-
41 Grenzwert der Nichtbetätigungs-Überstromstärke bei symmetrischer Last
предельное значение тока несрабатывания при равномерной нагрузке
-
[IEV number 442-05-64]EN
limiting value of the non-operating current in case of balanced load
Maximum value of current which, in the absence of any fault to frame or to earth, and of an earth leakage current, can flow in a circuit without any load unbalance, without causing operation of the part of the residual current device performing the evaluation.
[IEV number 442-05-64]FR
valeur limite du courant de non-fonctionnement en service équilibré
Valeur maximale du courant pouvant circuler dans un circuit, en l'absence de tout défaut à la masse ou à la terre et de tout courant de fuite à la terre en l'absence de tout déséquilibre de charge, sans provoquer le fonctionnement de la partie du dispositif de coupure différentiel assurant la fonction mesure.
[IEV number 442-05-64]EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Grenzwert der Nichtbetätigungs-Überstromstärke bei symmetrischer Last
-
42 Grenzwert der Betriebsspannung der Hilfsenergieversorgung
- предельное наименьшее значение рабочего напряжения вспомогательного источника питания
предельное наименьшее значение рабочего напряжения вспомогательного источника питания
-
[IEV number 442-05-33]EN
limiting value of the operating voltage of the auxiliary source
minimum value of the voltage of the auxiliary source, at which the residual current device still operates under specified conditions in the case of decreasing voltage of the auxiliary source
[IEV number 442-05-33]FR
valeur limite de la tension de fonctionnement de la source auxiliaire
valeur minimale de la tension de la source auxiliaire pour laquelle le dispositif de coupure différentiel fonctionne encore dans des conditions spécifiées en cas de diminution de la tension de la source auxiliaire
[IEV number 442-05-33]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Grenzwert der Betriebsspannung der Hilfsenergieversorgung
-
43 Natürliche Ressource
природный ресурс
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
natural resource
A feature or component of the natural environment that is of value in serving human needs, e.g. soil, water, plantlife, wildlife, etc. Some natural resources have an economic value (e.g. timber) while others have a "noneconomic" value (e.g. scenic beauty). (Source: UNUN)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Natürliche Ressource
-
44 Fehlerstrom-Schutzeinrichtung
устройство дифференциального тока
УДТ
Механическое коммутационное устройство, предназначенное включать, проводить и отключать токи в нормальных рабочих условиях и вызывать размыкание контактов, когда дифференциальный ток достигает заданного значения в определенных условиях.
Примечание - Устройство дифференциального тока может быть комбинацией различных отдельных элементов, предназначенных обнаруживать и оценивать дифференциальный ток, а также включать и отключать электрический ток.
Примечание - В национальной нормативной документации вместо термина «устройство дифференциального тока» применяют термин « устройство защитного отключения».
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]
устройство дифференциального тока
УДТ
Механическое коммутационное устройство или комплекс устройств, которые вызывают размыкание контактов, когда дифференциальный или несбалансированный ток достигнет заданного значения в заданных условиях.
[ ГОСТ Р 51992-2011( МЭК 61643-1: 2005)]EN
residual current device
RCD, (abbreviation)
a mechanical switching device designed to make, carry and break currents under normal service conditions and to cause the opening of the contacts when the residual current attains a given value under specified conditions
NOTE – A residual current device can be a combination of various separate elements designed to detect and evaluate the residual current and to make and break current.
[IEV number 442-05-02]FR
dispositif (de coupure) différentiel
dispositif (à courant) différentiel résiduel
DDR (abréviation)
dispositif mécanique de coupure destiné à établir, supporter et couper des courants dans les conditions de service normales et à provoquer l'ouverture des contacts quand le courant différentiel atteint, dans des conditions spécifiées, une valeur donnée
NOTE – Un dispositif de coupure différentiel peut être une combinaison de divers éléments séparés conçus pour détecter et mesurer le courant différentiel et pour établir ou interrompre le courant.
[IEV number 442-05-02]Параллельные тексты EN-RU Operating principle of residual current devices
The operating principle of residual current devices consists in the detection of an earth fault current by means of a toroidal transformer which encloses all the live conductors, included the neutral, if distributed.
In absence of an earth fault the vectorial sum of the currents IΔ is equal to zero; in case of an earth fault, if the value of IΔ exceeds the value of the trip threshold, called IΔ n, the circuit at the secondary of the toroid sends a command signal to a dedicated opening device causing the circuit-breaker tripping.
