Saloio Women: An Analysis of Informal and Formal Political and Economic Roles of Portuguese Peasant Women." Anthropological Quarterly 40, 3 (July 1967): 109-26.■. "Festas and Padres: The Organization of Religious Action in a Portuguese Parish." American Anthropologist 75 (1973): 835-52.■. "Peasants and Politics in Salazar's Portugal: The Corporate State and Village 'Nonpolitics'" In L. S. Graham and H. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal: The Revolution and Its Antecedents, 167-90. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■ Rodrigues, Julieta E. S. de Almeida. "Continuity and Change in Urban Portuguese Women's Roles: Emerging New Household Structures." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Sociology, Columbia University, 1979.■ Rowland, Robert. "Demographic Patterns and Rural Society in Portugal." So-ciologica Ruralis 26, 1 (1986): 36-47.■ Sanchis, Pierre. Arraial. La Fête d'un Peuple: Les Pélerinages Populaires au Portugal. Paris, 1976.■ Siegel, Bernard J. "Social Structure and Medical Practitioners in Rural Brazil and Portugal." Sociologia (São Paulo) 20, 4 (Oct. 1958): 463-76.■. "Conflict, Parochialism and Social Differentiation in Portuguese Society." Journal of Conflict Resolution V, 1 (March 1961): 35-12.■ Smith, T. Lynn. "The Social Relationships of Man to the Land in Portugal." Sociologia 25, 1 (Dec. 1963): 319-43.■ Sousa Santos, Boaventura. "Estado e sociedade na semiperíferia do sistema mundiale: O caso português." Análise Social 87-89 (1985): 869-902.■. "Social Crisis and the State." In Kenneth Maxwell, ed., Portugal in the 1980s: Dilemmas of Democratic Consolidation, 167-95. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1986.■ Vasconcellos, Joaquim Leite de. Ethnograia Portuguesa, 8 vols. Lisbon, 1941-82.■. Tradições Populares Portugueses. New ed. Lisbon, 1986.■ Willems, Emilio. "On Portuguese Family Structure." International Journal of Comparative Society (Dharwar, India) 3, 1 (Sept. 1962): 65-79.■ ARTS, ARCHITECTURE, URBAN PLANNING, MUSIC■ Almeida, Rodrigo Vicente de. História da Arte em Portugal: ( Segundo Estudo) Documentos lnéditos. Oporto, 1883. Almeida D'Eca, Admiral Vicente M. Castles of Portugal. Lisbon, 1925. Amaral, Francisco K. Lisboa: Uma Cidade em Transformação. Lisbon, 1969. Azevedo, Carlos de, and Chester Brummel. Churches of Portugal. New York: Scala Books, 1985.■ Barreira, João, ed. Arte Portuguesa: As Decorativas, 2 vols. Lisbon, n.d.■ Barretto, Mascarenhas, and George Dykes. Fado: Lyrical Origins and Poetical Motivation. Lisbon, 1977.■ Binney, Marcus. Country Manors of Portugal. London: Scala, 1987.■ Branco, Luís de Freitas. A Música em Portugal. Lisbon, 1930.■ Brito, Manuel Carlos de. Opera in Portugal in the Eighteenth Century. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1989.■ Carvalho, Pinto de. História de Fado. Lisbon, 1903 and 1982 eds.■ Castro d'Aire, Teresa. O Fado. Lisbon: Temas da Actualidade, 1996.■ Chicó, Mário Tavares. A Architectura Gótica em Portugal. Lisbon, 1968.■ França, José-Augusto. A Arte em Portugal No Século XIX. Lisbon, 1966.■. Lisboa Pombalina e o Illuminismo, 2nd ed. Lisbon, 1977.■. A Reconstrucão e a Arquitectura Pombalina. Lisbon, 1978.■ Gallop, Rodney. "The Fado (The Portuguese Song of Fate)." Musical Quarterly XIX (1933): 199-213.■. Eight Portuguese Folksongs. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1936.■ Gil, Júlio. The Finest Churches in Portugal. Lisbon, 1988.■. The Finest Castles in Portugal, 3rd ed. George F. W. Dykes, trans. Lisbon, 1996.■ Gonçalves, Rui Mário. Pintura e escultura em Portugal. Lisbon: Instituto de Cultura, 1984.■. 100 Pintores Portugueses do século XX. Lisbon: Alfa, 1986.■ Kubler, George. Portuguese Plain Architecture: Between Spices and Diamonds, 1521-1706. Middletown, Conn.: Wesleyan University Press, 1972.■. Studies in Ancient American and European Art: The Collected Essays of George Kubler. New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 1985.■, and Martin Soria. Art and Architecture in Spain and Portugal. Harmondsworth, U.K.: Penguin, 1959.■ Lacerda, Aarão de. História da Arte em Portugal, 2 vols. Oporto, 1942-48.■ Leão, Joaquim de Sousa. "Decorative Art: The Azulejo." In H. V. Livermore, ed. Portugal and Brazil: An Introduction. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1953.■ Lopes Graça, Fernando. A canção popular portuguesa. Lisbon, 1953.■. A música portuguesa e os sus problemas: Ensaios. Lisbon, 1959.■ Moita, Luís. O fado: canção de vencidos. Lisbon, 1936.■ Neves, José Cassiano. The Palace and Gardens of Fronteira: Seventeenth and Eighteenth Century Portuguese Style. Lisbon: Quetzal and Scala, 1995. North, C.T. Guia dos castelos antigos de Portugal, 2 vols. Lisbon: Bertrand Ed., 2002.■ Pacheco, Jose. Stuart Carvalhais. O desenho grafico e a imprensa. Lisbon: Biblioteca do Empresario, 2000. Pereira, Paulo, ed. Arte portuguesa. Lisbon: Círculo de Leitores, 1995. Picchio, Luciana Stegagno. Storia del Teatro Portoghese. Rome: Edizinio deli' Ateneo, 1964.■ Queirós, José. Cerâmica Portuguesa, 2 vols. 2nd rev. ed. Lisbon, 1948.■ Santos, Luís Reis. Monuments of Portugal. Lisbon, 1940.■ Santos, Reinaldo dos. A Escultura em Portugal, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1948-50.■. História da Arte em Portugal. Oporto, 1953.■ Sasportes, José. História da Dança em Portugal. Lisbon, 1970. Simões, J. M. dos Santos. "Azulejos in a Land of Many Colours." Connoisseur (London) CXXXVII, 551 (1956): 15-21.■. Azulejaria em Portugal no Século X VIII. Lisbon, 1979.■ Smith, Robert C. A Talha em Portugal. Lisbon, 1963.■. The Art of Portugal, 1500-1800. London, Weidenfeld and Nicolson, 1968.■. "The Building of Mafra." Apollo 97, 134 (April 1973): 360-67.■ Stoop, Anne de. Demeures portugaises dans les environs de Lisbonne. Paris: Weber, 1986.■. Palais et manoirs: Le Minho. Paris: Ed. du Seuil, 1995.■ Tannock, Michael. Portuguese 20th Century Artists: A Biographical Dictionary. Chichester, U.K.: Phillimore, 1978.■ Taylor, René. "The Architecture of Port Wine." The Architectural Review CXXIX, 772 (1961): 368-99.■ Terol, Marylene. Azulejos a Lisbonne. Paris: Hervas, 1992.■ Veiga de Oliveira, Ernesto. Instrumentos musicais populares portugueses. Lisbon, 1982.■ Watson, Walter Crum. Portuguese Architecture. London: Constable, 1908. Wohl, Hellmut. "Carlos Mardel and His Lisbon Architecture." Apollo 97, 134 (April 1973): 350-59.■ Andrade, Sergio de. "Presepios." In Dicionario de Arte Barroca em Portugal. Lisbon: Presenca, 1989. Barreira, Joao. Arte Portuguesa, Arquitectura e Escultura. Lisbon: Excelsior, n.d.■ Cardoso, Arnaldo Pinto. O Presepio Barroco Portugues. Lisbon: Bertrand, 2003.■ Chaves, Luis. Os Barristas Portugueses. Coimbra, 1925.■. Natal Portugues. Oporto: Liv. Classica Editora, 1942.■ Gargano, Pietro. Il Presepio. Otto Secoli di Storia, Arte, Tradizione. Milan: Fenice, 1995.■ Lima, Henrique de Campos F. Joaquim Machado de Castro, Escultor Conimbricense. Coimbra: Instituto de Historia de Arte, 1989. Macedo, Diogo de. Presepios Portugueses. Lisbon: Artis, 1951.■. Machado de Castro. Lisbon: Artis, 1958.■ Morais, Heitor. Natal do Meu Coracao. Braga: Ed. A.O., 1991.■ Pais, Alexandre Nobre. Presepios Portugueses Monumentos do Seculo XVIII em Terracotta, 2 vols. Master's thesis in history of art, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, 1998.■ Queiros, Jose. Ceramica Portuguesa. Lisbon: Presenca, 1998. Santos, Reinaldo dos. A Escultura em Portugal. Lisbon: Bertrand, 1951. Serrao, Vitor. Historia da Arte em Portugal IV-O Barroco. Lisbon: Presenca, 2003.■ Smith, Robert C. The Art Of Portugal 1500-1800. New York: Meredith Press, 1968.■ Sousa, Ernesto de. Presepios. Lisbon: Bertrand, 1998.■ Cinema■ Antunes, Joao and Jose de Matos-Cruz, Cinema Portugues 1896-1998. Lisbon: Lusomundo, 1997.■ Bandeira, Jose Gomes. Porto: 100 anos de cinema portugues. Oporto: Camara Municipal do Porto, 1996. Duarte, Fernando. Primitivos do Cinema Portugues. Lisbon: Cinecultura, 1960.■ Faria de Almeida, M., Resumo da Historia do Cinema. Lisbon: RTP, 1982. Nobre, Roberto. Singularidades do Cinema Portugues. Lisbon: Portugalia, n.d.■ Pina, Luis de. Aventura do Cinema Portugues. Lisbon: Vega, 1977.■. Documentarismo Portugues. Lisbon: IPC, 1977.■. Panorama do Cinema Portugues. Lisbon: Terra Livre, 1978.■. Historia do Cinema Portugues. Mem Martins: Europa-America, 1986.■ Ribeiro, Felix. O Cinema Portugues antes do Sonoro. Esboco Historiconema Portugues. Lisbon: Terra Livre, 1978.■. Panorama do Cinema Portugues. Lisbon: n.d.■ Andresen, Sofia de Melo Breyner. A Fada Oriana. 9th ed. Lisbon: Figueiri-nhas, 1985.■ Araújo, Matilde Rosa. A estrada fascinante. Lisbon: Livros Horizonte, 1988. Barreto, Garcia. Literatura Para Crianças E Jovens Em Portugal. Oporto:■ Campo Das Letras, 1998. Bastos, Glória. A escrita para crianças em Portugal no seculo XIX. Lisbon:■ Caminho da Educaçao, 1997. Cadet, Maria Rita Chiappe. Os Contos da Mamã. Lisbon: Lallement Freres, 1883.■ Castro, Fernanda. Mariazinha em Africa, 2nd ed. Lisbon: Portugália, 1947. Cross, Esther, and Wilbur Cross. Portugal. Chicago: Childrens Press, 1986. DeSkalon, Anna, and Christa Stadtler. We Live in Portugal. New York: Watts, 1987.■ Gomes, Alice. A Nau Catrineta, 2nd ed. Lisbon: Portugália, 1973.■. A literatura para a infância. Lisbon: Torres & Abreu, 1979.■ Letria, José Jorge. Do sentimento mágico da vida. Lisbon: Escritor, 1994. Müller, Adolfo Simões. Historiazinha de Portugal, 6th ed. Oporto: Tavares Martins, 1983.■ Osório, Ana de Castro. Para as crianças. Illustr. by Leal da Câmara. Setúbal: Liv. Crianças, 1908.■ Pires, Maria Laura Bettencourt. História da literatura infantil portuguesa. Lisbon: Vega, 1981. Ribeiro, Aquilino. Arca de Noé-III Classe. Lisbon, 1989. Rocha, Natércia. Breve História da Literatura para Crianças em Portugal. Lisbon: Instituto de Cultura e Língua Portuguesa, 1984.■. Bibliografia geral da literatura portuguesa para crianças. Lisbon: Edit. Comunicação, 1987.■ Sá, Domingos Guimarães de. A literatura infantil em Portugal. Braga: Edit. Franciscana, 1981.