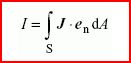-
1 автоматический выключатель
автоматический выключатель
Механический коммутационный аппарат1), способный включать, проводить и отключать токи при нормальном состоянии электрической цепи, а также включать, проводить в течение заданного времени и автоматически отключать токи в указанном аномальном состоянии электрической цепи, например, при коротком замыкании.
(МЭС 441-14-20)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 2-99 ( МЭК 60947-2-98)]
автоматический выключатель
-
[IEV number 442-05-01]EN
circuit breaker
a mechanical switching device, capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying for a specified time and breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
circuit breaker
A device designed to open and close a circuit by nonautomatic means and to open the circuit automatically on a predetermined overcurrent without damage to itself when properly applied within its rating.
NOTE The automatic opening means can be integral, direct acting with the circuit breaker, or remote from the circuit breaker.
Adjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker can be set to trip at various values of current, time, or both within a predetermined range. Instantaneous-trip (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that no delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker.
Inverse-time (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating a delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker, which delay decreases as the magnitude of the current increases.
Nonadjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker does not have any adjustment to alter the value of current at which it will trip or the time required for its operation.
Setting (of a circuit breaker). The value of current, time, or both at which an adjustable circuit breaker is set to trip.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
disjoncteur
1) Должно быть контактный коммутационный аппарат
appareil mécanique de connexion capable d’établir, de supporter et d’interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit, ainsi que d’établir, de supporter pendant une durée spécifiée et d’in- terrompre des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit telles que celles du court-circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
[Интент]КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ
- По роду тока
- По напряжению
- По числу полюсов
- По виду корпуса
- По месту установки
- По изолирующей среде
- По установленным расцепителям
- По дополнительным защитам
- По назначению
- По категории применения
- По виду привода взвода пружины
- По выполняемой функции
-
По влиянию монтажного положения
 Автоматические выключатели ABB
Автоматические выключатели ABB
 Модульные автоматические выключатели
Модульные автоматические выключатели
1. НЕКОТОРЫЕ СВЕДЕНИЯ ОБ АВТОМАТИЧЕСКИХ ВЫКЛЮЧАТЕЛЯХ Автоматический выключатель — это электрический аппарат, который автоматически отключает (и тем самым защищает) электрическую цепь при возникновении в ней аномального режима. Режим становится аномальным, когда в цепи начинает недопустимо изменяться (т. е. увеличиваться или уменьшаться относительно номинального значения) ток или напряжение.
Другими словами (более "инженерно") можно сказать, что автоматический выключатель защищает от токов короткого замыкания и токов перегрузки отходящую от него питающую линию, например, кабель и приемник(и) электрической энергии (осветительную сеть, розетки, электродвигатель и т. п.).
Как правило, автоматический выключатель может применятся также для нечастого (несколько раз в сутки) включения и отключения защищаемых электроприемников (защищаемой нагрузки).
[Интент]Выключатель предназначен для проведения тока в нормальном режиме и отключения тока при коротких замыканиях, перегрузках, недопустимых снижениях напряжения, а также до 30 оперативных включений и отключений электрических цепей в сутки и рассчитан для эксплуатации в электроустановках с номинальным рабочим напряжением до 660 В переменного тока частоты 50 и 60 Гц и до 440 В постоянного тока.
[Типовая фраза из российской технической документации] 2. ПРИНЦИП ДЕЙСТВИЯ Для защиты цепи от короткого замыкания применяется автоматический выключатель с электромагнитным расцепителем.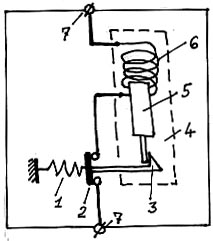
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Автоматический выключатель устроен таким образом, что сначала необходимо взвести пружину и только после этого его можно включить. У многих автоматических выключателей для взвода пружины необходимо перевести ручку вниз. После этого ручку переводят вверх. При этом замыкаются главные контакты.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Электромагнитный расцепитель;
5 - Сердечник
6 - Катушка
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
На рисунке показан один полюс автоматического выключателя во включенном положении: пружина 1 взведена, а главный контакт 2 замкнут.