[ABB]Принцип действия устройств дифференциального тока
Принцип действия устройств дифференциального тока заключается в обнаружении тока замыкания на землю с помощью тороидального трансформатора, который охватывает все токоведущие, в том числе и нейтральный проводник, если он используется для распределения электроэнергии.
При отсутствии замыкания на землю векторная сумма токов IΔ равна нулю. Если при возникновении замыкания на землю значение IΔ превысит уставку срабатывания, обозначаемую как IΔn, то во вторичной обмотке тороидального трансформатора будет наведена ЭДС, достаточная для включения специального устройства, вызывающего срабатывание автоматического выключателя
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- электроустановки
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
- RCD, (abbreviation)
- residual current device
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Fehlerstrom-Schutzeinrichtung
-
45 Bezugswert einer Einflußgröße (für eine Fehlerstrom-Schutzeinrichtung)
эталонное значение влияющей величины
-
[IEV number 442-05-36]EN
reference value of an influencing quantity
the value of an influencing quantity to which the manufacturer's stated characteristics are referred
[IEV number 442-05-36]FR
valeur de référence d'une grandeur d'influence
valeur d'une grandeur d'influence à laquelle sont rapportées les caractéristiques indiquées par le constructeur
[IEV number 442-05-36]EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Bezugswert einer Einflußgröße (für eine Fehlerstrom-Schutzeinrichtung)
-
46 Leistungsschalter
автоматический выключатель
Механический коммутационный аппарат1), способный включать, проводить и отключать токи при нормальном состоянии электрической цепи, а также включать, проводить в течение заданного времени и автоматически отключать токи в указанном аномальном состоянии электрической цепи, например, при коротком замыкании.
(МЭС 441-14-20)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 2-99 ( МЭК 60947-2-98)]
автоматический выключатель
-
[IEV number 442-05-01]EN
circuit breaker
a mechanical switching device, capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying for a specified time and breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
circuit breaker
A device designed to open and close a circuit by nonautomatic means and to open the circuit automatically on a predetermined overcurrent without damage to itself when properly applied within its rating.
NOTE The automatic opening means can be integral, direct acting with the circuit breaker, or remote from the circuit breaker.
Adjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker can be set to trip at various values of current, time, or both within a predetermined range. Instantaneous-trip (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that no delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker.
Inverse-time (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating a delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker, which delay decreases as the magnitude of the current increases.
Nonadjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker does not have any adjustment to alter the value of current at which it will trip or the time required for its operation.
Setting (of a circuit breaker). The value of current, time, or both at which an adjustable circuit breaker is set to trip.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
disjoncteur
1) Должно быть контактный коммутационный аппарат
appareil mécanique de connexion capable d’établir, de supporter et d’interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit, ainsi que d’établir, de supporter pendant une durée spécifiée et d’in- terrompre des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit telles que celles du court-circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
[Интент]КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ
- По роду тока
- По напряжению
- По числу полюсов
- По виду корпуса
- По месту установки
- По изолирующей среде
- По установленным расцепителям
- По дополнительным защитам
- По назначению
- По категории применения
- По виду привода взвода пружины
- По выполняемой функции
-
По влиянию монтажного положения
 Автоматические выключатели ABB
Автоматические выключатели ABB
 Модульные автоматические выключатели
Модульные автоматические выключатели
1. НЕКОТОРЫЕ СВЕДЕНИЯ ОБ АВТОМАТИЧЕСКИХ ВЫКЛЮЧАТЕЛЯХ Автоматический выключатель — это электрический аппарат, который автоматически отключает (и тем самым защищает) электрическую цепь при возникновении в ней аномального режима. Режим становится аномальным, когда в цепи начинает недопустимо изменяться (т. е. увеличиваться или уменьшаться относительно номинального значения) ток или напряжение.
Другими словами (более "инженерно") можно сказать, что автоматический выключатель защищает от токов короткого замыкания и токов перегрузки отходящую от него питающую линию, например, кабель и приемник(и) электрической энергии (осветительную сеть, розетки, электродвигатель и т. п.).
Как правило, автоматический выключатель может применятся также для нечастого (несколько раз в сутки) включения и отключения защищаемых электроприемников (защищаемой нагрузки).
[Интент]Выключатель предназначен для проведения тока в нормальном режиме и отключения тока при коротких замыканиях, перегрузках, недопустимых снижениях напряжения, а также до 30 оперативных включений и отключений электрических цепей в сутки и рассчитан для эксплуатации в электроустановках с номинальным рабочим напряжением до 660 В переменного тока частоты 50 и 60 Гц и до 440 В постоянного тока.