■ Selfridge. John. Portugal. New York: Chelsea House, 1990. Vaz de Carvalho, Maria Amália. Contos para os Nossos Filhos, 11th ed. Oporto: Barreira, 1947.■ Viana, António Manuel Couto. Jõao de Deus e um século de literatura infantil em Portugal. Lisbon: Ed. do Templo, 1978.■ Lisbon, Capital City, in History and Literature■ Castelo-Branco, Fernando. Lisboa Seiscentista, 3rd ed. Lisbon: 1969.■ Castilho, Júlio de. Lisboa Antiga, 7 vols. Lisbon, 1935-45.■ Couto, Dejanirah. Histoire de Lisbonne. Paris: Fayard, 2000.■ Crespo, Ángel. Lisboa Mítica e Literária. Lisbon: Liv. Horizonte, 1987.■ Dias, Marina Tavares. Lisboa Desaparecida. Lisbon: Quimera, 1990.■ Dionísio, Sant'anna, ed. Guia de Portugal. Vol. I: Lisboa e Arredores. Lisbon: Biblioteca Nacional de Lisboa, 1924, orig. ed; reprint, Gulbenkian Foundation, 1979.■ França, José-Augusto. Lisboa Pombalina e o Iluminismo. Lisbon: Bertrand, 1977.■ Moita, Irisalva, ed. O Livro de Lisboa. Lisbon: Liv. Horizonte, 1994.■ Neves, Orlando. Lisboa em Crónica. Lisbon: Author's Ed., 1968.■ Pavão, Luís, and Mário Pereira. Tabernas de Lisboa. Lisbon: Assírio & Alvim, 1981.■ Pessoa, Fernando. Lisboa. O que o turista deve ver: What the Tourist Should See. Lisbon: Liv. Horizonte, 1997.■ Queirós, José Maria Eça de. À Capital. Lisbon: Sá da Costa, 1960.■ Santos, Piedade Braga, et al. Lisboa Setecentista vista por Estrangeiros. Lisbon: Liv. Horizonte, 1996.■ Vieira, Alice. Esta Lisboa. Lisbon: Caminho, 1993.■ Wright, David, and Patrick Swift. Lisbon: A Portrait and Guide. New York: Scribners, 1971.■ Azevedo, João Lúcio. Historia das Cristãos-Novos. Lisbon: Liv. Clássica, 1975.■ Baião, António. A Inquisição em Portugal e no Brasil: Subsídios para a sua história. Lisbon: Arquivo Histórico Portugues, 1906. Bethencourt, Francisco. "Portugal: A Scrupulous Inquisition," In Bengt Ankarloo and Gustav Henningsen, eds., Early Modern Witchcraft: Centres and Peripheries, 403-22. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1990.■. "Os equilíbrios sociais do Poder." In José Mattoso, ed., Historia De Portugal, Vol. 3, No Alvorecer Da Modernidade ( 1480-1620). Lisbon: Estampa, 1993.■ Braga, Maria Luísa. A Inquisição em Portugal na primeira metade do Séc. XVIII. Lisbon: Inst. Nacional de Investigação Científica, 1992.■ Haliczer, Stephen, ed. Inquisition and Society in Early Modern Europe. London: Croom Helm, 1987.■ Herculano, Alexandre. History of the Origin and Establishment of the Inquisition in Portugal. Reprint. New York: AMS Press, 1968.■ Magalhães, Joaquim Romero. "Em Busca dos Tempos da Inquisição (15731615)." Revista de História das Ideias 9 (1987): 191-228.■ Mea, Elvira Cunha Azevedo. A Inquisição de Coimbra no Século XVI. Oporto, 1989.■ Mendonça, José Lourenço D. de, and António Joaquim Moreira. História da Inquisição em Portugal. Lisbon: Círculo de Leitores, 1980.■ Novinsky, Anita, and Luísa M. Carneiro, eds. Inquisição: Ensaios sobre Mentalidade, Heresias e Arte. Rio de Janeiro: Expressão e Cultura, 1992.■ Pereira, Isais da Rosa. Documentos para a história da Inquisição em Portugal. Lisbon, 1987.■ Rego, Yvonne Cunha, ed. Feiticeiros, Profetas e Visionários: Textos Antigos Portugueses. Lisbon: Imprensa Nacional e Casa da Moeda, 1981.■ Saraiva, António José. Inquisição e cristãos-novos. Lisbon: Estampa, 1985.■ Walker, Timothy Dale. "Doctors, Folk Medicine and the Inquisition: The Repression of Popular Healing in Portugal during the Enlightenment Era." Ph.D. dissertation, Department of History, Boston University, 2001.■ Literature in English Translation: Selection■ Alcaforado, Mariana. The Letters of a Portuguese Nun ( Mariana Alcaforado). Edgar Prestage, trans. London: D. Nutt, 1893.■ Andrade, Eugénio de. "White on White." Alexis Levitin, trans. Quarterly Review of Literature. Poetry Series VIII. Vol. 27. Princeton, N.J., 1987.■. Another Name for Earth; O outro nome da terra. Alexis Levitin, trans. Ft. Bragg, Calif.: QED Press, 1997.■ Andresen, Sophia de Mello Breyner. Marine Rose: Selected Poems. Ruth Fain-light, trans. Redding Ridge, Conn.: Swan Books, 1989.■ Antunes, António Lobo. South of Nowhere. Elizabeth Lowe, trans. New York: Random House, 1983.■. Fado Alexandrino. Gregory Rabassa, trans. New York: Grove Weidenfeld, 1990.■. An Explanation of the Birds. Richard Zenith, trans. New York: Grove Weidenfeld, 1991.■. Act of the Damned. New York: Grove Press, 1995.■. The Natural Order of Things. New York: Grove Press, 2000.■ Barreno, Maria Isabel, Maria Teresa Horta, and Maria Velho da Costa. The Three Marias: New Portuguese Letters. Helen R. Lane, trans. New York: Doubleday, 1975.■ Bell, Aubrey F. G. Poems from the Portuguese ( with the Portuguese text). A.■ Bell, trans. Oxford: Blackwell, 1913.■ Camões, Luís de. The Lusiads of Luís de Camões. Leonard Bacon, trans. New York: Hispanic Society of America, 1950.■. The Lusiads. William C. Atkinson, trans. Harmondsworth, U.K.: Penguin, 1952.■. The Lusiads. Landeg White, trans. New York: Oxford University Press, 1997.■ Castelo Branco, Camilo. Doomed Love ( A Family Memoir). Alice R. Clemente, trans Providence, R.I.: Gávea-Brown, 1995. Castro, José Maria Ferreira de. Emigrants. Dorothy Ball, trans. New York: Macmillan, 1962.■. Jungle. Charles Duff, trans. New York: Viking, 1935.■. The Mission. Ann Stevens, trans. London: Hamilton, 1963.■ Dantas, Júlio. The Cardinals' Collation, 48th ed. A. Saintsbury, trans. London, 1962.■ Dias de Melo. Dark Stones. Gregory McNab, trans. Providence, R.I.: Gávea-Brown, 1996.■ Dinis, Júlio. The Fidalgos of Casa Mourisca. Rosanna Dabney, trans. Boston: D. Lothrop, 1891.■ Garrett, Almeida. Brother Luiz de Sousa [play]. Edgar Prestage, trans. London: Elkin Mathess, 1909.■. Travels in My Homeland. John M. Parker, trans. London: Peter Owen and UNESCO, 1987. Griffin, Jonathan. Camões: Some Poems Translated from the Portuguese by Jonathan Griffin. London: Menard Press, 1976. Jorge, Lídia. The Murmuring Coast. Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press, 1995.■ Lisboa, Eugénio, ed. Portuguese Short Fiction. Manchester, U.K.: Carcanet, 1997.■ Lopes, Fernão. The English in Portugal 1367-87: Extracts from the Chronicles of Dom Fernando and Dom João. Derek W. Lomax and R. J. Oakley, eds. and trans. Warminster, U.K.: Aris & Phillips, 1988.■ Macedo, Helder, ed. Contemporary Portuguese Poetry: An Anthology in English. Helder Macedo, et al., trans. Manchester, U.K.: Carcanet New Press, 1978.■ Martins, J. P. De Oliveira. A History of Iberian Civilization. Aubrey F. G. Bell, trans.; preface by Salvador de Madariaga. New York: Cooper Square, 1969.■ Mendes Pinto, Fernão. The Travels of Mendes Pinto [Orig. title: Peregrinação].■ Rebecca D. Catz, trans., with introduction and notes. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1989. Miguéis, José Rodrigues. A Man Smiles at Death with Half a Face. George■ Monteiro, trans. Hanover, N.H.: University Press of New England, 1991.■. Happy Easter. John Byrne, trans. Manchester, U.K.: Carcanet, 1995.■. Steerage and Ten Other Stories. George Monteiro, ed. Providence, R.I.: Gávea-Brown, 1998. Monteiro, Luís De Sttau. The Rules of the Game. Ann Stevens, trans. London: Hamilton, 1965.■ Mourão-Ferreira, David. Lucky in Love. Christine Robinson, trans. Manchester, U.K.: Carcanet, 1999. Namora, Fernando. Field of Fate. Dorothy Ball, trans. London: Macmillan, 1970.■. Mountain Doctor. Dorothy Ball, trans. London: Macmillan, 1956.■ Nemésio, Vitorino. Inclement Weather over the Channel. Francisco Cota Fagundes, trans. Providence, R.I.: Gávea-Brown, 1993.■. Stormy Isles: An Azorean Tale. Francisco C. Fagundes, trans. Providence, R.I.: Gávea-Brown, 2000.■ Paço D'Arcos, Joaquim. Memoirs of a Banknote. Robert Lyle, trans. London, 1968.■ Pedroso, Consiglieri, comp. Portuguese Folk-Tales. Henriqueta Monteiro, trans. Reprint of orig. 1882 ed. New York: Benjamin Blom, 1969.■ Pessoa, Fernando. Fernando Pessoa: Sixty Portuguese Poems. F. E. G. Quintanilha, ed. and trans. Cardiff: University of Wales Press, 1971.■. Selected Poems: Fernando Pessoa. 2nd rev. ed. Jonathan Griffin, trans. Harmondsworth, U.K.: Penguin, 1982.■. The Book of Disquiet. Alfred MacAdams, trans. New York: Pantheon, 1991.■. Fernando Pessoa: Selected Poems. Peter Rickard, ed. and trans. Edinburgh, U.K.: Edinburgh University Press, 1991.■. "The Mariner: A 'Static Drama' in One Act." In Translation: Portugal.■ George Ritchie, et al., trans. The Journal of Literary Translation. Vol. XXV, 38-56. New York: Translation Center, Columbia University, 1991.■. Message: Bilingual Edition. Jonathan Griffin, trans. London: Menard Press and King's College, 1992.■ Pires, José Cardoso. Ballad of a Dog's Beach. Mary Fitton, trans. London: J. M. Dent, 1986.■ Queirós, José Maria Eça de. Cousin Bazilio. Roy Campbell, trans. London: Max Reinhardt, 1953.■. The Relic. Aubrey F. G. Bell, trans. London: Max Reinhardt, 1954.■. The City and the Mountains. Roy Campbell, trans. London: Max Reinhardt, 1955.■. The Sin of Father Amaro. Nan Flanagan, trans. London: Max Reinhardt, 1962.■. The Maias. Patricia McGowan Pinheiro, trans. London: Bodley Head, 1965.■. The Illustrious House of Ramires. Ann Stevens, trans. London: Bodley Head, 1968.■. Letters from England. Ann Stevens, trans. London: Bodley Head, 1970.■. To the Capital. John Vetch, trans. Manchester, U.K.: Carcanet, 1995.■ Quental, Antero de. Sixty-four Sonnets. Edgar Prestage, trans. London: David Nutt, 1894.■ Redol, Alves. The Man with Seven Names. L. L. Barrett, trans. New York: Knopf, 1964.■ Resende, André de. André deResende's 'Poema Latina'/ 'Latinpoems.' J. C. R. Martyn, ed. and trans. Lewiston N.Y.: Lampeter and Edwin Mellen, 1998. Ribeiro, Aquilino. When the Wolves Howl. Patricia McGowan Pinheiro, trans. New York: Macmillan; London: Cape, 1963. Sá Carneiro, Mário de. The Great Shadow ( and Other Stories). Margaret Jull Costa, trans. Sawtry, U.K.: Dedalus, 1996. Santareno, Bernardo. The Promise. Nelson H. Vieira, trans. Providence, R.I.: Gávea-Brown, 1981.■ Saramago, José. Baltasar and Blimunda. Giovanni Pontiero, trans. New York: Harcourt, Brace, 1987.