-
1 Illnesses, aches and pains
Where does it hurt?where does it hurt?= où est-ce que ça vous fait mal? or (more formally) où avez-vous mal?his leg hurts= sa jambe lui fait malhe has a pain in his leg= il a mal à la jambeNote that with avoir mal à French uses the definite article (la) with the part of the body, where English has a possessive (his), hence:his head was aching= il avait mal à la têteEnglish has other ways of expressing this idea, but avoir mal à fits them too:he had toothache= il avait mal aux dentshis ears hurt= il avait mal aux oreillesAccidentsshe broke her leg= elle s’est cassé la jambeElle s’est cassé la jambe means literally she broke to herself the leg ; because the se is an indirect object, the past participle cassé does not agree. This is true of all such constructions:she sprained her ankle= elle s’est foulé la chevillethey burned their hands= ils se sont brûlé les mainsChronic conditionsNote that the French often use fragile (weak) to express a chronic condition:he has a weak heart= il a le cœur fragilehe has kidney trouble= il a les reins fragileshe has a bad back= il a le dos fragileBeing illMostly French uses the definite article with the name of an illness:to have flu= avoir la grippeto have measles= avoir la rougeoleto have malaria= avoir la malariaThis applies to most infectious diseases, including childhood illnesses. However, note the exceptions ending in -ite (e.g. une hépatite, une méningite) below.When the illness affects a specific part of the body, French uses the indefinite article:to have cancer= avoir un cancerto have cancer of the liver= avoir un cancer du foieto have pneumonia= avoir une pneumonieto have cirrhosis= avoir une cirrhoseto have a stomach ulcer= avoir un ulcère à l’estomacMost words in -ite ( English -itis) work like this:to have bronchitis= avoir une bronchiteto have hepatitis= avoir une hépatiteWhen the illness is a generalized condition, French tends to use du, de l’, de la or des:to have rheumatism= avoir des rhumatismesto have emphysema= avoir de l’emphysèmeto have asthma= avoir de l’asthmeto have arthritis= avoir de l’arthriteOne exception here is:to have hay fever= avoir le rhume des foinsWhen there is an adjective for such conditions, this is often preferred in French:to have asthma= être asthmatiqueto have epilepsy= être épileptiqueSuch adjectives can be used as nouns to denote the person with the illness, e.g. un/une asthmatique and un/une épileptique etc.French has other specific words for people with certain illnesses:someone with cancer= un cancéreux/une cancéreuseIf in doubt check in the dictionary.English with is translated by qui a or qui ont, and this is always safe:someone with malaria= quelqu’un qui a la malariapeople with Aids= les gens qui ont le SidaFalling illThe above guidelines about the use of the definite and indefinite articles in French hold good for talking about the onset of illnesses.French has no general equivalent of to get. However, where English can use catch, French can use attraper:to catch mumps= attraper les oreillonsto catch malaria= attraper la malariato catch bronchitis= attraper une bronchiteto catch a cold= attraper un rhumeSimilarly where English uses contract, French uses contracter:to contract Aids= contracter le Sidato contract pneumonia= contracter une pneumonieto contract hepatitis= contracter une hépatiteFor attacks of chronic illnesses, French uses faire une crise de:to have a bout of malaria= faire une crise de malariato have an asthma attack= faire une crise d’asthmeto have an epileptic fit= faire une crise d’épilepsieTreatmentto be treated for polio= se faire soigner contre la polioto take something for hay fever= prendre quelque chose contre le rhume des foinshe’s taking something for his cough= il prend quelque chose contre la touxto prescribe something for a cough= prescrire un médicament contre la touxmalaria tablets= des cachets contre la malariato have a cholera vaccination= se faire vacciner contre le cholérato be vaccinated against smallpox= se faire vacciner contre la varioleto be immunized against smallpox= se faire immuniser contre la varioleto have a tetanus injection= se faire vacciner contre le tétanosto give sb a tetanus injection= vacciner qn contre le tétanosto be operated on for cancer= être opéré d’un cancerto operate on sb for appendicitis= opérer qn de l’appendicite -
2 аномальные условия (работы)
аномальные условия (работы)
-EN
abnormal conditions
conditions which may occur in the appliance or in the switch during normal operation
[IEC 61058-1, ed. 3.0 (2000-07)]
abnormal conditions of operation
operating conditions of low occurrence (typical only a few times during equipment lifetime)
NOTE These include human errors, loss of power supply, overvoltages, earthquake, etc. After such a condition has occurred, equipment inspection may be required.
[IEC 61936-1, ed. 2.0 (2010-08)]FR
conditions anormales
conditions qui peuvent se présenter dans l’appareil ou dans l'interrupteur durant une manoeuvre normale
[IEC 61058-1, ed. 3.0 (2000-07)]
conditions anormales de fonctionnement
conditions de fonctionnement rares (seulement quelques fois au cours de la vie du matériel)
NOTE Cela inclut les erreurs humaines, pertes d’alimentation, surtensions, séismes, etc. Après de telles conditions d'exploitation, une inspection de ces matériels peut être exigée.
[IEC 61936-1, ed. 2.0 (2010-08)]Тематики
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > аномальные условия (работы)
-
3 разъединитель
разъединитель
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, в разомкнутом положении отвечающий требованиям к функции разъединения.
Примечание.
1 Это определение отличается от формулировки МЭК 60050(441-14-05), поскольку требования к функции разъединения не ограничиваются соблюдением изолирующего промежутка.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
2 Разъединитель способен включать и отключать цепь с незначительным током или при незначительном изменении напряжения на зажимах каждого из полюсов разъединителя.
Разъединитель может проводить токи в нормальных условиях работы, а также в течение определенного времени в аномальных условиях работы выдерживать токи короткого замыкания.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 3-99 ( МЭК 60947-3-99)]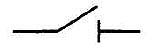 Условное обозначение контакта разъединителя
Условное обозначение контакта разъединителя
разъединитель
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, который обеспечивает в отключенном положении изоляционный промежуток, удовлетворяющий нормированным требованиям.
Примечания
1 Разъединитель способен размыкать и замыкать цепь при малом токе или малом изменении напряжения на выводах каждого из его полюсов. Он также способен проводить токи при нормальных условиях в цепи и проводить в течение нормированного времени токи при ненормальных условиях, таких как короткое замыкание.
2 Малые токи - это такие токи, как емкостные токи вводов, шин, соединений, очень коротких кабелей, токи постоянно соединенных ступенчатых сопротивлений выключателей и токи трансформаторов напряжения и делителей. Для номинальных напряжений до 330 кВ включительно ток, не превышающий 0,5 А, считается малым током по этому определению; для номинального напряжения от 500 кВ и выше и токов, превышающих 0,5 А, необходимо проконсультироваться с изготовителем, если нет особых указаний в руководствах по эксплуатации разъединителей.
