-
61 part of a cable
элемент кабельного изделия
Любая конструктивная часть кабельного изделия.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
conductor (of a cable)
part of a cable which has the specific function of carrying current
[IEV number 461-01-01]токопроводящая жила
Элемент кабельного изделия, предназначенный для прохождения электрического тока
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > part of a cable
-
62 insulated conductor
- изолированный проводник
- изолированный провод
- изолированная жила (термин употребляется в Северной Америке)
изолированная жила (термин употребляется в Северной Америке)
совокупность элементов, состоящая из жилы, ее изоляции (и экранов, если они есть)
Примечание. В Северной Америке термин «core of a cable» определяется как совокупность компонентов кабеля, расположенных под общим защитным покровом, таким как оболочка. Такое применение этого термина не допустимо
[IEV number 461-04-04]EN
core
insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor with its own insulation (and screens if any)
NOTE – In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath. Such usage is deprecated.
[IEV number 461-04-04]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
NOTE – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
[IEV number 461-04-04]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
- Ader, f
FR
изолированный провод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
core insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
[IEC 61892-4, ed. 1.0 (2007-06)]
core-insulated conductor (North America)
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
NOTE In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath (jacket).
[IEC 60092-350, ed. 3.0 (2008-02)]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
Note – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
[ IEV ref 461-04-04]Рис. Schneider Electric
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
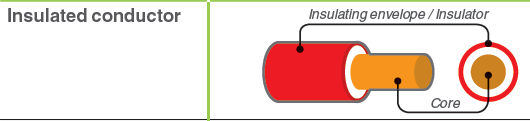
An insulated conductor is made up of a conductor core and its
insulating envelope.
[Schneider Electric]Изолированный провод состоит из токопроводящей жилы и изоляции провода.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- core insulated conductor
- core-insulated conductor
- covered conductor
- covered wire
- insulated conductor
DE
- Ader, f
FR
изолированный проводник
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > insulated conductor
-
63 external conductor
внешний проводник
-
[IEV number 442-01-37]
внешний провод
Любой кабель, гибкий шнур, токопроводящая жила или провод, часть которого выступает наружу из управляющего устройства, встроенного в шнур, из управляющего устройства с независимым монтажом или из оборудования, в (или на) котором установлено управляющее устройство.
Примечание - Такой провод может быть либо питающим, либо функциональным, либо промежуточным шнуром между различными частями оборудования, либо может быть частью стационарной электропроводки.
[ГОСТ IЕС 60730-1-2011]EN
external conductor
any cable, flexible cable or cord, core or conductor, a part of which is external to an accessory
NOTE – Such a conductor can be a supply lead or interconnecting cord between separate parts of an accessory; it can form part of the fixed wiring.
[IEV number 442-01-37]
external conductor
any cable, flexible cord, core or conductor, a part of which is external to an in line cord control, an independently mounted control or to an equipment in or on which a control is mounted
Note 1 to entry: Such a conductor may be a supply lead, a function cord or interconnecting cord between different parts of an equipment; or it may form part of the fixed wiring.
[IEC 60730-1, ed. 5.0 (2013-11)]FR
conducteur externe
tout câble souple, âme conductrice ou conducteur dont une partie est extérieure à l'appareil
NOTE – Un tel conducteur peut-être un câble d'alimentation ou un cordon de raccordement entre des parties séparées d'un appareil ou encore constituer une partie du câblage fixe.
[IEV number 442-01-37]
conducteur externe
câble souple, cordon, âme conductrice ou conducteur dont une partie sort d'un dispositif de commande intercalé, d'un dispositif de commande à montage indépendant ou d'un matériel dans ou sur lequel un dispositif de commande est monté
Note 1 à l'article: Un tel conducteur peut soit être un câble d'alimentation, un câble fonctionnel ou un cordon de raccordement entre différentes parties d'un appareil, soit constituer une partie du câblage fixe d'un matériel.
[IEC 60730-1, ed. 5.0 (2013-11)]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > external conductor
-
64 core insulated conductor
изолированный провод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
core insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
[IEC 61892-4, ed. 1.0 (2007-06)]
core-insulated conductor (North America)
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
NOTE In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath (jacket).