Как только в защищаемой цепи возникнет короткое замыкание, ток, протекающий через соответствующий полюс автоматического выключателя, многократно возрастет. В катушке 6 сразу же возникнет сильное магнитное поле. Сердечник 5 втянется в катушку и освободит удерживающее устройство. Под действием пружины 1 главный контакт 2 разомкнется, в результате чего автоматический выключатель отключит и тем самым защитит цепь, в которой возникло короткое замыкание. Такое срабатывание автоматического выключателя происходит практически мгновенно (за сотые доли секунды).
Для защиты цепи от тока перегрузки применяют автоматические выключатели с тепловым расцепителем.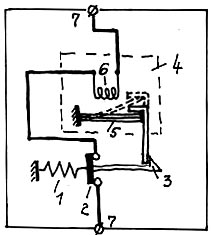
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Принцип действия такой же как и в первом случае, с той лишь разницей, что удерживающее устройство 3 освобождается под действием биметаллической пластины 5, которая изгибается от тепла, выделяемого нагревательным элементом 6. Количество тепла определяется током, протекающим через защищаемую цепь.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Тепловой расцепитель
5 - Биметаллическая пластина
6 - Нагревательный элемент
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
[Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- включение автоматического выключателя
- оперирование автоматического выключателя
- отключение автоматического выключателя
- срабатывание автоматического выключателя
EN
- auto-cutout
- automatic circuit breaker
- automatic cutout
- automatic switch
- breaker
- CB
- circuit breaker
- circuit-breaker
- cutout
DE
FR
Смотри также
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > автоматический выключатель
2 длительный допустимый ток
- courant permanent admissible, m
- courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > длительный допустимый ток
3 ток проводимости
ток проводимости
Явление направленного движения свободных носителей электрического заряда в веществе или в пустоте, количественно характеризуемое скалярной величиной, равной производной по времени от электрического заряда, переносимого свободными носителями заряда сквозь рассматриваемую поверхность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]EN
(electric) current
(conduction) current
scalar quantity equal to the flux of the electric current density J through a given directed surface S:
where endA is the vector surface element
NOTE 1 – The electric current through a surface is equal to the limit of the quotient of the electric charge transferred through that surface during a time interval by the duration of this interval when this duration tends to zero.
NOTE 2 – For charge carriers confined to a surface, the electric current is defined through a curve of this surface (see the note to term “lineic electric current”).
[IEV number 121-11-13]FR
courant (électrique), m
courant (de conduction), m
grandeur scalaire égale au flux de la densité de courant électrique J à travers une surface orientée donnée S:
où endA est l'élément vectoriel de surface
NOTE 1 – Le courant électrique à travers une surface est égal à la limite du quotient de la charge électrique traversant cette surface pendant un intervalle de temps par la durée de cet intervalle lorsque cette durée tend vers zéro.
NOTE 2 – Pour des porteurs de charge confinés sur une surface, le courant électrique est défini à travers une courbe de cette surface (voir la note au terme "densité linéique de courant").
[IEV number 121-11-13]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (elektrische) Stromstärke
- Leitungsstromstärke
- Stromstärke, (elektrische)
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ток проводимости
4 дифференциальная защита от замыканий на землю
дифференциальная защита от замыканий на землю
Защита, в которой остаточный ток комплекта из трех фазных трансформаторов тока уравновешен остаточным током на выходе такого же комплекта трансформаторов тока или, как это чаще бывает, одного трансформатора тока, расположенного на заземляющем соединении, если таковое имеется в нейтральной точке.
Примечание - Этот термин также употребляется в случаях, когда нейтраль защищаемой установки не заземлена, т.е. когда для защиты участка не требуется ни второй комплект из трех фазных трансформаторов тока, ни трансформатор тока в соединении нейтрали.