3 К малым изменениям напряжения относятся изменения напряжения, возникающие при шунтировании регуляторов индуктивного напряжения или выключателей.
4 Для разъединителей номинальным напряжением от 110 кВ и выше может быть установлена коммутация уравнительных токов.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]EN
disconnector
a mechanical switching device which provides, in the open position, an isolating distance in accordance with specified requirements
NOTE – A disconnector is capable of opening and closing a circuit when either negligible current is broken or made, or when no significant change in the voltage across the terminals of each of the poles of the disconnector occurs. It is also capable of carrying currents under normal circuit conditions and carrying for a specified time currents under abnormal conditions such as those of short circuit.
[IEV number 441-14-05]
disconnector
IEV 441-14-05 is applicable with the following additional notes:
NOTE 1
"Negligible current" implies currents such as the capacitive currents of bushings, busbars, connections, very short lengths of cable, currents of permanently connected grading impedances of circuit-breakers and currents of voltage transformers and dividers. For rated voltages of 420 kV and below, a current not exceeding 0,5 A is a negligible current for the purpose of this definition; for rated voltage above 420 kV and currents exceeding 0,5 A, the manufacturer should be consulted.
"No significant change in voltage" refers to such applications as the by-passing of induction voltage regulators or circuit-breakers.
NOTE 2
For a disconnector having a rated voltage of 52 kV and above, a rated ability of bus transfer current switching may be assigned
[IEC 62271-102]FR
sectionneur
appareil mécanique de connexion qui assure, en position d'ouverture, une distance de sectionnement satisfaisant à des conditions spécifiées
NOTE – Un sectionneur est capable d'ouvrir et de fermer un circuit lorsqu'un courant d'intensité négligeable est interrompu ou établi, ou bien lorsqu'il ne se produit aucun changement notable de la tension aux bornes de chacun des pôles du sectionneur. Il est aussi capable de supporter des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit et de supporter des courants pendant une durée spécifiée dans des conditions anormales telles que celles du court-circuit.
[IEV number 441-14-05]Указанные в 5.3.2 перечислениях а)-d) устройства отключения ( выключатель-разъединитель, разъединитель или выключатель) должны:
- изолировать электрооборудование от цепей питания и иметь только одно положение ОТКЛЮЧЕНО (изоляция) и одно положение ВКЛЮЧЕНО, четко обозначаемые символами «О» и «I» [МЭК 60417-5008 (DB:2002-10) и МЭК 60417-5007 (DB:2002-10), см. 10.2.2];
- иметь видимое разъединение или индикатор положения, который может указывать положение ОТКЛЮЧЕНО только в случае, если все контакты в действительности открыты, т.е. разомкнуты и удалены друг от друга на расстояние, удовлетворяющее требованиям по изолированию;
- быть снабжены расположенным снаружи ручным приводом (например, ручкой). Исключение для управляемых внешним источником энергии, когда воздействие вручную невозможно при наличии иного внешнего привода. Если внешние приводы не используются для выполнения аварийных функций управления, то рекомендуется применять ЧЕРНЫЙ и СЕРЫЙ цвета для окраски ручного привода (см. 10.7.4 и 10.8.4);
- обладать средствами для запирания в положении ОТКЛЮЧЕНО (например, с помощью висячих замков). При таком запирании возможность как дистанционного, так и местного включения должна быть исключена;
Разъединители служат для создания видимого разрыва, отделяющего выводимое в ремонт оборудование от токоведущих частей, находящихся под напряжением, для безопасного производства работ.
Разъединители не имеют дугогасящих устройств и поэтому предназначаются для включения и отключения электрических цепей при отсутствии тока нагрузки и находящихся только под напряжением или даже без напряжения. Лишь в некоторых случаях допускается включение и отключение разъединителями небольших токов, значительно меньше номинальных.
Разъединители используются также при различного рода переключениях в схемах электрических соединений подстанций, например при переводе присоединений с одной системы шин на другую.
Требования, предъявляемые к разъединителям с точки зрения оперативного обслуживания, следующие:- Разъединители в отключенном положении должны создавать ясно видимый разрыв цепи, соответствующий классу напряжения установки.
- Приводы разъединителей должны иметь устройства фиксации в каждом из двух оперативных положений: включенном и отключенном. Кроме того, они должны иметь надежные упоры, ограничивающие поворот главных ножей на угол больше заданного.
- Опорные изоляторы и изолирующие тяги должны выдерживать механическую нагрузки при операциях.
- Главные ножи разъединителей должны иметь блокировку с ножами стационарных заземлителей и не допускать возможности одновременного включения тех и других.
- Разъединители должны беспрепятственно включаться и отключаться при любых наихудших условиях окружающей среды (например, при обледенении).
- Разъединители должны иметь надлежащую изоляцию, обеспечивающую не только надежную работу при возможных перенапряжениях и ухудшении атмосферных условий (гроза, дождь, туман), но и безопасное обслуживание.
[ http://forca.ru/stati/podstancii/obsluzhivanie-razediniteley-otdeliteley-i-korotkozamykateley.html]
Разъединители применяются для коммутации обесточенных при помощи выключателей участков токоведущих систем, для переключения РУ с одной ветви на другую, а также для отделения на время ревизии или ремонта силового электротехнического оборудования и создания безопасных условий от смежных частей линии, находящихся под напряжением. Разъединители способны размыкать электрическую цепь только при отсутствии в ней тока или при весьма малом токе. В отличие от выключателей разъединители в отключенном состоянии образуют видимый разрыв цепи. После отключения разъединителей с обеих сторон объекта, например выключателя или трансформатора, они должны заземляться с обеих сторон либо при помощи переносных заземлителей, либо специальных заземляющих ножей, встраиваемых в конструкцию разъединителя.
[ http://relay-protection.ru/content/view/46/8/1/1/]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
b) disconnector, with or without fuses, in accordance with IEC 60947-3, that has an auxiliary contact that in all cases causes switching devices to break the load circuit before the opening of the main contacts of the disconnector;
[IEC 60204-1-2006]
б) разъединитель с или без предохранителей, соответствующий требованиям МЭК 60947-3 со вспомогательным контактом, срабатывающим до того, как разомкнутся главные контакты разъединителя, используемым для коммутации другого аппарата, отключающего питание цепей нагрузки.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- релейная защита
- электротехника, основные понятия
Классификация
>>>EN
- disconnect
- disconnect device
- disconnect switch
- disconnecting device
- disconnecting switch
- disconnector
- DS
- isolating facility
- isolating switch
- isolator
- main disconnect device
DE
FR
Смотри также
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > разъединитель
4 прибор класса II
прибор класса II
Прибор, в котором защита от поражения электрическим током обеспечивается не только основной изоляцией, но в котором предусмотрены дополнительные меры безопасности, такие как двойная или усиленная изоляция, причем не предусмотрено защитное заземление, а условия установки не являются дополнительной гарантией.
