-
1 machine
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine[Swahili Word] enchini[Part of Speech] noun[Note] Engl. rare------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine[English Plural] machines[Swahili Word] enjine[Swahili Plural] enjine[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Note] Engl. rare------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine[Swahili Word] injini[Part of Speech] noun[Swahili Example] injini ya moshi------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine[Swahili Word] mashine[Swahili Plural] mashine[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[English Example] His hands worked like a machine.[Swahili Example] Mikono yake ilifanya kazi kama mashine [Chambati Masomo 242]------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine[Swahili Word] mashine[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] Engl.[English Example] typewriter[Swahili Example] machine ya kuandika------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine[Swahili Word] mashini[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] Engl.[English Example] typewriter[Swahili Example] machine ya kuandika------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine[English Plural] machines[Swahili Word] kinu[Swahili Plural] vinu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 7/8------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine for turning[Swahili Word] kerezo[Swahili Plural] kerezo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Derived Word] kereza V------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine(in gen.)[Swahili Word] mtambo[Swahili Plural] mitambo[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] small machine[Swahili Word] charahani[Part of Speech] noun[English Example] sew with the sewing machine[Swahili Example] shona kwa charahani[Terminology] personal------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] small machine[English Plural] really means sewing machine[Swahili Word] cherahani[Part of Speech] noun[English Example] tailor[Swahili Example] fundi wa cherahani------------------------------------------------------------ -
2 derived type
English-Russian dictionary of Information technology > derived type
-
3 part
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] central part[Swahili Word] uchukuti[Swahili Plural] chukuti[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 11/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] have a part in[Swahili Word] -shariki[Part of Speech] verb[Derived Word] shirika N------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] have a part in[Swahili Word] -shiriki[Part of Speech] verb[Derived Word] shirika N[English Example] (s)he took a part in the OAU meeting[Swahili Example] Yeye alishiriki katika mkutano wa OAU------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] leave from each other[Swahili Word] -tokana[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] aria[Swahili Plural] aria[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] (rare)------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] awamu[Swahili Plural] awamu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Swahili Definition] sehemu[English Example] The buildings of this college are being repaired and the first part will be complete next year.[Swahili Example] Majengo ya chuo hiki yamekuwa yakirekebishwa na awamu ya kwanza itakamilika mwaka ujao [Masomo 362]------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] aya[Swahili Plural] aya[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] divisheni[Part of Speech] noun[Note] Engl.------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] fungu[Swahili Plural] mafungu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] gawo[Swahili Plural] magawo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] hisa[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[English Plural] parts[Swahili Word] juzuu[Swahili Plural] majuzuu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[Derived Language] Arabic------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[English Plural] parts[Swahili Word] kataa[Swahili Plural] kataa[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Derived Language] Arabic[English Example] room (part of a house)[Swahili Example] kataa ya nyumba------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[English Plural] parts[Swahili Word] kipande[Swahili Plural] vipande[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 7/8[Related Words] pande, pandikizi, upande------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] kasama[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] kasimu------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] mgao[Swahili Plural] migao[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] gawa V[English Example] dividend.[Swahili Example] mgao wa faida------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] mgawo[Swahili Plural] migawo[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] gawa V[English Example] dividend.[Swahili Example] mgao wa faida------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] mkasama[Swahili Plural] mikasama[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] kasimu------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] nusu[Swahili Plural] nusu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[English Example] partly[Swahili Example] nusu nusu------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[English Plural] parts[Swahili Word] pande[Swahili Plural] mapande[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[Related Words] kipande[English Example] In this section of the country there are no coconuts[Swahili Example] pande hizi hatuna nazi------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] sehemu[Swahili Plural] sehemu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[English Example] part of a machine[Swahili Example] sehemu ya mtambo.------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] tarafa[Swahili Plural] tarafa[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] tarafu[Swahili Plural] tarafu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] ugawanyaji[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[English Plural] parts[Swahili Word] kiasi[Swahili Plural] viasi[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 7/8[Derived Language] Arabic------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part[Swahili Word] -achana na[Part of Speech] verb[Class] reciprocal[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] -acha[English Example] she did not want to part with those children[Swahili Example] hakutaka kuachana na watoto hao [Kez]------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part ( of a whole)[English Plural] parts (of a whole)[Swahili Word] toto[Swahili Plural] matoto[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part (of a larger whole)[Swahili Word] baadhi[Swahili Plural] baadhi[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part (small)[English Plural] parts[Swahili Word] kisehemu[Swahili Plural] visehemu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 7/8[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] sehemu------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] part with reluctantly[Swahili Word] -sunza[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] take part in[Swahili Word] -ingia[Part of Speech] verb[Derived Word] kiingilio, maingiano, maingiliano, mwingilizi, mwingizaji, uingizaji[Swahili Example] ingia safarini------------------------------------------------------------ -
4 gun
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] antitank gun[English Plural] antitank guns[Swahili Word] bunduki ya kupigia vifaru[Swahili Plural] bunduki za kupigia vifaru[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Related Words] pigia, vifaru[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] double-barrelled gun[English Plural] double-barrelled guns[Swahili Word] bunduki ya midomo miwili[Swahili Plural] bunduki za midomo miwili[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Related Words] mdomo, miwili[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] gun[English Plural] guns[Swahili Word] bunduki[Swahili Plural] bunduki[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Derived Language] Arabic[Derived Word] bunduq[Swahili Definition] chombo kinachotumia risasi [Masomo, 59]------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] gun nipple[Swahili Word] kifa[Swahili Plural] vifa[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 7/8------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] load a gun[Swahili Word] -tia risasi[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine gun[English Plural] machine guns[Swahili Word] mzinga wa bombom[Swahili Plural] mizinga wa bombom[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4[Related Words] bombom[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] machine gun[English Plural] machine guns[Swahili Word] bunduki ya mtombo[Swahili Plural] bunduki za mtombo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Related Words] mtombo[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] matchlock gun[English Plural] matchlock guns[Swahili Word] bunduki ya mrao[Swahili Plural] bunduki za mrao[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Dialect] archaic[Related Words] mrao[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] muzzle-loader gun[Swahili Word] gobori[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] spear gun used by divers to hunt fish[English Plural] spear guns[Swahili Word] bunduki[Swahili Plural] bunduki[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Dialect] Kimvita[Terminology] marine------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] submachine gun[English Plural] submachine guns[Swahili Word] bunduki ya nusu mtombo[Swahili Plural] bunduki za nusu mtombo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Related Words] nusu, mtombo[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------ -
