-
1 baff I ont
прил.общ. бах!, бум!, бух! -
2 knapp
knapp halten hålla kort;mit knapper Not nätt och jämnt;die Zeit ist knapp det är ont om tid;das Geld ist bei ihm knapp han har ont om pengar;eine knappe Stunde knappt en timme -
3 wehtun
wehtun göra ont, värka;jdm wehtun göra ngn illa; fig såra ngn;der Kopf tut mir weh jag har ont i huvudet -
4 abgeleitete Einheit
производная единица системы единиц физических величин
производная единица
Единица производной физической величины системы единиц, образованная в соответствии с уравнением, связывающим ее с основными единицами или с основными и уже определенными производными.
Примеры
1. 1 м/с - единица скорости, образованная из основных единиц СИ - метра и секунды.
2. 1 Н - единица силы, образованная из основных единиц СИ - килограмма, метра, и секунды.
[РМГ 29-99]EN
derived unit
unit of measurement for a derived quantity
NOTE 1 – Some derived units in the International System of Units (SI) have special names, e.g. hertz for frequency and joule for energy, but others have compound names, e.g. metre per second for speed. Compounds including units with special names are also used, e.g. volt per metre for the electric field strength, and newton metre for torque. See in particular ISO 31 and ISO/IEC 80000.
NOTE 2 – Derived units can also be expressed by using multiples and submultiples. For example, the metre per second, symbol m/s, and the centimetre per second, symbol cm/s, are derived units of speed in the SI. The kilometre per hour, symbol km/h, is a unit of speed outside the SI but accepted for use with the SI, because the unit hour is accepted for use with the SI. The knot, equal to one nautical mile per hour, is a unit of speed outside the SI, that is used by special interest groups.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.11
[IEV number 112-01-19]FR
unité dérivée, f
unité de mesure d'une grandeur dérivée
NOTE 1 – Certaines unités dérivées dans le SI ont des noms spéciaux, par exemple le hertz pour la fréquence et le joule pour l'énergie, tandis que d'autres ont des noms composés, par exemple le mètre par seconde pour la vitesse. Les unités ayant des noms spéciaux sont aussi utilisées dans des noms composés, par exemple le volt par mètre pour le champ électrique et le newton mètre pour le moment de torsion. Voir en particulier l'ISO 31 et l'ISO/CEI 80000.
NOTE 2 – On peut aussi exprimer les unités dérivées en utilisant des multiples et des sous-multiples. Par exemple, le mètre par seconde, symbole m/s, et le centimètre par seconde, symbole cm/s, sont des unités dérivées de vitesse dans le SI. Le kilomètre par heure, symbole km/h, est une unité de vitesse en dehors du SI mais en usage avec le SI, parce que l'heure est une unité en usage avec le SI. Le nœud, égal à un mille marin par heure, est une unité de vitesse en dehors du SI, qui répond aux besoins spécifiques de certains groupes d’utilisateurs.
Source: ISO/IEC GUIDE 99:2007 1.11
[IEV number 112-01-19]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > abgeleitete Einheit
-
5 Dimension einer Grösse
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
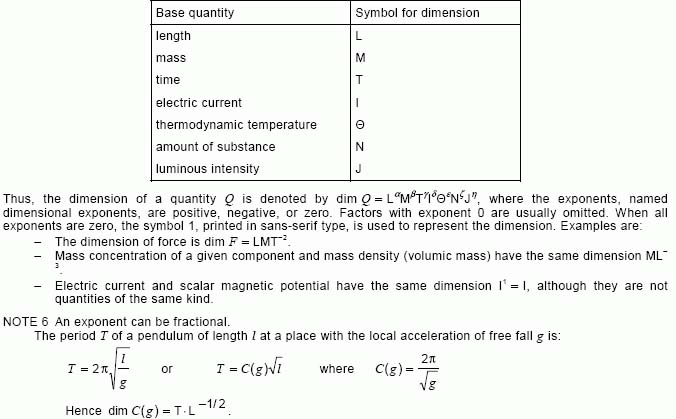
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:
[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dimension einer Grösse
-
6 Dimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dimension, f
-
7 Größendimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Größendimension, f
-
8 Eukaryont
-
9 Symbiont
-
10 Eukaryont
-
11 Symbiont
-
12 Charakter
ka'raktərmCharakter2 (Mensch) personnalité Feminin; Beispiel: sie sind ganz gegensätzliche Charaktere ils ont des personnalités opposées3 Plural (Gestalt) caractère Maskulin; Beispiel: die typischen Charaktere in den Komödien Molières les personnages typiques des comédies de MolièreWendungen: Charakter haben avoir du caractère -
13 Ganztagsschule
-
14 Mitte
'mɪtəf1) ( örtlich) milieu m, centre m2) ( zeitlich) milieu mMitteMị tte ['mɪtə] <-, -n>1 milieu Maskulin; Beispiel: in der Mitte der Straße au milieu de la route; Beispiel: sie nahmen ihn in die Mitte ils l'ont pris entre eux3 (bei Zeitangaben) Beispiel: Mitte des Jahres au milieu de l'année; Beispiel: Mitte Januar à la mi-janvier -
15 fallen
'falənv irr1) ( stürzen) tomber, faire une chute2) (fig: sinken) baisser, chuter3)Er ließ das Messer fallen. — Le couteau lui échappa.