Примечания:
1. Такие приборы могут быть отнесены к одному из следующих типов:
a) прибор, имеющий прочный и практически сплошной кожух из изоляционного материала, который покрывает все металлические части, за исключением небольших деталей, таких как заводская табличка, винты и заклепки, которые изолированы от токоведущих частей изоляцией, по крайней мере эквивалентной усиленной изоляции;
такой прибор называют прибором класса II с изолирующим кожухом;
b) прибор, имеющий практически сплошной металлический кожух, в котором повсюду применена двойная или усиленная изоляция; такой прибор называют прибором класса II с металлическим кожухом;
c) прибор, являющийся комбинацией типов, указанных в перечислениях а) и b).
2. Кожух прибора класса II с изолирующим кожухом может образовывать часть или всю дополнительную или усиленную изоляцию.
3. Если прибор, имеющий повсюду двойную или усиленную изоляцию, снабжен заземляющим зажимом или заземляющим контактом, то его относят к приборам класса 0 или 0I.
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]EN
class II appliance
appliance in which protection against electric shock does not rely on basic insulation only but in which additional safety precautions are provided, such as double insulation or reinforced insulation, there being no provision for protective earthing or reliance upon installation conditions
NOTE 1 - Such an appliance may be of one of the following types:
– an appliance having a durable and substantially continuous enclosure of insulating material which envelops all metal parts, with the exception of small parts, such as nameplates, screws and rivets, which are isolated from live parts by insulation at least equivalent to reinforced insulation; such an appliance is called an insulation-encased class II appliance;
– an appliance having a substantially continuous metal enclosure, in which double insulation or reinforced insulation is used throughout; such an appliance is called a metal-encased class II appliance;
– an appliance which is a combination of an insulation-encased class II appliance and a metal-encased class II appliance.
NOTE 2 - The enclosure of an insulation-encased class II appliance may form a part or the whole of the supplementary insulation or of the reinforced insulation.
NOTE 3 - If an appliance with double insulation or reinforced insulation throughout has provision for earthing, it is considered to be a class I appliance or a class 0I appliance.
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]FR
appareil de la classe II
appareil dans lequel la protection contre les chocs électriques ne repose pas uniquement sur l'isolation principale mais dans lequel ont été prises des mesures supplémentaires de sécurité, telles que la double isolation ou l'isolation renforcée, ces mesures ne comportant pas de moyen de mise à la terre de protection et ne dépendant pas des conditions d'installation
NOTE 1 - Un tel appareil peut être de l'un des types suivants:
– un appareil ayant une enveloppe durable et pratiquement continue en matière isolante enfermant toutes les parties métalliques, à l'exception de petites pièces telles que plaques signalétiques, vis et rivets, qui sont séparées des parties actives par une isolation au moins équivalente à l'isolation renforcée; un tel appareil est appelé appareil de la classe II à enveloppe isolante;
– un appareil ayant une enveloppe métallique pratiquement continue, dans lequel la double isolation ou l'isolation renforcée est partout utilisée; un tel appareil est appelé appareil de la classe II à enveloppe métallique;
– un appareil qui est la combinaison d’un appareil de la classe II à enveloppe isolante et d’un appareil de la classe II à enveloppe métallique.
NOTE 2 - L'enveloppe d'un appareil de la classe II à enveloppe isolante peut former tout ou partie de l'isolation supplémentaire ou de l'isolation renforcée.
NOTE 3 - Si un appareil ayant en toutes ses parties une double isolation ou une isolation renforcée comporte des dispositions en vue de la mise à la terre, il est considéré comme étant un appareil de la classe I ou un appareil de la classe 0I.
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]Тематики
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > прибор класса II
5 выключатель (контактный)
выключатель (контактный)
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, способный включать, проводить и отключать токи в нормальных условиях, в том числе при оговоренных рабочих перегрузках, а также в течение установленного времени проводить ток в оговоренных аномальных условиях, например при коротком замыкании.
МЭК 60050(441-14-10)
Примечание. Выключатель может быть способен включать, но не отключать ток короткого замыкания.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
(mechanical) switch
a mechanical switching device capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions which may include specified operating overload conditions and also carrying for a specified time currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit
NOTE – A switch may be capable of making but not breaking short-circuit currents.
[IEV number 441-14-10]FR
interrupteur (mécanique)
appareil mécanique de connexion capable d'établir, de supporter et d'interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit y compris éventuellement les conditions spécifiées de surcharge en service, ainsi que de supporter pendant une durée spécifiée des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit telles que celles du court-circuit
NOTE – Un interrupteur peut être capable d'établir des courants de court-circuit mais n'est pas capable de les couper
[IEV number 441-14-10]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- выключатель, переключатель
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > выключатель (контактный)
6 автоматический выключатель
автоматический выключатель
Механический коммутационный аппарат1), способный включать, проводить и отключать токи при нормальном состоянии электрической цепи, а также включать, проводить в течение заданного времени и автоматически отключать токи в указанном аномальном состоянии электрической цепи, например, при коротком замыкании.
(МЭС 441-14-20)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 2-99 ( МЭК 60947-2-98)]
автоматический выключатель
-
[IEV number 442-05-01]EN
circuit breaker
a mechanical switching device, capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying for a specified time and breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
circuit breaker
A device designed to open and close a circuit by nonautomatic means and to open the circuit automatically on a predetermined overcurrent without damage to itself when properly applied within its rating.
NOTE The automatic opening means can be integral, direct acting with the circuit breaker, or remote from the circuit breaker.
Adjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker can be set to trip at various values of current, time, or both within a predetermined range. Instantaneous-trip (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that no delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker.
Inverse-time (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating a delay is purposely introduced in the tripping action of the circuit breaker, which delay decreases as the magnitude of the current increases.
Nonadjustable (as applied to circuit breakers). A qualifying term indicating that the circuit breaker does not have any adjustment to alter the value of current at which it will trip or the time required for its operation.
Setting (of a circuit breaker). The value of current, time, or both at which an adjustable circuit breaker is set to trip.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
disjoncteur
1) Должно быть контактный коммутационный аппарат
appareil mécanique de connexion capable d’établir, de supporter et d’interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit, ainsi que d’établir, de supporter pendant une durée spécifiée et d’in- terrompre des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit telles que celles du court-circuit.