5 water
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] water[Swahili Word] maji[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 6[Related Words] kimaji, umaji[English Example] when I was thirsty, I drank <b>water</b>[Swahili Example] wakati nilisikia kiu, nilikunywa <b>maji</b>------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drinking water[Swahili Word] maji ya kunywa[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 6[Related Words] -nywa------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] mineral water[Swahili Word] soda[Swahili Plural] soda[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Derived Word] Eng.------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] salt water[Swahili Word] maji chumvi[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 6[Related Words] chumvi------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] salt water[Swahili Word] maji bahari[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 6[Related Words] bahari------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] water used for rinsing out the mouth[Swahili Word] masuo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 6[Derived Word] sua V------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] running water[Swahili Word] mfereji[Swahili Plural] mifereji[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4[Derived Language] Arabic[English Example] when will you get running water in this house?[Swahili Example] lini utatia mfereji nyumba hii? [Ya]------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] draw water[Swahili Word] -teka maji[Part of Speech] verb[Related Words] -teka------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] water down[Swahili Word] -chujua[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] allow water to pass through[Swahili Word] -papa maji[Part of Speech] verb[Related Words] -papa------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] let in water (of a roof or wall)[Swahili Word] -vuja[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] water-carrier (one who carries two water-tins suspended from either end of a carrying pole)[Swahili Word] mzegazega[Swahili Plural] wazegazega[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] watering machine[English Plural] watering machines[Swahili Word] gari la maji[Swahili Plural] magari ya maji[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[Related Words] maji[Terminology] agriculture------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] something thrown into the water[Swahili Word] kizamaji[Swahili Plural] vizamaji[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] zama N------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] rising (of water)[Swahili Word] mafuriko[Part of Speech] noun[Derived Word] fura------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] water tin[Swahili Word] mzegazega[Swahili Plural] mizegazega[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] water level[Swahili Word] pimasharazi[Swahili Plural] pimasharazi[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Note] rare------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] make someone's mouth water[Swahili Word] -rambitia[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Item(s) below have not yet been grouped within the headword water[English Word] fresh water[Swahili Word] maji matamu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 6[Related Words] maji------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] make someone's mouth water[Swahili Word] -lambitia[Part of Speech] verb[Class] contactive[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] -lamba------------------------------------------------------------ -
6 Lace
LACE, Passement, French, also Dentelle, and GuipureLace was originally a heavy texture more like embroidery and of two kinds, Lacis or "darned netting" and Cutwork. Laces, often worked in gold threads and coloured silks was also called " spiderwork." Lace is purely an English word, derived from the Anglo-Norman lacier, to lace, bind, tie or fasten, etc. The word appears to have been first used in 1519. It is a fabric of open mesh or net formed by crossing and intertwining threads. Lace was originally purely a hand craft, but today it is machine made as well. There are three main classes: - Point lace, pillow lace and machine-made lace. Point Lace - When the term " Point " is applied to a lace fabric it should mean that the lace has been made by the needle with a single line of thread, but it is now given to many machine-made laces. There are numerous laces sold as point laces and each has some feature not possessed by any other, many of these laces are known by the town where they are manufactured. Pillow Lace - These laces are made by intertwining threads on pins fixed in a cushion over a pattern fastened on to the cushion. Many pillow laces are part hand and part machine made such as Honiton, Valenciennes, Irish, etc. Machine-made Laces - There are three principal classes which can be placed (1) warp fabrics; (2) plain nets; (3) Levers' laces. Warp Laces - This is the earliest form of lace produced on a machine which was the invention of the Rev. William Lee in 1589, and was an adaption of the stocking frame. A warp lace is a series of upright threads that twist upon each other to form a fabric. There are no crossing threads. They are made in widths up to 10-in. and are the cheapest laces made. Plain Nets - John Heathcote, the inventor of the bobbin-net machine in 1809, laid the foundation of the machine-made lace trade. These are formed by a diagonal bobbin thread intertwining with the upright warp threads so that when the web is taken off the machine the mesh is honeycomb shaped. Other shapes followed, such as the square mesh. Cotton, silk, mohair and rayon are all used in making plain nets. Standard plain nets are as follows: - Brussels Net - Close mesh, specially selected fine yarns, in widths 36-in. to 80-in. The mesh varies up to 20 holes per inch. Both stiff and soft finish. Mosquito Net - Made in many qualities and closeness of mesh and from 54-in. to 108-in. Cable Net - Made up to 300-in. wide and from coarser yarns than other laces. This fabric is used as the ground fabric for curtains, etc. Bretonne Net - A very fine fabric, close mesh and finer yarns than Brussels, very soft and smooth finish. Point d'esprit - Fabrics with spots at regular distances. The yarns are not as good a quality as Brussels. Finished both soft and stiff. Paris Nets - Very stiff finish, used by the millinery trade for foundation work. Illusion Nets - A star-shaped mesh fabric, very fine yarns, used for veils and evening dress purposes. Silk Mechlins, or Tulles - A net more round than square in mesh and made from fine silk yarns. Malines is a tulle made in Belgium. Chantilly, or Silk Brussels - Similar to Brussels, but made from black dyed silk yarns. Chambray Nets - A finer all silk net than Chantilly. Levers' Lace Fabrics - These are various fancy laces and are produced on the lace machine fitted with a jacquard. Samuel Draper of Nottingham combined the jacquard with the lace machine in 1813. John Levers invented the machine. Varieties of these laces are Cluny laces. Torchons, Maltese lace. All-overs and numerous others. -
7 Paul, Lewis
SUBJECT AREA: Textiles[br]d. April 1759 Brook Green, London, England[br]English inventor of hand carding machines and partner with Wyatt in early spinning machines.[br]Lewis Paul, apparently of French Huguenot extraction, was quite young when his father died. His father was Physician to Lord Shaftsbury, who acted as Lewis Paul's guardian. In 1728 Paul made a runaway match with a widow and apparently came into her property when she died a year later. He must have subsequently remarried. In 1732 he invented a pinking machine for making the edges of shrouds out of which he derived some profit.Why Paul went to Birmingham is unknown, but he helped finance some of Wyatt's earlier inventions. Judging by the later patents taken out by Paul, it is probable that he was the one interested in spinning, turning to Wyatt for help in the construction of his spinning machine because he had no mechanical skills. The two men may have been involved in this as early as 1733, although it is more likely that they began this work in 1735. Wyatt went to London to construct a model and in 1736 helped to apply for a patent, which was granted in 1738 in the name of Paul. The patent shows that Paul and Wyatt had a number of different ways of spinning in mind, but contains no drawings of the machines. In one part there is a description of sets of rollers to draw the cotton out more finely that could have been similar to those later used by Richard Arkwright. However, it would seem that Paul and Wyatt followed the other main method described, which might be called spindle drafting, where the fibres are drawn out between the nip of a pair of rollers and the tip of the spindle; this method is unsatisfactory for continuous spinning and results in an uneven yarn.The spinning venture was supported by Thomas Warren, a well-known Birmingham printer, Edward Cave of Gentleman's Magazine, Dr Robert James of fever-powder celebrity, Mrs Desmoulins, and others. Dr Samuel Johnson also took much interest. In 1741 a mill powered by two asses was equipped at the Upper Priory, Birmingham, with, machinery for spinning cotton being constructed by Wyatt. Licences for using the invention were sold to other people including Edward Cave, who established a mill at Northampton, so the enterprise seemed to have great promise. A spinning machine must be supplied with fibres suitably prepared, so carding machines had to be developed. Work was in hand on one in 1740 and in 1748 Paul took out another patent for two types of carding device, possibly prompted by the patent taken out by Daniel Bourn. Both of Paul's devices were worked by hand and the carded fibres were laid onto a strip of paper. The paper and fibres were then rolled up and placed in the spinning machine. In 1757 John Dyer wrote a poem entitled The Fleece, which describes a circular spinning machine of the type depicted in a patent taken out by Paul in 1758. Drawings in this patent show that this method of spinning was different from Arkwright's. Paul endeavoured to have the machine introduced into the Foundling Hospital, but his death in early 1759 stopped all further development. He was buried at Paddington on 30 April that year.[br]Bibliography1738, British patent no. 562 (spinning machine). 1748, British patent no. 636 (carding machine).1758, British patent no. 724 (circular spinning machine).Further ReadingG.J.French, 1859, The Life and Times of Samuel Crompton, London, App. This should be read in conjunction with R.L.Hills, 1970, Power in the Industrial Revolution, Manchester, which shows that the roller drafting system on Paul's later spinning machine worked on the wrong principles.A.P.Wadsworth and J.de L.Mann, 1931, The Cotton Trade and Industrial Lancashire, 1600–1780, Manchester (provides good coverage of the partnership of Paul and Wyatt and the early mills).E.Baines, 1835, History of the Cotton Manufacture in Great Britain, London (this publication must be mentioned, but is now out of date).A.Seymour-Jones, 1921, "The invention of roller drawing in cotton spinning", Transactions of the Newcomen Society 1 (a more modern account).RLH -