[Типовая фраза из российской технической документации] 2. ПРИНЦИП ДЕЙСТВИЯ Для защиты цепи от короткого замыкания применяется автоматический выключатель с электромагнитным расцепителем.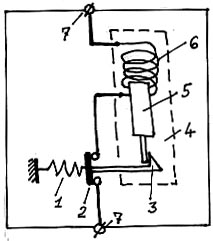
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Автоматический выключатель устроен таким образом, что сначала необходимо взвести пружину и только после этого его можно включить. У многих автоматических выключателей для взвода пружины необходимо перевести ручку вниз. После этого ручку переводят вверх. При этом замыкаются главные контакты.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Электромагнитный расцепитель;
5 - Сердечник
6 - Катушка
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
На рисунке показан один полюс автоматического выключателя во включенном положении: пружина 1 взведена, а главный контакт 2 замкнут.
Как только в защищаемой цепи возникнет короткое замыкание, ток, протекающий через соответствующий полюс автоматического выключателя, многократно возрастет. В катушке 6 сразу же возникнет сильное магнитное поле. Сердечник 5 втянется в катушку и освободит удерживающее устройство. Под действием пружины 1 главный контакт 2 разомкнется, в результате чего автоматический выключатель отключит и тем самым защитит цепь, в которой возникло короткое замыкание. Такое срабатывание автоматического выключателя происходит практически мгновенно (за сотые доли секунды).
Для защиты цепи от тока перегрузки применяют автоматические выключатели с тепловым расцепителем.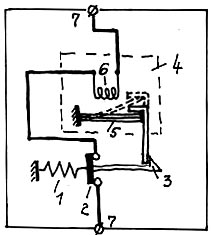
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Принцип действия такой же как и в первом случае, с той лишь разницей, что удерживающее устройство 3 освобождается под действием биметаллической пластины 5, которая изгибается от тепла, выделяемого нагревательным элементом 6. Количество тепла определяется током, протекающим через защищаемую цепь.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Тепловой расцепитель
5 - Биметаллическая пластина
6 - Нагревательный элемент
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
[Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- включение автоматического выключателя
- оперирование автоматического выключателя
- отключение автоматического выключателя
- срабатывание автоматического выключателя
EN
- auto-cutout
- automatic circuit breaker
- automatic cutout
- automatic switch
- breaker
- CB
- circuit breaker
- circuit-breaker
- cutout
DE
FR
Смотри также
силовой выключатель
-
[Интент]EN
circuit-breaker
a mechanical switching device, capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying for a specified time and breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit
[IEV ref 441-14-20]FR
disjoncteur
appareil mécanique de connexion capable d'établir, de supporter et d'interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit, ainsi que d'établir, de supporter pendant une durée spécifiée et d'interrompre des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit telles que celles du court-circuit
[IEV ref 441-14-20]
Рис. Siemens
Силовой ( баковый элегазовый) выключатель 3AP1 DT
Рис. Siemens
Силовой (колонковый элегазовый) выключательТематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- комплектное распред. устройство (КРУ)
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Leistungsschalter
47 Selbstschalter
автоматический выключатель
Механический коммутационный аппарат1), способный включать, проводить и отключать токи при нормальном состоянии электрической цепи, а также включать, проводить в течение заданного времени и автоматически отключать токи в указанном аномальном состоянии электрической цепи, например, при коротком замыкании.
(МЭС 441-14-20)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 2-99 ( МЭК 60947-2-98)]
автоматический выключатель
-
[IEV number 442-05-01]EN
circuit breaker
a mechanical switching device, capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying for a specified time and breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
circuit breaker
A device designed to open and close a circuit by nonautomatic means and to open the circuit automatically on a predetermined overcurrent without damage to itself when properly applied within its rating.
NOTE The automatic opening means can be integral, direct acting with the circuit breaker, or remote from the circuit breaker.
Adjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker can be set to trip at various values of current, time, or both within a predetermined range. Instantaneous-trip (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that no delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker.
Inverse-time (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating a delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker, which delay decreases as the magnitude of the current increases.
Nonadjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker does not have any adjustment to alter the value of current at which it will trip or the time required for its operation.