■. The Stone Raft. Giovanni Pontiero, trans. New York: Harcourt, Brace, 1991.■. The Year of the Death of Ricardo Reis. Giovanni Pontiero, trans. New York: Harcourt, Brace, 1991.■. The History of the Siege of Lisbon. Giovanni Pontiero, trans. New York: Harcourt Brace, 1996.■. Blindness. New York: Harcourt, Brace, 1999.■. Tale of the Unknown Island. New York: Harcourt Brace, 2000.■. All the Names. Margaret Jull Costa, trans. New York: Harcourt, 2000.■. Journey to Portugal. New York: Harcourt Brace, 2001.■ Sena, Jorge de. The Poetry of Jorge de Sena: A Bilingual Selection. Frederick G. Williams et al., trans. Santa Barbara, Calif.: Mudborn Press, 1980.■. By the Rivers of Babylon and Other Stories. New Brunswick, N.J.: Rutgers University Press, 1989.■ Vicente, Gil. Four Plays of Gil Vicente: Edited from the Editio Princeps ( 1562). Aubrey F. G. Bell, ed. and trans. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1920.■. Lyrics of Gil Vicente. Aubrey F. G. Bell, trans. Oxford: Oxford University Press, Hispanic Notes and Monographs, Portuguese Series 1, 1921.■. The Play of Rubena. Jack E. Tomlins, trans.; Rene P. Garay and José I. Suarez, eds. New York: National Hispanic Foundation for Humanities, 1993.■. The Boat Plays. David Johnston, trans. and adaptation. London: Oberon, 1996.■. Three Discovery Plays. Anthony Lappin, trans. Warminster, U.K.: Aris & Phillips, 1997.■ Vieira, António. Dust Thou Art. Rev. W. Anderson, trans. London, 1882.■ Portuguese and Portuguese-American Cooking: Cuisine■ Anderson, Jean. Food of Portugal. New York: Hearst, 1994. Asselin, E. Donald. A Portuguese-American Cookbook. Rutland, Vt.: Charles E. Tuttle, 1966.■ Bourne, Ursula. Portuguese Cookery. Harmondsworth, U.K.: Penguin, 1973. Crato, Maria Helena Tavares. Cozinha Portuguesa I, II. Lisbon: Editorial Presença, 1978.■ Dienhart, Miriam, and Anne Emerson, ed. Cooking in Portugal. Cascais: American Women of Lisbon, 1978.■ Feibleman, Peter S. The Cooking of Spain and Portugal. New York: Time-Life Books; Foods of the World, 1969.■ Koehler, Margaret H. Recipes from the Portuguese of Provincetown. Riverside, Conn.: Chatham Press, 1973. Manjny, Maite. The Home Book of Portuguese Cookery. London: Faber & Faber, 1974.■ Marques, Susan Lowndes. Good Food from Spain and Portugal. London: Muller, 1956.■ Modesto, Maria de Lourdes. Cozinha Tradicional Portuguesa. Lisbon: Verbo, 1982.■ Ortiz, Elisabeth Lambert. The Food of Spain and Portugal. The Complete Iberian Cuisine. New York: Atheneum, 1989. Pinto, Elvira. La Bonne Cuisine Portugaise. Paris: Edicions Garanciere, 1985.■ Robertson, Carol. Portuguese Cooking: The Authentic and Robust Cuisine of Portugal. Berkeley Calif.: North Atlantic, 1993. Schmaeling, Tony. The Cooking of Spain and Portugal. Ware, U.K.: Omega, 1983.■ Vieira, Édite. The Taste of Portugal. London: Robinson, 1989.■ Von Treskow, Maria. Zü Gast in Portugal: Eine Kulnarische Reise in Garten Europas. Weingarten: Kunstverlag, 1989. Wright, Carol. Portuguese Food. London: Dent, 1969.■. Self-catering in Portugal: Making the Most of Local Food and Drink. London: Croom Helm, 1986.■ Afonso, Simonetta Luz, and Angela Delaforce. Palace of Queluz— The Gardens. Lisbon, 1989.■ Araújo, Iluídio Alves de. Arte Paisagista e Arte das Jardins em Portugal. Lisbon, 1962.■ Azeredo, Francisco de. Casas Senhoriais Portuguesas. Barcelos, 1986.■ Binney, Marcus. Country Manors of Portugal. New York: Scala Books, 1987.■ Bowe, Patrick, and Nicolas Sapieha. Gardens of Portugal. New York: Scala Books and Harper and Row, 1989.■ Cane, Florence du. The Flowers and Gardens of Madeira. London, 1924.■ Cardoso, Pedro Homem, and Helder Carita. Da Grandeza das Jardins em Portugal. Lisbon, 1987.■ Carita, Helder, and Homem Cardoso. Portuguese Gardens. London: Antique Collector's Club, 1987.■ Costa, António da, and Luís de O. Franquinho. Madeira: Plantas e Floras. Funchal, 1986.■ Nichols, Rose Standish. Spanish and Portuguese Gardens. Boston, 1926.■ Pereira, Arthur D. Sintra and Its Farm Manors. Sintra, 1983.■ Sampaio, Gonçalo. Flora Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1946.■ Sitwell, Sacheverell. Portugal and Madeira. London: Batsford, 1945.■ Underwood, John, and Pat Underwood. Landscapes of Madeira. London, 1980.■ Vieira, Rui. Flowers of Madeira. Funchal, 1973.■ Viterbo, Francisco Marques de Sousa. A Jardinagem em Portugal, 2 vols. Coimbra, 1906-9.■ Education, Science, Health, and Medical History■ Albuquerque, Luís de. Estudos de História, 3 vols. Coimbra, 1973-81.■. Ciência e experiência nos Descobrimentos portugueses. Lisbon, 1983.■. Para a História de Ciência em Portugal. Lisbon, 1983.■. As Navegaçoes E A Sua Projecção Na Ciência E Na Cultura. Lisbon, 1987.■ Baião, Antônio. Episódios Dramáticos da Inquisição Portuguesa, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1936-55.■ Cabreira, Antônio. Portugal nos mares e nas ciências. Lisbon, 1929. Carvalho, Rômulo de. A Astronomia em Portugal (séc. xviii). Lisbon, 1985. Fernandes, Barahona. Egas Moniz: Pioneiro de descobrimentos médicos. Lisbon, 1983.■ Gaitonde, P. D. Portuguese Pioneers in India: Spotlight on Medicine. London: Sangam Books, 1983.■ Hanson, Carl A. "Portuguese Cosmology in the Late Seventeenth Century." In Benjamin F. Taggie and Richard W. Clement, eds., Iberia & the Mediterranean, 75-85. Warrensburg: Central Missouri State University, 1989.■ Higgins, Michael H., and Charles F. S. de Winton. Survey of Education in Portugal. London, 1942.■ Hirsch, Elizabeth Feist. Damião de Góis: The Life and Thought of a Portuguese Humanist. The Hague, 1967.■ Lemos, Maximiano. Arquivos de História da Medicina Portuguesa. Several vols. Lisbon, 1886-1923. Vol. I. História da Medicina em Portugal. Doutrina e Instituições. Lisbon, 1899.■ Mira, Matias Ferreira de. História da Medicina Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1948.■ Orta, Garcia de. Colóquios dos Simples e Drogas e Cousas Medicinais da India. Conde de Ficalho, ed., 2 vols. Lisbon, 1891-95.■ Osório, J. Pereira. História e Desenvolvimento da Ciência em Portugal, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1986-89.■ Pina, Luís de. "Uma prioridade portuguesa do século XVI. João de Barros e a Dactiloscópia Oriental." Arquivo da Repartição de Antropologia Criminal IV (1936).■. "As Ciências na História do Império Colonial Português — Séculos XV a XIX." Anais de Faculdade de Ciências do Porto ( 1939-10).■. "Os Portugueses Mestres de Ciência e Metras no Estrangeiro." Actas do Congresso do Mundo Português. Lisbon, 1940.■. "A Ciência em Portugal (bosquejo Histórico)." In Secretariado Nacional da Informação, ed., Portugal: Breviário Da Pátria Para Os Portugueses Ausentes, 277-301. Lisbon, 1946.■ Richards, Robert A. C., ed. Guide to World Science: Vol. 9: Spain and Portugal, 2nd ed. Guernsey, U.K.: F. H. Books, 1974.■ Saraiva, António José. História da Cultura em Portugal, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1950-62.■ ———. "João de Barros." In Serrao, ed., Dicionário de História de Portugal 1 (1963): 307-8.■ Silvestre Ribeiro, José. História dos Establecimentos Scientíficos, Literários e Artísticos de Portugal nos Successivos Reinados da Monarchia, 3 vols. Lisbon, 1871-83.■ Veiga-Pires, J. A., and Ronald G. Grainger, eds. Pioneers in Angiography: The Portuguese School ofAngiography. Lancaster, U.K.: MTP Press, 1982.■ Walker, Timothy. "Doctors, Folk Medicine and the Inquisition: The Repression of Popular Healing in Portugal during the Enlightenment Era." Ph.D. dissertation, History Department, Boston University, 2001.■ Barbosa, Madelena. "Women in Portugal." Women's Studies International Quarterly 4 (1981): 477-80.■ Barreno, Maria Isabel, Maria Teresa Horta, and Maria Velho da Costa. Novas Cartas Portuguesas. Lisbon, 1972.■ ———. The Three Marias. New Portuguese Letters. Helen R. Lane, trans. New York: Doubleday, 1975.■ Brettell, Caroline B. We Have Already Cried Many Tears: The Stories of Three Portuguese Migrant Women. Cambridge, Mass.: Schenkman, 1982.■ Ferreira, Virginia. "Engendering Portugal: Social Change, State Politics, and Women's Social Mobilization." In António Costa Pinto, ed., Modern Portugal, 162-88. Palo Alto, Calif.: SPOSS, 1998.■ Goodwin, Mary. "Portuguese Feminism." Portuguese Studies Newsletter 17 (Spring-Summer 1987): 12-13.■ Lamas, Maria. As Mulheres do Meu País. Lisbon, 1948.■ "Mulheres Portuguesas e Feminismo." Análise Social [special number on Portuguese Women and Feminism] 22 (1986): 92-93.■ Osório, Ana de Castro. As Mulheres Portuguesas. Lisbon, 1905.■ Sadlier, Darlene J. The Question of How: Women Writers and New Portuguese Literature. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood; Contributions in Women's Studies, no. 109, 1989.■ Silva, Manuela. The Employment of Women in Portugal. Luxembourg: Office for Official Publications, European Communities, 1984. Velho da Costa, Maria. Maina Mendes. Lisbon, 1974.■ Vicente, Ana, and Maria Reynolds de Souza. Family Planning in Portugal. Lisbon, 1984.■ Almeida, Fortunato de. História da Igreja em Portugal. 6 vols. Coimbra, 1910-24, and Oporto, 1967-72. Alonso, Joaquim Maria. The Secret of Fátima: Fact and Legend. Cambridge, Mass.: Ravengate Press, 1979. Alves, José da Felicidade, ed. Católicos e política de Humberto Delgado à Marcelo Caetano. Lisbon, 1969. Araújo, Miguel de, ed. Dicionario político; 1; Os Bispos e a revoluçao de Abril. Lisbon, 1976. Bishko, Charles Julian. Spanish and Portuguese Monastic History 600-1300. London, Variorum Reprints, 1984.■ Blanshard, Paul. Freedom and Catholic Power in Spain and Portugal. Boston: Beacon Press, 1962.■ Boxer, C. R. The Church Militant and Iberian Expansion 1440-1770. Baltimore, Md.: Johns Hopkins University Press, 1978. Bruneau, Thomas C. "Church and State in Portugal: Crises of Cross and Sword." Journal of Church and State XVIII (1976): 463-90. Freire, José Geraldes. Resistência Católico ao Salazarismo-Marcelismo. Oporto, 1976.■ Herculano, Alexandre. History of the Origin and Establishment of the Inquisition in Portugal. John C. Banner, trans. