-
21 рычаг
mFRA levier mDEU Hebel mENG leverITA leva fPLN dźwignia fRUS рычаг mсм. поз. 714 на, ,
,  ,
,  FRA timon mDEU Deichsel fENG draw-barITA timone mPLN dyszel mRUS рычаг mсм. поз. 2804 на
FRA timon mDEU Deichsel fENG draw-barITA timone mPLN dyszel mRUS рычаг mсм. поз. 2804 на —FRA levier m de déverrouillageDEU Entriegelungshebel mENG release leverITA leva f di aperturaPLN dźwignia f ryglowaniaRUS рычаг m для открывания люкасм. поз. 1383 на
—FRA levier m de déverrouillageDEU Entriegelungshebel mENG release leverITA leva f di aperturaPLN dźwignia f ryglowaniaRUS рычаг m для открывания люкасм. поз. 1383 на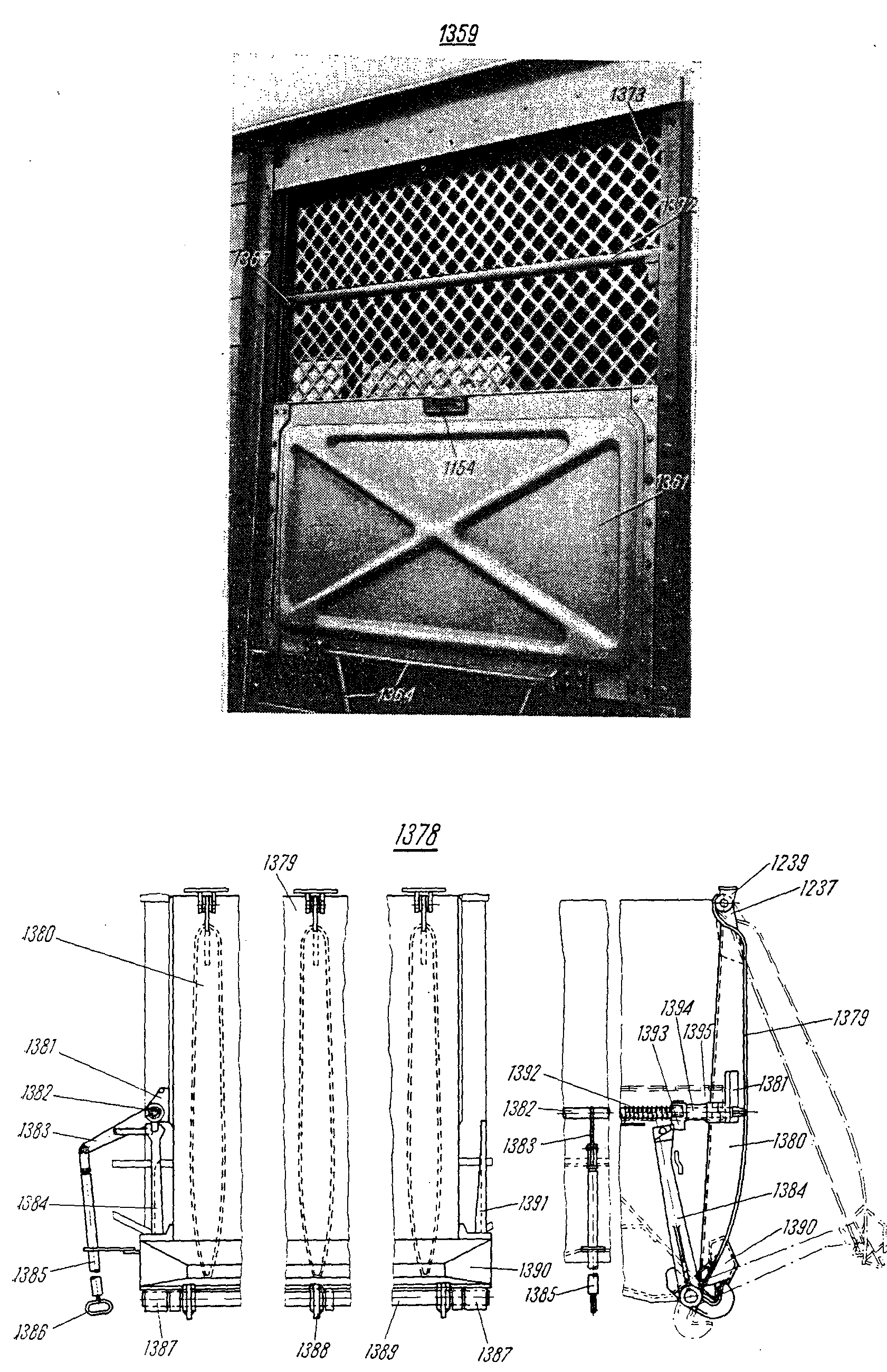
рычаг для установки задних опор
—FRA dispositif m de blocage arrièreDEU Feststelleinrichtung f, hintereITA dispositivo m di bloccaggio posteriorePLN urządzenie n ustalające, tylneRUS рычаг m для установки задних опорсм. поз. 2802 на
рычаг для установки передних опор
—FRA dispositif m de blocage avantDEU Feststelleinrichtung f, vordereITA dispositivo m di bloccaggio anteriorePLN urządzenie n ustalające, przednieRUS рычаг m для установки передних опорсм. поз. 2801 на —FRA béquille f de verrouillageDEU Verschlußhebel mENG locking handleITA leva f di chiusuraPLN dźwignia f walu ryglowaniaRUS рычаг m запорасм. поз. 1384 на,
—FRA béquille f de verrouillageDEU Verschlußhebel mENG locking handleITA leva f di chiusuraPLN dźwignia f walu ryglowaniaRUS рычаг m запорасм. поз. 1384 на, FRA dispositif m de fermetureDEU Verschluß m für BehälterklappeENG fastening deviceITA dispositivo m di chiusuraPLN zamek m ściany odchylnejRUS рычаг m запорасм. поз. 2765 на
FRA dispositif m de fermetureDEU Verschluß m für BehälterklappeENG fastening deviceITA dispositivo m di chiusuraPLN zamek m ściany odchylnejRUS рычаг m запорасм. поз. 2765 на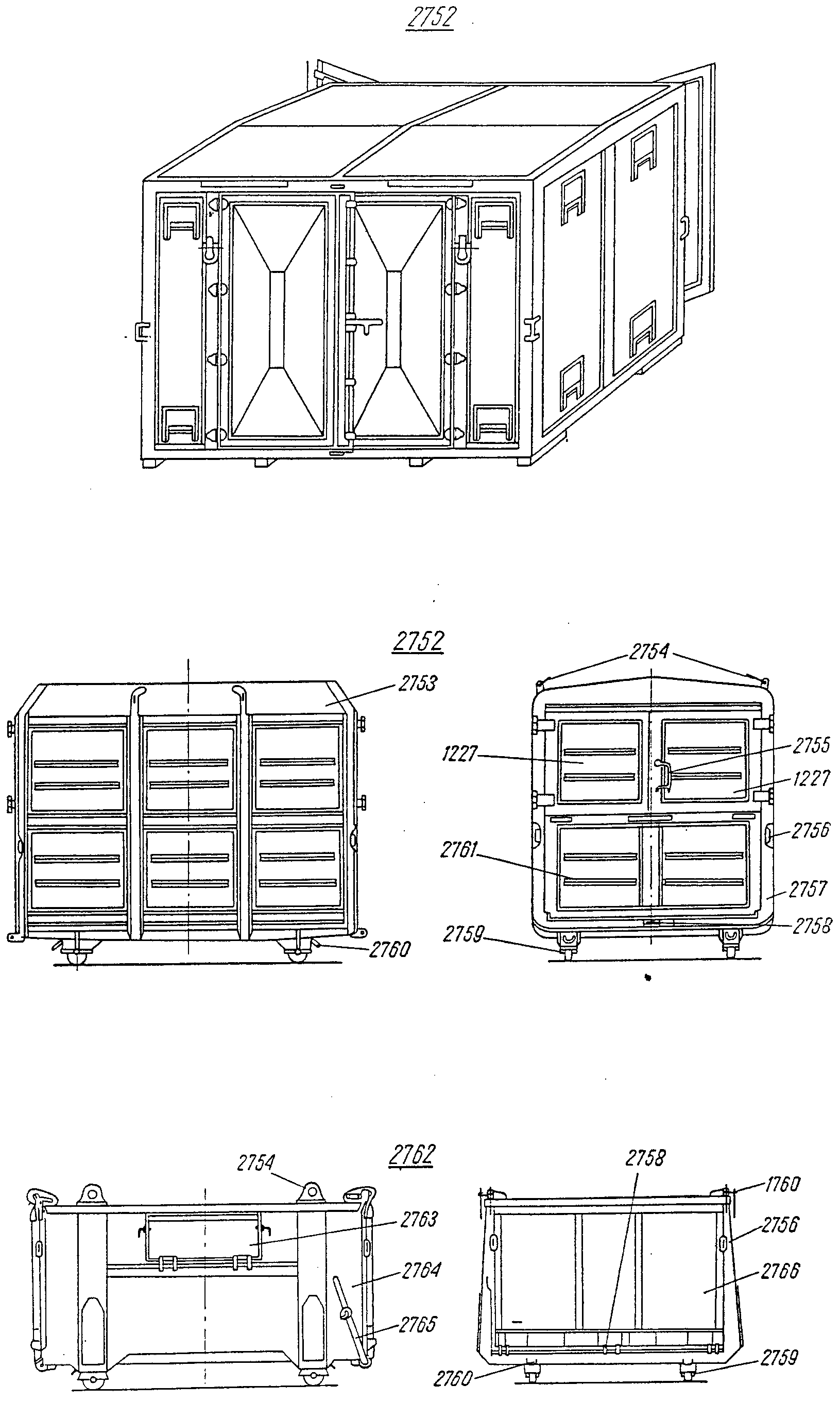 ,
,  —FRA poignée fDEU Verschlußhebel mENG handleITA maniglia fPLN rękojeść f ryglaRUS рычаг m запорного ригелясм. поз. 1236 на
—FRA poignée fDEU Verschlußhebel mENG handleITA maniglia fPLN rękojeść f ryglaRUS рычаг m запорного ригелясм. поз. 1236 на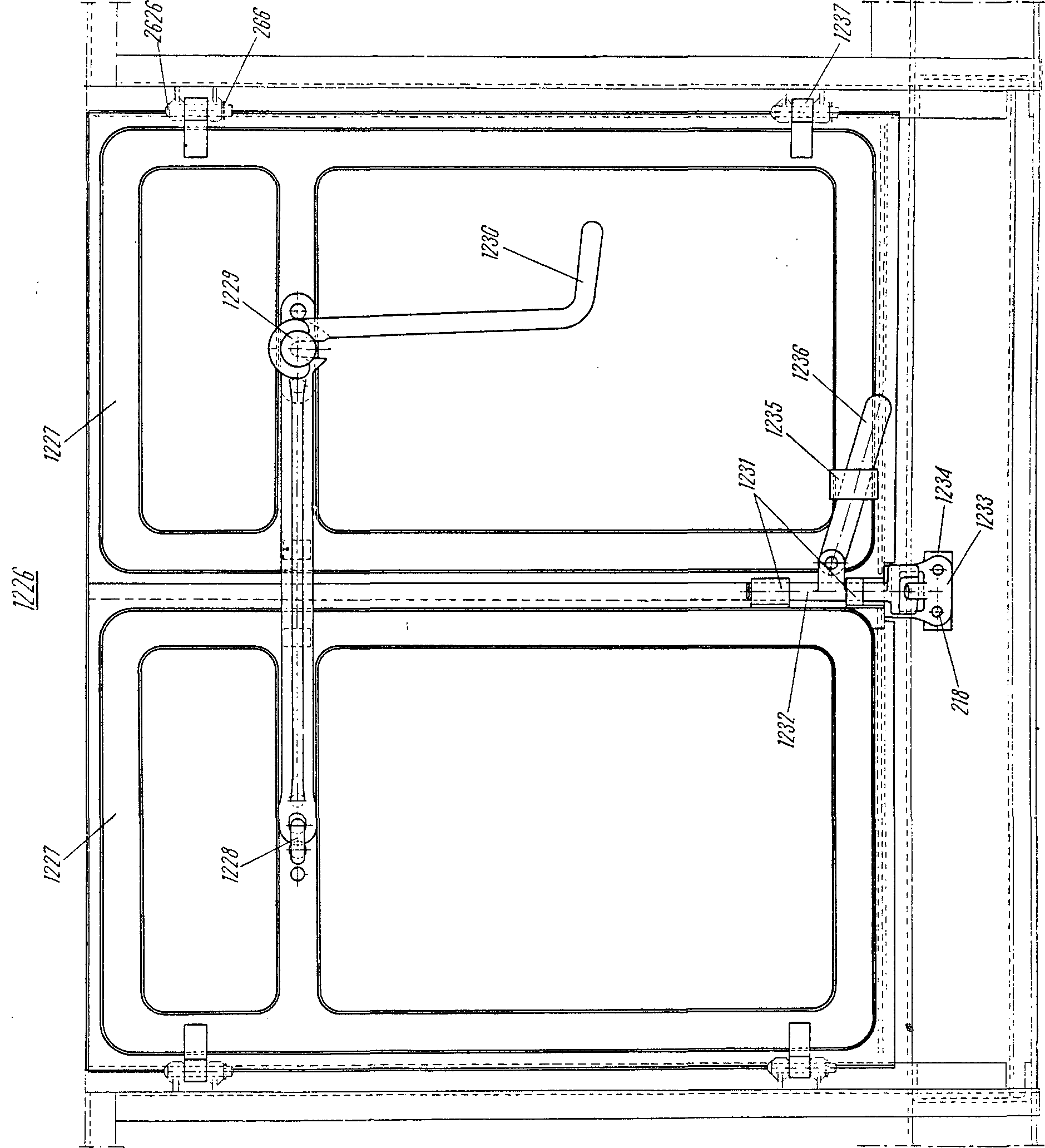 ,
, 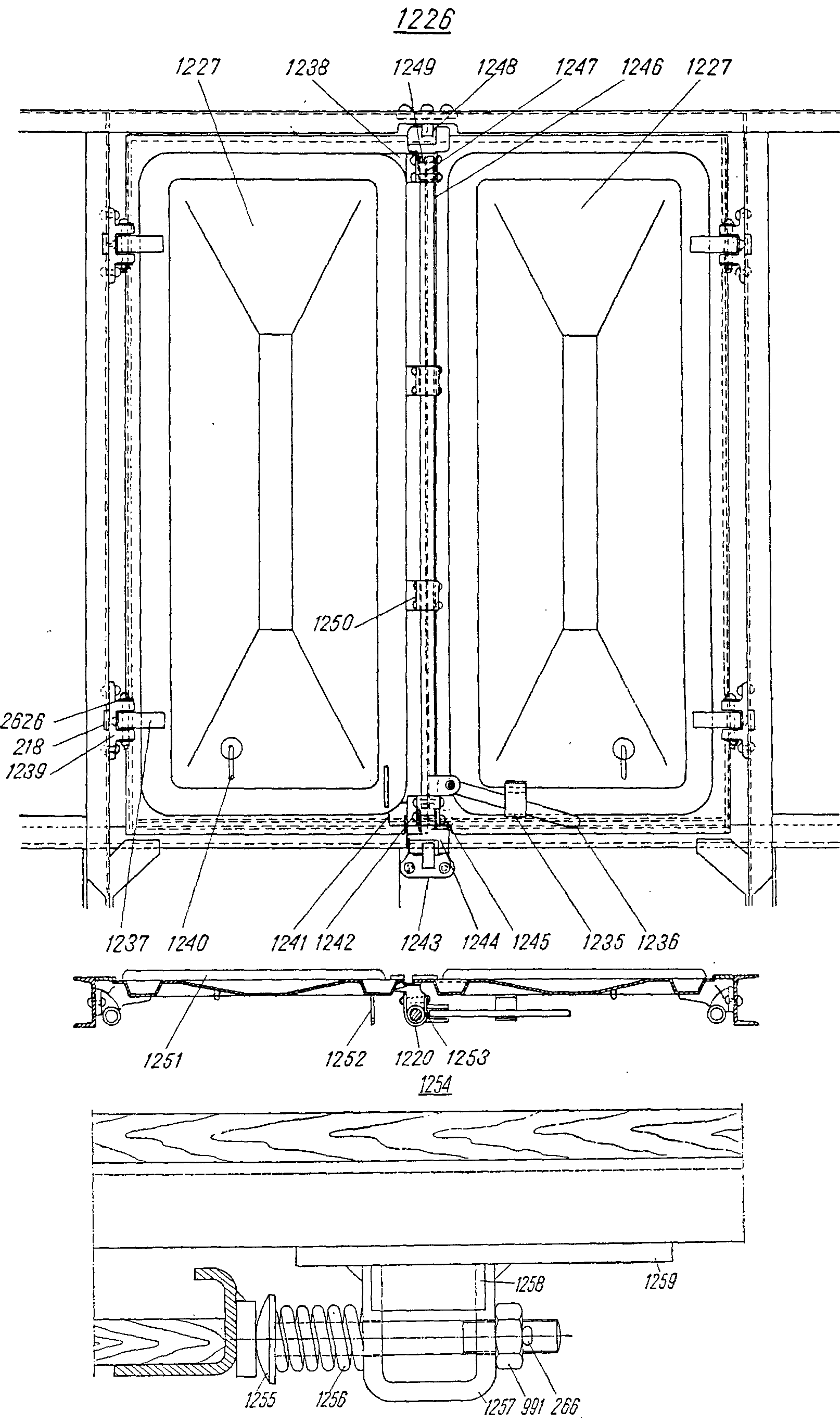 —FRA tringle f de manœuvreDEU Betätigungsgestänge f für SchieberENG operating rodITA barra f di manovraPLN drążek m zasuwyRUS рычаг m заслонки люкасм. поз. 1364 на
—FRA tringle f de manœuvreDEU Betätigungsgestänge f für SchieberENG operating rodITA barra f di manovraPLN drążek m zasuwyRUS рычаг m заслонки люкасм. поз. 1364 на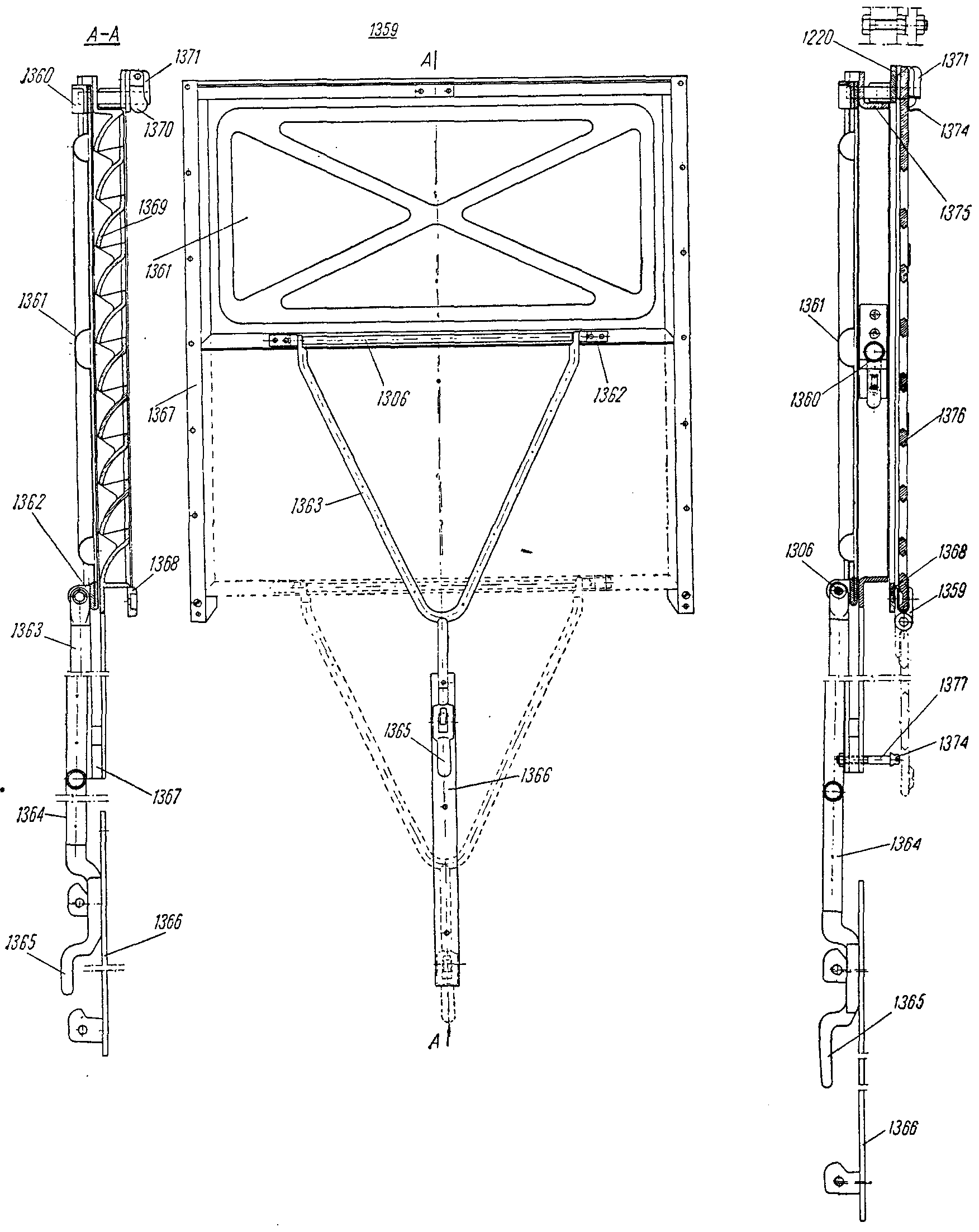 ,
,  —FRA levier m coudéDEU Kniewellenhebel mENG crank handleITA leva f a gomitoPLN dźwignia f wału zaciskowregoRUS рычаг m коленчатого валасм. поз. 964 на
—FRA levier m coudéDEU Kniewellenhebel mENG crank handleITA leva f a gomitoPLN dźwignia f wału zaciskowregoRUS рычаг m коленчатого валасм. поз. 964 на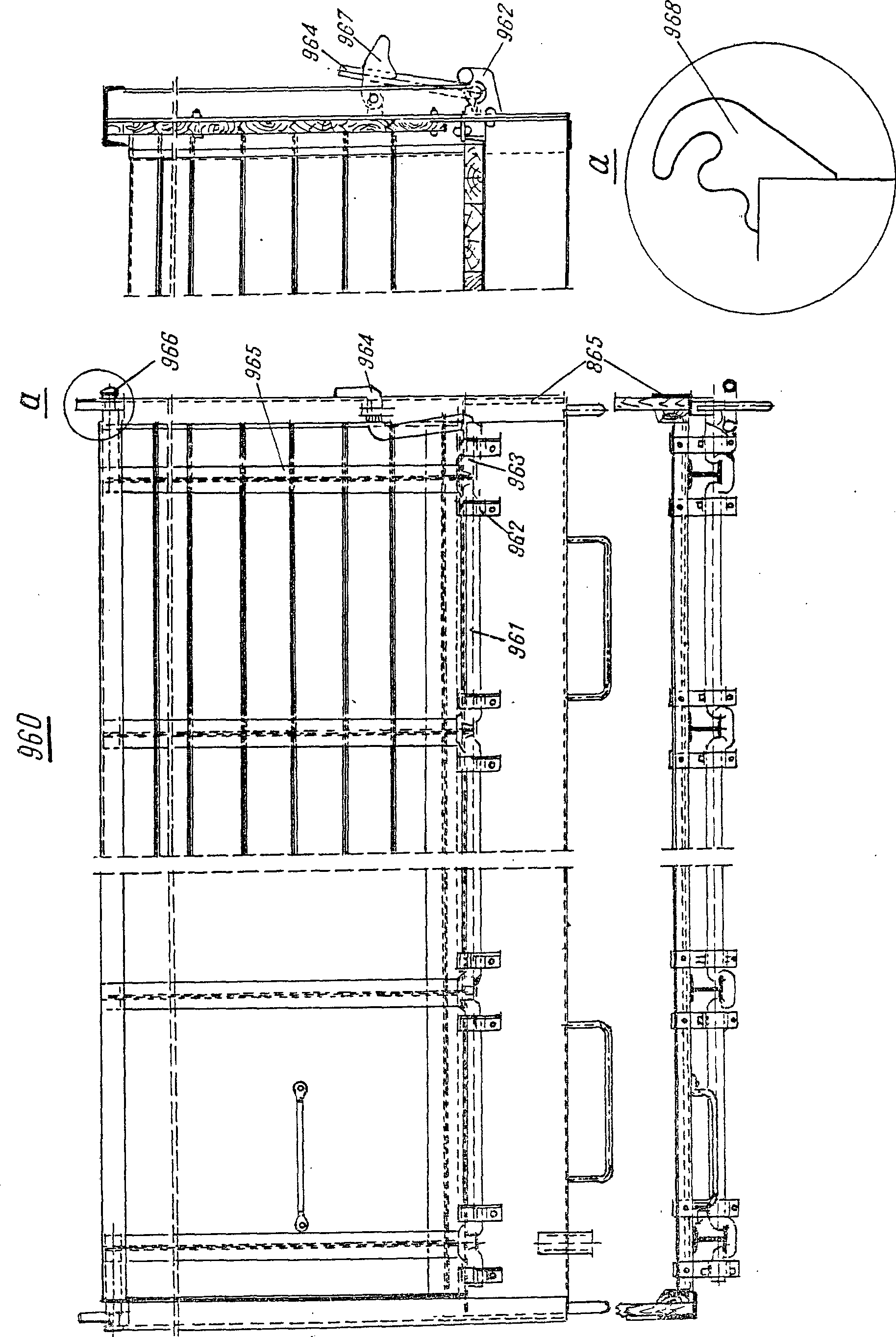
рычаг кронштейна торсионного вала
