-
1 armature
armature [aʀmatyʀ]feminine nouna. [de tente, parapluie] frame ; ( = infrastructure) framework* * *aʀmatyʀ1) (de tente, store, d'abat-jour) frame; ( de soutien-gorge) underwiring [U]; ( de voûte) arch reinforcement; ( de béton armé) reinforcing steel rods (pl)à armature — [soutien-gorge] underwired
sans armature — [soutien-gorge] light control (épith)
2) (de région, parti, d'entreprise) infrastructure3) ( de roman) structure* * *aʀmatyʀ nf[construction] framework, [tente] frame, [corset] bone, [soutien-gorge] underwiring* * *armature nf1 (de tente, store, d'abat-jour) frame; ( de soutien-gorge) underwiring ¢; ( de voûte) arch reinforcement; ( de béton armé) reinforcing steel rods (pl); à armature [soutien-gorge] underwired; sans armature [soutien-gorge] light control ( épith);2 (de région, de parti, d'entreprise) infrastructure; l'armature commerciale de la région the region's commercial infrastructure;3 (de roman, pièce de théâtre) structure;4 Mus key signature;5 Électrotech armament;6 ( d'aimant) armature.[armatyr] nom féminin1. [cadre - d'une tente, d'un abat-jour] frame -
2 inducido
adj.induced.m.armature.past part.past participle of spanish verb: inducir.* * *SM (Elec) armature* * *----* inducido por el ejercicio = exercise-induced.* inducido por el estrés = stress-induced.* inducido por la luz = light-induced.* * ** inducido por el ejercicio = exercise-induced.* inducido por el estrés = stress-induced.* inducido por la luz = light-induced.* * *inducido nmElec armature* * *m EL armature -
3 секция
section, segment
- закрылка — flap section /segment/
- маслоагрегата (гтд) — oil pump block section
-, нагнетающая (маслоагрегата) — oil pressure section (contains oil pressure pump)
- обмотки якоря — armature winding coil
концы секции обмотки якоря припаяны к петушкам ламелей коллектора, — two ends of each armature winding coils are soldered into grooves in risers, of the commutator.
-, основная, откачивающая (маслоагрегата) — main oil scavenge section
- откачки масла (маслоагрегата) — oil scavenge section (contains oil scavenge pumps)
- откачки масла из задней опоры ротора турбины (маслоагрегата) — turbine (rotor) tail bearing oil scavenge section
- откачки масла из полости подшипников передних опор (маслоагрегата) — front bearing oil scavenge section
- предкрылка — slat section /segment/
в случае незагорания зеленой лампы сигнализации убранного положения секции предкрылка загорается табло "к взлету не готов". — the unsafe-takeoff annunciator is lit if а slat segment green light is not illuminated.
-, расходная (топливного бака) — fuel feed reservoir
each fuel tank has a fuel reservoir to feed the engine.
- руля высоты (левая, правая) — elevator section /segment/
- руля направления (верхняя, нижняя) — rudder (upper, lower) section /segment/
- снайпера — spoiler section /segment/
если не горит одна из зеленых ламп, сигнализирующая убранное положение сектора предкрылка, загорается табло "к взлету не готов" — unsafe takeoff condition signal is activated when any of spoiler segment green lights is not illuminated.
-, фильтрующая (фильтроэлемента) — filtering section
- элерона (внутренняя, внешняя) — aileron (inboard, outboard) section /segment/Русско-английский сборник авиационно-технических терминов > секция
-
4 определять
•Magnitude of the principal stresses controls (or governs) the degree of birefringence.
•Covalent bonds are responsible for atomic combinations in many elements.
•θ is the angle defining the position of the rotor with respect to the stator.
•These elements define the geometry of the orbit.
•The take-off condition dictates (or determines, or defines) the amount of wing area required for an airplane.
•The armature of the rudder motor dictates the direction in which the rudder motor rotates.
•The rate at which a furnace can melt scrap governs the rate at which it can accommodate successive portions of the charge.
•These equations govern simple waves.
•It is the naval architect who settles (or decides on) the form of the vessel.
•Three points determine a circle.
•The geometry of the small ring compounds fixes their configuration.
•The equation specifies the topography of the potential surface.
II•These variables are difficult to appraise accurately.
•The cost of steam generation required by the power plant can be arrived at (or defined) from Fig. 2.
•A number of coils were rolled to assess the performance of the controller.
•The pressure was determined (or deduced) from the weight of steam and...
•Reserves are estimated (or evaluated) at 100,000,000 bbl.
•To assess the distribution and level of the pollutant...
•This knowledge enables the analyst to gauge the meaning and reliability of the results obtained.
•Information about temperatures below the surface can be inferred from the magnetic properties of rocks.
•The adequacy of the global supply can be gauged through a simple analysis of the per capita need for water.
см. классифицироватьIV•If the wavelength composition of the light is known, its colour can be specified (or determined, or identified).
