-
61 Vad
1) Компьютерная техника: Value Added Dealer2) Медицина: vincristine adriblastine dexamethasone, (Ventricular assist device) Желудочковый аппарат вспомогательного кровообращения (Кардиология), дефицит витамина А3) Военный термин: Voluntary Aide Detachment, Volunteer Army Department, Vulcan air defense, velocity and azimuth display, voluntary ambulance detachment4) Техника: vapor-phase axial deposition, velocity-azimuth display, vertical-air-discharge, voice activity detector, алюминий вакуумного напыления ( на плёнки) (vacuum deposited aluminum)5) Оптика: vapor axial deposition6) Сокращение: Vehicule d'Appui Direct (Direct support vehicle (France)), Velocity / Azimuth Display, Voluntary Aid Detachment, Vulnerability Assessment Device7) Физиология: Ventricular Access Device, Vertebral Artery Dissection, Vitamin A Deficiency8) Электроника: Vertical Axial Deposition9) Вычислительная техника: Value Added Driver, Visual Application Designer, voice activity detection, voltmeter with analog-to-digital converter, Voice Activity Detection (GSM, Mobile-Systems)10) Транспорт: Vintage Aircraft Division11) Сетевые технологии: value-added distributor12) Полимеры: vertical air discharge13) Кабельные производство: vapour phase axial deposition -
62 driver
1) возбудитель; запускающее устройство; задающее устройство3) рлк подмодулятор5) вчт драйвер8) инструмент для завинчивания или вывинчивания (напр. отвёртка)•- bias driver
- blocking-oscillator driver
- bootstrap driver
- bubble memory driver
- bus driver
- clock driver
- current driver
- device driver
- disk driver
- display driver
- dongle driver
- extended packet driver
- file system driver
- frame driver
- graphics device driver
- line driver
- memory driver
- modulator driver
- mouse driver
- open-collector driver
- packet driver
- printer driver
- pulse driver
- relay driver
- sweep driver
- tape punch driver
- teletype driver
- test driver
- three-phase driver
- time sharing driver
- TWAIN driver
- two-phase driver
- user-written driver
- virtual device driver
- WIA driver -
63 driver
1) возбудитель; запускающее устройство; задающее устройство3) рлк. подмодулятор5) вчт. драйвер8) инструмент для завинчивания или вывинчивания (напр. отвёртка)•- bias driver
- blocking-oscillator driver
- bootstrap driver
- bubble memory driver
- bus driver
- clock driver
- current driver
- device driver
- disk driver
- display driver
- dongle driver
- extended packet driver
- file system driver
- frame driver
- graphics device driver
- line driver
- memory driver
- modulator driver
- mouse driver
- open-collector driver
- packet driver
- printer driver
- pulse driver
- relay driver
- sweep driver
- tape punch driver
- teletype driver
- test driver
- three-phase driver
- time sharing driver
- TWAIN driver
- two-phase driver
- user-written driver
- virtual device driver
- WIA driverThe New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > driver
-
64 circuit
1) схема; цепь; контур2) эл. сеть4) шлейф ( в телефонии)•to track circuits — сопрягать контуры-
in-line hydraulic circuit
-
tee-test hydraulic circuit
-
absorption circuit
-
ac circuit
-
active circuit
-
adapter circuit
-
adder circuit
-
addressing circuit
-
aerial circuit
-
aerodrome circuit
-
aerodrome taxi circuit
-
aerodrome traffic circuit
-
aeromagnetic circuit
-
alarm circuit
-
alive circuit
-
amplifying circuit
-
analogous circuit
-
analog circuit
-
ancillary circuit
-
AND circuit
-
AND-to-OR circuit
-
AND-OR circuit
-
anticoincidence circuit
-
antihunt circuit
-
antireciprocal circuit
-
antiresonance circuit
-
antiresonant circuit
-
aperiodic circuit
-
approach circuit
-
astable circuit
-
autodyne circuit
-
automatic frequency control circuit
-
automatic reciprocation pneumatic circuit
-
auxiliary circuit
-
auxiliary coolant circuit
-
averaging circuit
-
back-to-back circuit
-
balanced circuit
-
balancing circuit
-
bias and erase circuit
-
bias circuit
-
bidirectional hydraulic motor circuit
-
bipolar circuit
-
bistable circuit
-
black-level restoring circuit
-
blanking circuit
-
blasting circuit
-
blocking circuit
-
booster hydraulic circuit
-
bound circuit
-
boxcar circuit
-
brake retraction circuit
-
branched circuit
-
branch circuit
-
breadboard circuit
-
break circuit
-
bridge circuit
-
bridged circuit
-
broken circuit
-
bubble circuit
-
bucket-brigade circuit
-
buffer circuit
-
burst-gating circuit
-
calibrating circuit
-
call circuit
-
carrier recovery circuit
-
cascode circuit
-
cavity circuit
-
charge circuit
-
charge-coupied device circuit
-
charging circuit
-
checkout circuit
-
cholesteric circuit
-
chopping circuit
-
chromatic circuit
-
circulating lubrication circuit
-
clamp circuit
-
cleaning circuit
-
clearing circuit
-
clipping circuit
-
clocked circuit
-
closed circuit
-
close circuit
-
closed loop circuit
-
closed loop hydraulic motor circuit
-
coaxial circuit
-
code track circuit
-
coincidence circuit
-
color-killer circuit
-
color-processing circuit
-
combination air-oil circuit
-
combinational circuit
-
common-base circuit
-
common-collector circuit
-
common-drain circuit
-
common-emitter circuit
-
common-gate circuit
-
common-source circuit
-
communication circuit
-
comparator circuit
-
compensating circuit
-
complementary circuit
-
completed circuit
-
composite circuit
-
condensate circuit
-
control circuit
-
convergence circuit
-
coolant circuit
-
cooling short circuit
-
cord circuit
-
correcting circuit
-
counter circuit
-
coupled circuits
-
cross rectifier circuit
-
crushing circuit
-
current circuit
-
current-feedback circuit
-
current-limiting circuit
-
current-limit circuit
-
damping circuit
-
Danington circuit
-
dc circuit
-
dead circuit
-
decision making circuit
-
decision circuit
-
decoding circuit
-
decoupling circuit
-
dedicated circuit
-
de-emphasis circuit
-
degaussing circuit
-
degenerative circuit
-
delay circuit
-
delta circuit
-
derived circuit
-
detecting circuit
-
detuned circuit
-
dial toll circuit
-
dial-up circuit
-
differentiating circuit
-
digital circuit
-
diplex circuit
-
direct circuit
-
direct speech circuit
-
discharge circuit
-
distributed-element circuit
-
dividing circuit
-
double-rail track circuit
-
drive circuit
-
driver circuit
-
dual circuit
-
dual-relief braking hydraulic motor circuit
-
duplex circuit
-
dynamic braking circuit
-
earthed circuit
-
earth circuit
-
edge-activated circuit
-
electric circuit
-
electrical safety circuit
-
electrolysis circuit
-
electronic circuit
-
emphasis circuit
-
enabling circuit
-
energized circuit
-
engineering circuit
-
enhancement circuit
-
equilization circuit
-
equivalent circuit
-
error correcting circuit
-
evaporating circuit
-
exciting circuit
-
exclusive OR circuit
-
exposure control circuit
-
exposure measuring circuit
-
external circuit
-
external load circuit
-
fallback circuit
-
feed circuit
-
feed motor circuit
-
feedback circuit
-
feedrate override circuit
-
filament circuit
-
filter hydraulic circuit
-
firing circuit
-
flip-flop circuit
-
flotation circuit
-
flow circuit
-
fluid circuit
-
forked circuit
-
four-terminal circuit
-
four-wire circuit
-
frame-scanning circuit
-
free-running circuit
-
frequency determining circuit
-
frequency-changing circuit
-
full-wave circuit
-
gain circuit
-
gas circuit
-
gate circuit
-
grinding circuit
-
ground short circuit
-
grounded circuit
-
ground circuit
-
half-duplex circuit
-
half-phantom circuit
-
half-wave circuit
-
half-wave track circuit
-
heat transport main circuit
-
heater circuit
-
holding circuit
-
horizontal scanning circuit
-
hotline circuit
-
hybrid-type circuit
-
hybrid circuit
-
hydraulic circuit
-
hydraulic servo circuit
-
identification circuit
-
idler circuit
-
ignition circuit
-
ignition primary circuit
-
ignition secondary circuit
-
impulse circuit
-
impulsing circuit
-
incoming track circuit
-
inductive circuit
-
inhibit circuit
-
input circuit
-
insulated circuit
-
integrated circuit
-
integrating circuit
-
intentional short circuit
-
interface circuit
-
interlocking circuit
-
interlock circuit
-
international television circuit
-
inverter circuit
-
invert circuit
-
iron circuit
-
jointless pulse track circuit
-
junction circuit
-
keep-alive circuit
-
ladder circuit
-
lagging circuit
-
latching circuit
-
LC circuit
-
leakage circuit
-
leak circuit
-
leased circuit
-
level circuit
-
linear circuit
-
linearizing circuit
-
line-scanning circuit
-
line-to-ground short circuit
-
live circuit
-
load circuit
-
locking circuit
-
locking hydraulic circuit
-
locking track circuit
-
logic circuit
-
long-distance transmission circuit
-
loop circuit
-
low-loss circuit
-
lumped-element lumped-parameter circuit
-
lumped lumped-parameter circuit
-
lumped-element circuit
-
lumped circuit
-
magnetic circuit
-
magnetic-core circuit
-
main circuit
-
majority circuit
-
make circuit
-
matching circuit
-
match circuit
-
matrix circuit
-
maximum power control circuit
-
measuring circuit
-
memory circuit
-
mesh circuit
-
metallic circuit
-
meter-current circuit
-
metering circuit
-
meter-voltage circuit
-
microelectronic circuit
-
microwave circuit
-
molecular circuit
-
monitoring circuit
-
monostable circuit
-
motor control circuit
-
multidrop circuit
-
multiplication circuit
-
multipoint circuit
-
multistable circuit
-
multistage circuit
-
muting circuit
-
NAND circuit
-
narrowband circuit
-
network circuit
-
neutral track circuit
-
neutralizing circuit
-
noise-balancing circuit
-
noninductive circuit
-
NOR circuit
-
NOT circuit
-
NOT-AND circuit
-
NOT-OR circuit
-
offset compensating circuit
-
one-pole circuit
-
one-rail track circuit
-
one-wire circuit
-
open circuit
-
open loop circuit
-
open-wire circuit
-
OR circuit
-
order wire circuit
-
OR-ELSE circuit
-
oscillating circuit
-
oscillation circuit
-
oscillatory circuit
-
output circuit
-
overflux circuit
-
overhead circuit
-
packaged circuit
-
paging circuit
-
parallel circuit
-
parallel-resonant circuit
-
parallel-series circuit
-
passive circuit
-
peak white-limiting circuit
-
peaking circuit
-
phantom circuit
-
phase switching circuit
-
phase-comparison circuit
-
phase-compensating circuit
-
phase-equalizing circuit
-
phase-inverting circuit
-
phase-sensitive track circuit
-
phase-shifting circuit
-
phase-shift circuit
-
pilot circuit
-
pneumatic circuit
-
points control circuit
-
points track circuit
-
point-to-point circuit
-
polarity circuit
-
polarized track circuit
-
polling circuit
-
polyphase circuit
-
potential circuit
-
power circuit
-
precharge circuit
-
precision timing circuit
-
pressure control hydraulic circuit
-
primary circuit
-
primary coolant circuit
-
printed circuit
-
protection circuit
-
pulse circuit
-
pulse-shaping circuit
-
pump unloading hydraulic circuit
-
pumping circuit
-
pump circuit
-
push-pull circuit
-
push-to-type circuit
-
quadruplex circuit
-
radiation-hardened circuit
-
radio communication circuit
-
radio circuit
-
RC circuit
-
reaction circuit
-
reaction track circuit
-
reactive circuit
-
reclosing circuit
-
rectification circuit
-
reference circuit
-
reflex circuit
-
regenerative circuit
-
register mark recognition circuit
-
regrinding circuit
-
regulating circuit
-
rejector circuit
-
relay circuit
-
relay contact switching circuit
-
relay contact circuit
-
remote-ring circuit
-
replenishing hydraulic motor circuit
-
reset circuit
-
resonance circuit
-
retaining circuit
-
return circuit
-
ring circuit
-
ringing circuit
-
route locking circuit
-
sample circuit
-
sample-and-hold circuit
-
sampler circuit
-
scaling circuit
-
scanning circuit
-
schematic circuit
-
screening circuit
-
secondary circuit
-
secondary coolant circuit
-
selecting circuit
-
selection circuit
-
self-bias circuit
-
self-checking circuit
-
self-holding circuit
-
self-test circuit
-
semiconductor circuit
-
separation circuit
-
sequencing circuit
-
series circuit
-
series-resonant circuit
-
series-tuned circuit
-
service circuit
-
shell circuit
-
shifting circuit
-
short circuit
-
shunt circuit
-
shutoff circuit
-
signal circuit
-
signaling circuit
-
simplex circuit
-
single-phase circuit
-
single-rail track circuit
-
single-wire circuit
-
slow-wave circuit
-
smoothing circuit
-
sneak circuit
-
solid-state circuit
-
solid circuit
-
spare circuit
-
speaker circuit
-
speed regulating circuit
-
squelch circuit
-
standby circuit
-
star-connected circuit
-
starting circuit
-
station conventional track circuit
-
steady energy track circuit
-
stripline circuit
-
strip circuit
-
subcarrier recovery circuit
-
subtransmission circuit
-
superconducting circuit
-
supply circuit
-
suppression circuit
-
sustained short circuit
-
sweep circuit
-
switched circuit
-
switching circuit
-
symbolic circuit
-
symmetrical circuit
-
symmetric circuit
-
synchronization circuit
-
synchronizing hydraulic circuit
-
synchronous circuit
-
table circuit
-
tank circuit
-
tap circuit
-
tapped circuit
-
T-circuit
-
telegraph circuit
-
telephone circuit
-
temperature stabilized circuit
-
tension sensing circuit
-
terminal circuit
-
test circuit
-
thickening circuit
-
three-phase circuit
-
threshold circuit
-
throttled circuit
-
through circuit
-
tilt kickout hydraulic circuit
-
time-base circuit
-
time-delay circuit
-
timer circuit
-
time-slot assigner circuit
-
timing circuit
-
toll circuit
-
tool selector circuit
-
toroidal magnetic circuit
-
touch sensing circuit
-
track circuit
-
train dispatching circuit
-
transient short circuit
-
transmission hydraulic circuit
-
trap circuit
-
tree circuit
-
triggering circuit
-
trigger circuit
-
trouble-detecting circuit
-
trunk circuit
-
tube circuit
-
tuned circuit
-
two-port circuit
-
two-state circuit
-
two-terminal circuit
-
two-wire circuit
-
unbalanced circuit
-
unidirectional hydraulic motor circuit
-
unipolar circuit
-
vertical-scanning circuit
-
virtual circuit
-
voltage-feedback circuit
-
warning circuit
-
white clip circuit
-
wideband circuit
-
wire circuit
-
wired AND circuit
-
wired circuit
-
wired OR circuit
-
wye-connected circuit
-
wye circuit
-
zero-lose circuit -
65 circuit
1) схема; цепь; контур2) канал; линия; тракт3) тлф. шлейф5) круговое движение, движение по окружности || совершать круговое движение, двигаться по окружности•- 2D circuit
- 3D circuit
- absorbing circuit
- absorption circuit
- ac circuit
- acceptor circuit
- adaptive logic circuit
- additive printed circuit
- adjustable threshold logic circuit
- aerial circuit
- alive circuit
- aluminium-gate MOS integrated circuit
- aluminum-gate MOS integrated circuit
- AM detecting circuit
- analog circuit
- ancillary circuit
- AND circuit
- anode circuit
- antenna circuit
- anticlutter circuit
- anticoincidence circuit
- antihunt circuit
- antijamming circuit
- anti-Karp circuit
- antiresonance circuit
- antiresonant circuit
- antisidetone circuit
- aperiodic circuit
- application-specific integrated circuit
- approved circuit
- array integrated circuit
- astable circuit
- autodyne circuit
- automatic start circuit
- averaging circuit
- azimuth-sweep circuit
- back-plate circuit
- back-to-back circuit
- balanced circuit
- base-line marker circuit
- basic circuit
- beta circuit
- beta feedback circuit
- bias circuit
- bidirectional clamping circuit
- bilateral circuit
- bipolar circuit
- bipolar integrated circuit
- bistable circuit
- bistable multivibrator circuit
- black stretch circuit
- black-level restoring circuit
- black-level setting circuit
- blanking circuit
- bootstrap circuit
- bound circuit
- boxcar circuit
- branch circuit
- branched circuit
- bridge circuit
- bridged circuit
- broken circuit
- bubble annihilation circuit
- bubble circuit
- bubble detection circuit
- bubble propagation circuit
- bubble replication circuit
- bubble stretching circuit
- bubble switching circuit
- bubble-domain annihilation circuit
- bubble-domain detection circuit
- bubble-domain propagation circuit
- bubble-domain replication circuit
- bubble-domain stretching circuit
- bubble-domain switching circuit
- bucket-brigade circuit
- buffer circuit
- building-out circuit
- built-up circuit
- bulk-effect integrated circuit
- butterfly circuit
- butterfly tank circuit
- calibrating circuit
- call circuit
- capacitive differentiator circuit
- capacitive oscillatory circuit
- cathode circuit
- central-battery circuit
- ceramic printed circuit
- charge-coupled device integrated circuit
- chemically deposited printed circuit
- chemically reduced printed circuit
- chemically-assembled integrated circuit
- chevron bubble propagation circuit
- chevron bubble-domain propagation circuit
- chip integrated circuit
- cholesteric circuit
- chopping circuit
- chrominance matrix circuit
- chrominance separation circuit
- chrominance take-off circuit
- circuit of graph
- clamping circuit
- clamp-on circuit
- clipping circuit
- clock circuit
- clocked circuit
- close-coupled circuits
- closed circuit
- closed magnetic circuit
- CMOS integrated circuit
- coaxial circuit
- coincidence circuit
- collector circuit
- collector-diffusion isolated integrated circuit
- color processing circuit
- color purity circuit
- color-balance circuit
- color-indexing circuit
- color-killer circuit
- Colpitts oscillatory circuit
- combinational circuit
- combinatorial circuit
- combiner circuit
- common-base circuit
- common-battery circuit
- common-cathode circuit
- common-collector circuit
- common-drain circuit
- common-emitter circuit
- common-gate circuit
- common-grid circuit
- common-source circuit
- common-use circuit
- compander circuit
- comparator circuit
- comparison circuit
- compatible circuit
- compensating circuit
- complementary circuit
- complementary MOS integrated circuit
- complementary symmetry circuit
- complementary symmetry MOS integrated circuit
- complementary-output circuit
- composite circuit
- compound circuit
- compression circuit
- computer circuits
- conference circuit
- consumer integrated circuit
- contiguous-disk bubble propagation circuit
