-
1 cessation of service
-
2 cessation of service
English-Russian dictionary of modern telecommunications > cessation of service
-
3 cessation of service
прекращение служебной деятельности, увольнение со службыEnglish-russian dctionary of contemporary Economics > cessation of service
-
4 cessation
n
- cessation of activity
- cessation of circumstances
- cessation of deliveries
- cessation of membership
- cessation of payment
- cessation of service
- cessation of a trademark
- cessation of workEnglish-russian dctionary of contemporary Economics > cessation
-
5 cessation, of, a, vital, service
interruption f d'un service essentielEnglish-French legislative terms > cessation, of, a, vital, service
-
6 early termination of service
départ/cessation de service par anticipation ( * LSEnglish-French insurance dictionari > early termination of service
-
7 separation of a participant
cessation de service d'un participant (LGA)English-French insurance dictionari > separation of a participant
-
8 final clearance certificate
Adm. attestation de cessation de serviceEnglish-French dictionary of law, politics, economics & finance > final clearance certificate
-
9 final entitlements
Adm., Org. indemnités de départ (ou de cessation de service)English-French dictionary of law, politics, economics & finance > final entitlements
-
10 suspension
nounbe under suspension — [Schüler:] [zeitweilig] vom Unterricht ausgeschlossen sein; [Sportler:] [zeitweilig] gesperrt sein
2) (temporary cessation) Suspendierung, die; (of train service, hostilities) [vorübergehende] Einstellung3) (Motor Veh.) Federung, die* * *[-ʃən]1) (the act of suspending.) der Aufhängen2) (in a motor vehicle etc, the system of springs etc supporting the frame on the axles.) die Federung3) (a liquid with solid particles that do not sink.) die Suspension* * *sus·pen·sion[səˈspen(t)ʃən]nthere have been calls for the drug's immediate \suspension es wurde gefordert, das Medikament sofort aus dem Verkehr zu ziehen\suspension of fighting Waffenruhe f\suspension of trading Handelsaussetzung f\suspension of payment Stundungsfrist f\suspension of payments Zahlungseinstellung fto be under \suspension worker, student [zeitweilig] suspendiert [o beurlaubt] sein; player [zeitweilig] gesperrt sein[spring] \suspension Federung f* * *[sə'spenSən]n1) (of publication, payment) zeitweilige Einstellung; (of flights) Aufschub m; (of campaign, talks, judgement) Aussetzung f; (of prison sentence) Aussetzung f (zur Bewährung)2) (of person) Suspendierung f; (of member, pupil, student) zeitweiliger Ausschluss; (SPORT) Sperrung f; (of laws, privileges) Aussetzen nthe got or received a five-match suspension — er wurde für fünf Spiele gesperrt
5) (MUS)to be in suspension — suspendiert sein, gehalten werden
* * *suspension [-ʃn] s1. Aufhängen nsuspension bridge Hängebrücke f;suspension spring Tragfeder f3. TECH Federung f4. CHEM, PHYS Suspension f:a) Schweben nb) Aufschlämmung f5. (einstweilige) Einstellung:suspension of payment(s) WIRTSCH Zahlungseinstellung;suspension of the statute of limitations Hemmung f der Verjährung7. Aufschub m, Verschiebung f9. (zeitweiliger) Ausschluss (eines Vereinsmitglieds etc)10. SPORT Sperre f:be under suspension gesperrt sein11. MUS Vorhalt m* * *nounbe under suspension — [Schüler:] [zeitweilig] vom Unterricht ausgeschlossen sein; [Sportler:] [zeitweilig] gesperrt sein
2) (temporary cessation) Suspendierung, die; (of train service, hostilities) [vorübergehende] Einstellung3) (Motor Veh.) Federung, die* * *(cable) railway n.Schwebebahn f. (from) n.Suspendierung (von) f. n.Aufhängen n.Aufhängung f.Aufschub -¨e m.Aussetzung f.Federung -en f.Hemmung -en f.Startverbot n.Verschiebung f.einstweilige Einstellung f.vorübergehende Aufhebung f.zeitweilige Entziehung f.zeitweiliger Ausschluss m. -
11 failure
- сбой (в информационных технологиях)
- сбой (в информационных технологиях)
- разрушение
- повреждение
- отказ (функционального блока)
- отказ (объекта)
- отказ (в работе)
- отказ
- неудачная скважина (по статистической терминологии)
- неудачная попытка
- неудача (разработки или эксперимента)
- неудача
- несрабатывание
- несостоятельность (уравнения)
- неисправность
- недостаток или отсутствие
- авария
авария
Неожиданный выход из строя конструкции, машины, системы инженерного оборудования сооружений
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
авария
Опасное техногенное происшествие, создающее на объекте, определенной территории или акватории угрозу жизни и здоровью людей и приводящее к разрушению зданий, сооружений, оборудования и транспортных средств, нарушению производственного или транспортного процесса, а также к нанесению ущерба окружающей природной среде.
Примечание
Крупная авария, как правило с человеческими жертвами, является катастрофой.
[ ГОСТ Р 22.0.05-94]
авария
Опасное техногенное происшествие, создающее на объекте, определенной территории или акватории угрозу жизни и здоровью людей и приводящее к разрушению зданий, сооружений, оборудования и транспортных средств, нарушению производственного или транспортного процесса, а также к нанесению ущерба окружающей природной среде.
[СО 34.21.307-2005]
авария
Разрушение сооружений и (или) технических устройств, применяемых на опасном производственном объекте, неконтролируемые взрыв и (или) выброс опасных веществ
[Федеральный закон от 21. 07.1 997 № 116-ФЗ «О промышленной безопасности опасных производственных объектов»]
[СТО Газпром РД 2.5-141-2005]
авария
Разрушение сооружений и (или) технических устройств, применяемых на опасном производственном объекте, неконтролируемый взрыв и (или) выброс опасных веществ.
[ ГОСТ Р 12.3.047-98]
авария
Разрушение сооружений, оборудования, технических устройств, неконтролируемые взрыв и/или выброс опасных веществ, создающие угрозу жизни и здоровью людей.
[ ГОСТ Р 12.0.006-2002]
авария
Событие, заключающееся в переходе объекта с одного уровня работоспособности или относительного уровня функционирования на другой, существенно более низкий, с крупным нарушением режима работы объекта.
Примечание.
Авария может привести к частичному или полному нарушению объекта, массовому нарушению питания потребителей, созданию опасных условий для человека и окружающей среды. Признаки аварии указываются в нормативно-технической документации.
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
авария
аварийная ситуация
crash
Неустранимая неисправность, приводящая к перерыву в работе и потери части информации. Восстановление работоспособности аппаратных средств обычно осуществляется путем неоперативной замены неисправных модулей на исправные.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- безопасность гидротехнических сооружений
- газораспределение
- пожарная безопасность
- техногенные чрезвычайные ситуации
EN
DE
FR
недостаток или отсутствие
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
неисправность
отказ в работе
Состояние машины, характеризующееся неспособностью выполнять заданную функцию, исключая случаи проведения профилактического технического обслуживания, других запланированных действий или недостаток внешних ресурсов (например, отключение энергоснабжения).
Примечание 1
Неисправность часто является результатом повреждения самой машины, однако она может иметь место и без повреждения.
Примечание 2
На практике термины «неисправность», «отказ» и «повреждение» часто используются как синонимы.
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 12100-1:2007]
неисправность
Состояние оборудования, характеризуемое его неспособностью выполнять требуемую функцию, исключая профилактическое обслуживание или другие планово-предупредительные действия, а также исключая неспособность выполнять требуемую функцию из-за недостатка внешних ресурсов.
Примечание - Неисправность часто является следствием отказа самого оборудования, но может существовать и без предварительного отказа.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
неисправность
Состояние технического объекта (элемента), характеризуемое его неспособностью выполнять требуемую функцию, исключая периоды профилактического технического обслуживания или другие планово-предупредительные действия, или в результате недостатка внешних ресурсов.
Примечания
1 Неисправность является часто следствием отказа самого технического объекта, но может существовать и без предварительного отказа.
2 Английский термин «fault» и его определение идентичны данному в МЭК 60050-191 (МЭС 191-05-01) [1]. В машиностроении чаще применяют французский термин «defaut» или немецкий термин «Fehler», чем термины «panne» и «Fehlzusstand», которые употребляют с этим определением.
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 13849-1-2003]Тематики
EN
- abnormality
- abort
- abortion
- breakage
- breakdown
- bug
- defect
- disease
- disrepair
- disturbance
- fail
- failure
- failure occurrence
- fault
- faultiness
- fouling
- health problem
- layup
- malfunction
- problem
- shutdown
- trouble
DE
FR
несостоятельность (уравнения)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
неудача
провал
—
[Англо-русский глоссарий основных терминов по вакцинологии и иммунизации. Всемирная организация здравоохранения, 2009 г.]Тематики
- вакцинология, иммунизация
Синонимы
EN
неудача (разработки или эксперимента)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
неудачная скважина (по статистической терминологии)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
отказ
Нарушение способности оборудования выполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечания
1. После отказа оборудование находится в неисправном состоянии.
2. «Отказ» является событием, в отличие от «неисправности», которая является состоянием.
3. Это понятие, как оно определено, не применяют коборудованиюобъекту, состоящему только из программных средств.
4. На практике термины «отказ» и «неисправность» часто используют как синонимы.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 13849-1-2003]
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
отказ
Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния объекта.
[ ГОСТ 27.002-89]
[ОСТ 45.153-99]
[СТО Газпром РД 2.5-141-2005]
[СО 34.21.307-2005]
отказ
Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния машины и (или) оборудования вследствие конструктивных нарушений при проектировании, несоблюдения установленного процесса производства или ремонта, невыполнения правил или инструкций по эксплуатации.
[Технический регламент о безопасности машин и оборудования]EN
failure
the termination of the ability of an item to perform a required function
NOTE 1 – After failure the item has a fault.
NOTE 2 – "Failure" is an event, as distinguished from "fault", which is a state.
NOTE 3 – This concept as defined does not apply to items consisting of software only.
[IEV number 191-04-01]
NOTE 4 - In practice, the terms fault and failure are often used synonymously
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
défaillance
cessation de l'aptitude d'une entité à accomplir une fonction requise
NOTE 1 – Après défaillance d'une entité, cette entité est en état de panne.
NOTE 2 – Une défaillance est un passage d'un état à un autre, par opposition à une panne, qui est un état.
NOTE 3 – La notion de défaillance, telle qu'elle est définie, ne s'applique pas à une entité constituée seulement de logiciel.