8 unit
1) сборочная единица; узел; блок2) установка; агрегат3) единица, единица измерения || единичный; удельный4) часть; секция || секционный•as a unit — 1) в сборе 2) как единая сборочная единица; как единый узел
unit under test — 1) объект контроля 2) объект диагностирования, объект технического диагностирования
- AC unit- actuating unit
- adapter plate unit
- adaptive control unit
- address and data interface unit
- address unit
- adjusting unit
- air-aspirating unit
- answer-back unit
- arithmetic unit
- arithmetic/logic unit
- arithmetical unit
- ASC unit
- assembly unit of N-order
- assembly unit
- audio response unit
- autoloading unit
- automatic calling unit
- auxiliary data translator unit
- availability control unit
- axis unit
- axis-processing unit
- balancer unit
- banking unit
- bar feed unit
- base assembly unit
- base unit
- basic information unit
- basic length unit
- basic logic unit
- batch control unit
- bearing unit
- behind-the-tape reader unit
- belt shuttle unit
- belt-driven shuttle unit
- bench-testing unit
- blemished unit
- bolt-on unit
- booster unit
- boring spindle unit
- boring unit
- boring-and-milling unit
- brake unit
- broach retriever unit
- broach-handling unit
- broken tool sensing unit
- buffer unit
- building-block machining unit
- bulk transfer unit
- business unit
- card punching unit
- carousel loading unit
- carousel unit
- carrier unit
- cartridge unit
- cellular unit
- center unit for machine frame
- central processing unit
- central processor unit
- chain storage unit
- changer unit
- changing unit
- check unit
- chiller unit
- chip disposal unit
- clamping unit
- claw unit
- CNC machining unit
- CNC standard unit
- CNC unit
- coating application unit
- coating removal unit
- coherent unit
- column unit
- combination valve unit
- command unit
- communications central processing unit
- complementary unit
- computerized numerical control unit
- condensing unit
- cone variable-speed friction drive unit
- console unit
- constant coefficient unit
- constant delay unit
- construction unit
- control unit
- controlling unit
- conveying unit
- conveyor unit
- coolant management unit
- coolant recovery unit
- coolant unit
- cooler unit
- cooling unit
- coordinate preprogramming unit
- copying unit
- correction unit
- cover unit
- CPC handling unit
- cross tapping unit
- cross-slide unit
- cutoff unit
- cutting unit
- D unit
- damping unit
- data preparation unit
- data transmission control unit
- deep hole boring unit
- delay unit
- derived unit
- detecting unit
- detection unit
- developing unit
- digital display unit
- digital readout unit
- digital unit
- dimension readout unit
- diode array unit
- disk-type variable-speed friction drive unit
- displacement unit
- display unit
- distance-keeping unit
- double-acting unit
- double-notching unit
- double-pump and combination unit
- double-pump unit
- double-reduction gear unit
- double-reduction right-angle reduction gear unit
- double-reduction twin gear unit
- double-reduction twin unit
- double-reduction wormgear unit
- double-spindle unit
- down-hole internal deburrer unit
- dresser unit
- dressing unit
- drill unit
- drilling and milling unit
- drilling spindle unit
- drilling unit
- drilling/tapping unit
- drive unit
- drive/feed unit
- DRO unit
- dual work pallet shuttle unit
- dual-head laser beam unit
- dust-collecting unit
- dust-removing unit
- dynamic unit
- EDM unit
- electrical machining units
- electromagnetic unit
- electron-beam unit
- entry level dedicated unit
- environmental compensation unit
- exchanger unit
- fabricated unit
- facing unit
- fan coil unit
- feed box unit
- feed change unit
- feed drive cartridge unit
- feed unit
- feedback unit
- feed-in boring unit
- feed-out boring unit
- fetch-and-carry unit
- filtration unit
- fine boring unit
- flexible spindle units
- flexible tray unit
- floor unit
- focusing unit
- free-standing unit
- free-wheel unit
- free-wheeling unit
- frontal variable-speed friction drive unit
- functional unit
- fundamental unit
- gage control unit
- gage indicating unit
- gage unit
- gaging unit
- gas turbine starter auxiliary power unit
- gear unit
- gearbox unit
- gear-reversing unit
- grasping unit
- grinding spindle unit
- gripper unit
- guide unit
- handling unit
- hardware/software add-on unit
- harmonic drive unit
- head unit
- headstock-type workpiece holding unit
- hoisting unit
- horizontal power unit
- horizontal way unit
- hydraulic clamping unit
- hydraulic feed unit
- hydraulic power unit
- hydraulic testing unit
- hydraulic unit
- hydrostatic bearing unit
- ICAM manufacturing unit
- ICAM unit
- icon-driven control unit
- indexer/fourth axis unit
- indexing head unit
- indexing platen unit
- indexing table unit
- indexing unit
- in-die tapping unit
- information retrieval unit
- information unit
- input batch control unit
- input unit
- input-output unit
- in-system unit
- integral unit
- interface unit
- intermediate storage unit
- interpolating unit
- inverting unit
- keyboard unit
- knee-type unit
- lapping and superfinishing unit
- laser beam composition unit
- laser beam unit
- laser processing unit
- laser unit
- laser-calibration unit
- laser-source unit
- lead screw tap unit
- lexical unit
- lift unit
- lift-and-carry unit
- light unit
- linear ball bearing unit
- linear drive unit
- linear screw unit
- linear slide roller bearing unit
- linear unit
- live storage unit
- load/unload unit
- loading unit
- loading-and-unloading unit
- logic unit
- logical unit
- lubricating pump unit
- machine control unit
- machine tool control unit
- machine tooling unit
- machine unit
- machine-dedicated unit
- machining center unit
- machining head unit
- machining unit
- magnetic pickup unit
- magnetic tape unit
- manned flexible unit
- marking unit
- master unit
- material-handling unit
- MDI unit
- measurement unit
- measuring unit
- memory unit
- message display unit
- microdispensing unit
- microprocessor correction unit
- microprocessor NC unit
- microprocessor unit
- microprocessor-based unit
- microprocessor-type NC unit
- middle-level 3-D representation unit
- milling spindle unit
- minicomputer control unit
- miniload AS/RS unit
- mist coolant unit
- miter saw unit
- mobile unit
- mobile work storage unit
- modular cell unit
- modular loading unit
- modular unit
- motor unit
- motor-reduction unit
- multichannel analyzer unit
- multidrill unit
- multiple screw-driving unit
- multiple-power path gear unit
- multiple-reduction gear unit
- multiple-reduction unit
- multiple-spindle torque unit
- multipurpose machining unit
- multispindle boring unit
- multitap unit
- NC data creation unit
- NC unit
- nested gear unit
- notching unit
- nutating unit
- off-machine unit
- off-system unit
- oil coalescer unit
- oil-filled feed unit
- one stage gear unit
- one stage unit
- on-machine unit
- operation unit
- operational unit
- operator-friendly program unit
- orientation transfer unit
- output batch control unit
- output unit
- overhead gantry unit
- overhead spindle unit
- pack unit
- pallet change unit
- pallet exchange unit
- pallet shuttle unit
- pallet-pool unit
- parallel-shaft reduction gear unit
- PC expansion board unit
- PC-based CAD unit
- pendant control unit
- pendant pushbutton control unit
- pendant unit
- peripheral control unit
- peripheral processing unit
- photo-eye tracing unit
- pick-and-place unit
- pickup unit
- piece-holding unit
- pilot unit
- placement unit
- planetary gear unit
- planetary reduction gearing unit
- plant unit
- plasma-arc unit
- plasmarc unit
- platen unit
- PLC unit
- plugboard input unit
- plugboard unit
- plug-in unit
- pneumatic unit
- portable unit
- power feed unit
- power supply unit
- power train unit
- power unit
- power-generating unit
- power-tooling unit
- practical correction unit
- practical unit
- presetting unit
- pressurized air bearing unit
- primary storage unit
- probe unit
- processing unit
- production unit
- program unit
- programming unit
- propulsion unit
- pulling unit
- pump unit
- pumping unit
- pump-motor unit
- quill feed cam unit
- quill spindle unit
- quill unit
- raster unit
- readout unit
- reducing unit
- reduction gear unit
- reduction gearing unit
- reduction unit
- reed make contact unit
- regulating unit
- remote display unit
- replacement unit
- retriever unit
- right-angle milling unit
- right-angled milling unit
- robot power unit
- robot unit
- robot-transfer unit
- roller bearing unit
- roller unit
- roller-marking unit
- rotary unit
- rotating seal unit
- S unit
- scanning unit
- scheduling unit
