-
1 carrier blocking network
фильтр подавления несущей частоты
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > carrier blocking network
-
2 non-blocking network calls
Программирование: неблокирующие вызовы сетиУниверсальный англо-русский словарь > non-blocking network calls
-
3 blocking protocol
сетевой протокол, допускающий потерю части трафика при возникновении перегрузки сетисм. тж. network protocolАнгло-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. > blocking protocol
-
4 layer
1) слой; плёнка || формировать слой или слои; наносить плёнку2) прокладка; разделительный слой || использовать прокладку; разделять слоем3) расслаивать(ся); отслаиваться4) вчт уровень || вводить уровни; использовать многоуровневое представление (напр. иерархической системы)5) уровень шифрования, один из (последовательно применяемых неидентичных) шагов шифрования ( в блочных шифрах)•- layer of weaker air movement
- layer of weights
- accumulation layer
- adhesion layer
- Appleton layer
- application layer - barrier layer
- base layer
- Beilby layer
- blocking layer
- bonding layer
- bottom layer
- boundary layer
- buried layer
- cathode layer
- Chapman layer
- charge layer
- collector layer
- competitive layer
- confusion layer
- control layer
- D-layer
- data-link layer
- daytime layer
- dead layer
- depletionlayer
- deposited layer
- diffusion layer
- dipole layer
- doped layer
- ducting layer
- E-layer
- Es layer
- electroluminescent powder layer
- electron-barrier layer
- elevated layer
- embedded metal layer
- emitter layer
- enriched layer
- epitaxial layer
- evaporation layer
- F-layer
- F1 layer
- F2 layer
- fencing layer
- fused layer
- Gaussian-doped layer
- gettering layer
- Grossberg layer
- half-value layer - heteroepitaxial layer
- hidden layer of neural network
- hole-barrier layer
- homoepitaxial layer
- i-layer
- implanted layer
- input layer of neural network
- interfacial layer
- intrinsic layer
- inversion layer
- ion-implanted layer
- Kennelly-Heaviside layer
- Kohonen layer
- light-blocking layer
- link layer
- liquid-crystal layer
- low-latitude boundary layer
- metal layer
- metallization layer
- microtwinned layer
- microvia layer
- momentum boundary layer
- n-layer
- narrow band-gap layer
- near-intrinsic layer
- network layer
- neural layer
- optical waveguiding layer
- output layer of neural network
- overgrown layer
- oxide layer
- ozone layer
- p-layer
- passivation layer
- phosphor layer
- photoconductive control layer
- physical layer
- pi layer
- plasma sheet boundary layer
- polysilicon layer
- presentation layer
- recording layer
- secure sockets layer
- self-assembled layer
- semi-transparent layer
- sensor layer
- separating layer
- session layer
- signal layer
- space-charge layer
- spontaneous inversion layer
- sporadic-E layer
- surface boundary layer
- swept-out layer
- transaction layer
- transition layer
- transport layer
- tropospheric layer
- unswept layer
- unswept epitaxial layer
- vacuum-deposited layer
- vacuum-evaporated layer
- wide band-gap layer
- wiring layer
- ν-layer
- π-layer -
5 layer
1) слой; плёнка || формировать слой или слои; наносить плёнку2) прокладка; разделительный слой || использовать прокладку; разделять слоем3) расслаивать(ся); отслаиваться4) вчт. уровень || вводить уровни; использовать многоуровневое представление (напр. иерархической системы)5) уровень шифрования, один из (последовательно применяемых неидентичных) шагов шифрования ( в блочных шифрах)•- ν layer- π layer
- accumulation layer
- adhesion layer
- Appleton layer
- application layer
- ATM adaptation layer
- atom layer
- barrier layer
- base layer
- Beilby layer
- blocking layer
- bonding layer
- bottom layer
- boundary layer
- buried layer
- cathode layer
- Chapman layer
- charge layer
- collector layer
- competitive layer
- confusion layer
- control layer
- D layer
- data-link layer
- daytime layer
- dead layer
- depletion layer
- deposited layer
- diffusion layer
- dipole layer
- doped layer
- ducting layer
- E layer
- Es layer
- electroluminescent powder layer
- electron-barrier layer
- elevated layer
- embedded metal layer
- emitter layer
- enriched layer
- epitaxial layer
- evaporation layer
- F layer
- F2 layer
- F1 layer
- fencing layer
- fused layer
- Gaussian-doped layer
- gettering layer
- Grossberg layer
- half-value layer
- hardware abstraction layer
- Heaviside layer
- heteroepitaxial layer
- hidden layer of neural network
- hole-barrier layer
- homoepitaxial layer
- i layer
- implanted layer
- input layer of neural network
- interfacial layer
- intrinsic layer
- inversion layer
- ion-implanted layer
- Kennelly-Heaviside layer
- Kohonen layer
- layer of units
- layer of weaker air movement
- layer of weights
- light-blocking layer
- link layer
- liquid-crystal layer
- low-latitude boundary layer
- metal layer
- metallization layer
- microtwinned layer
- microvia layer
- momentum boundary layer
- n layer
- narrow band-gap layer
- near-intrinsic layer
- network layer
- neural layer
- optical waveguiding layer
- output layer of neural network
- overgrown layer
- oxide layer
- ozone layer
- p layer
- passivation layer
- phosphor layer
- photoconductive control layer
- physical layer
- pi layer
- plasma sheet boundary layer
- polysilicon layer
- presentation layer
- recording layer
- secure sockets layer
- self-assembled layer
- semi-transparent layer
- sensor layer
- separating layer
- session layer
- signal layer
- space-charge layer
- spontaneous inversion layer
- sporadic-E layer
- surface boundary layer
- swept-out layer
- transaction layer
- transition layer
- transport layer
- tropospheric layer
- unswept epitaxial layer
- unswept layer
- vacuum-deposited layer
- vacuum-evaporated layer
- wide band-gap layer
- wiring layerThe New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > layer
-
6 protocol
протокол (формат передаваемых сообщений, соглашения и правила, по которым происходит обмен информацией между компьютерами или системами)- application-oriented protocol
- binary protocol
- BISYNC protocol
- bisynchronous protocol
- bit-oriented protocol
- blocking protocol
- bridging protocol
- broadcast protocol
- bus polling protocol
- bus protocol
- carrier sense multiple access protocol
- character-asynchronous protocol
- character-oriented protocol
- code-independent protocol
- commit protocol
- communications protocol
- data collection protocol
- data communications protocol
- echo-handling protocol
- end-to-end protocol
- feedback-based protocol
- fixed path protocol
- format protocol
- function management protocol
- handshaking protocol
- high-level protocol
- host-host protocol
- infrared communication protocol
- interactive protocol
- interface protocol
- interfacing protocol
- internet protocol
- internetwork transport protocol
- interrupt protocol
- intralayer management protocol
- intranet protocol
- lightweight protocol
- line protocol
- link-level protocol
- link protocol
- link-state protocol
- locking protocol
- log-tape-write-ahead protocol
- long-haul protocol
- low-level-access protocol
- market-based protocol
- message-level protocol
- network control protocol
- network graphics protocol
- network voice protocol
- network-wide access protocol
- nonblocking protocol
- OSI protocol
- packet protocol
- pass-the-buck protocol
- path control protocol
- path independent protocol
- peer-to-peer protocol
- peer protocol - post office protocol
- reliable status control protocol
- SDLC protocol
- security protocol
- service protocol
- session control protocol
- session protocol
- signaling protocol
- SNA protocol
- split-transaction protocol
- stream protocol
- thinking-out loud protocol
- timed-token protocol
- token-access protocol - transport protocol
- virtual-circuit protocol
- virtual protocolEnglish-Russian dictionary of computer science and programming > protocol
-
7 relay
1) реле5) ретрансляция; переприём || ретранслировать•relay with latching — реле с механической самоблокировкой, реле с механической фиксацией воздействия
- ac relay- acoustic relay
- active-power relay
- add-and-subtract relay
- alarm relay
- Allström relay
- all-to-all relay
- annunciation relay
- antenna relay
- antiplugging relay
- armature relay
- auxiliary relay
- balanced relay
- baseband relay
- biased relay
- bistable relay
- blocking relay
- break-in relay
- calling relay
- capacitance relay
- center-stable polar relay
- clapper relay
- clearing relay
- close-differential relay
- closing relay
- coaxial relay
- code relay
- command relay
- compelled relay
- conductance relay
- connector relay
- contact relay
- contactless relay
- continuous duty relay
- control relay
- correed relay
- current relay
- dc relay
- definite-purpose relay
- delay relay
- diaphragm relay
- differential relay
- digital radio relay
- direct-action relay
- directional relay
- directional-current relay
- directional-overcurrent relay
- directional-polarity relay
- directional-power relay
- directional-resistance relay
- directional-voltage relay
- directivity relay
- distance relay
- dry-reed relay
- earth-fault relay
- electrical relay
- electrical-mechanical relay
- electromagnetic relay
- electromechanical relay
- electronic relay
- electronic-tube relay
- electrostatic relay
- electrostrictive relay
- enclosed relay
- extraterrestrial relay
- fast-operate relay
- fast-packet frame-relay
- fast-release relay
- fault selective relay
- ferrodynamicrelay
- field application relay
- field loss relay
- flat-type relay
- flow relay
- frequency relay
- frequency-selective relay
- frequency-sensitive relay
- gas-filled relay
- gas-filled reed relay
- general-purpose relay
- ground relay
- ground protective relay
- group-selector relay
- guard relay
- heavy-duty relay
- hermetically sealed relay
- high G-relay
- high-speed relay
- homing relay
- hot-wire relay
- impedance relay
- indicating relay
- indirect-action relay
- inertia relay
- initiating relay
- instantaneous overcurrent relay
- instrument-type relay
- integrating relay
- interlock relay
- intersatellite relay
- key relay
- Kipp relay
- lag relay
- latch-in relay
- latching relay
- LED-coupled solid-state relay
- light relay
- light-activated switching relay
- line relay
- line-break relay
- locking relay
- lockout relay
- lock-up relay
- logic relay
- magnetic reed relay
- magnetostrictive relay
- manual-automatic relay
- marginal relay
- mechanical locking relay
- memory relay
- mercury relay
- mercury-contact relay
- mercury-wetted reed relay
- metering relay
- meter-type relay
- mho relay
- microwave relay
- microwave-radio relay
- motor-field failure relay
- multiposition relay
- NC relay
- net-to-net relay
- network relay
- network master relay
- network phasing relay
- neutral relay
- NO relay
- nonpolarized relay
- normally-closed relay
- normally-open relay
- notching relay
- open relay
- open-phase relay
- oscillating relay
- overcurrent relay
- overfrequency relay
- overload relay
- overpower relay
- overvoltage relay
- percentage-differential relay
- phase-balance relay
- phase-reversal relay
- phase-rotation relay
- phase-sequence relay
- phase-shift relay
- photoelectric relay
- plunger relay
- polar relay
- polarized relay
- polyphase relay
- power relay
- pressure relay
- protective relay
- pulse reed relay
- radar relay
- radio relay
- ratchet relay
- rate-of-change relay
- rate-of-change temperature relay
- rate-of-rise relay
- ratio-balance relay
- ratio-differential relay
- reactance relay
- reactive-power relay
- reclosing relay
- reed relay
- register relay
- regulating relay