[IEV number 191-04-01]Тематики
- безопасность в целом
- безопасность гидротехнических сооружений
- безопасность машин и труда в целом
- газораспределение
- надежность средств электросвязи
- надежность, основные понятия
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
отказ (в работе)
выход из строя
повреждение
поломка
неисправность
несрабатывание
сбой
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
отказ (объекта)
Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния объекта (ГОСТ 27. 002).
[ОСТ 45.152-99 ]Тематики
- тех. обсл. и ремонт средств электросвязи
EN
отказ
Прекращение способности функционального блока выполнять необходимую функцию.
Примечания
1. Определение в МЭС 191-04-01 является идентичным, с дополнительными комментариями [ИСО/МЭК 2382-14-01-11].
2. Соотношение между сбоями и отказами в МЭК 61508 и МЭС 60050(191) см. на рисунке.
3. Характеристики требуемых функций неизбежно исключают определенные режимы работы, некоторые функции могут быть определены путем описания режимов, которых следует избегать. Возникновение таких режимов представляет собой отказ.
4. Отказы являются либо случайными (в аппаратуре), либо систематическими (в аппаратуре или в программном обеспечении).
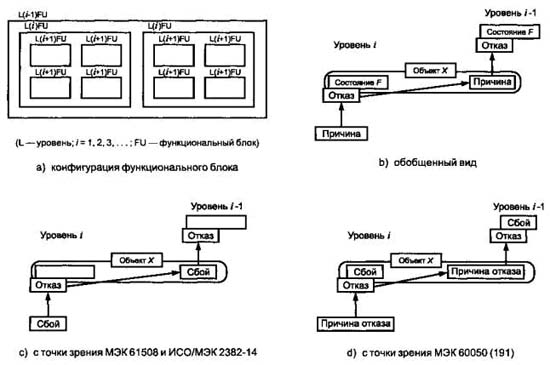
Рис. Модель отказа
Примечания
1. Как показано на рисунке а), функциональный блок может быть представлен в виде многоуровневой иерархической конструкции, каждый из уровней которой может быть, в свою очередь, назван функциональным блоком. На уровне i «причина» может проявить себя как ошибка (отклонение от правильного значения или состояния) в пределах функционального блока, соответствующего данному уровню i. Если она не будет исправлена или нейтрализована, эта ошибка может привести к отказу данного функционального блока, который в результате перейдет в состояние F, в котором он более не может выполнять необходимую функцию (см. рисунок b)). Данное состояние F уровня i может в свою очередь проявиться в виде ошибки на уровне функционального блока i - 1, которая, если она не будет исправлена или нейтрализована, может привести к отказу функционального блока уровня i - 1.
2. В этой причинно - следственной цепочке один и тот же элемент («объект X ») может рассматриваться как состояние F функционального блока уровня i, в которое он попадает в результате отказа, а также как причина отказа функционального блока уровня i - 1. Данный «объект X » объединяет концепцию «отказа» в МЭК 61508 и ИСО/МЭК 2382-14, в которой внимание акцентируется на причинном аспекте, как показано на рисунке c), и концепцию «отказа» из МЭС 60050(191), в которой основное внимание уделено аспекту состояния, как показано на рисунке d). В МЭС 60050(191) состояние F называется отказом, а в МЭК 61508 и ИСО/МЭК 2382-14 оно не определено.
3. В некоторых случаях отказ или ошибка могут быть вызваны внешним событием, таким как молния или электростатические помехи, а не внутренним отказом. Более того, ошибка (в обоих словарях) может возникать без предшествующего отказа. Примером такой ошибки может быть ошибка проектирования.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61508-4-2007]Тематики
EN
повреждение
Неспособность машины выполнять заданную функцию.
Примечание 1
Неисправность, отказ в работе машины является результатом ее повреждения.
Примечание 2
Повреждение является событием в отличие от неисправности и отказа, которые являются состоянием.
Примечание 3
Рассматриваемое понятие не распространяется на программное обеспечение (см. МЭС 191-04-01
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 12100-1:2007]
повреждение
Событие, заключающееся в нарушении исправного состояния объекта при сохранении работоспособного состояния.
[ ГОСТ 27.002-89]
[ОСТ 45.153-99]
[СТО Газпром РД 2.5-141-2005]
повреждение
По ГОСТ 13377-75
[ ГОСТ 24166-80]EN
damage
any change in visual appearance or alteration of mechanical integrity
[IEC 60571, ed. 2.0 (1998-02)]
damage
degradation of a component leading to penetration by acid or moisture
[IEC 62662, ed. 1.0 (2010-08)]FR
détérioration
tout changement dans l’aspect ou toute altération de l’intégrité mécanique
[IEC 60571, ed. 2.0 (1998-02)]Тематики
- безопасность машин и труда в целом
- газораспределение
- надежность средств электросвязи
- надежность, основные понятия
- ремонт судов
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
разрушение
Кинетический процесс зарождения и (или) развития трещин в результате действия внешних или внутренних напряжений, завершающегося разделением изделия (образца) на части. Разрушение классифицируют по разным признакам на следующие виды: по характеру силового воздействия на статически кратковременное, статически длительное, усталостное и ударное (динамическое); по ориентировке макроскопической поверхности разрушения — на разрушение путем отрыва (поверхность разрушения перпендикулярна направлению наибольших растягивающих напряжений или среза (поверхность разрушения составляет угол около 45°); по величине пластической деформации, предшествующей разрушению — на хрупкое и вязкое; по расположению поверхности разрушения относительно структуры — на транскристаллическое (внутрикристалл.), интеркристаллическое (межкристалл.) и смешанное; по влиянию внешней среды — на водородное, жидкометаллическое, коррозионное и т.п. В механике разрушения различают три способа взаимного смещения поверхностей трещины: I — отрыв; II — поперечный и III — продольный (чистый) сдвиг. Если трещина распространяется так же легко (без заметных следов пластической деформации), как и ее зарождение, то разрушение называют хрупким. Когда распространение трещины значительно более энергоемкий (на несколько порядков), чем ее зарождение, процесс, сопровождаемый значительной пластической деформацией не только вблизи поверхности разрушения, но и в объеме тела, то разрушение вязкое. Энергетические затраты на распространение трещины определяет ее трещиностойкость. Характер разрушения проявляется в структуре поверхности излома, изучаемого фрактографией.
разрушение
Неровная поверхность, возникающая при разрушении фрагмента металла.
[ http://www.manual-steel.ru/eng-a.html]Тематики
EN
сбой (в информационных технологиях)
Потеря способности функционировать в соответствии со спецификацией или предоставлять требуемый результат. Термин «сбой» может быть использован по отношению к ИТ-услугам, процессам, видам деятельности, конфигурационным единицам и т. п. Сбой часто служит причиной инцидента.
[ http://www.dtln.ru/slovar-terminov]Тематики
EN
сбой (в информационных технологиях)
(ITIL Service Operation)
Потеря способности функционировать в соответствии со спецификацией или предоставлять требуемый результат. Этот термин может быть использован по отношению к ИТ-услугам, процессам, деятельности, конфигурационным единицам и т.п. Сбой часто служит причиной инцидента.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]EN
failure
(ITIL Service Operation)
Loss of ability to operate to specification, or to deliver the required output. The term may be used when referring to IT services, processes, activities, configuration items etc. A failure often causes an incident.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]Тематики
EN
отказ (failure): Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния объекта
[ ГОСТ 27.002-89, статья 3.3].
Источник: ГОСТ Р 52527-2006: Установки газотурбинные. Надежность, готовность, эксплуатационная технологичность и безопасность оригинал документа
3.5 отказ (failure): Прекращение способности элемента исполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечания
1 После отказа элемент становится неисправным.
2 Отказ является событием в отличие от неисправности, которая является состоянием.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51901.5-2005: Менеджмент риска. Руководство по применению методов анализа надежности оригинал документа
3.3. Отказ
Failure
Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния объекта
Источник: ГОСТ 27.002-89: Надежность в технике. Основные понятия. Термины и определения оригинал документа
3.32 повреждение (failure): Неспособность машины выполнять заданную функцию.
Примечание 1 - Неисправность, отказ в работе машины является результатом ее повреждения.
Примечание 2 - Повреждение является событием в отличие от неисправности и отказа, которые являются состоянием.
Примечание 3 - Рассматриваемое понятие не распространяется на программное обеспечение (см. МЭС 191-04-01 [11]).
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 12100-1-2007: Безопасность машин. Основные понятия, общие принципы конструирования. Часть 1. Основные термины, методология оригинал документа
3.4 отказ (failure): Утрата изделием способности выполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечание - Отказ является событием в отличие от неисправности, которая является состоянием.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 13379-2009: Контроль состояния и диагностика машин. Руководство по интерпретации данных и методам диагностирования оригинал документа
3.2 отказ (failure): Утрата объектом способности выполнять требуемую функцию1).
___________
1) Более детально см. [1].
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51901.12-2007: Менеджмент риска. Метод анализа видов и последствий отказов оригинал документа
3.29 отказ (failure): Событие, происходящее с элементом или системой и вызывающее один или оба следующих эффекта: потеря элементом или системой своих функций или ухудшение работоспособности до степени существенного снижения безопасности установки, персонала или окружающей среды.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54382-2011: Нефтяная и газовая промышленность. Подводные трубопроводные системы. Общие технические требования оригинал документа
3.1.3 отказ (failure): Потеря объектом способности выполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечания
1. После отказа объект имеет неисправность.
2. Отказ - это событие в отличие от неисправности, которое является состоянием.
3. Данное понятие по определению не касается программного обеспечения в чистом виде.
[МЭК 60050-191 ][1]
Источник: ГОСТ Р 50030.5.4-2011: Аппаратура распределения и управления низковольтная. Часть 5.4. Аппараты и элементы коммутации для цепей управления. Метод оценки рабочих характеристик слаботочных контактов. Специальные испытания оригинал документа
3.5 отказ (failure): Неспособность конструкции, системы или компонента функционировать в пределах критериев приемлемости.
[Глоссарий МАГАТЭ по безопасности, издание 2.0, 2006]
Примечание 1 - Отказ - это результат неисправности аппаратных средств, дефекта программного обеспечения, неисправности системы или ошибки оператора, связанной с ними сигнальной траекторией, которая и вызывает отказ.
Примечание 2 - См. также «дефект», «отказ программного обеспечения».
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62340-2011: Атомные станции. Системы контроля и управления, важные для безопасности. Требования по предотвращению отказов по общей причине оригинал документа
3.3 отказ (failure): Утрата изделием способности выполнять требуемую функцию.