- screen projection unit
- screwing unit
- sealed reed contact unit
- self-contained NC unit
- self-contained unit
- sensing unit
- sensor unit
- servo unit
- shankless boring unit
- sheet metal stamping automatic unit
- shop replaceable unit
- shuttle unit
- shuttle-and-lift unit
- side unit
- single-acting unit
- single-light unit
- single-reduction gear unit
- single-reduction unit
- sizing unit
- slant bed unit
- slave unit
- slide unit
- sliding table unit
- smallest replaceable unit
- spare unit
- speeder unit
- speed-increase unit
- speed-up spindle unit
- speed-up unit
- spindle box unit
- spindle cartridge unit
- spindle drive unit
- spindle unit
- stabilizing unit
- stand-alone unit
- standard build units
- starter auxiliary power unit
- static tooling unit
- steam generating unit
- stock feed unit
- storage unit
- stylus unit
- sub-multiple unit
- swing arm-mounted control unit
- tangent unit
- tapping unit
- teach control unit
- terminal control unit
- test unit
- testing unit
- thermal detecting unit
- tilting unit
- tolerance unit
- tool storage unit
- tool-presetting unit
- tool-spindle unit
- toroidal variable-speed friction drive unit
- track and store unit
- transfer unit
- transmission control unit
- transmission unit
- transmitter/receiver unit
- transport unit
- triple-reduction gear unit
- triple-reduction unit
- tuning unit
- turnaround unit
- turning spindle unit
- turnround unit
- turret unit
- twin gear unit
- twin saw unit
- twin-drive unit
- twin-screen unit
- unit of displacement
- unit of measure
- unit of measurement
- unit of physical quantity
- unit of product
- unit of work per unit of time
- unmanned machining unit
- vacuum unit
- variable coefficient unit
- variable delay unit
- variable preload bearing unit
- variable ratio unit
- variable speed unit
- variable-speed friction drive unit
- V-axis grinding unit
- V-belt variable-speed drive unit
- V-drive unit
- vertical way unit
- vibratory feed unit
- vise unit
- visual display unit
- vocal output unit
- VTL unit
- waveform gear reduction unit
- wheel-dressing unit
- wheel-head unit
- wing unit
- wing-base unit
- work storage unit
- work-holding headstock unit
- workshop video unit
- work-testing unit
- worm reduction unit
- writing unit
- yet-to-be-assembled unitEnglish-Russian dictionary of mechanical engineering and automation > unit
-
9 data
данные; сведения; информацияto display the tooling data — выводить данные инструмента на дисплей-
AC data
-
actual data
-
actuation data
-
adjusted data
-
aeronautical data
-
air data
-
aircraft loading data
-
aircraft main data
-
aircraft operational data
-
aircraft test data
-
aircraft weight data
-
air-derived data
-
alphanumeric data
-
alphameric data
-
alphabetic data
-
analog data
-
angular data
-
application-specific data
-
area-averaged data
-
arrayed data
-
array data
-
asynoptic data
-
attributes data
-
attribute data
-
bearing preload data
-
behavioral data
-
biased data
-
binary data
-
binocular data
-
blast data
-
boundary data
-
brightness data
-
buoy data
-
business data
-
captioning data
-
channel data
-
characteristic data
-
clear data
-
CNC control data
-
coded data
-
combined data
-
confidential data
-
continuous data
-
control data
-
corrected profile data
-
correction data
-
current data
-
cutting data
-
decimal data
-
delayed-mode data
-
delayed data
-
descriptive data
-
design data
-
digital data
-
digital profile data
-
digital program data
-
digitized data
-
dimensions data
-
dimension data
-
discrepant data
-
discrete data
-
disembodied data
-
displayed data
-
display data
-
enciphered data
-
encoded data
-
engine performance data
-
engineering data
-
environmental data
-
erroneous data
-
error data
-
failure analysis data
-
field data
-
fixed-point data
-
flight data
-
floating-point data
-
geodetic data
-
geological and engineering data
-
gridded data
-
grid data
-
grid-point data
-
ground truth data
-
ground-derived data
-
hemispheric data
-
historical data
-
hydroclime data
-
hydrologic data
-
ice data
-
image data
-
imagery data
-
imaging data
-
impure data
-
incoming data
-
indicative data
-
infrared tracking data
-
initial data
-
input data
-
input shape data
-
in-reactor observational data
-
in-situ data
-
intensional data
-
lithogeochemical data
-
location data
-
long-term data
-
machinable data
-
machine tool data
-
machine-readable data
-
marine data
-
master data
-
meaningful data
-
meaning data
-
meaningless data
-
measuring data
-
meta data
-
metrological data
-
missing data
-
model data
-
motion data
-
multispectral data
-
nadir-viewed data
-
NC data
-
noiseless data
-
null data
-
numerical data
-
numeric data
-
observational data
-
observed data
-
offset curve data
-
on-line data
-
operational data
-
operator-entered data
-
outgoing data
-
output data
-
packed data
-
part-programming data
-
past data
-
performance data
-
pictorial data
-
plant data
-
plotted data
-
point data
-
position data
-
present-position data
-
private data
-
problem data
-
pseudo-observed data
-
public data
-
published data
-
raw data
-
real-time data
-
real-time tool data
-
redundant data
-
reference data
-
refined data
-
relevant data
-
reliability data
-
remotely-sensed data
-
remote-sensed data
-
reservoir engineering data
-
sampled data
-
sea truth data
-
sensory data
-
service data
-
shareable data
-
shipping data
-
simulation data
-
size data
-
snap data
-
source data
-
space-acquired data
-
space-based data
-
spatial data
-
standard sewing data
-
static tool data
-
status data
-
streamflow data
-
string data
-
structured tool data
-
summarized data
-
supplier data
-
surface-based data
-
surface data
-
tabular data
-
tabulated data
-
target data
-
task data
-
telemetry data
-
test data
-
tool condition data
-
topo data
-
torque data
-
transaction data
-
transient response data
-
transparent data
-
true data
-
unpacked data
-
valid data
-
verified data
-
video data
-
vision data
-
voice data
-
voice-band data
-
way-point data
-
workcycle data
-
workpiece shape data
-
zero data -
10 drill
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] be drilled[Swahili Word] -peketeka[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill[English Plural] drills[Swahili Word] kekee[Swahili Plural] kekee[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill[Swahili Word] kekee[Part of Speech] noun------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill[English Plural] drills[Swahili Word] kwata[Swahili Plural] kwata[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Related Words] kiatu, kwato, -enda kikwata, liwato[English Definition] training in marching and the use of weapons[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill[English Plural] drills[Swahili Word] tabura[Swahili Plural] tabura[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Terminology] military------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill[Swahili Word] -elimisha[Part of Speech] verb[Class] causative[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] elimu------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill[Swahili Word] -pekecha[Part of Speech] verb[English Example] drill holes.[Swahili Example] pekecha mashimo------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill (kind of)[English Plural] drills[Swahili Word] mfuo[Swahili Plural] mifuo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4[Derived Word] fua[Note] rare------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill (soldiers)[Swahili Word] -amrisha[Part of Speech] verb[Derived Word] -amuru------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill a hole[Swahili Word] -peketa[Part of Speech] verb[English Example] drill holes.[Swahili Example] pekecha mashimo------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drill exercises[Swahili Word] gwaride[Swahili Plural] magwaride[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] drilling machine[English Plural] drilling machines[Swahili Word] mashine ya kekee[Swahili Plural] mashine za kekee[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] shaft and barrel of drill[English Plural] shafts and barrels (of drills)[Swahili Word] msukwano[Swahili Plural] misukwano[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4------------------------------------------------------------ -
11 sew
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sew[Swahili Word] -sheleli[Part of Speech] verb[Note] rare------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sew[Swahili Word] -shona[Part of Speech] verb[Derived Word] mashono N, mshona N------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sew[Swahili Word] -shulu[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sew[Swahili Word] -shuru[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sew for[Swahili Word] -shonea[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sew together[Swahili Word] -fuma[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sewing machine[English Plural] sewing machines[Swahili Word] cherehani[Swahili Plural] macherehani[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[English Example] machine sewn work[Swahili Example] kazi ya cherehani------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] sewing machine repairman[English Plural] sewing machine repairmen[Swahili Word] fundi cherehani[Swahili Plural] mafundi cherehani[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6an------------------------------------------------------------ -
12 indicator