[IEC 60092-350, ed. 3.0 (2008-02)]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
Note – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
[ IEV ref 461-04-04]Рис. Schneider Electric
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
An insulated conductor is made up of a conductor core and its
insulating envelope.
[Schneider Electric]Изолированный провод состоит из токопроводящей жилы и изоляции провода.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- core insulated conductor
- core-insulated conductor
- covered conductor
- covered wire
- insulated conductor
DE
- Ader, f
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > core insulated conductor
-
65 core-insulated conductor
изолированный провод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
core insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
[IEC 61892-4, ed. 1.0 (2007-06)]
core-insulated conductor (North America)
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
NOTE In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath (jacket).
[IEC 60092-350, ed. 3.0 (2008-02)]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
Note – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
[ IEV ref 461-04-04]Рис. Schneider Electric
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
An insulated conductor is made up of a conductor core and its
insulating envelope.
[Schneider Electric]Изолированный провод состоит из токопроводящей жилы и изоляции провода.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- core insulated conductor
- core-insulated conductor
- covered conductor
- covered wire
- insulated conductor
DE
- Ader, f
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > core-insulated conductor
-
66 covered conductor
изолированный провод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]EN
core insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
[IEC 61892-4, ed. 1.0 (2007-06)]
core-insulated conductor (North America)
assembly comprising a conductor and its own insulation (and screens, if any)
NOTE In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath (jacket).
[IEC 60092-350, ed. 3.0 (2008-02)]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
Note – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
[ IEV ref 461-04-04]Рис. Schneider Electric
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
An insulated conductor is made up of a conductor core and its
insulating envelope.
[Schneider Electric]Изолированный провод состоит из токопроводящей жилы и изоляции провода.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- core insulated conductor
- core-insulated conductor
- covered conductor
- covered wire
- insulated conductor
DE
- Ader, f
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > covered conductor
-
67 prepared conductor
подготовленный проводник
Проводник, жилы которого спаяны или конец которого снабжен кабельным наконечником, ушком и т. п
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
проводник, подготовленный к присоединению
-
[IEV number 442-01-27]EN
prepared conductor
conductor, the strands of which are soldered or the end of which is fitted with a cable lug, eyelet, etc.
[IEC 61095, ed. 2.0 (2009-02)]
prepared conductor
a conductor the end of which is fitted with an attachment such as eyelet, sleeve or cable lug
[IEV number 442-01-27]FR
conducteur préparé
conducteur dont les torons sont soudés ou dont l'extrémité est munie d'une cosse, d'un œillet, etc.
[IEC 61095, ed. 2.0 (2009-02)]
conducteur préparé
conducteur dont l'extrémité dénudée est munie d'un accessoire tel que manchon ou cosse ou raccord de câbles
[IEV number 442-01-27]

Проводник с луженым торцом многопроволочной жилы
Проводник с штифтовым плоским кабельным наконечником


Проводник с штифтовым втулочным кабельным наконечником
Проводник с кольцевым кабельным наконечником
EN
DE
FR
3.3.24 подготовленный проводник (prepared conductor): Проводник, жилы которого облужены или конец которого снабжен кабельным наконечником и т.д.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51731-2010: Контакторы электромеханические бытового и аналогичного назначения оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > prepared conductor
-
68 flexible conductor
гибкая токопроводящая жила
скрученная токопроводящая жила, состоящая из проволок достаточно небольшого диаметра и расположенных таким образом, чтобы жила могла быть использована в гибком кабеле
[IEV number 461-01-11]EN
flexible conductor
stranded conductor having wires of diameters small enough and so assembled that the conductor is suitable for use in a flexible cable
[IEV number 461-01-11]FR
âme souple
âme câblée constituée de fils suffisamment fins et assemblés de façon à pouvoir être utilisés dans un câble souple
[IEV number 461-01-11]
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- flexibler Leiter, m
FR
гибкий провод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
шнур
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > flexible conductor
-
69 neutral conductor
нейтральный провод
нейтраль
—
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
нулевая жила
Основная жила, предназначенная для присоединения к заземленной или незаземленной нейтрали источника тока.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
нулевая жила
Изолированная токопроводящая жила кабеля, выполняющая функцию нулевого рабочего проводника (N).