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford University Press, 1962.■ IPOPE. Estudo sobre liberdade e religião em Portugal. Lisbon, 1973. Johnston, Francis. Fátima: The Great Sign. Chulmleigh, U.K.: Augustine Publications, 1980.■ Kondor, Fr. Louis. Fátima in Lucia's Own Words: Sister Lucia's Memoirs. Fatima: Postulation Center, 1976. Lourenço, Joaquim Maria. Situação jurídica da Igreja em Portugal. Coimbra, 1943.■ Mattoso, José. Religião e Cultura na Idade Média Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1982. Miller, Samuel J. Portugal and Rome c. 1748-1830: An Aspect of Catholic Enlightenment. Rome: Universita Gregoriana Editrice, 1978. O'Malley, John W. The First Jesuits. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press, 1993.■ Pattee, Richard. Portugal and the Portuguese World. Milwaukee, Wisc.: Bruce, 1957.■ Prestage, Edgar. Portugal: A Pioneer of Christianity. Lisbon, 1945.■ Richard, Robert. Etudes sur l'histoire morale et religieuse de Portugal. Paris: Centro Cultural de Gulbenkian, 1970.■ Robinson, Richard A. H. "The Religious Question and Catholic Revival in Portugal, 1900-1930." Journal of Contemporary History XII (1977): 345-62.■. Contemporary Portugal: A History. London: Allen & Unwin, 1979.■ Rodrigues, R. P. Francisco. História da Companhia de Jesus na Assistência de Portugal, 7 vols. Lisbon, 1931-50.■ Roth, Cecil. A History of the Marranos. Philadelphia: Jewish Publication Society of America, 1932.■ Agriculture, Viticulture, and Fishing■ Abreu-Ferreira, Darlene. "The Portuguese in Newfoundland: Documentary Evidence Examined." Portuguese Studies Review 4, 1 (1995-96): 11-33.■ Allen, H. Warner. The Wines of Portugal. London: Michael Joseph, 1963.■ Barros, Afonso de. A reforma agrária em Portugal. Oeiras, 1979.■ Beamish, Huldine V. The Hills of Alentejo. London: Geoffrey Bles, 1958.■ Bennett, Norman R. "The Golden Age of the Port Wine System, 1781-1807." The International History Review XII (1990): 221-18.■ Black, Richard. "The Myth of Subsistence: Market Production in the Small Farm Sector of Northern Portugal." Iberian Studies 1, 8 (1989): 25-41.■ Bravo, Pedro, and Duarte de Oliveira. Viticulture Moderna. Lisbon, 1974.■. Vinhas e Vinhos De Portugal. Lisbon, 1979.■ Cabral, Manuel V. "Agrarian Structures and Recent Movements in Portugal." Journal of Peasant Studies 4, 5 (July 1978): 411-45.■ Cardoso, José Carvalho. A Agricultura Portuguesa. Lisbon, 1973.■ Carvalho, Bento de. Guía Dos Vinhos Portugueses. Lisbon, 1982.■ Clarke, Robert. Open Boat Whaling in the Azores: The History and Present Methods of a Relic Industry. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1954.■ Cockburn, Ernest. Port Wine and Oporto. London: Wine & Spirit, 1949. Cole, S. C. "Cod, Cod Country and Family: The Portuguese Newfoundland Fishery." Mast 3, 1 (1990): 1-29.■ Coull, James. The Fisheries of Europe. London: G. Bell & Sons, 1972.■ Croft-Cooke, Rupert. Port. London: Putnam, 1957.■. Madeira. London: Putnam, 1961.■ Delaforce, John. The Factory House at Oporto. London: Christie's Wine Publications, 1979 and later eds.■ Doel, Patricia A. Port O'Call: Memories of the Portuguese White Fleet in St. John's Newfoundland. St. John's, Newfoundland: ISER, 1992.■ Fletcher, Wyndham. Port: An Introduction to Its History and Delights. London: Bernet, 1978.■ Francis, A. D. The Wine Trade. London: Adam and Charles Black, 1972.■ Freitas, Eduardo, João Ferreira de Almeida, and Manuel Villaverde Cabral. Modalidades de penetração do capitalismo na agricultura: estruturas agrárias em Portugal Continental, 1950-1970. Lisbon, 1976.■ Gonçalves, Francisco Esteves. Portugal: A Wine Country. Lisbon, 1984.■ Gulbenkian Foundation. Agrarian Reform. Lisbon, 1981.■ Kurlansky, Mark. Cod: A Biography of the Fish That Changed the World. New York: Walker, 1997.■ Malefakis, Edward. "Two Iberian Land Reforms Compared: Spain, 1931-1936 and Portugal, 1974—1978." In Gulbenkian Foundation, Agrarian Reform. Lisbon, 1981.■ Moutinho, M. História da pesca do bacalhau. Lisbon: Imprensa Universitária, 1985.■ Oliveira Marques, A. H. de. lntrodução a história da agricultura em Portugal.■ Lisbon, 1968. Pato, Octávio. O Vinho. Lisbon, 1971.■ Pearson, Scott R. Portuguese Agriculture in Transition. Ithaca, N.Y.: Cornell University Press, 1987.■ Postgate, Raymond. Portuguese Wine. London: Dent, 1969.■ Read, Jan. The Wines of Portugal. London: Faber & Faber, 1982.■ Robertson, George. Port. London: Faber & Faber, 1982 ed.■ Rutledge, Ian. "Land Reform and the Portuguese Revolution." Journal of Peasant Studies 5, 1 (Oct. 1977): 79-97.■ Sanceau, Elaine. The British Factory at Oporto. Oporto, 1970.■ Simon, Andre L. Port. London: Constable, 1934.■ Simões, J. Os grandes trabalhadores do Mar: Reportagens na Terra Nova e na Groenlândia. Lisbon: Gazeta dos Caminho de Ferro, 1942.■ Smith, Diana. Portugal and the Challenge of 1992: Special Report. New York: Camões Center/RIIC, Columbia University, 1990.■ Stanislawski, Dan. Landscapes of Bacchus: The Vine in Portugal. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1970.■ Teixeira, Carlos, and Victor M. Pereira da Rosa, eds. The Portuguese in Canada: From the Seat to the City. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2000.■ Unwin, Tim. "Farmers' Perceptions of Agrarian Change in Northwest Portugal." Journal of Rural Studies 1, 4 (1985): 339-57.■ Valadão do Valle, E. Bacalhau: tradições históricas e económicos. Lisbon, 1991.■ Venables, Bernard. Baleia! The Whalers of Azores. London: Bodley Head, 1968.■ Villiers, Alan. The Quest of the Schooner Argus: A Voyage to the Banks and Greenland. New York: Scribners, 1951. World Bank. Portugal: Agricultural Survey. Washington, D.C.: World Bank, 1978.■ ECONOMY, INDUSTRY, AND DEVELOPMENT■ Aiyer, Srivain, and Shahid A. Chandry. Portugal and the E.E.C.: Employment and Implications. Lisbon, 1979.■ Baklanoff, Eric N. The Economic Transformation of Spain and Portugal. New York: Praeger, 1978.■. "Changing Systems: The Portuguese Revolution and the Public Enterprise Sector." ACES ( Association of Comparative Economic Studies) Bulletin 26 (Summer-Fall 1984): 63-76.■. "Portugal's Political Economy: Old and New." In K. Maxwell and M. Haltzel, eds., Portugal: Ancient Country, Young Democracy, 37-59. Washington, D.C.: Wilson Center Press, 1990.■ Barbosa, Manuel P. Growth, Migration and the Balance of Payments in a Small, Open Economy. New York: Garland, 1984.■ Braga de Macedo, Jorge, and Simon Serfaty, eds. Portugal since the Revolution: Economic and Political Perspectives. Boulder, Colo.: Westview, 1981.■ Carvalho, Camilo, et al. Sabotagem Econômica: " Dossier" Banco Espírito Santo e Comercial de Lisboa. Lisbon, 1975.■ Corkill, David. The Development of the Portuguese Economy: A Case of Euro-peanization. London: Routledge, 1999.■ Cravinho, João. "The Portuguese Economy: Constraints and Opportunities." In K. Maxwell, ed., Portugal in the 1980s, 111-65. Westport, Conn.: Greenwood, 1986.■ Dornsbusch, Rudiger, Richard S. Eckhaus, and Lane Taylor. "Analysis and Projection of Macroeconomic Conditions in Portugal." In L. S. Graham and H. M. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal, 299-330. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979.■ The Economist (London). "On the Edge of Europe: A Survey of Portugal." (June 30, 1981): 3-27.■. "Coming Home: A Survey of Portugal." (May 28, 1988).■. 'The New Iberia: Not Quite Kissing Cousins" [Spain and Portugal]. (May 5, 1990): 21-24.■ Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian and German Marshall Fund of the U.S., eds. II Conferência Internacional sobre e Economia Portuguesa, 2 vols. Lisbon, 1979.■ Hudson, Mark. Portugal to 1993: Investing in a European Future. London: The Economist Intelligence Unit/Special Report No. 11 57/EIU Economic Prospects Series, 1989.■ International Labour Office (ILO). Employment and Basic Needs in Portugal. Geneva: ILO, 1979.■ Kavalsky, Basil, and Surendra Agarwal. Portugal: Current and Prospective Economic Trends. Washington, D.C.: World Bank, 1978.■ Krugman, Paul, and Jorge Braga de Macedo. "The Economic Consequences of the April 25th Revolution." Economia III (1979): 455-83.■ Lewis, John R., and Alan M. Williams. "The Sines Project: Portugal's Growth Centre or White Elephant?" Town Planning Review 56, 3 (1985): 339-66.■ Makler, Harry M. "The Consequences of the Survival and Revival of the Industrial Bourgeoisie." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal, 251-83. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■ Marques, A. La Politique Economique Portugaise dans la Période de la Dictature ( 1926-1974). Doctoral thesis, 3rd cycle, University of Grenoble, France, 1980.■ Martins, B. Sociedades e grupos em Portugal. Lisbon, 1973.■ Mata, Eugenia, and Nuno Valério. História Econômica De Portugal: Uma Perspectiva Global. Lisbon: Edit. Presença, 1994. Murteira, Mário. "The Present Economic Situation: Its Origins and Prospects." In L. S. Graham and H. M. Makler, eds., Contemporary Portugal, 331-42. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1979. OCED. Economic Survey: Portugal: 1988. Paris: OCED, 1988 [see also this series since 1978].■ Pasquier, Albert. L'Economie du Portugal: Données et Problémes de Son Expansion. Paris: Librarie Generale de Droit, 1961. Pereira da Moura, Francisco. Para onde vai e economia portuguesa? Lisbon, 1973.■ Pintado, V. Xavier. Structure and Growth of the Portuguese Economy. Geneva: EFTA, 1964.■ Pitta e Cunha, Paulo. "Portugal and the European Economic Community." In L. S. Graham and D. L. Wheeler, eds., In Search of Modern Portugal, 321-38. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press, 1983.■. "The Portuguese Economic System and Accession to the European Community." In E. Sousa Ferreira and W. C. Opello, Jr., eds., Conflict and Change in Portugal, 1974-1984, 281-300. Lisbon, 1985. Porto, Manuel. "Portugal: Twenty Years of Change." In Alan Williams, ed., Southern Europe Transformed, 84-112. London: Harper & Row, 1984. Quarterly Economic Review. London: The Economist Intelligence Unit, 1974-present.