Setting (of a circuit breaker). The value of current, time, or both at which an adjustable circuit breaker is set to trip.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
disjoncteur
1) Должно быть контактный коммутационный аппарат
appareil mécanique de connexion capable d’établir, de supporter et d’interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit, ainsi que d’établir, de supporter pendant une durée spécifiée et d’in- terrompre des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit telles que celles du court-circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
[Интент]КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ
- По роду тока
- По напряжению
- По числу полюсов
- По виду корпуса
- По месту установки
- По изолирующей среде
- По установленным расцепителям
- По дополнительным защитам
- По назначению
- По категории применения
- По виду привода взвода пружины
- По выполняемой функции
-
По влиянию монтажного положения
 Автоматические выключатели ABB
Автоматические выключатели ABB
 Модульные автоматические выключатели
Модульные автоматические выключатели
1. НЕКОТОРЫЕ СВЕДЕНИЯ ОБ АВТОМАТИЧЕСКИХ ВЫКЛЮЧАТЕЛЯХ Автоматический выключатель — это электрический аппарат, который автоматически отключает (и тем самым защищает) электрическую цепь при возникновении в ней аномального режима. Режим становится аномальным, когда в цепи начинает недопустимо изменяться (т. е. увеличиваться или уменьшаться относительно номинального значения) ток или напряжение.
Другими словами (более "инженерно") можно сказать, что автоматический выключатель защищает от токов короткого замыкания и токов перегрузки отходящую от него питающую линию, например, кабель и приемник(и) электрической энергии (осветительную сеть, розетки, электродвигатель и т. п.).
Как правило, автоматический выключатель может применятся также для нечастого (несколько раз в сутки) включения и отключения защищаемых электроприемников (защищаемой нагрузки).
[Интент]Выключатель предназначен для проведения тока в нормальном режиме и отключения тока при коротких замыканиях, перегрузках, недопустимых снижениях напряжения, а также до 30 оперативных включений и отключений электрических цепей в сутки и рассчитан для эксплуатации в электроустановках с номинальным рабочим напряжением до 660 В переменного тока частоты 50 и 60 Гц и до 440 В постоянного тока.
[Типовая фраза из российской технической документации] 2. ПРИНЦИП ДЕЙСТВИЯ Для защиты цепи от короткого замыкания применяется автоматический выключатель с электромагнитным расцепителем.
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Автоматический выключатель устроен таким образом, что сначала необходимо взвести пружину и только после этого его можно включить. У многих автоматических выключателей для взвода пружины необходимо перевести ручку вниз. После этого ручку переводят вверх. При этом замыкаются главные контакты.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Электромагнитный расцепитель;
5 - Сердечник
6 - Катушка
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
На рисунке показан один полюс автоматического выключателя во включенном положении: пружина 1 взведена, а главный контакт 2 замкнут.
Как только в защищаемой цепи возникнет короткое замыкание, ток, протекающий через соответствующий полюс автоматического выключателя, многократно возрастет. В катушке 6 сразу же возникнет сильное магнитное поле. Сердечник 5 втянется в катушку и освободит удерживающее устройство. Под действием пружины 1 главный контакт 2 разомкнется, в результате чего автоматический выключатель отключит и тем самым защитит цепь, в которой возникло короткое замыкание. Такое срабатывание автоматического выключателя происходит практически мгновенно (за сотые доли секунды).
Для защиты цепи от тока перегрузки применяют автоматические выключатели с тепловым расцепителем.
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Принцип действия такой же как и в первом случае, с той лишь разницей, что удерживающее устройство 3 освобождается под действием биметаллической пластины 5, которая изгибается от тепла, выделяемого нагревательным элементом 6. Количество тепла определяется током, протекающим через защищаемую цепь.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Тепловой расцепитель
5 - Биметаллическая пластина
6 - Нагревательный элемент
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
[Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- включение автоматического выключателя
- оперирование автоматического выключателя
- отключение автоматического выключателя
- срабатывание автоматического выключателя
EN
- auto-cutout
- automatic circuit breaker
- automatic cutout
- automatic switch
- breaker
- CB
- circuit breaker
- circuit-breaker
- cutout
DE
FR
Смотри также
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Selbstschalter
48 Úberlauf
водослив
Устройство в гидротехническом сооружении, в котором сброс воды осуществляется через отверстие со свободной поверхности потока
[ ГОСТ 26966-86]
водослив
Гидротехническое сооружение в виде препятствия или горизонтального стеснения, через которое происходит перелив воды.
[СО 34.21.308-2005]
водослив
Водосброс, в котором пропуск воды осуществляется со свободной поверхностью потока через гребень преграды
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
гидрометрический водослив
Гидрологический расходомер, представляющий собой порог или перегораживающий русло стенку с вырезом - определенной формы для истечения воды.
[ ГОСТ 19179-73]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
перегрузка
Условия появления сверхтока в электрически не поврежденной цепи.