[ ГОСТ Р 53769-2010]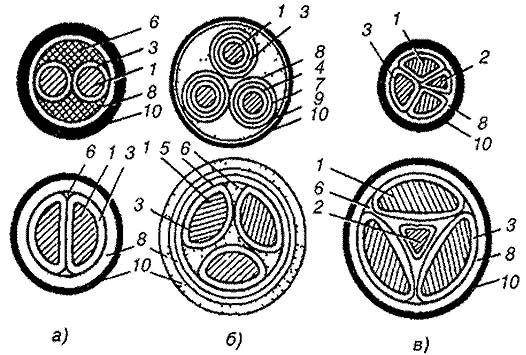
[ http://energ2010.narod.ru/silkabel.htm]
Конструкция силовых кабелейа) - двухжильные кабели с круглыми и сегментными жилами,
6) - трехжильные кабели с поясной изоляцией и отдельными оболочками,
в) - четырехжильные кабели с нулевой жилой круглой, секторной или треугольной формы,
1 - токопроводящая жила,
2 - нулевая жила,
3 - изоляция жилы,
4 - экран на токопроводящей жиле,
5 - поясная изоляция,
6 - заполнитель,
7 - экран на изоляции жилы,
8 - оболочка
9 - бронепокров,
10 - наружный защитный покровТематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
нулевой рабочий проводник N
Проводник, присоединенный к нейтральной точке системы и способствующий передаче электрической энергии.
МЭК 60050(826-01-03).
Примечание. В некоторых случаях и установленных условиях возможно объединение функций нулевого рабочего и защитного проводников в одном проводнике с условным обозначением PEN.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
нейтральный проводник
нулевой рабочий проводник
Проводник, присоединенный к нейтральной точке и используемый для распределения электрической энергии.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
В Правилах устройства электроустановок широко используют термин «нулевой рабочий проводник». Однако в Международном электротехническом словаре (МЭС) и в других стандартах Международной электротехнической комиссии (МЭК) этот термин не применяют. Во всех стандартах МЭК употребляют термин «нейтральный проводник». Поэтому термин «нулевой рабочий проводник» следует исключить из национальной нормативной и правовой документации, распространяющейся на низковольтные электроустановки. Вместо него следует использовать термин «нейтральный проводник», который соответствует МЭС.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CD/view/38/]EN
neutral conductor
conductor electrically connected to the neutral point and capable of contributing to the distribution of electric energy
Source: 601-03-10 MOD, 826-01-03 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-06]FR
conducteur (de) neutre
conducteur relié électriquement au point neutre et pouvant contribuer à la distribution de l'énergie électrique
Source: 601-03-10 MOD, 826-01-03 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-06]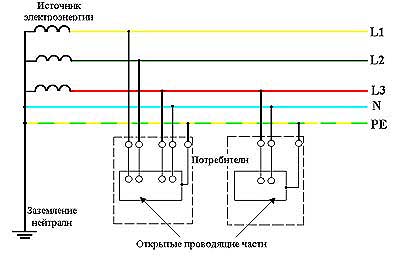
[http://bgd.alpud.ru/images/tn_s.htm]L1, L2, L3 - линейные проводники
N - нулевой рабочий проводник
PE - защитный проводник
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
EN
DE
FR
провод нулевой
Электрический провод сети, соединённый с глухозаземлённой нейтралью трансформатора или генератора, или средний заземлённый провод в сети постоянного тока, служащий обратным проводником при неравномерной нагрузке фаз или полюсов
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
- электроснабжение в целом
EN
DE
FR
3.1.44 нейтральный проводник (neutral conductor): Провод, электрически подсоединенный к нейтральной точке, содействующий распределению электрической энергии.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54828-2011: Комплектные распределительные устройства в металлической оболочке с элегазовой изоляцией (КРУЭ) на номинальные напряжения 110 кВ и выше. Общие технические условия оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > neutral conductor
-
70 plain conductor
металлический провод
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
неизолированный провод
Провод, состоящий из одной или нескольких скрученных проволок.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
голый провод
Электрический провод из одного или нескольких неизолированных проводников
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
FR
токопроводящая жила без защитных покрытий
металлическая токопроводящая жила, в которой проволока или проволоки не покрыты дополнительным металлическим слоем
[IEV number 461-01-02]EN
plain conductor
metal cable conductor in which the wire or wires are not coated with an additional metal
[IEV number 461-01-02]FR
âme (en métal) nue
âme dont le ou les fils ne sont pas recouverts d'une couche d'un autre métal
[IEV number 461-01-02]
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
- blanker Leiter, m
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > plain conductor
-
71 многожильный кабель
многожильный кабель
многожильный провод
многожильный шнур
Кабель (провод, шнур), в котором число жил более трех.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]EN
multicore cable
cable having more than one core
Note – The French term «câble multipolaire» is more specifically used to designate the cable constituting the phases of a multiphase system (example: three-core cable).