- contiguous-disk bubble-domain propagation circuit
- control circuit
- controller circuit
- convergence circuit
- cord circuit
- core-diode circuit
- core-transistor circuit
- correction input circuit
- COSMOS circuit
- countdown circuits
- counter circuit
- counter timer circuit
- counting circuit
- coupled circuits
- cross-control circuit
- crossed-waveguide circuit
- crosspoint integrated circuit
- cryotron circuit
- cue circuit
- current-access bubble circuit
- current-feedback circuit
- current-limited circuit
- current-source equivalent circuit
- custom circuit
- customer-specific integrated circuit
- custom-wired integrated circuit
- cutoff circuit
- damping circuit
- dash circuit
- data circuit
- dc circuit
- dc restoration circuit
- dead-on-arrival integrated circuit
- decision circuit
- decision making circuit
- decoupling circuit
- dedicated integrated circuit
- deep-submicron integrated circuit
- degenerative circuit
- delay circuit
- delay-insensitive circuit
- delay-sensitive circuit
- delta circuit
- demultiplexing circuit
- deposited integrated circuit
- derived circuit
- despiker circuit
- despiking circuit
- detector circuit
- detuned circuit
- dial toll circuit
- dial-up circuit
- diamond circuit
- die integrated circuit
- dielectric isolated integrated circuit
- differential-frequency circuit
- differentiating circuit
- diffused-isolation integrated circuit
- digital circuit
- digital integrated circuit
- digital logic circuit
- diode array integrated circuit
- diode integrated circuit
- diode-coupled circuit
- diplex circuit
- direct international circuit
- direct transit international circuit
- direct-coupled circuit
- direct-wire circuit
- discharge circuit
- discrete circuit
- discrete-component circuit
- disjunction circuit
- distributed-element circuit
- divided circuit
- dividing circuit
- Doppler tracking circuit
- dot circuit
- double-coincidence circuit
- double-ended cord circuit
- double-ridge easitron circuit
- double-ridge Karp circuit
- double-sided circuit
- double-tuned circuit
- down-scaled integrated circuit
- driven circuit
- dry circuit
- dry-processed integrated circuit
- DTF circuit
- dual-in-line integrated circuit
- duplex circuit
- duplicated circuit
- dynamic-convergence circuit
- dynamic-focus circuit
- dynamic-track following circuit
- earth circuit
- earthed circuit
- E-beam litho circuit
- EC circuit
- Eccles-Jordan circuit
- EITHER-OR circuit
- electric circuit
- electronic circuit
- elevated-electrode integrated circuit
- embossed-foil printed circuit
- emitter-coupled circuit
- emitter-follower logic integrated circuit
- engineering circuit
- epitaxial circuit
- epitaxial passivated integrated circuit
- equalization circuit
- equivalent circuit
- equivalent integrated circuit
- etched printed circuit
- evaporated circuit
- exclusive OR circuit
- expanded-sweep circuit
- expander circuit
- external circuit
- external magnetic circuit
- extra LSI circuit
- face-down integrated circuit
- fail-safe circuit
- fallback circuit
- fan-in circuit
- fan-out circuit
- fast time-constant circuit
- feed circuit
- feedback circuit
- ferrite-diode circuit
- ferrite-transistor circuit
- ferroresonant circuit
- field-access bubble circuit
- field-programmable integrated circuit
- filament circuit
- film integrated circuit
- fine-line integrated circuit
- fine-pattern integrated circuit
- flat-pack integrated circuit
- flexible printed circuit
- flip-chip integrated circuit
- flip-flop circuit
- flux transfer circuit
- flywheel circuit
- forced coupled circuits
- forked circuit
- four-wire circuit
- frame-grounding circuit
- frame-scanning circuit
- free coupled circuits
- freely oscillating coupled circuits
- free-running circuit
- frequency-changing circuit
- full-wave circuit
- fully integrated circuit
- function circuit
- g equivalent circuit
- ganged circuits
- gate circuit
- gate equivalent circuit
- Giacoletto circuit
- Goto-pair circuit
- grid circuit
- grounded circuit
- grounded-base circuit
- grounded-collector circuit
- grounded-emitter circuit
- grounded-grid circuit
- ground-return circuit
- grouping circuit
- guard-ring isolated monolithic integrated circuit
- Gunn-effect circuit
- h equivalent circuit
- half-phantom circuit
- half-wave circuit
- Hamilton circuit
- hardened circuit
- Hartley oscillatory circuit
- Hazeltine neutralizing circuit
- head circuit
- heater circuit
- high-temperature superconductor integrated circuit
- holding circuit
- horizontal scanning circuit
- horizontal sync circuit
- horizontal-deflection circuit
- hotline circuit
- hybrid circuit
- hybrid integrated circuit
- hybrid pi equivalent circuit
- hybrid thin-film circuit
- hybrid thin-film integrated circuit
- hybrid-type circuit
- I2L circuit
- ideal-transformer equivalent circuit
- identification circuit
- idler circuit
- ignition circuit
- image circuit
- impulsing circuit
- inclusive NOR circuit
- inclusive OR circuit
- incoming circuit
- individually wired circuit
- inductance-capacitance coupling circuit
- inductive circuit
- inductive differentiator circuit
- inductive oscillatory circuit
- inductively coupled circuit
- injection circuit
- injection integrated circuit
- input circuit
- inquiry circuit
- insulated-substrate integrated circuit
- integrate-and-dump circuit
- integrated circuit
- integrated injection logic circuit
- integrated optical circuit
- integrating circuit
- interaction circuit
- interface circuit
- inter-integrated circuit
- interlock circuit
- intermediate-frequency circuit
- inverter circuit
- ion-implanted bubble propagation circuit
- ion-implanted bubble-domain propagation circuit
- ion-implanted MOS integrated circuit
- iron circuit
- isolated integrated injection logic circuit
- isolated-substrate solid circuit
- isoplanar integrated circuit
- isoplanar-based integrated circuit
- joint circuit
- joint denial circuit
- Josephson logic integrated circuit
- Josephson-junction logic integrated circuit
- junction circuit
- junction-isolation integrated circuit
- Karp circuit
- keep-alive circuit
- keying circuit
- killer circuit
- label circuit
- ladder circuit
- lagging circuit
- large-scale hybrid integration circuit
- large-scale integration circuit
- laser-configured application-specific integrated circuit
- latched circuit
- latching Boolean circuit
- latching circuit
- leak circuit
- leakage circuit
- leased circuit
- line circuit
- linear circuit
- linear integrated circuit
- line-scan circuit
- line-scanning circuit
- live circuit
- load circuit
- local circuit
- local-battery circuit
- locking circuit
- Loftin-White circuit
- logic circuit
- long-distance telephone circuit
- longitudinal circuit
- losser circuit
- low-energy circuit
- low-temperature superconductor integrated circuit
- L-section circuit
- lumped circuit
- lumped-constant circuit
- made-to-order circuit
- magnetic circuit
- magnetic convergence circuit
- magnetic integrated circuit
- magnetic-core circuit
- majority circuit
- master-slice integrated circuit
- matching circuit
- matrix circuit
- matrix integrated circuit
- McCulloh circuit
- medium-scale integration circuit
- memory circuit
- merged transistor logic integrated circuit
- Mesny circuit
- message circuit
- metal-dielectric-semiconductor integrated circuit
- metallic circuit
- metal-oxide-semiconductor integrated circuit
- metal-oxide-semiconductor large scale integration circuit
- meter-current circuit
- meter-voltage circuit
- microcomputer integrated circuit
- microelectronic integrated circuit
- microenergy logic circuit
- micrologic circuit
- micropower circuit
- microprinted circuit
- microprocessor integrated circuit
- microprocessor logic-support circuit
- microprogrammed circuit
- microwatt circuit
- microwave circuit
- microwave integrated circuit
- mix circuit
- mixing circuit
- molecular integrated circuit
- monobrid integrated circuit
- monolithic integrated circuit
- monolithic microwave integrated circuit
- monophase integrated circuit
- monostable circuit
- MOS integrated circuit
- MOS-on-sapphire integrated circuit
- MTL integrated circuit
- mu circuit
- mu feedback circuit
- multibrid integrated circuit
- multichip integrated circuit
- multidrop circuit
- multifunctional integrated circuit
- multilayer circuit
- multilevel-metallized integrated circuit
- multiphase integrated circuit
- multiplanar circuit
- multiple circuit
- multiple-chip circuit
- multiple-substrate solid circuit
- multipoint circuit
- multistable circuit
- multistage circuit
- muting circuit
- NAND circuit
- nanotube integrated circuit
- n-channel logic MOS integrated circuit
- negative OR circuit
- NEITHER-NOR circuit
- neutral magnetic circuit
- neutralizing circuit
- noise equivalent circuit
- noise suppression circuit
- nondisjunction circuit
- noninductive circuit
- nonlinear circuit
- nonphantomed circuits
- nonredundant circuit
- NOR circuit
- NOT circuit
- NOT-AND circuit
- NOT-OR circuit
- off-the-shelf circuit
- one-chip integrated circuit
- one-sided circuit
- one-wire circuit
- open circuit
- open magnetic circuit
- open-wire circuit
- optical integrated circuit
- optically coupled circuit
- optoelectronic integrated circuit
- optron integrated circuit
- OR circuit
- OR-ELSE circuit
- oscillator circuit
- oscillatory circuit
- output circuit
- overcoupled circuits
- overlap telling circuit
- oxide-isolated integrated circuit
- packaged circuit
- painted printed circuit
- parallel circuit
- parallel LCR circuit
- parallel-resonant circuit
- parallel-series circuit
- passivated integrated circuit
- p-channel logic MOS integrated circuit
- peak-holding circuit
- peaking circuit
- peak-riding clipping circuit
- perforated bubble propagation circuit
- perforated bubble-domain propagation circuit
- periodic circuit
- peripheral integrated circuit
- permalloy circuit
- permanent virtual circuit
- phantom circuit
- phase-advance circuit
- phase-comparison circuit
- phase-compensating circuit
- phase-delay circuit
- phase-equalizing circuit
- phase-inverting circuit
- phase-lag circuit
- phase-shift circuit
- photonic integrated circuit
- physical circuits
- physical equivalent circuit
- pi circuit
- pickax bubble propagation circuit
- pickax bubble-domain propagation circuit
- piezoelectric-crystal equivalent circuit
- pilot circuit
- planar integrated circuit
- planex integrated circuit
- plastic integrated circuit
- plastic-encapsulated integrated circuit
- plate circuit
- plated circuit
- plated printed circuit
- p-n junction isolated integrated circuit
- point-to-point circuit
- polar circuit
- polarized magnetic circuit
- polling circuit
- polymer integrated circuit
- polymer logic circuit
- polymer-based logic circuit
- polyphase circuit
- positioning circuit
- potentiometer circuit
- potted circuit
- power adder circuit
- preemphasis circuit
- presetting circuit
- primary circuit
- primary series circuit
- printed circuit
- printed wiring circuit
- printed-component circuit
- program circuit
- programmed interconnection pattern large-scale integration circuit
- propagation circuit
- proprietary integrated circuit
- pulse-actuated circuit
- pulse-shaping circuit
- pulsing circuit
- pump circuit
- pumping circuit
- purity circuit
- push-pull circuit
- push-push circuit
- push-to-talk circuit
- push-to-type circuit
- quadruplex circuit
- quasi-bistable circuit
- quasi-monostable circuit
- quenching circuit
- quiet-tuning circuit
- r equivalent circuit
- radiating circuit
- radiation hardened integrated circuit
- radio circuit
- radio communication circuit
- radio-frequency integrated circuit
- radio-receiving circuit
- radio-transmitting circuit
- range-marker circuit
- range-sweep circuit
- range-tracking circuit
- rapid single flux quantum circuit
- RC circuit
- RCG circuit
- RCTL circuit
- RDTL circuit
- reactance control circuit
- reaction circuit
- reactive circuit
- read-and-write circuit
- redundant circuit
- reflex circuit
- regenerative circuit
- rejector circuit
- repeat circuit
- reset circuit
- reset control circuit
- reshaping circuit
- resistance-capacitance circuit
- resistance-inductance circuit
- resistance-inductance-capacitance circuit
- resistor-capacitor-transistor logic circuit
- resistor-coupled transistor logic circuit
- resistor-diode-transistor logic circuit
- resistor-transistor logic circuit
- resonant circuit
- retroactive circuit
- reverberation-controlled gain circuit
- right-plane circuit
- ring circuit
- ring-and-bar circuit
- ringdown circuit
- ringing circuit
- RL circuit
- RLC circuit
- RSFQ circuit
- RTL circuit
- sample-and-hold circuit
- sampling circuit
- scaled integrated circuit
- scale-of-eight circuit
- scale-of-ten circuit
- scale-of-two circuit
- scaling circuit
- scanning circuit
- scrambler circuit
- screened circuit
- sealed circuit
- sealed-junction integration circuit
- selective circuit
- self-holding circuit
- self-repairing circuit
- self-saturating circuit
- semiconductor integrated circuit
- semiconductor-magnetic circuit
- semicustom integrated circuit
- separation circuit
- series circuit
- series RLC circuit
- series-peaking circuit
- series-resonant circuit
- service circuit
- short circuit
- shunt circuit
- shunt-peaking circuit
- shunt-series circuit
- side circuits
- sidetone suppression circuit
- signal circuit
- signal-processing circuit
- silent circuit
- silicon integrated circuit
- silicon-on-sapphire integrated circuit
- simple parallel circuit
- simplex circuit
- single-chip integrated circuit
- single-ended circuit
- single-mask level bubble circuit
- single-phase circuit
- single-ridge easitron circuit
- single-ridge Karp circuit
- single-shot trigger circuit
- single-trip trigger circuit
- single-tuned circuit
- single-wire circuit
- slave circuit
- sliding short circuit
- slow-wave circuit
- small outline integrated circuit
- small-scale integrated circuit
- smoothing circuit
- sneak circuit
- software circuit
- solid-state circuit
- spare circuit
- spark circuit
- speaker circuit
- sprayed printed circuit
- square-rooting circuit
- squaring circuit
- squelch circuit
- stacked circuit
- staggered circuits
- stamped printed circuit
- standard scale circuit
- star-connected circuit
- starting circuit
- start-stop circuit
- static-induction transistor integrated circuit
- stenode circuit
- stick circuit
- stopper circuit
- storage circuit
- straightforward circuit
- stripline circuit
- submicron integrated circuit
- subscriber line interface circuit
- subscriber-line audio-processing circuit
- superconducting tank circuit
- superimposed circuit
- superposed circuit
- supervising circuit
- support circuit
- sweep circuit
- switch virtual circuit
- switched circuit
- switching circuit
- sync separator circuit
- sync stretch circuit
- synchronous circuit
- T2L circuit
- talk-back circuit
- tank circuit
- tantalum thin-film circuit
- tap circuit
- tapped circuit
- tapped resonant circuit
- tapped-capacitor circuit
- tapped-capacitor resonant circuit
- tapped-coil circuit
- tapped-coil resonant circuit
- tapped-inductor circuit
- tapped-inductor resonant circuit
- T-bar bubble propagation circuit
- T-bar bubble-domain propagation circuit
- T-circuit
- telegraph circuit
- telephone circuit
- telling circuit
- terminating circuit
- Thevenin equivalent circuit
- thick-film circuit
- thin-film circuit
- three-dimensional circuit
- three-phase circuit
- threshold circuit
- through circuit
- tie-line circuit
- time-base circuit
- time-delay circuit
- toll-circuit
- totem-pole circuit
- transfer circuit
- transformer-coupled circuit
- transistor equivalent circuit
- transistor-transistor logic circuit
- traveling-wave-tube interaction circuit
- tributary circuit
- trigger circuit
- trunk circuit
- trunk terminating circuit
- trunk-junction circuit
- tse circuit
- TTL circuit
- tube circuit
- tube equivalent circuit
- tuned circuit
- tuning circuit
- twin-circuit
- twin-T circuit
- two-dimensional circuit
- two-state circuit
- two-way circuit
- two-wire circuit
- UHS integrated circuit
- ultra-audion circuit
- ultra-high-speed integrated circuit
- unbalanced circuit
- undefined function circuit
- underdamped circuit
- unilateral circuit
- unipolar integrated circuit
- universal cord circuit
- vacuum integrated circuit
- vacuum-deposited integrated circuit
- vapor-deposited printed circuit
- vertical deflection circuit
- vertical scanning circuit
- vertical sync circuit
- very high-speed integrated circuit
- very large-scale integration circuit
- V-groove isolated integrated injection logic circuit
- vibrating circuit
- video circuit
- virtual circuit
- voltage-feedback circuit
- voltage-source equivalent circuit
- wafer-on-scale integrated circuit
- warning circuit
- watch integrated circuit
- waveguide circuit
- waveguide short circuit
- weakly superconducting circuit
- weighting circuit
- welded electronic circuit
- white circuit
- wire circuit
- wired circuit
- wire-wrapped circuit
- writing circuit
- X-bar bubble propagation circuit
- X-bar bubble-domain propagation circuit
- XNOR circuit
- XOR circuit
- X-ray litho integrated circuit
- y equivalent circuit
- Y-bar bubble propagation circuit
- Y-bar bubble-domain propagation circuit
- Y-connected circuit
- z equivalent circuit
- zig-zag asymmetrical permalloy-wedges circuit
- zigzag permalloy track circuitThe New English-Russian Dictionary of Radio-electronics > circuit
-
66 busbar
сборная шина
Шина, к которой могут быть присоединены одна или несколько распределительных шин и/или блоков ввода или вывода.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439.1-2013]
сборные шины
Система проводников, соединяемых с блоком ввода и предназначенных для присоединения к ним фазных, нулевых защитных РЕ и нулевых рабочих N проводников нескольких распределительных и групповых электрических цепей.