4)fallenfạ llen ['falən] <fạ̈llt, f74b95b6die/74b95b6dl, gefạllen>1 (hinabfallen, umfallen) tomber; Beispiel: auf den Boden/ins Wasser fallen tomber par terre/dans l'eau; Beispiel: auf/durch/in etwas Akkusativ fallen Licht tomber sur/passer par/pénétrer dans quelque chose4 (sinken) Wert, Preise baisser; Beispiel: die Aktien sind gefallen les actions ont connu une baisse6 (treffen) Beispiel: auf jemanden fallen Wahl, Verdacht se porter sur quelqu'un; Beispiel: auf einen Dienstag fallen tomber un mardi11 (sein, sich erweisen) Beispiel: jemandem leicht fallen être facile pour quelqu'un; Beispiel: es fällt mir schwer das zu sagen j'ai du mal à dire ça -
16 gemeinsam
-
17 herauskommen
hɛ'rauskɔmənv irr1) sortir, déboucher de2) ( resultieren aus) résulter de3) ( bekannt werden) transpirer, s'ébruiter4) ( Buch) paraître, sortir5)herauskommenherd73538f0au/d73538f0s|kommen [hε'r42e5dc52au/42e5dc52skɔmən]1 (zum Vorschein kommen) sortir; Beispiel: aus etwas herauskommen sortir de quelque chose; Beispiel: wieder herauskommen ressortir3 (umgangssprachlich: sich ergeben) Beispiel: bei den Verhandlungen ist kein greifbares Ergebnis herausgekommen les pourparlers n'ont abouti à aucun résultat concret; Beispiel: das kommt dabei heraus, wenn... c'est ce qui arrive quand...; Beispiel: das kommt aufs Gleiche heraus c'est du pareil au même4 (überwinden können) Beispiel: aus dem Staunen nicht herauskommen ne pas cesser de s'étonner; Beispiel: aus dem Lachen nicht herauskommen ne pas arrêter de rigoler6 (umgangssprachlich: Publicity haben) Beispiel: mit etwas groß herauskommen (umgangssprachlich) faire un malheur avec quelque chose8 (umgangssprachlich: bekannt werden) Schwindel être découvert; Beispiel: es wird nichts herauskommen rien ne transpirera; Beispiel: es kam heraus, dass on découvrit que10 (aus der Übung kommen) perdre la main12 (zur Geltung kommen) Beispiel: bei Tageslicht besser herauskommen ressortir mieux à la lumière du jour -
18 schlagen
'ʃlaːgənv irr1) ( hauen) battre, frapper, taper, cogner2) (fig: besiegen) battre, vaincre3) ( Uhr) sonnerschlagenschlc1bb8184a/c1bb8184gen ['∫la:gən] <schl47474eebä/47474eebgt, schl403584beu/403584beg, geschle7297af5a/e7297af5gen>1 frapper; Beispiel: jemanden ins Gesicht schlagen frapper quelqu'un au visage2 (besiegen) battre1 haben (hämmern) Beispiel: mit etwas auf etwas Akkusativ /gegen etwas schlagen frapper avec quelque chose sur/contre quelque chose2 haben (hauen, zuschlagen) Beispiel: jemandem mit der Faust ins Gesicht schlagen frapper quelqu'un avec le poing au visage; Beispiel: um sich schlagen se débattre3 sein (auftreffen) Beispiel: an etwas Akkusativ schlagen Regen, Wellen frapper contre quelque chose7 sein Medizin; Beispiel: die Erkältung ist ihm auf die Blase geschlagen le rhume a entraîné une inflammation de la vessie1 (rangeln) Beispiel: sich mit jemandem schlagen se battre avec quelqu'un; Beispiel: sich um etwas schlagen se battre pour [obtenir] quelque chose -
19 wollen
'vɔlənv irrvouloir, avoir la volonté deWie Sie wollen. — Comme vous voudrez.