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
[IEV number 442-05-01]
[Интент]КЛАССИФИКАЦИЯ
- По роду тока
- По напряжению
- По числу полюсов
- По виду корпуса
- По месту установки
- По изолирующей среде
- По установленным расцепителям
- По дополнительным защитам
- По назначению
- По категории применения
- По виду привода взвода пружины
- По выполняемой функции
-
По влиянию монтажного положения
 Автоматические выключатели ABB
Автоматические выключатели ABB
 Модульные автоматические выключатели
Модульные автоматические выключатели
1. НЕКОТОРЫЕ СВЕДЕНИЯ ОБ АВТОМАТИЧЕСКИХ ВЫКЛЮЧАТЕЛЯХ Автоматический выключатель — это электрический аппарат, который автоматически отключает (и тем самым защищает) электрическую цепь при возникновении в ней аномального режима. Режим становится аномальным, когда в цепи начинает недопустимо изменяться (т. е. увеличиваться или уменьшаться относительно номинального значения) ток или напряжение.
Другими словами (более "инженерно") можно сказать, что автоматический выключатель защищает от токов короткого замыкания и токов перегрузки отходящую от него питающую линию, например, кабель и приемник(и) электрической энергии (осветительную сеть, розетки, электродвигатель и т. п.).
Как правило, автоматический выключатель может применятся также для нечастого (несколько раз в сутки) включения и отключения защищаемых электроприемников (защищаемой нагрузки).
[Интент]Выключатель предназначен для проведения тока в нормальном режиме и отключения тока при коротких замыканиях, перегрузках, недопустимых снижениях напряжения, а также до 30 оперативных включений и отключений электрических цепей в сутки и рассчитан для эксплуатации в электроустановках с номинальным рабочим напряжением до 660 В переменного тока частоты 50 и 60 Гц и до 440 В постоянного тока.
[Типовая фраза из российской технической документации] 2. ПРИНЦИП ДЕЙСТВИЯ Для защиты цепи от короткого замыкания применяется автоматический выключатель с электромагнитным расцепителем.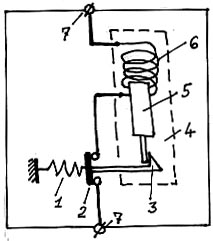
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Автоматический выключатель устроен таким образом, что сначала необходимо взвести пружину и только после этого его можно включить. У многих автоматических выключателей для взвода пружины необходимо перевести ручку вниз. После этого ручку переводят вверх. При этом замыкаются главные контакты.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Электромагнитный расцепитель;
5 - Сердечник
6 - Катушка
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
На рисунке показан один полюс автоматического выключателя во включенном положении: пружина 1 взведена, а главный контакт 2 замкнут.
Как только в защищаемой цепи возникнет короткое замыкание, ток, протекающий через соответствующий полюс автоматического выключателя, многократно возрастет. В катушке 6 сразу же возникнет сильное магнитное поле. Сердечник 5 втянется в катушку и освободит удерживающее устройство. Под действием пружины 1 главный контакт 2 разомкнется, в результате чего автоматический выключатель отключит и тем самым защитит цепь, в которой возникло короткое замыкание. Такое срабатывание автоматического выключателя происходит практически мгновенно (за сотые доли секунды).
Для защиты цепи от тока перегрузки применяют автоматические выключатели с тепловым расцепителем.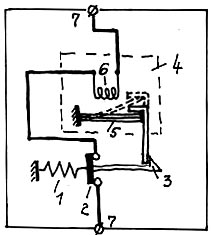
1 - Пружина (в данном случае во взведенном положении растянута)
Принцип действия такой же как и в первом случае, с той лишь разницей, что удерживающее устройство 3 освобождается под действием биметаллической пластины 5, которая изгибается от тепла, выделяемого нагревательным элементом 6. Количество тепла определяется током, протекающим через защищаемую цепь.
2 - Главный контакт автоматического выключателя
3 - Удерживающее устройство
4 - Тепловой расцепитель
5 - Биметаллическая пластина
6 - Нагревательный элемент
7 - Контактные зажимы автоматического выключателя
[Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- включение автоматического выключателя
- оперирование автоматического выключателя
- отключение автоматического выключателя
- срабатывание автоматического выключателя
EN
- auto-cutout
- automatic circuit breaker
- automatic cutout
- automatic switch
- breaker
- CB
- circuit breaker
- circuit-breaker
- cutout
DE
FR
Смотри также
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > автоматический выключатель
7 автоматический выключатель постоянного тока
автоматический выключатель постоянного тока
-En
d.c. circuit-breaker
switching device capable of making, carrying and breaking direct currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying (up to a specified limit and for a specified time) and breaking currents under specified abnormal conditions, such as those of short-circuit.
[IEC 61992-1, ed. 2.0 (2006-02)]Fr
disjoncteur à courant continu
appareil de connexion capable d'établir, de supporter et d'interrompre des courants continus dans les conditions normales du circuit ainsi que d'établir, de supporter (jusqu'à une limite spécifiée et pendant une durée spécifiée) et d'interrompre des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit, telles que celles du court-circuit.
[IEC 61992-1, ed. 2.0 (2006-02)]Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
EN
- circuit-breaker for direct current
- circuit-breaker for direct current applications
- d.c. circuit breaker
- d.c. circuit-breaker
- direct current circuit breaker
- direct current circuit-breaker
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > автоматический выключатель постоянного тока
8 воздействующая величина электрического реле
- Grandeur d’alimentation
- grandeur d'alimentation
воздействующая величина электрического реле
Электрическая величина, которая одна или в сочетании с другими электрическими величинами должна быть приложена к электрическому реле в заданных условиях для достижения ожидаемого функционирования
[ ГОСТ 16022-83]EN
energizing quantity
an electrical quantity (either current or voltage) which alone, or in combination with other such quantities, applied to a relay under specified conditions enables it to fulfil its purpose
[IEV number 446-12-01]
energizing quantity (for elementary relays)electrical quantity which, when applied to the input circuit of an elementary relay under specified conditions, enables it to fulfill its purpose
NOTE – For elementary relays the energizing quantity is usually a voltage. Therefore, the input voltage as energizing quantity is used in the definitions given below. Where a relay is energized by a given current instead, the respective terms and definitions apply with "current" used instead of "voltage".