Примечание - Обычно отказ является следствием неисправности одного или нескольких узлов машины.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 17359-2009: Контроль состояния и диагностика машин. Общее руководство по организации контроля состояния и диагностирования оригинал документа
3.16 отказ (failure): Отклонение реального функционирования от запланированного. [МЭК 61513, пункт 3.21, изменено]
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60880-2010: Атомные электростанции. Системы контроля и управления, важные для безопасности. Программное обеспечение компьютерных систем, выполняющих функции категории А оригинал документа
3.6.4 отказ (failure): Прекращение способности функционального блока выполнять необходимую функцию.
Примечания
1. Определение в МЭС 191-04-01 является идентичным, с дополнительными комментариями [ИСО/МЭК 2382-14-01-11].
2. Соотношение между сбоями и отказами в МЭК 61508 и МЭС 60050(191) см. на рисунке 4.
3. Характеристики требуемых функций неизбежно исключают определенные режимы работы, некоторые функции могут быть определены путем описания режимов, которых следует избегать. Возникновение таких режимов представляет собой отказ.
4. Отказы являются либо случайными (в аппаратуре), либо систематическими (в аппаратуре или в программном обеспечении), см. 3.6.5 и 3.6.6.

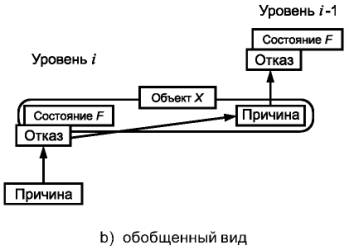
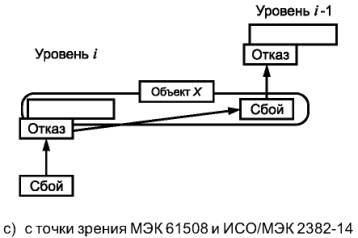
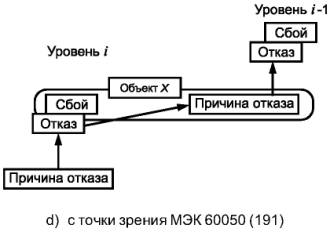
Примечания
1. Как показано на рисунке 4а), функциональный блок может быть представлен в виде многоуровневой иерархической конструкции, каждый из уровней которой может быть, в свою очередь, назван функциональным блоком. На уровне i «причина» может проявить себя как ошибка (отклонение от правильного значения или состояния) в пределах функционального блока, соответствующего данному уровню i. Если она не будет исправлена или нейтрализована, эта ошибка может привести к отказу данного функционального блока, который в результате перейдет в состояние F, в котором он более не может выполнять необходимую функцию (см. рисунок 4b)). Данное состояние F уровня i может в свою очередь проявиться в виде ошибки на уровне функционального блока i - 1, которая, если она не будет исправлена или нейтрализована, может привести к отказу функционального блока уровня i - 1.
2. В этой причинно-следственной цепочке один и тот же элемент («объект X») может рассматриваться как состояние F функционального блока уровня i, в которое он попадает в результате отказа, а также как причина отказа функционального блока уровня i - 1. Данный «объект X» объединяет концепцию «отказа» в МЭК 61508 и ИСО/МЭК 2382-14, в которой внимание акцентируется на причинном аспекте, как показано на рисунке 4с), и концепцию «отказа» из МЭС 60050(191), в которой основное внимание уделено аспекту состояния, как показано на рисунке 4d). В МЭС 60050(191) состояние F называется отказом, а в МЭК 61508 и ИСО/МЭК 2382-14 оно не определено.
3. В некоторых случаях отказ или ошибка могут быть вызваны внешним событием, таким как молния или электростатические помехи, а не внутренним отказом. Более того, ошибка (в обоих словарях) может возникать без предшествующего отказа. Примером такой ошибки может быть ошибка проектирования.
Рисунок 4 - Модель отказа
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61508-4-2007: Функциональная безопасность систем электрических, электронных, программируемых электронных, связанных с безопасностью. Часть 4. Термины и определения оригинал документа
3.21 отказ (failure): Отклонение реального функционирования от запланированного (см. рисунок 3). [МЭК 60880-2, пункт 3.8]
Примечание 1 - Отказ является результатом сбоя в аппаратуре, программном обеспечении, системе или ошибки оператора или обслуживания и отражается на прохождении сигнала.
Примечание 2 - См. также «дефект», «отказ программного обеспечения».
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61513-2011: Атомные станции. Системы контроля и управления, важные для безопасности. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.22 отказ (failure): Событие, заключающееся в нарушении работоспособного состояния элементов или систем платформы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54483-2011: Нефтяная и газовая промышленность. Платформы морские для нефтегазодобычи. Общие требования оригинал документа
5. Повреждение
D. Beschädigung
E. Failure
F. Endommagement
Источник: ГОСТ 24166-80: Система технического обслуживания и ремонта судов. Ремонт судов. Термины и определения оригинал документа
3.1.29 отказ (failure): Окончание способности изделия выполнять требуемую функцию.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54828-2011: Комплектные распределительные устройства в металлической оболочке с элегазовой изоляцией (КРУЭ) на номинальные напряжения 110 кВ и выше. Общие технические условия оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > failure
-
12 stop
1. transitive verb,- pp-1) (not let move further) anhalten [Person, Fahrzeug]; aufhalten [Fortschritt, Verkehr, Feind]; verstummen lassen (geh.) [Gerücht, Geschichte, Lüge]; [Tormann:] halten [Ball]stop thief! — haltet den Dieb!
there's no stopping somebody — jemand lässt sich nicht aufhalten
2) (not let continue) unterbrechen [Redner, Spiel, Gespräch, Vorstellung]; beenden [Krieg, Gespräch, Treffen, Spiel, Versuch, Arbeit]; stillen [Blutung]; stoppen [Produktion, Uhr, Streik, Inflation]; einstellen [Handel, Zahlung, Lieferung, Besuche, Subskriptionen, Bemühungen]; abstellen [Strom, Gas, Wasser, Missstände]; beseitigen [Schmerz]stop that/that nonsense/that noise! — hör damit/mit diesem Unsinn/diesem Lärm auf!
bad light stopped play — (Sport) das Spiel wurde wegen schlechter Lichtverhältnisse abgebrochen
stop the show — (fig.) Furore machen
just you try and stop me! — versuch doch, mich daran zu hindern!
stop smoking/crying — aufhören zu rauchen/weinen
he tried to stop us parking — er versuchte uns am Parken zu hindern
he phoned his mother to stop her [from] worrying — er rief seine Mutter an, damit sie sich keine Sorgen machte
stop something [from] happening — verhindern, dass etwas geschieht
4) (cause to cease working) abstellen [Maschine usw.]; [Streikende:] stilllegen [Betrieb]5) (block up) zustopfen [Loch, Öffnung, Riß, Ohren]; verschließen [Wasserhahn, Rohr, Schlauch, Flasche]6) (withhold) streichen2. intransitive verb,stop [payment of] a cheque — einen Scheck sperren lassen
- pp-1) (not extend further) aufhören; [Straße, Treppe:] enden; [Ton:] verstummen; [Ärger:] verfliegen; [Schmerz:] abklingen; [Zahlungen, Lieferungen:] eingestellt werden2) (not move or operate further) [Fahrzeug, Fahrer:] halten; [Maschine, Motor:] stillstehen; [Uhr, Fußgänger, Herz:] stehen bleibenhe never stops to think [before he acts] — er denkt nie nach [bevor er handelt]
stop dead — plötzlich stehen bleiben; [Redner:] abbrechen
3) (coll.): (stay) bleiben3. nounstop at a hotel/at a friend's house/with somebody — in einem Hotel/im Hause eines Freundes/bei jemandem wohnen
1) (halt) Halt, derthere will be two stops for coffee on the way — es wird unterwegs zweimal zum Kaffeetrinken angehalten
this train goes to London with only two stops — dieser Zug fährt mit nur zwei Zwischenhalten nach London
bring to a stop — zum Stehen bringen [Fahrzeug]; zum Erliegen bringen [Verkehr]; unterbrechen [Arbeit, Diskussion, Treffen]
come to a stop — stehen bleiben; [Fahrzeug:] zum Stehen kommen; [Gespräch:] abbrechen; [Arbeit, Verkehr:] zum Erliegen kommen; [Vorlesung:] abgebrochen werden
make a stop at or in a place — in einem Ort haltmachen
put a stop to — abstellen [Missstände, Unsinn]; unterbinden [Versuche]; aus der Welt schaffen [Gerücht]
without a stop — ohne Halt [fahren, fliegen]; ohne anzuhalten [gehen, laufen]; ununterbrochen [arbeiten, reden]
2) (place) Haltestelle, diethe ship's first stop is Cairo — der erste Hafen, den das Schiff anläuft, ist Kairo
the plane's first stop is Frankfurt — die erste Zwischenlandung des Flugzeuges ist in Frankfurt
Phrasal Verbs:- stop by- stop off- stop out- stop up* * *[stop] 1. past tense, past participle - stopped; verb1) (to (make something) cease moving, or come to rest, a halt etc: He stopped the car and got out; This train does not stop at Birmingham; He stopped to look at the map; He signalled with his hand to stop the bus.) anhalten2) (to prevent from doing something: We must stop him (from) going; I was going to say something rude but stopped myself just in time.) zurückhalten3) (to discontinue or cease eg doing something: That woman just can't stop talking; The rain has stopped; It has stopped raining.) aufhören4) (to block or close: He stopped his ears with his hands when she started to shout at him.) verstopfen5) (to close (a hole, eg on a flute) or press down (a string on a violin etc) in order to play a particular note.) greifen6) (to stay: Will you be stopping long at the hotel?) bleiben2. noun1) (an act of stopping or state of being stopped: We made only two stops on our journey; Work came to a stop for the day.) der Halt2) (a place for eg a bus to stop: a bus stop.) die Haltestelle3) (in punctuation, a full stop: Put a stop at the end of the sentence.) der Punkt4) (a device on a flute etc for covering the holes in order to vary the pitch, or knobs for bringing certain pipes into use on an organ.) das Griffloch, die Klappe, das Register5) (a device, eg a wedge etc, for stopping the movement of something, or for keeping it in a fixed position: a door-stop.) die Sperre•- stoppage- stopper
- stopping
- stopcock
- stopgap
- stopwatch
- put a stop to
- stop at nothing
- stop dead
- stop off
- stop over