- remanent relay
- reset relay
- residual relay
- resistance relay
- resonant-reed relay
- reverse relay
- reverse-current relay
- ringing relay
- rotary stepping relay
- satellite relay
- selector relay
- self-latching relay
- semiconductor relay
- sensitive relay
- separating relay
- sequence relay
- sequential relay
- side-stable relay
- signal-actuated relay
- single-phase relay
- slave relay
- slow-acting relay
- slow-action relay
- slow-cutting relay
- slow-operate relay
- slow-release relay
- solenoid relay
- solid-state relay
- space relay
- speed-sensitive relay
- spring-actuated stepping relay
- SR relay
- stepping relay
- storage relay
- supersensitive relay
- surge relay
- synchronizing relay
- tape relay
- temperature relay
- test relay
- thermal relay
- thermostat relay
- three-position relay
- three-step relay
- time relay
- time-delay relay
- timing relay
- transformer-coupled solid-state relay
- transhorizon radio relay
- trip-free relay
- tripping relay
- trunk relay
- tuned relay
- two-position relay
- two-step relay
- undercurrent relay
- underfrequency relay
- underpower relay
- undervoltage relay
- vacuum reed relay
- valve relay
- vibrating relay
- voltage relay
- zero phase-sequence relay -
8 relay
1) реле5) ретрансляция; переприём || ретранслировать•relay with latching — реле с механической самоблокировкой, реле с механической фиксацией воздействия
- ac relay- acoustic relay
- active-power relay
- add-and-subtract relay
- alarm relay
- Allström relay
- all-to-all relay
- annunciation relay
- antenna relay
- antiplugging relay
- armature relay
- auxiliary relay
- balanced relay
- baseband relay
- biased relay
- bistable relay
- blocking relay
- break-in relay
- calling relay
- capacitance relay
- center-stable polar relay
- clapper relay
- clearing relay
- close-differential relay
- closing relay
- coaxial relay
- code relay
- command relay
- compelled relay
- conductance relay
- connector relay
- contact relay
- contactless relay
- continuous duty relay
- control relay
- correed relay
- current relay
- dc relay
- definite-purpose relay
- delay relay
- diaphragm relay
- differential relay
- digital radio relay
- direct-action relay
- directional relay
- directional-current relay
- directional-overcurrent relay
- directional-polarity relay
- directional-power relay
- directional-resistance relay
- directional-voltage relay
- directivity relay
- distance relay
- dry-reed relay
- earth-fault relay
- electrical relay
- electrical-mechanical relay
- electromagnetic relay
- electromechanical relay
- electronic relay
- electronic-tube relay
- electrostatic relay
- electrostrictive relay
- enclosed relay
- extraterrestrial relay
- fast-operate relay
- fast-packet frame-relay
- fast-release relay
- fault selective relay
- ferrodynamic relay
- field application relay
- field loss relay
- flat-type relay
- flow relay
- frequency relay
- frequency-selective relay
- frequency-sensitive relay
- gas-filled reed relay
- gas-filled relay
- general-purpose relay
- ground protective relay
- ground relay
- group-selector relay
- guard relay
- heavy-duty relay
- hermetically sealed relay
- high G relay
- high-speed relay
- homing relay
- hot-wire relay
- impedance relay
- indicating relay
- indirect-action relay
- inertia relay
- initiating relay
- instantaneous overcurrent relay
- instrument-type relay
- integrating relay
- interlock relay
- intersatellite relay
- key relay
- Kipp relay
- lag relay
- latch-in relay
- latching relay
- LED-coupled solid-state relay
- light relay
- light-activated switching relay
- line relay
- line-break relay
- locking relay
- lockout relay
- lock-up relay
- logic relay
- magnetic reed relay
- magnetostrictive relay
- manual-automatic relay
- marginal relay
- mechanical locking relay
- memory relay
- mercury relay
- mercury-contact relay
- mercury-wetted reed relay
- metering relay
- meter-type relay
- mho relay
- microwave relay
- microwave-radio relay
- motor-field failure relay
- multiposition relay
- NC relay
- net-to-net relay
- network master relay
- network phasing relay
- network relay
- neutral relay
- NO relay
- nonpolarized relay
- normally-closed relay
- normally-open relay
- notching relay
- open relay
- open-phase relay
- oscillating relay
- overcurrent relay
- overfrequency relay
- overload relay
- overpower relay
- overvoltage relay
- percentage-differential relay
- phase-balance relay
- phase-reversal relay
- phase-rotation relay
- phase-sequence relay
- phase-shift relay
- photoelectric relay
- plunger relay
- polar relay
- polarized relay
- polyphase relay
- power relay
- pressure relay
- protective relay
- pulse reed relay
- radar relay
- radio relay
- ratchet relay
- rate-of-change relay
- rate-of-change temperature relay
- rate-of-rise relay
- ratio-balance relay
- ratio-differential relay
- reactance relay
- reactive-power relay
- reclosing relay
- reed relay
- register relay
- regulating relay
- remanent relay
- reset relay
- residual relay
- resistance relay
- resonant-reed relay
- reverse relay
- reverse-current relay
- ringing relay
- rotary stepping relay
- satellite relay
- selector relay
- self-latching relay
- semiconductor relay
- sensitive relay
- separating relay
- sequence relay
- sequential relay
- side-stable relay
- signal-actuated relay
- single-phase relay
- slave relay
- slow-acting relay
- slow-action relay
- slow-cutting relay
- slow-operate relay
- slow-release relay
- solenoid relay
- solid-state relay
- space relay
- speed-sensitive relay
- spring-actuated stepping relay
- SR relay
- stepping relay
- storage relay
- supersensitive relay
- surge relay
- synchronizing relay
- tape relay
- temperature relay
- test relay
- thermal relay
- thermostat relay
- three-position relay
- three-step relay
- time relay
- time-delay relay
- timing relay
- transformer-coupled solid-state relay
- transhorizon radio relay
- trip-free relay
- tripping relay
- trunk relay
- tuned relay
- two-position relay
- two-step relay
- undercurrent relay
- underfrequency relay
- underpower relay
- undervoltage relay
- vacuum reed relay
- valve relay
- vibrating relay
- voltage relay
- zero phase-sequence relayThe New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > relay
-
9 ion
-
acceptor ion
-
acid ion
-
active ion
-
aggressive ions
-
ampholytic ion
-
amphoteric ion
-
aqua ion
-
aromatic ion
-
basic ion
-
biatomic ion
-
capillary-active ion
-
carrier ion
-
channelled ion
-
colloidal ions
-
colloidal ion
-
compensating ion
-
competing ion
-
complex ion
-
diatomic ion
-
divalent ion
-
donor ion
-
double-charged ion
-
electrolyte ion
-
eluting ion
-
exchangeable ion
-
extraneous ion
-
fast ion
-
fixed ion
-
following ions
-
free ion
-
glass-forming ion
-
heavy ion
-
hybrid ion
-
hydrogen ion
-
hydronium ion
-
hydroxyl ion
-
implanted ion
-
impure ion
-
indicator ion
-
interstitial ion
-
light ion
-
likely charged ions
-
like ions
-
mobile ion
-
molecular ion
-
monoatomic ion
-
monovalent ion
-
multicharged ion
-
negative ion
-
network-forming ion
-
network-modifying ion
-
one-atomic ion
-
pit-blocking ions
-
platable ions
-
polyatomic ion
-
polybasic ion
-
polyvalent ion
-
positive ion
-
predissociated ion
-
primary ion
-
reactive ion
-
same ion
-
secondary ion
- structure breaking ions -
structure forming ions
-
tracer ion
-
trapped ion
-
vagabonding ion -
10 relay
1) реле || ставить реле2) снабжать релейной защитой; ставить релейную защиту4) трансляция; передача ( сигнала) || транслировать; передавать ( сигнал)5) ретрансляция; переприём || ретранслировать•-
ac relay
-
ac system relays
-
accelerating relay
-
acoustic relay
-
actuating relay
-
alarm relay
-
allotter relay
-
all-to-all relay
-
amplitude comparison relay
-
angle armature relay
-
annunciation relay
-
antifailure automatics relay
-
armature relay
-
automatic reclosing relay
-
back-current relay
-
backup relay
-
balance beam relay
-
balanced relay
-
banked relay
-
biased relay
-
bimetallic-strip relay
-
bistable relay
-
blocking relay
-
block relay
-
brake application relay
-
brake release relay
-
braking relay
-
Buchholz relay
-
calling relay
-
call relay
-
capacitance relay
-
carrier-actuated relay
-
center-stable polarized relay
-
center-stable polar relay
-
central disconnection relay
-
change-of-current relay
-
charging rate relay
-
circuit-control relay
-
clappers-type relay
-
clappers relay
-
clearing relay
-
clock relay
-
closing relay
-
code relay
-
compelling relay
-
conductance relay
-
contact relay
-
contactless relay
-
continuous-duty relay
-
control relay
-
crossing relay
-
current relay
-
current-balance relay
-
current-overload relay
-
cut-in relay
-
cut-off relay
-
dc relay
-
definite minimum time-limit relay
-
definite-time-lag relay
-
delay relay
-
dependent-time measuring relay
-
dependent-time-lag relay
-
differential relay
-
digital radio relay
-
digital relay
-
direct-action relay
-
directional impedance relay
-
directional power relay
-
directional relay
-
directional-overcurrent relay
-
discriminating relay
-
distance relay
-
double-acting relay
-
draw-out relay
-
dry-feed relay
-
earth-fault relay
-
earthing relay
-
electrical relay
-
electrodynamic relay
-
electromagnetic relay
-
electromechanical relay
-
electronic relay
-
electron relay
-
electrostatic relay
-
element relay
-
enclosed relay
-
entrance relay
-
erase relay
-
excitation-loss relay
-
fast-operating relay
-
fast-release relay
-
ferrodynamic relay
-
ferromagnetic relay
-
field relay
-
field-application relay
-
field-failure relay
-
field-removal relay
-
frequency relay
-
frequency-selective relay
-
gas-actuated relay
-
gas relay
-
gas-filled relay
-
graded time-lag relay
-
grounding relay
-
ground relay
-
guard relay
-
hermetically sealed relay
-
high-speed relay
-
hinged-armature relay
-
holding relay
-
horn relay
-
hot-wire relay
-
impedance relay
-
independent time-lag relay
-
indicating relay
-
indirect-action relay
-
individual point relay
-
induction relay
-
inertia relay
-
initiating relay
-
instantaneous overcurrent relay
-
instantaneous relay
-
interlock relay
-
intermediate switching-off relay
-
interposing relay
-
inverse-time relay
-
keying relay
-
key relay
-
lagged relay
-
lag relay
-
latched relay
-
latch-in relay
-
latching relay
-
leakage relay
-
leak relay
-
LED-coupled solid-state relay
-
light relay
-
light-out relay
-
line relay
-
line-break relay
-
load relay
-
local-remote relay
-
locking relay
-
lock-up relay
-
low-voltage relay
-
low-voltage release relay
-
magnetic relay
-
magnetoelectric relay
-
main locomotive relay
-
main starting relay
-
maximum power relay
-
maximum-voltage relay
-
measuring relay
-
memory relay
-
mercury relay
-
mercury-contact relay
-
mercury-wetted-contact relay
-
metering relay
-
mho relay
-
microprocessor controlled relay for overcurrent protection
-
microwave radio relay
-
microwave relay
-
monostable relay
-
moving-iron relay
-
multiposition relay
-
negative phase-sequence relay
-
net-to-net relay
-
network master relay
-
network-phasing relay
-
neutral relay
-
no-load relay
-
nondirectional relay
-
nonpolarized relay
-
nonspecified-time relay
-
normally closed relay
-
normally open relay
-
notching relay
-
no-voltage relay
-
ohm relay
-
open-frame relay
-
open relay
-
open-phase relay
-
open-track-circuit relay
-
out-of-step relay
-
overcurrent relay
-
overload relay
-
overpower relay
-
overtemperature relay
-
overvoltage relay
-
percentage-differential relay
-
phase relay
-
phase-balance relay
-
phase-comparison relay
-
phase-failure relay
-
phase-reversal relay
-
phase-rotation relay
-
photocell relay