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] indicator[English Plural] indicators[Swahili Word] akarabu[Swahili Plural] akarabu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] indicator[English Plural] indicators[Swahili Word] akrabu[Swahili Plural] akrabu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] indicator[English Plural] indicators[Swahili Word] indiketa[Swahili Plural] indiketa[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] indicator[English Plural] indicators[Swahili Word] kiashirio[Swahili Plural] viashirio[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 7/8[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] -ashiria[Related Words] ishara------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] indicator[English Plural] indicators[Swahili Word] mshale[Swahili Plural] mishale[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 3/4------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] indicator (on a machine)[English Plural] indicators[Swahili Word] onyo[Swahili Plural] maonyo[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6[Derived Word] ona V------------------------------------------------------------ -
13 technician
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] technician[English Plural] technicians[Swahili Word] fundi[Swahili Plural] mafundi[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6an[Derived Language] Swahili[Derived Word] -funda[English Example] sewing-machine repairman[Swahili Example] fundi wa cherehani------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] technician[English Plural] technicians[Swahili Word] fundisanifu[Swahili Plural] mafundisanifu[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 5/6an[Derived Word] fundi n, sanaa n------------------------------------------------------------ -
14 Snodgrass, Neil
SUBJECT AREA: Textiles[br]fl. late 1790s Scotland[br]Scottish inventor of the scutcher for opening and cleaning raw cotton.[br]Raw cotton arrived in Britain in tightly packed bales. Before spinning, the fibres had to be opened out, and dirt, seeds and bits of plant had to be removed. This was an unpleasant and fatiguing job usually carried out by women and children. By 1800 it could be done by two machines. The first stage in opening was the "willow" and then the cotton was passed through the "scutcher" to open it further and give it a more effective cleaning. These machines reduced the labour of the operation to about one-twentieth of what it had been. The scutching machine was constructed by Snodgrass and first used at Houston's mill in Johnstone, near Paisley, in 1797. It was derived from the threshing machine invented by Andrew Meikle of Phantassie in 1786. In the scutcher, revolving bars beat the cotton to separate the fibres from the trash. As the dirt fell out, the cotton was blown forward by a fan and was rolled up into a lap at the end of the machine. Scutchers were not introduced to Manchester until 1808 or 1809 and further improvements were soon made to them.[br]Further ReadingR.L.Hills, 1970, Power in the Industrial Revolution, Manchester (covers the development of the scutcher).W.English, 1970, The Textile Industry, London (provides a brief account).RLH -
15 weigh
------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weigh[Swahili Word] -pima[Part of Speech] verb[English Example] weigh potatoes.[Swahili Example] pima viazi------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weigh down[Swahili Word] -elemea[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weigh down[Swahili Word] -elemea[Part of Speech] verb[Swahili Example] mzigo huu unamlemea [Rec]------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weigh down[Swahili Word] -songa[Part of Speech] verb[English Example] My troubles are weighing me down[Swahili Example] taabu zinanisonga------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weigh down on[Swahili Word] -vama[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weigh down on[Swahili Word] -vamia[Part of Speech] verb------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weighing machine[Swahili Word] mizani[Swahili Plural] mizani[Part of Speech] noun[Class] 9/10[Derived Word] Arabic------------------------------------------------------------[English Word] weighing one's thoughts[Swahili Word] -wazua[Part of Speech] verb[Class] converse[Derived Word] waza------------------------------------------------------------ -
16 Jeanneret, Charles-Edouard (Le Corbusier)
SUBJECT AREA: Architecture and building[br]b. 6 October 1887 La Chaux-de-Fonds, Switzerlandd. 27 August 1965 Cap Martin, France[br]Swiss/French architect.[br]The name of Le Corbusier is synonymous with the International style of modern architecture and city planning, one utilizing functionalist designs carried out in twentieth-century materials with modern methods of construction. Charles-Edouard Jeanneret, born in the watch-making town of La Chaux-de-Fonds in the Jura mountain region, was the son of a watch engraver and dial painter. In the years before 1918 he travelled widely, studying building in many countries. He learned about the use of reinforced concrete in the studio of Auguste Perret and about industrial construction under Peter Behrens. In 1917 he went to live in Paris and spent the rest of his life in France; in 1920 he adopted the name of Le Corbusier, one derived from that of his ancestors (Le Corbesier), and ten years later became a French citizen.Le Corbusier's long working life spanned a career divided into three distinct parts. Between 1905 and 1916 he designed a number of simple and increasingly modern houses; the years 1921 to 1940 were ones of research and debate; and the twenty years from 1945 saw the blossoming of his genius. After 1917 Le Corbusier gained a reputation in Paris as an architect of advanced originality. He was particularly interested in low-cost housing and in improving accommodation for the poor. In 1923 he published Vers une architecture, in which he planned estates of mass-produced houses where all extraneous and unnecessary features were stripped away and the houses had flat roofs and plain walls: his concept of "a machine for living in". These white boxes were lifted up on stilts, his pilotis, and double-height living space was provided internally, enclosed by large areas of factory glazing. In 1922 Le Corbusier exhibited a city plan, La Ville contemporaine, in which tall blocks made from steel and concrete were set amongst large areas of parkland, replacing the older concept of city slums with the light and air of modern living. In 1925 he published Urbanisme, further developing his socialist ideals. These constituted a major reform of the industrial-city pattern, but the ideas were not taken up at that time. The Depression years of the 1930s severely curtailed architectural activity in France. Le Corbusier designed houses for the wealthy there, but most of his work prior to 1945 was overseas: his Centrosoyus Administration Building in Moscow (1929–36) and the Ministry of Education Building in Rio de Janeiro (1943) are examples. Immediately after the end of the Second World War Le Corbusier won international fame for his Unité d'habitation theme, the first example of which was built in the boulevard Michelet in Marseille in 1947–52. His answer to the problem of accommodating large numbers of people in a small space at low cost was to construct an immense all-purpose block of pre-cast concrete slabs carried on a row of massive central supports. The Marseille Unité contains 350 apartments in eight double storeys, with a storey for shops half-way up and communal facilities on the roof. In 1950 he published Le Modular, which described a system of measurement based upon the human male figure. From this was derived a relationship of human and mathematical proportions; this concept, together with the extensive use of various forms of concrete, was fundamental to Le Corbusier's later work. In the world-famous and highly personal Pilgrimage Church of Notre Dame du Haut at Ronchamp (1950–5), Le Corbusier's work was in Expressionist form, a plastic design in massive rough-cast concrete, its interior brilliantly designed and lit. His other equally famous, though less popular, ecclesiastical commission showed a contrasting theme, of "brutalist" concrete construction with uncompromisingly stark, rectangular forms. This is the Dominican Convent of Sainte Marie de la Tourette at Eveux-sur-l'Arbresle near Lyon, begun in 1956. The interior, in particular, is carefully worked out, and the lighting, from both natural and artificial sources, is indirect, angled in many directions to illuminate vistas and planes. All surfaces are carefully sloped, the angles meticulously calculated to give optimum visual effect. The crypt, below the raised choir, is painted in bright colours and lit from ceiling oculi.One of Le Corbusier's late works, the Convent is a tour de force.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsHonorary Doctorate Zurich University 1933. Honorary Member RIBA 1937. Chevalier de la Légion d'honneur 1937. American Institute of Architects Gold Medal 1961. Honorary Degree University of Geneva 1964.BibliographyHis chief publications, all of which have been numerously reprinted and translated, are: 1923, Vers une architecture.1935, La Ville radieuse.1946, Propos d'urbanisme.1950, Le Modular.Further ReadingP.Blake, 1963, Le Corbusier: Architecture and Form, Penguin. R.Furneaux-Jordan, 1972, Le Corbusier, Dent.W.Boesiger, 1970, Le Corbusier, 8 vols, Thames and Hudson.——1987, Le Corbusier: Architect of the Century, Arts Council of Great Britain.DYBiographical history of technology > Jeanneret, Charles-Edouard (Le Corbusier)
-
17 DDM
1) Компьютерная техника: Data Diffusion Machine2) Авиация: depth of differential modulation, digital data module3) Спорт: Deadliest Death Match4) Техника: data display module, data display monitoring, department of data management, derived delta modulation, digestible dry matter, digital display machine, digital display makeup, double-diffused mesa, МЭП (механизм (исполнительный) электрический прямоходный - direct drive mechanism)5) Сельское хозяйство: dry matter digestibility6) Экономика: dividend discount model (Семейство финансовых моделей, рассчитывающих "справедливую" стоимость акций, основанную на дисконтировании будущих дивидендных поступлений.)7) Автомобильный термин: driver door module8) Политика: Direct Democracy Manifesto9) Телекоммуникации: Digital Data Multiplexer, Distributed Data Manager (IBM)10) Сокращение: Detecteur de Dйpart de Missile (Missile launch detector), Difference in Depth of Modulation11) Электроника: Dave Dan And Mike12) Вычислительная техника: Distributed Data Management (IBM, CCS)13) Биотехнология: dodecylmaltoside14) СМИ: Digital Distribution Of Music15) Деловая лексика: Document Data Maintenance16) Глоссарий компании Сахалин Энерджи: downhole drilling motor17) Сетевые технологии: distributed data manager, распределённое управление данными, система управления распределёнными данными18) Полимеры: dodecyl mercaptan19) Автоматика: design, drafting and manufacturing20) Расширение файла: Distributed Data Management21) Программное обеспечение: Device Driver Module, Drop Down Menu -