—FRA levier m du point fixe de la barre de torsionDEU Festpunkthebel m für WiegenlenkerITA braccio m del punto fisso della barra di torsionePLN dźwignia f stala drążka skrętnegoRUS рычаг m кронштейна торсионного валасм. поз. 289 на —FRA levier m du déverseur escamotableDEU Hebel m für Rutschenverlängerung fITA leva f dello scivoloPLN dźwignia f przedłużacza zsypuRUS рычаг m лоткасм. поз. 1405 на
—FRA levier m du déverseur escamotableDEU Hebel m für Rutschenverlängerung fITA leva f dello scivoloPLN dźwignia f przedłużacza zsypuRUS рычаг m лоткасм. поз. 1405 на —FRA balancier m à point fixeDEU Festpunkthebel mITA leva f del punto fissoPLN dźwignia f przycylindrowa tylnaRUS рычаг m мёртвой точкисм. поз. 524 на
—FRA balancier m à point fixeDEU Festpunkthebel mITA leva f del punto fissoPLN dźwignia f przycylindrowa tylnaRUS рычаг m мёртвой точкисм. поз. 524 на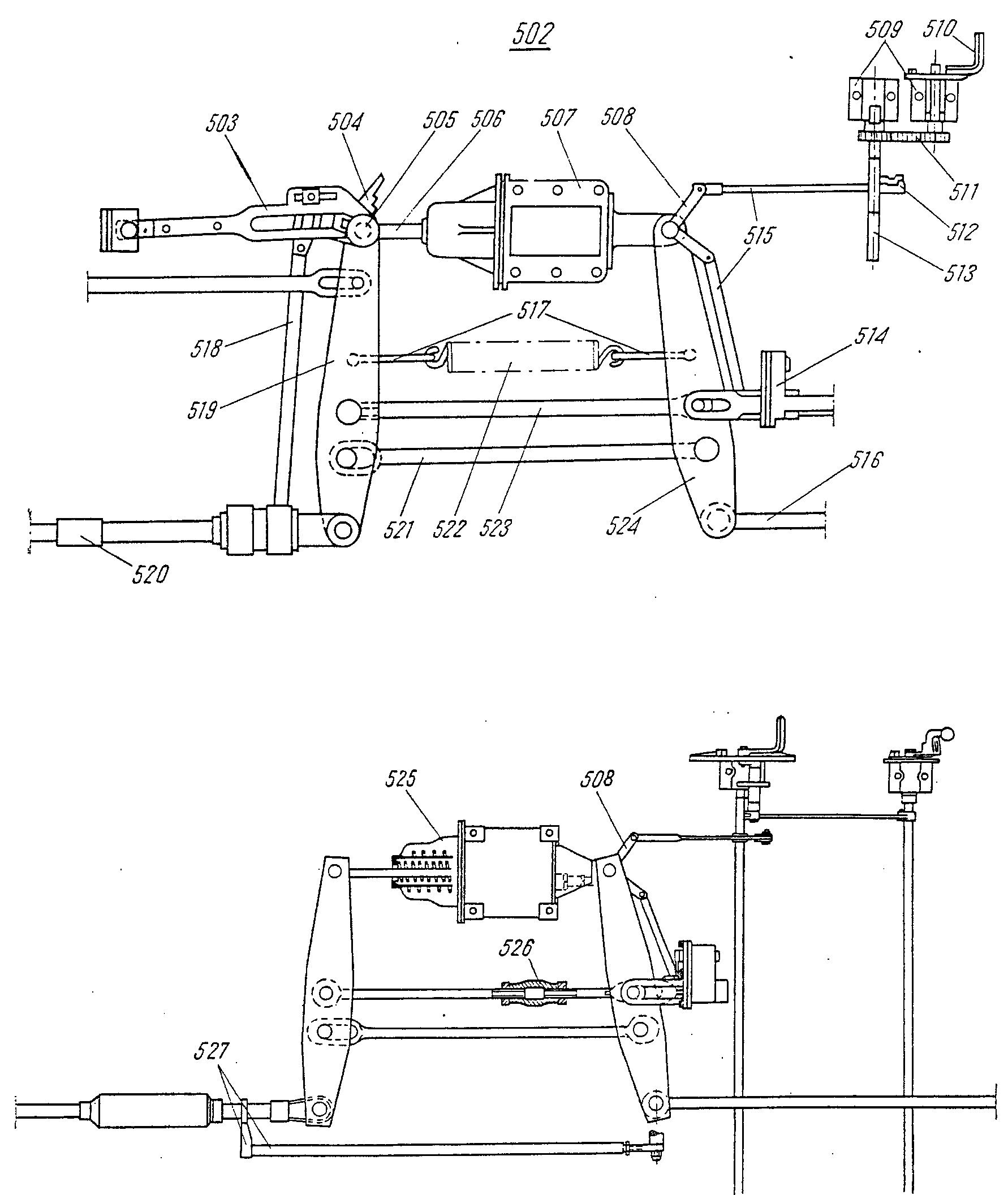 —FRA bielle f de commandeDEU Umstellhebel mENG control leverITA biella f di comandoPLN dźwignia f wału sterującegoRUS рычаг m переводного валасм. поз. 660 на
—FRA bielle f de commandeDEU Umstellhebel mENG control leverITA biella f di comandoPLN dźwignia f wału sterującegoRUS рычаг m переводного валасм. поз. 660 на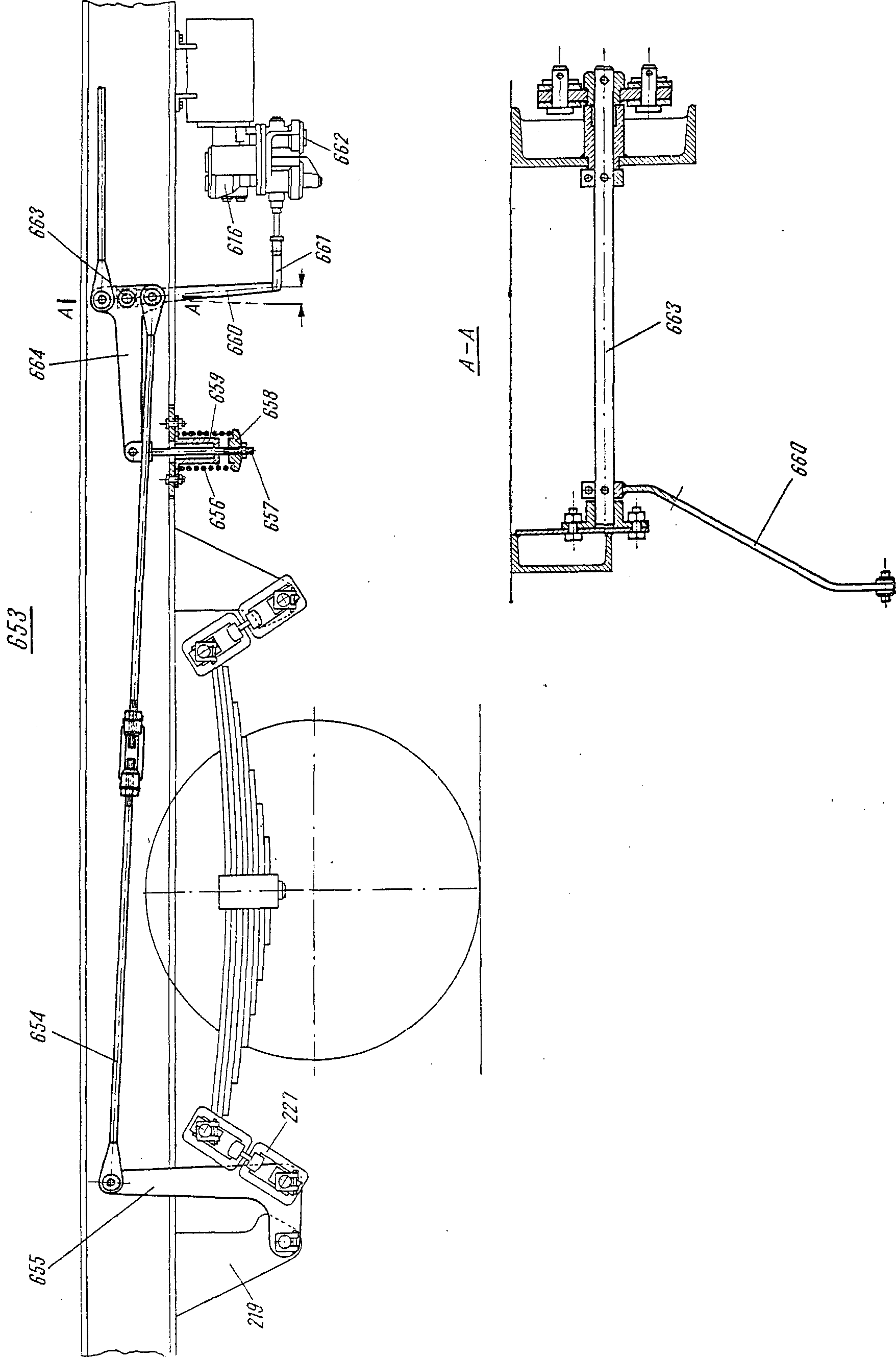
рычаг поворотного люка, запорный
—FRA levier m de la trappeDEU Verschlußhebel m für RundschieberENG trap leverITA leva f della paratoiaPLN dźwignia f klapy obrotowejRUS рычаг m поворотного люка, запорныйсм. поз. 1403 на
рычаг регулятора, приводной
—FRA levier m de commandeDEU Stellhebel mENG control leverITA leva f di comandoPLN dźwignia f nastawczaRUS рычаг m регулятора, приводнойсм. поз. 2239 на ,
,  ,
, 
рычаг с постоянной точкой опоры
—FRA balancier mENG brake leversITA leva f orizzontalePLN dźwignia f główna przekładniRUS рычаг m с постоянной точкой опорысм. поз. 798 на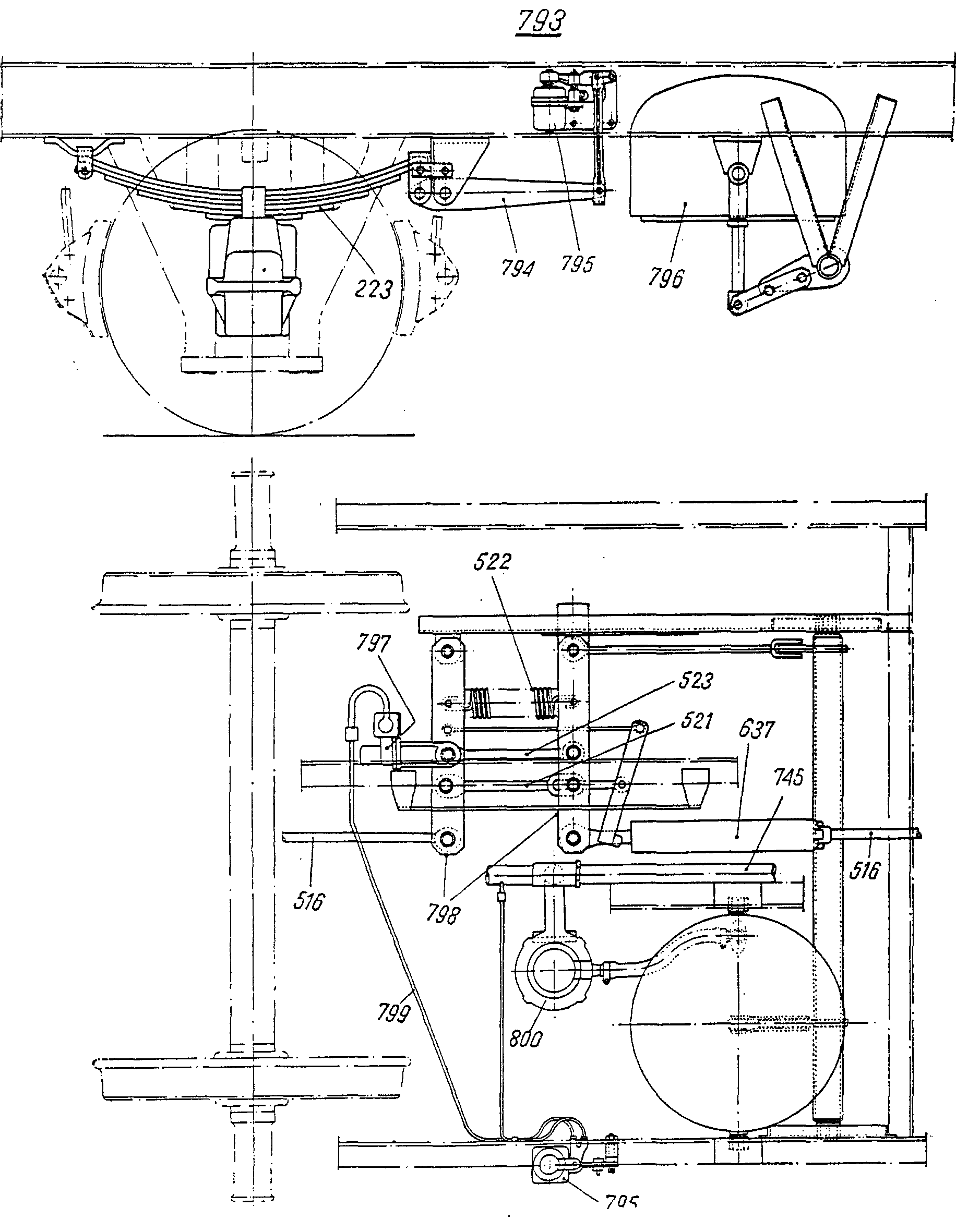 —FRA levier m de renvoiDEU Bremswellenhebel mITA leva f di rinvioPLN dźwignia f bocznaRUS рычаг m тормозного валасм. поз. 597 на
—FRA levier m de renvoiDEU Bremswellenhebel mITA leva f di rinvioPLN dźwignia f bocznaRUS рычаг m тормозного валасм. поз. 597 на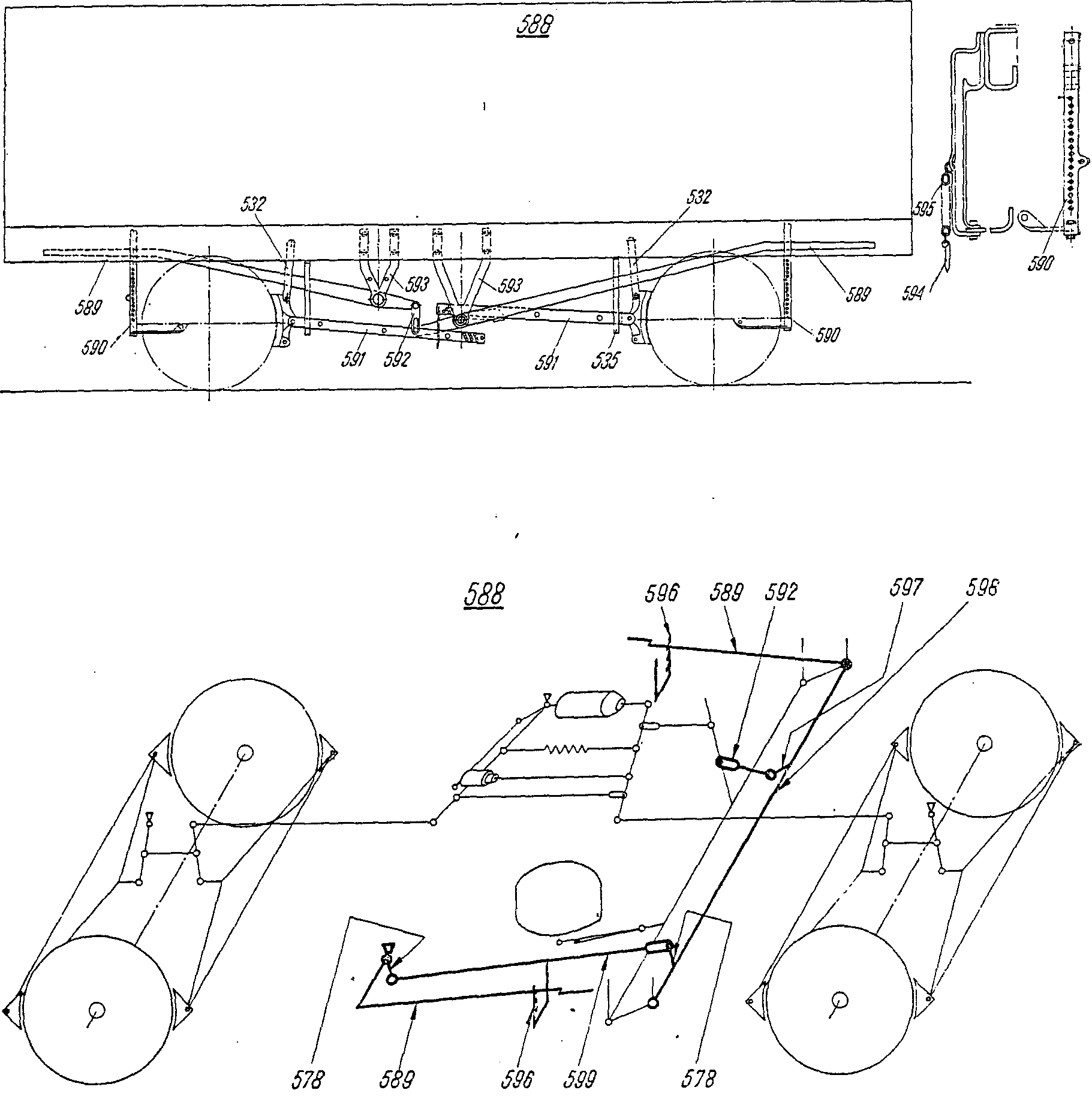 —FRA bielle f de pousséeDEU Druckstange fENG brake push rodITA biella f di spintaPLN drążek m dociskowyRUS рычаг m тормозной колодкисм. поз. 591 на
—FRA bielle f de pousséeDEU Druckstange fENG brake push rodITA biella f di spintaPLN drążek m dociskowyRUS рычаг m тормозной колодкисм. поз. 591 на —FRA levier m de la barre de torsionDEU Hebel m für Torsionsstab mITA braccio m della barra di torsionePLN dźwignia f drążka skrętnegoRUS рычаг m торсионного валасм. поз. 284 на
—FRA levier m de la barre de torsionDEU Hebel m für Torsionsstab mITA braccio m della barra di torsionePLN dźwignia f drążka skrętnegoRUS рычаг m торсионного валасм. поз. 284 на —FRA levier m de transmissionDEU Übertragungshebel mITA leva f di trasmissionePLN dźwignia f napędowaRUS рычаг m тяги регуляторасм. поз. 2322 на
—FRA levier m de transmissionDEU Übertragungshebel mITA leva f di trasmissionePLN dźwignia f napędowaRUS рычаг m тяги регуляторасм. поз. 2322 на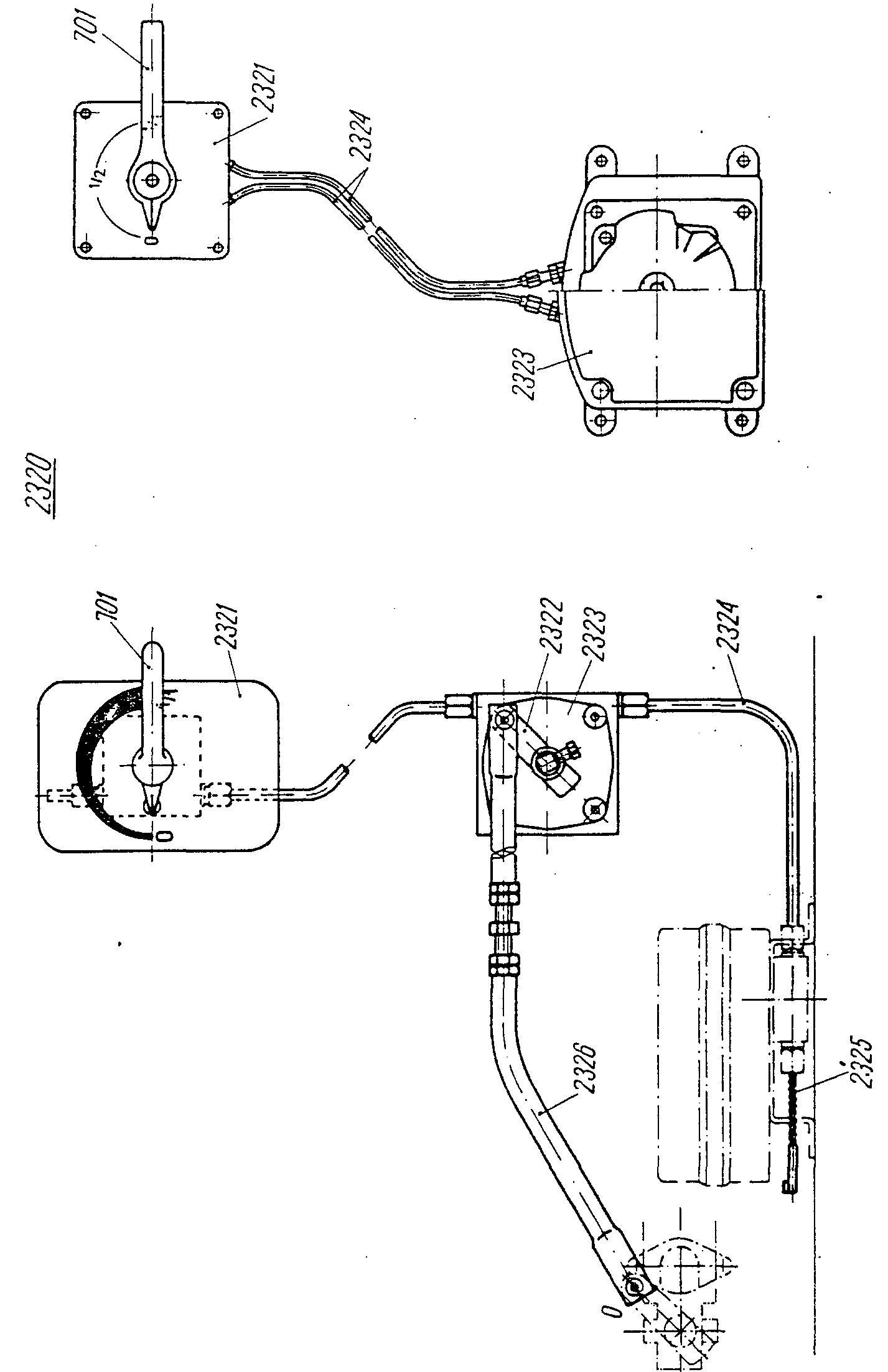 —FRA levier m de renvoi (petit)DEU Handbremshebel m, kurzerENG double brake lever, smallITA braccio m piccolo della leva a campanellaPLN ramię n dźwigni kątowej, krótkieRUS рычаг m тяги ручного тормозасм. поз. 584 на