[IEV number 444-03-01]FR
grandeur d'alimentation
grandeur électrique, courant ou tension, qui, seule ou en combinaison avec d'autres grandeurs électriques, courant ou tension, doit être appliquée dans des conditions spécifiées à un relais pour en obtenir le comportement attendu
[IEV number 446-12-01]
grandeur d'alimentation (pour les relais élémentaires), f
grandeur électrique qui, appliquée au circuit d'entrée d'un relais élémentaire dans des conditions spécifiées, lui permet d'accomplir sa fonction
NOTE – Pour les relais élémentaires, la grandeur d'alimentation est en général une tension. En conséquence, on utilise la tension d'entrée comme grandeur d'alimentation dans les définitions données ci-dessous. Lorsqu'un relais est alimenté par un courant, les termes et définitions respectifs sont à utiliser avec le terme "courant" au lieu du terme "tension".
[IEV number 444-03-01]Тематики
Классификация
>>>EN
DE
FR
49. Воздействующая величина электрического реле
D. Eingangsgrösse
Е. Energizing quantity
F. Grandeur d’alimentation
Источник: ГОСТ 16022-83: Реле электрические. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > воздействующая величина электрического реле
9 входное полное сопротивление
входное полное сопротивление
-
[IEV number 312-06-18]EN
input impedance
impedance of the input circuit measured between the input terminals under operating conditions
NOTE 1 – The impedance can be expressed in terms of admittance.
NOTE 2 – In certain instances, for example, sampling devices or self-balancing potentiometers, the impedance can be different according to the instant when it is determined, before, during or after the instant of measurement.
NOTE 3 – When the input circuit is such that the instantaneous value of the current flowing into the input terminals is a non-linear function of the instantaneous value of the input voltage under specified conditions of frequency and voltage, the combination of resistance and reactance which would absorb the same active power and in which would flow a reactive current equal to the fundamental component that is flowing in the actual input circuit, is sometimes called the "equivalent input impedance".
[IEV number 312-06-18]FR
impédance du circuit d'entrée
impédance du circuit d'entrée entre les bornes d'entrée dans les conditions de fonctionnement
NOTE 1 – L'impédance peut être exprimée en termes d'admittance.
NOTE 2 – Dans certains cas, par exemple les dispositifs d'échantillonnage ou les potentiomètres à rééquilibrage automatique, l'impédance peut être différente selon l’instant où elle est déterminée, avant, pendant ou après la mesure.
NOTE 3 – Lorsque le circuit d'entrée est tel que la valeur instantanée du courant traversant les bornes d'entrée est une fonction non linéaire de la valeur instantanée de la tension d'entrée dans des conditions spécifiées de fréquence et de tension, l'impédance d'une combinaison formée par une résistance et une réactance qui absorberaient la même puissance active et dans laquelle circulerait un courant réactif égal à la composante fondamentale qui circule dans le circuit d'entrée réel, est parfois appelée "impédance équivalente d'entrée".
[IEV number 312-06-18]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > входное полное сопротивление
10 выходное полное сопротивление
выходное полное сопротивление
-
[IEV number 312-06-19]EN
output impedance
impedance of the output circuit measured between the output terminals under operating conditions
NOTE 1 – The impedance can be expressed in terms of admittance.
NOTE 2 – In certain instances, for example, sampling devices or self-balancing potentiometers, the impedance can be different according to the instant when it is determined, before, during or after the instant of measurement.
NOTE 3 – When the output circuit is such that the instantaneous value of the current flowing into the output terminals is a non-linear function of the instantaneous value of the output voltage under specified conditions of frequency and voltage, the combination of resistance and reactance which would absorb the same active power and in which would flow a reactive current equal to the fundamental component that is flowing in the actual output circuit, is sometimes called the "equivalent output impedance".
[IEV number 312-06-19]FR
impédance du circuit de sortie
impédance du circuit de sortie entre les bornes de sortie dans les conditions de fonctionnement
NOTE 1 – L'impédance peut être exprimée en termes d'admittance.
NOTE 2 – Dans certains cas, par exemple les dispositifs d'échantillonnage ou les potentiomètres à rééquilibrage automatique, l'impédance peut être différente selon l’instant où elle est déterminée, avant, pendant ou après la mesure.
NOTE 3 – Lorsque le circuit de sortie est tel que la valeur instantanée du courant traversant les bornes de sortie est une fonction non linéaire de la valeur instantanée de la tension de sortie dans des conditions spécifiées de fréquence et de tension, l'impédance d'une combinaison formée par une résistance et une réactance qui absorberaient la même puissance active et dans laquelle circulerait un courant réactif égal à la composante fondamentale qui circule dans le circuit de sortie réel, est parfois appelée "impédance équivalente de sortie".
[IEV number 312-06-19]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > выходное полное сопротивление
11 заземлитель (коммутационный аппарат)
заземлитель
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, используемый для заземления частей цепи, способный выдерживать в течение нормированного времени токи при ненормальных условиях, таких как короткое замыкание, но не предусмотренный для проведения тока при нормальных условиях в цепи.
Примечания
1 Заземлитель может обладать включающей способностью при коротком замыкании.
2 Заземлитель на номинальное напряжение 110 кВ и выше может отключать (коммутировать) и проводить наведенные токи.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
выключатель заземления
Механический 1) коммутационный аппарат для заземления частей электрической цепи, способный выдерживать электрические токи заданной продолжительности при ненормальных режимах, например при коротких замыканиях, но не предназначенный для пропускания электрического тока в нормальных режимах работы электрической цепи.
Примечание - Выключатель может быть стойким к токам короткого замыкания.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]EN
earthing switch
mechanical switching device for earthing parts of an electric circuit, capable of withstanding for a specified duration electric currents under abnormal conditions such as those of short-circuit, but not required to carry electric current under normal conditions of the electric circuit
NOTE – An earthing switch can have a short circuit making capacity.
Source: 441-14-11 MOD, 605-02-43 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-34]FR
connecteur de terre
appareil mécanique de connexion utilisé pour mettre à la terre des parties d'un circuit électrique, capable de supporter, pendant une durée spécifiée, des courants dans des conditions anormales telles que celles de court-circuit, mais non prévu pour transporter le courant électrique dans les conditions normales du circuit électrique
NOTE – Un connecteur de terre peut avoir un pouvoir de fermeture en court circuit.
Source: 441-14-11 MOD, 605-02-43 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-34]1) Должно быть контактный
[Интент]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- заземление
- электробезопасность
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > заземлитель (коммутационный аппарат)
12 микросреда (воздушного зазора или расстояния утечки)
микросреда (воздушного зазора или расстояния утечки)
Атмосфера вокруг данного воздушного зазора или расстояния утечки.
Примечание. Эффективность изоляции определяет микросреда расстояния утечки или воздушного зазора, а не макросреда аппарата. Эта микросреда может быть лучше или хуже макросреды аппарата. К ней относятся все факторы, влияющие на изоляцию: климатические и электромагнитные условия, образование загрязнений и т. п.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
micro-environment (of a clearance or creepage distance)
ambient conditions which surround the clearance or creepage distance under consideration
NOTE - The micro-environment of the creepage distance or clearance and not the environment of the equipment determines the effect on the insulation. The micro-environment might be better or worse than the environment of the equipment. It includes all factors influencing the insulation, such as climatic and electromagnetic conditions, generation of pollution, etc.