•Identify the two chemicals in the equation for which...
•The closer you want to pinpoint the exact orbit, the more corrections you must make.
Русско-английский научно-технический словарь переводчика > определять
-
5 поток
blast, circulation строит., current, effluent, flood, flow, flux, moving stream, stream, streamflow, streaming* * *пото́к м.1. ( течение) flow, streamвверх по пото́ку — upstreamвозмуща́ть пото́к — disturb the flow [the stream]пото́к восхо́дит — the stream flows [moves] upwards, the stream ascendsпото́к достига́ет крити́ческого режи́ма гидр. — the flow chokesни́же по пото́ку — downstreamпото́к нисхо́дит — the stream flows [moves] downwards; the stream descendsпото́к па́дает (на пове́рхность) — the stream is incident (on a surface)перекрыва́ть пото́к (напр. расплавленного металла, стекла) [m2]на вы́ходе из пе́чи — dam the (out)flowпото́к ( в реакторе) [m2]проска́льзывает — хим. the stream short-circuitsпото́к раздва́ивается — the flow bifurcates, the flow is divided between two pathsсвя́зывать пото́ки — couple (the) flowsсо стороны́ набега́ющего пото́ка аргд. — windwardсрыва́ть пото́к аргд. — stall the flowсужа́ть [ущемля́ть] пото́к — constrict [restrict] the flow2. (количество вещества, энергии и т. п., протекающее за единицу времени) физ. fluxзахва́тывать, напр. магни́тный пото́к — trap, e. g., the magnetic flux3. ( движения) трансп. trafficадиабати́ческий пото́к — adiabatic flowбезвихрево́й пото́к1. физ. nonedding [noncirculatory, irrotational] flow2. ав. clean flowбезнапо́рный пото́к гидр. — gravity [free-surface] flowпото́к ве́ктора — flux of a vector, vector fluxвихрево́й пото́к — eddy [vortex] flowпото́к в котлоагрега́те — circuitпото́к во́здуха — air flow, air current, air streamвосходя́щий пото́к — ascending [upward] currentвытека́ющий пото́к — outward flow, outflowпото́к вытесне́ния хим. — plug flowвыходя́щий пото́к хим. — exit streamвя́зкий пото́к — frictional flowгиперзвуково́й пото́к — hypersonic flowдвои́чный пото́к — binary streamдвухни́точный пото́к тепл. — double-circuit flowдозвуково́й пото́к — subsonic flowпото́к за винто́м, возду́шный — slip streamзапылё́нный пото́к — dust-laden flowзаторможё́нный пото́к — stagnated flowпото́к излуче́ния — flux of radiation, radiation fluxизотерми́ческий пото́к — isothermal flowпото́к и́мпульса — momentum flux, flux of momentumкольцево́й пото́к — annular flowконвекцио́нный пото́к — convection current, convective flowламина́рный пото́к — laminar flowмагни́тный пото́к — magnetic flux, magnetic inductionмагни́тный пото́к спада́ет — the magnetic flux collapses [decays]магни́тный пото́к сцепля́ет [прони́зывает] индукти́вность колеба́тельного ко́нтура — the magnetic flux links the tuned-circuit coilневихрево́й пото́к — potential flowнисходя́щий пото́к — descending [downward] currentосновно́й пото́к1. main flow2. (напр. газа в химическом реакторе) bulk streamпо́лный пото́к — ( количество) total flow; ( скорость изменения количества) total fluxпоршнево́й пото́к — plug flowпото́к Пуассо́на ( в теории трафика) — Poisson input(s), Poisson arrival(s)пото́к рассе́яния — leakage fluxсверхзвуково́й пото́к — supersonic flowсверхкрити́ческий пото́к — supercritical flowсветово́й пото́к — luminous [light] fluxсвобо́дный пото́к — free [unrestricted] flow, free streamпото́к смеще́ния — displacement fluxстру́йный пото́к — jet flowтеплово́й пото́к — ( количество) heat flow; ( скорость теплопередачи) heat flux, rate of heat flowтра́нспортный пото́к — traffic [transportation] flowпото́к тре́бований, входя́щий ( в теории массового обслуживания) — input (process), arrival of units, arriving units, arrivalsтурбуле́нтный пото́к — turbulent flowциркуляцио́нный пото́к — circulating flow; хим. recycleпото́к че́рез систе́му обслу́живания ( в теории массового обслуживания) — traffic (of units flowing) through a waiting systemпото́к эне́ргии — energy fluxпото́к я́коря эл. — armature flux -
6 реакция