—FRA levier m de renvoi (petit)DEU Handbremshebel m, kurzerENG double brake lever, smallITA braccio m piccolo della leva a campanellaPLN ramię n dźwigni kątowej, krótkieRUS рычаг m тяги ручного тормозасм. поз. 584 на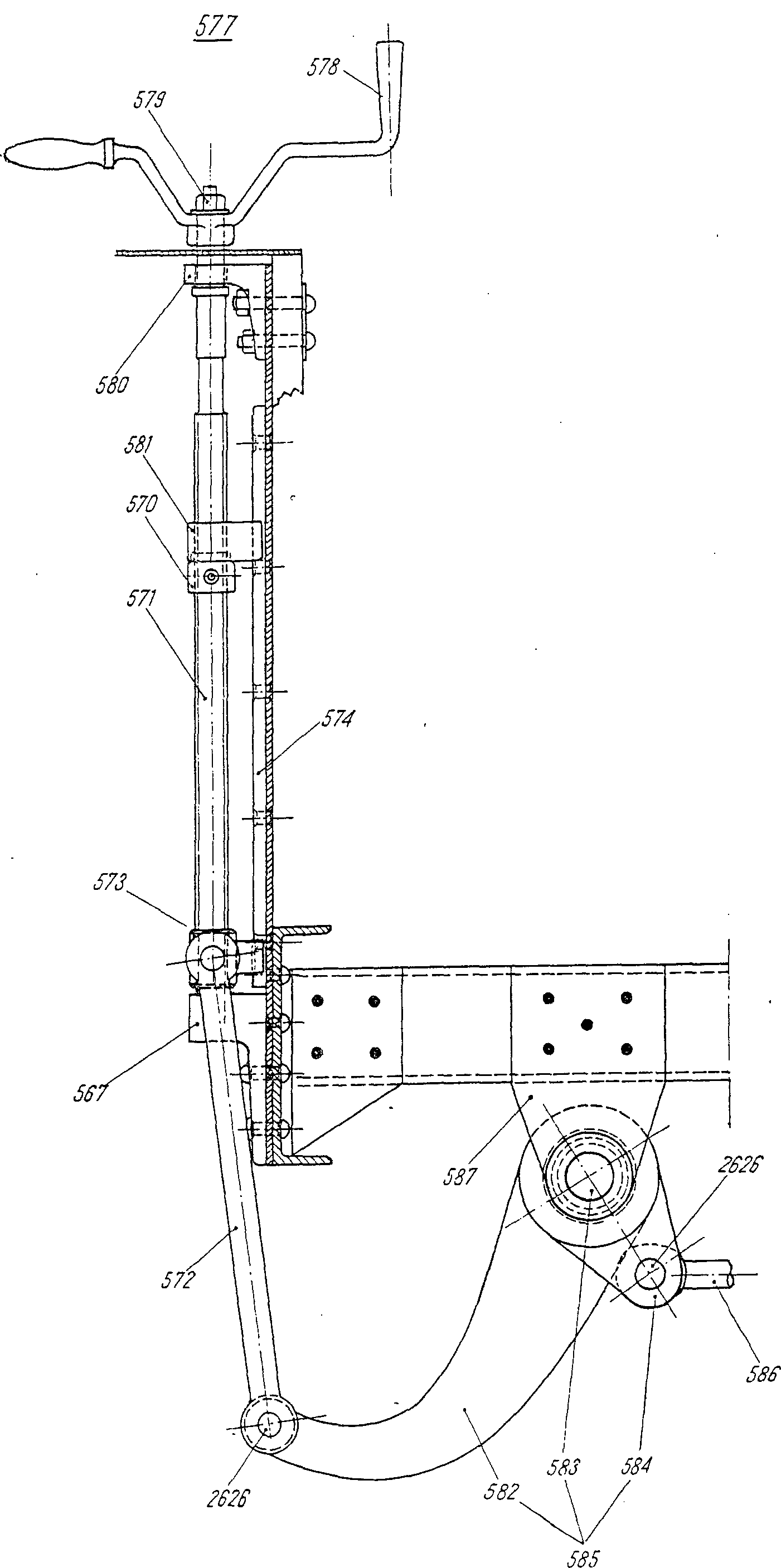 —FRA bielle f de commande du voletDEU Steuerhebel m für DrehflügelITA biella f di comando delle stecche orientabiliPLN cięgło n zasłonyRUS рычаг m управления жалюзисм. поз. 2268 на
—FRA bielle f de commande du voletDEU Steuerhebel m für DrehflügelITA biella f di comando delle stecche orientabiliPLN cięgło n zasłonyRUS рычаг m управления жалюзисм. поз. 2268 на
рычаг уравновешивающего механизма
—FRA levier m de l'équilibreurDEU Ausgleichhebel m mit FührungsrolleITA leva f dell'equilibratorePLN dźwignia f wyrównywaczaRUS рычаг m уравновешивающего механизмасм. поз. 1350 на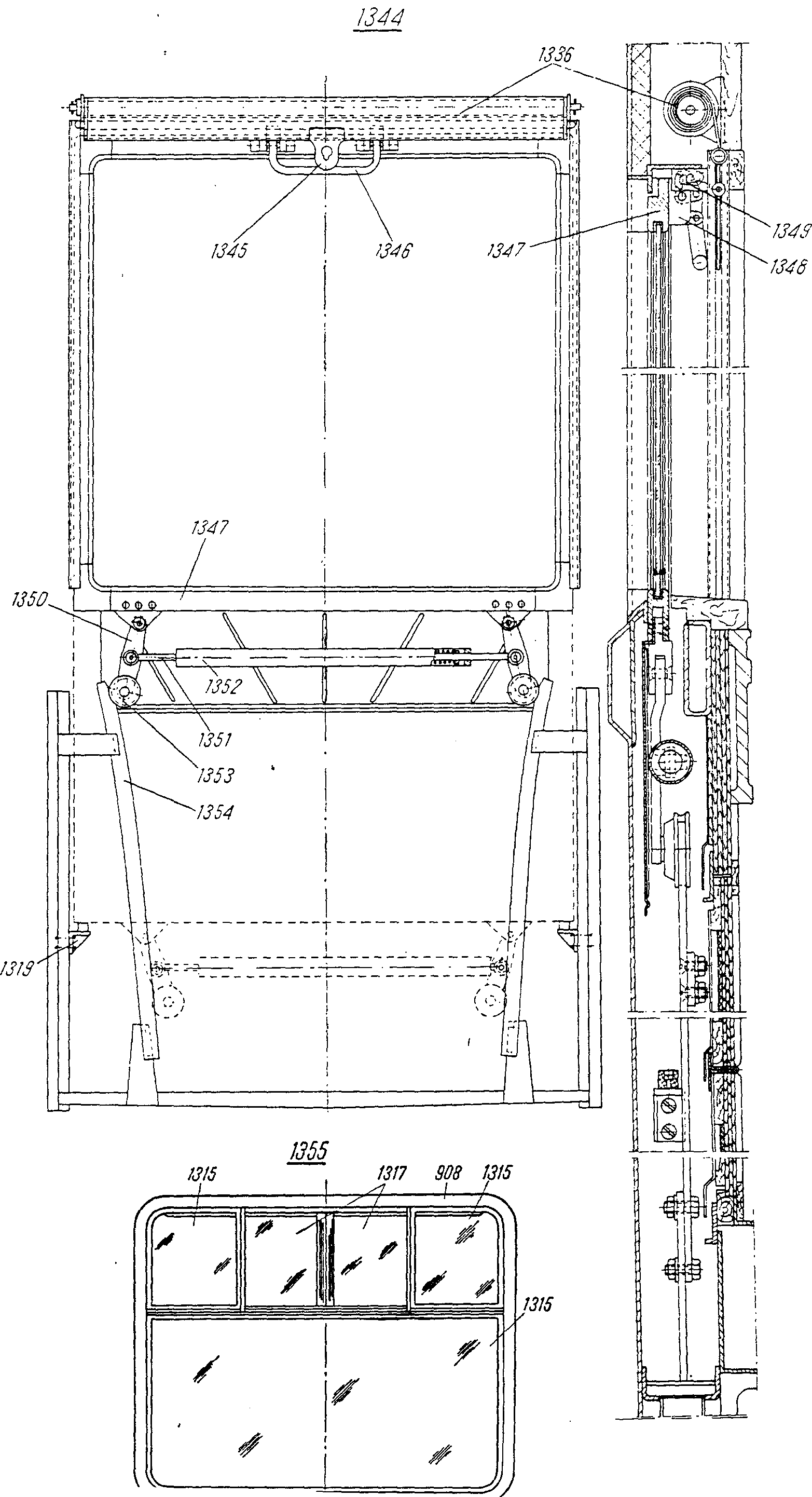
рычаг устройства для сцепления тягача с контрейлером
—FRA dispositif m de commande de calage d’axe d’attelageDEU Betätigungseinrichtung f zum Festlegen der Kupplung fITA dispositivo m di comando di calettamento dell'asse di aggancio del semirimorchioPLN dźwignia f umocowania sworznia sprzęgu naczepyRUS рычаг m устройства для сцепления тягача с контрейлеромсм. поз. 2702 на —FRA cale fDEU Wechselkloben mITA zeppa fPLN wkładka f odstępowaRUS рычаг m фиксаторасм. поз. 534 на
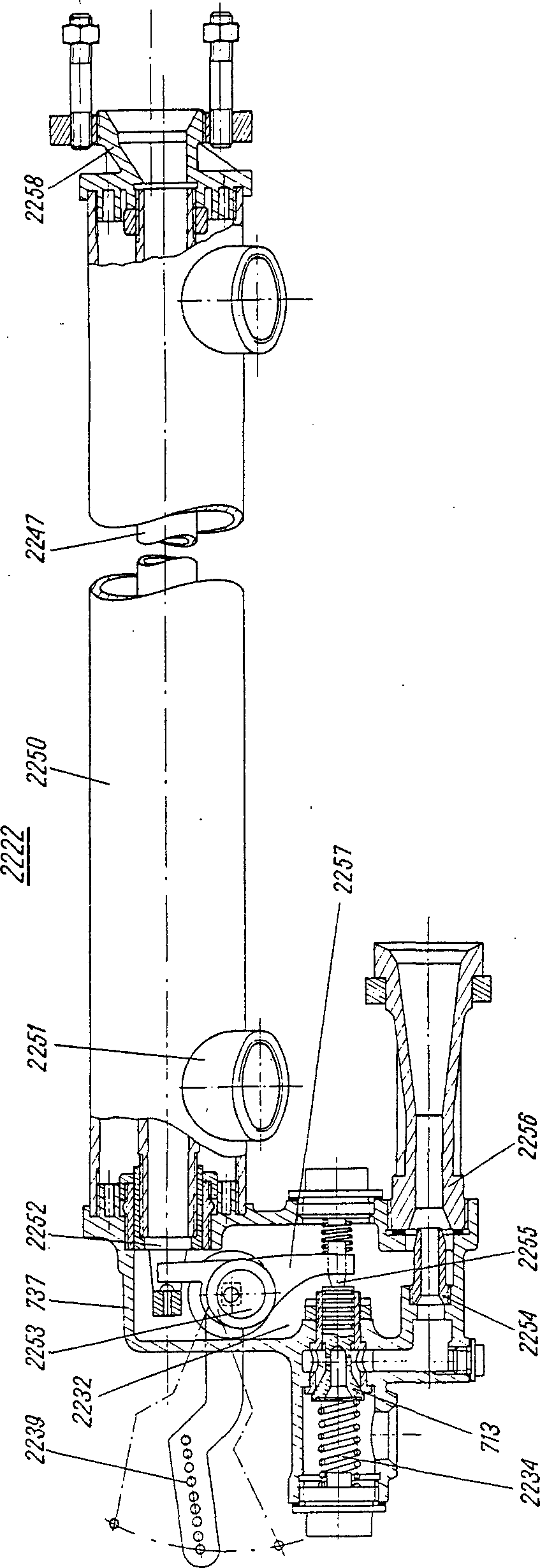
—FRA cale fDEU Wechselkloben mITA zeppa fPLN wkładka f odstępowaRUS рычаг m фиксаторасм. поз. 534 на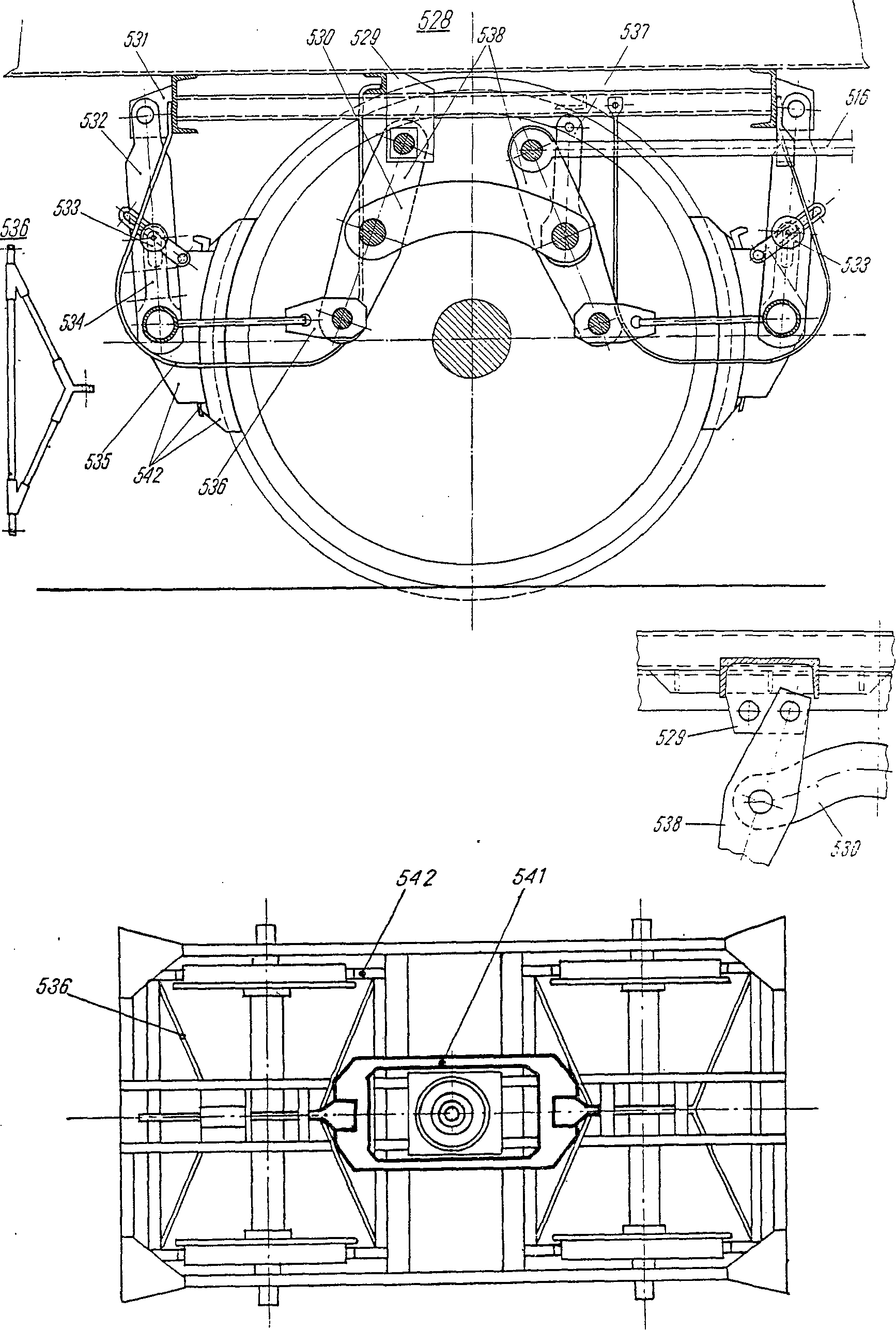 —FRA levier m excentréDEU Exzenterhebel mENG eccentric leverITA leva f eccentricaPLN dźwignia f mimośrodowaRUS рычаг m эксцентрикасм. поз. 2257 на
—FRA levier m excentréDEU Exzenterhebel mENG eccentric leverITA leva f eccentricaPLN dźwignia f mimośrodowaRUS рычаг m эксцентрикасм. поз. 2257 на
рычаг, вертикальный
—FRA balancier m d’essieuxDEU Bremshebel mENG brake leverITA leva f verticalePLN dźwignia f przyosiowaRUS рычаг m, вертикальныйсм. поз. 538 на ,
, 
рычаг, запорный
—FRA levier m de condamnationDEU Sperrhebel mENG locking leverITA leva f del dispositivo di bloccaggioPLN dźwignia f trzpienia kluczowegoRUS рычаг m, запорныйсм. поз. 1127 на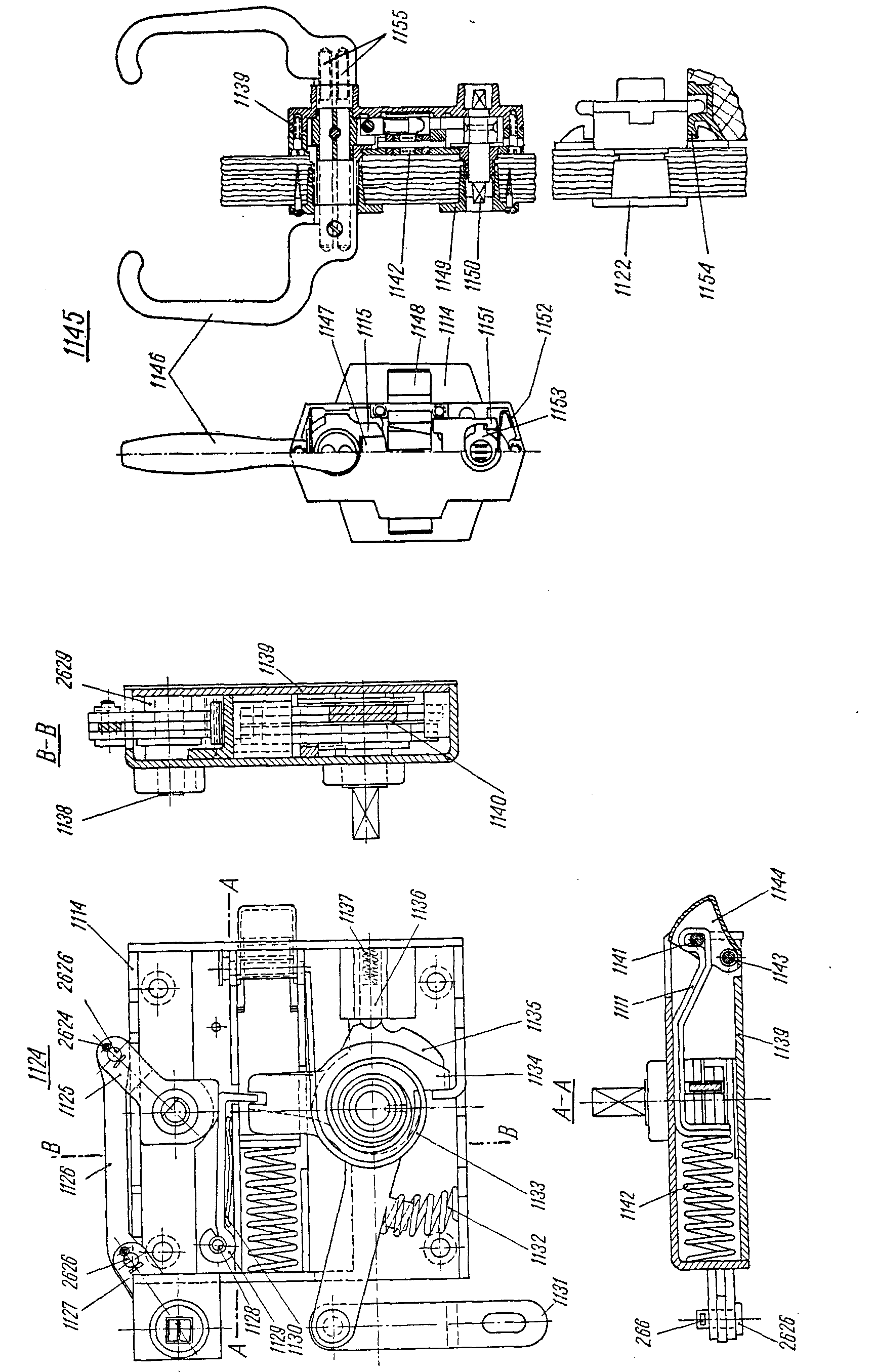
рычаг, запорный, большой
—FRA levier m de fermeture (grand)DEU Verschlußhebel m, großerENG door lever, largeITA leva f di chiusura, grandePLN dźwignia f zamykająca, dużaRUS рычаг m, запорный, большойсм. поз. 1203 на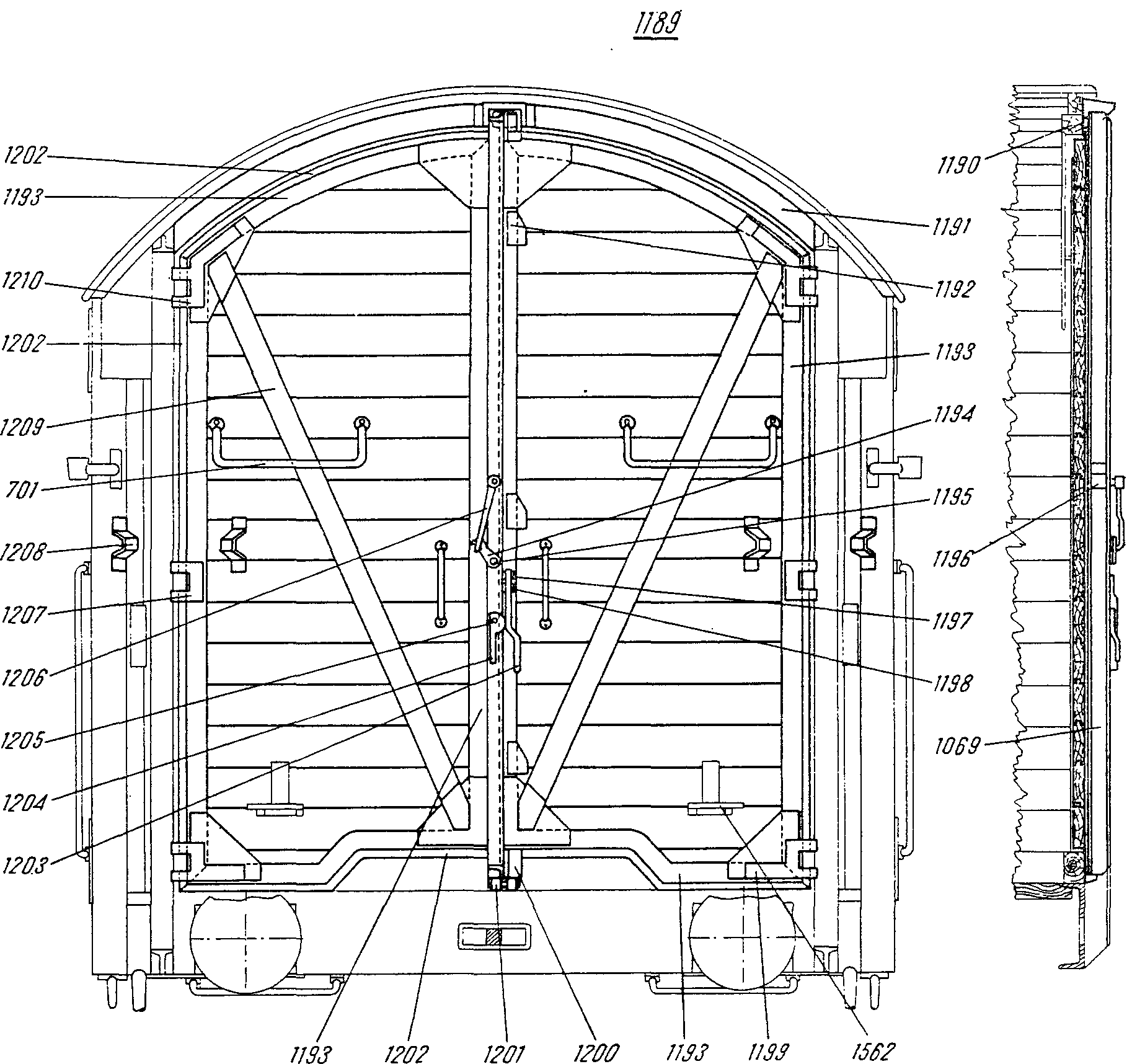
рычаг, запорный, малый
—FRA levier m de fermeture (petit)DEU Verschlußhebel m, kleinerENG door lever, smallITA leva f di sicurezza (piccola)PLN dźwignia f zamykająca, małaRUS рычаг m, запорный, малыйсм. поз. 1206 на
рычаг, коленчатый
—FRA levier m coudéDEU Winkelhebel mENG crank leverITA leva f a gomitoPLN dźwignia f kątowaRUS рычаг m, коленчатыйсм. поз. 655 на
рычаг, коленчатый, привода переключателя тормозного режима