wollenwọ llen ['vɔlən] <wịll, wọllte, wọllen>1 vouloir; Beispiel: arbeiten wollen vouloir travailler; Beispiel: wir wollten gerade gehen/essen nous nous apprêtions à partir/manger; Beispiel: ich wollte Sie fragen, ob...; (Höflichkeitsfloskel) je voulais vous demander si...; Beispiel: willst du lieber eine Kassette oder eine CD haben? tu préfères avoir une cassette ou un CD?2 (in Aufforderungssätzen) Beispiel: wollen Sie einen Moment Platz nehmen? auriez-vous l'obligeance de prendre place un instant?; Beispiel: willst du wohl still sein! tu vas te taire!5 (werden) Beispiel: es sieht aus, als wolle es gleich ein Gewitter geben on dirait qu'il va bientôt faire de l'orageII <wịll, wọllte, gewọllt> intransitives Verb1 vouloir2 (gehen, reisen wollen) Beispiel: zu jemandem wollen vouloir voir quelqu'un; Beispiel: zu wem wollen Sie? qui voulez-vous voir?3 (umgangssprachlich: funktionieren) Beispiel: das Herz will nicht mehr so richtig le cœur est très fatigué4 (wünschen) Beispiel: [ganz] wie du willst c'est comme tu veux; Beispiel: ich wollte,... j'aimerais que +Subjonctif ; Beispiel: jemandem übel wollen (umgangssprachlich) vouloir du mal à quelqu'unWendungen: dann wollen wir mal! eh bien allons-y!; ob du willst oder nicht que tu le veuilles ou non; wenn man so will pour ainsi dire1 (haben wollen, wünschen) vouloir; Beispiel: willst du lieber Kaffee oder Tee? tu préfères du café ou du thé?; Beispiel: was hat sie von dir gewollt? qu'est-ce qu'elle te voulait?; Beispiel: ohne es zu wollen sans le vouloir3 (umgangssprachlich: brauchen) Beispiel: Kinder wollen viel Liebe les enfants ont besoin de beaucoup d'amour; da ist nichts zu wollen (umgangssprachlich) y a pas moyen; etwas von jemandem wollen (umgangssprachlich: böse Absichten haben) en avoir après quelqu'un; (sexuelles Interesse haben) en pincer pour quelqu'un; was will man mehr! que demande le peuple! -
20 her/stellen
produire, fabriquer, l’ensemble des activités qui ont un impact sur le produit (m.), syn.: erzeugen, produzieren
См. также в других словарях:
ont — ont … Dictionnaire des rimes
ont- — ⇒ONT(O) , (ONT , ONTO )élém. formant I. PHILOS., LING. Élém. tiré du gr. , , part. prés. substantivé au neutre du gr. «je suis», entrant dans la constr. de subst. pour la plupart, auxquels correspondent gén. des adj. en ique et éventuellement des … Encyclopédie Universelle
ONT — could mean: LA/Ontario International Airport (IATA code ONT), in Ontario, California, United States Optical Network Terminal, an interface between a telephone company s fiber optic network and premises wiring Ontario Northland Railway, a Canadian … Wikipedia
-ont — suff. Cell; organism: biont. [From Greek ōn, ont present participle of einai, to be. See es . * * * … Universalium
ont... — ont..., Ont... vgl. ↑onto..., Onto … Das große Fremdwörterbuch
ONT — steht für: 2 Nitrotoluol Flughafen Los Angeles Ontario im US Bundesstaat Kalifornien als IATA Code Optical Network Terminal, siehe HYTAS Ordo Novi Templi (dt: Neutempler Orden), ein von Lanz von Liebenfels gegründeter, rassistischer und okkulter… … Deutsch Wikipedia
ont- — pref. Variant of onto . * * * … Universalium
Ont — abbrev. Ontario * * * … Universalium
...ont — <aus gr. o̅n, Gen. óntos, Part. Präs. von eĩnai »sein«> Endung männlicher Substantive, die eine bestimmte Lebensweise kennzeichnet, z. B. Symbiont … Das große Fremdwörterbuch
Ont — (ontario) n. province and lake in Canada … English contemporary dictionary
Ont — abbrev. Ontario … English World dictionary