Примечание — Термин «шина» не определяет ее конструкцию
[ ГОСТ Р 51732-2001]
главная шина
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
main busbar
busbar to which one or several distribution busbars and/or incoming and outgoing units can be connected
[IEC 61439-1, ed. 2.0 (2011-08)]FR
jeu de barres principal
jeu de barres auquel un ou plusieurs jeux de barres de distribution et/ou des unités d'arrivée et de départ peuvent être raccordés
[IEC 61439-1, ed. 2.0 (2011-08)]
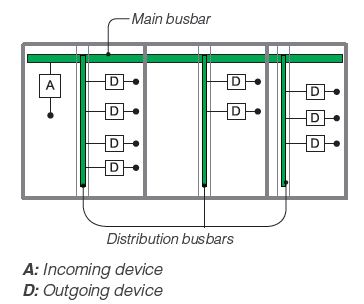
Рис. Legrand1 - Сборная шина
2 - Распределительные шины
Рис. Schneider Electric:Main busbar - Сборная шина
Distribution busbars - Распределительные шины
A: Incoming device - А: Аппарат ввода
D: Outgoing device - D: Аппарат выводаТематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
EN
FR
система шин
Комплект элементов, связывающих между собой все присоединения электрического распределительного устройства.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]EN
busbars (commonly called busbar)
in a substation, the busbar assembly necessary to make a common connection for several circuits
Example: three busbars for a three-phase system.
[IEV number 605-02-02]FR
jeu de barres (omnibus)
dans un poste, ensemble des barres omnibus nécessaires pour connecter des circuits
Exemple: trois barres pour un réseau triphasé.
[IEV number 605-02-02]Различают следующие системы:
-
одиночная система шин:
- одиночная несекционированная система шин;
- одиночная секционированная система шин;
-
двойная система шин
-
полуторная система шин
-
обходная система шин
- несекционированная система шин
-
секционированная система шин
- рабочая система шин
- резервная система шин
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
шина
Проводник с низким сопротивлением, к которому можно подсоединить несколько отдельных электрических цепей.
Примечание — Термин «шина» не включает в себя геометрическую форму, габариты или размеры проводника.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439.1-2013]
шина
Конструктивный элемент низковольтного комплектного устройства (НКУ).
Такой конструктивный элемент предназначен для того, чтобы к нему можно было легко присоединить отдельные электрические цепи (другие шины, отдельные проводники). Такие шины могут иметь различную конструкцию, геометрическую форму и размеры.
[Интент]
шинопроводшина
Медная, алюминиевая, реже стальная полоса, служащая для присоединения кабелей электрогенераторов, трансформаторов и т.д. к проводам питающей сети
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
общаяшина
-
[IEV number 151-12-30]
шина
-
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]EN
busbar
low-impedance conductor to which several electric circuits can be connected at separate points
NOTE – In many cases, the busbar consists of a bar.
[IEV number 151-12-30]
busbar
An electrical conductor that makes a common connection between several circuits. Sometimes, electrical wire cannot accommodate high-current applications, and electricity must be conducted using a more substantial busbar — a thick bar of solid metal (usually copper or aluminum). Busbars are uninsulated, but are physically supported by insulators. They are used in electrical substations to connect incoming and outgoing transmission lines and transformers; in a power plant to connect the generator and the main transformers; in industry, to feed large amounts of electricity to equipment used in the aluminum smelting process, for example, or to distribute electricity in large buildings
[ABB. Glossary of technical terms. 2010]FR
barre omnibus, f
conducteur de faible impédance auquel peuvent être reliés plusieurs circuits électriques en des points séparés
NOTE – Dans de nombreux cas, une barre omnibus est constituée d’une barre.
[IEV number 151-12-30]
2. Проводник прямоугольного сечения из меди, предназначенный для электротехнических целей
(см. ГОСТ 434-78).
Поставляется в бухтах, а также в полосах длиной не менее 2,5 м; По существу, это просто проволока прямоугольного сечения. В указанном ГОСТе и в технической документации, в которой она применяется, обязательно указываются размеры этой проволоки. Например, "Шина ШММ 8,00х40,00 ГОСТ 434-78"
шина
Пруток прямоугольного сечения, применяемый в электротехнике в качестве проводника тока, изготовляемый прессованием или волочением.
[ ГОСТ 25501-82]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- заготовки и полуфабрикаты в металлургии
- кабели, провода...
Действия
- расположение шин «на ребро» [ПУЭ]
- расположение шин «плашмя» [ПУЭ]
Сопутствующие термины
- гибкая шина
- жесткая шина [ПУЭ]
- изолированные шины [ПУЭ]
- круглые шины [ПУЭ]
- неизолированные шины [ПУЭ]
- обходные шины [ПУЭ]
- профильные шины [ПУЭ]
- секционные шины [ПУЭ]
- фазная шина [ ГОСТ Р 51321.1-2000]
- четырехполосные шины с расположением полос по сторонам квадрата ("полый пакет") [ПУЭ]
- шина PEN-проводника
- шина для присоединения защитных проводников
- шина нулевого защитного проводника
- шина фазы А (B, C) [ПУЭ]
- шины однофазного тока [ПУЭ]
- шины прямоугольного (круглого, трубчатого, коробчатого) сечения [ПУЭ]
- шины трехфазного тока [ПУЭ]
EN
DE
FR
система сборных шин
шинопровод
Устройство, представляющее собой систему проводников, состоящее из шин, установленных на опорах из изоляционного материала или в каналах, коробах или подобных оболочках, и прошедшее типовые испытания.
Устройство может состоять из следующих элементов:
- прямые секции с узлами ответвления или без них;
- секции для изменения положения фаз, разветвления, поворота, а также вводные и переходные;
- секции ответвленные.
Примечание — Термин «шинопровод» не определяет геометрическую форму, габариты и размеры проводников.
(МЭС 441-12-07, с изменением)
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод до 1 кВ заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями.
[ПУЭ]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод напряжением до 1000 В заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями.
[ОСТ 36-115-85]
шинопровод
Жесткий токопровод напряжением до 1 кВ, предназначенный для передачи и распределения электроэнергии, состоящий из неизолированных или изолированных проводников (шин) и относящихся к ним изоляторов, защитных оболочек, ответвительных устройств, поддерживающих и опорных конструкций.
[ ГОСТ Р 53310-2012]EN
busway
A prefabricated assembly of standard lengths of busbars rigidly supported by solid insulation and enclosed in a sheet-metal housing.
[ http://www.answers.com/topic/busway]
busway
Busway is defined by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) as a prefabricated electrical distribution system consisting of bus bars in a protective enclosure, including straight lengths, fittings, devices, and accessories. Busway includes bus bars, an insulating and/or support material, and a housing.
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]1.1. Шинопроводы по назначению подразделяются на:
- распределительные, предназначенные для распределения электрической энергии;
- магистральные, предназначенные для передачи электрической энергии от источника к месту распределения (распределительным пунктам, распределительным шинопроводам) или мощным приемникам электрической энергии.
1.2. По конструктивному исполнению шинопроводы подразделяются на:
- трехфазные;
- трехфазные с нулевым рабочим проводником;
- трехфазные с нулевым рабочим и нулевым защитным проводником.
2. Основные параметры и размеры
2.1. Основные элементы шинопроводов
2.1.1. Основными элементами распределительных шинопроводов являются:а) прямые секции - для прямолинейных участков линии, имеющие места для присоединения одного или двух ответвительных устройств для секций длиной до 2 м включительно, двух, трех, четырех или более - для секций длиной 3 м;
б) прямые прогоночные секции - для прямолинейных участков линий, где присоединение ответвительных устройств не требуется;
в) угловые секции - для поворотов линии на 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
г) вводные секции или вводные коробки с коммутационной, защитной и коммутационной аппаратурой или без нее - для подвода питания к шинопроводам кабелем, проводами или шинопроводом;
д) переходные секции или устройства - для соединения двух шинопроводов на различные номинальные токи или шинопроводов разных конструкций;
е) ответвительные устройства (коробки, штепсели) - для разъемного присоединения приемников электрической энергии. Коробки должны выпускаться с разъединителем, с разъединителем и с предохранителями или с автоматическим выключателем;
з) присоединительные фланцы - для сочленения оболочек шинопроводов с оболочками щитов или шкафов;
и) торцовые крышки (заглушки) - для закрытия торцов крайних секций шинопровода;
к) устройства для крепления шинопроводов к элементам строительных конструкций зданий и сооружений;2.1.2. Основными элементами магистральных шинопроводов являются:
а) прямые секции - для прямолинейных участков линий;
б) угловые секции - для поворотов линий на 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
в) тройниковые секции - для разветвления в трех направлениях под углом 90° в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях;
г) подгоночные секции - для подгонки линии шинопроводов до необходимой длины;
д) разделительные секции с разъединителем - для секционирования магистральных линий шинопроводов;
е) компенсационные секции - для компенсации температурных изменений длины линии шинопроводов;
ж) переходные секции - для соединения шинопроводов на разные номинальные токи;
з) ответвительные устройства (секции, коробки) - для неразборного, разборного или разъемного присоединения распределительных пунктов, распределительных шинопроводов или приемников электрической энергии. Коробки должны выпускаться с разъединителем, с разъединителем и предохранителями или с автоматическим выключателем; секции могут выпускаться без указанных аппаратов;
и) присоединительные секции - для присоединения шинопроводов к комплектным трансформаторным подстанциям;
к) проходные секции - для прохода через стены и перекрытия;
л) набор деталей и материалов для изолирования мест соединения секций шинопроводов с изолированными шинами;
м) устройства для крепления шинопроводов к элементам строительных конструкций зданий и сооружений;
н) крышки (заглушки) торцовые и угловые для закрытия торцов концевых секций шинопровода и углов.
2.2.3. В зависимости от вида проводников токопроводы подразделяются на гибкие (при использовании проводов) и жесткие (при использовании жестких шин).
Жесткий токопровод до 1 кВ заводского изготовления, поставляемый комплектными секциями, называется шинопроводом.
В зависимости от назначения шинопроводы подразделяются на:- магистральные, предназначенные в основном для присоединения к ним распределительных шинопроводов и силовых распределительных пунктов, щитов и отдельных мощных электроприемников;
- распределительные, предназначенные в основном для присоединения к ним электроприемников;
- троллейные, предназначенные для питания передвижных электроприемников;
- осветительные, предназначенные для питания светильников и электроприемников небольшой мощности.
[ПУЭ, часть 2]
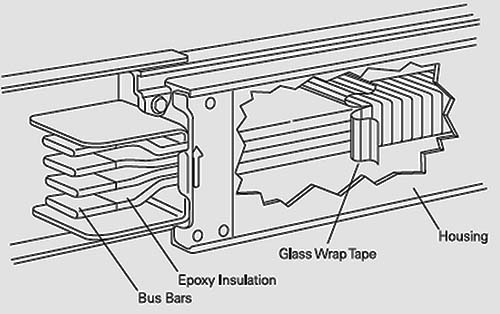
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]
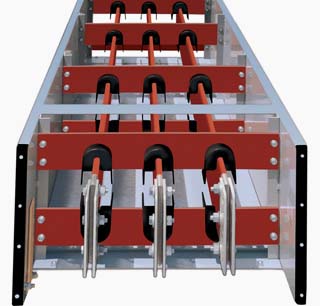
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/standards-and-applications-of-medium-voltage-bus-duct]
Конструкция шинопровода на среднее напряжениеПараллельные тексты EN-RU
A major advantage of busway is the ease in which busway sections are connected together.
Electrical power can be supplied to any area of a building by connecting standard lengths of busway.
It typically takes fewer man-hours to install or change a busway system than cable and conduit assemblies.Основное преимущество шинопровода заключается в легкости соединения его секций.
Соединяя эти стандартные секции можно легко снабдить электроэнергией любую часть здания.
Как правило, установить или изменить систему шинопроводов занимает гораздо меньше времени, чем выполнить аналогичные работы, применяя разводку кабелем в защитных трубах.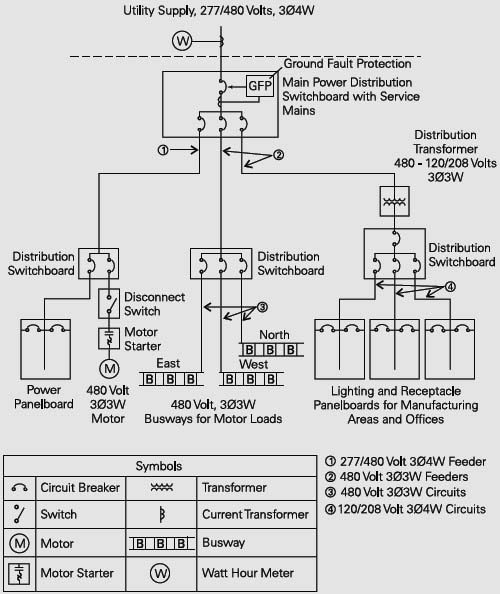
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]
The total distribution system frequently consists of a combination of busway and cable and conduit.
In this example power from the utility company is metered and enters the plant through a distribution switchboard.
The switchboard serves as the main disconnecting means.Как правило, распределение электроэнергии производится как через шинопроводы, так и через проложенные в защитных трубах кабели.
В данном примере поступающая от питающей сети электроэнергия измеряется на вводе в главное распределительный щит (ГРЩ).
ГРЩ является главным коммутационным устройством.
The feeder on the left feeds a distribution switchboard, which in turn feeds a panelboard and a 480 volt, three-phase, three-wire (3Ø3W) motor.
Распределительная цепь, изображенная слева, питает распределительный щит, который в свою очередь питает групповой щиток и электродвигатель.
Электродвигатель получает питание через трехфазную трехпроводную линию напряжением 480 В.The middle feeder feeds another switchboard, which divides the power into three, three-phase, three-wire circuits. Each circuit feeds a busway run to 480 volt motors.
Средняя (на чертеже) распределительная цепь питает другой распределительный щит, от которого электроэнергия распределяется через три трехфазные трехпроводные линии на шинопроводы.
Каждый шинопровод используется для питания электродвигателей напряжением 480 В.The feeder on the right supplies 120/208 volt power, through a step-down transformer, to lighting and receptacle panelboards.
Распределительная цепь, изображенная справа, питает напряжением 120/208 В через понижающий трансформатор щитки для отдельных групп светильников и штепсельных розеток.
Branch circuits from the lighting and receptacle panelboards supply power for lighting and outlets throughout the plant.