—FRA équerre f de renvoiDEU Winkelhebel m zum LastwechselkastenITA leva f a squadra di rinvioPLN dźwignia f kątowa zmieniacza hamownościRUS рычаг m, коленчатый, привода переключателя тормозного режимасм. поз. 508 на
рычаг, кривой
—FRA levier m de renvoi (grand)DEU Handbremshebel m, langerENG brake lever, largeITA braccio m grande della leva a campanellaPLN ramię n dźwigni kątowej, długieRUS рычаг m, кривойсм. поз. 582 на
рычаг, перекидной
—FRA équerre f basculante du régleurDEU Kipphebel mITA leva f a squadre (oscillante) del regolatorePLN krzywka f nastawiaczaRUS рычаг m, перекиднойсм. поз. 504 на
рычаг, предохранительный
—FRA levier m de fermeture de sûretéDEU Türsicherungshebel mENG safety leverITA leva f di chiusura di sicurezzaPLN dźwignia f zabezpieczającaRUS рычаг m, предохранительныйсм. поз. 1204 на
рычаг, приводной
—FRA levier m de manœuvreDEU Handhebel mENG operating leverITA leva f di manovraPLN dźwignia f ręcznaRUS рычаг m, приводнойсм. поз. 1396 на
рычаг, тормозной
—FRA levier m de frein à mainDEU Handbremshebel mENG hand brake leverITA leva f del freno a stangaPLN dźwignia f bocznaRUS рычаг m, тормознойсм. поз. 589 на, FRA balancier m (coté point fixe)DEU Bremshebel m (am Festpunkt)ITA bilanciere m (di punto fisso)PLN dźwignia f hamulcowaRUS рычаг m, тормознойсм. поз. 758 на
FRA balancier m (coté point fixe)DEU Bremshebel m (am Festpunkt)ITA bilanciere m (di punto fisso)PLN dźwignia f hamulcowaRUS рычаг m, тормознойсм. поз. 758 на
рычаг, тормозной, главный
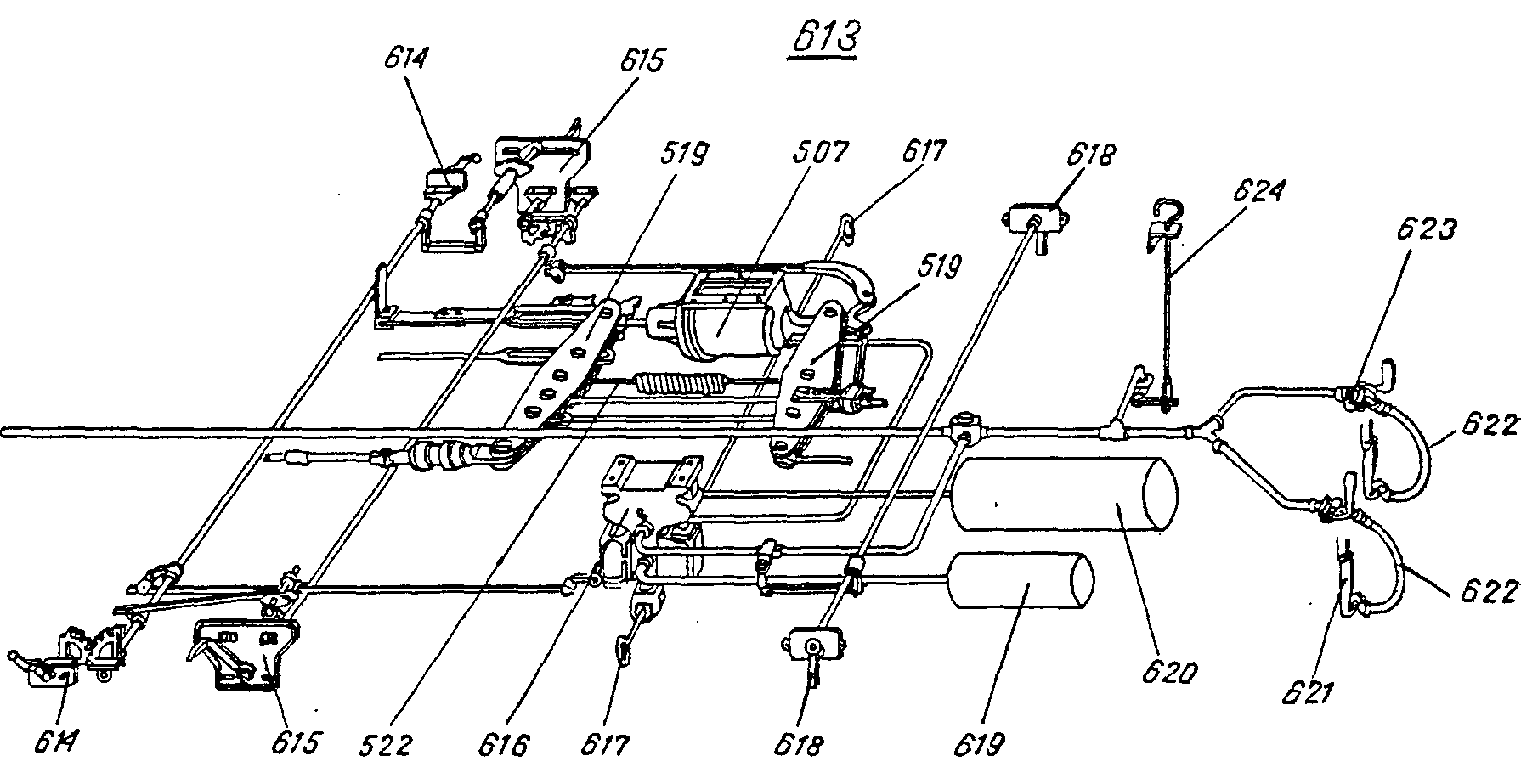
—FRA balancier m du cylindreDEU Zylinderhebel mENG fulcrum leverITA leva f motrice del cilindroPLN dźwignia f przycylindrowa przedniaRUS рычаг m, тормозной, главныйсм. поз. 519 на ,
, 
рычаг, тормозной, с зубчатой рейкой
—FRA guide m du levier, à crémaillèreDEU Führung f für Handbremshebel mit Feststellung durch ZahnstangeITA guida f a cremagliera della levaPLN ustalacz m zaczepowyRUS рычаг m, тормозной, с зубчатой рейкойсм. поз. 596 на
рычаг, уравнительный
—FRA balancier m compensateurDEU Ausgleichhebel mENG equalising leverITA leva f compensatricePLN dźwignia f wyrównawczaRUS рычаг m, уравнительныйсм. поз. 664 на
рычаг, шарнирный, коленчатый запорного механизма
—FRA biellette f d’articulationDEU Gelenkhebel mENG joint pinITA bielletta f d'articolazionePLN łubka fRUS рычаг m, шарнирный, коленчатый запорного механизмасм. поз. 145 на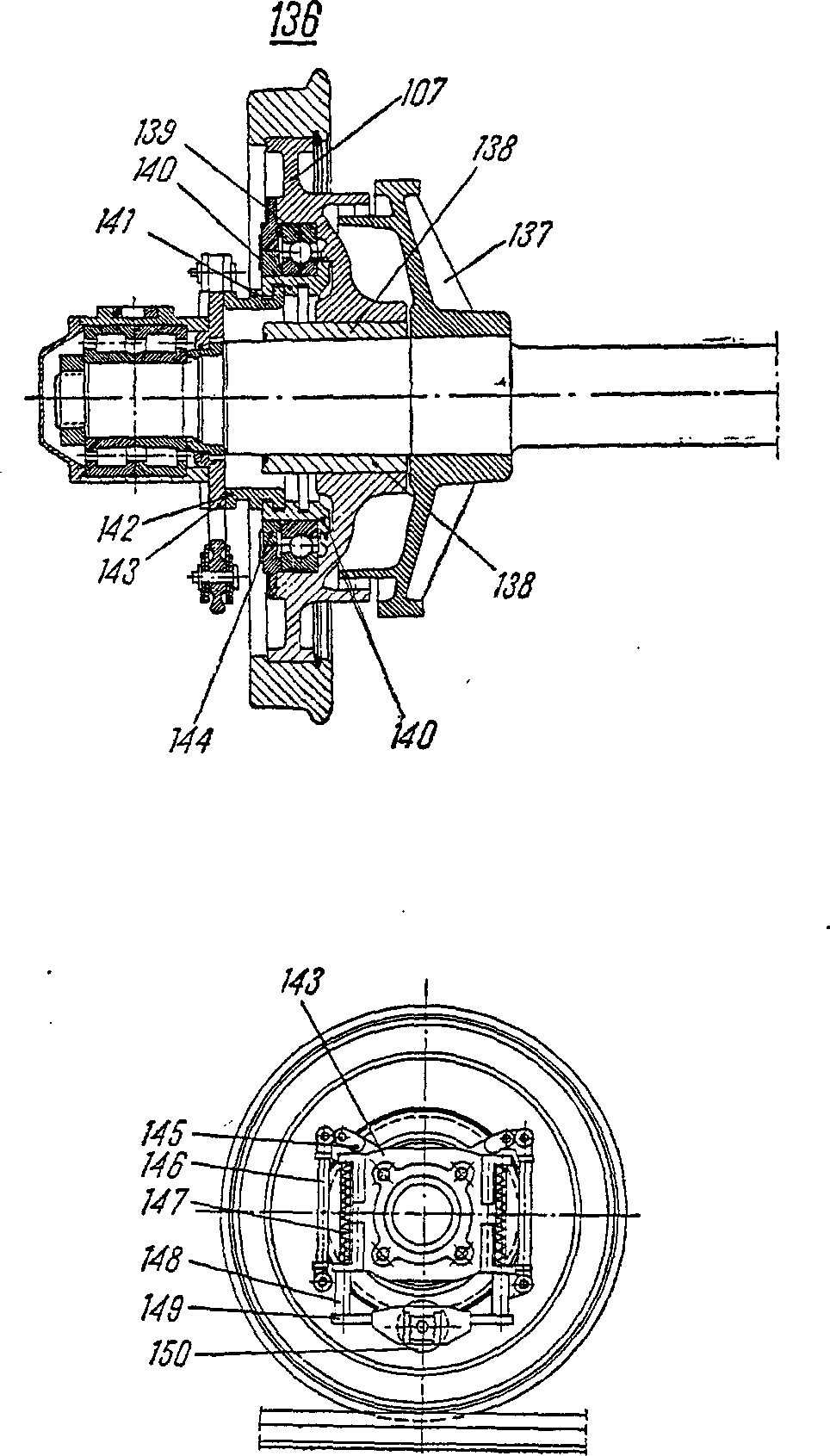
рычаг, соединительный
—FRA rail m portantDEU Tragschiene fENG connecting linkITA rotaia f portanteRUS рычаг m, соединительныйсм. поз. 1477 на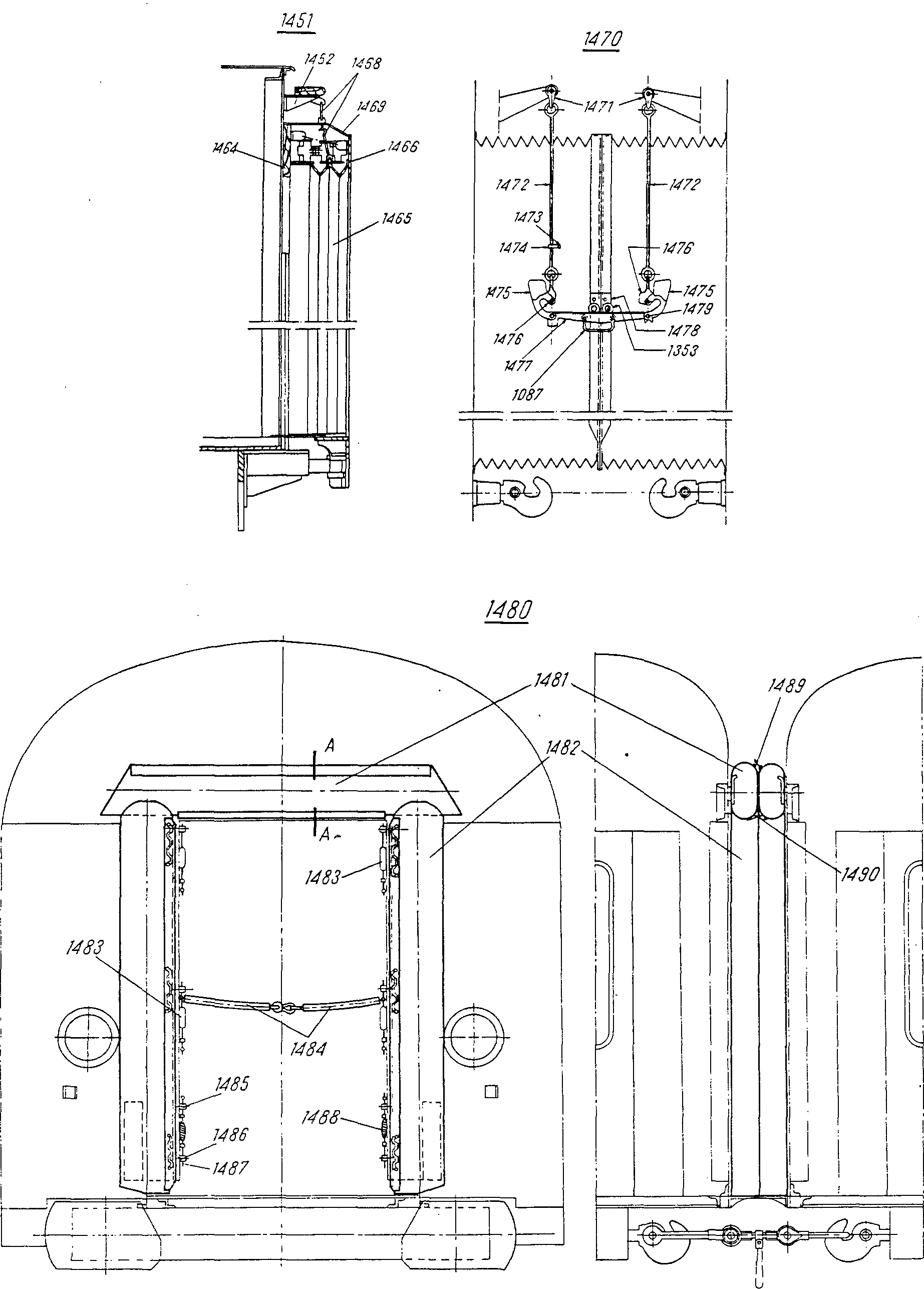
-
22 аппаратура формирования предгрупповых (первичных, вторичных, третичных) широкополосных каналов
- Vergruppen- (Primar-, Sekundar-, Tertiargruppen-) Breibandkanalenbildung-Einrichtungen
аппаратура формирования предгрупповых (первичных, вторичных, третичных) широкополосных каналов
Совокупность устройств, обеспечивающих образование предгрупповых (первичных, вторичных, третичных) широкополосных каналов на базе соответствующих групповых трактов.
[ ГОСТ 22832-77]Тематики
EN
- pregroup (group, supergroup, mastergroup) wideband channel forming equipment
DE