[IEC 60947-1, ed. 5.0 (2007-06)]FR
micro-environnement (d'une distance d'isolement ou d'une ligne de fuite)
conditions ambiantes à proximité immédiate des distances d'isolement ou des lignes de fuite considérées
NOTE - C'est le micro-environnement des lignes de fuite ou des distances d'isolement et non l'environnement du matériel qui détermine l'effet sur l'isolation. Le micro-environnement peut être meilleur ou pire que l'environnement du matériel. Il comprend tous les facteurs influant sur l'isolation, tels que conditions climatiques, influences électromagnétiques, production de pollution, etc.
[IEC 60947-1, ed. 5.0 (2007-06)]EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > микросреда (воздушного зазора или расстояния утечки)
13 силовой выключатель
силовой выключатель
-
[Интент]EN
circuit-breaker
a mechanical switching device, capable of making, carrying and breaking currents under normal circuit conditions and also making, carrying for a specified time and breaking currents under specified abnormal circuit conditions such as those of short circuit
[IEV ref 441-14-20]FR
disjoncteur
appareil mécanique de connexion capable d'établir, de supporter et d'interrompre des courants dans les conditions normales du circuit, ainsi que d'établir, de supporter pendant une durée spécifiée et d'interrompre des courants dans des conditions anormales spécifiées du circuit telles que celles du court-circuit
[IEV ref 441-14-20]
Рис. Siemens
Силовой ( баковый элегазовый) выключатель 3AP1 DT
Рис. Siemens
Силовой (колонковый элегазовый) выключательТематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- комплектное распред. устройство (КРУ)
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > силовой выключатель
14 нарушение условий конкуренции
нарушение условий конкуренции
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
distortion of competition
Article 85(1) of the EEC Treaty prohibits all agreements between undertakings, decisions by associations of undertakings and concerted practices which may affect trade between member states and which have as their object or effect the prevention, restriction or distortion of competition within the common market. All such arrangements are automatically null and void under Article 85(2), unless exempted by the Commission pursuant to Article 85(3). The text of Article 85 is as follows: "1. The following shall be prohibited as incompatible with the common market: all agreements between undertakings, decisions by associations of undertakings and concerted practices which may affect trade between member states and which have as their object or effect the prevention, restriction or distortion of competition within the common market, and in particular those which: (a) directly or indirectly fix purchase or selling prices or any other trading conditions; (b) limit or control production, markets, technical development, or investment; (c) share markets or sources of supply; (d) apply dissimilar conditions to equivalent transactions with other trading parties, thereby placing them at a competitive disadvantage; (e) make the conclusion of contracts subject to acceptance by the other parties of supplementary obligations which, by their nature or according to commercial usage, have no connection with the subject of such contracts. (Source: CLAORG)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > нарушение условий конкуренции
15 ограничение конкуренции
ограничение конкуренции
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
restriction on competition
Article 85(1) of the EEC Treaty prohibits all agreements between undertakings, decisions by associations of undertakings and concerted practices which may affect trade between member states and which have as their object or effect the prevention, restriction or distortion of competition within the common market. All such arrangements are automatically null and void under Article 85(2), unless exempted by the Commission pursuant to Article 85(3). The text of Article 85 is as follows: "1. The following shall be prohibited as incompatible with the common market: all agreements between undertakings, decisions by associations of undertakings and concerted practices which may affect trade between member states and which have as their object or effect the prevention, restriction or distortion of competition within the common market, and in particular those which: (a) directly or indirectly fix purchase or selling prices or any other trading conditions; (b) limit or control production, markets, technical development, or investment; (c) share markets or sources of supply; (d) apply dissimilar conditions to equivalent transactions with other trading parties, thereby placing them at a competitive disadvantage; (e) make the conclusion of contracts subject to acceptance by the other parties of supplementary obligations which, by their nature or according to commercial usage, have no connection with the subject of such contracts. (Source: CLAORG)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > ограничение конкуренции
16 номинальное напряжение
номинальное напряжение
Напряжение, установленное изготовителем для прибора
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]
номинальное напряжение Uном, кВ
Номинальное междуфазное напряжение электрической сети, для работы в которой предназначены коммутационные аппараты.
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
номинальное напряжение
Un
Напряжение, применяемое для обозначения или идентификации системы электроснабжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51317.4.30-2008 (МЭК 61000-4-30:2008)]EN
rated voltage
voltage assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
rated voltage
quantity value assigned, generally by the manufacturer, for a specified operating condition of a machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
rated voltage
input or output supply voltage for which equipment is designed or specified
[IEC 88528-11, ed. 1.0 (2004-03)]
rated voltage
specified value of the voltage at the terminals of the machine when operating at a rating. If unidirectional, the voltage is the arithmetic mean of the recurring waveform and if alternating it is the root mean square value of the fundamental frequency component of the recurring waveform
NOTE - In the case of a machine with a protective resistor permanently in series, the resistor is considered as an integral part of the machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
rated voltage
the value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer to a component, device or equipment and to which operation and performance characteristics are referred
NOTE - Equipment may have more than one rated voltage value or may have a rated voltage range.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
rated voltage
reference voltage for which the cable is designed, and which serves to define the electrical tests
NOTE 1 - The rated voltage is expressed by the combination of two values: Uo/U expressed in volts (V):
Uo being the r.m.s. value between any insulated conductor and "earth" (metal covering of the cable or the surrounding medium);
U being the r.m.s. value between any two phase conductors of a multicore cable or of a system of single-core cables.
In an alternating-current system, the rated voltage of a cable is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system for which it is intended.
This condition applies both to the value Uo and to the value U.
In a direct current system, the nominal voltage of the system is not higher than 1,5 times the rated voltage of the cable.