-
photoemissive relay
-
phototube relay
-
plunger relay
-
pneumatic amplifier relay
-
pneumatic relay
-
pneumatic time-delay relay
-
point detection relay
-
point operating relay
-
polarity-directional relay
-
polarized relay
-
positive phase-sequence relay
-
potential relay
-
power direction relay
-
power relay
-
power-transfer relay
-
pressure relay
-
primary relay
-
product relay
-
protection relay
-
pulse relay
-
pulse track relay
-
quick-operating relay
-
quotient relay
-
radio relay
-
rate-of-change relay
-
ratio-balance relay
-
reactance relay
-
reactive power relay
-
reclosing relay
-
reed relay
-
register relay
-
regulating relay
-
reply and call relay
-
reset relay
-
residual relay
-
resistance relay
-
reverse-current relay
-
reverse-phase relay
-
rinding relay
-
route relay
-
route-release relay
-
satellite relay
-
secondary relay
-
sector-type relay
-
selector relay
-
self-resetting relay
-
semiconductor relay
-
service restoring relay
-
shaded-pole relay
-
short-circuit relay
-
shunt relay
-
side-stable relay
-
signal selector relay
-
signaling relay
-
slave relay
-
slew relay
-
slow-acting relay
-
slow-release relay
-
solenoid relay
-
solid-state relay
-
speed relay
-
starting relay
-
static relay with output contact
-
static relay without output contact
-
static relay
-
step-back relay
-
stepping-type relay
-
stepping relay
-
storage relay
-
supervisory relay
-
switch control relay
-
switch indication relay
-
switch lock relay
-
switch position relay
-
switching relay
-
synchronizing relay
-
temperature relay
-
three-position relay
-
time relay
-
time-delay relay
-
timing relay
-
track indicating relay
-
track relay
-
trailing relay
-
train control relay
-
train-stop relay
-
transfer relay
-
transistor relay
-
trip-free relay
-
tuned relay
-
two-element selector relay
-
two-position relay
-
undercurrent relay
-
undervoltage relay
-
unenclosed relay
-
voltage-response relay
-
warning signal relay
-
wet-reed relay
-
wire-break relay
-
zero phase-sequence relay -
11 circuit
1) схема; цепь; контур2) эл. сеть4) шлейф ( в телефонии)•to track circuits — сопрягать контуры-
in-line hydraulic circuit
-
tee-test hydraulic circuit
-
absorption circuit
-
ac circuit
-
active circuit
-
adapter circuit
-
adder circuit
-
addressing circuit
-
aerial circuit
-
aerodrome circuit
-
aerodrome taxi circuit
-
aerodrome traffic circuit
-
aeromagnetic circuit
-
alarm circuit
-
alive circuit
-
amplifying circuit
-
analogous circuit
-
analog circuit
-
ancillary circuit
-
AND circuit
-
AND-to-OR circuit
-
AND-OR circuit
-
anticoincidence circuit
-
antihunt circuit
-
antireciprocal circuit
-
antiresonance circuit
-
antiresonant circuit
-
aperiodic circuit
-
approach circuit
-
astable circuit
-
autodyne circuit
-
automatic frequency control circuit
-
automatic reciprocation pneumatic circuit
-
auxiliary circuit
-
auxiliary coolant circuit
-
averaging circuit
-
back-to-back circuit
-
balanced circuit
-
balancing circuit
-
bias and erase circuit
-
bias circuit
-
bidirectional hydraulic motor circuit
-
bipolar circuit
-
bistable circuit
-
black-level restoring circuit
-
blanking circuit
-
blasting circuit
-
blocking circuit
-
booster hydraulic circuit
-
bound circuit
-
boxcar circuit
-
brake retraction circuit
-
branched circuit
-
branch circuit
-
breadboard circuit
-
break circuit
-
bridge circuit
-
bridged circuit
-
broken circuit
-
bubble circuit
-
bucket-brigade circuit
-
buffer circuit
-
burst-gating circuit
-
calibrating circuit
-
call circuit
-
carrier recovery circuit
-
cascode circuit
-
cavity circuit
-
charge circuit
-
charge-coupied device circuit
-
charging circuit
-
checkout circuit
-
cholesteric circuit
-
chopping circuit
-
chromatic circuit
-
circulating lubrication circuit
-
clamp circuit
-
cleaning circuit
-
clearing circuit
-
clipping circuit
-
clocked circuit
-
closed circuit
-
close circuit
-
closed loop circuit
-
closed loop hydraulic motor circuit
-
coaxial circuit
-
code track circuit
-
coincidence circuit
-
color-killer circuit
-
color-processing circuit
-
combination air-oil circuit
-
combinational circuit
-
common-base circuit
-
common-collector circuit
-
common-drain circuit
-
common-emitter circuit
-
common-gate circuit
-
common-source circuit
-
communication circuit
-
comparator circuit
-
compensating circuit
-
complementary circuit
-
completed circuit
-
composite circuit
-
condensate circuit
-
control circuit
-
convergence circuit
-
coolant circuit
-
cooling short circuit
-
cord circuit
-
correcting circuit
-
counter circuit
-
coupled circuits
-
cross rectifier circuit
-
crushing circuit
-
current circuit
-
current-feedback circuit
-
current-limiting circuit
-
current-limit circuit
-
damping circuit
-
Danington circuit
-
dc circuit
-
dead circuit
-
decision making circuit
-
decision circuit
-
decoding circuit
-
decoupling circuit
-
dedicated circuit
-
de-emphasis circuit
-
degaussing circuit
-
degenerative circuit
-
delay circuit
-
delta circuit
-
derived circuit
-
detecting circuit
-
detuned circuit
-
dial toll circuit
-
dial-up circuit
-
differentiating circuit
-
digital circuit
-
diplex circuit
-
direct circuit
-
direct speech circuit
-
discharge circuit
-
distributed-element circuit
-
dividing circuit
-
double-rail track circuit
-
drive circuit
-
driver circuit
-
dual circuit
-
dual-relief braking hydraulic motor circuit
-
duplex circuit
-
dynamic braking circuit
-
earthed circuit
-
earth circuit
-
edge-activated circuit
-
electric circuit
-
electrical safety circuit
-
electrolysis circuit
-
electronic circuit
-
emphasis circuit
-
enabling circuit
-
energized circuit
-
engineering circuit
-
enhancement circuit
-
equilization circuit
-
equivalent circuit
-
error correcting circuit
-
evaporating circuit
-
exciting circuit
-
exclusive OR circuit
-
exposure control circuit
-
exposure measuring circuit
-
external circuit
-
external load circuit
-
fallback circuit
-
feed circuit
-
feed motor circuit
-
feedback circuit
-
feedrate override circuit
-
filament circuit
-
filter hydraulic circuit
-
firing circuit
-
flip-flop circuit
-
flotation circuit
-
flow circuit
-
fluid circuit
-
forked circuit
-
four-terminal circuit
-
four-wire circuit
-
frame-scanning circuit
-
free-running circuit
-
frequency determining circuit
-
frequency-changing circuit
-
full-wave circuit
-
gain circuit
-
gas circuit
-
gate circuit
-
grinding circuit
-
ground short circuit
-
grounded circuit
-
ground circuit
-
half-duplex circuit
-
half-phantom circuit
-
half-wave circuit
-
half-wave track circuit
-
heat transport main circuit
-
heater circuit
-
holding circuit
-
horizontal scanning circuit
-
hotline circuit
-
hybrid-type circuit
-
hybrid circuit
-
hydraulic circuit
-
hydraulic servo circuit
-
identification circuit
-
idler circuit
-
ignition circuit
-
ignition primary circuit
-
ignition secondary circuit
-
impulse circuit
-
impulsing circuit
-
incoming track circuit
-
inductive circuit
-
inhibit circuit
-
input circuit
-
insulated circuit
-
integrated circuit
-
integrating circuit
-
intentional short circuit
-
interface circuit
-
interlocking circuit
-
interlock circuit
-
international television circuit
-
inverter circuit
-
invert circuit
-
iron circuit
-
jointless pulse track circuit
-
junction circuit
-
keep-alive circuit
-
ladder circuit
-
lagging circuit
-
latching circuit
-
LC circuit
-
leakage circuit
-
leak circuit
-
leased circuit
-
level circuit
-
linear circuit
-
linearizing circuit
-
line-scanning circuit
-
line-to-ground short circuit
-
live circuit
-
load circuit
-
locking circuit
-
locking hydraulic circuit
-
locking track circuit
-
logic circuit
-
long-distance transmission circuit
-
loop circuit
-
low-loss circuit
-
lumped-element lumped-parameter circuit
-
lumped lumped-parameter circuit
-
lumped-element circuit
-
lumped circuit
-
magnetic circuit
-
magnetic-core circuit
-
main circuit
-
majority circuit
-
make circuit
-
matching circuit
-
match circuit
-
matrix circuit
-
maximum power control circuit
-
measuring circuit
-
memory circuit
-
mesh circuit
-
metallic circuit
-
meter-current circuit
-
metering circuit
-
meter-voltage circuit
-
microelectronic circuit
-
microwave circuit
-
molecular circuit
-
monitoring circuit
-
monostable circuit
-
motor control circuit
-
multidrop circuit
-
multiplication circuit
-
multipoint circuit
-
multistable circuit
-
multistage circuit
-
muting circuit
-
NAND circuit
-
narrowband circuit
-
network circuit
-
neutral track circuit
-
neutralizing circuit
-
noise-balancing circuit
-
noninductive circuit
-
NOR circuit
-
NOT circuit
-
NOT-AND circuit
-
NOT-OR circuit
-
offset compensating circuit
-
one-pole circuit
-
one-rail track circuit
-
one-wire circuit
-
open circuit
-
open loop circuit
-
open-wire circuit
-
OR circuit
-
order wire circuit
-
OR-ELSE circuit
-
oscillating circuit
-
oscillation circuit
-
oscillatory circuit
-
output circuit
-
overflux circuit
-
overhead circuit
-
packaged circuit
-
paging circuit
-
parallel circuit
-
parallel-resonant circuit
-
parallel-series circuit
-
passive circuit
-
peak white-limiting circuit
-
peaking circuit
-
phantom circuit
-
phase switching circuit
-
phase-comparison circuit
-
phase-compensating circuit
-
phase-equalizing circuit
-
phase-inverting circuit
-
phase-sensitive track circuit
-
phase-shifting circuit
-
phase-shift circuit
-
pilot circuit
-
pneumatic circuit
-
points control circuit
-
points track circuit
-
point-to-point circuit
-
polarity circuit
-
polarized track circuit
-
polling circuit
-
polyphase circuit
-
potential circuit
-
power circuit
-
precharge circuit
-
precision timing circuit
-
pressure control hydraulic circuit
-
primary circuit
-
primary coolant circuit
-
printed circuit
-
protection circuit
-
pulse circuit
-
pulse-shaping circuit
-
pump unloading hydraulic circuit
-
pumping circuit
-
pump circuit
-
push-pull circuit
-
push-to-type circuit
-
quadruplex circuit
-
radiation-hardened circuit
-
radio communication circuit
-
radio circuit
-
RC circuit
-
reaction circuit
-
reaction track circuit
-
reactive circuit
-
reclosing circuit
-
rectification circuit
-
reference circuit
-
reflex circuit
-
regenerative circuit
-
register mark recognition circuit
-
regrinding circuit
-
regulating circuit
-
rejector circuit
-
relay circuit
-
relay contact switching circuit
-
relay contact circuit
-
remote-ring circuit
-
replenishing hydraulic motor circuit
-
reset circuit
-
resonance circuit
-
retaining circuit
-
return circuit
-
ring circuit
-
ringing circuit
-
route locking circuit
-
sample circuit
-
sample-and-hold circuit
-
sampler circuit
-
scaling circuit
-
scanning circuit
-
schematic circuit
-
screening circuit
-
secondary circuit
-
secondary coolant circuit
-
selecting circuit
-
selection circuit
-
self-bias circuit
-
self-checking circuit
-
self-holding circuit
-
self-test circuit
-
semiconductor circuit
-
separation circuit
-
sequencing circuit
-
series circuit
-
series-resonant circuit
-
series-tuned circuit
-
service circuit
-
shell circuit
-
shifting circuit
-
short circuit
-
shunt circuit
-
shutoff circuit
-
signal circuit
-
signaling circuit
-
simplex circuit
-
single-phase circuit
-
single-rail track circuit
-
single-wire circuit
-
slow-wave circuit
-
smoothing circuit
-
sneak circuit
-
solid-state circuit
-
solid circuit
-
spare circuit
-
speaker circuit
-
speed regulating circuit
-
squelch circuit
-
standby circuit
-
star-connected circuit
-
starting circuit
-
station conventional track circuit
-
steady energy track circuit
-
stripline circuit
-
strip circuit
-
subcarrier recovery circuit
-
subtransmission circuit
-
superconducting circuit