МЭК 60050(441-11-08).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
перегрузка
Условия оперирования в электрически неповреждённой цепи, которые вызывают сверхток.
В электрических цепях электроустановки здания могут возникать сверхтоки при отсутствии в них электрических повреждений. Причиной появления этих сверхтоков является перегрузка электрических цепей. Перегрузка характеризуется током перегрузки, который превышает номинальный ток электрической цепи и допустимые длительные токи её проводников. Длительная перегрузка проводников может вызвать их сильный нагрев и стать причиной пожара в здании. Поэтому в электроустановках зданий выполняют защиту от перегрузок с помощью устройств защиты от сверхтока. Перегрузки могут также возникать при переходных процессах в электрических цепях, например, при включении электрооборудования.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CF/view/46/]
перегрузка
Отношение время/электрический ток для цепи, в которой превышена максимальная допустимая нагрузка, когда цепь находится в исправном состоянии.
Примечание - Не следует использовать термин «перегрузка» как синоним термина «сверхток».
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
перегрузка (цепи)
Времятоковая зависимость для цепи, в которой превышена максимальная нагрузка, когда цепь находится в исправном состоянии.
Примечание
Не следует использовать термин «перегрузка» как синоним сверхтока.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
перегрузка
Превышение фактического значения мощности или тока электротехнического изделия (устройства) над номинальным значением.
Примечание. Допускается с введением соответствующего пояснения оценивать перегрузку полным значением параметра, превышающим номинальное значение.
[ ГОСТ 18311-80]
перегрузка
-
[IEV number 314-02-09]EN
overload
operating conditions in an electrically undamaged circuit which cause an over-current.
[IEC 60947-1, ed. 5.0 (2007-06)]
overload, noun
excess of the actual load over the full load, expressed by their difference
Source: 151-15-16
[IEV number 151-15-30]
overflow
condition which occurs when the numerical value of the output information exceeds the maximum possible value which can be displayed or represented
[IEV number 314-02-09]FR
surcharge
conditions de fonctionnement d’un circuit électriquement sain, qui provoquent une surintensité.
[IEC 60947-1, ed. 5.0 (2007-06)]
surcharge, f
excédent de la charge réelle sur la pleine charge, exprimé par leur différence
Source: 151-15-16
[IEV number 151-15-30]
débordement
condition de fonctionnement pour lequel la valeur numérique de l'information de sortie dépasse la possibilité maximale d'affichage ou de représentation de l'appareil
[IEV number 314-02-09]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
- OL
- overcharge
- overdrive
- overflow
- overload
- overload of a circuit
- overloading
- ovId
- surcharge load
- thermal overload situation
DE
FR
- débordement
- surcharge
- surcharge d’un circuit
слив
Часть пульпы, в которой содержание твердой фазы ниже, чем в исходном питании.
[ ГОСТ 17321-71]Тематики
EN
DE
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Úberlauf
49 Spannungswiederkehr
восстановление напряжения
Увеличение напряжения после его посадки, провала или исчезновения до значения, находящегося в допустимых пределах для установившегося режима работы системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ 23875-88]
восстановление напряжения в системе электроснабжения
Увеличение напряжения после его снижения или исчезновения до значения, находящегося в допустимых пределах для установившегося режима работы системы электроснабжения
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]EN
voltage recovery
the restoration of voltage to a value near to its previous value after a reduction, a collapse or a loss of voltage
[IEV number 604-01-24]FR
retour de la tension
remontée de la tension jusqu'à une valeur voisine de la valeur antérieure, après une baisse, un effondrement ou un manque de tension
[IEV number 604-01-24]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Смотри также
D. Spannungswiederkehr
E. Voltage recovery
F. Retour de la tension
Увеличение напряжения после его посадки, провала или исчезновения до значения, находящегося в допустимых пределах для установившегося режима работы системы электроснабжения
Источник: ГОСТ 23875-88: Качество электрической энергии. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Spannungswiederkehr
50 Ansprech-Rückfallzeit
время устойчивого замыкания (размыкания) контакта электрического реле
Интервал времени от момента достижения входной воздействующей величины электрического реле определенного значения до момента, когда цепь контакта электрического реле замкнется (разомкнется)
[ ГОСТ 16022-83]EN
time to stable closed condition
the time interval between the instant when a specified value of the input energizing quantity is applied and the instant when a contact is closed and fulfils specified requirements
[IEV number 446-17-24]
time to stable open condition
the time interval between the instant when a specified value of the input energizing quantity is applied and the instant when a contact is open and fulfils specified requirements
[IEV number 446-17-25]FR
temps de fermeture stable
temps écoulé entre l'instant d'application d'une valeur spécifiée de la grandeur d'alimentation d'entrée et l'instant où un circuit de contact est fermé et répond aux prescriptions spécifiées
[IEV number 446-17-24]
temps d'ouverture stable
temps écoulé entre l'instant d'application d'une valeur spécifiée de la grandeur d'alimentation d'entrée et l'instant où un circuit de contact est ouvert et répond aux prescriptions spécifiées
[IEV number 446-17-25]
Тематики
EN
DE
FR
136. Время устойчивого замыкания (размыкания) контакта электрического реле
D. Ansprech-Rückfallzeit
Е. Time to stable closed (open) condition
F. Temps de fermeture (d’ouverture) stable
Интервал времени от момента достижения входной воздействующей величины электрического реле определенного значения до момента, когда цепь контакта электрического реле замкнется (разомкнется)
Источник: ГОСТ 16022-83: Реле электрические. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Ansprech-Rückfallzeit
51 komplexer Kleinsignaleingangsleitwert
- входная полная проводимость биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
входная полная проводимость биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
Отношение изменений комплексных величин входного тока к вызванному им изменению напряжения на входе при коротком замыкании по переменному току на выходе.