[ http://electrical-engineering-portal.com/siemens-busway-purpose-and-definition]Групповые электрические цепи, идущие от групповых щитков, предназначены для питания всех светильников и штепсельных розеток предприятия.
[Перевод Интент]Selection of the busbar trunking system based on voltage drop.
[Legrand]Выбор шинопровода по падению напряжения.
[Перевод Интент]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1)- Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Обобщающие термины
Близкие понятия
- электропроводки, выполненные шинопроводами
Действия
- выбор шинопровода по...
- крепление шинопровода к опорным конструкциям
- монтаж шинопроводов
- применение шинопроводов в пожароопасных зонах
- проектирование шинопровода
- прокладка шинопровода
Сопутствующие термины
- вертикальный участок шинопровода
- горизонтальный участок шинопровода
- прямой участок шинопровода
- устройства для крепления шинопроводов
- шинопровод переменного тока на 1600 А
- электрическая сеть, выполняемая шинопроводами
EN
DE
FR
3.1.31 сборная шина (busbar): Проводник с низким сопротивлением, к которому могут быть подсоединены несколько различных электрических цепей.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54828-2011: Комплектные распределительные устройства в металлической оболочке с элегазовой изоляцией (КРУЭ) на номинальные напряжения 110 кВ и выше. Общие технические условия оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > busbar
-
67 circuit
1) схема; цепь; контур2) линия3) канал4) сеть•- adapter circuit
- adjustment circuit
- alive circuit
- announcing circuit
- anode circuit
- antisidetone circuit
- asynchronous circuit
- automatic reset-data circuit
- automatic ringdown circuit
- automatic start circuit
- auxiliary circuit
- balanced circuit
- balanced-wire circuit
- balancing circuit
- band-switching circuit
- basic circuit
- black-level restoring circuit
- black-level stretch circuit
- bootstrap circuit
- branch circuit
- branched circuit
- bridge antisidetone circuit
- building-out circuit
- built-up circuit
- Buttler circuit
- bypass circuit
- cached circuit
- call circuit
- capacitor-coupled circuit
- capacitor-switched circuit
- capacitor-switching circuit
- central-battery circuit
- chain-type connection circuit
- character generator large-scale integration circuit
- charge-coupled device circuit
- check parity circuit
- checkout circuit
- chrominance matrix circuit
- chrominance separation circuit
- chrominance takeoff circuit
- clamp-on circuit
- closed circuit
- coarse phasing circuit
- coaxial circuit
- coincidence circuit
- color-balance circuit
- color-indexing circuit
- color-purity circuit
- combinational-circuit circuit
- combined-supply circuit
- common-base circuit
- common-battery circuit
- common-collector circuit
- common-drain circuit
- common-emitter circuit
- common-gate circuit
- common-source circuit
- common-user circuit
- communication circuit
- comparing circuit
- compensating antisidetone circuit
- complemental metal-oxide-semiconductor circuit
- composite circuit
- conductor-bundled static wire circuit
- conference circuit
- connecting circuit
- constant-closed circuit
- contactor-relay circuit
- continental circuit
- convergence circuit
- cord circuit
- correcting circuit
- Costas circuit
- counter-coupling circuit
- counting-down circuit
- coupled circuit
- cross-bus matrix circuit
- crossed-waveguide circuit
- cue circuit
- cutoff circuit
- Darlingtone circuit
- data circuit
- data-transmission circuit
- dc restoration circuit
- decoder circuit
- delay circuit
- demodulation circuit
- dial-up circuit
- diamond circuit
- differencing circuit
- differential-frequency circuit
- digital circuit
- digital-excitation circuit
- digital-leased circuit
- diode-clamping circuit
- diode-clipping circuit
- diode-stabilitron circuit
- direct international circuit
- direct-connection circuit
- direct-transit international circuit
- direct-wire circuit
- double half-wave circuit
- double-ended cord circuit
- double-loop circuit
- dual circuit
- earth circuit
- earthed circuit
- echo-absorption circuit
- edge derivation circuit
- electric circuit
- electronic circuit
- elementary circuit
- encoding circuit
- energized circuit
- engineering circuit
- equivalent circuit
- error-subtracting circuit
- external circuit
- fallback circuit
- feed circuit
- feedback circuit
- fiber-optic circuit
- fire-control circuit
- fixed-virtual circuit
- flexible circuit
- flexible-stage circuit
- flywheel circuit
- forked circuit
- four-wire circuit
- frame scanning circuit
- frequency-changing circuit
- frequency-protection circuit
- full-accessible circuit
- full-period allocated circuit
- functional-switching circuit
- gallium-arsenide integrated circuit
- gating circuit
- generating circuit
- Gilbert circuit
- Grets circuit
- grid circuit
- ground-return circuit
- grouping circuit
- half-bridge circuit
- half-wave circuit
- hardened circuit
- head circuit
- HF-correction circuit
- holding circuit
- horizontal deflection circuit
- hybrid circuit
- hypothetical reference circuit
- idle lighting limiting circuit
- inclined adjustment circuit
- incoming circuit
- independent circuit
- inductive circuit
- input circuit
- input-by-output matrix circuit
- inquiry circuit
- integrated circuit
- integrating circuit
- interchange circuit
- interface-integrated circuit
- interferenced circuit
- interferencing circuit
- international leased circuit
- interstage coupling circuit
- invertor circuit
- ISDN echo cancellation circuit
- isochronic circuit
- Jiakoletto circuit
- junction circuit
- Karp circuit
- keep-alive circuit
- key section power circuit
- killer circuit
- ladder circuit
- lamp circuit
- large-scale integration circuit
- latched circuit
- LCR circuit
- lead changeover circuit
- LF-correction circuit
- line circuit
- linear circuit
- link circuit
- live circuit
- local circuit
- lock-in circuit
- locking circuit
- lock-out circuit
- long circuit
- long-distance circuit
- longitudinal circuit
- loop circuit
- lossless resonant circuit
- L-shaped circuit
- magnetic convergence circuit
- main supply circuit
- make circuit
- Marx circuit
- match circuit
- matching circuit
- matrix circuit
- message circuit
- microelectronic circuit
- microphone supply circuit
- multidrop circuit
- multijunctor circuit
- multiloop circuit
- multipoint circuit
- muting circuit
- neodymium magnetic circuit
- neutral circuit
- neutralization circuit
- neutralizing circuit
- noise-rejecting circuit
- noise-suicide circuit
- nonlinear circuit
- NOT circuit
- on-call circuit
- open circuit
- optoelectronic integrated circuit
- OR circuit
- order wire circuits
- OR-ELSE circuit
- oscillating circuit
- oscillation circuit
- output circuit
- output voltage tracking circuit
- packaged circuit
- paging circuit
- parallel circuit
- partially accessible circuit
- peaking circuit
- periodic closed circuit
- phantom circuit
- phase comparating circuit
- phase compensating circuit
- phase-shift circuit
- phase-substitution circuit
- physical circuit
- pilot circuit
- pilot-make-busy circuit
- planar circuit
- point-to-point circuit
- polling circuit
- polyphase circuit
- power circuit
- power-supply circuit
- precision phasing circuit
- primary circuit
- printed circuit
- private leased circuit
- protection circuit
- pulse-phase control circuit
- push-to-talk circuit
- push-to-type circuit
- quenching circuit
- quiet-tuning circuit
- radial supply circuit
- radio circuit
- RC circuit
- reactance control circuit
- reading circuit
- rectification circuit
- reference circuit
- rejecting circuit
- relay cutout circuit
- remote control circuit
- remote-ring circuit
- repeat circuit
- reset circuit
- resonance circuit
- resonant circuit
- reverse circuit
- reverse diode circuit
- ring circuit
- ringing circuit
- sample-and-hold circuit
- scaling circuit
- Scott circuit
- secondary circuit
- section substitution circuit
- selecting circuit
- selective circuit
- self-locked circuit
- series circuit
- series-oscillating circuit
- series-parallel circuit
- series-peaking circuit
- series-tuned circuit
- shaping circuit
- shaved single frequency circuit
- short circuit
- shunt circuit
- shunting circuit
- shunt-peaking circuit
- side circuit
- signal circuit
- signal processing circuit
- signal recovery circuit
- single-current circuit
- single-ended push-pull circuit
- single-frequency resonance circuit
- single-phase bridge circuit
- single-phase circuit
- snap-acting circuit
- solving circuit
- sound-program circuit
- spark-safe circuit
- speech circuit
- speed regulating circuit
- squaring circuit
- stabilizer circuit
- stable circuit
- stage circuit
- stage control circuit
- standard cable circuit
- standard circuit
- standby circuit
- stenode circuit
- storage large-scale integration circuit
- storage locking circuit
- straightforward circuit
- strap magnetic circuit
- strip-line circuit
- super large scale integration circuit
- superimposed circuit
- superposed circuit
- supply circuit
- sweep circuit
- switched circuit
- switching circuit
- symistor control circuit
- synchronous circuit
- tail circuit
- talk-back circuit
- tandem data circuit
- tank circuit
- tapped magnetic circuit
- tapped stage circuit
- telecommunication circuit
- telecommunication-protection circuit
- telegraph circuit
- telegraph grade circuit
- telegraph signal generating circuit
- telephone circuit
- telephone signal generating circuit
- telesignaling receiving circuit
- telesignaling sending circuit
- television circuit
- terminal circuit
- test circuit
- testing circuit
- third circuit
- three-loop circuit
- three-phase input circuit
- three-wire circuit
- through circuit
- thyristor control circuit
- time protection circuit
- time-delay circuit
- time-interval protection circuit
- time-setting circuit
- timing circuit
- toll circuit
- touch sensing circuit
- touch tone dial circuit
- transformer substitution circuit
- transformer-coupled circuit
- transistor clipping circuit
- transistor collector circuit
- transistor control circuit
- transistor protection circuit
- tributary circuit
- triode clamp circuit
- trunk circuit
- T-shaped circuit
- tuned circuit
- twelve-pulse circuit
- two-frequency resonance circuit
- two-loop circuit
- two-wire-ground circuit
- uniform circuit
- unstable circuit
- untapped circuit
- untapped magnetic circuit
- U-shaped circuit
- variometer controlling circuit
- video circuit
- virtual circuit
- voice circuit
- voltage multiplying circuit
- voltage sensor circuit
- watching output circuit
- wideband circuit
- wire circuit
- wired circuitEnglish-Russian dictionary of telecommunications and their abbreviations > circuit
-
68 relay
1) реле3) ретрансляция; ретранслировать•- ac relay- accelerating relay
- active relay
- actuating relay
- air-borne radio relay
- all-or-nothing relay
- all-to-all relay
- amateur relay
- armature relay
- automating reclosing relay
- balanced relay
- bimetallic relay
- bimetallic strip relay
- blocking relay
- break-in relay
- burglar alarm device relay
- bypass relay
- calling relay
- capacitance relay
- cell relay
- center-zero relay
- clearing relay
- clock relay
- closing relay
- coaxial relay
- conductance relay
- connector relay
- corner relay
- current relay
- cut-in relay
- cut-off relay
- data-transmission relay
- dc relay
- delay relay
- differential relay
- digital relay
- directional relay
- disconnecting link relay
- distance relay
- double-pole relay
- double-wound relay
- dry-reed relay
- electric relay
- electromagnetic relay
- electromechanical relay
- electronic relay
- executive relay
- fast-release relay
- fast-speed relay
- flat-type relay
- frame relay
- frequency relay
- functional relay
- gas-filled relay
- group-selector relay
- guard relay
- heat relay
- homing relay
- impulse relay
- indicating relay
- indirect acting relay
- indirect action relay
- induction relay
- induction-disk relay
- inductive relay
- initiating relay
- instantaneous relay
- instrument-type relay
- interlock relay
- intermediate relay
- Kipp relay
- L-armature relay
- latch-in relay
- lock-up relay
- low-voltage relay
- magnetic locking relay
- marginal relay
- maximum-current relay
- metering relay
- meter-type relay
- microwave relay
- minimal relay
- network master relay
- neutral relay
- nonpolarized relay
- normally-closed relay
- normally-open relay
- no-voltage relay
- ohm relay
- optical-electronic relay
- output relay
- overload relay
- overpower relay
- overtemperature relay
- overvoltage relay
- peak relay
- phase relay
- phase-balance relay
- phase-comparison relay
- phase-sequence relay
- phase-shift relay
- phase-undervoltage relay
- photocell relay
- photoelectric relay
- phototube relay
- polarized relay
- polyphase relay
- positive sequence relay
- power relay
- primary relay
- programed-time relay
- protective relay
- pulse relay
- quick-operation relay
- radio relay
- ratio-balance relay
- reactance relay
- reclosing relay
- redundant relay
- reed relay
- register relay
- regulating relay
- reverse-current relay
- ringing relay
- rotary-stepping relay
- satellite relay
- SDI-relay
- SDV-relay
- secondary relay
- selective call relay
- self-reset relay
- shunt relay
- shutdown relay
- sidestable relay
- single-phase relay
- single-pole relay
- single-wound relay
- slow-acting relay
- slow-operate relay
- slow-release relay
- solenoid relay
- solid-state relay
- speed relay
- starting relay
- stepping relay
- storage relay
- switching relay
- switching-through relay
- synchronizing relay
- tape relay
- telephone relay
- terminal relay
- test relay
- thermionic relay
- three-phase relay
- thyratron relay
- time relay
- timing relay
- transistor relay
- trip-free relay
- trunk relay
- ultrafast relay
- undercurrent relay
- voltage relay
- wet-reed relay
- wholly-static relay
- zero-base sequence relayEnglish-Russian dictionary of telecommunications and their abbreviations > relay
-
69 terminal
- штуцер
- тупиковый склад
- тупиковое хранилище
- ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ СРЕДСТВА
- терминальный
- терминал (службы Игр «Сочи 2014»)
- терминал
- СОЕДИНИТЕЛЬ
- плата за погрузочно разгрузочные работы (pl.)
- перевалочная база для перегрузки материалов для бурения с одного вида транспорта на другой
- перевалочная база
- концевая кабельная муфта
- контактный зажим
- конечный пункт
- конечная станция на трубопроводе
- кабельный наконечник
- зажим (электрический)
- зажим
- Вывод электротехнического изделия (устройства)
- вывод химического источника тока
- вывод главной цепи автоматического выключателя
- вывод герметизированного магнитоуправляемого контакта
- вывод (предохранителя)
- вывод
- абонентский пункт
абонентский пункт
АП
Комплекс технических и программных средств, предназначенный для связи удаленного пользователя с ЭВМ или другим абонентским пунктом посредством каналов связи.
[ ГОСТ 24402-88]Тематики
Синонимы
- АП
EN
вывод
Проводящая часть аппарата, предназначенная для электрического соединения с внешними цепями.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
вывод
Часть выключателя с контактами, служащими для присоединения к выключателю проводников внешней цепи
[ ГОСТ Р 52565-2006]
вывод электротехнического изделия (устройства)
Ндп. клемма
Часть электротехнического изделия (устройства), предназначенная для электрического соединения его с другими изделиями (устройствами).
[ ГОСТ 18311-80]
вывод (трансформатора)
Токоведущая часть, предназначенная для присоединения обмотки к внешним проводникам
[ ГОСТ 30830-2002]
вывод
Точка электрической цепи, предназначенная для выполнения соединений с другой электрической цепью.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
вывод
-
[IEV number 151-12-12]EN
terminal
component provided for the connection of a device to external conductors.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
terminal
the conductive part of one pole, composed of one or more clamping unit(s) and insulation if necessary
[IEC 60669-1, ed. 3.0 (1998-02)]
terminal
conductive part of a device, electric circuit or electric network, provided for connecting that device, electric circuit or electric network to one or more external conductors
NOTE – The term "terminal" is also used for a connection point in circuit theory.
Source: see IEC 60050-131
[IEV number 151-12-12]FR
borne
composant destiné à raccorder un disjoncteur à des conducteurs extérieurs.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
borne
partie unipolaire conductrice composée d'un ou plusieurs organes de serrage, isolée si nécessaire
[IEC 60669-1, ed. 3.0 (1998-02)]
borne, f
partie conductrice d'un dispositif, d'un circuit électrique ou d'un réseau électrique, destinée à le connecter à un ou plusieurs conducteurs extérieurs
NOTE – Le terme "borne" désigne aussi un point de connexion en théorie des circuits.
Source: voir la CEI 60050-131
[IEV number 151-12-12]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- вывод, зажим электрический
Классификация
>>>Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
вывод
Токоведущая часть плавкого предохранителя, предназначенная для электрического присоединения к внешним цепям.
Примечание:
Выводы можно различить по роду цепи, для которой они предназначены (например, главный вывод, заземляющий вывод и т. п.), и по конструкции (например, резьбовой вывод, втычной вывод и т. п.).