- Vergruppen- (Primar-, Sekundar-, Tertiargruppen-) Breibandkanalenbildung-Einrichtungen
FR
- equipement de formation des voies de transmission a large bande (de pregroupe, groupe primaire, secondaire, tertiaire)
34. Аппаратура формирования предгрупповых (первичных, вторичных, третичных) широкополосных каналов
D. Vergruppen- (Primar-, Sekundar-, Tertiargruppen-) Breibandkanalenbildung-Einrichtungen
Е. Pregroup (group, supergroup, mastergroup) wideband channel forming equipment
F. Equipement de formation des voies de transmission a large bande (de pregroupe, groupe primaire, secondaire, tertiaire)
Совокупность устройств, обеспечивающих образование предгрупповых (первичных, вторичных, третичных) широкополосных каналов на базе соответствующих групповых трактов
Источник: ГОСТ 22832-77: Аппаратура систем передачи с частотным разделением каналов. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > аппаратура формирования предгрупповых (первичных, вторичных, третичных) широкополосных каналов
-
23 длительный допустимый ток
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > длительный допустимый ток
-
24 змея
змея
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
snake
Any reptile of the suborder Ophidia, typically having a scaly cylindrical limbless body, fused eyelids, and a jaw modified for swallowing large prey: includes venomous forms such as cobras and rattlesnakes, large nonvenomous constrictors, and small harmless types such as the grass snake. (Source: CED)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > змея
-
25 конструкции крупноблочные
конструкции крупноблочные
Строительные конструкции из природных или искусственных крупных блоков, монтируемых кранами
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > конструкции крупноблочные
-
26 крупногабаритные мусор и отходы
крупногабаритные мусор и отходы
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
bulky waste
Large items of waste material, such as appliances, furniture, large auto parts, trees, branches, stumps, etc. (Source: LANDY)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > крупногабаритные мусор и отходы
-
27 крупномерный сортимент
крупномерный сортимент
Круглый сортимент, имеющий толщину в верхнем отрезе без коры от 26 см и более при измерении с градацией 2 см.
[ ГОСТ 17462-84]Тематики
- продукц. лесозаготовит. промышленности
EN
DE
23. Крупномерный сортимент
D. Sortiment groberer Durchmesser
E. Large-sized wood
Круглый сортимент, имеющий толщину в верхнем отрезе без коры от 26 см и более при измерении с градацией 2 см
Источник: ГОСТ 17462-84: Продукция лесозаготовительной промышленности. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > крупномерный сортимент
-
28 крупный промышленный завод, работающий на основе сжигания топлива
крупный промышленный завод, работающий на основе сжигания топлива
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
large combustion plant
Any sizable building which relies on machinery that converts energy released from the rapid burning of a fuel-air mixture into mechanical energy. (Source: PMA)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > крупный промышленный завод, работающий на основе сжигания топлива