■ Salgado de Matos, Luís. Investimentos Estrangeiros em Portugal. Lisbon, 1973 and later eds.■ Schmitt, Hans O. Economic Stabilisation and Growth in Portugal. Washington, D.C.: International Monetary Fund, 1981.■ Smith, Diana. Portugal and the Challenge of 1992. New York: Camões Center, RIIC, Columbia University, 1989.■ Tillotson, John. The Portuguese Bank Note Case [ 1920s]: Legal, Economic and Financial Approaches to the Measure of Damages in Contract. Manchester, U.K.: Faculty of Law, University of Manchester, 1992.■ Tovias, Alfred. Foreign Economic Relations of the Economic Community: The Impact of Spain and Portugal. Boulder, Colo.: Rienner, 1990.■ Valério, Nuno. A moeda em Portugal, 1913-1947. Lisbon: Sá da Costa, 1984.■. As Finanças Públicas Portuguesas Entre As Duas Guerras Mundiais. Lisbon: Cosmos, 1994.■ World Bank. Portugal: Current and Prospective Economic Trends. Washington, D.C.: World Bank, 1978 and to the present.■ PHOTOGRAPHY ON PORTUGAL■ Alves, Afonso Manuel, Antônio Sacchetti, and Moura Machado. Lisboa. Lisbon, 1991.■ Antunes, José. Lisboa do nosso olhar; A look on Lisbon. Lisbon: Câmara Municipal de Lisboa, 1991. Beaton, Cecil. Near East. London: Batsford, 1943.■. Lisboa 1942: Cecil Beaton, Lisbon 1942. Lisbon: British Historical Society of Portugal/Fundação Calouste Gulbenkian, 1995.■ Bottineau, Yves. Portugal. London: Thames & Hudson, 1957.■ Câmara Municipal de Lisboa. 7 Olhares ( Seven Viewpoints). Lisbon: Câmara Municipal de Lisboa, 1998.■ Capital, A. Lisboa: Imagens d'A Capital. Lisbon: Edit. Notícias, 1984.■ Dias, Marina Tavares. Photographias de Lisboa, 1900 ( Photographs of Lisbon, 1900). Lisbon: Quimera, 1991.■. Os melhores postais antigos de Lisboa ( The best old postcards of Lisbon). Lisbon: Químera, 1995.■ Finlayson, Graham, and Frank Tuohy. Portugal. London: Thames & Hudson, 1970.■ Glassner, Helga. Portugal. Berlin-Zurich: Atlantis-Verlag, 1942. Hopkinson, Amanda, ed. Reflections by Ten Portuguese photographers. Bark-way, U.K.: Frontline/Portugal 600, 1996.■ Lima, Luís Leiria, and Isabel Salema. Lisboa de Pedra e Bronze. Lisbon, 1990.■ Martins, Miguel Gomes. Lisboa ribeirinha ( Riverside Lisbon). Lisbon: Arquivo Municipal, Câmara Municipal de Lisboa, Livros Horizonte, 1994. Vieira, Alice. Esta Lisboa ( This Lisbon). Lisbon: Caminho, 1994. Wohl, Hellmut, and Alice Wohl. Portugal. London: Frederick Muller, 1983.■ EQUESTRIANISM■ Andrade, Manoel Carlos de, Luz da Liberal e Nobre Arte da Cavallaria. Lisbon, 1790.■ Graciosa, Filipe. Escola Portuguesa de Arte Equestre. Lisbon, 2004.■ Horsetalk Magazine. Published in New Zealand.■ Oliveira, Nuno. Reflections on the Equestrian Art. London, 2000.■ Russell, Eleanor, ed. The Truth in the Teaching of Nuno Oliveira. Stanhope,■ Queensland, Australia, 2003. Vilaca, Luis V., and Pedro Yglesias d'Oliveira, eds. LUSITANO. Coudelarias De Portugal. O Cavalo ancestral do Sudoeste da Europa. Lisbon: ICONOM, 2005.■ Websites of interest: www.equestrian.pt portugalweb.comHistorical dictionary of Portugal > CULTURE, LITERATURE, AND LANGUAGE
-
17 Mark
1. n Марк2. n знакinterrogation mark, mark of interrogation — вопросительный знак
mark of accent — ударение, знак ударения
trade mark — фабричная марка; фабричный знак; товарный знак
textual mark — корректурный знак, проставляемый в тексте
3. n метка, пометкаcontaining mark — метка сосуда, калиброванного на наливание
tank "full" mark — отметка верхнего уровня топливного бака
4. n штамп, штемпель5. n клеймо, тавро; фабричная марка, фабричное клеймо; торговый знак6. n штемпель7. n ярлык; ценник8. n ориентир; метка; зарубка; веха9. n отметка, черта10. n спорт. линия старта, стартto get off the mark — стартовать, взять старт
11. n спорт. линия финиша12. n шрам, рубец; порез; царапинаarrow mark — веерообразная царапина; «комета»
scratch mark — царапина; риска
13. n след, отпечаток14. n пятно, родинка15. n норма; стандарт; уровеньto be near the mark — приближаться к принятой норме, приближаться к принятому стандарту
datum mark — базис, репер, отметка уровня
16. n отметка, балл, оценкаthe highest mark — высший балл, высшая оценка
she got top marks in the exam — она сдала экзамен на «отлично»
17. n цель; мишеньto overshoot the mark — стрелять с перелётом, давать перелёт
you have overshot the mark — ты зашёл слишком далеко, это ты хватил
off the mark — неточно; ошибочно, неправильно, неверно
you are right off the mark — ты ошибаешься; ты попал пальцем в небо
he was afraid to become a mark for talkers — он опасался стать мишенью для признак, показатель
18. n известность; значительностьa man of mark — известный человек; значительный человек; человек, достойный внимания
of great mark — очень известный, заслуживающий внимания
of little mark — малоизвестный, не стоящий внимания
19. n ист. рубеж, граница; марка20. n ист. марка, крестьянская община в средневековой Германии21. n ист. спорт. жарг. подложечная ямка22. n ист. груб. то, что по вкусуfield mark — метка поля; маркер поля
23. n ист. лингв. помета, знак; признак24. n ист. стирание зубов у лошади, по которому можно определить её возрастto toe the mark — подчиняться требованиям, строго придерживаться правил; выполнять свой долг;
25. v ставить знак, меткуdot mark — точка; метка в виде точки
end mark — метка конца; маркер конца
26. v штамповать, штемпелевать27. v клеймить, таврить28. v маркировать; ставить фабричную марку, фабричное клеймо или торговый знакall furs are plainly marked as to the country of origin — на всех шкурках стоит клеймо страны-экспортёра
long mark — знак долготы,
29. v ставить расценку30. v отмечать, обозначать; размечать; расставлять указательные знакиhe marked the passage I was to read — он отметил отрывок, который мне следовало прочесть
31. v наносить32. v отмечать; указыватьthe thermometer marked 40° in the shade — термометр показывал 40 градусов в тени
33. v оставлять след, пятноthe wet cups have marked the table badly — стол испортили, потому что ставили на него мокрые чашки
34. v оставаться35. v оставлять шрам, рубец36. v оставлять след, отпечатокher face was marked with suffering — по её лицу было видно, что она много страдала в жизни
37. v иметь родимые пятна или естественные метиныhole registration mark — световое пятно, используемое для приводки
38. v выставлять отметку, балл39. v выставлять балл40. v вести счёт, записывать очки41. v отмечать, характеризовать; отличать, выделятьgreat scientific discoveries marked the 19th century — девятнадцатый век был отмечен великими научными открытиями
qualities which mark him off from his colleagues — качества, которые отличают его от его коллег
42. v отмечать, ознаменовыватьhe called for champaign to mark the event — он велел подать шампанского, чтобы отпраздновать это событие
43. v выражать, проявлять44. v замечать, запоминать45. v поэт. замечать, наблюдать46. v книжн. назначать, предназначать; предопределятьhe was marked for greatness by his extraordinary talents — при таких необыкновенных способностях его, несомненно, ждало большое будущее
47. v опекать, прикрыватьСинонимический ряд:1. blemish (noun) blemish; dent; scar; scratch; stain2. effect (noun) consequence; effect; impact; influence; manifestation; repercussion; result3. fool (noun) butt; chump; dupe; easy mark; fall guy; fish; fool; gudgeon; gull; monkey; patsy; pigeon; sap; saphead; simple; sitting duck; sucker; target; tool; victim4. imprint (noun) blaze; impression; imprint; underlining5. indication (noun) evidence; index; indication; indicator; indicia; sign; significant; signification; stamp; symbol; symptom; token; witness6. logo (noun) badge; brand; emblem; label; logo; logotype; representation; trade mark; trademark7. note (noun) distinction; eminence; glory; illustriousness; lustre; notability; note; pre-eminence; prestige; prominence; renown8. notice (noun) attention; cognisance; cognizance; ear; heed; notice; observance; observation; regard; remark9. quality (noun) affection; attribute; character; characteristic; difference; feature; idiosyncrasy; peculiarity; property; quality; savor; savour; trait; virtue10. test (noun) benchmark; criterion; gauge; measure; standard; test; touchstone; yardstick11. use (noun) aim; ambition; bull's-eye; duty; function; goal; object; objective; purpose; quaesitum; use12. aim for (verb) aim for; target13. argue (verb) argue; attest; bespeak; betoken; point to; testify; witness14. beat (verb) beat; count15. brand (verb) brand; earmark; impress16. characterize (verb) characterise; characterize; individualize; individuate; qualify; signalize; singularize17. choose (verb) choose; cull; elect; opt for; optate; pick; pick out; prefer; select; single out; take18. deface (verb) deface; disfigure; grade; score19. denote (verb) denote; designate; indicate20. dirty (verb) dirty; soil; stain21. distinguish (verb) differentiate; discriminate; distinguish; individualise; set apart; signalise22. imprint (verb) blaze; identify; imprint; inscribe; label; print; sign; tag23. see (verb) behold; descry; discern; espy; mind; note; notice; observe; perceive; remark; see; twig; view24. show (verb) chronicle; demonstrate; evidence; evince; exhibit; illustrate; list; manifest; ostend; proclaim; read; record; register; say; showАнтонимический ряд:clean; conceal; ignore; obliteration; omit; overlook; plainness -
18 line
- электрическая линия
- шина (в электротехнике)
- силовая магнитная линия
- проводить линию
- провод
- облицовывать
- обивать (чем-либо) изнутри
- линия транспорта
- линия спуска
- линия коммуникаций
- линия вектора
- линия (связи)
- линия (передачи данных)
- линия (в фигурном катании)
- линия
- кривая на графике
- кривая (на диаграмме)
- канал (аппаратуры)
- агрегат (металлургия)
агрегат
1. Сборочная ед., обладающая полной взаимозаменяемостью, возможностью сборки отдельно от других составных частей или изделия в целом и способностью выполнять определенные функции в изделии или самостоятельно.
2. Механическое соединение неск. машин, станов или устройств, работающих в комплексе (напр., многоклетевой прокатный стан).
3. См. Металлургический агрегат.