18 power
1) мощность; энергия; сила, движущая сила || силовой; энергетический3) способность4) усиление; увеличение5) матем. степень6) приводить (в действие, в движение)•to rotate under power — вращать от механического привода, вращаться от механического привода
- acceleration powerto power up — включать питание; приводить в действие
- accumulating power
- active power
- adhesive power
- air power
- apparent power
- available power
- average power
- beam power
- belt power
- brake power
- braking power
- calculated power
- climbing power
- computational power
- computer power
- computing power
- cooling power
- cutter power
- cutting power
- decay power
- derived power
- disturbance power
- driving power
- effective power
- electric power
- elevating power
- estimated power
- fluid power
- generalized power
- gripping power
- gross power
- hogging power
- holding power
- hydraulic fluid power
- hydraulic power
- idle power
- input power
- installed machine power
- instantaneous power
- interference power
- lifting power
- light-gathering power
- line power
- machine power
- mass power
- mean power
- mechanical power
- motive power
- networking power
- normalized laser power
- operating power
- output power
- peak power
- pneumatic fluid power
- pneumatic power
- power of force
- power of motor
- propulsion power
- propulsive power
- pump power
- rated power
- required power
- reserve power
- resolving power
- retaining power
- rotational power
- shaft horse power
- specific accumulating power
- spindle power
- spring power
- starting power
- stopping power
- sustained power
- switching power
- tractive power
- useful power
- utility line power
- yielded-up power
- zero powerEnglish-Russian dictionary of mechanical engineering and automation > power
-
19 Ford, Henry
[br]b. 30 July 1863 Dearborn, Michigan, USAd. 7 April 1947 Dearborn, Michigan, USA[br]American pioneer motor-car maker and developer of mass-production methods.[br]He was the son of an Irish immigrant farmer, William Ford, and the oldest son to survive of Mary Litogot; his mother died in 1876 with the birth of her sixth child. He went to the village school, and at the age of 16 he was apprenticed to Flower brothers' machine shop and then at the Drydock \& Engineering Works in Detroit. In 1882 he left to return to the family farm and spent some time working with a 1 1/2 hp steam engine doing odd jobs for the farming community at $3 per day. He was then employed as a demonstrator for Westinghouse steam engines. He met Clara Jane Bryant at New Year 1885 and they were married on 11 April 1888. Their only child, Edsel Bryant Ford, was born on 6 November 1893.At that time Henry worked on steam engine repairs for the Edison Illuminating Company, where he became Chief Engineer. He became one of a group working to develop a "horseless carriage" in 1896 and in June completed his first vehicle, a "quadri cycle" with a two-cylinder engine. It was built in a brick shed, which had to be partially demolished to get the carriage out.Ford became involved in motor racing, at which he was more successful than he was in starting a car-manufacturing company. Several early ventures failed, until the Ford Motor Company of 1903. By October 1908 they had started with production of the Model T. The first, of which over 15 million were built up to the end of its production in May 1927, came out with bought-out steel stampings and a planetary gearbox, and had a one-piece four-cylinder block with a bolt-on head. This was one of the most successful models built by Ford or any other motor manufacturer in the life of the motor car.Interchangeability of components was an important element in Ford's philosophy. Ford was a pioneer in the use of vanadium steel for engine components. He adopted the principles of Frederick Taylor, the pioneer of time-and-motion study, and installed the world's first moving assembly line for the production of magnetos, started in 1913. He installed blast furnaces at the factory to make his own steel, and he also promoted research and the cultivation of the soya bean, from which a plastic was derived.In October 1913 he introduced the "Five Dollar Day", almost doubling the normal rate of pay. This was a profit-sharing scheme for his employees and contained an element of a reward for good behaviour. About this time he initiated work on an agricultural tractor, the "Fordson" made by a separate company, the directors of which were Henry and his son Edsel.In 1915 he chartered the Oscar II, a "peace ship", and with fifty-five delegates sailed for Europe a week before Christmas, docking at Oslo. Their objective was to appeal to all European Heads of State to stop the war. He had hoped to persuade manufacturers to replace armaments with tractors in their production programmes. In the event, Ford took to his bed in the hotel with a chill, stayed there for five days and then sailed for New York and home. He did, however, continue to finance the peace activists who remained in Europe. Back in America, he stood for election to the US Senate but was defeated. He was probably the father of John Dahlinger, illegitimate son of Evangeline Dahlinger, a stenographer employed by the firm and on whom he lavished gifts of cars, clothes and properties. He became the owner of a weekly newspaper, the Dearborn Independent, which became the medium for the expression of many of his more unorthodox ideas. He was involved in a lawsuit with the Chicago Tribune in 1919, during which he was cross-examined on his knowledge of American history: he is reputed to have said "History is bunk". What he actually said was, "History is bunk as it is taught in schools", a very different comment. The lawyers who thus made a fool of him would have been surprised if they could have foreseen the force and energy that their actions were to release. For years Ford employed a team of specialists to scour America and Europe for furniture, artefacts and relics of all kinds, illustrating various aspects of history. Starting with the Wayside Inn from South Sudbury, Massachusetts, buildings were bought, dismantled and moved, to be reconstructed in Greenfield Village, near Dearborn. The courthouse where Abraham Lincoln had practised law and the Ohio bicycle shop where the Wright brothers built their first primitive aeroplane were added to the farmhouse where the proprietor, Henry Ford, had been born. Replicas were made of Independence Hall, Congress Hall and the old City Hall in Philadelphia, and even a reconstruction of Edison's Menlo Park laboratory was installed. The Henry Ford museum was officially opened on 21 October 1929, on the fiftieth anniversary of Edison's invention of the incandescent bulb, but it continued to be a primary preoccupation of the great American car maker until his death.Henry Ford was also responsible for a number of aeronautical developments at the Ford Airport at Dearborn. He introduced the first use of radio to guide a commercial aircraft, the first regular airmail service in the United States. He also manufactured the country's first all-metal multi-engined plane, the Ford Tri-Motor.Edsel became President of the Ford Motor Company on his father's resignation from that position on 30 December 1918. Following the end of production in May 1927 of the Model T, the replacement Model A was not in production for another six months. During this period Henry Ford, though officially retired from the presidency of the company, repeatedly interfered and countermanded the orders of his son, ostensibly the man in charge. Edsel, who died of stomach cancer at his home at Grosse Point, Detroit, on 26 May 1943, was the father of Henry Ford II. Henry Ford died at his home, "Fair Lane", four years after his son's death.[br]Bibliography1922, with S.Crowther, My Life and Work, London: Heinemann.Further ReadingR.Lacey, 1986, Ford, the Men and the Machine, London: Heinemann. W.C.Richards, 1948, The Last Billionaire, Henry Ford, New York: Charles Scribner.IMcN -
20 supply
- электроснабжение
- предложение
- поставки
- подводить электропитание
- подача
- источник электропитания радиоэлектронной аппаратуры
- источник питания (в электроснабжении)
- источник (электро)питания
- блок питания
блок питания
устройство питания
—
[Е.С.Алексеев, А.А.Мячев. Англо-русский толковый словарь по системотехнике ЭВМ. Москва 1993]
блок питания
блок электропитания
источник питания
источник электропитания
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
источник (электро)питания
Устройство, преобразующее различные виды энергии (химической, тепловой, электромагнитной) в электрическую. См. UPS.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
EN
источник питания
Характеристики внешних источников питания следует принимать по техническим условиям на присоединение, выдаваемым энегоснабжающей организацией в соответствии с Правилами пользования электрической энергией...
источник питания электроэнергией
-
[Интент]
источник электропитания
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]
Основными источниками питания должны служить электростанции и сети районных энергосистем. Исключение представляют большие предприятия с большим теплопотреблением, где основным источником питания может быть собственная электростанция (ТЭЦ). Но и в этом случае обязательно должна предусматриваться связь системы электроснабжения предприятия с сетью энергосистемы.