[ ГОСТ Р 50339. 0-2003 ( МЭК 60269-1-98)]EN
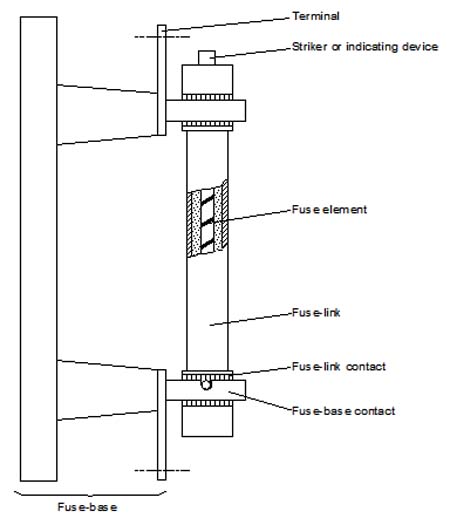
[IEC 60282-1, ed. 7.0 (2009-10)]FR
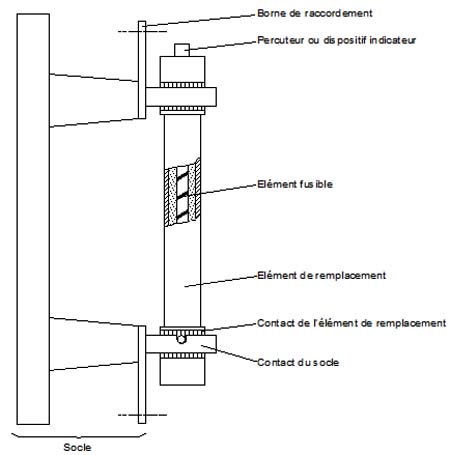
[IEC 60282-1, ed. 7.0 (2009-10)]Тематики
EN
FR
вывод герметизированного магнитоуправляемого контакта
Токоведущая деталь герметизированного магни-тоуправляемого контакта, не покрытая герметичной оболочкой и предназначенная для присоединения к внешней электрической цепи
[ ГОСТ 17499-82]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
вывод главной цепи автоматического выключателя
-
Рис. LS Industrial Systems1 - Вывод (зажим) главной цепи автоматического выключателя
Главный вывод автоматического выключателяИмпульсы прикладывают ко всем главным выводам, выводам цепей управления или вспомогательных цепей, независимо от того, содержат ли они электронные или обычные контакты.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030.4.1-2002 (МЭК 60947-4-1-2000)]
Выводы можно различить по роду цепи, для которой они предназначены (например, главный вывод, заземляющий вывод и т. п.), и по конструкции (например, резьбовой вывод, втычной вывод и т. п.).
[ ГОСТ Р 50339. 0-2003 ( МЭК 60269-1-98)]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
вывод химического источника тока
вывод
Часть химического источника тока, предназначенная для присоединения его к внешней электрической цепи.
[ ГОСТ 15596-82]EN
terminal
conductive part of a device, electric circuit or electric network, provided for connecting that device, electric circuit or electric network to one or more external conductors
Source: 151-12-12
[IEV number 482-02-22]FR
borne, f
partie conductrice d'un dispositif, d'un circuit électrique ou d'un réseau électrique, destinée à le connecter à un ou plusieurs conducteurs extérieurs
Source: 151-12-12
[IEV number 482-02-22]Тематики
Классификация
>>>Синонимы
EN
DE
- Anschlusspunkt, m
- Anschluß
- Anschluß der chemischen Stromquelle
- Klemme, f
- Pol, m
FR
- borne, f
1. Часть вывода электрического изделия, аппарата или устройства
зажим
Одна или несколько частей вывода, необходимые для механического крепления и электрического присоединения одного или нескольких проводников
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
зажим
Проводящая часть одного полюса, состоящая из одного или более зажимного устройства и изолированная, если необходимо.
[ ГОСТ Р 51324.1—2005 (МЭК 60669-1-2000)]
контактный зажим
-
[Интент]
зажим
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]EN
terminal
conductive part of a device provided for electrical connection to external circuits
[IEC 60947-1, ed. 5.0 (2007-06)]FR
borne
partie conductrice d'un appareil prévue pour le raccordement électrique à des circuits extérieurs
[IEC 60947-1, ed. 5.0 (2007-06)]Любое электрическое изделие, аппарат или устройство, будь то резистор, трансформатор, выключатель и т. п., имеет выводы, через которые осуществляется соединение с другими изделиями, аппаратами или устройствами. Соединение может быть неразборным (например, выполненное пайкой), разъемным (например, состоящим из вилки и розетки) и разборным. В последнем случае вывод оснащен зажимом, который служит для механического крепления и электрического присоединения одного или нескольких проводников.
[Интент]-
5.4.49. Напряжение на зажимах электродвигателей и в цепях управления ими при всех режимах работы электрооборудования крана должно быть не ниже 85% номинального. [ПУЭ]
- 6.2.15. В щитках без отключающего аппарата на вводе должны быть зажимы для присоединения проводников питающей цепи. [ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001]
-
6.3.1. В щитках должны быть предусмотрены следующие виды контактных зажимов (далее — зажимы) для присоединения внешних проводников:
-
вводные зажимы для присоединения фазных проводников питающей цепи (при отсутствии аппарата на вводе щитка);
-
зажимы для присоединения нулевых рабочих проводников N питающей и групповых цепей;
-
зажимы для присоединения нулевых защитных проводников РЕ или PEN-проводников питающей цепи и проводников РЕ групповых цепей.
[ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001]
-
вводные зажимы для присоединения фазных проводников питающей цепи (при отсутствии аппарата на вводе щитка);
-
Способ крепления проводов к зажимам должен обеспечивать надежный контакт, чтобы не возникало опасности ослабления соединения или чрезмерного нагрева. [ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61038-2001]
-
В некоторых случаях, например при ослаблении контакта в зажимах, недостаточном механическом давлении или при неправильном монтаже в соединениях, может выделяться большое количество теплоты, что также зависит от конструкции соединений и значения проходящего через них тока. [ ГОСТ 27924-88( МЭК 695-2-3-84)]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
There is a wide range of cable terminal solutions for 1,5 – 95mm² cables
[ABB]Контактные зажимы допускают присоединение кабелей сечением 1,5…95 мм2.
[Перевод Интент]
2. Отдельное устройство (приспособление) для механического крепления и электрического присоединения проводника или его экранирующей оплетки, например:

Рис. Phoenix Contact
Рис. Phoenix ContactНедопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- вывод, зажим электрический
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- binder
- binding post
- clamp
- clamp-type terminal
- cleat
- clip
- connecting terminal
- connection terminal
- connection terminal block
- dog
- ear
- electrical connection
- fixture
- grip
- jack
- mechanical lug
- post
- retaining clip
- staple
- terminal
- terminal clamp
- terminal point
FR
кабельный наконечник
Контакт-деталь, обеспечивающаяразъемноеразборноеконтактное соединение между проводом или жилой кабеля и выводом электротехнического устройства или контактным зажимом.
[ ГОСТ 23587-96]
наконечник
Часть, посредством которой проводник может быть соединен с управляющим устройством так, что его замена требует или применения специального инструмента или специального процесса, или специальной подготовки конца провода.
Примечание - Пайка требует специального инструмента. Сварка требует специального процесса. Закрепление наконечника на проводнике рассматривают как специальную подготовку провода.
[ГОСТ IЕС 60730-1-2011]EN
termination
part by which a conductor can be connected to a control in such a way that its replacement requires either a special purpose tool, a special process or a specially prepared end of the conductor
Note 1 to entry: Soldering requires a special purpose tool. Welding requires a special process. A cable lug attached to a conductor is a specially prepared end.
[IEC 60730-1, ed. 5.0 (2013-11)]FR
connexion
pièce permettant la connexion d'un conducteur à un dispositif de commande de telle manière que son remplacement nécessite un outil spécial, un procédé spécial ou une préparation spéciale de l'extrémité d'un conducteur
Note 1 à l'article: Le soudage à l'étain nécessite un outil spécial. Le soudage électrique est un procédé spécial. La pose d'une cosse sur l'extrémité d'un conducteur est considérée comme une préparation spéciale.
[IEC 60730-1, ed. 5.0 (2013-11)]
1 - Хвостовик кабельного наконечника;
2 - Зажимная часть
[ ГОСТ 7386-80]Наконечник кабельный медный, закрепляемый опрессовкой.
Кабельные наконечники должны изготавливаться из медных труб марки...
[ ГОСТ 7386-80]Тематики
EN
- anchoring base
- cable end
- cable grip
- cable lug
- cable shoe
- cable thimble
- compression lug
- conductor connector
- conductor contact
- connection lug
- connector
- crimp connection
- ferrule
- tag
- terminal
- terminal end
- terminal plug
- termination
- thimble
- wire end ferrule
- wire lug
- wiring terminal connector
FR
конечная станция на трубопроводе
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
контактный зажим
Часть светильника или его компонента, обеспечивающая электрическое соединение проводов.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60598-1-2026]Тематики
- лампы, светильники, приборы и комплексы световые
EN
концевая кабельная муфта
Муфта, предназначенная для подключения кабеля.
[Интент]
Тематики
Обобщающие термины
EN
перевалочная база для перегрузки материалов для бурения с одного вида транспорта на другой
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
плата за погрузочно разгрузочные работы (pl.)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
терминал
Устройство ввода-вывода, обеспечивающее взаимодействие пользователей в локальной вычислительной сети или с удаленной ЭВМ через средства телеобработки данных
[ ГОСТ 25868-91]
[ ГОСТ Р 50304-92 ]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
HMI port warning
[Schneider Electric]Предупредительное состояние об ошибке обмена данными через порт связи с терминалом оператора
[Перевод Интент]HMI display max current phase enable
[Schneider Electric]Разрешается отображение на терминале оператора максимального линейного тока
[Перевод Интент]Config via HMI keypad enable
[Schneider Electric]Конфигурирование (системы) с помощью клавиатуры терминала оператора
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
- оборуд. перифер. систем обраб. информации
- системы для сопряж. радиоэлектр. средств интерфейсные
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
терминал
Эксплуатационное предприятие, занимающееся техническим обслуживанием автобусов, обеспечивающее выпуск их на линию, укомплектованное штатом водителей, диспетчеров, ремонтных рабочих. Терминалы являются центральными или промежуточными пунктами, удовлетворяющими потребность в перевозке пассажиров.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]EN
terminal
Any location where freight and passengers either originates, terminates, or is handled in the transportation process. Terminals are central and intermediate locations in the movements of passengers and freight. They often require specific facilities to accommodate the traffic they handle.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]Тематики
EN
терминальный
терминал (оконечное абонентское устройство)
—
[ http://www.rfcmd.ru/glossword/1.8/index.php?a=index&d=4713]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
тупиковое хранилище
(напр. газа)
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
тупиковый склад
тупиковый резервуарный парк
тупиковый нефтяной склад
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
3.3 зажим (terminal): Проводящая часть одного полюса, состоящая из одного или более зажимного устройства и изолированная, если необходимо.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51324.1-2005: Выключатели для бытовых и аналогичных стационарных электрических установок. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
76. Вывод электротехнического изделия (устройства)
Terminal
Вывод
Ндп. Клемма
Часть электротехнического изделия (устройства), предназначенная для электрического соединения его с другими изделиями (устройствами)
Источник: ГОСТ 18311-80: Изделия электротехнические. Термины и определения основных понятий оригинал документа
3.13 контактный зажим (terminal): Проводящая часть одного полюса, состоящая из одного или более зажимного устройства и изолированная, если необходимо.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51322.1-2011: Соединители электрические штепсельные бытового и аналогичного назначения. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
3.80 штуцер (terminal): Фланцевое или подготовленное под сварку подсоединение к змеевику, обеспечивающее вход и выход среды.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53682-2009: Установки нагревательные для нефтеперерабатывающих заводов. Общие технические требования оригинал документа
4. ТЕХНИЧЕСКИЕ СРЕДСТВА
АП
Terminal
Комплекс технических и программных средств, предназначенный для связи удаленного пользователя с ЭВМ или другим абонентским пунктом посредством каналов связи
Источник: ГОСТ 24402-88: Телеобработка данных и вычислительные сети. Термины и определения оригинал документа
1.2.47 контактный зажим (terminal): Часть светильника или его компонента, обеспечивающая электрическое соединение проводов.
См. разделы 14 и 15.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60598-1-2011: Светильники. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
3.3.12 вывод (terminal): Токопроводящая часть аппарата, предназначенная для электрического соединения с внешними цепями.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 50345-2010: Аппаратура малогабаритная электрическая. Автоматические выключатели для защиты от сверхтоков бытового и аналогичного назначения. Часть 1. Автоматические выключатели для переменного тока оригинал документа
3.1.1 СОЕДИНИТЕЛЬ (TERMINAL): Компонент, обеспечивающий контакт устройства с внешним проводником (разъем, клемма и т.д.) (см. [1], позиция 151-01-03).
Примечание - СОЕДИНИТЕЛЬ может содержать один или несколько контактов, исполненных в виде углублений, штырей, элементов трубчатых соединений и т.д.
3.1.43 вывод (terminal): Место соединения элемента электрической цепи, электрической цепи или сети с другими элементами электрической цепи, электрическими цепями или сетями.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54828-2011: Комплектные распределительные устройства в металлической оболочке с элегазовой изоляцией (КРУЭ) на номинальные напряжения 110 кВ и выше. Общие технические условия оригинал документа
2.1.8 вывод (terminal): Токоведущая часть плавкого предохранителя, предназначенная для электрического присоединения к внешним цепям.
Примечание - Выводы различают по роду цепи, для которой они предназначены (например, главный вывод, заземляющий вывод и т.п.), и по конструкции (например, резьбовой вывод, вставной вывод и т.п.).
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60269-1-2010: Предохранители низковольтные плавкие. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > terminal
-
70 PDM
- широтно-импульсная модуляция
- фазоразностная модуляция
- управление данными об изделии
- поверхностная акустическая волна
- модуляция по длительности импульса
- модуль распределения питания
модуль распределения питания
-
[Интент]
Рис. APC
Модуль для подачи питания на трехфазную нагрузку

Рис. APC
Модуль для подачи питания на однофазные нагрузкиПараллельные тексты EN-RU
Factory assembled and tested Power Distribution Modules include circuit breaker, power cord, power connection, and circuit monitoring.
Собранные и проверенные на заводе-изготовиетеле модули распределения питания включают в себя автоматический выключатель, кабель, кабельную розетку и средства контроля состояния линии питания.
A variety of breaker and connector options can be chosen to supply either three-phase or single-phase power to the load.
Широкий выбор автоматических выключателей и кабельных розеток позволяет легко подобрать нужный модуль для подачи питания на трехфазные и однофазные нагрузки.
When demand rises and expansion becomes necessary, simply plug in new Power Distribution Modules. The factory-assembled modules, which include circuit breaker, power cord, and power connection, can be installed in mere minutes. There are multiple power ratings and power cord lengths for low to high power, guaranteeing compatibility and quick, easy, and convenient installation.
[APC]Когда потребляемая мощность увеличивается и необходимо расширение системы бесперебойного питания, то достаточно просто вставить новые модули распределения питания. Собранные на заводе-изготовителе модули, состоящие из автоматического выключателя, кабеля и кабельной розетки, можно установить за несколько минут. Модули поставляются на различные номинальные токи и с кабелями различной длины, что позволяет легко подобрать нужный модуль, быстро и без особого труда его установить.
[Перевод Интент]
How to install the PDM
Note: Some Power Distribution Units have filler plates installed. When a PDM is to be installed, the filler plate must be removed from the busbar.
1 Press down on the clip.
2 Pull out the plate from the unit. (Do not throw away the filler plate. Keep it for potential later use).3 Verify that all the breakers are in the OFF position.
4 Press the red button to release the latch.
5 Pull open the latch.Vertical Rack Distribution Panel
Horizontal Rack Distribution Panel
6 Feed the cable(s) up through the top opening in the enclosure and into the cable power troughs (if applicable) on top of enclosures.
How to install a PDM circuit breaker handle tie1 Locate the handle tie above the circuit breaker handles aligning the two tabs between the three handles.
2 Push the handle tie towards the circuit breaker handles until it snaps into position. Check to make sure that the handle tie is secure.
3 The handle tie can be removed by pulling it from the circuit breaker handles.Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- источники и системы электропитания
EN
модуляция по длительности импульса
широтно-импульсная модуляция
ШИМ
—
[Е.С.Алексеев, А.А.Мячев. Англо-русский толковый словарь по системотехнике ЭВМ. Москва 1993]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
управление данными об изделии
Системы PDM обобщают такие технологии, как:
EDM (engineering data management) - управление инженерными данными,
PIM (product information management) - управление информацией об изделии,
TDM (technical data management) - управление техническими данными,
TIM (technical information management) - управление технической информацией,
а также другие системы, которые используются для манипулирования информацией, всесторонне определяющей конкретное изделие. Короче говоря, любая информация, необходимая на том или ином этапе жизненного цикла изделия, может управляться системой PDM, которая предоставляет корректные данные всем пользователям и всем промышленным информационным системам по мере надобности. Наряду с данными, PDM управляет и проектом - процессом разработки изделия, контролируя собственно информацию об изделии - "продукте", о состоянии объектов данных, об утверждении вносимых изменений, осуществляя авторизацию и другие операции, которые влияют на данные об изделии и режимы доступа к ним каждого конкретного пользователя.