-
29 макрофит
макрофит
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
macrophyte
A large macroscopic plant, used especially of aquatic forms such as kelp (variety of large brown seaweed which is a source of iodine and potash). (Source: LBC / PHC)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > макрофит
-
30 манипулирование репродукцией
манипулирование репродукцией
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
reproductive manipulation
The technology involved in altering in some prescribed way the genetic constitution of an organism. Typically "useful" genes, i.e. very short sequence of DNA, are isolated from one organism and inserted into the DNA of a bacterium of yeast. These microorganisms multiply rapidly and can be cultured easily, enabling large quantities of the gene product to be obtained. Reproductive manipulation has been used for the large-scale production of antibiotics, enzymes, and hormones (e.g. insulin). Organisms into which foreign DNA has been artificially inserted are called "transgenic organisms". (Source: UVAROV)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > манипулирование репродукцией
-
31 НКУ распределения и управления
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления (НКУ)
Низковольтные коммутационные аппараты и устройства управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования, собранные совместно, со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями и конструктивными элементами.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439-1-2012]
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления
Комбинация низковольтных коммутационных аппаратов с устройствами управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования и т. п., полностью смонтированных изготовителем НКУ (под его ответственность на единой конструктивной основе) со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями с соответствующими конструктивными элементами
Примечания
1. В настоящем стандарте сокращение НКУ используют для обозначения низковольтных комплектных устройств распределения и управления.
2. Аппараты, входящие в состав НКУ, могут быть электромеханическими или электронными.
3. По различным причинам, например по условиям транспортирования или изготовления, некоторые операции сборки могут быть выполнены на месте установки, вне предприятия-изготовителя.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]EN
power switchgear and controlgear assembly (PSC-assembly)
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly used to distribute and control energy for all types of loads, intended for industrial, commercial and similar applications where operation by ordinary persons is not intended
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
combination of one or more low-voltage switching devices together with associated control, measuring, signalling, protective, regulation equipment, etc., completely assembled under the responsibility of the manufacturer with all the internal electrical and mechanical interconnections and structural parts.