[ http://metaltrade.ru/abc/a.htm]Тематики
EN
канал (аппаратуры)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
кривая (на диаграмме)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
кривая на графике
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
- line
- L
линия
-
[IEV number 151-12-27]EN
line
device connecting two points for the purpose of conveying electromagnetic energy between them
NOTE 1 – Electromagnetic energy may be extracted from or supplied to a line at an intermediate point.
NOTE 2 – Examples of lines are two-wire line, polyphase line, coaxial line, waveguide.
Source: 466-01-01 MOD, 601-03-03 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-27]FR
ligne, f
dispositif reliant deux points et destiné à transmettre de l'énergie électromagnétique entre eux
NOTE 1 – De l'énergie électromagnétique peut être extraite d'une ligne ou lui être fournie en un point intermédiaire.
NOTE 2 – Des exemples de lignes sont une ligne bifilaire, une ligne polyphasée, une ligne coaxiale, un guide d'ondes.
Source: 466-01-01 MOD, 601-03-03 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-27]EN
DE
FR
линия
Позиция фигуриста относительно поверхности льда.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]EN
line
Skater's position relative to the ice surface.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]Тематики
EN
линия (передачи данных)
—
[Е.С.Алексеев, А.А.Мячев. Англо-русский толковый словарь по системотехнике ЭВМ. Москва 1993]Тематики
EN
линия вектора
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
line
Term used in GIS technologies in the vector type of internal data organization: spatial data are divided into point, line and polygon types. In most cases, point entities (nodes) are specified directly as coordinate pairs, with lines (arcs or edges) represented as chains of points. Regions are similarly defined in terms of the lines which form their boundaries. Some vector GIS store information in the form of points, line segments and point pairs; others maintain closed lists of points defining polygon regions. Vector structures are especially suited to storing definitions of spatial objects for which sharp boundaries exist or can be imposed. (Source: YOUNG)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
линия спуска
Точный путь или оптимальная траектория спуска саней по желобу.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]EN
line
Precise path or the optimum trajectory of the sled.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]Тематики
- санный спорт, бобслей, скелетон
EN
линия транспорта
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
обивать (чем-либо) изнутри
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
облицовывать
футеровать (топку)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
провод
-
[IEV number 151-12-28]EN
wire
flexible cylindrical conductor, with or without an insulating covering, the length of which is large with respect to its cross-sectional dimensions
NOTE – The cross-section of a wire may have any shape, but the term "wire" is not generally used for ribbons or tapes.
[IEV number 151-12-28]FR
fil, m
conducteur cylindrique flexible, avec ou sans revêtement isolant, dont la longueur est grande par rapport aux dimensions de la section droite
NOTE – La section droite d'un fil peut avoir une forme quelconque, mais le terme "fil" n'est généralement pas employé pour une bande ou un ruban.
[IEV number 151-12-28]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Действия
EN
DE
FR
силовая магнитная линия
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
шина
Проводник с низким сопротивлением, к которому можно подсоединить несколько отдельных электрических цепей.
Примечание — Термин «шина» не включает в себя геометрическую форму, габариты или размеры проводника.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439.1-2013]
шина
Конструктивный элемент низковольтного комплектного устройства (НКУ).
Такой конструктивный элемент предназначен для того, чтобы к нему можно было легко присоединить отдельные электрические цепи (другие шины, отдельные проводники). Такие шины могут иметь различную конструкцию, геометрическую форму и размеры.
[Интент]
шинопроводшина
Медная, алюминиевая, реже стальная полоса, служащая для присоединения кабелей электрогенераторов, трансформаторов и т.д. к проводам питающей сети
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
общаяшина
-
[IEV number 151-12-30]
шина
-
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]EN
busbar
low-impedance conductor to which several electric circuits can be connected at separate points
NOTE – In many cases, the busbar consists of a bar.
[IEV number 151-12-30]
busbar
An electrical conductor that makes a common connection between several circuits. Sometimes, electrical wire cannot accommodate high-current applications, and electricity must be conducted using a more substantial busbar — a thick bar of solid metal (usually copper or aluminum). Busbars are uninsulated, but are physically supported by insulators. They are used in electrical substations to connect incoming and outgoing transmission lines and transformers; in a power plant to connect the generator and the main transformers; in industry, to feed large amounts of electricity to equipment used in the aluminum smelting process, for example, or to distribute electricity in large buildings
[ABB. Glossary of technical terms. 2010]FR
barre omnibus, f
conducteur de faible impédance auquel peuvent être reliés plusieurs circuits électriques en des points séparés
NOTE – Dans de nombreux cas, une barre omnibus est constituée d’une barre.
[IEV number 151-12-30]
2. Проводник прямоугольного сечения из меди, предназначенный для электротехнических целей
(см. ГОСТ 434-78).
Поставляется в бухтах, а также в полосах длиной не менее 2,5 м; По существу, это просто проволока прямоугольного сечения. В указанном ГОСТе и в технической документации, в которой она применяется, обязательно указываются размеры этой проволоки. Например, "Шина ШММ 8,00х40,00 ГОСТ 434-78"
шина
Пруток прямоугольного сечения, применяемый в электротехнике в качестве проводника тока, изготовляемый прессованием или волочением.
[ ГОСТ 25501-82]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- заготовки и полуфабрикаты в металлургии
- кабели, провода...
Действия
- расположение шин «на ребро» [ПУЭ]
- расположение шин «плашмя» [ПУЭ]
Сопутствующие термины
- гибкая шина
- жесткая шина [ПУЭ]
- изолированные шины [ПУЭ]
- круглые шины [ПУЭ]
- неизолированные шины [ПУЭ]
- обходные шины [ПУЭ]
- профильные шины [ПУЭ]
- секционные шины [ПУЭ]
- фазная шина [ ГОСТ Р 51321.1-2000]
- четырехполосные шины с расположением полос по сторонам квадрата ("полый пакет") [ПУЭ]
- шина PEN-проводника
- шина для присоединения защитных проводников
- шина нулевого защитного проводника
- шина фазы А (B, C) [ПУЭ]
- шины однофазного тока [ПУЭ]
- шины прямоугольного (круглого, трубчатого, коробчатого) сечения [ПУЭ]
- шины трехфазного тока [ПУЭ]
EN
DE
FR
электрическая линия
Совокупность проводов, изоляторов и несущих конструкций для передачи электрической энергии между двумя пунктами электрической сети
[ОСТ 45.55-99]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
3.1.11 линия коммуникаций (line): Линия электропередачи или телекоммуникационная линия, подведенные к защищаемому зданию (сооружению).
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62305-2-2010: Менеджмент риска. Защита от молнии. Часть 2. Оценка риска оригинал документа
3.23 линия коммуникаций (line): Линия электропередачи или телекоммуникационная линия, подведенные к защищаемому зданию (сооружению).
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62305-1-2010: Менеджмент риска. Защита от молнии. Часть 1. Общие принципы оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > line
-
19 mark
I 1. noun1) (trace) Spur, die; (of finger, foot also) Abdruck, der; (stain etc.) Fleck, der; (scratch) Kratzer, derdirty mark — Schmutzfleck, der
leave one's/its mark on something — (fig.) einer Sache (Dat.) seinen Stempel aufdrücken
make one's/its mark — (fig.) sich (Dat.) einen Namen machen
distinguishing mark — Kennzeichen, das
Mark 2 version/model — Version/Modell 2
be a mark of good taste/breeding — ein Zeichen guten Geschmacks/guter Erziehung sein
something is the mark of a good writer — an etwas (Dat.) erkennt man einen guten Schriftsteller
get good/bad/35 marks in or for a subject — gute/schlechte Noten od. Zensuren/35 Punkte in einem Fach bekommen
4) (line etc. to indicate position) Markierung, die5) (level) Marke, diereach the 15 % mark — die 15 %-Marke erreichen
on your marks! [get set! go!] — auf die Plätze! [Fertig! Los!]
be quick/slow off the mark — einen guten/schlechten Start haben; (fig.) fix (ugs.) /langsam sein
hit the mark — (fig.) ins Schwarze treffen
be wide of the mark — (lit. or fig.) danebentreffen
2. transitive verbbe close to the mark — (fig.) der Sache nahe kommen
the bottle was marked ‘poison’ — die Flasche trug die Aufschrift "Gift"
mark an item with its price — eine Ware auszeichnen od. mit einem Preisschild versehen
ceremonies to mark the tenth anniversary — Feierlichkeiten aus Anlass des 10. Jahrestages
mark an answer wrong — eine Antwort als falsch bewerten
4)mark time — (Mil.; also fig.) auf der Stelle treten
5) (characterize) kennzeichnen; charakterisieren6) (heed) hören auf (+ Akk.) [Person, Wort][you] mark my words — höre auf mich; eins kann ich dir sagen; (as a warning) lass dir das gesagt sein
Phrasal Verbs:- academic.ru/45241/mark_down">mark down- mark off- mark out- mark upII noun(monetary unit) Mark, die* * *1. noun1) ((also Deutsche Mark, Deutschmark) the standard unit of German currency before the euro.)2) (a point given as a reward for good work etc: She got good marks in the exam.)3) (a stain: That spilt coffee has left a mark on the carpet.)4) (a sign used as a guide to position etc: There's a mark on the map showing where the church is.)5) (a cross or other sign used instead of a signature: He couldn't sign his name, so he made his mark instead.)6) (an indication or sign of a particular thing: a mark of respect.)2. verb1) (to put a mark or stain on, or to become marked or stained: Every pupil's coat must be marked with his name; That coffee has marked the tablecloth; This white material marks easily.)4) (to note: Mark it down in your notebook.)5) ((in football etc) to keep close to (an opponent) so as to prevent his getting the ball: Your job is to mark the centre-forward.)•- marked- markedly
- marker
- marksman
- marksmanship
- leave/make one's mark
- mark out