Обозначение
y11
y11
Примечание
В схеме с общей базой или общим эмиттером добавляется индекс соответственно "б" или "э" для отечественных буквенных обозначений и "b" и "е" для международных обозначений.
[ ГОСТ 20003-74]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
- valeur de l'admittance d’entrée, sortie en court-circuit pour de petits signaux
21. Входная полная проводимость биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
D. Komplexer Kleinsignaleingangsleitwert
E. Small-signal value of the short-circuit input admittance
F. Valeur de l’admittance d’entrée, sortie en court-circuit pour de petits signaux
y*11
Отношение изменений комплексных величин входного тока к вызванному им изменению напряжения на входе при коротком замыкании по переменному току на выходе
Источник: ГОСТ 20003-74: Транзисторы биполярные. Термины, определения и буквенные обозначения параметров оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > komplexer Kleinsignaleingangsleitwert
52 Eingangsimpedanz
входное полное сопротивление
-
[IEV number 312-06-18]EN
input impedance
impedance of the input circuit measured between the input terminals under operating conditions
NOTE 1 – The impedance can be expressed in terms of admittance.
NOTE 2 – In certain instances, for example, sampling devices or self-balancing potentiometers, the impedance can be different according to the instant when it is determined, before, during or after the instant of measurement.
NOTE 3 – When the input circuit is such that the instantaneous value of the current flowing into the input terminals is a non-linear function of the instantaneous value of the input voltage under specified conditions of frequency and voltage, the combination of resistance and reactance which would absorb the same active power and in which would flow a reactive current equal to the fundamental component that is flowing in the actual input circuit, is sometimes called the "equivalent input impedance".
[IEV number 312-06-18]FR
impédance du circuit d'entrée
impédance du circuit d'entrée entre les bornes d'entrée dans les conditions de fonctionnement
NOTE 1 – L'impédance peut être exprimée en termes d'admittance.
NOTE 2 – Dans certains cas, par exemple les dispositifs d'échantillonnage ou les potentiomètres à rééquilibrage automatique, l'impédance peut être différente selon l’instant où elle est déterminée, avant, pendant ou après la mesure.
NOTE 3 – Lorsque le circuit d'entrée est tel que la valeur instantanée du courant traversant les bornes d'entrée est une fonction non linéaire de la valeur instantanée de la tension d'entrée dans des conditions spécifiées de fréquence et de tension, l'impédance d'une combinaison formée par une résistance et une réactance qui absorberaient la même puissance active et dans laquelle circulerait un courant réactif égal à la composante fondamentale qui circule dans le circuit d'entrée réel, est parfois appelée "impédance équivalente d'entrée".
[IEV number 312-06-18]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Eingangsimpedanz
53 oberer Heizwert
высшая теплота сгорания угля
Ндп. высшая теплотворная способность угля
калорийность топлива
Количество тепла, выделившееся при полном сгорании единицы массы угля в калориметрической бомбе в среде сжатого кислорода в установленных стандартом условиях.
Примечание. Остаточными продуктами являются газообразный кислород, азот, диоксид углерода, диоксид серы, вода в виде жидкости и зола.