[IEC 61892-3, ed. 2.0 (2007-11)]
switchgear and controlgear
a general term covering switching devices and their combination with associated control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment, also assemblies of such devices and equipment with associated interconnections, accessories, enclosures and supporting structures
[IEV number 441-11-01]
switchgear and controlgear
electric equipment intended to be connected to an electric circuit for the purpose of carrying out one or more of the following functions: protection, control, isolation, switching
NOTE – The French and English terms can be considered as equivalent in most cases. However, the French term has a broader meaning than the English term and includes for example connecting devices, plugs and socket-outlets, etc. In English, these latter devices are known as accessories.
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
switchboard
A large single electric control panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted (either on the back or on the face, or both) switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and usually instruments; not intended for installation in a cabinet but may be completely enclosed in metal; usually is accessible from both the front and rear.
[ McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture & Construction]
switchboard
One or more panels accommodating control switches, indicators, and other apparatus for operating electric circuits
[ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language]FR
ensemble d'appareillage de puissance (ensemble PSC)
ensemble d'appareillage à basse tension utilisé pour répartir et commander l'énergie pour tous les types de charges et prévu pour des applications industrielles, commerciales et analogues dans lesquelles l'exploitation par des personnes ordinaires n'est pas prévue
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
appareillage, m
matériel électrique destiné à être relié à un circuit électrique en vue d'assurer une ou plusieurs des fonctions suivantes: protection, commande, sectionnement, connexion
NOTE – Les termes français et anglais peuvent être considérés comme équivalents dans la plupart des cas. Toutefois, le terme français couvre un domaine plus étendu que le terme anglais, et comprend notamment les dispositifs de connexion, les prises de courant, etc. En anglais, ces derniers sont dénommés "accessories".
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
appareillage
terme général applicable aux appareils de connexion et à leur combinaison avec des appareils de commande, de mesure, de protection et de réglage qui leur sont associés, ainsi qu'aux ensembles de tels appareils avec les connexions, les accessoires, les enveloppes et les charpentes correspondantes
[IEV number 441-11-01]
A switchboard as defined in the National Electrical Code is a large single panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted, on the face or back or both switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and, usually, instruments.