- mark time* * *mark1[mɑ:k, AM mɑ:rk]I. n1. (spot, stain) Fleck m; (on the skin) Mal nt; (when burnt) Brandmal nt geh; (scratch) Kratzer m, Schramme f; (trace) Spur f; (scar) Narbe f; (fingerprint, footprint) Abdruck mthe wine left a permanent \mark on his shirt der Wein hinterließ bleibende Flecken auf seinem Hemdhis fingers had left \marks all over the table auf dem Tisch waren überall seine Fingerabdrücke zu sehendirt/paint \marks Schmutz-/Farbflecken pl▪ \marks pl Zeichnung fit's the [distinguishing] \mark of a gentleman/good newspaper to... es zeichnet einen Gentleman/eine gute Zeitung aus [o man erkennt einen Gentleman/eine gute Zeitung daran], dass er/sie...the crime bears all the \marks of a planned murder alle Anzeichen weisen auf einen geplanten Mord hindistinguishing [or identifying] \marks unverwechselbare Kennzeichena \mark of appreciation/respect ein Zeichen nt der Wertschätzung/des Respekts\mark of origin Herkunftszeichen nttrade \mark Warenzeichen nt, Schutzmarke fto make one's \mark [on sth] sein Kreuz [unter etw akk] setzenexclamation/quotation \mark Ausrufe-/Fragezeichen ntquotation \marks Anführungszeichen plwhat \mark did you get for biology? was hast du in Biologie bekommen?to get bad/good \marks for sth schlechte/gute Noten für etw akk bekommenfull \marks for guessing who I met at the party ( fig fam) hundert Punkte, wenn du drauf kommst, wen ich auf der Party getroffen habe famto be up to the \mark den Anforderungen [o Erwartungen] entsprechento not feel up to the \mark nicht ganz auf der Höhe sein famhe is a man of \mark er ist eine Persönlichkeit von Rangsales have already passed the million \mark die Verkaufszahlen haben die Millionenmarke bereits überschrittento be over the halfway \mark über die Hälfte geschafft habento be wide of [or quite off] the \mark das Ziel um Längen verfehlen a. figto hit the \mark [genau] ins Schwarze treffen a. figto miss the \mark vorbeischießen; ( fig) seinen Zweck verfehlento overshoot the \mark über das Ziel hinausschießen a. figa \mark 4 Escort ein Escort Modell 417.▶ to leave its/one's \mark on sb/sth seine Spuren bei jdm/etw hinterlassenshe left her \mark on the company sie hat den Betrieb sehr geprägt▶ to make one's \mark auffallen▶ to be slow/quick off the \mark (understand) schwer/schnell von Begriff sein fam; (take action) langsam/[blitz]schnell reagierenyou'll have to be quick off the \mark with that application du musst dich mit der Bewerbung beeilenII. vt1. (stain)▪ to \mark sth etw schmutzig machenhis face was \marked for life er hat bleibende Narben im Gesicht zurückbehaltenthe man's body was \marked with blows from a blunt weapon die Leiche des Mannes trug Spuren von Schlägen mit einer stumpfen Waffe3. (indicate)▪ to \mark sth etw markieren [o bezeichnen] [o kennzeichnen4. (label)the bottle was \marked ‘poison’ die Flasche trug die Aufschrift ‚Gift‘they \marked the shirts at €20 sie zeichneten die Hemden mit 20 Euro austo \mark a route on a plan eine Route auf einem Plan einzeichnen5.to \mark the beginning/end of sth den Anfang/das Ende einer S. gen markierento \mark a turning point einen Wendepunkt darstellen6. (commemorate)a concert to \mark the 10th anniversary ein Konzert aus Anlass des zehnten Jahrestagesa speech to \mark the occasion eine Rede zur Feier des Tages7. SCH▪ to \mark sth etw zensieren▪ to \mark sb jdn benoten8. (clearly identify)▪ to \mark sb/sth as sb/sth jdn/etw als jdn/etw kennzeichnen [o auszeichnen]your clothes \mark you as a man of good taste Ihre Kleider lassen erkennen, dass Sie ein Mann von gutem Geschmack sind10. SPORT, FBALL▪ to \mark sb jdn decken11. SCI12.▶ to \mark time (in a parade) auf der Stelle marschieren; ( fig: not move forward) die Zeit überbrücken▶ [you] \mark my words! lass dir das gesagt sein!III. vi1. (get dirty) schmutzig [o SCHWEIZ a. dreckig] werden, schmutzen, verdrecken SCHWEIZ; (scratch) Kratzer [o Schrammen] bekommen3. (pay attention)\mark! Achtung!mark2<pl -s or ->[mɑ:k, AM mɑ:rk]* * *[mAːk]nMarkus m* * *mark1 [mɑː(r)k]A s1. Markierung f, Mal n, besonders TECH Marke f:make a mark in the calendar sich einen Tag rot anstreichen2. fig Zeichen n:mark of confidence Vertrauensbeweis m;mark of favo(u)r Gunstbezeigung f;mark of respect Zeichen der Hochachtung;distinctive mark Kennzeichen4. (Schrift-, Satz-) Zeichen n:mark of correction Korrekturzeichen5. Orientierungs-, Sichtzeichen n:6. (An)Zeichen n:7. a) (Eigentums)Zeichen nb) Brandmal n10. Kerbe f, Einschnitt m11. (Hand-, Namens) Zeichen n, Kreuz n (eines Analphabeten)12. Ziel n (auch fig), Zielscheibe f:a) (das Ziel) treffen,b) fig ins Schwarze treffen;miss the mark das Ziel verfehlen, danebenschießen (beide a. fig);a) (weit) danebenschießen,b) fig sich (gewaltig) irren, (Schätzung etc) (weit) danebenliegen;£1,000 will be nearer to the mark kommen (schon) eher hin umg13. fig Norm f:a) unter dem Durchschnitt,b) gesundheitlich etc nicht auf der Höhe umg;a) innerhalb der erlaubten Grenzen,b) berechtigt ( in doing sth etwas zu tun);a) über das Ziel hinausschießen umg,b) zu weit gehen, den Bogen überspannen14. (aufgeprägter) Stempel, Gepräge n15. a) (Fuß-, Brems- etc) Spur f:leave one’s mark (up)on fig seinen Stempel aufdrücken (dat); bei jemandem seine Spuren hinterlassen;make one’s mark sich einen Namen machen, sich profilieren ( beide:on, upon in einem Betrieb etc)b) Fleck mc) Abdruck m:leave a mark einen Abdruck hinterlassen, sich abdrücken16. fig Bedeutung f, Rang m:a man of mark eine markante oder bedeutende Persönlichkeit17. Marke f, Sorte f:mark of quality Qualitätsmarke18. WIRTSCHa) (Fabrik-, Waren) Zeichen n, (Schutz-, Handels-) Marke fb) Preisangabe f19. SCHIFFa) (abgemarkte) Fadenlänge (der Lotleine)b) Landmarke fc) Bake f, Leitzeichen nd) Mark n, Ladungsbezeichnung fe) Marke f20. MIL, TECH Modell n, Type f:a mark V tank ein Panzer(wagen) der Type V21. SCHULEgive sb full marks for sth fig jemandem für etwas höchstes Lob zollen;he gained 20 marks for Greek im Griechischen bekam er 20 Punkte;bad mark Note für schlechtes Betragenb) pl Zeugnis n:bad marks ein schlechtes Zeugnis22. umg (das) Richtige:that’s not my mark das ist nicht mein Geschmack, das ist nicht das Richtige für mich24. SPORTa) Fußball: (Elfmeter) Punkt mon your marks! auf die Plätze!;be quick (slow) off the mark einen guten (schlechten) Start haben, fig schnell (langsam) reagieren oder umg schalten26. HISTa) Mark f, Grenzgebiet nb) Gemeindemark f, Allmende f:mark moot Gemeindeversammlung fB v/t1. markieren:a) Wege, Gegenstände etc kennzeichnenc) Wäsche zeichnen:mark by a dotted line durch eine punktierte Linie kennzeichnen;mark (with a hot iron) brandmarken;a) MIL auf der Stelle treten (a. fig),b) fig nicht vom Fleck kommen,c) abwarten,d) MUS den Takt schlagen2. a) Spuren hinterlassen auf (dat):b) fig jemanden zeichnen (Krankheit etc)3. eine Ära etc kennzeichnen, kennzeichnend sein für:the day was marked by heavy fighting der Tag stand im Zeichen schwerer Kämpfe;no triumph marks her manner es ist nicht ihre Art aufzutrumpfen4. ein Zeichen sein für:that marks him for a leader das zeigt, dass er sich zum Führer eignet;he has all the qualities that mark a good doctor er hat alle Eigenschaften, die einen guten Arzt ausmachenfor für)6. hervorheben:mark the occasion (Redew) zur Feier des Tages, aus diesem Anlass7. zum Ausdruck bringen, zeigen:mark one’s displeasure by hissing8. SCHULE benoten, zensieren, SPORT bewerten9. notieren, vermerken10. sich etwas merken:mark my words denke an meine Worte oder an mich!11. bemerken, beachten, achtgeben auf (akk)12. WIRTSCHa) Waren auszeichnenb) Br (öffentlich) notieren (lassen)14. SPORTmark sb man to man jemanden manndecken, jemanden in Manndeckung nehmen;mark sb out of the game jemanden (völlig) abmelden umgb) Punkte, Tore etc aufschreiben, notieren:mark the game → C 4 bC v/i1. markieren2. achtgeben, aufpassen3. sich etwas merken:mark you wohlgemerkt4. SPORTa) deckenb) den Spielstand laufend notieren5. mark easily (quickly) leicht (schnell) schmutzenmark2 [mɑː(r)k] s WIRTSCH1. (deutsche) Mark2. HIST Mark f:M abk3. mega-4. million* * *I 1. noun1) (trace) Spur, die; (of finger, foot also) Abdruck, der; (stain etc.) Fleck, der; (scratch) Kratzer, derdirty mark — Schmutzfleck, der
leave one's/its mark on something — (fig.) einer Sache (Dat.) seinen Stempel aufdrücken
make one's/its mark — (fig.) sich (Dat.) einen Namen machen
distinguishing mark — Kennzeichen, das
Mark 2 version/model — Version/Modell 2
be a mark of good taste/breeding — ein Zeichen guten Geschmacks/guter Erziehung sein
something is the mark of a good writer — an etwas (Dat.) erkennt man einen guten Schriftsteller
get good/bad/35 marks in or for a subject — gute/schlechte Noten od. Zensuren/35 Punkte in einem Fach bekommen
4) (line etc. to indicate position) Markierung, die5) (level) Marke, diereach the 15 % mark — die 15 %-Marke erreichen
on your marks! [get set! go!] — auf die Plätze! [Fertig! Los!]
be quick/slow off the mark — einen guten/schlechten Start haben; (fig.) fix (ugs.) /langsam sein
7) (target, desired object) Ziel, dashit the mark — (fig.) ins Schwarze treffen
be wide of the mark — (lit. or fig.) danebentreffen
2. transitive verbbe close to the mark — (fig.) der Sache nahe kommen
1) (stain, dirty) Flecke[n] machen auf (+ Dat.); schmutzig machen; (scratch) zerkratzen2) (put distinguishing mark on, signal) kennzeichnen, markieren ( with mit)the bottle was marked ‘poison’ — die Flasche trug die Aufschrift "Gift"
mark an item with its price — eine Ware auszeichnen od. mit einem Preisschild versehen
ceremonies to mark the tenth anniversary — Feierlichkeiten aus Anlass des 10. Jahrestages
4)mark time — (Mil.; also fig.) auf der Stelle treten
5) (characterize) kennzeichnen; charakterisieren6) (heed) hören auf (+ Akk.) [Person, Wort][you] mark my words — höre auf mich; eins kann ich dir sagen; (as a warning) lass dir das gesagt sein
Phrasal Verbs:- mark off- mark out- mark upII noun(monetary unit) Mark, die* * *Schulnote f. (german monetary unit) n.Mark nur sing. m. (school) n.Zensur -en f. n.Eindruck -¨e m.Marke -n f.Markierung f.Zeichen - n. (on) v.einzeichnen (auf) ausdr.markieren v. v.beachten v.kennzeichnen v.zensieren (Zensuren geben) v.zensieren v. -
20 conductor
- электрический провод
- трубопровод для подвода и отвода рабочей среды
- проводник (тепла, тока)
- проводник
- печатный проводник
- направляющая колонна (спускаемая иногда вместо кондуктора)
- направляющая колонна
- направляющая жила (геол.)
- направление (первая колонна обсадных труб)
- направление
- кабель
- жила
токопроводящая жила
жила
Элемент кабельного изделия, предназначенный для прохождения электрического тока
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
токопроводящая жила (кабеля)
Элемент кабеля, специфической функцией которого является передача электрического тока
[IEV number 461-01-01]
жила токопроводящая
Изолированный одно- или многопроволочный металлический проводник внутри электрического кабеля
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
жила
-
[IEV number 151-12-37]EN
conductor (of a cable)
part of a cable which has the specific function of carrying current
[IEV number 461-01-01]
strand
one of the wires of a stranded conductor
Source: 466-10-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-37]FR
âme
conducteur (d'un câble) (terme déconseillé dans ce sens)
partie d'un câble dont la fonction spécifique est de conduire le courant
[IEV number 461-01-01]
brin, m
un des fils d'un conducteur câblé
Source: 466-10-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-37]Все жилы двухжильных кабелей должны быть одинакового сечения.
Все жилы трех- и четырехжильных кабелей должны быть одинакового сечения или одна жила должна быть меньшего сечения (нулевая или жила заземления)
Номинальное сечение, мм2
основная жила: 25
нулевая жила: 16
жила заземления: 10
Изолированные жилы многожильных кабелей должны иметь отличительную расцветку или обозначение цифрами, начиная с нуля.
[ ГОСТ 433-73]
Токопроводящие жилы должны быть изолированы поливинилхлоридным пластикатом.
Изолированные жилы должны быть скручены в кабель.