Таким образом, речь идет о полном, централизованном и постоянном автоматизированном контроле за всей совокупностью данных, описывающих как само изделие, так и процессы его конструирования, производства, эксплуатации и утилизации.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]Тематики
EN
фазоразностная модуляция
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
EN
широтно-импульсная модуляция
ШИМ
Последовательный сигнал, информативным в котором является ширина импульса при постоянной частоте следования.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]
широтно-импульсная модуляция
-
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
06.04.13 поверхностная акустическая волна [ surface acoustic wave; SAW]: Электроакустический эффект, используемый в системах автоматической идентификации, когда микроволновые радиосигналы малой мощности с помощью пьезоэлектрического кристалла в радиочастотной метке преобразуются в ультразвуковые поверхностные акустические волны.
Примечание - Информация об уникальной идентификации содержится в фазово-временных вариациях отраженного радиочастотной меткой сигнала.
<2>4 Сокращения
ARQ
Автоматический запрос повтора [Automatic Repeat Request]
ASK
Амплитудная манипуляция [Amplitude Shift Keying]
BPSK
Бинарная фазовая манипуляция [Binary Phase Shift Keying]
CDMA
Множественный доступ с кодовым разделением каналов [Code Division Multiple Access]
CSMA
Множественный доступ с анализом состояния канала передачи данных [Carrier Sense Multiple Access]
CSMA/CD
Множественный доступ с анализом состояния канала передачи данных и обнаружением конфликтов [Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection]
DBPSK
Дифференциальная бинарная фазовая манипуляция [Differential binary phase shift keying]
DSSS
Широкополосная модуляция с непосредственной передачей псевдослучайной последовательности [Direct sequence spread spectrum modulation]
EIRP (ЭИИМ)
Эквивалентная изотропно-излучаемая мощность [Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power]
EMI
Электромагнитная помеха [ElectroMagnetic Interference]
ETR
Технический отчет ETSI [European Telecommunications Report]
ETS
Телекоммуникационный стандарт ETSI [European Telecommunications Standard]
ETSI
Европейский институт по стандартизации в области телекоммуникаций [European Telecommunications Standards Institute]
FHSS
Широкополосная модуляция с дискретной перестройкой несущей частоты [Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum]
FSK
Частотная манипуляция [Frequency Shift Keying]
GHz (ГГц)
Гигагерц [Gigahertz]
GMSK
Минимальная гауссовская манипуляция [Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying]
kHz (кГц)
Килогерц [Kilohertz]
MSK
Минимальнофазовая частотная манипуляция [Minimum shift keying]
MHz (МГц)
Мегагерц [Megahertz]
OBE
Навесное оборудование [On-Board Equipment]
PDM
Модуляция импульса по длительности, широтно-импульсная модуляция [Pulse Duration Modulation]
PM
Фазовая модуляция [Phase modulation]
PPM (ФИМ)
Фазоимпульсная модуляция [Modulation (pulse position)]
PSK
Фазовая манипуляция [Phase Shift Keying]
PWM
Широтно-импульсная модуляция [Pulse Width Modulation]
RF/DC
Обмен данными системы радиочастотной идентификации [Radio frequency data communication]
RFI
Радиопомеха [Radio frequency interference]
RSSI
Индикатор уровня принимаемого сигнала [Receiving Signal Strength Indicator]
S/N
Отношение сигнала к шуму [Signal/noise ratio]
SAW
Поверхностная акустическая волна [Surface Acoustic Wave]
SIN AD
Отношение сигнала к шуму и искажению [Signal to Noise & Distortion]
SRD
Устройство малого радиуса действия [Short Range Device]
TBR
Технические основы регулирования [Technical Basis for Regulation]
TDD
Дуплексная связь с временным разделением каналов [Time Division Duplexing]
TDM
Временное разделение каналов [Time Division Multiplexing]
<2>Библиография
[1]
МЭК 60050-713
(IEC 60050-713)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Часть 713. Радиосвязь: приемники, передатчики, сети и их режим работы
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Part 713: Radiocommunications: transmitters, receivers, networks and operation)
[2]
МЭК 60050-705
(IEC 60050-705)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 705: Распространение радиоволн ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 705: Radio wave propagation)
[3]
МЭК 60050-702
(IEC 60050-702)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 702: Колебания, сигналы и соответствующие устройства
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 702: Oscillations, signals and related devices)
[4]
МЭК 60050-121
(IEC 60050-121)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 121: Электромагнетизм ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Part 121: Electromagnetism)
[5]
МЭК 60050-712
(IEC 60050-712)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 712: Антенны ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 712: Antennas)
[6]
МЭК 60050-221
(IEC 60050-221)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 221: Магнитные материалы и компоненты
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 221: Magnetic materials and components)
[7]
ИСО/МЭК 2382-9:1995
(ISO/IEC2382-9:1995)
Информационная технология. Словарь. Часть 9. Обмен данными ( Information technology - Vocabulary - Part 9: Data communication)
[8]
МЭК 60050-725
(IEC 60050-725)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 725: Космическая радиосвязь ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 725: Space radiocommunications)
[9]
МЭК 60050-714
(IEC 60050-714)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 714: Коммутация и сигнализация в электросвязи
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 714: Switching and signalling in telecommunications)
[10]
МЭК 60050-704
(IEC 60050-704)
Международный Электротехнический словарь. Глава 704. Техника передачи ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 704: Transmission)
[11]
МЭК 60050-161
(IEC 60050-161)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 161: Электромагнитная совместимость ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary. Chapter 161: Electromagnetic compatibility)
[12]
ИСО/МЭК 8824-1
(ISO/IEC 8824-1)
Информационные технологии. Абстрактная синтаксическая нотация версии один
(АСН.1). Часть 1. Спецификация основной нотации
(Information technology - Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1): Specification of basic notation)1)
[13]
ИСО/МЭК 9834-1
(ISO/IEC 9834-1)
Информационные технологии. Взаимосвязь открытых систем. Процедуры действий уполномоченных по регистрации ВОС. Часть 1. Общие процедуры и верхние дуги дерева идентификатора объекта АСН.1
( Information technology - Open Systems Interconnection - Procedures for the operation of OSI Registration Authorities: General procedures and top arcs of the ASN. 1 Object Identifier tree)
[14]
ИСО/МЭК 15962]
(ISO/IEC 15962)
Информационные технологии. Радиочастотная идентификация (RFID) для управления предметами. Протокол данных: правила кодирования данных и функции логической памяти
( Information technology - Radio frequency identification ( RFID) for item management - Data protocol: data encoding rules and logical memory functions)
[15]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-1
(ISO/IEC 19762-1)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 1. Общие термины в области АIDC ( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 1: General terms relating to AIDC)
[16]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-2
(ISO/IEC 19762-2)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 2. Оптические носители данных (ОНД)
( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 2: Optically readable media ( ORM))
[17]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-3
(ISO/IEC 19762-3)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 3. Радиочастотная идентификация (РЧИ)
( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 3: Radio frequency identification ( RFID))
[18]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-5
(ISO/IEC 19762-5)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 5. Системы определения места нахождения
( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 5: Locating systems)
[19]
ИСО/МЭК 18000-6
(ISO/IEC 18000-6)
Информационные технологии. Радиочастотная идентификация для управления предметами. Часть 6. Параметры радиоинтерфейса для диапазона частот 860 - 960 МГц ( Information technology - Radio frequency identification for item management - Part 6: Parameters for air interface communications at 860 MHz to 960 MHz)
_____________
1)В оригинале ИСО/МЭК 19762-4 стандарты [12] - [19] включены в раздел «Библиография», однако следует учитывать, что в основном тексте стандарта ссылок на них нет.
<2>
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 19762-4-2011: Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 4. Общие термины в области радиосвязи оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > PDM
-
71 control
1. регулирование, регулировка; управление; регулировать, управлять2. регулировочное устройство3. элементы системы управления4. автоматическое регулирование приводки5. устройство для автоматической регулировки приводки красок6. автоматическое регулирование боковой приводки7. устройство для автоматической регулировки боковой приводкиbackward-acting control — регулирование; регулировка
8. автоматическое регулирование натяжения9. устройство для регулировки натяжения10. регулирование приводки по окружности цилиндра11. устройство для регулировки приводки по окружности цилиндраclosed-loop control — замкнутый цикл контроля, контроль с обратной связью
12. контроль положения линии рубки; контроль положения линии поперечной резки13. автоматическое устройство, контролирующее положение изображения относительно линии рубкиdiaphragm control — номограмма, связывающая индекс диафрагмы с масштабом съёмки
14. управление экспозицией15. устройство для управления экспозициейgradation control — управление градацией; управление градационным процессом; контроль градации, регулирование градации
gripper control — управление захватами, регулировка захватов
highlight control — управление градацией «высоких светов», регулирование градационных характеристик «высоких светов»
16. регулировка подачи краски17. регулятор подачи краски18. регулирование режима работы передаточного валика по отношению к дукторному валу, регулирование передаточного валика19. устройство для регулирования режима работы передаточного валика20. регулирование продольной приводки21. устройство для регулировки долевой приводки22. регулирование боковой и продольной приводки23. устройство для регулировки боковой и продольной приводки24. контроль неподачи листов25. устройство, контролирующее неподачу листов26. регулировка положения валика печатного станка27. устройство для регулирования положения валика печатного станка28. авторегулирование натяжения с помощью пневматически нагруженного «плавающего» валика29. пневматическое устройство с «плавающим» валиком для авторегулирования натяжения30. регулирование окружного смещения формного цилиндра31. устройство для управления окружным смещением формного цилиндра32. управление экспозицией при копировании33. устройство для автоматического отсчёта времени экспонированияprint to cut register control — приводка рубки по печати, регулирование положения линии рубки ленты
34. регулирование приводки35. устройство для регулирования приводкиexchange control — валютный контроль; валютное регулирование
control margin — диапазон регулирования; диапазон управления
36. регулирование приводки на рабочем ходу37. устройство для регулирования приводки на рабочем ходу38. контроль подачи листов39. устройство, контролирующее подачу листов40. регулирование боковой приводки41. устройство для регулирования боковой приводкиtime control — управление временем, автоматический отсчёт времени
tonal control — управление градацией изображения или градационным процессом, регулирование градационной характеристики
42. управление движением лентыfailsoft control — управление с "мягким отказом"
43. устройство для контроля за движением ленты44. регулирование положения боковой кромки ленты45. устройство для выравнивания ленты46. управление длиной подачи ленты47. устройство для регулирования подачи лентыfeed control slide — заслонка, регулирующая подачу
-
72 BPSK
- поверхностная акустическая волна
- двухпозиционная фазовая манипуляция
- двукратная фазовая модуляция
- двоичная фазовая манипуляция
двоичная фазовая манипуляция
Метод фазовой модуляции, при котором смена входного двоичного символа с 1 на 0 или наоборот приводит к изменению фазы сигнала на 180°. Например сдвиг фазы на выходе модулятора может быть +90° для символа 0 и -90° для символа 1.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
двукратная фазовая модуляция
Метод модуляции, в котором носитель может находиться в одном из двух различных состояний (0 или 1). Как одна из разновидностей частотной модуляции, фазовая модуляция PSK (Phased Shift Keying) предполагает кодирование информации изменениями фазы волны в носителе.
[ http://www.iks-media.ru/glossary/index.html?glossid=2400324]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
двухпозиционная фазовая манипуляция
двоичная фазовая манипуляция
бинарная фазовая манипуляция
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
06.04.13 поверхностная акустическая волна [ surface acoustic wave; SAW]: Электроакустический эффект, используемый в системах автоматической идентификации, когда микроволновые радиосигналы малой мощности с помощью пьезоэлектрического кристалла в радиочастотной метке преобразуются в ультразвуковые поверхностные акустические волны.
Примечание - Информация об уникальной идентификации содержится в фазово-временных вариациях отраженного радиочастотной меткой сигнала.
<2>4 Сокращения
ARQ
Автоматический запрос повтора [Automatic Repeat Request]
ASK
Амплитудная манипуляция [Amplitude Shift Keying]
BPSK
Бинарная фазовая манипуляция [Binary Phase Shift Keying]
CDMA
Множественный доступ с кодовым разделением каналов [Code Division Multiple Access]
CSMA
Множественный доступ с анализом состояния канала передачи данных [Carrier Sense Multiple Access]
CSMA/CD
Множественный доступ с анализом состояния канала передачи данных и обнаружением конфликтов [Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection]
DBPSK
Дифференциальная бинарная фазовая манипуляция [Differential binary phase shift keying]
DSSS
Широкополосная модуляция с непосредственной передачей псевдослучайной последовательности [Direct sequence spread spectrum modulation]
EIRP (ЭИИМ)
Эквивалентная изотропно-излучаемая мощность [Equivalent Isotropically Radiated Power]
EMI
Электромагнитная помеха [ElectroMagnetic Interference]
ETR
Технический отчет ETSI [European Telecommunications Report]
ETS
Телекоммуникационный стандарт ETSI [European Telecommunications Standard]
ETSI
Европейский институт по стандартизации в области телекоммуникаций [European Telecommunications Standards Institute]
FHSS
Широкополосная модуляция с дискретной перестройкой несущей частоты [Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum]
FSK
Частотная манипуляция [Frequency Shift Keying]
GHz (ГГц)
Гигагерц [Gigahertz]
GMSK
Минимальная гауссовская манипуляция [Gaussian Minimum Shift Keying]
kHz (кГц)
Килогерц [Kilohertz]
MSK
Минимальнофазовая частотная манипуляция [Minimum shift keying]
MHz (МГц)
Мегагерц [Megahertz]
OBE
Навесное оборудование [On-Board Equipment]
PDM
Модуляция импульса по длительности, широтно-импульсная модуляция [Pulse Duration Modulation]
PM
Фазовая модуляция [Phase modulation]
PPM (ФИМ)
Фазоимпульсная модуляция [Modulation (pulse position)]
PSK
Фазовая манипуляция [Phase Shift Keying]
PWM
Широтно-импульсная модуляция [Pulse Width Modulation]
RF/DC
Обмен данными системы радиочастотной идентификации [Radio frequency data communication]
RFI
Радиопомеха [Radio frequency interference]
RSSI
Индикатор уровня принимаемого сигнала [Receiving Signal Strength Indicator]
S/N
Отношение сигнала к шуму [Signal/noise ratio]
SAW
Поверхностная акустическая волна [Surface Acoustic Wave]
SIN AD
Отношение сигнала к шуму и искажению [Signal to Noise & Distortion]
SRD
Устройство малого радиуса действия [Short Range Device]
TBR
Технические основы регулирования [Technical Basis for Regulation]
TDD
Дуплексная связь с временным разделением каналов [Time Division Duplexing]
TDM
Временное разделение каналов [Time Division Multiplexing]
<2>Библиография
[1]
МЭК 60050-713
(IEC 60050-713)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Часть 713. Радиосвязь: приемники, передатчики, сети и их режим работы
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Part 713: Radiocommunications: transmitters, receivers, networks and operation)
[2]
МЭК 60050-705
(IEC 60050-705)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 705: Распространение радиоволн ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 705: Radio wave propagation)
[3]
МЭК 60050-702
(IEC 60050-702)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 702: Колебания, сигналы и соответствующие устройства
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 702: Oscillations, signals and related devices)
[4]
МЭК 60050-121
(IEC 60050-121)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 121: Электромагнетизм ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Part 121: Electromagnetism)
[5]
МЭК 60050-712
(IEC 60050-712)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 712: Антенны ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 712: Antennas)
[6]
МЭК 60050-221
(IEC 60050-221)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 221: Магнитные материалы и компоненты
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 221: Magnetic materials and components)
[7]
ИСО/МЭК 2382-9:1995
(ISO/IEC2382-9:1995)
Информационная технология. Словарь. Часть 9. Обмен данными ( Information technology - Vocabulary - Part 9: Data communication)
[8]
МЭК 60050-725
(IEC 60050-725)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 725: Космическая радиосвязь ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 725: Space radiocommunications)
[9]
МЭК 60050-714
(IEC 60050-714)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 714: Коммутация и сигнализация в электросвязи
( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 714: Switching and signalling in telecommunications)
[10]
МЭК 60050-704
(IEC 60050-704)
Международный Электротехнический словарь. Глава 704. Техника передачи ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary - Chapter 704: Transmission)
[11]
МЭК 60050-161
(IEC 60050-161)
Международный электротехнический словарь. Глава 161: Электромагнитная совместимость ( International Electrotechnical Vocabulary. Chapter 161: Electromagnetic compatibility)
[12]
ИСО/МЭК 8824-1
(ISO/IEC 8824-1)
Информационные технологии. Абстрактная синтаксическая нотация версии один
(АСН.1). Часть 1. Спецификация основной нотации
(Information technology - Abstract Syntax Notation One (ASN.1): Specification of basic notation)1)
[13]
ИСО/МЭК 9834-1
(ISO/IEC 9834-1)
Информационные технологии. Взаимосвязь открытых систем. Процедуры действий уполномоченных по регистрации ВОС. Часть 1. Общие процедуры и верхние дуги дерева идентификатора объекта АСН.1
( Information technology - Open Systems Interconnection - Procedures for the operation of OSI Registration Authorities: General procedures and top arcs of the ASN. 1 Object Identifier tree)
[14]
ИСО/МЭК 15962]
(ISO/IEC 15962)
Информационные технологии. Радиочастотная идентификация (RFID) для управления предметами. Протокол данных: правила кодирования данных и функции логической памяти
( Information technology - Radio frequency identification ( RFID) for item management - Data protocol: data encoding rules and logical memory functions)
[15]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-1
(ISO/IEC 19762-1)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 1. Общие термины в области АIDC ( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 1: General terms relating to AIDC)
[16]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-2
(ISO/IEC 19762-2)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 2. Оптические носители данных (ОНД)
( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 2: Optically readable media ( ORM))
[17]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-3
(ISO/IEC 19762-3)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 3. Радиочастотная идентификация (РЧИ)
( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 3: Radio frequency identification ( RFID))
[18]
ИСО/МЭК 19762-5
(ISO/IEC 19762-5)
Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 5. Системы определения места нахождения
( Information technology - Automatic identification and data capture ( AIDC) techniques - Harmonized vocabulary - Part 5: Locating systems)
[19]
ИСО/МЭК 18000-6
(ISO/IEC 18000-6)
Информационные технологии. Радиочастотная идентификация для управления предметами. Часть 6. Параметры радиоинтерфейса для диапазона частот 860 - 960 МГц ( Information technology - Radio frequency identification for item management - Part 6: Parameters for air interface communications at 860 MHz to 960 MHz)
_____________
1)В оригинале ИСО/МЭК 19762-4 стандарты [12] - [19] включены в раздел «Библиография», однако следует учитывать, что в основном тексте стандарта ссылок на них нет.