-
supply circuit
-
suppression circuit
-
sustained short circuit
-
sweep circuit
-
switched circuit
-
switching circuit
-
symbolic circuit
-
symmetrical circuit
-
symmetric circuit
-
synchronization circuit
-
synchronizing hydraulic circuit
-
synchronous circuit
-
table circuit
-
tank circuit
-
tap circuit
-
tapped circuit
-
T-circuit
-
telegraph circuit
-
telephone circuit
-
temperature stabilized circuit
-
tension sensing circuit
-
terminal circuit
-
test circuit
-
thickening circuit
-
three-phase circuit
-
threshold circuit
-
throttled circuit
-
through circuit
-
tilt kickout hydraulic circuit
-
time-base circuit
-
time-delay circuit
-
timer circuit
-
time-slot assigner circuit
-
timing circuit
-
toll circuit
-
tool selector circuit
-
toroidal magnetic circuit
-
touch sensing circuit
-
track circuit
-
train dispatching circuit
-
transient short circuit
-
transmission hydraulic circuit
-
trap circuit
-
tree circuit
-
triggering circuit
-
trigger circuit
-
trouble-detecting circuit
-
trunk circuit
-
tube circuit
-
tuned circuit
-
two-port circuit
-
two-state circuit
-
two-terminal circuit
-
two-wire circuit
-
unbalanced circuit
-
unidirectional hydraulic motor circuit
-
unipolar circuit
-
vertical-scanning circuit
-
virtual circuit
-
voltage-feedback circuit
-
warning circuit
-
white clip circuit
-
wideband circuit
-
wire circuit
-
wired AND circuit
-
wired circuit
-
wired OR circuit
-
wye-connected circuit
-
wye circuit
-
zero-lose circuit -
12 junction
1) соединение2) сочленение3) стык; спай4) пересечение, скрещение, скрещивание (напр. дорог, путей)5) хим. перенос7) точка разветвления; узел (напр. электрической цепи)8) разветвление ( волноводов)9) p-n-переход•-
abrupt junction
-
active junction
-
alloyed junction
-
alloy junction
-
asymmetric junction
-
attractive junction
-
avalanching junction
-
backward-biased junction
-
back-biased junction
-
barrier junction
-
base-emitter junction
-
biaxial hybrid junction
-
blocking junction
-
bolt-on junction
-
boundary Josephson junction
-
cable junction
-
canal junction
-
cold junction
-
collector-to-base junction
-
collector junction
-
conecylindrical shell junction
-
conversion junction
-
degenerate junction
-
diffused junction
-
doped junction
-
double-beveled junction
-
double-doped junction
-
drain junction
-
electrochemical junction
-
electron-beam addressed junction
-
electron-hole junction
-
emitter-to-base junction
-
emitter junction
-
emitting p-n junction
-
epitaxial junction
-
Esaki junction
-
face junction
-
flat junction
-
floating junction
-
flying junction
-
fly-over junction
-
forward-biased junction
-
fused junction
-
gate junction
-
gate-to-channel junction
-
gate-channel junction
-
gate-to-drain junction
-
gate-drain junction
-
gate-to-source junction
-
gate-source junction
-
graded junction
-
graph junction
-
grown junction
-
grown-diffused junction
-
heterogeneous junction
-
high-low junction
-
homogeneous junction
-
hot junction
-
H-plane tee junction
-
hybrid junction
-
injector junction
-
inspection junction
-
ion-bombardment junction
-
isolation junction
-
isotype junction
-
Josephson junction
-
junction of channels
-
laser junction
-
laser processed junction
-
lateral junction
-
liquid junction
-
low-high junction
-
measuring junction
-
mesa junction
-
metallurgical junction
-
metal-semiconductor junction
-
multiple junction
-
network junction
-
n-n junction
-
nonrectifying junction
-
n-p junction
-
ohmic junction
-
oxide charge induced junction
-
photoresponsive junction
-
photovoltaic junction
-
p-i-n junction
-
pipe junction
-
planar junction
-
plug junction
-
p-n junction
-
radial-to-coaxial line junction
-
rail junction
-
rate-grown junction
-
recrystallized junction
-
rectifier junction
-
reference junction
-
remelt junction
-
reverse-biased junction
-
road junction
-
Schottky barrier junction
-
Schottky junction
-
sealed junction
-
semiconductor junction
-
semiconductor-electrolyte junction
-
shallow junction
-
source junction
-
step junction
-
surface junction
-
T junction
-
thermal junction
-
through-diffused junction
-
transversal junction
-
tunneling junction
-
tunnel junction
-
unbiased junction
-
waveguide junction
-
wavy junction
-
weak-link junctions -
13 layer
2) горн. пласт7) вчт. уровень ( иерархической структуры)•layer free from base — кфт. бесподложечный слой-
ablation layer
-
absorbed layer
-
acceptor layer
-
accumulation layer
-
adsorbed layer
-
alignment layer
-
amorphous layer
-
anode layer
-
antihalation layer
-
antireflection layer
-
antireflective layer
-
antistatic layer
-
Appleton layer
-
application layer
-
as-grown layer
-
atmospheric boundary layer
-
back layer
-
backing layer
-
back-up layer
-
ballast layer
-
barrier layer
-
base layer
-
batch layer
-
blending layer
-
blocking layer
-
bottom layer
-
boundary layer
-
buffer layer
-
buried layer
-
cable layer
-
cap layer
-
cathode interface layer
-
cathode layer
-
chalcogenide layer
-
Chapman layer
-
chemisorption layer
-
chilling layer
-
chill layer
-
cladding layer
-
clad layer
-
cloud layer
-
cloud-topped boundary layer
-
coal layer
-
coil layers
-
collector layer
-
composite layer
-
compression layer
-
concentric layers
-
conducting layer
-
confining layer
-
contact layer
-
continuous layer
-
convective unstable layer
-
covering layer
-
cushion layer
-
D layer
-
dan layer
-
dead layer
-
depletion layer
-
deposited layer
-
diamond-bearing layer
-
dielectric layer
-
diffused layer
-
diffusion-source layer
-
dipole layer
-
dislocation layer
-
doped layer
-
drain layer
-
driving layer
-
dueling layer
-
dummy layer
-
dust layer
-
E layer
-
effective layer
-
elastomer layer
-
elevated layer
-
embedded metal layer
-
emitter layer
-
emitting layer
-
emulsion layer
-
enriched layer
-
epitaxial layer
-
epoxy layer
-
evaporated layer
-
extension layer
-
F layer
-
fettled layer
-
field oxide layer
-
filter layer
-
fog layer
-
gate insulation layer
-
ground layer
-
gunned layer
-
hanging layer
-
heat-insulating layer
-
Heaviside layer
-
heavy layer
-
high-concentration layer
-
high-mobility layer
-
hydraulic fill layer
-
image receiving layer
-
impurity layer
-
insulating layer
-
interface layer
-
intermediate layer
-
intrinsic layer
-
inversion layer
-
ion-implanted layer
-
ionized layer
-
ionospheric layer
-
Kennelly-Heaviside layer
-
light-sensitive layer
-
link layer
-
low-emission layer
-
low-mobility layer
-
masking layer
-
metallic layer
-
metallization layer
-
moderating layer
-
monoatomic layer
-
monocrystalline layer
-
monomolecular layer
-
multiple layer
-
n layer
-
native layer
-
negative layer
-
network layer
-
neutral layer
-
nonconducting layer
-
nonducting layer
-
nucleating layer
-
oceanic mixed layer
-
ohmic layer
-
oil layer
-
ozone layer
-
p layer
-
paper layer
-
passivation layer
-
photoconductive layer
-
photographic layer
-
photosensitive layer
-
physical layer
-
physisorption layer
-
planarization layer
-
planetary boundary layer
-
plank layer
-
polycrystalline silicon layer
-
poly silicon layer
-
presentation layer
-
protective layer
-
receiving layer
-
restraining layer
-
sandwiched layer
-
scattering layer
-
scuff resisting layer
-
sealing layer
-
seal layer
-
semiconducting layer
-
separation layer
-
session layer
-
shallow diffused layer
-
shallow layer
-
sintered layer
-
slag-impregnated surface layer
-
solvent layer
-
sporadic-E layer
-
sputtered layer
-
sputter layer
-
stratified layers
-
strip layers
-
subbing layer
-
subcloud layer
-
substrate layer
-
subsurface layer
-
superconducting layer
-
supernatant layer
-
surface layer
-
thermal boundary layer
-
transition layer
-
transmission control layer
-
transparent layer
-
transport layer
-
trapping layer
-
tropospheric layer
-
turbulent boundary layer
-
underglaze layer
-
undoped layer
-
unsteady boundary layer
-
velocity boundary layer
-
velocity layer
-
wall boundary layer
-
wearing layer
-
web cross layers
-
wind-mixed layer
-
wire reinforcement layer
-
wiring layer -
14 circuit
1) сеть
2) кругооборот
3) циркуляционный
4) циркуляционный контур
5) <tech.> цепь
6) схема
7) поток
8) неупорядоченный цикл
9) оборудование
10) обход
11) схемный
12) выключатель
– absorption circuit
– alarm circuit
– alternating-current circuit
– analog circuit
– analogous circuit
– AND-to OR circuit
– AND-to-AND circuit
– antenna circuit
– anti-coincidence circuit
– anticoincidence circuit
– antihunt circuit
– arm circuit
– arm of circuit
– astable circuit
– balanced circuit
– balancing of a circuit
– band-elimination circuit
– be in traffic circuit
– bias circuit
– bipartite circuit
– blanking circuit
– blocking circuit
– boosted circuit
– bootstrap circuit
– braking circuit
– breadboard circuit
– break in circuit
– bridge circuit
– built-up circuit
– carry circuit
– cascode circuit
– cathode-coupled circuit
– checking circuit
– circuit algebra
– circuit analysis
– circuit breaker
– circuit capacitance
– circuit card
– circuit closer
– circuit closure
– circuit continuity
– circuit design
– circuit diagram
– circuit element
– circuit grade
– circuit matrix
– circuit noise
– circuit order
– circuit switching
– circuit technology
– circuit tester
– circuit theory
– circuit time
– circuit wiring
– clipper-limiter circuit
– closed circuit
– coding circuit
– coincidence circuit
– communication circuit
– comparison circuit
– compensating circuit
– complete circuit
– composite circuit
– control circuit
– conveyer circuit
– cord circuit
– corrector circuit
– counting circuit
– coupled circuit
– cryotron circuit
– current circuit
– cut in circuit
– de-emphasis circuit
– de-energize circuit
– dead circuit
– decoding circuit
– deemphasis circuit
– deenergizing circuit
– delay circuit
– derivation circuit
– derived circuit
– differentiating circuit
– digital circuit
– direct-current circuit
– disabling circuit
– discharge circuit
– distributed-parameter circuit
– divide-by-two circuit
– dividing circuit
– doubling circuit
– draw up circuit
– drive circuit
– dual circuit
– earth-return circuit
– electronic circuit
– enabling circuit
– energizing circuit
– engineer's circuit
– equalize circuit
– equivalent circuit
– excitation circuit
– exciting circuit
– exclusive OR circuit
– extend circuit
– feedback circuit
– ferroresonance circuit
– filament circuit
– finite circuit
– forward circuit
– gang circuit
– gate circuit
– ground circuit
– grounded-cathode circuit
– grounded-emitter circuit
– grounded-grid circuit
– guard circuit
– halving circuit
– high-frequency circuit
– high-speed circuit
– high-tension circuit
– hold a circuit
– hold circuit
– hybrid circuit
– idler circuit
– ignition circuit
– impulse circuit
– inclusive OR circuit
– incomplete circuit
– information circuit
– inhibit circuit
– injection circuit
– inland circuit
– inoperative circuit
– input circuit
– insulate circuit
– integrated circuit
– integrating circuit
– interruption of circuit
– interstage circuit
– inverter circuit
– isolating circuit
– isolation circuit
– keying circuit
– ladder circuit
– level circuit
– line circuit
– linear circuit
– linearity circuit
– load circuit
– local circuit
– logic circuit
– made circuit
– magnetic circuit
– main circuit
– marking circuit
– matrix circuit
– measuring circuit
– memory circuit
– metering circuit
– micrologic circuit
– microminiature circuit
– microprinted circuit
– microvave circuit
– mixing circuit
– mnemonic circuit
– modular circuit
– modulator circuit
– monitoring circuit
– monolithic circuit
– multichip circuit
– multifunction circuit
– multiple circuit
– multiplex circuit
– multiply-by-two circuit
– multiplying circuit
– multistable circuit