[ ГОСТ 10348-80]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- cable
- cable conductors
- conductor
- conductor core
- conductor of a cable
- conductors
- core
- electric conductor
- strand
DE
- Einzeldraht
- Leiter (eines Kabels), m
- stromführende Ader
FR
электрический кабель
кабель
Кабельное изделие, содержащее одну или более изолированных жил (проводников), заключенных в металлическую или неметаллическую оболочку, поверх которой в зависимости от условий прокладки и эксплуатации может иметься соответствующий защитный покров, в который может входить броня, и пригодное, в частности, для прокладки в земле и под водой.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
кабель
1. Одна или несколько изолированных токопроводящих жил или проводников, заключённых в герметическую оболочку с верхним защитным покрытием
2. Гибкий несущий элемент висячих систем, кабель-кранов и канатных подвесных дорог
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
кабель электрический
Кабель 1. для передачи на расстояние электрической энергии либо сигналов высокого или низкого напряжений
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
кабель
Один или несколько скрученных изолированных гибких проводников, предназначенных для обматывания объектов контроля в целях их продольного или тороидного намагничивания.
кабель
Экранированный проводник, соединяющий электронный блок с преобразователем или электронные блоки между собой
кабель
-
[IEV number 151-12-38]EN
cable
assembly of one or more conductors and/or optical fibres, with a protective covering and possibly filling, insulating and protective material
[IEV number 151-12-38]FR
câble, m
assemblage d'un ou plusieurs conducteurs ou fibres optiques, muni d'une enveloppe protectrice et éventuellement de matériaux de remplissage, d'isolation et de protection
[IEV number 151-12-38]
Пример конструкции кабеля:
1 - Токопроводящие жилы;
2 - Бумага, пропитанная маслом;
3 - Джутовый заполнитель;
4 - Свинцовая оболочка;
5 - Бумажная лента;
6 - Прослойка из джута;
7 - Стальная ленточная броня;
8 - Джутовый покров.
Кабели на напряжение до 1 кВ и выше...
[ГОСТ 12.2.007.14-75]
... силовые кабели с медными или алюминиевыми жилами с резиновой изоляцией, в свинцовой, поливинилхлоридной или резиновой оболочке, с защитными покровами или без них, предназначенные для неподвижной прокладки в электрических сетях напряжением 660 В переменного тока частотой 50 Гц или 1000 В постоянного тока и на напряжение 3000, 6000 и 10000 В постоянного тока.
Кабели предназначены для прокладки:
- на трассах с неограниченной разностью уровней.
- внутри помещений, в каналах, туннелях, в местах, не подверженных вибрации, в условиях отсутствия механических воздействий на кабель..
- в земле (траншеях), если кабель не подвергается значительным растягивающим усилиям
Строительная длина кабелей должна быть не менее 125 м. Допускаются маломерные отрезки длиной не менее 20 м в количестве не более 10 % от общей длины сдаваемой партии кабелей.
[ ГОСТ 433-73]
... монтажные многожильные кабели с поливинилхлоридной изоляцией и оболочкой, предназначенные для фиксированного межприборного монтажа электрических устройств, работающих при номинальном переменном напряжении до 500 В частоты до 400 Гц или постоянном напряжении до 750 В.
Требования к стойкости при механических воздействиях
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии вибрационных нагрузок в диапазоне частот 1-5000 Гц с ускорением до 392 м/с2 (40 g).
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии многократных ударов с ускорением 1471 м/с2 (150 g) при длительности удара 1-3 мс.
- Кабели должны быть механически прочными при воздействии одиночных ударов с ускорением 9810 м/с2(1000 g) и линейных нагрузок с ускорением до 4905 м/с2 (500 g).
Требования к стойкости при климатических воздействиях
-Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию повышенной температуры 343 К (70°С), при этом за повышенную температуру принимают температуру наиболее нагреваемого элемента конструкции кабеля.
- Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию пониженной температуры - 223 К (минус 50°С).
- Кабели должны быть стойкими к воздействию относительной влажности воздуха до 98 % при температуре 308 К (35°С).
- Кабели климатического исполнения Т должны быть стойкими к воздействию плесневых грибов.
[ ГОСТ 10348-80]
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- вводить кабель в отверстие
- вводить кабель в эксплуатацию
- наматывать кабель на барабан
- подключать кабель
- присоединять кабель
- прокладывать кабель
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
- неподвижная прокладка
- прокладка кабеля
- прокладка кабеля в земляной траншее
- прокладка кабеля непосредственно в грунте
- фиксированный межприборный монтаж электрических устройств
EN
DE
FR
направление (первая колонна обсадных труб)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
направляющая жила (геол.)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
направляющая колонна
Первая колонна обсадных труб, спускаемая в буровую скважину на сравнительно небольшую глубину для придания скважине правильного направления и перекрытия почвы, наносов и элювиальных образований
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
направляющая колонна (спускаемая иногда вместо кондуктора)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
печатный проводник
Одна полоска в проводящем рисунке печатной платы.
[ ГОСТ Р 53386-2009]
печатный проводник
Одна проводящая полоска или площадка в проводящем рисунке.
[ ГОСТ 20406-75]Тематики
EN
FR
проводник (1)
Вещество, основным электрическим свойством которого является электропроводность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
проводник (2)
Всё то, что используется (предназначается) для проведения электрического тока:
- провод;
- кабель;
- шина;
- шинопровод;
- жила провода (кабеля);
- проводник печатной платы.
[Интент]
проводник (2)
Проводящая часть, предназначенная для проведения электрического тока определенного значения.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
проводник (2)
Проводящая часть, предназначенная для проведения электрического тока определённого значения.
Проводники представляют собой проводящие части, которые предназначены для проведения электрического тока в электрических цепях электрооборудования и электроустановки здания. Помимо качественной характеристики проводника, указывающей на его способность проводить электрический ток, каждый проводник имеет количественную характеристику, называемую допустимым длительным током. Протекание по проводнику сверхтока вызывает перегрев проводника, который может быть причиной пожара. Поэтому проводники в электроустановках зданий защищают от сверхтоков.
К проводникам, прежде всего, относят жилы проводов и кабелей, из которых выполнены стационарные электропроводки в электроустановке здания, жилы гибких проводов и кабелей, используемых для подключения переносного и передвижного электрооборудования к стационарным электропроводкам, различные шины, применяемые в низковольтных распределительных устройствах и в шинопроводах, а также другие проводящие части, выполняющие функции проводников.
В электроустановках зданий применяют проводники различного назначения. Для обеспечения электрооборудования электрической энергией в электрических цепях переменного тока используют фазные проводники, нейтральные проводники и PEN-проводники, а в электрических цепях постоянного тока – полюсные проводники, средние проводники и PEM-проводники. Защитные проводники, а также PEN-проводники, PEM-проводники и PEL-проводники применяют в электроустановках зданий для защиты от поражения электрическим током.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CF/view/49/]EN
conductor
element intended to carry electric current
NOTE 1 – The term "conductor" is often used for an element the length of which is large with respect to the cross-sectional dimensions, e.g. conductors of a line or of a cable.
NOTE 2 – The English term "conductor" and the French term "conducteur" have also the meaning of "conducting medium".
NOTE 3 – In French, the term "conducteur" is also used as an adjective corresponding to the English "conductive".
[IEV number 151-12-05]FR
conducteur, m
élément destiné à assurer le passage d'un courant électrique
NOTE 1 – Le terme "conducteur" est souvent utilisé pour un élément dont la longueur est grande par rapport aux dimensions de la section droite, par exemple les conducteurs d'une ligne ou d'un câble.
NOTE 2 – Le terme français "conducteur" et le terme anglais " conductor " ont aussi le sens de "milieu conducteur".
NOTE 3 – En français, le terme "conducteur" est aussi employé comme adjectif correspondant à l'anglais "conductive".
[IEV number 151-12-05]К зажиму допускается присоединение двух медных проводников сечением от 1,0 до 4,0 мм2.
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- обесточивать проводник
- определять сечение проводника
- отключать проводник
- отсоединять проводник
- присоединять проводник
- присоединять проводник накруткой
- проводник должен пропускать ток
- соединять проводники
EN
DE
FR
проводник (тепла, тока)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
трубопровод для подвода и отвода рабочей среды
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
электрический провод
провод
Кабельное изделие, содержащее одну или несколько скрученных проволок или одну или более изолированных жил, поверх оторых в зависимости от условий прокладки и эксплуатации может иметься легкая неметаллическая оболочка, обмотка и (или) оплетка из волокнистых материалов или проволоки, и не предназначенное, как правило, для прокладки в земле.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
провод электрический
Металлический проводник, состоящий из одной или нескольких проволок, служащий для передачи и распределения электрической энергии
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
E. Conductor
F. Conducteur
Одна проводящая полоска или площадка в проводящем рисунке
Источник: ГОСТ 20406-75: Платы печатные. Термины и определения оригинал документа
3.16 направление (conductor): Внешняя колонна обсадных труб скважины.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54483-2011: Нефтяная и газовая промышленность. Платформы морские для нефтегазодобычи. Общие требования оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > conductor
См. также в других словарях:
Guide des 100 meilleurs restaurants de France — Sommaire 1 Historique 2 Le guide gastronomique 3 Interactivité du guide 4 Palmarès 2007/2008 … Wikipédia en Français
Guide Du Routard — Le Guide du routard est une collection de guides touristiques française fondée en avril 1973 par Michel Duval et Philippe Gloaguen, dans le sillage des back packers guides américains et du célèbre Hitch hiker s Guide to Europe publié en 1971. La… … Wikipédia en Français
Guide du Routard — Le Guide du routard est une collection de guides touristiques française fondée en avril 1973 par Michel Duval et Philippe Gloaguen, dans le sillage des back packers guides américains et du célèbre Hitch hiker s Guide to Europe publié en 1971. La… … Wikipédia en Français
Guide du Rôliste Galactique — Cet article fait partie de la série Jeu de rôle Jeux : Liste par genre • Catégories par genre • Liste alphabétique • Autres : Éditeurs • … Wikipédia en Français
Guide Rock — Guide Rock, NE U.S. village in Nebraska Population (2000): 245 Housing Units (2000): 162 Land area (2000): 0.504389 sq. miles (1.306361 sq. km) Water area (2000): 0.000000 sq. miles (0.000000 sq. km) Total area (2000): 0.504389 sq. miles… … StarDict's U.S. Gazetteer Places
Guide Rock, NE — U.S. village in Nebraska Population (2000): 245 Housing Units (2000): 162 Land area (2000): 0.504389 sq. miles (1.306361 sq. km) Water area (2000): 0.000000 sq. miles (0.000000 sq. km) Total area (2000): 0.504389 sq. miles (1.306361 sq. km) FIPS… … StarDict's U.S. Gazetteer Places
Guide Parker — Robert M. Parker, Jr. Robert M. Parker, Jr. Robert M. Parker, Jr., né le 23 juillet 1947 à Baltimore, Maryland aux États Unis, est un dégustateur américain de vins, fils de paysan et avocat de profession. Il s est fait connaître, grâce à son… … Wikipédia en Français
Note (typography) — Endnote redirects here. For other uses, see Endnote (disambiguation). Footnote redirects here. For the Hebrew film, see Footnote (film). For the usage of footnoting on Wikipedia, see Wikipedia:Cite sources and Wikipedia:Footnotes. A note is a… … Wikipedia
Guide Michelin — Pour les articles homonymes, voir Michelin (homonymie). Couverture du Guide Michelin de 1929. Le Guide Michelin, souvent surnommé Guide rouge … Wikipédia en Français
Guide du routard — Le Guide du routard est une collection de guides touristiques française fondée en avril 1973 par Michel Duval et Philippe Gloaguen, dans le sillage des back packers guides américains. Ces guides, au nombre de 140 en 2007, sont édités depuis 1975… … Wikipédia en Français
Note of hand — Hand Hand (h[a^]nd), n. [AS. hand, hond; akin to D., G., & Sw. hand, OHG. hant, Dan. haand, Icel. h[ o]nd, Goth. handus, and perh. to Goth. hin[thorn]an to seize (in comp.). Cf. {Hunt}.] 1. That part of the fore limb below the forearm or wrist in … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