[ ГОСТ 17070-87]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Обобщающие термины
- состав, свойства и анализ углей
EN
DE
FR
93. Высшая теплота сгорания угля
Ндп. Высшая теплотворная способность угля
D. Oberer Heizwert
Е. Gross calorific value
F. Pouvoir calorifique superieur
Количество тепла, выделившееся при полном сгорании единицы массы угля в калориметрической бомбе в среде сжатого кислорода в установленных стандартом условиях.
Примечание. Остаточными продуктами являются газообразный кислород, азот, диоксид углерода, диоксид серы, вода в виде жидкости и зола
Источник: ГОСТ 17070-87: Угли. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > oberer Heizwert
54 1. Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
- выходная полная проводимость биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
выходная полная проводимость биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
1. Отношение изменения выходного тока к вызвавшему его изменению выходного напряжения в режиме холостого хода входной цепи по переменному току.
Обозначение
h22
2. Отношение изменений комплексных величин выходного тока к вызванному им изменению выходного напряжения при коротком замыкании по переменному току на входе.
Обозначение
y22
Примечание
В схеме с общей базой или общим эмиттером добавляется индекс соответственно "б" или "э" для отечественных буквенных обозначений и "b" и "е" для международных обозначений.
[ ГОСТ 20003-74]Тематики
EN
- 1. small-signal value of the open-circuit output admittance
- 2. small-signal value of the short-circuit output admittance
DE
- 1. Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
- 2. komplexer Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
FR
- 1. valeur de l'admittance de sortie, entrée en circuit ouvert pour de petits signaux
- 2. valeur de l'admittance de sortie, entrée en court-circuit pour de petits signaux
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > 1. Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
55 2. komplexer Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
- выходная полная проводимость биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
выходная полная проводимость биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
1. Отношение изменения выходного тока к вызвавшему его изменению выходного напряжения в режиме холостого хода входной цепи по переменному току.
Обозначение
h22
2. Отношение изменений комплексных величин выходного тока к вызванному им изменению выходного напряжения при коротком замыкании по переменному току на входе.
Обозначение
y22
Примечание
В схеме с общей базой или общим эмиттером добавляется индекс соответственно "б" или "э" для отечественных буквенных обозначений и "b" и "е" для международных обозначений.
[ ГОСТ 20003-74]Тематики
EN
- 1. small-signal value of the open-circuit output admittance
- 2. small-signal value of the short-circuit output admittance
DE
- 1. Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
- 2. komplexer Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
FR
- 1. valeur de l'admittance de sortie, entrée en circuit ouvert pour de petits signaux
- 2. valeur de l'admittance de sortie, entrée en court-circuit pour de petits signaux
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > 2. komplexer Kleinsignalausgangsleitwert
56 Ausgangsimpedanz
выходное полное сопротивление
-
[IEV number 312-06-19]EN
output impedance
impedance of the output circuit measured between the output terminals under operating conditions
NOTE 1 – The impedance can be expressed in terms of admittance.
NOTE 2 – In certain instances, for example, sampling devices or self-balancing potentiometers, the impedance can be different according to the instant when it is determined, before, during or after the instant of measurement.
NOTE 3 – When the output circuit is such that the instantaneous value of the current flowing into the output terminals is a non-linear function of the instantaneous value of the output voltage under specified conditions of frequency and voltage, the combination of resistance and reactance which would absorb the same active power and in which would flow a reactive current equal to the fundamental component that is flowing in the actual output circuit, is sometimes called the "equivalent output impedance".
[IEV number 312-06-19]FR
impédance du circuit de sortie
impédance du circuit de sortie entre les bornes de sortie dans les conditions de fonctionnement
NOTE 1 – L'impédance peut être exprimée en termes d'admittance.
NOTE 2 – Dans certains cas, par exemple les dispositifs d'échantillonnage ou les potentiomètres à rééquilibrage automatique, l'impédance peut être différente selon l’instant où elle est déterminée, avant, pendant ou après la mesure.
NOTE 3 – Lorsque le circuit de sortie est tel que la valeur instantanée du courant traversant les bornes de sortie est une fonction non linéaire de la valeur instantanée de la tension de sortie dans des conditions spécifiées de fréquence et de tension, l'impédance d'une combinaison formée par une résistance et une réactance qui absorberaient la même puissance active et dans laquelle circulerait un courant réactif égal à la composante fondamentale qui circule dans le circuit de sortie réel, est parfois appelée "impédance équivalente de sortie".
[IEV number 312-06-19]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Ausgangsimpedanz
57 Spannungsänderungszeit
длительность изменения напряжения
Интервал времени от начала одиночного изменения напряжения до его конечного значения.