NOTE 2 - The operating voltage of a system may permanently exceed the nominal voltage of such a system by 10 %. A cable can be used at a 10 % higher operating voltage than its rated voltage if the latter is at least equal to the nominal voltage of the system
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
rated voltage
highest allowable voltage between the conductors in a twin and multi conductor cable, or between one conductor and an electrical conductive screen, or between the two ends of a single core cable, or earth in unscreened cables
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
rated voltage
the r.m.s. line-to-line voltage under rated conditions
Primary side of input transformer: ULN
Converter input: UVN
Converter output: UaN
Motor voltage: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
rated voltage
input or output voltage (for three-phase supply, the phase-to-phase voltage) as declared by the manufacturer
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
nominal voltage, Un
voltage by which a system is designated or identified
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]FR
tension assignée
tension attribuée à l'appareil par le fabricant
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]
tension nominale
tension assignée, généraleme<>value of voltage assigned by the manufacturer, to a componentnt par le constructeur pour des conditions spécifiées de fonctionnement de la machine
[IEC 60034-18-41, ed. 1.0 (2006-10)]
tension assignée
tension spécifiée aux bornes de la machine quand celle-ci fonctionne au régime assigné. Dans le cas d'une tension redressée, sa valeur est égale à la valeur moyenne de l'onde périodique. Dans le cas d'une tension alternative, sa valeur est égale à la valeur efficace de la composante fondamentale de l'onde périodique
NOTE - Dans le cas d'une machine équipée d'une résistance de protection connectée en permanence en série, la résistance est considérée comme faisant partie intégrante de la machine
[IEC 60349-1, ed. 1.0 (1999-11)]
tension assignée
valeur de la tension, assignée par le constructeur à un composant, à un dispositif ou à un matériel, et à laquelle on se réfère pour le fonctionnement et pour les caractéristiques fonctionnelles
NOTE - Les matériels peuvent avoir plusieurs valeurs ou une plage de tensions assignées.
[IEC 62497-1, ed. 1.0 (2010-02)]
tension assignée
tension de référence pour laquelle le conducteur ou le câble est prévu et qui sert à définir les essais électriques
NOTE 1 - La tension assignée est exprimée par la combinaison de deux valeurs Uo /U, exprimées en volts (V):
Uo étant la valeur efficace entre l'âme d'un conducteur isolé quelconque et la «terre» (revêtement métallique du câble au milieu environnant);
U étant la valeur efficace entre les âmes conductrices de deux conducteurs de phase quelconques d'un câble multiconducteur ou d'un système de câbles monoconducteurs ou de conducteurs.
Dans un système à courant alternatif, la tension assignée d'un conducteur ou d’un câble est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système pour lequel il est prévu.
Cette condition s'applique à la fois à la valeur Uo et à la valeur U.
Dans un système à courant continu, la tension nominale admise du système n’est pas supérieure à 1,5 fois la tension assignée du conducteur ou du câble.
NOTE 2 - La tension de service d'un système peut en permanence dépasser la tension nominale dudit système de 10 %. Un conducteur ou un câble peut être utilisé à une tension de service supérieure de 10 % à sa tension assignée si cette dernière est au moins égale à la tension nominale du système
[IEC 60245-1, ed. 4.0 (2003-12)]
tension assignée
tension maximale admissible entre les âmes dans un câble ayant une paire ou multi conducteur ou entre une âme et un écran conducteur électrique ou avec la terre pour un câble non écranté ou encore entre les deux extrémités d’un câble à âme unique
[IEC 60800, ed. 3.0 (2009-07)]
tension assignée
valeur efficace de la tension de ligne (entre phases) dans les conditions assignées
Primaire du transformateur d’entrée: ULN
Entrée du convertisseur: UVN
Sortie du convertisseur: UaN
Moteur: UAN
[IEC 61800-4, ed. 1.0 (2002-09)]
tension assignée
tension d’alimentation d’entrée ou de sortie (dans le cas d’une alimentation triphasée, tension entre phases) déclarée par le constructeur
[IEC 62040-1, ed. 1.0 (2008-06)]
tension nominale, Un
tension par laquelle un réseau est désigné ou identifié
[IEC 61000-4-30, ed. 2.0 (2008-10)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- прибор электрический
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
- Un
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > номинальное напряжение
17 wonder
wonder ['wʌndə(r)]1 noun∎ the seven wonders of the world les sept merveilles du monde;∎ the wonders of science les miracles de la science;∎ the wonders of nature les merveilles de la nature;∎ a hot bath worked wonders for her aching body un bain chaud la soulagea à merveille de ses douleurs∎ the wonder (of it) is that he manages to get any work done at all le plus étonnant dans tout cela, c'est qu'il arrive à travailler;∎ it's a wonder that anyone can work in such awful conditions cela me semble incroyable qu'on puisse travailler dans des conditions aussi épouvantables;∎ it's a wonder (that) she didn't resign on the spot c'est étonnant qu'elle n'ait pas démissionné sur-le-champ;∎ no wonder they refused ce n'est pas étonnant qu'ils aient refusé;∎ no wonder! ce n'est pas étonnant!, cela vous étonne?;∎ is it any wonder that he got lost? cela vous étonne qu'il se soit perdu?;∎ it's little or small wonder no one came ce n'est guère étonnant que personne ne soit venu;∎ humorous wonders will never cease! on n'a pas fini d'être étonné!∎ the children were filled with wonder les enfants étaient émerveillés;∎ they looked on, lost in wonder ils regardaient, totalement émerveillés ou éblouis;∎ there was a look of wonder in his eyes il avait les yeux pleins d'étonnement∎ a boy wonder un petit prodige ou génie(drug, detergent) miracle; (child) prodige(a) (ask oneself) se demander;∎ I wonder where she's gone je me demande où elle est allée;∎ I wonder how he managed it je me demande comment il s'y est pris;∎ I wonder why je me demande bien pourquoi;∎ I wonder who invented that je suis curieux de savoir qui a inventé cela;∎ it makes you wonder how safe these power stations are on en vient à se demander si ces centrales électriques sont vraiment sûres;∎ I often wonder that myself je me pose souvent la question;∎ I wonder whether or if she'll come je me demande si elle viendra∎ I was wondering if you were free tomorrow est-ce que par hasard vous êtes libre demain?;∎ I wonder if you could help me pourriez-vous m'aider, s'il vous plaît?(c) (be surprised) s'étonner;∎ I wonder that he wasn't hurt je m'étonne ou cela m'étonne qu'il n'ait pas été blessé;∎ I shouldn't wonder if he were already married cela ne m'étonnerait pas ou cela ne me surprendrait pas qu'il soit déjà marié;∎ she knows a lot more, I shouldn't wonder cela ne m'étonnerait pas qu'elle en sache beaucoup plus long que ça(a) (think, reflect) penser, réfléchir;∎ it makes you wonder cela donne à penser ou à réfléchir;∎ his remarks set me wondering ses remarques m'ont laissé songeur ou m'ont donné à réfléchir;∎ I'm wondering about going tomorrow je me demande si je ne vais pas y aller demain;∎ I was wondering about it too je me posais la même question;∎ the war will be over in a few days - I wonder la guerre sera finie dans quelques jours - je n'en suis pas si sûr;∎ why? - oh, I just wondered pourquoi? - oh, pour rien, comme ça(b) (marvel, be surprised) s'étonner, s'émerveiller;∎ to wonder at sth s'émerveiller de qch;∎ the people wondered at the magnificent sight les gens s'émerveillaient de ce magnifique spectacle;∎ I don't wonder (that) you're annoyed cela ne m'étonne pas que vous soyez contrarié;∎ I don't wonder cela ne m'étonne pas18 защитный импеданс
защитный импеданс
Компонент, совокупность компонентов или комбинация основной изоляции и устройства, ограничивающего ток или напряжение, импеданс, конструкция и надежность которых таковы, что, будучи включенными между доступными токопроводящими частями и частями, опасными для жизни, они обеспечивают защиту в соответствии с требованиями настоящего стандарта при нормальных условиях и условиях единичной неисправности.