[СН 174-75 Инструкция по проектированию электроснабжения промышленных предприятий]
1.1.2 Зануление следует выполнять электрическим соединением металлических частей электроустановок с заземленной точкой источника питания электроэнергией при помощи нулевого защитного проводника.
[ ГОСТ 12.1.030-81]
Параллельные тексты EN-RUIt is recommended that, where practicable, the electrical equipment of a machine is connected to a single incoming supply. Where another supply is necessary for certain parts of the equipment (for example, electronic equipment that operates at a different voltage), that supply should be derived, as far as is practicable, from devices (for example, transformers, converters) forming part of the electrical equipment of the machine.
[IEC 60204-1-2006]Рекомендуется, там где это возможно, чтобы электрооборудование машины получало электропитание от одного источника. Если для каких-либо частей электрооборудования машины (например для электронного оборудования, работающего на другом напряжении) необходим отдельный источник питания, то, насколько это возможно, он должен являться частью (такой, например, как трансформатор, конвертор) электрооборудования этой же машины.
[Перевод Интент]
Power supplies
The required power supplies can be determined based on the criteria for definition of the installation (receivers, power, location, etc.) and the operating conditions (safety, evacuation of the public, continuity, etc.).
They are as follows:
- Main power supply
- Replacement power supply
- Power supply for safety services
- Auxiliary power supply
[Legrand]Источники электропитания
Источники электропитания определяют по различным критериям, в соответствии с характеристиками конкретной электроустановки. Определяют типы электроприемников, их мощность, территориальное расположение и др. При этом учитывают условия эксплуатации (безопасность, требования к аварийной эвакуации людей, непрерывность технологического процесса и т. д.).
Применяют следующие источники:
- основной источник питания;
- резервный источник питания;
- аварийный источник питания систем безопасности;
- дополнительный источник питания.
[Перевод Интент]
Рис. Legrand
Типовая схема электроснабжения: 1 - Main power supply - Основной источник питания
2 - Replacement power supply (2nd source) - Резервный источник питания (2-й источник)
3 - Replacement power supply (backup) - Резервный источник питания (независимый)
4 - Auxiliary power supply - Дополнительный источник питания
5 - Power supply for safety services - Аварийный источник питания для систем безопасности
6 - Management of sources - Управление источниками питания
7 - Control - Цепь управления
8 - Main LV distrib. board - Главный распределительный щит (ГРЩ)
9 - Safety panel - Панель безопасности
10 - Uninterruptible power supply - Источник бесперебойного питания
11 - Load shedding - Отключение нагрузки
12 - Non-priority circuits - Цепи неприоритетной нагрузки
14 - Uninterruptible circuits - Цепи бесперебойного питания
15 - Shed circuits - Цепи отключаемой нагрузки
16 - Safety circuits - Цепи систем безопасностиТематики
Близкие понятия
Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
- аварийный источник питания
- взаимно резервируемые источники питания
- внешний источник питания
- дополнительный источник питания
- источник бесперебойного питания
- источник питания с ограничением тока
- независимый источник питания
- основной источник питания
- резервный источник питания
EN
источник электропитания радиоэлектронной аппаратуры
источник электропитания РЭА
Нерекомендуемый термин - источник питания
Устройство силовой электроники, входящее в состав радиоэлектронной аппаратуры и преобразующее входную электроэнергию для согласования ее параметров с входными параметрами составных частей радиоэлектронной аппаратуры.
[< size="2"> ГОСТ Р 52907-2008]
источник питания
Часть устройства, обеспечивающая электропитание остальных модулей устройства.
[ http://www.lexikon.ru/dict/net/index.html]EN
power supply
An electronic module that converts power from some power source to a form which is needed by the equipment to which power is being supplied.
[Comprehensive dictionary of electrical engineering / editor-in-chief Phillip A. Laplante.-- 2nd ed.]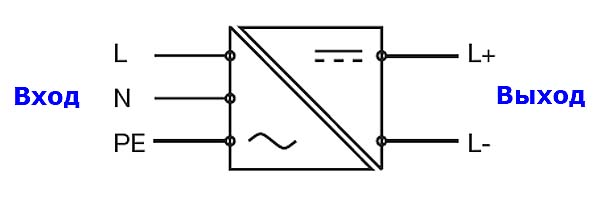
Рис. ABB
Структурная схема источника электропитанияThe input side and the output side are electrically isolated against each other
Вход и выход гальванически развязаны
Терминология относящая к входу
Primary side
Первичная сторона
Input voltage
Входное напряжение
Primary grounding
Current consumption
Потребляемый ток
Inrush current
Пусковой ток
Input fuse
Предохранитель входной цепи
Frequency
Частота
Power failure buffering
Power factor correction (PFC)
Коррекция коэффициента мощности
Терминология относящая к выходу
Secondary side
Вторичная сторона
Output voltage
Выходное напряжение
Secondary grounding
Short-circuit current
То короткого замыкания
Residual ripple
Output characteristics
Выходные характеристики
Output current
Выходной ток
Различают первичные и вторичные источники питания.
К первичным относят преобразователи различных видов энергии в электрическую, например:
- аккумулятор (преобразует химическую энергию.
Вторичные источники не генерируют электроэнергию, а служат лишь для её преобразования с целью обеспечения требуемых параметров (напряжения, тока, пульсаций напряжения и т. п.)Задачи вторичного источника питания
- Обеспечение передачи мощности — источник питания должен обеспечивать передачу заданной мощности с наименьшими потерями и соблюдением заданных характеристик на выходе без вреда для себя. Обычно мощность источника питания берут с некоторым запасом.
- Преобразование формы напряжения — преобразование переменного напряжения в постоянное, и наоборот, а также преобразование частоты, формирование импульсов напряжения и т. д. Чаще всего необходимо преобразование переменного напряжения промышленной частоты в постоянное.
- Преобразование величины напряжения — как повышение, так и понижение. Нередко необходим набор из нескольких напряжений различной величины для питания различных цепей.
- Стабилизация — напряжение, ток и другие параметры на выходе источника питания должны лежать в определённых пределах, в зависимости от его назначения при влиянии большого количества дестабилизирующих факторов: изменения напряжения на входе, тока нагрузки и т. д. Чаще всего необходима стабилизация напряжения на нагрузке, однако иногда (например для зарядки аккумуляторов) необходима стабилизация тока.
- Защита — напряжение или ток нагрузки в случае неисправности (например, короткого замыкания) каких-либо цепей может превысить допустимые пределы и вывести электроприбор или сам источник питания из строя. Также во многих случаях требуется защита от прохождения тока по неправильному пути: например прохождения тока через землю при прикосновении человека или постороннего предмета к токоведущим частям.
- Гальваническая развязка цепей — одна из мер защиты от протекания тока по неверному пути.
- Регулировка — в процессе эксплуатации может потребоваться изменение каких-либо параметров для обеспечения правильной работы электроприбора.
- Управление — может включать регулировку, включение/отключение каких-либо цепей или источника питания в целом. Может быть как непосредственным (с помощью органов управления на корпусе устройства), так и дистанционным, а также программным (обеспечение включения/выключения, регулировка в заданное время или с наступлением каких-либо событий).
- Контроль — отображение параметров на входе и на выходе источника питания, включения/выключения цепей, срабатывания защит. Также может быть непосредственным или дистанционным.
Трансформаторный (сетевой) источник питания
Чаще всего состоит из следующих частей:- Сетевого трансформатора, преобразующего величину напряжения, а также осуществляющего гальваническую развязку;
- Выпрямителя, преобразующего переменное напряжение в пульсирующее;
- Фильтра для снижения уровня пульсаций;
- Стабилизатора напряжения для приведения выходного напряжения в соответствие с номиналом, также выполняющего функцию сглаживания пульсаций за счёт их «срезания».
В сетевых источниках питания применяются чаще всего линейные стабилизаторы напряжения, а в некоторых случаях и вовсе отказываются от стабилизации.
Достоинства такой схемы:- Простота построения и обслуживания
- Надёжность
- Низкий уровень радиопомех.
Недостатки:
- Большой вес и габариты, особенно при большой мощности: по большей части за счёт габаритов трансформатора и сглаживающего фильтра
- Металлоёмкость
- Применение линейных стабилизаторов напряжения вводит компромисс между стабильностью выходного напряжения и КПД: чем больше диапазон изменения напряжения, тем больше потери мощности.