– narrow-gate circuit
– network circuit
– non-coincidence circuit
– nonlinear circuit
– NOR logic circuit
– NOT AND circuit
– not circuit
– NOT OR circuit
– NOT-AND circuit
– obtain circuit
– off-centering circuit
– open circuit
– open-wire circuit
– opposition circuit
– OR circuit
– OR-to-AND circuit
– OR-to-OR circuit
– oscillatory circuit
– output circuit
– parallel circuit
– parasitic circuit
– passive circuit
– period-computing circuit
– phantom circuit
– physical circuit
– planar circuit
– plank-magnetic circuit
– plated circuit
– polyphase circuit
– potted circuit
– power circuit
– primary circuit
– principle circuit
– printed circuit
– protect circuit
– protection circuit
– pulmonary circuit
– pulse-actuated circuit
– pulse-generating circuit
– pump circuit
– push-pull circuit
– radiotelephone circuit
– read circuit
– reciprocal circuit
– regenerative circuit
– reheat circuit
– rejecter circuit
– relaxation circuit
– reset circuit
– resistive circuit
– resonance circuit
– resonant circuit
– response of circuit
– return circuit
– ring-bus circuit
– ring-down circuit
– ringdown circuit
– safety circuit
– scale-of-five circuit
– scale-of-ten circuit
– scale-of-two circuit
– scaling circuit
– schematic circuit
– secondary circuit
– see-saw circuit
– seize a circuit
– self-exciting circuit
– semibutterfly circuit
– separation circuit
– sequence circuit
– sequential circuit
– series circuit
– shift circuit
– short circuit
– side circuit
– simplexed circuit
– single-channel circuit
– single-core circuit
– single-ended circuit
– single-wire circuit
– sling circuit
– software circuit
– solid-state circuit
– squaring circuit
– squelch circuit
– stabilizing circuit
– staggered circuit
– starting circuit
– steam-generating circuit
– stick circuit
– storage circuit
– subtraction circuit
– sweep circuit
– switch circuit
– switching circuit
– symmetrical circuit
– sync circuit
– synchronizing circuit
– systemic circuit
– talking circuit
– tank circuit
– tapped circuit
– telephone circuit
– testing circuit
– thick-film circuit
– thin-film circuit
– three-phase circuit
– through circuit
– timer circuit
– totem-pole-type circuit
– track circuit
– transfer circuit
– transistor circuit
– trap circuit
– voltage-doubling circuit
– water-slurry circuit
– water-steam circuit
– welding circuit
– write circuit
alignment of tuned circuit — < radio> подстройка контура
analog integrated circuit — аналоговая микросхема, аналоговая интегральная микросхема
aperiodic oscillatory circuit — колебательный апериодический
automatic circuit breaker — автомат защиты сети, выключатель автоматический
bridge-type balancing circuit — <electr.> схема мостовая компенсационная
deposited integrated circuit — осажденная интегральная схема
digital integrated circuit — цифровая микросхема, цифровая ИМС
directly-coupled transistor circuit — схема с непосредственной связью на полупроводниковых триодах
double flip-flop circuit — <comput.> схема двухперекидная
double-rail track circuit — < railways> цепь рельсовая двухниточная
ferroresonant computing circuit — феррорезонансная вычислительная схема
film integrated circuit — пленочная микросхема, пленочная интегральная микросхема
gas-blast circuit breaker — выключатель с газовым дутьем, выключатель автокомпрессионный элегазовый
half-wave track circuit — импульсная рельсовая цепь < railways>
hybrid integrated circuit — гибридная микросхема, гибридная интегральная микросхема
integrated circuit amplifier — усилитель на интегральных схемах
large-scale integration circuit — большая интегральная микросхема
meter-reading access circuit — схема вывода показаний измерительного прибора
microprocessor integrated circuit — микропроцессорная интегральная микросхема
microwave integrated circuit — интегральная схема СВЧ диапазона, сверхвысокочастотная ИМС
monolithic integrated circuit — полупроводниковая микросхема
multitank oil circuit breaker — камерный масляный выключатель
semiconducnor integrated circuit — полупроводниковая интегральная микросхема
series track circuit — < railways> цепь рельсовая конденсаторная
short circuit current — <electr.> ток короткого замыкания
single-path magnetic circuit — неразветвленный магнитопровод
single-rail track circuit — однониточная рельсовая цепь, < railways> цепь рельсовая однониточная
single-tank oil circuit breaker — баковый масляный выключатель
turn-to-turn short circuit — междувитковое короткое замыкание
-
15 temperature
- aerial temperature
- alloy-diffusion temperature
- ambient temperature
- antenna noise temperature
- antiferromagnetic Néel temperature
- asymptotic Curie temperature
- background temperature
- blocking temperature
- brightness temperature
- carrier temperature
- case temperature
- cold-load temperature
- color temperature
- compensation temperature
- critical temperature
- cryogenic temperature
- Curie temperature
- decalescent temperature
- dew temperature
- distribution temperature
- effective input noise temperature
- electron temperature
- environment temperature
- equivalent noise temperature
- excess noise temperature
- flash temperature
- freezing temperature
- full-radiator temperature
- glass temperature
- growth temperature
- hole temperature
- hot-load temperature
- ice temperature
- ion temperature
- ionospheric temperature
- isotropic transition temperature
- junction temperature
- lattice temperature
- lower-air temperature
- lower-atmosphere temperature
- luminance temperature
- magnetic-ordering temperature
- magnetic-transition temperature
- meltback temperature
- melting freezing temperature
- Morin temperature
- Néel temperature
- network noise temperature
- noise temperature
- phase-transition temperature
- photometric standard color temperature
- radiance temperature
- relative noise temperature
- room temperature
- saturation temperature
- silver temperature
- sky temperature
- spin temperature of transition
- standard noise temperature
- steady-state temperature
- steam temperature
- storage temperature
- substrate temperature
- superconductor critical temperature
- thermodynamic temperature
- transformation temperature
- upper-air temperature
- upper-atmosphere temperature -
16 loop
1) циклв программировании - повторяющееся выполнение последовательности операторов (тела цикла), контролируемое с помощью специального счётчика (счётчика цикла, loop counter), а также по логическому условию его продолжения или завершения. В зависимости от того, когда проверяется это условие - в начале цикла или в конце - различают циклы с предпроверкой (pretested loop) и с постпроверкой (posttested loop). Циклы бывают одиночными и вложенными (nested loop)Ant:см. тж. conditional loop, counted loop, embedded loop, empty loop, endless loop, event loop, induction variable, infinite loop, inner loop, iteration, loop blocking, loop body, loop collapsing, loop distribution, loop exit, loop fission, loop fusion, loop header, loop interchange, loop invariant, loop inversion, loop optimization, loop parallelization, loop peeling, loop repeat, loop splitting, loop statement, loop termination, loop transformation, loop unrolling, loop unswitching, loop variable, loop vectorization, wait loop2) петляв теории графов - ребро, которое соединяет вершину саму с собойсм. тж. graph3) петля, кольцо, контур4) (см. тж. looping) - зацикливание [пакетов]в компьютерной сети - ситуация, когда пакеты передаваемых данных не попадают к адресату, а просто постоянно проходят по некоторой круговой последовательности сетевых узлов (network node)5) двигаться по кругу; проходить циклнапример, the inner loop counter loops five times - внутренний цикл прокрутится пять разАнгло-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. > loop
-
17 protocol
1) в общем случае - формализованный (документально зафиксированный, стандартизованный) набор правил, соглашений, сигналов, временных диаграмм, форматов, сообщений и процедур, регламентирующий взаимодействие между двумя устройствами (в частности, форматы и процедуры обмена данными между ними). Различают протоколы нижнего и верхнего уровней, а также стеки протоколов. Протоколы могут быть реализованы (поддержаны) аппаратно, программно или программно-аппаратносм. тж. authentication protocol, bit-oriented protocol, blocking protocol, byte-oriented protocol, communications protocol, connectionless protocol, connection-oriented protocol, cryptographic protocol, data-compression protocol, handshaking, in-band protocol, line protocol, modulation protocol, network protocol, OSI, protocol stack, protocol converter, protocol decoding, protocol independent, protocol overhead, protocol stack, protocol switching, protocol translator, RFC, routing protocol, security protocol, stateless protocol, transport protocol2) в ООП - совокупность сообщений, которые может принимать (и на которые может отвечать) объектАнгло-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. > protocol
-
18 interference
•- adjacent-channel interference
- alternate-channel interference
- atmospheric interference
- background interference
- beat interference
- blocking interference
- broadband interference
- broadcast interference
- burst interference
- co-channel interference
- common-mode interference
- concentrated interference
- conducted interference
- contact interference
- contact network interference
- corona-generated interference
- criss-cross interference
- cross-color interference
- diathermy interference
- difference interference
- differential-mode interference
- digital interference
- discontinuous interference
- electrical interference
- electromagnetic interference
- equipment interference
- extraneous interference
- fluctuating interference
- harmful interference
- harmonic interference
- hazardous interference
- heterodyne interference
- HF-interference
- hydroacoustic interference
- ignition interference
- image interference
- in-band interference
- inductive interference
- interburst interference
- interchannel interference
- interpath interference
- interstation interference
- intersymbol interference
- intersystem interference
- irregular interference
- magnetic interference
- man-made interference
- mobile radio-to-TV receiver interference
- modal interference
- multiple-beam interference
- multiplicative interference
- natural interference
- noise interference
- normal-mode interference
- optical interference
- oscillator-harmonic interference
- out-of-band interference
- over-reach interference
- permissible interference
- physiological interference
- power line interference
- pulse interference
- radar interference
- radiated interference
- radio interference
- radiostation interference
- selective interference
- series-mode interference
- single-frequency interference
- single-tone interference
- sinusoidal interference
- spatial interference
- spread-spectrum interference
- switching interference
- symbol-to-symbol interference
- synphased interference
- systematic interference
- taxicab radio-to-police radiosystem interference
- telegraph interference
- television interference
- tone interference
- two-beam interference
- unaccessible interference
- unit-to-unit interference
- wave interferenceEnglish-Russian dictionary of telecommunications and their abbreviations > interference
-
19 relay
1) реле3) ретрансляция; ретранслировать•- ac relay- accelerating relay
- active relay
- actuating relay
- air-borne radio relay
- all-or-nothing relay
- all-to-all relay
- amateur relay
- armature relay
- automating reclosing relay
- balanced relay
- bimetallic relay
- bimetallic strip relay
- blocking relay
- break-in relay