[EV ref 461-06-04]
multiconductor cable
cable having more than one conductor, some of which may be uninsulated
[IEV ref 461-06-03]FR
câble multiconducteur
câble multipolaire
câble comprenant plus d'un conducteur isolé
Note – Le terme câble multipolaire est plus particulièrement utilisé pour désigner le câble constituant les phases d'un système polyphasé (exemple: câble tripolaire).
[EV ref 461-06-04]
câble multiconducteur
câble multipolaire
câble comprenant plus d'une âme, dont éventuellement certaines non isolées
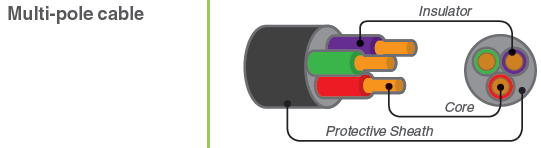
[IEV ref 461-06-03]Core - (токопроводящая) жила;
Insulator - изоляция жилы;
Protective Sheath - оболочка кабеля.Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1) Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- bundled cable
- multi-pole cable
- multiconductor cable
- multicore cable
- multiple cable
- multiple-conductor cable
- multiple-core cable
- multistrand cable
- N-conductor cable
- polycore cable
DE
- mehradriges Kabel, n
- Mehrleiterkabel, n
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > многожильный кабель
-
72 одножильный кабель
одножильный кабель
кабель, имеющий только одну изолированную жилу
Примечание. Французский термин «cable unipolaire» более приемлем для обозначения кабеля, составляющего одну из фаз многофазной системы
[ IEV ref 461-06-02]EN
single-conductor cable
single-core cable
cable having only one core
Note – The French term «câble unipolaire» is more specifically used to designate the cable constituting one of the phases of a multiphase system.
[ IEV ref 461-06-02]FR
câble à un conducteur
câble unipolaire
câble comprenant un seul conducteur isolé
Note – Le terme câble unipolaire est plus particulièrement utilisé pour désigner le câble constituant l'une des phases d'un système polyphasé.
[ IEV ref 461-06-02]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
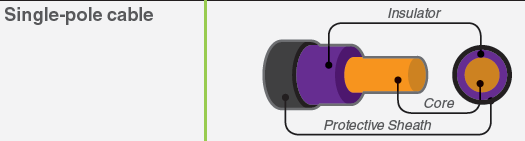
The cables must be multi strand, single core and PVC insulated.
[Schneider Electric]Должны применяться одножильные кабели с многопроволочной жилой с ПВХ изоляцией.
[Перевод Интент]
Рис. Schneider Electric
Core - (токопроводящая) жила;
Insulator - изоляция жилы;
Protective Sheath - оболочка кабеля.Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- monoconductor cable
- single cable
- single conductor cable
- single core cable
- single-conductor cable
- single-core cable
- single-pole cable
DE
- einadriges Kabel, n
- Einleiterkabel, n
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > одножильный кабель
73 проводник
проводник (1)
Вещество, основным электрическим свойством которого является электропроводность.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
проводник (2)
Всё то, что используется (предназначается) для проведения электрического тока:
- провод;
- кабель;
- шина;
- шинопровод;
- жила провода (кабеля);
- проводник печатной платы.
[Интент]
проводник (2)
Проводящая часть, предназначенная для проведения электрического тока определенного значения.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
проводник (2)
Проводящая часть, предназначенная для проведения электрического тока определённого значения.
Проводники представляют собой проводящие части, которые предназначены для проведения электрического тока в электрических цепях электрооборудования и электроустановки здания. Помимо качественной характеристики проводника, указывающей на его способность проводить электрический ток, каждый проводник имеет количественную характеристику, называемую допустимым длительным током. Протекание по проводнику сверхтока вызывает перегрев проводника, который может быть причиной пожара. Поэтому проводники в электроустановках зданий защищают от сверхтоков.