- При отсутствии стабилизатора на выход источника питания проникают пульсации с частотой 100Гц.
В целом ничто не мешает применить в трансформаторном источнике питания импульсный стабилизатор напряжения, однако большее распространение получила схема с полностью импульсным преобразованием напряжения.
Импульсный источник питания
Широко распространённая схема импульсного источника питания состоит из следующих частей:- Входного фильтра, призванного предотвращать распространение импульсных помех в питающей сети
- Входного выпрямителя, преобразующего переменное напряжение в пульсирующее
- Фильтра, сглаживающего пульсации выпрямленного напряжения
- Прерывателя (обычно мощного транзистора, работающего в ключевом режиме)
- Цепей управления прерывателем (генератора импульсов, широтно-импульсного модулятора)
- Импульсного трансформатора, который служит накопителем энергии импульсного преобразователя, формирования нескольких номиналов напряжения, а также для гальванической развязки цепей (входных от выходных, а также, при необходимости, выходных друг от друга)
- Выходного выпрямителя
- Выходных фильтров, сглаживающих высокочастотные пульсации и импульсные помехи.
Достоинства такого блока питания:
- Можно достичь высокого коэффициента стабилизации
- Высокий КПД. Основные потери приходятся на переходные процессы, которые длятся значительно меньшее время, чем устойчивое состояние.
- Малые габариты и масса, обусловленные как меньшим выделением тепла на регулирующем элементе, так и меньшими габаритами трансформатора, благодаря тому, что последний работает на более высокой частоте.
- Меньшая металлоёмкость, благодаря чему мощные импульсные источники питания стоят дешевле трансформаторных, несмотря на бо́льшую сложность
- Возможность включения в сети широкого диапазона напряжений и частот, или даже постоянного тока. Благодаря этому возможна унификация техники, производимой для различных стран мира, а значит и её удешевление при массовом производстве.
Однако имеют такие источники питания и недостатки, ограничивающие их применение:
- Импульсные помехи. В связи с этим часто недопустимо применение импульсных источников питания для некоторых видов аппаратуры.
- Невысокий cosφ, что требует включения компенсаторов коэффициента мощности.
- Работа большей части схемы без гальванической развязки, что затрудняет обслуживание и ремонт.
- Во многих импульсных источниках питания входной фильтр помех часто соединён с корпусом, а значит такие устройства требуют заземления.
[Википедия]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
подача
1. Порция одноврем. загружаемых в шахтную печь рудных материалов, флюсов и тв. топлива с определ. соотношением компонентов.
2. Операция перемещения заготовки в одном из направлений (продольном, поперечном, или др.) в промежутках между единичными обжатиями при ковке. В количественном отношении подача — величина перемещения заготовки (абсолютная подача) или отношение поперечного размера заготовки к ее высотному размеру в зоне обжатия (между бойками) — относительная подача.
3. Длина кольцевого участка гильзы или заготовки, обжимаемого и раскатываемого за цикл пилигримовой прокатки труб.
4. Относительное перемещение режущего инструмента и обрабатываемой на станке заготовки. Различают подачу непрерывную (например, на токарных, сверлильных, фрезерных станках) и прерывную или периодическую подачу (например, на строгальных, долбежных станках).
[ http://www.manual-steel.ru/eng-a.html]Тематики
EN
подводить электропитание
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
поставки
1. Означают продажу, включая перепродажу электроэнергии потребителям (Директива 2003/54/ЕС).
2. Продажа электроэнергии, как правило, включает снятие показаний счетчиков и выписывание счетов, в отличие от другой деятельности, такой как генерация, передача, эксплуатация системы и распределение.
[Англо-русский глосcарий энергетических терминов ERRA]EN
supply
1. Means the sale, including resale, of electricity to customers (Directive 2003/54/EC).
2. The sale of electricity, usually including metering and billing, in contrast to other activities such as generation, transmission, system operation and distribution.
[Англо-русский глосcарий энергетических терминов ERRA]Тематики
EN
предложение
Совокупность слов, образующих текстовую единицу, выражающую законченную мысль. Обычно начинается с заглавной буквы и заканчивается знаком препинания, таким как точка, вопросительный или восклицательный знак.
[ http://www.morepc.ru/dict/]
предложение
Одно из основных понятий экономики рынка. Можно определить П. блага (товара) как количество этого блага, которое может быть представлено для продажи на рынке по данной цене. Соответственно, совокупное П. на рынке — общее количество благ, которые могут быть представлены для продажи при данной структуре цен. В нормальных условиях, когда загрузка производственных мощностей близка к полной, выпуск каждой дополнительной единицы продукции требует дополнительных затрат. Чтобы побудить к этому производителя, надо предложить ему повышенную цену (См. Кривая предложения). С другой стороны, потребитель заинтересован в возможно более низкой цене (см. Кривая спроса). Взаимодействие этих интересов и формирует рыночный механизм.
[ http://slovar-lopatnikov.ru/]Тематики
EN
электроснабжение
Обеспечение потребителей электрической энергией.
[ ГОСТ 19431-84]Качество электрической энергии (КЭ) тесно связано с надежностью электроснабжения, поскольку нормальным режимом электроснабжения потребителей является такой режим, при котором потребители получают электроэнергию бесперебойно, в количестве, заранее согласованном с энергоснабжающей организацией, и нормированного качества.
[В. В. Суднова. Качество электрической энергии]Тематики
Действия
Сопутствующие термины
- бесперебойность электроснабжения
- надежность электроснабжения
- нарушение электроснабжения
- нормальный режим электроснабжения
- проект электроснабжения
- электроснабжение от автономного источника питания электроэнергией
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > supply
СтраницыСм. также в других словарях:
machine tool — machine tooled, adj. a power operated machine, as a lathe, used for general cutting and shaping of metal and other substances. [1860 65] * * * Stationary, power driven machine used to cut, shape, or form materials such as metal and wood. Machine… … Universalium
Machine gun — [ thumb|200px|An illustration of later model 19th century Gatling gun. It was a multi barreled rotary machine gun fired via a manual crank, which mechanically loaded and primed cartridges from the hopper above the gun] : For other uses of the… … Wikipedia
Machine — This article is about devices that perform tasks. For other uses, see Machine (disambiguation). A machine manages power to accomplish a task, examples include, a mechanical system, a computing system, an electronic system, and a molecular machine … Wikipedia
Machine vision glossary — Common definitions related to the machine vision field.Compiled for application on the Society of Manufacturing Engineers interest area.General related fields *Machine vision *Computer vision *Image processing *Signal processing NOTOC 0 9*1394.… … Wikipedia
Derived row — For other uses, see Partition (disambiguation). The term partition is also French for the sheet music of a transcription. In music using the twelve tone technique, derivation is the construction of a row through segments. A derived row is a tone… … Wikipedia
Machine Robo Mugenbine — The current logo of the Machine Robo Mugenbine toyline. Machine Robo Mugenbine (マシンロボムゲンバイン?), also called Multiple General Node Combine System … Wikipedia
machine — [[t]məʃi͟ːn[/t]] ♦♦ machines, machining, machined 1) N COUNT: also by N A machine is a piece of equipment which uses electricity or an engine in order to do a particular kind of work. I put the coin in the machine and pulled the lever... The… … English dictionary
machine — [16] The ultimate source of both machine and mechanic [14] was makhos, a Greek word meaning ‘contrivance, means’, and related distantly to English may ‘be able’ and might. From it was derived mēkhané, whose Doric dialect form mākhaná passed into… … The Hutchinson dictionary of word origins
machine — [16] The ultimate source of both machine and mechanic [14] was makhos, a Greek word meaning ‘contrivance, means’, and related distantly to English may ‘be able’ and might. From it was derived mēkhané, whose Doric dialect form mākhaná passed into… … Word origins
Counter machine reference model — The Counter machine s reference model is a set of choices and conventions to be used with the Counter machine and other model variants of the Register machine concept. It permits comparisons between models, and serves a didactic function with… … Wikipedia
State machine replication — Introduction from Schneider s 1990 survey: : Distributed software is often structured in terms of clients and services. Each service comprises one or more servers and exports operations that clients invoke by making requests. Although using a… … Wikipedia
Перевод: с английского на все языки
со всех языков на английский- Со всех языков на:
- Английский
- С английского на:
- Все языки
- Арабский
- Русский
- Суахили