- stop up* * *[stɒp, AM stɑ:p]<- pp->to \stop a ball einen Ball stoppen; goalkeeper einen Ball haltento \stop a blow einen Schlag abblockento \stop sb/a car jdn/ein Auto anhaltento \stop one's car anhaltento \stop the enemy den Feind aufhaltento \stop a thief/the traffic einen Dieb/den Verkehr aufhalten\stop thief! haltet den Dieb!\stop that man! haltet den Mann!2. (make cease)this will \stop the pain das wird dir gegen die Schmerzen helfen\stop that nonsense! hör auf mit dem Unsinn!\stop it! hör auf [damit]!what can I do to \stop this nosebleed? was kann ich gegen dieses Nasenbluten tun?something must be done to \stop the fighting den Kämpfen muss ein Ende gesetzt werdenthis fighting has to be \stopped! die Kämpfe müssen aufhören!\stop being silly! hör auf mit dem Unsinn!I just couldn't \stop myself ich konnte einfach nicht andersto \stop the bleeding die Blutung stillento \stop the clock die Uhr anhaltenthe clock is \stopped when a team scores a goal die Spielzeit wird unterbrochen, wenn ein Team ein Tor schießtto \stop the engine den Motor abstellento \stop the fighting die Kämpfe einstellento \stop inflation/progress die Inflation/den Fortschritt aufhaltento \stop a machine eine Maschine abstellento \stop a match ein Spiel beenden; referee ein Spiel abbrechento \stop the production of sth die Produktion einer S. gen einstellento \stop a rumour einem Gerücht ein Ende machento \stop a speech eine Rede unterbrechento \stop a subscription ein Abonnement kündigento \stop a war einen Krieg beenden3. (cease an activity)what time do you usually \stop work? wann hören Sie normalerweise auf zu arbeiten?4. (prevent)▪ to \stop sb [from] doing sth jdn davon abhalten, etw zu tunif she really wants to leave, I don't understand what's \stopping her wenn sie wirklich weggehen will, verstehe ich nicht, was sie davon abhältsome people smoke because they think it \stops them putting on weight manche rauchen, weil sie meinen, dass sie dann nicht zunehmenI couldn't \stop myself from having another piece of cake ich musste einfach noch ein Stück Kuchen essenhe handed in his resignation — I just couldn't \stop him er hat gekündigt — ich konnte ihn einfach nicht davon abhaltenyou can't \stop me from doing that du kannst mich nicht davon abhalten5. (refuse payment)to \stop sb's allowance/pocket money jdm den Unterhalt/das Taschengeld streichento \stop [AM payment on] a cheque einen Scheck sperrento \stop wages keine Löhne mehr zahlenthe money will be \stopped out of his salary das Geld wird von seinem Gehalt abgezogen6. (block)▪ to \stop sth etw verstopfen; gap, hole, leak etw [zu]stopfento \stop one's ears sich dat die Ohren zuhaltenwhen he starts shouting I just \stop my ears wenn er anfängt zu schreien, mache ich einfach die Ohren zu! fam7. BOXING▪ to \stop sb jdn schlagenhe was \stopped by a knockout in the fourth round er schied durch K.o. in der vierten Runde austo \stop a left/right eine Linke/Rechte parierento \stop a punch einen Hieb einstecken [müssen]8. MUS\stopped pipe gedackte Pfeife fachsprto \stop a string eine Saite greifen9.▶ to \stop a bullet eine Kugel abbekommen▶ to \stop the show der absolute Höhepunkt einer Show sein<- pp->\stop! halt!to \stop dead abrupt innehaltenI \stopped to pick up the letter that I had dropped ich blieb stehen und hob den Brief auf, den ich hatte fallenlassen; ( fig)\stop to [or and] think before you speak erst denken, dann reden!2. (cease, discontinue) machine nicht mehr laufen; clock, heart, watch stehen bleiben; rain aufhören; pain abklingen, nachlassen; production, payments eingestellt werden; film, programme zu Ende sein; speaker abbrechenI will not \stop until they set them free ich werde keine Ruhe geben, bis sie sie freigelassen habenshe doesn't know where to \stop sie weiß nicht, wann sie aufhören musshis heart \stopped during the operation während der Operation hatte er einen Herzstillstandrain has \stopped play das Spiel wurde wegen Regens unterbrochenshe \stopped right in the middle of the sentence sie hielt mitten im Satz inneonce I start eating chocolate I can't \stop wenn ich einmal anfange, Schokolade zu essen, kann ich einfach nicht mehr aufhörenI just couldn't \stop laughing ich habe mich echt totgelacht slif you have to keep \stopping to answer the telephone, you'll never finish wenn du ständig unterbrechen musst, um ans Telefon zu gehen, wirst du nie fertig werdenI wish you'd \stop telling me what to do ich wünschte, du würdest endlich damit aufhören, mir zu sagen, was ich tun soll\stop being silly! hör auf mit dem Unsinn!\stop shouting! hör auf zu schreienI \stopped seeing him last year wir haben uns letztes Jahr getrenntI've \stopped drinking alcohol ich trinke keinen Alkohol mehrshe \stopped drinking sie trinkt nicht mehrplease, \stop crying hör doch bitte auf zu weinen!to \stop smoking mit dem Rauchen aufhören; (on plane etc.) das Rauchen einstellento \stop working aufhören zu arbeitenI'm not \stopping ich bleibe nicht langeI can't \stop — Malcolm's waiting for me outside ich kann nicht bleiben, Malcolm wartet draußen auf michwe \stopped for a quick bite at a motorway services wir machten kurz bei einer Autobahnraststätte Station, um etwas zu essenI \stopped at a pub for some lunch ich habe an einem Pub haltgemacht und was zu Mittag gegessencan you \stop at the fish shop on your way home? kannst du auf dem Nachhauseweg kurz beim Fischladen vorbeigehen?he usually \stops at a bar for a quick drink on the way home normalerweise schaut er auf dem Nachhauseweg noch kurz auf ein Gläschen in einer Kneipe vorbeiare you \stopping here bleibst du hier?to \stop for dinner/tea zum Abendessen/Tee bleibento \stop at a hotel in einem Hotel übernachtendoes this train \stop at Finsbury Park? hält dieser Zug in Finsbury Park?6. (almost)to \stop short of doing sth sich akk [gerade noch] bremsen [o ÖSTERR, SCHWEIZ a. zurückhalten], etw zu tunI \stopped short of telling him my secrets beinahe hätte ich ihm meine Geheimnisse verraten7.▶ to \stop at nothing vor nichts zurückschreckenIII. NOUNplease wait until the airplane has come to a complete \stop bitte warten Sie, bis das Flugzeug seine endgültige Parkposition erreicht hatemergency \stop Notbremsung fto bring a car to a \stop ein Auto anhaltento bring a conversation to a \stop ein Gespräch beendento bring the traffic to a \stop den Verkehr zum Erliegen bringento bring sth to a sudden \stop etw dat ein jähes Ende bereitento come to a \stop stehen bleiben; car also anhalten; rain aufhören; traffic, business zum Erliegen kommen; project, production eingestellt werdenthe conversation came to a \stop das Gespräch verstummteto come to a sudden [or dead] \stop car abrupt anhalten [o stehen bleiben]; project, undertaking ein jähes Ende findento make a \stop anhaltento put a \stop to sth etw dat ein Ende setzen [o einen Riegel vorschiebenwe made two \stops wir haben zweimal haltgemacht... including a thirty minute \stop for lunch... inklusive einer halben Stunde Pause für das Mittagessenthere were a lot of \stops and starts throughout the project die Entwicklung des Projekts verlief sehr stockendto drive without a \stop durchfahrento have a \stop haltmachento have a \stop for coffee ein Kaffeepause machento make a \stop at a service station an einer Raststätte haltmachenwithout a \stop ohne Pause [o Unterbrechungthe ship's first \stop is Sydney das Schiff läuft als Erstes Sydney an; (for plane) Zwischenlandung fthe plane's first \stop is Birmingham das Flugzeug wird zunächst in Birmingham zwischenlandenI'm getting off at the next \stop bei der nächsten Haltestelle steige ich ausis this your \stop? steigen Sie hier aus?is this our \stop? müssen wir hier aussteigen?bus/tram \stop Bus-/Straßenbahnhaltestelle frequest \stop Bedarfshaltestelle f (Haltestelle, bei der man den Bus herwinken muss, da er nicht automatisch hält)account on \stop gesperrtes Kontoto put a \stop on a cheque einen Scheck sperren lassen10.▶ to pull out all the \stops alle Register ziehen* * *[stɒp]1. nto bring sth to a stop (lit) — etw anhalten or stoppen, etw zum Stehen bringen; traffic etw zum Erliegen bringen; (fig) project, meeting, development einer Sache (dat) ein Ende machen; conversation etw verstummen lassen
to come to a stop (car, machine) — anhalten, stoppen; (traffic) stocken; ( fig, meeting, rain ) aufhören; (research, project) eingestellt werden; (conversation) verstummen
to come to a dead/sudden stop (vehicle) — abrupt anhalten or stoppen; (traffic) völlig/plötzlich zum Erliegen kommen; (rain) ganz plötzlich aufhören; (research, project, meeting) ein Ende nt/ein abruptes Ende finden; (conversation) völlig/abrupt verstummen
when the aircraft has come to a complete stop — wenn die Maschine völlig zum Stillstand gekommen ist
to make a stop (bus, train, tram) — (an)halten; (plane, ship) (Zwischen)station machen
to put a stop to sth — einer Sache (dat) einen Riegel vorschieben
3) (= stopping place) Station f; (for bus, tram, train) Haltestelle f; (for ship) Anlegestelle f; (for plane) Landeplatz m4) (Brit: punctuation mark) Punkt m5) (MUS of wind instruments) (Griff)loch nt; (on organ also stopknob) Registerzug m; (= organ pipe) Register nt7) (PHOT: f number) Blende f2. vt1) (= stop when moving) person, vehicle, clock anhalten; ball stoppen; engine, machine etc abstellen; blow abblocken, auffangen; (= stop from going away, from moving on) runaway, thief etc aufhalten; attack, enemy, progress aufhalten, hemmen; traffic (= hold up) aufhalten; (= bring to complete standstill) zum Stehen or Erliegen bringen; (policeman) anhalten; (= keep out) noise, light abfangen, auffangento stop sb dead or in his tracks — jdn urplötzlich anhalten lassen; (in conversation) jdn plötzlich verstummen lassen
2) (= stop from continuing) activity, rumour, threat, crime ein Ende machen or setzen (+dat); nonsense, noise unterbinden; match, conversation, work beenden; development aufhalten; (temporarily) unterbrechen; flow of blood stillen, unterbinden; progress, inflation aufhalten, hemmen; speaker, speech unterbrechen; production zum Stillstand bringen; (temporarily) unterbrechenhe was talking and talking, we just couldn't stop him — er redete und redete, und wir konnten ihn nicht dazu bringen, endlich aufzuhören
the referee stopped play — der Schiedsrichter hat das Spiel abgebrochen; (temporarily)
3) (= cease) aufhören mitto stop doing sth — aufhören, etw zu tun, etw nicht mehr tun
to stop smoking — mit dem Rauchen aufhören; (temporarily) das Rauchen einstellen
I'm trying to stop smoking — ich versuche, das Rauchen aufzugeben or nicht mehr zu rauchen
stop saying that — nun sag das doch nicht immer
4) (= suspend) stoppen; payments, production, fighting einstellen; leave, cheque, water supply, wages sperren; privileges unterbinden; subsidy, allowances, grant etc streichen; battle, negotiations, proceedings abbrechen; (= cancel) subscription kündigen; (temporarily) delivery, newspaper abbestellento stop oneself — sich beherrschen, sich bremsen (inf)
there's nothing stopping you or to stop you — es hindert Sie nichts, es hält Sie nichts zurück
6)(in participial construction)
to stop sb (from) doing sth — jdn davon abhalten or (physically) daran hindern, etw zu tunthat'll stop the gas (from) escaping/the pipe( from) leaking — das wird verhindern, dass Gas entweicht/das Rohr leckt
it will stop you from worrying — dann brauchen Sie sich (dat) keine Sorgen zu machen
7) (= block) verstopfen; (with cork, bung, cement etc) zustopfen (with mit); (= fill) tooth plombieren, füllen; (fig) gap füllen, stopfen; leak of information stopfen; (MUS) string greifen; finger hole zuhaltento stop one's ears with cotton wool/one's fingers — sich (dat) Watte/die Finger in die Ohren stecken
3. vi1) (= halt) anhalten; (train, car) (an)halten, stoppen; (traveller, driver, hiker) haltmachen; (pedestrian, clock, watch) stehen bleiben; (engine, machine) nicht mehr laufenstop right there! — halt!, stopp!