[ ГОСТ 13109-97]EN
duration of a voltage change
interval of time for the voltage to increase or decrease from the initial value to the final value
[IEV number 161-08-03]FR
durée d'une variation de tension
durée d'un intervalle de temps pendant lequel la tension croît ou décroît de sa valeur initiale avant une variation de tension à sa valeur finale
[IEV number 161-08-03]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Spannungsänderungszeit
58 Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
59 Strombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Strombelastbarkeit, f
60 Schutzimpedanz
защитный импеданс
Компонент, совокупность компонентов или комбинация основной изоляции и устройства, ограничивающего ток или напряжение, импеданс, конструкция и надежность которых таковы, что, будучи включенными между доступными токопроводящими частями и частями, опасными для жизни, они обеспечивают защиту в соответствии с требованиями настоящего стандарта при нормальных условиях и условиях единичной неисправности.
[ ГОСТ Р 52319-2005( МЭК 61010-1: 2001)]
защитный импеданс
Импеданс, включенный между токоведущими частями и доступными проводящими частями конструкций класса II; характеристики его должны быть такими, чтобы ток, проходящий в приборе при нормальной эксплуатации и при возможных повреждениях прибора, ограничивался безопасным значением.
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]EN
protective impedance
an impedance connected between live parts and exposed conductive parts, of such value that the current, in normal use and under likely fault conditions in the electronic switch, is limited to a safe value, and which is so constructed that the reliability is maintained throughout the life of the electronic switch
[IEV number 442-04-24]FR
impédance de protection
impédance connectée entre parties actives et masse, de valeur telle que le courant, en utilisation normale et dans des conditions possibles de panne de l'interrupteur électronique, soit limité à une valeur de sécurité, et qui est construite de façon telle que sa fiabilité soit maintenue au cours de la durée de vie de l'interrupteur électronique
[IEV number 442-04-24]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Schutzimpedanz
СтраницыСм. также в других словарях:
value — val·ue 1 / val yü/ n 1 a: a fair return or equivalent in goods, services, or money for something exchanged received good value for the price b: valuable consideration at consideration … Law dictionary
Value — Val ue, n. [OF. value, fr. valoir, p. p. valu, to be worth, fr. L. valere to be strong, to be worth. See {Valiant}.] 1. The property or aggregate properties of a thing by which it is rendered useful or desirable, or the degree of such property or … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
Value — may refer to: *Value (mathematics), the value of a variable in mathematics. *Value (philosophy), the degree of importance, including the value independent on subjective valuations by any individual *Value (personal and cultural), the principles,… … Wikipedia
Value — Val ue, v. t. [imp. & p. p. {Valued}; p. pr. & vb. n. {Valuing}.] [1913 Webster] 1. To estimate the value, or worth, of; to rate at a certain price; to appraise; to reckon with respect to number, power, importance, etc. [1913 Webster] The mind… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
value — [val′yo͞o] n. [ME < OFr, fem. of valu, pp. of valoir, to be strong, be worth < L valere < IE base * wal , to be strong > WIELD] 1. a fair or proper equivalent in money, commodities, etc., esp. for something sold or exchanged; fair… … English World dictionary
value — [valy] n. f. ÉTYM. V. 1180; archaïque depuis le XVIe (encore au XVIIIe, J. B. Rousseau in Littré); p. p. substantivé de valoir, remplacé par valeur, sauf dans plus value et moins value. ❖ ♦ Vx. Rapport, valeur. ❖ COMP … Encyclopédie Universelle
value — n *worth Analogous words: *price, charge, cost, expense: *importance, consequence, significance, weight: *use, usefulness, utility value vb 1 * … New Dictionary of Synonyms
value — [n1] financial worth amount, appraisal, assessment, charge, cost, equivalent, expense, market price, monetary worth, price, profit, rate; concepts 335,336 value [n2] advantage, worth account, bearing, benefit, caliber, condition, connotation,… … New thesaurus
value — ► NOUN 1) the regard that something is held to deserve; importance or worth. 2) material or monetary worth. 3) (values) principles or standards of behaviour. 4) the numerical amount denoted by an algebraic term; a magnitude, quantity, or number.… … English terms dictionary
Value — [engl.], Wert … Universal-Lexikon
value — / value judgments Ценность … Вестминстерский словарь теологических терминов
Перевод: с немецкого на русский
с русского на немецкий- С русского на:
- Немецкий
- С немецкого на:
- Все языки
- Английский
- Вьетнамский
- Русский
- Французский