<2>
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 19762-4-2011: Информационные технологии. Технологии автоматической идентификации и сбора данных (АИСД). Гармонизированный словарь. Часть 4. Общие термины в области радиосвязи оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > BPSK
-
73 control
1) контроль
2) контрольный
3) обоснование
4) обосновывать
5) оперативный
6) регулировать
7) регулировочный орган
8) совладать
9) управление
10) управляемость
11) управляющий
12) штурвальный
13) регулировка
14) управлять
15) проверять
16) регулирование
17) инструкция
18) исполнительный
19) контролировать
20) проверка
21) проверочный
22) регулирующий
– absence of control
– air traffic control
– air-traffic control
– analysis is in control
– anticipatory control
– arc control device
– association control
– attenuation control
– attitude control
– automatic control
– autonomous control
– autothrottle control
– bang-bang control
– be in control
– be out of control
– bin control gate
– brightness control
– bucket tip control
– bulge control
– centralized control
– closed-cycle control
– complete control
– context control
– continuous control
– contrast control
– control accuracy
– control action
– control actuator
– control agent
– control air
– control algorithm
– control amplifier
– control and display
– control assembly
– control beam
– control bus
– control button
– control cabinet
– control cable
– control cam
– control center
– control channel
– control character
– control characteristic
– control circuit
– control code
– control column
– control combination
– control computer
– control crank
– control criterion
– control current
– control cylinder
– control data
– control desk
– control electrode
– control electronics
– control element
– control equipment
– control factor
– control flutter
– control force
– control function
– control gate
– control gear
– control graphitization
– control instruction
– control jet
– control joint
– control key
– control knob
– control lag
– control lever
– control limit
– control linkages
– control links
– control loop
– control magnet
– control means
– control mode
– control module
– control motor
– control of airplane
– control office
– control operation
– control panel
– control pedal
– control position
– control problem
– control pulse
– control range
– control reactor
– control register
– control relay
– control response
– control room
– control shaft
– control spin
– control statement
– control stick
– control surface
– control survey
– control switch
– control temperature
– control theory
– control track
– control transistor
– control unit
– control vector
– control voltage
– control weeds
– control winding
– control wiring
– corrosion control
– dash control
– data control
– derivative control
– digital control
– direct control
– distance control
– disturbance-compensating control
– dive-recovery control
– duplicate control
– dust control
– ease of control
– elevator control
– emergency control
– end-point control
– engine control
– environment control
– error control
– error-closing control
– exclusive control
– extension of control
– feed control
– feed-back control
– feedback control
– filament control
– fine control
– fire control
– flight control
– floating control
– flood control
– flow-rate control
– focus control
– frequency control
– front-panel control
– gain control
– ganged control
– geodetic control
– go out of control
– ground control
– gyrorudder control
– hand control
– headwater control
– height control
– hierarchical control
– in-process control
– independent control
– indirect control
– industrial control
– input-output control
– integral control
– interacting control
– intermittent control
– inventory control
– jet control
– job control language
– layout of control
– leather control
– level control
– linearity control
– load control
– local control
– lose control
– loss of control
– manual control
– master control
– meduim-access control
– meduim-access control
– mission control
– multicircuit control
– noise control
– numerical control
– off-line control
– on-line control
– on-off control
– open-loop control
– operating control
– optimal control
– optimization control
– out of control
– pass control
– path control
– path of control
– pedal control
– pest control
– phase control
– phase-lock control
– piano-key control
– plan control
– point of control
– point-to-point control
– power-assisted control
– product control
– program control
– programmed control
– proportional control
– proportional-plus-floating control
– push-button control
– pushbutton control
– quality control
– radio control
– ramp control
– reaction control
– recovery control
– regain control
– register control
– remotability of control
– remote control
– roll control
– rudder control
– run-off control
– sampled-data control
– segregate control
– selectivity control
– self-acting control
– sensitivity control
– servo control
– slide control
– slope control
– statistical control
– steering control
– supervisory control
– take control
– technical control
– temperature control
– throttle control
– tone control
– touch control
– traffic control
– tuning control
– vertical control
– vibration control
– voice-activated control
– volume control
aerodynamic control surface — руль управления аэродинамический
automatic control equipment — аппаратура автоматического управления
automatic frequency control — частотная АПЧ, автоматическая настройка частоты
automatic gain control — <tech.> регулировка усиления автоматическая
automatic remote control — <comput.> телеавтоматика
automatic voltage control — регулирование напряжения автоматическое
bang-bang control system — <comput.> система управления релейная
cancelling control button — < railways> кнопка отмены
centralized traffic control — < railways> централизация
conditional transfer of control — условная передача управления
control aisle of a substation — коридор управления подстанции
control in pitch of airplane — продольное управление самолетом
control point adjustment — настройка точки регулирования, <engin.> задатчик
control tower service — <aeron.> служба диспетчерская
coordinated phosphate control — коррекционная обработка воды
differential control method — дифференцированный метод контроля
dispatcher's supervisory control — телеуправление диспетчерское
fire control computer — счетно-решающее устройство для управления артиллерийским огнем
fire control director — прибор управления артиллерийским огнем
floating control mode — <comput.> способ регулирования астатический
intermittent gain control — < radio> регулировка усиления временная
lateral control of airplane — поперечное управление самолетом
microprocessor control system — микропроцессорная система управления
pressure control instrument — <tech.> маностат
proportional control factor — <comput.> коэффициент пропорционального регулирования
range finder control — <geod.> метод дальномерно-базисный
reactor control system — <engin.> система управления и защиты
remote control interlocking — < railways> телецентрализация, централизация дистанционная
river control structure — <geol.> сооружение выправительное
servo control unit — <engin.> гидроусилитель
spray-type superheat control — впрысковое регулирование перегрева
supervisory control system — <comput.> автодиспетчер
thermostatic temperature control — ключевое термостатирование
volume range control — регулирование динамического диапазона
-
74 PAL
1) Компьютерная техника: Platform Abstraction Layer, Playlist Automation Language, Pooling Allying And Linking, Privileged Architecture Library, Process Assets Library2) Военный термин: Presence And Availability List, Protect All Life, parts authorization list, penetration aids launcher, permissive action link, permissive arming link, personnel accounting level, personnel augmentation list, portable ambush light, prescribed action link, price and availability list, prisoner-at-large, problem action log, pulsed argon laser, ПУЯБ, предохранительное устройство ядерного боеприпаса3) Техника: personnel airlock, ПАЛ (система цветного телевидения, ФРГ), система ПАЛ4) Шутливое выражение: Personal Android Lackey5) Метеорология: Present Atmospheric Level6) Железнодорожный термин: Paducah and Louisville Railroad7) Юридический термин: Police At Last, Protect A Life, patent associated literature8) Бухгалтерия: Passive Activity Loss, Programmatic Adjustment Loan9) Финансы: provisional allotment letter10) Страхование: Particular average loss11) Ветеринария: People And Animals Learning12) Телекоммуникации: Phase Alternate Line (television)13) Сокращение: Pahlavi, Panoramic Annular Lens (Sniper detection/location device), Paradox Application Language, Parcel Air Lift mail service (military space available mail), Phase Alternation Line, Phase Alternation Line-rate, Portable Advanced Laser, Portable, Accurate, Lightweight, Postal Advertising Label (New Zealand Post creates for private concerns, 2004), Postal Answer Line, Psycho-Acoustical Laboratory, Police Athletic League, Paid for Added Luxury, Pale and Lifeless, Peace At Last, Price/Availability List14) Физиология: Power- Assisted Liposuction15) Электроника: Phase Alternate Line16) Вычислительная техника: Programming Application Language, program assembly language, programmable array logic, programmed application library, Paradox Application Language (Borland, DB), Privileged Architecture Library (DEC, Alpha), библиотека прикладных программ, язык программирования приложений Paradox17) Нефть: pipe analysis log18) Транспорт: Philippines Airlines, Pitch, Angle, And Level, Plane Always Late19) Деловая лексика: Productivity, Accountability, And Learning, Professionalism Advocacy And Leadership, Purpose Agenda And Limit20) Бытовая техника: система цветного телевидения PAL21) Глоссарий компании Сахалин Энерджи: pressure alarm low22) Образование: Parents And Literature, Participant Active Learning, Partners At Learning, Partnership Approach To Literacy, Peer Assistance And Leadership, Peer Assistance Leadership, People Animals Learning, Performance Assessment Laboratory, Physically Active Lifestyle, Play And Learn, Positive And Loving, Program For Alternative Learners23) Сетевые технологии: phase alternating line24) Авиационная медицина: psychoacoustical laboratory25) Безопасность: Personal Access List26) Расширение файла: Color palette, Programmed Array Logic, Programming Assembly Language, Paradox Applications Language (Borland), Palette file (Microsoft Draw, Win. Paintbrush)27) Майкрософт: стандарт PAL28) Общественная организация: Physicians Against Landmines29) Должность: Peer Assistance Leader, Personal Assistant For Leisure30) Чат: Personal Assistance Link31) Программное обеспечение: Palmtop Application Library -
75 Pal
1) Компьютерная техника: Platform Abstraction Layer, Playlist Automation Language, Pooling Allying And Linking, Privileged Architecture Library, Process Assets Library2) Военный термин: Presence And Availability List, Protect All Life, parts authorization list, penetration aids launcher, permissive action link, permissive arming link, personnel accounting level, personnel augmentation list, portable ambush light, prescribed action link, price and availability list, prisoner-at-large, problem action log, pulsed argon laser, ПУЯБ, предохранительное устройство ядерного боеприпаса3) Техника: personnel airlock, ПАЛ (система цветного телевидения, ФРГ), система ПАЛ4) Шутливое выражение: Personal Android Lackey5) Метеорология: Present Atmospheric Level6) Железнодорожный термин: Paducah and Louisville Railroad7) Юридический термин: Police At Last, Protect A Life, patent associated literature8) Бухгалтерия: Passive Activity Loss, Programmatic Adjustment Loan9) Финансы: provisional allotment letter10) Страхование: Particular average loss11) Ветеринария: People And Animals Learning12) Телекоммуникации: Phase Alternate Line (television)13) Сокращение: Pahlavi, Panoramic Annular Lens (Sniper detection/location device), Paradox Application Language, Parcel Air Lift mail service (military space available mail), Phase Alternation Line, Phase Alternation Line-rate, Portable Advanced Laser, Portable, Accurate, Lightweight, Postal Advertising Label (New Zealand Post creates for private concerns, 2004), Postal Answer Line, Psycho-Acoustical Laboratory, Police Athletic League, Paid for Added Luxury, Pale and Lifeless, Peace At Last, Price/Availability List14) Физиология: Power- Assisted Liposuction15) Электроника: Phase Alternate Line16) Вычислительная техника: Programming Application Language, program assembly language, programmable array logic, programmed application library, Paradox Application Language (Borland, DB), Privileged Architecture Library (DEC, Alpha), библиотека прикладных программ, язык программирования приложений Paradox17) Нефть: pipe analysis log18) Транспорт: Philippines Airlines, Pitch, Angle, And Level, Plane Always Late19) Деловая лексика: Productivity, Accountability, And Learning, Professionalism Advocacy And Leadership, Purpose Agenda And Limit20) Бытовая техника: система цветного телевидения PAL21) Глоссарий компании Сахалин Энерджи: pressure alarm low22) Образование: Parents And Literature, Participant Active Learning, Partners At Learning, Partnership Approach To Literacy, Peer Assistance And Leadership, Peer Assistance Leadership, People Animals Learning, Performance Assessment Laboratory, Physically Active Lifestyle, Play And Learn, Positive And Loving, Program For Alternative Learners23) Сетевые технологии: phase alternating line24) Авиационная медицина: psychoacoustical laboratory25) Безопасность: Personal Access List26) Расширение файла: Color palette, Programmed Array Logic, Programming Assembly Language, Paradox Applications Language (Borland), Palette file (Microsoft Draw, Win. Paintbrush)27) Майкрософт: стандарт PAL28) Общественная организация: Physicians Against Landmines29) Должность: Peer Assistance Leader, Personal Assistant For Leisure30) Чат: Personal Assistance Link31) Программное обеспечение: Palmtop Application Library -
76 pal
1) Компьютерная техника: Platform Abstraction Layer, Playlist Automation Language, Pooling Allying And Linking, Privileged Architecture Library, Process Assets Library2) Военный термин: Presence And Availability List, Protect All Life, parts authorization list, penetration aids launcher, permissive action link, permissive arming link, personnel accounting level, personnel augmentation list, portable ambush light, prescribed action link, price and availability list, prisoner-at-large, problem action log, pulsed argon laser, ПУЯБ, предохранительное устройство ядерного боеприпаса3) Техника: personnel airlock, ПАЛ (система цветного телевидения, ФРГ), система ПАЛ4) Шутливое выражение: Personal Android Lackey5) Метеорология: Present Atmospheric Level6) Железнодорожный термин: Paducah and Louisville Railroad7) Юридический термин: Police At Last, Protect A Life, patent associated literature8) Бухгалтерия: Passive Activity Loss, Programmatic Adjustment Loan9) Финансы: provisional allotment letter10) Страхование: Particular average loss11) Ветеринария: People And Animals Learning12) Телекоммуникации: Phase Alternate Line (television)13) Сокращение: Pahlavi, Panoramic Annular Lens (Sniper detection/location device), Paradox Application Language, Parcel Air Lift mail service (military space available mail), Phase Alternation Line, Phase Alternation Line-rate, Portable Advanced Laser, Portable, Accurate, Lightweight, Postal Advertising Label (New Zealand Post creates for private concerns, 2004), Postal Answer Line, Psycho-Acoustical Laboratory, Police Athletic League, Paid for Added Luxury, Pale and Lifeless, Peace At Last, Price/Availability List14) Физиология: Power- Assisted Liposuction15) Электроника: Phase Alternate Line16) Вычислительная техника: Programming Application Language, program assembly language, programmable array logic, programmed application library, Paradox Application Language (Borland, DB), Privileged Architecture Library (DEC, Alpha), библиотека прикладных программ, язык программирования приложений Paradox17) Нефть: pipe analysis log18) Транспорт: Philippines Airlines, Pitch, Angle, And Level, Plane Always Late19) Деловая лексика: Productivity, Accountability, And Learning, Professionalism Advocacy And Leadership, Purpose Agenda And Limit20) Бытовая техника: система цветного телевидения PAL21) Глоссарий компании Сахалин Энерджи: pressure alarm low22) Образование: Parents And Literature, Participant Active Learning, Partners At Learning, Partnership Approach To Literacy, Peer Assistance And Leadership, Peer Assistance Leadership, People Animals Learning, Performance Assessment Laboratory, Physically Active Lifestyle, Play And Learn, Positive And Loving, Program For Alternative Learners23) Сетевые технологии: phase alternating line24) Авиационная медицина: psychoacoustical laboratory25) Безопасность: Personal Access List26) Расширение файла: Color palette, Programmed Array Logic, Programming Assembly Language, Paradox Applications Language (Borland), Palette file (Microsoft Draw, Win. Paintbrush)27) Майкрософт: стандарт PAL28) Общественная организация: Physicians Against Landmines29) Должность: Peer Assistance Leader, Personal Assistant For Leisure30) Чат: Personal Assistance Link31) Программное обеспечение: Palmtop Application Library -
77 UN
городская сеть
городская электросеть
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
3.11 уникальный идентификатор предмета (unique item identifier; UN): Номер, используемый для уникальной идентификации отдельного предмета учета, действительный в течение всего срока его службы.
Примечание 1 - В случае, если радиочастотная метка повторно используется для идентификации другого предмета, то ранее записанный на нее идентификатор предмета должен быть изменен.