- burglar alarm device relay
- bypass relay
- calling relay
- capacitance relay
- cell relay
- center-zero relay
- clearing relay
- clock relay
- closing relay
- coaxial relay
- conductance relay
- connector relay
- corner relay
- current relay
- cut-in relay
- cut-off relay
- data-transmission relay
- dc relay
- delay relay
- differential relay
- digital relay
- directional relay
- disconnecting link relay
- distance relay
- double-pole relay
- double-wound relay
- dry-reed relay
- electric relay
- electromagnetic relay
- electromechanical relay
- electronic relay
- executive relay
- fast-release relay
- fast-speed relay
- flat-type relay
- frame relay
- frequency relay
- functional relay
- gas-filled relay
- group-selector relay
- guard relay
- heat relay
- homing relay
- impulse relay
- indicating relay
- indirect acting relay
- indirect action relay
- induction relay
- induction-disk relay
- inductive relay
- initiating relay
- instantaneous relay
- instrument-type relay
- interlock relay
- intermediate relay
- Kipp relay
- L-armature relay
- latch-in relay
- lock-up relay
- low-voltage relay
- magnetic locking relay
- marginal relay
- maximum-current relay
- metering relay
- meter-type relay
- microwave relay
- minimal relay
- network master relay
- neutral relay
- nonpolarized relay
- normally-closed relay
- normally-open relay
- no-voltage relay
- ohm relay
- optical-electronic relay
- output relay
- overload relay
- overpower relay
- overtemperature relay
- overvoltage relay
- peak relay
- phase relay
- phase-balance relay
- phase-comparison relay
- phase-sequence relay
- phase-shift relay
- phase-undervoltage relay
- photocell relay
- photoelectric relay
- phototube relay
- polarized relay
- polyphase relay
- positive sequence relay
- power relay
- primary relay
- programed-time relay
- protective relay
- pulse relay
- quick-operation relay
- radio relay
- ratio-balance relay
- reactance relay
- reclosing relay
- redundant relay
- reed relay
- register relay
- regulating relay
- reverse-current relay
- ringing relay
- rotary-stepping relay
- satellite relay
- SDI-relay
- SDV-relay
- secondary relay
- selective call relay
- self-reset relay
- shunt relay
- shutdown relay
- sidestable relay
- single-phase relay
- single-pole relay
- single-wound relay
- slow-acting relay
- slow-operate relay
- slow-release relay
- solenoid relay
- solid-state relay
- speed relay
- starting relay
- stepping relay
- storage relay
- switching relay
- switching-through relay
- synchronizing relay
- tape relay
- telephone relay
- terminal relay
- test relay
- thermionic relay
- three-phase relay
- thyratron relay
- time relay
- timing relay
- transistor relay
- trip-free relay
- trunk relay
- ultrafast relay
- undercurrent relay
- voltage relay
- wet-reed relay
- wholly-static relay
- zero-base sequence relayEnglish-Russian dictionary of telecommunications and their abbreviations > relay
-
20 switching technology
технология коммутации
-
[Интент]Современные технологии коммутации
[ http://www.xnets.ru/plugins/content/content.php?content.84]Статья подготовлена на основании материалов опубликованных в журналах "LAN", "Сети и системы связи", в книге В.Олифер и Н.Олифер "Новые технологии и оборудование IP-сетей", на сайтах www.citforum.ru и опубликована в журнале "Компьютерные решения" NN4-6 за 2000 год.
- Введение
- Коммутация первого уровня.
- Коммутация второго уровня.
- Коммутация третьего уровня.
- Коммутация четвертого уровня.
- Критерии выбора оборудования, физическая и логическая структура сети
- Качество обслуживания (QoS) и принципы задания приоритетов
- Заключение
Введение
На сегодня практически все организации, имеющие локальные сети, остановили свой выбор на сетях типа Ethernet. Данный выбор оправдан тем, что начало внедрения такой сети сопряжено с низкой стоимостью и простотой реализации, а развитие - с хорошей масштабируемостью и экономичностью.
Бросив взгляд назад - увидим, что развитие активного оборудования сетей шло в соответствии с требованиями к полосе пропускания и надежности. Требования, предъявляемые к большей надежности, привели к отказу от применения в качестве среды передачи коаксиального кабеля и перевода сетей на витую пару. В результате такого перехода отказ работы соединения между одной из рабочих станций и концентратором перестал сказываться на работе других рабочих станций сети. Но увеличения производительности данный переход не принес, так как концентраторы используют разделяемую (на всех пользователей в сегменте) полосу пропускания. По сути, изменилась только физическая топология сети - с общей шины на звезду, а логическая топология по-прежнему осталась - общей шиной.
Дальнейшее развитие сетей шло по нескольким путям:- увеличение скорости,
- внедрение сегментирования на основе коммутации,
- объединение сетей при помощи маршрутизации.
Увеличение скорости при прежней логической топологии - общая шина, привело к незначительному росту производительности в случае большого числа портов.
Большую эффективность в работе сети принесло сегментирование сетей с использованием технология коммутации пакетов. Коммутация наиболее действенна в следующих вариантах:
Вариант 1, именуемый связью "многие со многими" – это одноранговые сети, когда одновременно существуют потоки данных между парами рабочих станций. При этом предпочтительнее иметь коммутатор, у которого все порты имеют одинаковую скорость, (см. Рисунок 1).
Вариант 2, именуемый связью "один со многими" – это сети клиент-сервер, когда все рабочие станции работают с файлами или базой данных сервера. В данном случае предпочтительнее иметь коммутатор, у которого порты для подключения рабочих станций имеют одинаковую небольшую скорость, а порт, к которому подключается сервер, имеет большую скорость,(см. Рисунок 2).
Когда компании начали связывать разрозненные системы друг с другом, маршрутизация обеспечивала максимально возможную целостность и надежность передачи трафика из одной сети в другую. Но с ростом размера и сложности сети, а также в связи со все более широким применением коммутаторов в локальных сетях, базовые маршрутизаторы (зачастую они получали все данные, посылаемые коммутаторами) стали с трудом справляться со своими задачами.
Проблемы с трафиком, связанные с маршрутизацией, проявляются наиболее остро в средних и крупных компаниях, а также в деятельности операторов Internet, так как они вынуждены иметь дело с большими объемами IP-трафика, причем этот трафик должен передаваться своевременно и эффективно.
С подключением настольных систем непосредственно к коммутаторам на 10/100 Мбит/с между ними и магистралью оказывается все меньше промежуточных устройств. Чем выше скорость подключения настольных систем, тем более скоростной должна быть магистраль. Кроме того, на каждом уровне устройства должны справляться с приходящим трафиком, иначе возникновения заторов не избежать.
Рассмотрению технологий коммутации и посвящена данная статья.Коммутация первого уровня
Термин "коммутация первого уровня" в современной технической литературе практически не описывается. Для начала дадим определение, с какими характеристиками имеет дело физический или первый уровень модели OSI:
физический уровень определяет электротехнические, механические, процедурные и функциональные характеристики активации, поддержания и дезактивации физического канала между конечными системами. Спецификации физического уровня определяют такие характеристики, как уровни напряжений, синхронизацию изменения напряжений, скорость передачи физической информации, максимальные расстояния передачи информации, физические соединители и другие аналогичные характеристики.
Смысл коммутации на первом уровне модели OSI означает физическое (по названию уровня) соединение. Из примеров коммутации первого уровня можно привести релейные коммутаторы некоторых старых телефонных и селекторных систем. В более новых телефонных системах коммутация первого уровня применяется совместно с различными способами сигнализации вызовов и усиления сигналов. В сетях передачи данных данная технология применяется в полностью оптических коммутаторах.Коммутация второго уровня
Рассматривая свойства второго уровня модели OSI и его классическое определение, увидим, что данному уровню принадлежит основная доля коммутирующих свойств.
Определение. Канальный уровень (формально называемый информационно-канальным уровнем) обеспечивает надежный транзит данных через физический канал. Канальный уровень решает вопросы физической адресации (в противоположность сетевой или логической адресации), топологии сети, линейной дисциплины (каким образом конечной системе использовать сетевой канал), уведомления о неисправностях, упорядоченной доставки блоков данных и управления потоком информации.
На самом деле, определяемая канальным уровнем модели OSI функциональность служит платформой для некоторых из сегодняшних наиболее эффективных технологий. Большое значение функциональности второго уровня подчеркивает тот факт, что производители оборудования продолжают вкладывать значительные средства в разработку устройств с такими функциями.
С технологической точки зрения, коммутатор локальных сетей представляет собой устройство, основное назначение которого - максимальное ускорение передачи данных за счет параллельно существующих потоков между узлами сети. В этом - его главное отличие от других традиционных устройств локальных сетей – концентраторов (Hub), предоставляющих всем потокам данных сети всего один канал передачи данных.
Коммутатор позволяет передавать параллельно несколько потоков данных c максимально возможной для каждого потока скоростью. Эта скорость ограничена физической спецификацией протокола, которую также часто называют "скоростью провода". Это возможно благодаря наличию в коммутаторе большого числа центров обработки и продвижения кадров и шин передачи данных.
Коммутаторы локальных сетей в своем основном варианте, ставшем классическим уже с начала 90-х годов, работают на втором уровне модели OSI, применяя свою высокопроизводительную параллельную архитектуру для продвижения кадров канальных протоколов. Другими словами, ими выполняются алгоритмы работы моста, описанные в стандартах IEEE 802.1D и 802.1H. Также они имеют и много других дополнительных функций, часть которых вошла в новую редакцию стандарта 802.1D-1998, а часть остается пока не стандартизованной.
Коммутаторы ЛВС отличаются большим разнообразием возможностей и, следовательно, цен - стоимость 1 порта колеблется в диапазоне от 50 до 1000 долларов. Одной из причин столь больших различий является то, что они предназначены для решения различных классов задач. Коммутаторы высокого класса должны обеспечивать высокую производительность и плотность портов, а также поддерживать широкий спектр функций управления. Простые и дешевые коммутаторы имеют обычно небольшое число портов и не способны поддерживать функции управления. Одним из основных различий является используемая в коммутаторе архитектура. Поскольку большинство современных коммутаторов работают на основе патентованных контроллеров ASIC, устройство этих микросхем и их интеграция с остальными модулями коммутатора (включая буферы ввода-вывода) играет важнейшую роль. Контроллеры ASIC для коммутаторов ЛВС делятся на 2 класса - большие ASIC, способные обслуживать множество коммутируемых портов (один контроллер на устройство) и небольшие ASIC, обслуживающие по несколько портов и объединяемые в матрицы коммутации.
Существует 3 варианта архитектуры коммутаторов:
- переключение (cross-bar) с буферизацией на входе,
- самомаршрутизация (self-route) с разделяемой памятью
- высокоскоростная шина.