[Разработка типовых структурных схем микропроцессорных устройств РЗА на объектах ОАО "ФКС ЕЭС". Пояснительная записка. Новосибирск 2006 г.]EN
restricted earth-fault protection
ground differential protection (US)
protection in which the residual current from a set of three-phase current transformers is balanced against the residual output from a similar set of current transformers or, more usually, from a single current transformer located on the earthing connection, if any, of a neutral point
Note – This term is also used when the neutral of the protected plant is unearthed i.e. neither a second set of three-phase current transformers nor a current transformer in the neutral connection is needed to restrict the protected section.
[ IEV ref 448-14-29]FR
protection différentielle de défaut à la terre
protection dans laquelle le courant résiduel en provenance d'un ensemble de trois transformateurs de courant de phase est comparé à celui en provenance d'un ensemble similaire de transformateurs de courant ou, plus habituellement, d'un seul transformateur de courant placé dans la connexion de mise à la terre d'un point neutre, s'il y en a un
Note – Ce terme est aussi utilisé lorsque le neutre de l'installation protégée n'est pas relié à la terre, c'est à dire que ni un deuxième ensemble de trois transformateurs de courant de phase ni un transformateur de courant dans la connexion de neutre ne sont nécessaires pour limiter la section protégée
[ IEV ref 448-14-29]Тематики
EN
DE
- Nullstromdifferentialschutz, m
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > дифференциальная защита от замыканий на землю
5 проводящий
- passant, adj
- conducteur (1), adj
проводящий (1)
-
[IEV number 151-15-56]
проводящий (2)
кондукционный
-
[IEV number 151-15-57]EN
conductive, adj
qualifies a medium to indicate that it can carry electric current
NOTE 1 – In French, the term "conducteur" is also used as a noun to designate a conductor or conductive medium.
NOTE 2 – In French, the term "conducteur" is also used as a noun corresponding to the English "conductor".
Source: see IEC 60050-121, 151-12-05
[IEV number 151-15-56]
conducting, adj
qualifies a device or an electric circuit to indicate that it is carrying electric current
[IEV number 151-15-57]FR
conducteur (1), adj
qualifie un milieu qui peut être parcouru par un courant électrique
NOTE 1 – En français, le terme "conducteur" est aussi employé comme nom pour désigner un milieu conducteur.
NOTE 2 – En français, le terme "conducteur" est aussi employé comme nom correspondant à l'anglais "conductor".
Source: voir la CEI 60050-121, 151-12-05
[IEV number 151-15-56]
passant, adj
conducteur (2), adj
qualifie un dispositif ou un circuit électrique parcouru par un courant électrique
[IEV number 151-15-57]EN
- conducting, adj
- conductive, adj
DE
FR
- conducteur (1), adj
- passant, adj
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > проводящий
6 проводник
проводник (1)
Вещество, основным электрическим свойством которого является электропроводность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
проводник (2)
Всё то, что используется (предназначается) для проведения электрического тока:
- провод;
- кабель;
- шина;
- шинопровод;
- жила провода (кабеля);
- проводник печатной платы.
[Интент]
проводник (2)
Проводящая часть, предназначенная для проведения электрического тока определенного значения.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
проводник (2)
Проводящая часть, предназначенная для проведения электрического тока определённого значения.
Проводники представляют собой проводящие части, которые предназначены для проведения электрического тока в электрических цепях электрооборудования и электроустановки здания. Помимо качественной характеристики проводника, указывающей на его способность проводить электрический ток, каждый проводник имеет количественную характеристику, называемую допустимым длительным током. Протекание по проводнику сверхтока вызывает перегрев проводника, который может быть причиной пожара. Поэтому проводники в электроустановках зданий защищают от сверхтоков.
К проводникам, прежде всего, относят жилы проводов и кабелей, из которых выполнены стационарные электропроводки в электроустановке здания, жилы гибких проводов и кабелей, используемых для подключения переносного и передвижного электрооборудования к стационарным электропроводкам, различные шины, применяемые в низковольтных распределительных устройствах и в шинопроводах, а также другие проводящие части, выполняющие функции проводников.