we stopped for a drink at the pub — wir machten in der Kneipe Station, um etwas zu trinken
to stop at nothing (to do sth) (fig) — vor nichts haltmachen(, um etw zu tun)
See:→ short2) (= finish, cease) aufhören; (heart) aufhören zu schlagen, stehen bleiben; (production, payments, delivery) eingestellt werden; (programme, show, match, film) zu Ende seinto stop doing sth — aufhören, etw zu tun, mit etw aufhören
ask him to stop — sag ihm, er soll aufhören
I will not stop until I find him/convince you — ich gebe keine Ruhe, bis ich ihn gefunden habe/dich überzeugt habe
stop to think before you speak — erst denken, dann reden
he never knows when or where to stop — er weiß nicht, wann er aufhören muss or Schluss machen muss
* * *A v/t prät und pperf stopped, obs stopt1. aufhören ( doing zu tun):stop doing sth auch etwas bleiben lassen;do stop that noise hör (doch) auf mit dem Lärm!;stop it hör auf (damit)!2. a) allg aufhören mitc) Verhandlungen etc abbrechennothing could stop him nichts konnte ihn aufhaltenc) einen Wagen, Zug etc stoppen, anhaltend) eine Maschine, den Motor, auch das Gas etc abstellene) eine Fabrik stilllegenf) Lärm etc unterbindeng) Boxen: einen Kampf abbrechen5. einen Sprecher etc unterbrechen6. SPORTa) Boxen, Fechten: einen Schlag, Hieb parierenb) einen Gegner besiegen, stoppen:stop a blow sich einen Schlag einfangen;stop sb (from) doing sth jemanden davon abhalten oder daran hindern, etwas zu tunstop one’s ears sich die Ohren zuhalten;stop sb’s mouth fig jemandem den Mund stopfen, jemanden zum Schweigen bringen (a. euph umbringen); → gap 19. versperren, -stopfen, blockieren10. Blut, auch eine Wunde stillen11. einen Zahn plombieren, füllenout of, from von)13. MUSa) eine Saite, einen Ton greifenb) ein Griffloch zuhalten, schließenc) ein Blasinstrument, einen Ton stopfen14. LING interpunktierenB v/i1. (an)halten, haltmachen, stehen bleiben (auch Uhr etc), stoppen2. aufhören, an-, innehalten, eine Pause machen:he stopped in the middle of a sentence er hielt mitten in einem Satz inne;he’ll stop at nothing er schreckt vor nichts zurück, er geht über Leichen;3. aufhören (Lärm, Zahlung etc)4. stop offa) kurz haltmachen,b) Zwischenstation machen5. stop over Zwischenstation machen7. bleiben:stop away (from) fernbleiben (dat), wegbleiben (von);stop behind noch dableiben;b) SCHULE nachsitzen;a) wegbleiben, nicht heimkommen,b) WIRTSCH weiterstreiken;stop up aufbleiben, wach bleibenC s1. a) Stopp m, Halt m, Stillstand mb) Ende n:come to a stop anhalten, weitS. zu einem Ende kommen, aufhören;2. Pause f3. BAHN etc Aufenthalt m, Halt m4. a) BAHN Station fc) SCHIFF Anlegestelle f5. Absteigequartier n6. Hemmnis n, Hindernis n7. TECH Anschlag m, Sperre f, Hemmung f8. WIRTSCHa) Sperrung f, Sperrauftrag m (für Scheck etc)9. MUSa) Griff m, Greifen n (einer Saite etc)b) Griffloch nc) Klappe fd) Ventil ne) Register n (einer Orgel etc)f) Registerzug m:pull out all the stops fig alle Register ziehen, alle Hebel in Bewegung setzen10. LINGa) Knacklaut mb) Verschlusslaut m11. FOTO f-Blende f (als Einstellmarke)12. a) Satzzeichen nb) Punkt m* * *1. transitive verb,- pp-1) (not let move further) anhalten [Person, Fahrzeug]; aufhalten [Fortschritt, Verkehr, Feind]; verstummen lassen (geh.) [Gerücht, Geschichte, Lüge]; [Tormann:] halten [Ball]2) (not let continue) unterbrechen [Redner, Spiel, Gespräch, Vorstellung]; beenden [Krieg, Gespräch, Treffen, Spiel, Versuch, Arbeit]; stillen [Blutung]; stoppen [Produktion, Uhr, Streik, Inflation]; einstellen [Handel, Zahlung, Lieferung, Besuche, Subskriptionen, Bemühungen]; abstellen [Strom, Gas, Wasser, Missstände]; beseitigen [Schmerz]stop that/that nonsense/that noise! — hör damit/mit diesem Unsinn/diesem Lärm auf!
bad light stopped play — (Sport) das Spiel wurde wegen schlechter Lichtverhältnisse abgebrochen
stop the show — (fig.) Furore machen
just you try and stop me! — versuch doch, mich daran zu hindern!
stop smoking/crying — aufhören zu rauchen/weinen
stop it! — hör auf [damit]!; (in more peremptory tone) Schluss damit!
3) (not let happen) verhindern [Verbrechen, Unfall]he phoned his mother to stop her [from] worrying — er rief seine Mutter an, damit sie sich keine Sorgen machte
stop something [from] happening — verhindern, dass etwas geschieht
4) (cause to cease working) abstellen [Maschine usw.]; [Streikende:] stilllegen [Betrieb]5) (block up) zustopfen [Loch, Öffnung, Riß, Ohren]; verschließen [Wasserhahn, Rohr, Schlauch, Flasche]6) (withhold) streichen2. intransitive verb,stop [payment of] a cheque — einen Scheck sperren lassen
- pp-1) (not extend further) aufhören; [Straße, Treppe:] enden; [Ton:] verstummen; [Ärger:] verfliegen; [Schmerz:] abklingen; [Zahlungen, Lieferungen:] eingestellt werden2) (not move or operate further) [Fahrzeug, Fahrer:] halten; [Maschine, Motor:] stillstehen; [Uhr, Fußgänger, Herz:] stehen bleibenhe never stops to think [before he acts] — er denkt nie nach [bevor er handelt]
stop dead — plötzlich stehen bleiben; [Redner:] abbrechen
3) (coll.): (stay) bleiben3. nounstop at a hotel/at a friend's house/with somebody — in einem Hotel/im Hause eines Freundes/bei jemandem wohnen
1) (halt) Halt, derthere will be two stops for coffee on the way — es wird unterwegs zweimal zum Kaffeetrinken angehalten
this train goes to London with only two stops — dieser Zug fährt mit nur zwei Zwischenhalten nach London
bring to a stop — zum Stehen bringen [Fahrzeug]; zum Erliegen bringen [Verkehr]; unterbrechen [Arbeit, Diskussion, Treffen]
come to a stop — stehen bleiben; [Fahrzeug:] zum Stehen kommen; [Gespräch:] abbrechen; [Arbeit, Verkehr:] zum Erliegen kommen; [Vorlesung:] abgebrochen werden
make a stop at or in a place — in einem Ort haltmachen
put a stop to — abstellen [Missstände, Unsinn]; unterbinden [Versuche]; aus der Welt schaffen [Gerücht]
without a stop — ohne Halt [fahren, fliegen]; ohne anzuhalten [gehen, laufen]; ununterbrochen [arbeiten, reden]
2) (place) Haltestelle, diethe ship's first stop is Cairo — der erste Hafen, den das Schiff anläuft, ist Kairo
4) (in telegram) stopPhrasal Verbs:- stop by- stop off- stop out- stop up* * *(mechanics) n.Sperre -n f. n.Halt -e m.Pause -n f. v.absperren v.anhalten v.arretieren v.aufhalten v.aufhören v.pfropfen v.zustöpseln v. -
13 stop
1)to \stop a ball einen Ball stoppen; goalkeeper einen Ball halten;to \stop a blow einen Schlag abblocken;to \stop sb/ a car jdn/ein Auto anhalten;to \stop one's car anhalten;to \stop the enemy den Feind aufhalten;to \stop a thief/ the traffic einen Dieb/den Verkehr aufhalten;\stop thief! haltet den Dieb!;\stop that man! haltet den Mann!2) ( make cease)this will \stop the pain das wird dir gegen die Schmerzen helfen;\stop that nonsense! hör auf mit dem Unsinn!;\stop it! hör auf [damit]!;what can I do to \stop this nosebleed? was kann ich gegen dieses Nasenbluten tun?;something must be done to \stop the fighting den Kämpfen muss ein Ende gesetzt werden;this fighting has to be \stopped! die Kämpfe müssen aufhören!;\stop being silly! hör auf mit dem Unsinn!;I just couldn't \stop myself ich konnte einfach nicht anders;to \stop the bleeding die Blutung stillen;to \stop the clock die Uhr anhalten;the clock is \stopped when a team scores a goal die Spielzeit wird unterbrochen, wenn ein Team ein Tor schießt;to \stop the engine den Motor abstellen;to \stop the fighting die Kämpfe einstellen;to \stop inflation/ progress die Inflation/den Fortschritt aufhalten;to \stop a machine eine Maschine abstellen;to \stop a match ein Spiel beenden; referee ein Spiel abbrechen;to \stop the production of sth die Produktion einer S. gen einstellen;to \stop a rumour ein Gerücht ein Ende machen;to \stop a speech eine Rede unterbrechen;to \stop a subscription ein Abonnement kündigen;to \stop a war einen Krieg beenden3) ( cease an activity)to \stop sth etw beenden, mit etw dat aufhören;what time do you usually \stop work? wann hören Sie normalerweise auf zu arbeiten?;you just can't \stop it, can you du kannst es einfach nicht lassen, oder?4) ( prevent)to \stop sb [from] doing sth jdn davon abhalten, etw zu tun;if she really wants to leave, I don't understand what's \stopping her wenn sie wirklich weggehen will, verstehe ich nicht, was sie davon abhält;some people smoke because they think it \stops them putting on weight manche rauchen, weil sie meinen, dass sie dann nicht zunehmen;I couldn't \stop myself from having another piece of cake ich musste einfach noch ein Stück Kuchen essen;he handed in his resignation - I just couldn't \stop him er hat gekündigt - ich konnte ihn einfach nicht davon abhalten;you can't \stop me from doing that du kannst mich nicht davon abhalten5) ( refuse payment)to \stop sb's allowance/ pocket money jdm den Unterhalt/das Taschengeld streichen;to \stop [ (Am) payment on] a cheque einen Scheck sperren;to \stop wages keine Löhne mehr zahlen;the money will be \stopped out of his salary das Geld wird von seinem Gehalt abgezogen6) ( block)to \stop sth etw verstopfen; gap, hole, leak etw [zu]stopfen;to \stop one's ears sich dat die Ohren zuhalten;when he starts shouting I just \stop my ears wenn er anfängt zu schreien, mache ich einfach die Ohren zu! ( fam)7) boxingto \stop sb jdn schlagen;he was \stopped by a knockout in the fourth round er schied durch K.o. in der vierten Runde aus;to \stop a left/ right eine Linke/Rechte parieren;to \stop a punch einen Hieb einstecken [müssen]8) mus\stopped pipe gedackte Pfeife fachspr;to \stop a string eine Saite greifenPHRASES:to \stop a bullet eine Kugel abbekommen;to \stop sb's mouth jdm den Mund stopfen ( fam)to \stop the rot die Talfahrt stoppen ( fig)\stop! halt!;to \stop dead abrupt innehalten;to \stop to do sth stehen bleiben, um etw zu tun; car anhalten, um etw zu tun;I \stopped to pick up the letter that I had dropped ich blieb stehen und hob den Brief auf, den ich hatte fallen lassen; ( fig)2) (cease, discontinue) machine nicht mehr laufen; clock, heart, watch stehen bleiben; rain aufhören; pain abklingen, nachlassen; production, payments eingestellt werden; film, programme zu Ende sein; speaker abbrechen;I will not \stop until they set them free ich werde keine Ruhe geben, bis sie sie freigelassen haben;she doesn't know where to \stop sie weiß nicht, wann sie aufhören muss;his heart \stopped during the operation während