[ ГОСТ Р 52319-2005( МЭК 61010-1: 2001)]
защитный импеданс
Импеданс, включенный между токоведущими частями и доступными проводящими частями конструкций класса II; характеристики его должны быть такими, чтобы ток, проходящий в приборе при нормальной эксплуатации и при возможных повреждениях прибора, ограничивался безопасным значением.
[ ГОСТ Р 52161. 1-2004 ( МЭК 60335-1: 2001)]EN
protective impedance
an impedance connected between live parts and exposed conductive parts, of such value that the current, in normal use and under likely fault conditions in the electronic switch, is limited to a safe value, and which is so constructed that the reliability is maintained throughout the life of the electronic switch
[IEV number 442-04-24]FR
impédance de protection
impédance connectée entre parties actives et masse, de valeur telle que le courant, en utilisation normale et dans des conditions possibles de panne de l'interrupteur électronique, soit limité à une valeur de sécurité, et qui est construite de façon telle que sa fiabilité soit maintenue au cours de la durée de vie de l'interrupteur électronique
[IEV number 442-04-24]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > защитный импеданс
19 класс II
класс II
К классу II должны относиться изделия, имеющие двойную или усиленную изоляцию и не имеющие элементов для заземления.
[ ГОСТ 12.2.007.0-75]EN
protective class II
equipment in which protection against electric shock does not rely on basic insulation only, but in which additional safety precautions such as double insulation or reinforced insulation are provided, there being no provision for protective earthing or reliance upon installation conditions
[IEC 62103, ed. 1.0 (2003-07)]FR
matériel de la classe II
matériel dans lequel la protection contre les chocs électriques ne repose pas uniquement sur l'isolation principale, mais qui comporte des mesures supplémentaires de sécurité, telles que la double isolation ou l'isolation renforcée. Ces mesures ne comportent pas de moyen de mise à la terre de protection et ne dépendent pas des conditions d'installation
[IEC 62103, ed. 1.0 (2003-07)]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > класс II
20 пульсация
пульсация
-
[IEV number 312-07-02]EN
ripple
set of unwanted periodic deviations with respect to the average value of the measured or supplied quantity, occurring at frequencies which can be related to that of the mains supply, or of some other definite source, such as a chopper
NOTE – Ripple is determined under specified conditions and is a part of PARD.
[IEV number 312-07-02]FR
ondulation
ensemble de déviations périodiques indésirables par rapport à la valeur moyenne de la grandeur mesurée ou fournie, se produisant à des fréquences qui peuvent être en rapport avec celles du réseau d'alimentation électrique ou de toute autre source, telle qu'un hacheur
NOTE – L'ondulation est déterminée dans des conditions spécifiées et fait partie des déviations périodiques et/ou erratiques.
[IEV number 312-07-02]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > пульсация
Страницы- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
CONDITIONS — (Heb. תְּנָאִים, tena im). Definition Conditions is an ambiguous word inasmuch as it refers not only to the external factors upon which the existence of an agreement is made to depend but also to the actual terms of the contract itself. Thus, one … Encyclopedia of Judaism
Conditions races — are horse races where the weights carried by the runners are laid down by the conditions attached to the race. Weights are allocated according to; the sex of the runners, with female runners carrying less weight than males; the age of the runners … Wikipedia
Conditions comorbid to autism spectrum disorders — There are many conditions comorbid to autism spectrum disorders, such as fragile X syndrome and epilepsy. In medicine and in psychiatry, comorbidity describes the effect of other diseases an individual patient might have other than the primary… … Wikipedia
performance-limiting conditions — Conditions in which the boundaries of aircraft performance are approached, such as when the stall warning, auto ignition, ground proximity warning systems, etc., begin to operate … Aviation dictionary
Karush–Kuhn–Tucker conditions — In mathematics, the Karush–Kuhn–Tucker (KKT) conditions (also known as the Kuhn–Tucker conditions) are necessary for a solution in nonlinear programming to be optimal, provided that some regularity conditions are satisfied. Allowing inequality… … Wikipedia
Gluten-sensitive enteropathy associated conditions — Gluten sensitive enteropathy (GSE) has key symptoms typically restricted to the bowel and associated tissues, however there are a wide variety of associated conditions. These include bowel disorders (diarrhoea, constipation, irritable bowel),… … Wikipedia
Causality conditions — In the study of Lorentzian manifold spacetimes there exists a hierarchy of causality conditions which are important in proving mathematical theorems about the global structure of such manifolds. These conditions were collected during the late… … Wikipedia
Coordinate conditions — In general relativity, the laws of physics can be expressed in a generally covariant form. In other words, the real world does not care about our coordinate systems. However, it is often useful to fix upon a particular coordinate system, in order … Wikipedia
List of cutaneous conditions — This is an incomplete list, which may never be able to satisfy particular standards for completeness. You can help by expanding it with reliably sourced entries. See also: Cutaneous conditions, Category:Cutaneous conditions, and ICD 10… … Wikipedia
Standard conditions for temperature and pressure — Not to be confused with Standard state. In chemistry, standard condition for temperature and pressure (informally abbreviated as STP) are standard sets of conditions for experimental measurements, to allow comparisons to be made between different … Wikipedia
Periodic boundary conditions — In molecular dynamics, periodic boundary conditions (PBC) are a set of boundary conditions used to simulate an effectively infinitely tiled system, usually applied to systems consisting of one or more macromolecules in a bath of explicit solvent … Wikipedia
Перевод: со всех языков на французский
с французского на все языки- С французского на:
- Все языки
- Со всех языков на:
- Все языки
- Английский
- Арабский
- Венгерский
- Греческий
- Датский
- Исландский
- Испанский
- Итальянский
- Латышский
- Литовский
- Македонский
- Монгольский
- Немецкий
- Норвежский
- Польский
- Португальский
- Румынский, Молдавский
- Русский
- Словацкий
- Словенский
- Турецкий
- Украинский
- Финский
- Французский
- Чешский
- Шведский