К проводникам, прежде всего, относят жилы проводов и кабелей, из которых выполнены стационарные электропроводки в электроустановке здания, жилы гибких проводов и кабелей, используемых для подключения переносного и передвижного электрооборудования к стационарным электропроводкам, различные шины, применяемые в низковольтных распределительных устройствах и в шинопроводах, а также другие проводящие части, выполняющие функции проводников.
В электроустановках зданий применяют проводники различного назначения. Для обеспечения электрооборудования электрической энергией в электрических цепях переменного тока используют фазные проводники, нейтральные проводники и PEN-проводники, а в электрических цепях постоянного тока – полюсные проводники, средние проводники и PEM-проводники. Защитные проводники, а также PEN-проводники, PEM-проводники и PEL-проводники применяют в электроустановках зданий для защиты от поражения электрическим током.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CF/view/49/]EN
conductor
element intended to carry electric current
NOTE 1 – The term "conductor" is often used for an element the length of which is large with respect to the cross-sectional dimensions, e.g. conductors of a line or of a cable.
NOTE 2 – The English term "conductor" and the French term "conducteur" have also the meaning of "conducting medium".
NOTE 3 – In French, the term "conducteur" is also used as an adjective corresponding to the English "conductive".
[IEV number 151-12-05]FR
conducteur, m
élément destiné à assurer le passage d'un courant électrique
NOTE 1 – Le terme "conducteur" est souvent utilisé pour un élément dont la longueur est grande par rapport aux dimensions de la section droite, par exemple les conducteurs d'une ligne ou d'un câble.
NOTE 2 – Le terme français "conducteur" et le terme anglais " conductor " ont aussi le sens de "milieu conducteur".
NOTE 3 – En français, le terme "conducteur" est aussi employé comme adjectif correspondant à l'anglais "conductive".
[IEV number 151-12-05]К зажиму допускается присоединение двух медных проводников сечением от 1,0 до 4,0 мм2.
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Действия
- обесточивать проводник
- определять сечение проводника
- отключать проводник
- отсоединять проводник
- присоединять проводник
- присоединять проводник накруткой
- проводник должен пропускать ток
- соединять проводники
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > проводник
74 кабельное изделие
кабельное изделие
Электрическое изделие, предназначенное для передачи по нему электрической энергии, электрических сигналов информации или служащее для изготовления обмоток электрических устройств, отличающееся гибкостью.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
conductor (of a cable)
part of a cable which has the specific function of carrying current
[IEV number 461-01-01]токопроводящая жила
Элемент кабельного изделия, предназначенный для прохождения электрического тока
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > кабельное изделие
75 core
- ядро
- сердцевина (оптического волокна)
- сердцевина
- сердечник электротехнического изделия
- сердечник
- пеньковый сердечник стального каната
- отбирать керн
- Международная программа исследований по проблемам разрушения активной зоны ядерного реактора при аварии
- конус породы, остающийся на забое при бурении
- керн горной породы
- керн
- карандаш
- изолированная жила (термин употребляется в Северной Америке)
- жила кабеля
- жила (кабеля)
- жила
- внутренний тор
- активная зона ядерного реактора
- активная зона (ядерного реактора)
активная зона (ядерного реактора)
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
активная зона ядерного реактора
активная зона
Часть ядерного реактора, содержащая ядерное топливо, которой происходит управляемая цепная ядерная реакция.
[ ГОСТ 23082-78]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
внутренний тор
Торовая или торообразная поверхность, которая является внутренней границей рабочей полости.
[ ГОСТ 19587-74]Тематики
EN
DE
токопроводящая жила
жила
Элемент кабельного изделия, предназначенный для прохождения электрического тока
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]
токопроводящая жила (кабеля)
Элемент кабеля, специфической функцией которого является передача электрического тока
[IEV number 461-01-01]
жила токопроводящая
Изолированный одно- или многопроволочный металлический проводник внутри электрического кабеля
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
жила
-
[IEV number 151-12-37]EN
conductor (of a cable)
part of a cable which has the specific function of carrying current
[IEV number 461-01-01]
strand
one of the wires of a stranded conductor
Source: 466-10-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-37]FR
âme
conducteur (d'un câble) (terme déconseillé dans ce sens)
partie d'un câble dont la fonction spécifique est de conduire le courant
[IEV number 461-01-01]
brin, m
un des fils d'un conducteur câblé
Source: 466-10-02 MOD
[IEV number 151-12-37]Все жилы двухжильных кабелей должны быть одинакового сечения.