На рисунке 3 показана блок-схема коммутатора с архитектурой, используемой для поочередного соединения пар портов. В любой момент такой коммутатор может обеспечить организацию только одного соединения (пара портов). При невысоком уровне трафика не требуется хранение данных в памяти перед отправкой в порт назначения - такой вариант называется коммутацией на лету cut-through. Однако, коммутаторы cross-bar требуют буферизации на входе от каждого порта, поскольку в случае использования единственно возможного соединения коммутатор блокируется (рисунок 4). Несмотря на малую стоимость и высокую скорость продвижения на рынок, коммутаторы класса cross-bar слишком примитивны для эффективной трансляции между низкоскоростными интерфейсами Ethernet или token ring и высокоскоростными портами ATM и FDDI.
Коммутаторы с разделяемой памятью имеют общий входной буфер для всех портов, используемый как внутренняя магистраль устройства (backplane). Буферизагия данных перед их рассылкой (store-and-forward - сохранить и переслать) приводит к возникновению задержки. Однако, коммутаторы с разделяемой памятью, как показано на рисунке 5 не требуют организации специальной внутренней магистрали для передачи данных между портами, что обеспечивает им более низкую цену по сравнению с коммутаторами на базе высокоскоростной внутренней шины.
На рисунке 6 показана блок-схема коммутатора с высокоскоростной шиной, связывающей контроллеры ASIC. После того, как данные преобразуются в приемлемый для передачи по шине формат, они помещаются на шину и далее передаются в порт назначения. Поскольку шина может обеспечивать одновременную (паралельную) передачу потока данных от всех портов, такие коммутаторы часто называют "неблокируемыми" (non-blocking) - они не создают пробок на пути передачи данных.
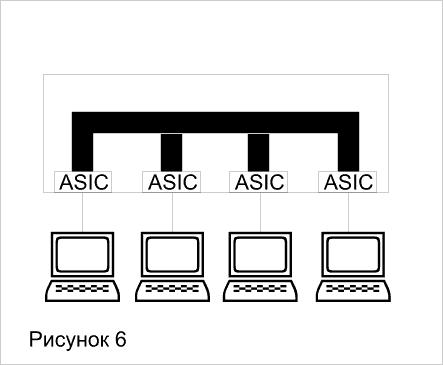
Применение аналогичной параллельной архитектуры для продвижения пакетов сетевых протоколов привело к появлению коммутаторов третьего уровня модели OSI.
Коммутация третьего уровня
В продолжении темы о технологиях коммутации рассмотренных в предыдущем номера повторим, что применение параллельной архитектуры для продвижения пакетов сетевых протоколов привело к появлению коммутаторов третьего уровня. Это позволило существенно, в 10-100 раз повысить скорость маршрутизации по сравнению с традиционными маршрутизаторами, в которых один центральный универсальный процессор выполняет программное обеспечение маршрутизации.
По определению Сетевой уровень (третий) - это комплексный уровень, который обеспечивает возможность соединения и выбор маршрута между двумя конечными системами, подключенными к разным "подсетям", которые могут находиться в разных географических пунктах. В данном случае "подсеть" это, по сути, независимый сетевой кабель (иногда называемый сегментом).
Коммутация на третьем уровне - это аппаратная маршрутизация. Традиционные маршрутизаторы реализуют свои функции с помощью программно-управляемых процессоров, что будем называть программной маршрутизацией. Традиционные маршрутизаторы обычно продвигают пакеты со скоростью около 500000 пакетов в секунду. Коммутаторы третьего уровня сегодня работают со скоростью до 50 миллионов пакетов в секунду. Возможно и дальнейшее ее повышение, так как каждый интерфейсный модуль, как и в коммутаторе второго уровня, оснащен собственным процессором продвижения пакетов на основе ASIC. Так что наращивание количества модулей ведет к наращиванию производительности маршрутизации. Использование высокоскоростной технологии больших заказных интегральных схем (ASIC) является главной характеристикой, отличающей коммутаторы третьего уровня от традиционных маршрутизаторов. Коммутаторы 3-го уровня делятся на две категории: пакетные (Packet-by-Packet Layer 3 Switches, PPL3) и сквозные (Cut-Through Layer 3 Switches, CTL3). PPL3 - означает просто быструю маршрутизацию (Рисунок_7). CTL3 – маршрутизацию первого пакета и коммутацию всех остальных (Рисунок 8).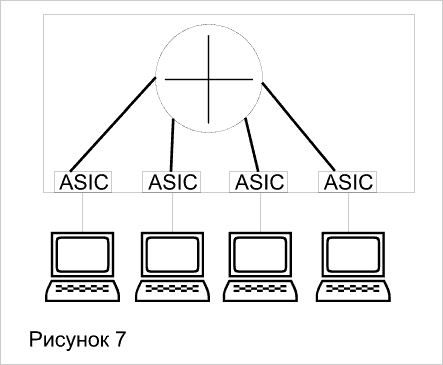
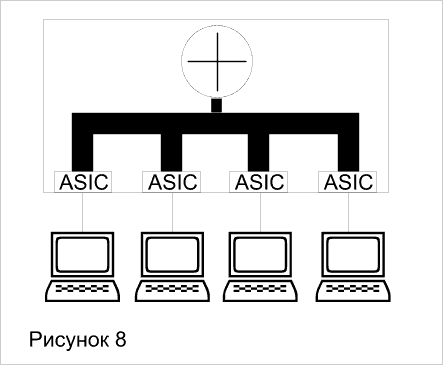
У коммутатора третьего уровня, кроме реализации функций маршрутизации в специализированных интегральных схемах, имеется несколько особенностей, отличающих их от традиционных маршрутизаторов. Эти особенности отражают ориентацию коммутаторов 3-го уровня на работу, в основном, в локальных сетях, а также последствия совмещения в одном устройстве коммутации на 2-м и 3-м уровнях:
- поддержка интерфейсов и протоколов, применяемых в локальных сетях,
- усеченные функции маршрутизации,
- обязательная поддержка механизма виртуальных сетей,
- тесная интеграция функций коммутации и маршрутизации, наличие удобных для администратора операций по заданию маршрутизации между виртуальными сетями.
Наиболее "коммутаторная" версия высокоскоростной маршрутизации выглядит следующим образом (рисунок 9). Пусть коммутатор третьего уровня построен так, что в нем имеется информация о соответствии сетевых адресов (например, IP-адресов) адресам физического уровня (например, MAC-адресам) Все эти МАС-адреса обычным образом отображены в коммутационной таблице, независимо от того, принадлежат ли они данной сети или другим сетям.
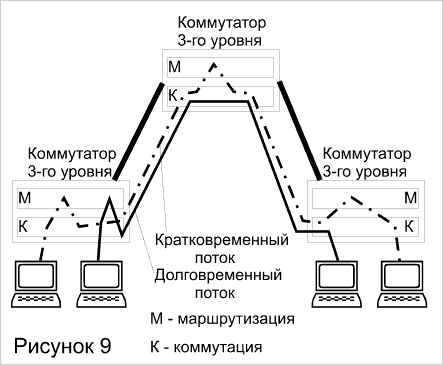
Первый коммутатор, на который поступает пакет, частично выполняет функции маршрутизатора, а именно, функции фильтрации, обеспечивающие безопасность. Он решает, пропускать или нет данный пакет в другую сеть Если пакет пропускать нужно, то коммутатор по IP-адресу назначения определяет МАС-адрес узла назначения и формирует новый заголовок второго уровня с найденным МАС-адресом. Затем выполняется обычная процедура коммутации по данному МАС-адресу с просмотром адресной таблицы коммутатора. Все последующие коммутаторы, построенные по этому же принципу, обрабатывают данный кадр как обычные коммутаторы второго уровня, не привлекая функций маршрутизации, что значительно ускоряет его обработку. Однако функции маршрутизации не являются для них избыточными, поскольку и на эти коммутаторы могут поступать первичные пакеты (непосредственно от рабочих станций), для которых необходимо выполнять фильтрацию и подстановку МАС-адресов.
Это описание носит схематический характер и не раскрывает способов решения возникающих при этом многочисленных проблем, например, проблемы построения таблицы соответствия IP-адресов и МАС-адресов
Примерами коммутаторов третьего уровня, работающих по этой схеме, являются коммутаторы SmartSwitch компании Cabletron. Компания Cabletron реализовала в них свой протокол ускоренной маршрутизации SecureFast Virtual Network, SFVN.
Для организации непосредственного взаимодействия рабочих станций без промежуточного маршрутизатора необходимо сконфигурировать каждую из них так, чтобы она считала собственный интерфейс маршрутизатором по умолчанию. При такой конфигурации станция пытается самостоятельно отправить любой пакет конечному узлу, даже если этот узел находится в другой сети. Так как в общем случае (см. рисунок 10) станции неизвестен МАС-адрес узла назначения, то она генерирует соответствующий ARP-запрос, который перехватывает коммутатор, поддерживающий протокол SFVN. В сети предполагается наличие сервера SFVN Server, являющегося полноценным маршрутизатором и поддерживающего общую ARP-таблицу всех узлов SFVN-сети. Сервер возвращает коммутатору МАС-адрес узла назначения, а коммутатор, в свою очередь, передает его исходной станции. Одновременно сервер SFVN передает коммутаторам сети инструкции о разрешении прохождения пакета с МАС-адресом узла назначения через границы виртуальных сетей. Затем исходная станция передает пакет в кадре, содержащем МАС-адрес узла назначения. Этот кадр проходит через коммутаторы, не вызывая обращения к их блокам маршрутизации. Отличие протокола SFVN компании Cabletron от - описанной выше общей схемы в том, что для нахождения МАС-адреса по IP-адресу в сети используется выделенный сервер.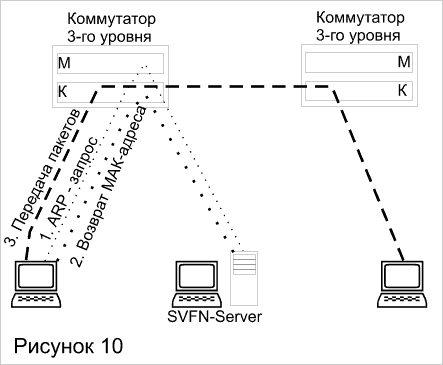
Протокол Fast IP компании 3Com является еще одним примером реализации подхода с отображением IP-адреса на МАС-адрес. В этом протоколе основными действующими лицами являются сетевые адаптеры (что не удивительно, так как компания 3Com является признанным лидером в производстве сетевых адаптеров Ethernet) С одной стороны, такой подход требует изменения программного обеспечения драйверов сетевых адаптеров, и это минус Но зато не требуется изменять все остальное сетевое оборудование.
При необходимости передать пакет узлу назначения другой сети, исходный узел в соответствии с технологией Fast IP должен передать запрос по протоколу NHRP (Next Hop Routing Protocol) маршрутизатору сети. Маршрутизатор переправляет этот запрос узлу назначения, как обычный пакет Узел назначения, который также поддерживает Fast IP и NHRP, получив запрос, отвечает кадром, отсылаемым уже не маршрутизатору, а непосредственно узлу-источнику (по его МАС-адресу, содержащемуся в NHRP-запросе). После этого обмен идет на канальном уровне на основе известных МАС-адресов. Таким образом, снова маршрутизировался только первый пакет потока (как на рисунке 9 кратковременный поток), а все остальные коммутировались (как на рисунке 9 долговременный поток).
Еще один тип коммутаторов третьего уровня — это коммутаторы, работающие с протоколами локальных сетей типа Ethernet и FDDI. Эти коммутаторы выполняют функции маршрутизации не так, как классические маршрутизаторы. Они маршрутизируют не отдельные пакеты, а потоки пакетов.