Switchboards are generally accessible from the rear as well as from the front and are not intended to be installed in cabinets.
The types of switchboards, classified by basic features of construction, are as follows:
1. Live-front vertical panels
2. Dead-front boards
3. Safety enclosed boards( metal-clad)
[American electricians’ handbook]
The switchboard plays an essential role in the availability of electric power, while meeting the needs of personal and property safety.
Its definition, design and installation are based on precise rules; there is no place for improvisation.
The IEC 61439 standard aims to better define " low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies", ensuring that the specified performances are reached.
It specifies in particular:
> the responsibilities of each player, distinguishing those of the original equipment manufacturer - the organization that performed the original design and associated verification of an assembly in accordance with the standard, and of the assembly manufacturer - the organization taking responsibility for the finished assembly;
> the design and verification rules, constituting a benchmark for product certification.
All the component parts of the electrical switchboard are concerned by the IEC 61439 standard.
Equipment produced in accordance with the requirements of this switchboard standard ensures the safety and reliability of the installation.
A switchboard must comply with the requirements of standard IEC 61439-1 and 2 to guarantee the safety and reliability of the installation.
Managers of installations, fully aware of the professional and legal liabilities weighing on their company and on themselves, demand a high level of safety for the electrical installation.
What is more, the serious economic consequences of prolonged halts in production mean that the electrical switchboard must provide excellent continuity of service, whatever the operating conditions.
[Schneider Electric]НКУ играет главную роль в обеспечении электроэнергией, удовлетворяя при этом всем требованиям по безопасности людей и сохранности имущества.
Выбор конструкции, проектирование и монтаж основаны на чётких правилах, не допускающих никакой импровизации.
Требования к низковольтным комплектным устройствам распределения и управления сформулированы в стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000).
В частности, он определяет:
> распределение ответственности между изготовителем НКУ - организацией, разработавшей конструкцию НКУ и проверившей его на соответствие требованиям стандарта, и сборщиком – организацией, выполнившей сборку НКУ;
> конструкцию, технические характеристики, виды и методы испытаний НКУ.
В стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000) описываются все компоненты НКУ.
Оборудование, изготовленное в соответствии с требованиями этого стандарта, обеспечивает безопасность и надежность электроустановки.
Для того чтобы гарантировать безопасность эксплуатации и надежность работы электроустановки, распределительный щит должен соответствовать требованиям стандарта МЭК 61439-1 и 2.
Лица, ответственные за электроустановки, должны быть полностью осведомлены о профессиональной и юридической ответственности, возложенной на их компанию и на них лично, за обеспечение высокого уровня безопасности эксплуатации этих электроустановок.
Кроме того, поскольку длительные перерывы производства приводят к серьезным экономическим последствиям, электрический распределительный щит должен обеспечивать надежную и бесперебойную работу независимо от условий эксплуатации.
[Перевод Интент]LV switchgear assemblies are undoubtedly the components of the electric installation more subject to the direct intervention of personnel (operations, maintenance, etc.) and for this reason users demand from them higher and higher safety requirements.
The compliance of an assembly with the state of the art and therefore, presumptively, with the relevant technical Standard, cannot be based only on the fact that the components which constitute it comply with the state of the art and therefore, at least presumptively, with the relevant technical standards.
In other words, the whole assembly must be designed, built and tested in compliance with the state of the art.
Since the assemblies under consideration are low voltage equipment, their rated voltage shall not exceed 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c. As regards currents, neither upper nor lower limits are provided in the application field of this Standard.
The Standard IEC 60439-1 states the construction, safety and maintenance requirements for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, without dealing with the functional aspects which remain a competence of the designer of the plant for which the assembly is intended.
[ABB]Низковольтные комплектные устройства (НКУ), вне всякого сомнения, являются частями электроустановок, которые наиболее подвержены непосредственному вмешательству оперативного, обслуживающего и т. п. персонала. Вот почему требования потребителей к безопасности НКУ становятся все выше и выше.
Соответствие НКУ современному положению дел и вследствие этого, гипотетически, соответствующим техническим стандартам, не может основываться только на том факте, что составляющие НКУ компоненты соответствуют современному состоянию дел и поэтому, по крайней мере, гипотетически, - соответствующим техническим стандартам
Другими словами, НКУ должно быть разработано, изготовлено и испытано в соответствии с современными требованиями.
Мы рассматриваем низковольтные комплектные устройства и это означает, что их номинальное напряжение не превышает 1000 В переменного тока или 1500 В постоянного тока. Что касается тока, то ни верхнее, ни нижнее значение стандартами, относящимися к данной области, не оговариваются
Стандарт МЭК 60439-1 устанавливает требования к конструкции, безопасности и техническому обслуживанию низковольтных комплектных устройств без учета их функций, полагая, что функции НКУ являются компетенцией проектировщиков электроустановки, частью которых эти НКУ являются.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
Классификация
>>>Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- assembly
- electrical switchboard
- low voltage controlgear and assembly
- low voltage switchboard
- low voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear assembly
- panel
- power switchgear and controlgear assembly
- PSC-assembly
- switchboard
- switchgear and controlgear
- switchgear/controlgear
DE
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > НКУ распределения и управления
-
32 шина (в электротехнике)
шина
Проводник с низким сопротивлением, к которому можно подсоединить несколько отдельных электрических цепей.
Примечание — Термин «шина» не включает в себя геометрическую форму, габариты или размеры проводника.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439.1-2013]
шина
Конструктивный элемент низковольтного комплектного устройства (НКУ).
Такой конструктивный элемент предназначен для того, чтобы к нему можно было легко присоединить отдельные электрические цепи (другие шины, отдельные проводники). Такие шины могут иметь различную конструкцию, геометрическую форму и размеры.
[Интент]
шинопроводшина
Медная, алюминиевая, реже стальная полоса, служащая для присоединения кабелей электрогенераторов, трансформаторов и т.д. к проводам питающей сети
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
общаяшина
-
[IEV number 151-12-30]
шина
-
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]EN
busbar
low-impedance conductor to which several electric circuits can be connected at separate points
NOTE – In many cases, the busbar consists of a bar.
[IEV number 151-12-30]
busbar
An electrical conductor that makes a common connection between several circuits. Sometimes, electrical wire cannot accommodate high-current applications, and electricity must be conducted using a more substantial busbar — a thick bar of solid metal (usually copper or aluminum). Busbars are uninsulated, but are physically supported by insulators. They are used in electrical substations to connect incoming and outgoing transmission lines and transformers; in a power plant to connect the generator and the main transformers; in industry, to feed large amounts of electricity to equipment used in the aluminum smelting process, for example, or to distribute electricity in large buildings
[ABB. Glossary of technical terms. 2010]FR
barre omnibus, f
conducteur de faible impédance auquel peuvent être reliés plusieurs circuits électriques en des points séparés
NOTE – Dans de nombreux cas, une barre omnibus est constituée d’une barre.
[IEV number 151-12-30]
2. Проводник прямоугольного сечения из меди, предназначенный для электротехнических целей
(см. ГОСТ 434-78).
Поставляется в бухтах, а также в полосах длиной не менее 2,5 м; По существу, это просто проволока прямоугольного сечения. В указанном ГОСТе и в технической документации, в которой она применяется, обязательно указываются размеры этой проволоки. Например, "Шина ШММ 8,00х40,00 ГОСТ 434-78"
шина
Пруток прямоугольного сечения, применяемый в электротехнике в качестве проводника тока, изготовляемый прессованием или волочением.
[ ГОСТ 25501-82]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- заготовки и полуфабрикаты в металлургии
- кабели, провода...
Действия
- расположение шин «на ребро» [ПУЭ]
- расположение шин «плашмя» [ПУЭ]
Сопутствующие термины
- гибкая шина
- жесткая шина [ПУЭ]
- изолированные шины [ПУЭ]
- круглые шины [ПУЭ]
- неизолированные шины [ПУЭ]
- обходные шины [ПУЭ]
- профильные шины [ПУЭ]
- секционные шины [ПУЭ]
- фазная шина [ ГОСТ Р 51321.1-2000]
- четырехполосные шины с расположением полос по сторонам квадрата ("полый пакет") [ПУЭ]
- шина PEN-проводника
- шина для присоединения защитных проводников
- шина нулевого защитного проводника
- шина фазы А (B, C) [ПУЭ]
- шины однофазного тока [ПУЭ]
- шины прямоугольного (круглого, трубчатого, коробчатого) сечения [ПУЭ]
- шины трехфазного тока [ПУЭ]
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > шина (в электротехнике)
-
33 широкополосный канал системы передачи с ЧРК
широкополосный канал системы передачи с ЧРК
широкополосный канал
Совокупность технических средств, обеспечивающая передачу сигналов электросвязи в нормализованной полосе частот групповых трактов системы передачи с ЧРК.
[ ГОСТ 22832-77]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
7. Широкополосный канал системы передачи с ЧРК
Широкополосный канал
D. TF-System-Breitbandkanal
Е. FDM-System Wideband channel
F. Voie de transmission a large bande
Совокупность технических средств, обеспечивающая передачу сигналов электросвязи в нормализованной полосе частот групповых трактов системы передачи с ЧРК
Источник: ГОСТ 22832-77: Аппаратура систем передачи с частотным разделением каналов. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > широкополосный канал системы передачи с ЧРК
-
34 широкополосный согласующий сигнальный трансформатор
широкополосный согласующий сигнальный трансформатор
Согласующий сигнальный трансформатор, у которого отношение наибольшей частоты к наименьшей частоте в полосе пропускания более двухсот
[ ГОСТ 20938-75]Тематики
Классификация
>>>Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
- transformateur d’adaptation à bande large de frequence
19. Широкополосный согласующий сигнальный трансформатор
Широкополосный трансформатор
D. Anpassender Breitbandsignaltransformator
E. Wide-band matching transformer
F. Transformateur d’adaptation à bande large de frequence
Согласующий сигнальный трансформатор, у которого отношение наибольшей частоты к наименьшей частоте в полосе пропускания более двухсот
Источник: ГОСТ 20938-75: Трансформаторы малой мощности. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > широкополосный согласующий сигнальный трансформатор
-
35 Raumfahrtteleskop
milit. (Large Space Telescope) LST -
36 БИС со степенью интеграции выше сверхвысокой
abbrmicroel. Super Large-Scale IntegrationУниверсальный русско-немецкий словарь > БИС со степенью интеграции выше сверхвысокой
-
37 ЗУ на больших интегральных схемах
abbrIT. "Large Scale Integration"-SpeicherУниверсальный русско-немецкий словарь > ЗУ на больших интегральных схемах
-
38 СБИС-модуль
-
39 УБИС-кристалл
-
40 большая околозвуковая западноевропейская аэродинамическая труба, рассчитанная на большие числа Рейнольдса
Универсальный русско-немецкий словарь > большая околозвуковая западноевропейская аэродинамическая труба, рассчитанная на большие числа Рейнольдса
См. также в других словарях:
large — large … Dictionnaire des rimes
large — [ larʒ ] adj., n. m. et adv. • XIe ; lat. largus « abondant; généreux », a remplacé latus, à cause de longus « long » I ♦ Adj. 1 ♦ Qui a une étendue supérieure à la moyenne dans le sens de la largeur. Une large avenue. Chapeau à larges bords.… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Large — (l[aum]rj), a. [Compar. {Larger} (l[aum]r j[ e]r); superl. {Largest}.] [F., fr. L. largus. Cf. {Largo}.] 1. Exceeding most other things of like kind in bulk, capacity, quantity, superficial dimensions, or number of constituent units; big; great;… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
large — [ lardʒ ] adjective *** bigger than usual in size: The house had an exceptionally large yard. Large crowds gather each year in St. Peter s Square to see the Pope. A large man with a long ginger beard stood in the doorway. a. used in clothing… … Usage of the words and phrases in modern English
large — [lärj] adj. larger, largest [OFr < L largus: see LARD] 1. Archaic liberal; generous 2. big; great; specif., a) taking up much space; bulky b) enclosing much space; spacious [a large office] … English World dictionary
large — large, big, great mean above the average of its kind in magnitude, especially physical magnitude. Large may be preferred when the dimensions, or extent, or capacity, or quantity, or amount is being considered {a large lot} {a large hall} {a large … New Dictionary of Synonyms
large — Large, Latus, Largus, Laxus. Large par le bas et allant en aguisant, Pyramidatus. Fort large, Perlatus. Fort large et spatieux, Spatiosus. Large outre mesure, Vastus. Un homme large, soit prodigue ou liberal, Largus. Trop large, Nimius. Devenir… … Thresor de la langue françoyse
large — 〈[la:(r)dʒ] Abk.: L〉 groß (als Kleidergröße) [engl.] * * * 1large [larʒ(ə) ] <Adj.> [frz. large < lat. largus = freigebig; reichlich] (bes. schweiz.): großzügig: der l. Schiedsrichter. 2large [la:ɐ̯d̮ʒ ] <indekl. Adj.> [engl. large … Universal-Lexikon
Large — ist der Familienname folgender Personen: Brian Large (* 1939), Fernsehregisseur von Opernübertragungen Josaphat Robert Large (* 1942), Dichter und Romancier Robert C. De Large (1842−1874), US amerikanischer Politiker Diese … Deutsch Wikipedia
large — large, largely Large is used as an adverb with the verbs bulk and loom and in the phrase by and large. Otherwise largely is the normal adverb and means ‘to a large extent’ (His failure was largely due to laziness) … Modern English usage
large — ► ADJECTIVE 1) of considerable or relatively great size, extent, or capacity. 2) pursuing an occupation or activity on a significant scale. 3) of wide range or scope. ► VERB (large it) Brit. informal ▪ go out and have a good time. ● … English terms dictionary