Все жилы трех- и четырехжильных кабелей должны быть одинакового сечения или одна жила должна быть меньшего сечения (нулевая или жила заземления)
Номинальное сечение, мм2
основная жила: 25
нулевая жила: 16
жила заземления: 10
Изолированные жилы многожильных кабелей должны иметь отличительную расцветку или обозначение цифрами, начиная с нуля.
[ ГОСТ 433-73]
Токопроводящие жилы должны быть изолированы поливинилхлоридным пластикатом.
Изолированные жилы должны быть скручены в кабель.
[ ГОСТ 10348-80]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- кабели, провода...
Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- cable
- cable conductors
- conductor
- conductor core
- conductor of a cable
- conductors
- core
- electric conductor
- strand
DE
- Einzeldraht
- Leiter (eines Kabels), m
- stromführende Ader
FR
жила (кабеля)
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
жила кабеля
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
изолированная жила (термин употребляется в Северной Америке)
совокупность элементов, состоящая из жилы, ее изоляции (и экранов, если они есть)
Примечание. В Северной Америке термин «core of a cable» определяется как совокупность компонентов кабеля, расположенных под общим защитным покровом, таким как оболочка. Такое применение этого термина не допустимо
[IEV number 461-04-04]EN
core
insulated conductor
assembly comprising a conductor with its own insulation (and screens if any)
NOTE – In North American usage, the core of a cable has been defined as the assembly of components of a cable lying under a common covering such as the sheath. Such usage is deprecated.
[IEV number 461-04-04]FR
conducteur (isolé)
ensemble comprenant l'âme, son enveloppe isolante et ses écrans éventuels
NOTE – En Amérique du Nord le terme “core of a cable” a été défini comme l'ensemble des constituants d'un câble disposés sous un revêtement commun, tel que la gaine. L'utilisation de ce terme est déconseillée dans ce sens.
[IEV number 461-04-04]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
- Ader, f
FR
карандаш
Оставшаяся после лущения часть фанерного чурака, имеющая форму цилиндра при цилиндрическом лущении или неправильного эллипса при эксцентрическом лущении.
[ ГОСТ 15812-87]Тематики
EN
FR
- noyaux de deroulage, âme
керн
В геологии - образец горной породы в виде цилиндрического столбика, извлекаемый в буровом снаряде при бурении скважины
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- геология, геофизика
EN
DE
FR
керн горной породы
Цилиндрический столбик горной породы, выбуриваемый из массива горных пород или штуфа.
[ ГОСТ Р 50544-93]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
конус породы, остающийся на забое при бурении
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
Международная программа исследований по проблемам разрушения активной зоны ядерного реактора при аварии
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
отбирать керн
бурить с отбором керна
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
пеньковый сердечник стального каната
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
EN
сердечник
Физический элемент, на котором крепится обмотка и который может влиять на магнитный поток.
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
сердечник
Часть магнитопровода электромагнита в виде цельного или пластинчатого тела из электротехнической стали, вокруг которого располагаются обмотки
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]Тематики
- виды (методы) и технология неразр. контроля
EN
сердечник электротехнического изделия
Ферромагнитная деталь, на которой или вокруг которой расположена обмотка электротехнического изделия.
[ ГОСТ 18311-80]
(магнитный) сердечник
-
[IEV number 151-14-02]EN
(magnetic) core
part of a device, composed of high-permeability material and intended to channel magnetic flux
NOTE – Generally a magnetic core is surrounded by one or more windings.
Source: 221-04-24 MOD
[IEV number 151-14-02]FR
noyau (magnétique), m
partie d'un dispositif constituée d'un matériau de perméabilité élevée et destinée à canaliser un flux magnétique
NOTE – Un noyau magnétique porte généralement un ou plusieurs enroulements.
Source: 221-04-24 MOD
[IEV number 151-14-02]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
- (magnetischer) Kern
- Kern, (magnetischer)
FR
сердцевина
[ ГОСТ 28833-90]
сердцевина
Материал детали под диффузионным слоем, не затронутый воздействием окружающей активной среды.