В электроустановках зданий применяют проводники различного назначения. Для обеспечения электрооборудования электрической энергией в электрических цепях переменного тока используют фазные проводники, нейтральные проводники и PEN-проводники, а в электрических цепях постоянного тока – полюсные проводники, средние проводники и PEM-проводники. Защитные проводники, а также PEN-проводники, PEM-проводники и PEL-проводники применяют в электроустановках зданий для защиты от поражения электрическим током.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CF/view/49/]EN
conductor
element intended to carry electric current
NOTE 1 – The term "conductor" is often used for an element the length of which is large with respect to the cross-sectional dimensions, e.g. conductors of a line or of a cable.
NOTE 2 – The English term "conductor" and the French term "conducteur" have also the meaning of "conducting medium".
NOTE 3 – In French, the term "conducteur" is also used as an adjective corresponding to the English "conductive".
[IEV number 151-12-05]FR
conducteur, m
élément destiné à assurer le passage d'un courant électrique
NOTE 1 – Le terme "conducteur" est souvent utilisé pour un élément dont la longueur est grande par rapport aux dimensions de la section droite, par exemple les conducteurs d'une ligne ou d'un câble.
NOTE 2 – Le terme français "conducteur" et le terme anglais " conductor " ont aussi le sens de "milieu conducteur".
NOTE 3 – En français, le terme "conducteur" est aussi employé comme adjectif correspondant à l'anglais "conductive".
[IEV number 151-12-05]К зажиму допускается присоединение двух медных проводников сечением от 1,0 до 4,0 мм2.
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- обесточивать проводник
- определять сечение проводника
- отключать проводник
- отсоединять проводник
- присоединять проводник
- присоединять проводник накруткой
- проводник должен пропускать ток
- соединять проводники
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > проводник
7 электродинамический прибор
электродинамический прибор
-
[IEV number 314-01-19]EN
electrodynamic instrument
instrument comprising one or more measuring elements which operate by the interaction of a current in one or more movable coils with a current in one or more fixed coils
NOTE – This term is generally reserved for instruments which do not have ferromagnetic material in the magnetic circuit.
[IEV number 314-01-19]FR
appareil électrodynamique
appareil comportant un ou plusieurs éléments de mesure dont le fonctionnement est basé sur l'interaction d'un courant dans une ou plusieurs bobines mobiles avec un courant dans une ou plusieurs bobines fixes
NOTE – Ce terme est généralement réservé aux appareils qui ne comportent pas de matériau ferromagnétique dans le circuit magnétique.
[IEV number 314-01-19]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электродинамический прибор
8 анод
- anode, f
анод (устройства)
электрод, через который электрический ток входит в среду, имеющую удельную проводимость, отличную от удельной проводимости анода
[СТ МЭК50(151)-78]
анод
-
[IEV number 151-13-02]EN
anode
electrode capable of emitting positive charge carriers to and/or receiving negative charge carriers from the medium of lower conductivity
NOTE 1 – The direction of electric current is from the external circuit, through the anode, to the medium of lower conductivity.
NOTE 2 – In some cases (e.g. electrochemical cells), the term "anode" is applied to one or another electrode, depending on the electric operating condition of the device. In other cases (e.g. electronic tubes and semiconductor devices), the term "anode" is assigned to a specific electrode.
[IEV number 151-13-02]FR
anode, f
électrode capable d’émettre des porteurs de charge positifs vers le milieu de plus faible conductivité ou de collecter des porteurs de charge négatifs qui en proviennent
NOTE 1 – Le sens du courant électrique va du circuit extérieur vers le milieu de plus faible conductivité à travers l’anode.
NOTE 2 – Dans certains cas (par exemple pour les éléments électrochimiques), le terme "anode" désigne l’une ou l’autre électrode selon le régime électrique du dispositif. Dans d’autres cas (par exemple pour les tubes électroniques et les dispositifs semiconducteurs), le terme "anode" désigne une électrode particulière.