Поток — это последовательность пакетов, имеющих некоторые общие свойства. По меньшей мере, у них должны совпадать адрес отправителя и адрес получателя, и тогда их можно отправлять по одному и тому же маршруту. Если классический способ маршрутизации использовать только для первого пакета потока, а все остальные обрабатывать на основании опыта первого (или нескольких первых) пакетов, то можно значительно ускорить маршрутизацию всего потока.
Рассмотрим этот подход на примере технологии NetFlow компании Cisco, реализованной в ее маршрутизаторах и коммутаторах. Для каждого пакета, поступающего на порт маршрутизатора, вычисляется хэш-функция от IP-адресов источника, назначения, портов UDP или TCP и поля TOS, характеризующего требуемое качество обслуживания. Во всех маршрутизаторах, поддерживающих данную технологию, через которые проходит данный пакет, в кэш-памяти портов запоминается соответствие значения хэш-функции и адресной информации, необходимой для быстрой передачи пакета следующему маршрутизатору. Таким образом, образуется квазивиртуальный канал (см. Рисунок 11), который позволяет быстро передавать по сети маршрутизаторов все последующие пакеты этого потока. При этом ускорение достигается за счет упрощения процедуры обработки пакета маршрутизатором - не просматриваются таблицы маршрутизации, не выполняются ARP-запросы.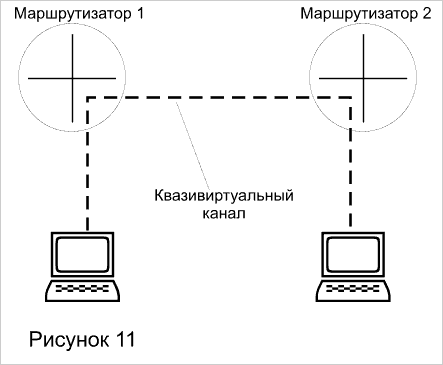
Этот прием может использоваться в маршрутизаторах, вообще не поддерживающих коммутацию, а может быть перенесен в коммутаторы. В этом случае такие коммутаторы тоже называют коммутаторами третьего уровня. Примеров маршрутизаторов, использующих данный подход, являются маршрутизаторы Cisco 7500, а коммутаторов третьего уровня — коммутаторы Catalyst 5000 и 5500. Коммутаторы Catalyst выполняют усеченные функции описанной схемы, они не могут обрабатывать первые пакеты потоков и создавать новые записи о хэш-функциях и адресной информации потоков. Они просто получают данную информацию от маршрутизаторов 7500 и обрабатывают пакеты уже распознанных маршрутизаторами потоков.
Выше был рассмотрен способ ускоренной маршрутизации, основанный на концепции потока. Его сущность заключается в создании квазивиртуальных каналов в сетях, которые не поддерживают виртуальные каналы в обычном понимании этого термина, то есть сетях Ethernet, FDDI, Token Ring и т п. Следует отличать этот способ от способа ускоренной работы маршрутизаторов в сетях, поддерживающих технологию виртуальных каналов — АТМ, frame relay, X 25. В таких сетях создание виртуального канала является штатным режимом работы сетевых устройств. Виртуальные каналы создаются между двумя конечными точками, причем для потоков данных, требующих разного качества обслуживания (например, для данных разных приложений) может создаваться отдельный виртуальный канал. Хотя время создания виртуального канала существенно превышает время маршрутизации одного пакета, выигрыш достигается за счет последующей быстрой передачи потока данных по виртуальному каналу. Но в таких сетях возникает другая проблема — неэффективная передача коротких потоков, то есть потоков, состоящих из небольшого количества пакетов (классический пример — пакеты протокола DNS).
Накладные расходы, связанные с созданием виртуального канала, приходящиеся на один пакет, снижаются при передаче объемных потоков данных. Однако они становятся неприемлемо высокими при передаче коротких потоков. Для того чтобы эффективно передавать короткие потоки, предлагается следующий вариант, при передаче нескольких первых пакетов выполняется обычная маршрутизация. Затем, после того как распознается устойчивый поток, для него строится виртуальный канал, и дальнейшая передача данных происходит с высокой скоростью по этому виртуальному каналу. Таким образом, для коротких потоков виртуальный канал вообще не создается, что и повышает эффективность передачи.
По такой схеме работает ставшая уже классической технология IP Switching компании Ipsilon. Для того чтобы сети коммутаторов АТМ передавали бы пакеты коротких потоков без установления виртуального канала, компания Ipsilon предложила встроить во все коммутаторы АТМ блоки IP-маршрутизации (рисунок 12), строящие обычные таблицы маршрутизации по обычным протоколам RIP и OSPF.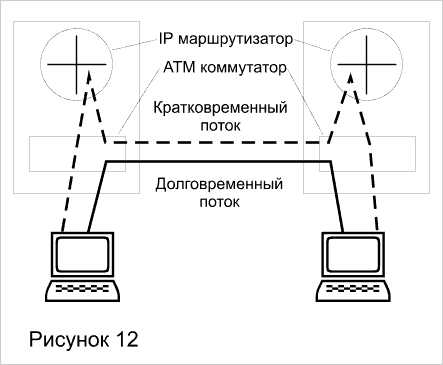
Компания Cisco Systems выдвинула в качестве альтернативы технологии IP Switching свою собственную технологию Tag Switching, но она не стала стандартной. В настоящее время IETF работает над стандартным протоколом обмена метками MPLS (Multi-Protocol Label Switching), который обобщает предложение компаний Ipsilon и Cisco, а также вносит некоторые новые детали и механизмы. Этот протокол ориентирован на поддержку качества обслуживания для виртуальных каналов, образованных метками.
Коммутация четвертого уровня
Свойства четвертого или транспортного уровня модели OSI следующие: транспортный уровень обеспечивает услуги по транспортировке данных. В частности, заботой транспортного уровня является решение таких вопросов, как выполнение надежной транспортировки данных через объединенную сеть. Предоставляя надежные услуги, транспортный уровень обеспечивает механизмы для установки, поддержания и упорядоченного завершения действия виртуальных каналов, систем обнаружения и устранения неисправностей транспортировки и управления информационным потоком (с целью предотвращения переполнения данными из другой системы).
Некоторые производители заявляют, что их системы могут работать на втором, третьем и даже четвертом уровнях. Однако рассмотрение описания стека TCP/IP (рисунок 1), а также структуры пакетов IP и TCP (рисунки 2, 3), показывает, что коммутация четвертого уровня является фикцией, так как все относящиеся к коммутации функции осуществляются на уровне не выше третьего. А именно, термин коммутация четвертого уровня с точки зрения описания стека TCP/IP противоречий не имеет, за исключением того, что при коммутации должны указываться адреса компьютера (маршрутизатора) источника и компьютера (маршрутизатора) получателя. Пакеты TCP имеют поля локальный порт отправителя и локальный порт получателя (рисунок 3), несущие смысл точек входа в приложение (в программу), например Telnet с одной стороны, и точки входа (в данном контексте инкапсуляции) в уровень IP. Кроме того, в стеке TCP/IP именно уровень TCP занимается формированием пакетов из потока данных идущих от приложения. Пакеты IP (рисунок 2) имеют поля адреса компьютера (маршрутизатора) источника и компьютера (маршрутизатора) получателя и следовательно могут наряду с MAC адресами использоваться для коммутации. Тем не менее, название прижилось, к тому же практика показывает, что способность системы анализировать информацию прикладного уровня может оказаться полезной — в частности для управления трафиком. Таким образом, термин "зависимый от приложения" более точно отражает функции так называемых коммутаторов четвертого уровня.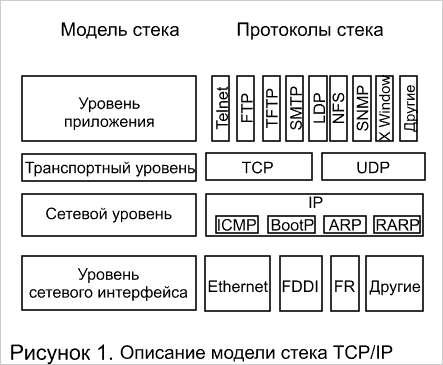
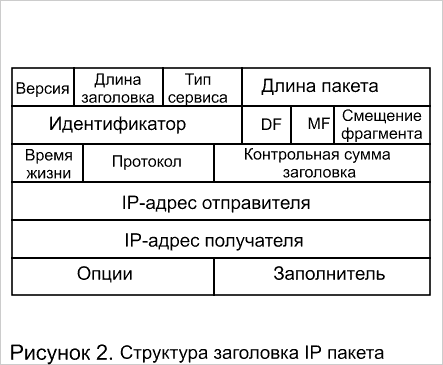
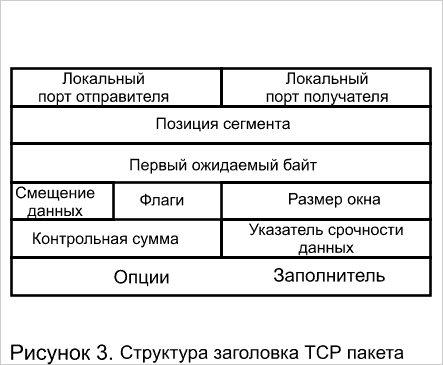
Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > switching technology
См. также в других словарях:
Network neutrality in the United States — Network Neutrality Related issues and topics Automatic telephone exchange Data discrimination End to end principle Internet Protocol Tiered Internet Bandwidth Throttling … Wikipedia
Network neutrality in Canada — Network Neutrality Related issues and topics Automatic telephone exchange Data discrimination End to end principle Internet Protocol Tiered Internet Bandwidth Throttling … Wikipedia
Network Based Application Recognition — (NBAR)[1] is the mechanism used by some Cisco routers and switches to recognize a dataflow by inspecting some packets sent. The networking equipment which uses NBAR does a deep packet inspection on some of the packets in a dataflow, to determine… … Wikipedia
Network neutrality — This article is about the general principle of network neutrality. For its specific application to Canada, see Network neutrality in Canada. For its application to the U.S., see Network neutrality in the United States. Network Neutrality Related… … Wikipedia
Blocking of Wikipedia by the People's Republic of China — On several occasions, the government and Internet service providers of the People s Republic of China (PRC) have blocked access to the online encyclopedia Wikipedia due to strict censorship laws enacted by the PRC. The blocks function in a… … Wikipedia
Blocking of Wikipedia in mainland China — On several occasions, the government and Internet service providers of the People s Republic of China (PRC) have blocked access to Wikipedia in mainland China due to strict censorship laws enacted by the PRC.The blocks function in a similar way… … Wikipedia
Network congestion — In data networking and queueing theory, network congestion occurs when a link or node is carrying so much data that its quality of service deteriorates. Typical effects include queueing delay, packet loss or the blocking of new connections. A… … Wikipedia
Network virtualization — In computing, Network Virtualization is the process of combining hardware and software network resources and network functionality into a single, software based administrative entity, a virtual network. Network virtualization involves platform… … Wikipedia
Network traffic measurement — In computer networks, network traffic measurement is the process of measuring the amount and type of traffic on a particular network. This is especially important with regard to effective bandwidth management. Contents 1 Tools 1.1 Functions and… … Wikipedia
Blocking (scheduling) — In a multitasking computer system, individual tasks, or threads of execution, must share the resources of the system. These resources might be:* the CPU * network * memory * diskor any other shared resource.When one task is using a resource, it… … Wikipedia
Clos network — In the field of telecommunications, a Clos network is a kind of multistage circuit switching network, first formalized by Charles Clos in 1953,[1] which represents a theoretical idealization of practical multi stage telephone switching systems.… … Wikipedia