[ ГОСТ 20495-75]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
EN
FR
сердцевина (оптического волокна)
Cветопроводящая жила из оптически более плотного материала, чем ее оболочка.
[Л.Г.Суменко. Англо-русский словарь по информационным технологиям. М.: ГП ЦНИИС, 2003.]Тематики
EN
4.3 ядро (core): Центр изображения отпечатка пальца.
Примечание - Точное расположение ядра определяется самой верхней точкой на внутреннем загнутом гребне изображения отпечатка пальца. В общем случае ядро расположено на или в пределах самого внутреннего загиба петли.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО/МЭК 19794-4-2006: Автоматическая идентификация. Идентификация биометрическая. Форматы обмена биометрическими данными. Часть 4. Данные изображения отпечатка пальца оригинал документа
32. Карандаш
E. Core
F. Noyaux de deroulage, ame
Оставшаяся после лущения часть фанерного чурака, имеющая форму цилиндра при цилиндрическом лущении или неправильного эллипса при эксцентрическом лущении
Источник: ГОСТ 15812-87: Древесина клееная слоистая. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > core
76 длительный допустимый ток
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > длительный допустимый ток
77 courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant admissible, m
78 courant permanent admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant permanent admissible, m
79 Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
80 Strombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Strombelastbarkeit, f
СтраницыСм. также в других словарях:
The Country Mouse and the City Mouse Adventures — Also known as The Mouse Adventures (UK) Genre Animation Written by Patrick Granleese Caroline R. Maria Bruce Robb Voices of Julie Burroughs Terrence Scammell … Wikipedia
Cable Liner — The Cable Liner and Cable Liner Shuttle is a range of automated people mover (APM) products designed by DCC Doppelmayr Cable Car for use at airports, in city centres, intermodal passenger transport connections, park and ride facilities, campuses … Wikipedia
The Hour of Power — is a weekly Christian television program now hosted by Robert A. Schuller with his father, Robert H. Schuller, and broadcast from the Crystal Cathedral in Garden Grove, California, USA. It first aired in 1970 with a multi host format until it was … Wikipedia
Cable — For other uses, see Cable (disambiguation). 6 inch (15 cm) outside diameter, oil cooled cables, traversing the Grand Coulee Dam throughout. An example of a heavy cable for power transmission … Wikipedia
cable — cablelike, adj. /kay beuhl/, n., v., cabled, cabling. n. 1. a heavy, strong rope. 2. a very strong rope made of strands of metal wire, as used to support cable cars or suspension bridges. 3. a cord of metal wire used to operate or pull a… … Universalium
Cable — /kay beuhl/, n. George Washington, 1844 1925, U.S. novelist and short story writer. * * * (as used in expressions) Cable News Network cable modem cable structure cable television coaxial cable * * * ▪ electronics … Universalium
The Muppet Show — At the Dance redirects here. For the song by Corey Hart, see First Offense. The Muppet Show Kermit the Frog as seen on the show s opening sequence. Format Live a … Wikipedia
Submarine communications cable — A cross section of a submarine communications cable. 1 Polyethylene 2 Mylar tape 3 Stranded steel wires 4 Aluminium water barrier 5 Polycarbonate 6 Copper or aluminium tube 7 Petroleum jelly 8 Optical fib … Wikipedia
Conductor support system — Conductor support systems, also known as conductor supported systems or satellite platforms, are installations which are small unmanned platforms consisting of little more than a well bay, and a small process plant. They are designed to operate… … Wikipedia
The New Woody Woodpecker Show — Format Children s animated television series Voices of Billy West Mark Hamill Andrea Martin B.J. Ward E.G. Daily Nika Futterman Jim Cummings Country of origin … Wikipedia
The Dark Knight — Título El caballero oscuro (España) Batman 2: el caballero de la noche (Venezuela) Batman: el caballero de la noche (Argentina, Chile, Colombia, Panamá, Ecuador, México, Perú, Uruguay) … Wikipedia Español
Перевод: со всех языков на все языки
со всех языков на все языки- Со всех языков на:
- Все языки
- Со всех языков на:
- Все языки
- Английский
- Испанский
- Немецкий
- Русский
- Французский