der Operation hatte er einen Herzstillstand;rain has \stopped play das Spiel wurde wegen Regens unterbrochen;she \stopped right in the middle of the sentence sie hielt mitten im Satz inne3) ( cease an activity)to \stop [doing sth] aufhören[, etw zu tun], [mit etw dat] aufhören;once I start eating chocolate I can't \stop wenn ich einmal anfange, Schokolade zu essen, kann ich einfach nicht mehr aufhören;I just couldn't \stop laughing ich habe mich echt totgelacht (sl)if you have to keep \stopping to answer the telephone, you 'll never finish wenn du ständig unterbrechen musst, um ans Telefon zu gehen, wirst du nie fertig werden;I wish you'd \stop telling me what to do ich wünschte, du würdest endlich damit aufhören, mir zu sagen, was ich tun soll;\stop being silly! hör auf mit dem Unsinn!;\stop shouting! hör auf zu schreien;I \stopped seeing him last year wir haben uns letztes Jahr getrennt;I've \stopped drinking alcohol ich trinke keinen Alkohol mehr;she \stopped drinking sie trinkt nicht mehr;please, \stop crying hör doch bitte auf zu weinen!;to \stop smoking mit dem Rauchen aufhören;(on plane etc.) das Rauchen einstellen;to \stop working aufhören zu arbeitenI'm not \stopping ich bleibe nicht lange;I can't \stop - Malcolm's waiting for me outside ich kann nicht bleiben, Malcolm wartet draußen auf mich;we \stopped for a quick bite at a motorway services wir machten kurz bei einer Autobahnraststätte Station, um etwas zu essen;I \stopped at a pub for some lunch ich habe an einem Pub Halt gemacht und was zu Mittag gegessen;can you \stop at the fish shop on your way home? kannst du auf dem Nachhauseweg kurz beim Fischladen vorbeigehen?;he usually \stops at a bar for a quick drink on the way home normalerweise schaut er auf dem Nachhauseweg noch kurz auf ein Gläschen in einer Kneipe vorbei;are you \stopping here bleibst du hier?;to \stop for dinner/ tea zum Abendessen/Tee bleiben;to \stop at a hotel in einem Hotel übernachten;does this train \stop at Finsbury Park? hält dieser Zug in Finsbury Park?;the train to Glasgow \stops at platform 14 der Zug nach Glasgow hält am Gleis 146) ( almost)to \stop short of doing sth sich akk [gerade noch] bremsen, etw zu tun;I \stopped short of telling him my secrets beinahe hätte ich ihm meine Geheimnisse verratenPHRASES:to \stop at nothing vor nichts zurückschrecken n1) (cessation of movement, activity) Halt m;please wait until the airplane has come to a complete \stop bitte warten Sie, bis das Flugzeug seine endgültige Parkposition erreicht hat;emergency \stop Notbremsung f;to bring a car to a \stop ein Auto anhalten;to bring a conversation to a \stop ein Gespräch beenden;to bring the traffic to a \stop den Verkehr zum Erliegen bringen;to bring sth to a sudden \stop etw dat ein jähes Ende bereiten;to come to a \stop stehen bleiben; car also anhalten; rain aufhören; traffic, business zum Erliegen kommen; project, production eingestellt werden;the conversation came to a \stop das Gespräch verstummte;to come to a sudden [or dead] \stop car abrupt anhalten [o stehen bleiben]; project, undertaking ein jähes Ende finden;to make a \stop anhalten;we made two \stops wir haben zweimal Halt gemacht;... including a thirty minute \stop for lunch... inklusive einer halben Stunde Pause für das Mittagessen;there were a lot of \stops and starts throughout the project die Entwicklung des Projekts verlief sehr stockend;to drive without a \stop durchfahren;to have a \stop Halt machen;to have a \stop for coffee ein Kaffeepause machen;to make a \stop at a service station an einer Raststätte Halt machen;without a \stop ohne Pause [o Unterbrechung];the ship's first \stop is Sydney das Schiff läuft als Erstes Sydney an;( for plane) Zwischenlandung f;the plane's first \stop is Birmingham das Flugzeug wird zunächst in Birmingham zwischenlanden;I'm getting off at the next \stop bei der nächsten Haltestelle steige ich aus;is this your \stop? steigen Sie hier aus?;is this our \stop? müssen wir hier aussteigen?;request \stop Bedarfshaltestelle f (Haltestelle, bei der man den Bus herwinken muss, da er nicht automatisch hält)PHRASES:to pull out all the \stops alle Register ziehen -
14 Chronology
15,000-3,000 BCE Paleolithic cultures in western Portugal.400-200 BCE Greek and Carthaginian trade settlements on coast.202 BCE Roman armies invade ancient Lusitania.137 BCE Intensive Romanization of Lusitania begins.410 CE Germanic tribes — Suevi and Visigoths—begin conquest of Roman Lusitania and Galicia.714—16 Muslims begin conquest of Visigothic Lusitania.1034 Christian Reconquest frontier reaches Mondego River.1064 Christians conquer Coimbra.1139 Burgundian Count Afonso Henriques proclaims himself king of Portugal; birth of Portugal. Battle of Ourique: Afonso Henriques defeats Muslims.1147 With English Crusaders' help, Portuguese seize Lisbon from Muslims.1179 Papacy formally recognizes Portugal's independence (Pope Alexander III).1226 Campaign to reclaim Alentejo from Muslims begins.1249 Last Muslim city (Silves) falls to Portuguese Army.1381 Beginning of third war between Castile and Portugal.1383 Master of Aviz, João, proclaimed regent by Lisbon populace.1385 April: Master of Aviz, João I, proclaimed king of Portugal by Cortes of Coimbra. 14 August: Battle of Aljubarrota, Castilians defeated by royal forces, with assistance of English army.1394 Birth of "Prince Henry the Navigator," son of King João I.1415 Beginning of overseas expansion as Portugal captures Moroccan city of Ceuta.1419 Discovery of Madeira Islands.1425-28 Prince D. Pedro, older brother of Prince Henry, travels in Europe.1427 Discovery (or rediscovery?) of Azores Islands.1434 Prince Henry the Navigator's ships pass beyond Cape Bojador, West Africa.1437 Disaster at Tangier, Morocco, as Portuguese fail to capture city.1441 First African slaves from western Africa reach Portugal.1460 Death of Prince Henry. Portuguese reach what is now Senegal, West Africa.1470s Portuguese explore West African coast and reach what is now Ghana and Nigeria and begin colonizing islands of São Tomé and Príncipe.1479 Treaty of Alcáçovas between kings of Portugal and Spain.1482 Portuguese establish post at São Jorge da Mina, Gold Coast (now Ghana).1482-83 Portuguese navigator Diogo Cão reaches mouth of Congo River and Angola.1488 Navigator Bartolomeu Dias rounds Cape of Good Hope, South Africa, and finds route to Indian Ocean.1492-93 Columbus's first voyage to West Indies.1493 Columbus visits Azores and Portugal on return from first voyage; tells of discovery of New World. Treaty of Tordesillas signed between kings of Portugal and Spain: delimits spheres of conquest with line 370 leagues west of Cape Verde Islands (claimed by Portugal); Portugal's sphere to east of line includes, in effect, Brazil.King Manuel I and Royal Council decide to continue seeking all-water route around Africa to Asia.King Manuel I expels unconverted Jews from Portugal.1497-99 Epic voyage of Vasco da Gama from Portugal around Africa to west India, successful completion of sea route to Asia project; da Gama returns to Portugal with samples of Asian spices.1500 Bound for India, Navigator Pedro Álvares Cabral "discovers" coast of Brazil and claims it for Portugal.1506 Anti-Jewish riots in Lisbon.Battle of Diu, India; Portugal's command of Indian Ocean assured for some time with Francisco de Almeida's naval victory over Egyptian and Gujerati fleets.Afonso de Albuquerque conquers Goa, India; beginning of Portuguese hegemony in south Asia.Portuguese conquest of Malacca; commerce in Spice Islands.1519 Magellan begins circumnavigation voyage.1536 Inquisition begins in Portugal.1543 Portuguese merchants reach Japan.1557 Portuguese merchants granted Chinese territory of Macau for trading factory.1572 Luís de Camões publishes epic poem, Os Lusíadas.1578 Battle of Alcácer-Quivir; Moroccan forces defeat army of King Sebastião of Portugal; King Sebastião dies in battle. Portuguese succession crisis.1580 King Phillip II of Spain claims and conquers Portugal; Spanish rule of Portugal, 1580-1640.1607-24 Dutch conquer sections of Asia and Brazil formerly held by Portugal.1640 1 December: Portuguese revolution in Lisbon overthrows Spanish rule, restores independence. Beginning of Portugal's Braganza royal dynasty.1654 Following Dutch invasions and conquest of parts of Brazil and Angola, Dutch expelled by force.1661 Anglo-Portuguese Alliance treaty signed: England pledges to defend Portugal "as if it were England itself." Queen Catherine of Bra-ganza marries England's Charles II.1668 February: In Portuguese-Spanish peace treaty, Spain recognizes independence of Portugal, thus ending 28-year War of Restoration.1703 Methuen Treaties signed, key commercial trade agreement and defense treaty between England and Portugal.1750 Pombal becomes chief minister of King José I.1755 1 November: Massive Lisbon earthquake, tidal wave, and fire.1759 Expulsion of Jesuits from Portugal and colonies.1761 Slavery abolished in continental Portugal.1769 Abandonment of Mazagão, Morocco, last Portuguese outpost.1777 Pombal dismissed as chief minister by Queen Maria I, after death of José I.1791 Portugal and United States establish full diplomatic relations.1807 November: First Napoleonic invasion; French forces under Junot conquer Portugal. Royal family flees to colony of Brazil and remains there until 1821.1809 Second French invasion of Portugal under General Soult.1811 Third French invasion of Portugal under General Masséna.1813 Following British general Wellington's military victories, French forces evacuate Portugal.1817 Liberal, constitutional movements against absolutist monarchist rule break out in Brazil (Pernambuco) and Portugal (Lisbon, under General Gomes Freire); crushed by government. British marshal of Portugal's army, Beresford, rules Portugal.Liberal insurrection in army officer corps breaks out in Cadiz, Spain, and influences similar movement in Portugal's armed forces first in Oporto.King João VI returns from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, and early draft of constitution; era of constitutional monarchy begins.1822 7 September: João VI's son Pedro proclaims independence ofBrazil from Portugal and is named emperor. 