Примечание 2 - Уникальный идентификатор Министерства обороны США (DoD Unique Identifier) и электронный код продукции (ЕРС) являются разновидностями идентификатора предмета. Например, идентификатор GS1 SSCC является идентификатором предмета (Item ID; IID) с ограниченным сроком действия, идентификатор GS1 GRAI - идентификатором предмета для присвоения возвратным активам, GS1 sGTIN - идентификатором предмета для присвоения товарной продукции.
Примечание 3 - Вместо термина «уникальный идентификатор предмета» не рекомендуется применять термин «уникальный идентификатор (UID)». То же самое относится к терминам «идентификатор микросхемы», «идентификатор радиочастотной метки» или «идентификатор объекта».
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 15963-2011: Информационные технологии. Радиочастотная идентификация для управления предметами. Уникальная идентификация радиочастотных меток оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > UN
-
78 design voltage
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
3.7 номинальное напряжение (design voltage): Объявленное изготовителем напряжение, к которому относятся все характеристики устройства управления лампами и которое должно быть не менее 85 % наибольшего значения диапазона нормируемого напряжения.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61347-1-2011: Устройства управления лампами. Часть 1. Общие требования и требования безопасности оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > design voltage
-
79 nominal voltage
- номинальное напряжение химического источника тока
- номинальное напряжение пьезоэлектрического (электромеханического) фильтра
- номинальное напряжение аккумулятора
- номинальное напряжение
- напряжение номинальное
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
номинальное напряжение пьезоэлектрического (электромеханического) фильтра (Uном, Unom)
Значение входного напряжения, при котором измеряют параметры пьезоэлектрического (электромеханического) фильтра.
[ ГОСТ 18670-84]Тематики
EN
FR
номинальное напряжение химического источника тока
номинальное напряжение
Условное напряжение, определяемое электрохимической системой химического источника тока.
[ ГОСТ 15596-82]EN
nominal voltage
suitable approximate value of the voltage used to designate or identify a cell, a battery or an electrochemical system
[IEV number 482-03-31]FR
tension nominale, f
valeur approchée appropriée d’une tension, utilisée pour désigner ou identifier un élément, une batterie, ou un système électrochimique
[IEV number 482-03-31]Тематики
Классификация
>>>Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
- tension nominale, f
1.3.2 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage): Номинальное напряжение герметичного никель-кадмиевого аккумулятора, равное 1,2 В.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60622-2010: Аккумуляторы и аккумуляторные батареи, содержащие щелочной и другие некислотные электролиты. Герметичные никель-кадмиевые призматические аккумуляторы оригинал документа
3.3.6 номинальное напряжение аккумулятора (nominal voltage): Номинальное напряжение герметичного никель-металл-гидридного аккумулятора, равное 1,2 В.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61951-2-2007: Аккумуляторы и аккумуляторные батареи, содержащие щелочной и другие некислотные электролиты. Портативные герметичные аккумуляторы. Часть 2. Никель-металл-гидрид оригинал документа
3.4 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage): Подходящее приблизительное значение напряжения, используемое для идентификации напряжения аккумулятора или батареи.
Примечания
1. Номинальное напряжение литиевых аккумуляторов указано в таблице 1.
2. Номинальное напряжение батареи, состоящей из n соединенных последовательно аккумуляторов, равно номинальному напряжению отдельного аккумулятора, увеличенному в n раз.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 61960-2007: Аккумуляторы и аккумуляторные батареи, содержащие щелочной и другие некислотные электролиты. Аккумуляторы и аккумуляторные батареи литиевые для портативного применения оригинал документа
1.3.2 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage): Номинальное напряжение открытого никель-кадмиевого аккумулятора с газовой рекомбинацией, равное 1,2 В.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60623-2008: Аккумуляторы и аккумуляторные батареи, содержащие щелочной и другие некислотные электролиты. Аккумуляторы никель-кадмиевые открытые призматические оригинал документа
3.22 напряжение номинальное (nominal voltage): Максимально приближенное значение напряжения, принятое для удобства обозначения и идентификации аккумулятора или батареи одной электрохимической системы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62485-2-2011: Батареи аккумуляторные и установки батарейные. Требования безопасности. Часть 2. Стационарные батареи оригинал документа
3.2 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage): Номинальное напряжение открытого никель-кадмиевого аккумулятора с газовой рекомбинацией, равное 1,2 В.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62259-2007: Аккумуляторы и аккумуляторные батареи, содержащие щелочной и другие некислотные электролиты. Аккумуляторы никель-кадмиевые призматические с газовой рекомбинацией оригинал документа
3.15 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage): Соответствующее приблизительное значение напряжения, которое используют при проектировании или идентификации элемента, батареи или электрохимической системы.
[IEV 482-03-31:2004]
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60086-4-2009: Батареи первичные. Часть 4. Безопасность литиевых батарей оригинал документа
3.10 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage): Соответствующее приблизительное значение напряжения, которое используют для идентификации первичной батареи.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60086-5-2009: Батареи первичные. Часть 5. Безопасность батарей с водным электролитом оригинал документа
3.18 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage) Un: Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008: Электрическая энергия. Совместимость технических средств электромагнитная. Методы измерений показателей качества электрической энергии оригинал документа
3.17 номинальное напряжение (nominal voltage): Номинальное значение напряжения, которое определяет тип источника питания.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 55266-2012: Совместимость технических средств электромагнитная. Оборудование сетей связи. Требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > nominal voltage
-
80 rated voltage
- регламентированное напряжение
- расчетное напряжение
- нормируемое напряжение
- номинальное напряжение конденсатора
- номинальное напряжение (во взрывозащите)
- номинальное напряжение
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
номинальное напряжение
Значение напряжения, на которое рассчитаны рабочие и эксплуатационные характеристики распределенных электронагревателей.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-426-2006]
Тематики
EN
номинальное напряжение конденсатора
Максимальное напряжение, при котором конденсатор может работать в течение минимальной наработки в условиях, указанных в нормативно-технической документации
[ ГОСТ 21415-75]
номинальное напряжение конденсатора
Действующее значение синусоидального переменного напряжения при номинальной частоте, на которое рассчитан конденсатор. Номинальное напряжение многофазного конденсатора - значение напряжения между выводами.
[ ГОСТ 1282-88]Тематики
- конденсаторы для повыш. коэф. мощности
- конденсаторы для электронной аппаратуры
EN
DE
FR
нормируемое напряжение
Питающее напряжение или напряжение, на которое светильник рассчитан изготовителем.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60598-1-2014]Тематики
- лампы, светильники, приборы и комплексы световые
EN
расчетное напряжение
номинальное напряжение
нормальное эксплуатационное напряжение
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
расчётное напряжение
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
3.17 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, установленное для выключателя изготовителем.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51324.1-2005: Выключатели для бытовых и аналогичных стационарных электрических установок. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
1.5.10 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Номинальное напряжение - это либо эффективное значение рабочего напряжения номинальной частоты, либо рабочее постоянное напряжение, которое можно длительно подавать на выводы конденсатора при любой температуре между нижней и верхней температурами категории. Это означает, что у конденсаторов, на которые распространяется настоящий стандарт, напряжение категории равно номинальному напряжению.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60384-14-2004: Конденсаторы постоянной емкости для электронной аппаратуры. Часть 14. Групповые технические условия на конденсаторы постоянной емкости для подавления электромагнитных помех и соединения с питающими магистралями оригинал документа
3.2.1 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, указанное изготовителем для этой машины, или напряжение между фазами (линейное) - при трехфазном питании.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60745-1-2005: Машины ручные электрические. Безопасность и методы испытаний. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.25 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, установленное изготовителем соединителей, которое указывается в стандартах или технических условиях.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51322.1-2011: Соединители электрические штепсельные бытового и аналогичного назначения. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
3.4 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение или диапазон напряжений, маркируемый на лампе.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53881-2010: Лампы со встроенными пускорегулирующими аппаратами для общего освещения. Требования безопасности оригинал документа
3.23 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Значение напряжения, на которое рассчитаны рабочие и эксплуатационные характеристики распределенных электронагревателей.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60079-30-1-2009: Взрывоопасные среды. Резистивный распределенный электронагреватель. Часть 30-1. Общие технические требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
1.5.9 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение или диапазон напряжения, заданное(ый) в соответствии с настоящим стандартом.
Примечание - Если в маркировке на лампе приведен диапазон напряжения, это значит, что возможна эксплуатация ламп при любом значении напряжения в пределах этого диапазона.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 52706-2007: Лампы накаливания вольфрамовые для бытового и аналогичного общего освещения. Эксплуатационные требования оригинал документа
2.1 нормируемое напряжение (rated voltage): Максимальное рабочее напряжение, заявленное изготовителем, на которое рассчитан патрон.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60838-1-2008: Патроны различные для ламп. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
1.2.1.1. номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Указанное изготовителем напряжение источника сетевого электропитания (для трехфазного источника электропитания принимают линейное напряжение).
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60950-1-2009: Оборудование информационных технологий. Требования безопасности. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
1.2.1.1 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Указанное изготовителем напряжение источника сетевого электропитания (для трехфазного источника электропитания принимают линейное напряжение).
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60950-1-2005: Оборудование информационных технологий. Требования безопасности. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.37 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Значение напряжения для заданных условий эксплуатации.
Значение и условия должны быть указаны в соответствующем стандарте или изготовителем, или ответственным поставщиком.
Примечание - Номинальное напряжение выражают в вольтах (В).
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54814-2011: Светодиоды и светодиодные модули для общего освещения. Термины и определения оригинал документа
3.4 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, указанное для прибора производителем.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62301-2011: Приборы бытовые электрические. Измерение потребляемой мощности в режиме ожидания оригинал документа
1.3.4 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение или диапазон напряжения, заданное(ый) в соответствии с настоящим стандартом.
Примечание - Если в маркировке на лампе приведен диапазон напряжения, это значит, что возможна эксплуатация ламп при любом значении напряжения в пределах этого диапазона.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 52712-2007: Требования безопасности для ламп накаливания. Часть 1. Лампы накаливания вольфрамовые для бытового и аналогичного общего освещения оригинал документа
3.40 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, установленное для машины изготовителем. При трехфазном питании - напряжение между фазами.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60745-1-2009: Машины ручные электрические. Безопасность и методы испытаний. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.2.1 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, указанное изготовителем для этой машины, или напряжение между фазами (линейное) - при трехфазном питании.
3.11 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage), UH (UN): Напряжение при номинальной частоте, прикладываемое между линейными выводами обмотки.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54801-2011: Трансформаторы тяговые и реакторы железнодорожного подвижного состава. Основные параметры и методы испытаний оригинал документа
1.3.4 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение или диапазон напряжений, маркируемые на лампе.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53879-2010: Лампы со встроенными пускорегулирующими аппаратами для общего освещения. Эксплуатационные требования оригинал документа
3.2 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение или диапазон напряжений, маркируемый на лампе.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 62560-2011: Лампы светодиодные со встроенным устройством управления для общего освещения на напряжения свыше 50 В. Требования безопасности оригинал документа
3.103 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, указанное изготовителем, для конкретного корпуса.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 50827.5-2009: Коробки и корпусы для электрических аппаратов, устанавливаемые в стационарные электрические установки бытового и аналогичного назначения. Часть 24. Специальные требования к коробкам и корпусам, предназначенным для установки защитных и аналогичных аппаратов с большой рассеиваемой мощностью оригинал документа
3.2.1 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage); Ur:Междуфазное напряжение на выводах генератора при номинальных частоте и мощности.
Примечание - Номинальное напряжение генератора для рабочих и эксплуатационных характеристик устанавливает изготовитель.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53986-2010: Электроагрегаты генераторные переменного тока с приводом от двигателя внутреннего сгорания. Часть 3. Генераторы переменного тока оригинал документа
3.2.1. номинальное напряжение (rated voltage):
Напряжение, для которого сконструирована установка (или ее часть).
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60519-1-2005: Безопасность электротермического оборудования. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.1.1 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 52161.1-2004: Безопасность бытовых и аналогичных электрических приборов. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
2.3 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Стандартное напряжение, на которое рассчитан кабель и которое служит для определения параметров электрических испытаний.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60245-1-2006: Кабели с резиновой изоляцией на номинальное напряжение до 450/750 В включительно. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
2.3 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Стандартное напряжение, на которое рассчитан кабель и которое служит для определения параметров электрических испытаний.
Примечание 1 - Номинальное напряжение выражается сочетанием двух значений U0/U, выраженных в вольтах (В):
U0 - среднеквадратическое значение между любой изолированной жилой и «землей» (металлическим покрытием кабеля или окружающей средой);
U - среднеквадратическое значение между любыми двумя фазными жилами многожильного кабеля или системы одножильных кабелей.
В системе переменного тока номинальное напряжение кабеля должно быть не менее номинального напряжения системы, для которой он предназначен.
Это условие относится как к значению U0, так и к значению U.
В системе постоянного тока номинальное напряжение системы должно быть не более полуторного значения номинального напряжения кабеля.
Примечание 2 - Рабочее напряжение системы может постоянно превышать номинальное напряжение такой системы до 10 %. Кабель можно использовать при рабочем напряжении на 10 % выше его номинального напряжения, если последнее по крайней мере равно номинальному напряжению системы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60245-1-2009: Кабели с резиновой изоляцией на номинальное напряжение до 450/750 В включительно. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
1.2.11 нормируемое напряжение (rated voltage): Питающее напряжение или напряжение, на которое светильник рассчитан изготовителем.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60598-1-2011: Светильники. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
2.3 номинальное напряжение (rated voltage): Стандартное напряжение, на которое рассчитан кабель, служащее для определения параметров электрических испытаний.
Номинальное напряжение выражают сочетанием двух значений - U0/U, выраженных в вольтах:
U0- среднеквадратическое значение между любой изолированной жилой и «землей» (металлическим покрытием кабеля или окружающей средой);
U - среднеквадратическое значение между любыми двумя фазными жилами многожильного кабеля или системы одножильных кабелей.
В системе переменного тока номинальное напряжение кабеля должно быть не менее номинального напряжения системы, для которого он предназначен.
Это требование относится как к значению U0, так и к значению U.
В системе постоянного тока номинальное напряжение системы должно быть не более полуторного значения номинального напряжения кабеля.
Примечание - Рабочее напряжение системы может постоянно превышать номинальное напряжение этой системы до 10 %. Кабель можно использовать при рабочем напряжении, на 10 % превышающем номинальное напряжение, если последнее по крайней мере равно номинальному напряжению системы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60227-1-2009: Кабели с поливинилхлоридной изоляцией на номинальное напряжение до 450/750 В включительно. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.2.4 регламентированное напряжение (rated voltage): Входное или выходное напряжение (напряжение фаза - фаза для трехфазного источника питания), указанное производителем.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 55061-2012: Совместимость технических средств электромагнитная. Статические системы переключения. Часть 2. Требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > rated voltage
См. также в других словарях:
Phase fired controllers — Phase control (PFC), also called phase cutting, is a method of pulse width modulation (PWM) for power limiting, applied to AC voltages. It works by modulating a thyristor, SCR, triac, thyratron, or other such gated diode like devices into and out … Wikipedia
Phase response — is the relationship between the phase of a sinusoidal input and the output signal passing through any device which accepts input and produces an output signal such as an amplifier or a filter.Amplifiers, filters and other devices are often… … Wikipedia
Phase splitter — (Elec.) A device by which a single phase current is split into two or more currents differing in phase. It is used in starting single phase induction motors. [Webster 1913 Suppl.] … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
Phase meter — Phase meter, or Phasemeter Phase me ter, n. (Elec.) A device for measuring the difference in phase of two alternating currents of electromotive forces. [Webster 1913 Suppl.] … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
Phase-change memory — Computer memory types Volatile RAM DRAM (e.g., DDR SDRAM) SRAM In development T RAM Z RAM TTRAM Historical Delay line memory Selectron tube Williams tube Non volatile … Wikipedia
Device Forts — Deal Castle in Kent was built between 1539 and 1540. The Device Forts, also known as Henrician Castles, are a series of artillery fortifications built to defend the southern coast of England by Henry VIII. After his divorce of Catherine of Aragon … Wikipedia
Phase-locked loop — PLL redirects here. For other uses, see PLL (disambiguation). A phase locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input reference signal. It is an electronic… … Wikipedia
phase-shifting device — fazės keitiklis statusas T sritis automatika atitikmenys: angl. phase changer; phase converter; phase shifter; phase shifting device vok. Phasendreher, m; Phasenschieber, m; Phasenumformer, m rus. фазовращатель, m; фазовый преобразователь, m;… … Automatikos terminų žodynas
Phase-shift keying — Passband modulation v · d · e Analog modulation AM · … Wikipedia
Phase detector — A phase detector is a frequency mixer or analog multiplier circuit that generates a voltage signal which represents the difference in phase between two signal inputs. It is an essential element of the phase locked loop (PLL).Detecting phase… … Wikipedia
Phase converter — A phase converter is a device that converts power provided as single or multiple phases to a different number of phases.The majority of phase converters are used to produce three phase electrical power from a single phase source, thus allowing… … Wikipedia