[IEV number 151-13-02]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
- anode, f
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > анод
9 катод
- cathode, f
катод
-
[IEV number 151-13-03]
катод
Плоская заготовка, получаемая методом электролиза, предназначенная для переплава.
[ ГОСТ 25501-82]
катод
Отрицательный электрод рентгеновской трубки
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]EN
cathode
electrode capable of emitting negative charge carriers to and/or receiving positive charge carriers from the medium of lower conductivity
NOTE 1 – The direction of electric current is from the medium of lower conductivity, through the cathode, to the external circuit.
NOTE 2 – In some cases (e.g. electrochemical cells), the term "cathode" is applied to one or another electrode, depending on the electric operating condition of the device. In other cases (e.g. electronic tubes and semiconductor devices), the term "cathode" is assigned to a specific electrode.
[IEV number 151-13-03]FR
cathode, f
électrode capable d’émettre des porteurs de charge négatifs vers le milieu de plus faible conductivité ou de collecter des porteurs de charge positifs qui en proviennent
NOTE 1 – Le sens du courant électrique va du milieu de plus faible conductivité vers le circuit extérieur à travers la cathode.
NOTE 2 – Dans certains cas (par exemple pour les éléments électrochimiques), le terme "cathode" désigne l’une ou l’autre électrode selon le régime électrique du dispositif. Dans d’autres cas (par exemple pour les tubes électroniques et les dispositifs semiconducteurs), le terme "cathode" désigne une électrode particulière.
[IEV number 151-13-03]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
- cathode, f
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > катод
10 измерительный трансформатор
EN
instrument transformer
a transformer intended to transmit an information signal to measuring instruments, meters and protective or control devices
NOTE – The term "instrument transformer" encompasses both current transformers and voltage transformers.
Source: see section 2, see section 3
[IEV number 321-01-01]FR
transformateur de mesure
transformateur destiné à transmettre un signal d'information à des appareils de mesure, à des compteurs, à des dispositifs de protection ou de commande
NOTE – Les transformateurs de mesure comprennent les transformateurs de courant et les transformateurs de tension.
Source: voir section 2, voir section 3
[IEV number 321-01-01]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > измерительный трансформатор
11 направленная защита с телеканалом
направленная защита с телеканалом
Защита с расширенной зоной, использующая телеканал связи, обычно не дистанционная, в которой для элемента, измеряющего сдвиг фаз, на каждом конце защищаемого участка используются напряжения или токи в месте установки защиты.
[Разработка типовых структурных схем микропроцессорных устройств РЗА на объектах ОАО "ФКС ЕЭС". Пояснительная записка. Новосибирск 2006 г.]
ВЧ-защита со сравнением направлений мощности по концам защищаемой линии
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
directional comparison protection
overreach protection, usually not a distance protection, using telecommunication, in which the relative operating conditions of phase angle measuring elements, at each end of the protected section, are compared using a locally derived voltage or current as a reference
Note – In the USA, the term "directional comparison protection" is applied to any non-unit protection using telecommunication, with or without overreaching or underreaching distance protection.
[ IEV ref 448-15-10]FR
protection à comparaison directionnelle
protection à portée étendue et à liaison de transmission, qui habituellement n'est pas une protection de distance, dans laquelle les conditions de fonctionnement relatives des éléments de mesure d'angle de phase à chaque extrémité de la section protégée sont comparées, en utilisant comme référence une tension ou un courant obtenus localement
Note – Aux Etats-Unis d'Amérique, le terme anglais "directional comparison protection" est utilisé pour toutes les protections à sélectivité relative de section et à liaison de transmission, qu'elles comportent ou non une protection de distance à portée étendue ou réduite.
[ IEV ref 448-15-10]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Richtungsvergleichsschutz, m
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > направленная защита с телеканалом
12 остающееся напряжение ОПН
остающееся напряжение ОПН
Uост
Максимальное значение напряжения на ограничителе при протекании через него импульсного тока с данной амплитудой и формой импульса.