23 September: Constitution of 1822 ratified.Portugal recognizes sovereign independence of Brazil.King João VI dies; power struggle for throne ensues between his sons, brothers Pedro and Miguel; Pedro, emperor of Brazil, abdicates Portuguese throne in favor of his daughter, D. Maria II, too young to assume crown. By agreement, Miguel, uncle of D. Maria, is to accept constitution and rule in her stead.1828 Miguel takes throne and abolishes constitution. Sections of Portugal rebel against Miguelite rule.1831 Emperor Pedro abdicates throne of Brazil and returns to Portugal to expel King Miguel from Portuguese throne.1832-34 Civil war between absolutist King Miguel and constitutionalist Pedro, who abandons throne of Brazil to restore his young daughter Maria to throne of Portugal; Miguel's armed forces defeated by those of Pedro. Miguel leaves for exile and constitution (1826 Charter) is restored.1834-53 Constitutional monarchy consolidated under rule of Queen Maria II, who dies in 1853.1851-71 Regeneration period of economic development and political stability; public works projects sponsored by Minister Fontes Pereira de Melo.1871-90 Rotativism period of alternating party governments; achieves political stability and less military intervention in politics and government. Expansion of colonial territory in tropical Africa.January: Following territorial dispute in central Africa, Britain delivers "Ultimatum" to Portugal demanding withdrawal of Portugal's forces from what is now Malawi and Zimbabwe. Portugal's government, humiliated in accepting demand under threat of a diplomatic break, falls. Beginning of governmental and political instability; monarchist decline and republicanism's rise.Anglo-Portuguese treaties signed relating to delimitation of frontiers in colonial Africa.1899 Treaty of Windsor; renewal of Anglo-Portuguese defense and friendship alliance.1903 Triumphal visit of King Edward VII to Portugal.1906 Politician João Franco supported by King Carlos I in dictatorship to restore order and reform.1908 1 February: Murder in Lisbon of King Carlos I and his heir apparent, Prince Dom Luís, by Portuguese anarchists. Eighteen-year-old King Manuel II assumes throne.1910 3-5 October: Following republican-led military insurrection in armed forces, monarchy falls and first Portuguese republic is proclaimed. Beginning of unstable, economically troubled, parliamentary republic form of government.May: Violent insurrection in Lisbon overturns government of General Pimenta de Castro; nearly a thousand casualties from several days of armed combat in capital.March: Following Portugal's honoring ally Britain's request to confiscate German shipping in Portuguese harbors, Germany declares war on Portugal; Portugal enters World War I on Allied side.Portugal organizes and dispatches Portuguese Expeditionary Corps to fight on the Western Front. 9 April: Portuguese forces mauled by German offensive in Battle of Lys. Food rationing and riots in Lisbon. Portuguese military operations in Mozambique against German expedition's invasion from German East Africa. 5 December: Authoritarian, presidentialist government under Major Sidónio Pais takes power in Lisbon, following a successful military coup.1918 11 November: Armistice brings cessation of hostilities on Western Front in World War I. Portuguese expeditionary forces stationed in Angola, Mozambique, and Flanders begin return trip to Portugal. 14 December: President Sidónio Pais assassinated. Chaotic period of ephemeral civil war ensues.1919-21 Excessively unstable political period, including January1919 abortive effort of Portuguese monarchists to restore Braganza dynasty to power. Republican forces prevail, but level of public violence, economic distress, and deprivation remains high.1921 October: Political violence attains peak with murder of former prime minister and other prominent political figures in Lisbon. Sectors of armed forces and Guarda Nacional Republicana are mutinous. Year of financial and corruption scandals, including Portuguese bank note (fraud) case; military court acquits guilty military insurrectionists, and one military judge declares "the country is sick."28 May: Republic overthrown by military coup or pronunciamento and conspiracy among officer corps. Parliament's doors locked and parliament closed for nearly nine years to January 1935. End of parliamentary republic, Western Europe's most unstable political system in this century, beginning of the Portuguese dictatorship, after 1930 known as the Estado Novo. Officer corps assumes reins of government, initiates military censorship of the press, and suppresses opposition.February: Military dictatorship under General Óscar Carmona crushes failed republican armed insurrection in Oporto and Lisbon.April: Military dictatorship names Professor Antônio de Oliveira Salazar minister of finance, with dictatorial powers over budget, to stabilize finances and rebuild economy. Insurrectionism among military elements continues into 1931.1930 Dr. Salazar named minister for colonies and announces balanced budgets. Salazar consolidates support by various means, including creation of official regime "movement," the National Union. Salazar engineers Colonial Act to ensure Lisbon's control of bankrupt African colonies by means of new fiscal controls and centralization of authority. July: Military dictatorship names Salazar prime minister for first time, and cabinet composition undergoes civilianization; academic colleagues and protégés plan conservative reform and rejuvenation of society, polity, and economy. Regime comes to be called the Estado Novo (New State). New State's constitution ratified by new parliament, the National Assembly; Portugal described in document as "unitary, corporative Republic" and governance influenced by Salazar's stern personality and doctrines such as integralism, Catholicism, and fiscal conservatism.1936 Violent instability and ensuing civil war in neighboring Spain, soon internationalized by fascist and communist intervention, shake Estado Novo regime. Pseudofascist period of regime features creation of imitation Fascist institutions to defend regime from leftist threats; Portugal institutes "Portuguese Youth" and "Portuguese Legion."1939 3 September: Prime Minister Salazar declares Portugal's neutrality in World War II. October: Anglo-Portuguese agreement grants naval and air base facilities to Britain and later to United States for Battle of the Atlantic and Normandy invasion support. Third Reich protests breach of Portugal's neutrality.6 June: On day of Allies' Normandy invasion, Portugal suspends mining and export of wolfram ore to both sides in war.8 May: Popular celebrations of Allied victory and Fascist defeat in Lisbon and Oporto coincide with Victory in Europe Day. Following managed elections for Estado Novo's National Assembly in November, regime police, renamed PIDE, with increased powers, represses opposition.1947 Abortive military coup in central Portugal easily crushed by regime. Independence of India and initiation of Indian protests against Portuguese colonial rule in Goa and other enclaves.1949 Portugal becomes founding member of NATO.1951 Portugal alters constitution and renames overseas colonies "Overseas Provinces." Portugal and United States sign military base agreements for use of air and naval facilities in Azores Islands and military aid to Lisbon. President Carmona dies in office, succeeded by General Craveiro Lopes (1951-58). July: Indians occupy enclave of Portuguese India (dependency of Damão) by means of passive resistance movement. August: Indian passive resistance movement in Portuguese India repelled by Portuguese forces with loss of life. December: With U.S. backing, Portugal admitted as member of United Nations (along with Spain). Air force general Humberto Delgado, in opposition, challenges Estado Novo's hand-picked successor to Craveiro Lopes, Admiral Américo Tomás. Delgado rallies coalition of democratic, liberal, and communist opposition but loses rigged election and later flees to exile in Brazil. Portugal joins European Free Trade Association (EFTA).January and February: Estado Novo rocked by armed African insurrection in northern Angola, crushed by armed forces. Hijacking of Portuguese ocean liner by ally of Delgado, Captain Henrique Galvão. April: Salazar defeats attempted military coup and reshuffles cabinet with group of younger figures who seek to reform colonial rule and strengthen the regime's image abroad. 18 December: Indian army rapidly defeats Portugal's defense force in Goa, Damão, and Diu and incorporates Portugal's Indian possessions into Indian Union. January: Abortive military coup in Beja, Portugal.1965 February: General Delgado and his Brazilian secretary murdered and secretly buried near Spanish frontier by political police, PIDE.1968 August and September: Prime Minister Salazar, aged 79, suffers crippling stoke. President Tomás names former cabinet officer Marcello Caetano as Salazar's successor. Caetano institutes modest reforms in Portugal and overseas.1971 Caetano government ratifies amended constitution that allows slight devolution and autonomy to overseas provinces in Africa and Asia. Right-wing loyalists oppose reforms in Portugal. 25 April: Military coup engineered by Armed Forces Movement overthrows Estado Novo and establishes provisional government emphasizing democratization, development, and decolonization. Limited resistance by loyalists. President Tomás and Premier Caetano flown to exile first in Madeira and then in Brazil. General Spínola appointed president. September: Revolution moves to left, as President Spínola, thwarted in his program, resigns.March: Military coup by conservative forces fails, and leftist response includes nationalization of major portion of economy. Polarization between forces and parties of left and right. 25 November: Military coup by moderate military elements thwarts leftist forces. Constituent Assembly prepares constitution. Revolution moves from left to center and then right.March: Constitution ratified by Assembly of the Republic. 25 April: Second general legislative election gives largest share of seats to Socialist Party (PS). Former oppositionist lawyer, Mário Soares, elected deputy and named prime minister.1977-85 Political pendulum of democratic Portugal moves from center-left to center-right, as Social Democratic Party (PSD) increases hold on assembly and take office under Prime Minister Cavaco Silva. July1985 elections give edge to PSD who advocate strong free-enterprise measures and revision of leftist-generated 1976 Constitution, amended modestly in 1982.1986 January: Portugal joins European Economic Community (EEC).1987 July: General, legislative elections for assembly give more than 50 percent to PSD led by Prime Minister Cavaco Silva. For first time, since 1974, Portugal has a working majority government.1989 June: Following revisions of 1976 Constitution, reprivatization of economy begins, under PS government.January: Presidential elections, Mário Soares reelected for second term. July: General, legislative elections for assembly result in new PSD victory and majority government.January-July: Portugal holds presidency of the Council of the European Economic Community (EEC). December: Tariff barriers fall as fully integrated Common Market established in the EEC.November: Treaty of Maastricht comes into force. The EEC officially becomes the European Union (EU). Portugal is signatory with 11 other member-nations.October: General, legislative elections for assembly result in PS victory and naming of Prime Minister Guterres. PS replace PSD as leading political party. November: Excavations for Lisbon bank uncover ancient Phoenician, Roman, and Christian ruins.January: General, presidential elections; socialist Jorge Sampaio defeats PSD's Cavaco Silva and assumes presidency from Dr. Mário Soares. July: Community of Portuguese Languages Countries (CPLP) cofounded by Portugal and Brazil.May-September: Expo '98 held in Lisbon. Opening of Vasco da Gama Bridge across Tagus River, Europe's longest (17 kilometers/ 11 miles). June: National referendum on abortion law change defeated after low voter turnout. November: National referendum on regionaliza-tion and devolution of power defeated after another low voter turnout.October: General, legislative elections: PS victory over PSD lacks clear majority in parliament. Following East Timor referendum, which votes for independence and withdrawal of Indonesia, outburst of popular outrage in streets, media, and communications of Portugal approves armed intervention and administration of United Nations (and withdrawal of Indonesia) in East Timor. Portugal and Indonesia restore diplomatic relations. December: A Special Territory since 1975, Colony of Macau transferred to sovereignty of People's Republic of China.January-June: Portugal holds presidency of the Council of the EU; end of Discoveries Historical Commemoration Cycle (1988-2000).United Nations forces continue to occupy and administer former colony of East Timor, with Portugal's approval.January: General, presidential elections; PS president Sampaio reelected for second term. City of Oporto, "European City of Culture" for the year, hosts arts festival. December: Municipal elections: PSD defeats PS; socialist prime minister Guterres resigns; President Sampaio calls March parliamentary elections.1 January: Portugal enters single European Currency system. Euro currency adopted and ceases use of former national currency, the escudo. March: Parliamentary elections; PSD defeats PS and José Durão Barroso becomes prime minister. Military modernization law passed. Portugal holds chairmanship of Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE).May: Municipal law passed permitting municipalities to reorganize in new ways.June: Prime Minister Durão Barroso, invited to succeed Romano Prodi as president of EU Commission, resigns. Pedro Santana Lopes becomes prime minister. European Parliament elections held. Conscription for national service in army and navy ended. Mass grave uncovered at Academy of Sciences Museum, Lisbon, revealing remains of several thousand victims of Lisbon earthquake, 1755.February: Parliamentary elections; PS defeats PSD, socialists win first absolute majority in parliament since 1975. José Sócrates becomes prime minister.January: Presidential elections; PSD candidate Aníbal Cavaco Silva elected and assumes presidency from Jorge Sampaio. Portugal's national soccer team ranked 7th out of 205 countries by international soccer association. European Union's Bologna Process in educational reform initiated in Portugal.July-December: Portugal holds presidency of the Council of the European Union. For reasons of economy, Portugal announces closure of many consulates, especially in France and the eastern US. Government begins official inspections of private institutions of higher education, following scandals.2008 January: Prime Minister Sócrates announces location of new Lisbon area airport as Alcochete, on south bank of Tagus River, site of air force shooting range. February: Portuguese Army begins to receive new modern battle tanks (Leopard 2 A6). March: Mass protest of 85,000 public school (primary and secondary levels) teachers in Lisbon schools dispute recent educational policies of minister of education and prime minister. -
15 Deane, Sir Anthony
SUBJECT AREA: Ports and shipping[br]b. 1638 Harwich (?), Englandd. 1721 England[br]English master shipwright, one of the most influential of seventeenth-century England.[br]It is believed that Deane was born in Harwich, the son of a master mariner. When 22 years of age, having been trained by Christopher Pett, he was appointed Assistant Master Shipwright at Woolwich Naval Dockyard, indicating an ability as a shipbuilder and also that he had influence behind him. Despite abruptness and a tendency to annoy his seniors, he was acknowledged by no less a man than Pepys (1633–1703) for his skill as a ship designer and -builder, and he was one of the few who could accurately estimate displacements and drafts of ships under construction. While only 26 years old, he was promoted to Master Shipwright of the Naval Base at Harwich and commenced a notable career. When the yard was closed four years later (on the cessation of the threat from the Dutch), Deane was transferred to the key position of Master Shipwright at Portsmouth and given the opportunity to construct large men-of-war. In 1671 he built his first three-decker and was experimenting with underwater hull sheathing and other matters. In 1672 he became a member of the Navy Board, and from then on promotion was spectacular, with almost full responsibility given him for decisions on ship procurement for the Navy. Owing to political changes he was out of office for some years and endured a short period in prison, but on his release he continued to work as a private shipbuilder. He returned to the King's service for a few years before the "Glorious Revolution" of 1688; thereafter little is known of his life, beyond that he died in 1721.Deane's monument to posterity is his Doctrine of Naval Architecture, published in 1670. It is one of the few books on ship design of the period and gives a clear insight into the rather pedantic procedures used in those less than scientific times. Deane became Mayor of Harwich and subsequently Member of Parliament. It is believed that he was Peter the Great's tutor on shipbuilding during his visit to the Thames in 1698.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsKnighted 1673.Bibliography1670, Doctrine of Naval Architecture; repub. 1981, with additional commentaries by Brian Lavery, as Deane's Doctrine of Naval Architecture 1670, London: Conway Maritime.Further ReadingWestcott Abell, 1948, The Shipwright's Trade, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.FMW
См. также в других словарях:
Service militaire chez les Temoins de Jehovah — Neutralité politique chez les Témoins de Jéhovah Cet article fait partie d une série sur Témoins de Jéhovah Présentation Histoire Dissidence … Wikipédia en Français
Service militaire chez les Témoins de Jéhovah — Neutralité politique chez les Témoins de Jéhovah Cet article fait partie d une série sur Témoins de Jéhovah Présentation Histoire Dissidence … Wikipédia en Français
Service militaire chez les témoins de jéhovah — Neutralité politique chez les Témoins de Jéhovah Cet article fait partie d une série sur Témoins de Jéhovah Présentation Histoire Dissidence … Wikipédia en Français
Service des Musées de France — Pour les articles homonymes, voir DMF. Le service des Musées de France, qui a succédé en 2009 à la direction des Musées de France (DMF), suite à sa fusion au sein de la Direction générale des patrimoines, est un service de l administration… … Wikipédia en Français
Smoking cessation — [ [http://www.who.int/tobacco/en/index.html World Health Organization, Tobacco Free Initiative] ] DescriptionResearch in Western countries has found that approximately 3 5% of quit attempts succeed using willpower alone (Hughes et al,… … Wikipedia
Témoins de Jéhovah et service militaire — Neutralité politique chez les Témoins de Jéhovah Cet article fait partie d une série sur Témoins de Jéhovah Présentation Histoire Dissidence … Wikipédia en Français
Sida Info Service — Contexte général Champs d’action Lutte contre le VIH/sida, les infections sexuellement transmissibles, les hépatites virales Fiche d’identité Fondateur Pierre Kneip Forme … Wikipédia en Français
Secret Intelligence Service — 51°29′13.9″N 0°07′26.6″O / 51.487194, 0.124056 … Wikipédia en Français
Auxiliary Territorial Service — The Auxiliary Territorial Service (ATS; often pronounced as an acronym) was the women s branch of the British Army during the Second World War. It was formed on 9 September 1938, initially as a women s voluntary service, and existed until 1… … Wikipedia
Hawaii Medical Service Association — (HMSA) is an insurance company in Hawaii. It was founded in 1938 and is affiliated with Blue Cross Blue Shield of Hawai i.External links* [http://www.hmsa.com/ official webpage] Hawaii Medical Service Association (HMSA) Company Description The… … Wikipedia
Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service — (APHIS) is an operating unit of the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA).APHIS mission (2003): To protect the health and value of American agriculture and natural resources. APHIS aims to protect American animals, plants, and the… … Wikipedia