[ ГОСТ Р 52725-2007]EN
residual voltage of an arrester, Ures
peak value of voltage that appears between the terminals of an arrester during the passage of discharge current
NOTE The term "discharge voltage" is used in some countries.
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]FR
tension résiduelle d'un parafoudre, Ures
valeur de crête de la tension entre les bornes d'un parafoudre pendant le passage du courant de décharge
NOTE L'expression «tension de décharge» est utilisée dans certains pays.
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]
Тематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > остающееся напряжение ОПН
13 электрическая дуга
электрическая дуга
-
[Интент]EN
(electric) arc
self-maintained gas conduction for which most of the charge carriers are electrons supplied by primary‑electron emission
[IEV ref 121-13-12]FR
arc (électrique), m
conduction gazeuse autonome dans laquelle la plupart des porteurs de charge sont des électrons produits par émission électronique primaire
[IEV ref 121-13-12]-
Материалы, стойкие к воздействию электрической дуги, используемые в качестве защитных средств, должны быть несгораемыми, иметь низкую теплопроводность и достаточную толщину для обеспечения механической стойкости.
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 4-94 ( МЭК 364-4-42-80)] -
Средства индивидуальной защиты от теплового воздействия электрической дуги...
[Технический регламент о безопасности средств индивидуальной защиты] -
Опасное и вредное воздействия на людей электрического тока, электрической дуги и электромагнитных полей проявляются в виде электротравм и профессиональных заболеваний.
[ ГОСТ 12.1.019-79] -
сопротивление электрической дуги в месте КЗ
[ ГОСТ 28249-93 ] -
... способствовать гашению электрической дуги
-
Аппараты управления, имеющие электрическую дугу на силовых контактах при
нормальной работе ( пускатели, станции управления), должны проходить испытания при коммутации нагрузки.
[ ГОСТ Р 51330.20-99]
An electric arc is an electrical breakdown of a gas which produces an ongoing plasma discharge, resulting from a current flowing through normally nonconductive media such as air. A synonym is arc discharge. An arc discharge is characterized by a lower voltage than a glow discharge, and relies on thermionic emission of electrons from the electrodes supporting the arc. The phenomenon was first described by Vasily V. Petrov, a Russian scientist who discovered it in 1802. An archaic term is voltaic arc as used in the phrase " voltaic arc lamp".
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electric_arc]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
In the last years a lot of users have underlined the question of safety in electrical assemblies with reference to one of the most severe and destructive electrophysical phenomenon: the electric arc.
[ABB]В последние годы многие потребители обращают особое внимание на безопасность НКУ, связанную с чрезвычайно разрушительным и наиболее жестко действующим электрофизическим явлением - электрической дугой.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
Сопутствующие термины
EN
DE
- elektrischer Lichtbogen, m
- Lichtbogen, m
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электрическая дуга
14 электрическая сеть
- Réseaud’energle électrique
- réseau électrique
- réseau d’énergie électrique (sens restraint)
- reseau d`energie electrique (sens restreint)
- Electrical network
<>электрическая сеть<>
Совокупность подстанций, распределительных устройств и соединяющих их электрических линий, размещенных на территории района, населенного пункта, потребителя электрической энергии.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]
<>электрическая сеть<>
Совокупность подстанций, распределительных устройств и соединяющих их линий электропередачи, предназначенная для передачи и распределения электрической энергии.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
сеть электрическая
Совокупность электрических линий, подстанций, распределительных и переключательных пунктов, связывающих электростанции с потребителями
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
электрическая сеть
Совокупность подстанций, распределительных устройств и соединяющих их электрических линий, размещенных на территории района, населенного пункта, и потребителей электрической энергии.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
<>электрическая сеть<>
-
[IEV number 151-12-02]<>
EN
electric network
electric circuit or set of electric circuits, interconnected or having intentional capacitive or inductive coupling between them
NOTE 1 – An electric network can form part of a larger electric network.
NOTE 2 – In IEC 60050-131, the term "electric network" has another meaning relative to circuit theory.
Source: 702-09-05 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-02]FR
réseau électrique, m
circuit électrique ou ensemble de circuits électriques interconnectés ou comportant entre eux des couplages capacitifs ou inductifs intentionnels
NOTE 1 – Un réseau électrique peut faire partie d'un réseau électrique plus grand.
NOTE 2 – Dans la CEI 60050-131, le terme "réseau électrique" a un sens approprié à la théorie des circuits.
Source: 702-09-05 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-02]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
The building is connected to a 23 kV grid.
Здание подключено к электрической сети напряжением 23 кВ.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
Классификация
>>>EN
- current network
- electric mains
- electric network
- electrical network
- electrical power network
- electrical power supply network
- grid
- network system
- power grid
- power network
DE
FR
- reseau d`energie electrique (sens restreint)
- réseau électrique
Совокупность подстанций, распределительных устройств и соединяющих их линий электропередачи, предназначенная для передачи и распределения электрической энергии по ГОСТ 19431
601-01-02
de Electrizitätsversorgungsnetz
en electrical power network
fr réseau d’énergie électrique (sens restraint)
Источник: ГОСТ 24291-90: Электрическая часть электростанции и электрической сети. Термины и определения оригинал документа
D. Elektrisches Netz
F. Electrical network
F. Réseaud’energle électrique
Совокупность подстанций, распределительных устройств и соединяющих их электрических линий, размещенных на территории района, населенного пункта, потребителя электрической энергии
Источник: ГОСТ 19431-84: Энергетика и электрификация. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электрическая сеть
См. также в других словарях:
current — [kʉr′ənt] adj. [altered (infl. by L) < ME curraunt < OFr curant, prp. of courre < L currere, to run < IE base * kers , to run, wagon > Gaul carros] 1. Obs. running or flowing 2. a) now going on; now in progress [the current month,… … English World dictionary
term — {{Roman}}I.{{/Roman}} noun 1 word or group of words ADJECTIVE ▪ specific ▪ blanket, broad, general, generic, umbrella ▪ descriptive … Collocations dictionary
Term of office — or term in office refers to the length of time a person (usually a politician) serves in a particular office. Contents 1 United Kingdom 1.1 Prime Minister 1.2 Devolved Administrations 2 … Wikipedia
Current sources and sinks — are analysis formalisms which distinguish points, areas, or volumes through which current enters or exits a system. While current sources or sinks are abstract elements used for analysis, generally they have physical counterparts in real world… … Wikipedia
Current limiting — is the practice in electrical or electronic circuits of imposing an upper limit on the current that may be delivered to a load with the purpose of protecting the circuit generating or transmitting the current from harmful effects due to a short… … Wikipedia
Current 93 — in 2007 Background information Origin Britain Genres Apo … Wikipedia
Term life insurance — or term assurance is life insurance which provides coverage at a fixed rate of payments for a limited period of time, the relevant term. After that period expires coverage at the previous rate of premiums is no longer guaranteed and the client… … Wikipedia
current monthly income — A bankruptcy filer s total gross income averaged over the six month period immediately preceding the bankruptcy filing. The debtor s current monthly income is used to determine whether the individual debtor qualifies for a Chapter 7 or a Chapter… … Glossary of Bankruptcy
Current quark — Current quarks (also called naked quarks or bare quarks) are defined as the constituent quark cores (constituent quarks with no covering) of a valence quark.[1] If, in one constituent quark, the current quark is hit inside the covering with large … Wikipedia
current asset — ➔ asset * * * current asset UK US noun [usually plural] (also circulating asset) ► FINANCE, PRODUCTION an asset such as cash, raw materials, parts, or products that are still being made, which a company will use up or sell during the same year:… … Financial and business terms
current algebra — current algebra, a form of algebra used in the study of charged elementary particles: »Current algebra involves a set of mathematical relations [in which] the term “current” refers to a current of some property of a particle in analogy with… … Useful english dictionary
Перевод: с русского на французский
с французского на русский- С французского на:
- Русский
- С русского на:
- Все языки
- Английский
- Немецкий
- Французский