(цепи, измерительного прибора) indicial admittance, answer, reacting force, reaction force, reaction, ( на воздействие) response, retroaction* * *реа́кция ж.1. ( взаимодействие химических элементов или соединений) reaction (with …)заде́рживать (наступле́ние) реа́кции — defer a reactionреа́кция идё́т до заверше́ния — a reaction goes to completionиндуци́ровать реа́кцию — induce a reactionреа́кция ме́жду A и B — a reaction A with Bнаступа́ет энерги́чная реа́кция — the vigorous reaction takes place the reaction proceeds vigorouslyопро́бовать реа́кцию — test a reaction equation, test a reactor (in order) to confirm a hypothesisподверга́ть реа́кции — cause smth. to reactподде́рживать ход реа́кции — sustain a reactionпрерыва́ть [остана́вливать] реа́кцию — arrest a reactionреа́кция (при)останавливается — the reaction comes to a haltреа́кция протека́ет — the reaction proceedsреа́кция протека́ет [прохо́дит] бу́рно — the violent reaction takes place, the reaction proceeds violentlyреа́кция протека́ет по ( такому-то) механи́зму — the reaction proceeds by the mechanismреа́кция разветвля́ется — the reaction branches (off)ускоря́ть реа́кцию введе́нием катализа́тора — catalyze a reaction2. (на приложенную силу, нагрузку и т. п.) reaction (to …); ( отклик на воздействие) responseавтокаталити́ческая реа́кция — autocatalytic reactionаналити́ческая реа́кция — analytical reactionреа́кция аннигиля́ции — annihilation reactionано́дная реа́кция — anodic reactionаэродинами́ческая реа́кция — aerodynamic [air] reactionвзрывна́я реа́кция — explosive reactionвосстанови́тельная реа́кция — reducing reactionреа́кция вытесне́ния — displacement reactionгетероге́нная реа́кция — heterogeneous reactionгетеролити́ческая реа́кция — heterolytic reactionгомоге́нная реа́кция — homogeneous reactionгомолити́ческая реа́кция — homolytic reactionреа́кция деле́ния — fission reactionреа́кция замеще́ния — substitution reactionреа́кция замеще́ния, радика́льная — radical substitution reactionреа́кция замеще́ния, электрофи́льная — electrophilic substitution reactionреа́кция захва́та — capture reactionизбира́тельная реа́кция — selective reactionреа́кция излуче́ния — radiation [radiative] reactionиндика́торная реа́кция — indicator testка́пельная реа́кция — drop reaction, spot [filter paper] testкаталити́ческая реа́кция — catalytic reactionка́чественная реа́кция — qualitative reactionреа́кция колё́с, бокова́я авто — cornering forceколи́чественная реа́кция — quantitative reactionреа́кция конденса́ции — condensation reactionконе́чная реа́кция — end reactionконкури́рующая реа́кция — concurrent [competing, competitive] reactionконсекути́вная реа́кция — consecutive [consequent, successive] reactionреа́кция на де́йствие о́ргана управле́ния ав. — control responseреа́кция на отклоне́ние руля́ высоты́ ав. — response to elevator deflectionреа́кция на отклоне́ние элеро́нов ав. — response to aileron deflectionреа́кция нейтрализа́ции — neutralization reactionнеобрати́мая реа́кция — irreversible reactionнеуправля́емая реа́кция — uncontrolled reactionреа́кция нулево́го поря́дка — zero-order reactionреа́кция обме́на — exchange reactionобрати́мая реа́кция — reversible reactionобра́тная реа́кция — reverse reactionреа́кция окисле́ния — oxidation reactionокисли́тельно-восстанови́тельная реа́кция — redox reactionреа́кция опо́р сопр. — reaction at (the) supportsреа́кция осажде́ния — precipitation reactionреа́кция отда́чи — recoil reactionпаралле́льная реа́кция — parallel [concurrent] reactionреа́кция пе́рвого поря́дка — first-order reactionпобо́чная реа́кция — side reactionпове́рхностная реа́кция — surface reactionпоро́говая реа́кция — threshold reactionреа́кция присоедине́ния — addition (reaction)пряма́я реа́кция — direct [forward, straight] reactionреа́кция разложе́ния — decomposition reactionсамоподде́рживающаяся реа́кция — self-sustaining reactionреа́кция свя́зей сопр. — constraint reactionселекти́вная реа́кция — selective reactionсопряжё́нная реа́кция — coupled reactionреа́кция струи́ — jet reactionтвердоте́льная реа́кция — solid-state reactionтермоя́дерная реа́кция — thermonuclear reactionуправля́емая реа́кция — controlled reactionустанови́вшаяся реа́кция — steady [stationary] reactionфотохими́ческая реа́кция — photochemical [light-induced] reactionфотоя́дерная реа́кция — photonuclear reactionхими́ческая реа́кция — chemical charge, chemical reactionреа́кция ( отклик) [m2]це́пи или схе́мы — response of a circuitцепна́я реа́кция — chain reactionчасти́чная реа́кция — partial reactionэкзотерми́ческая реа́кция — exothermic [exoenergic heat-producing] reactionэндотерми́ческая реа́кция — endothermic [endoergic] reactionя́дерная реа́кция — nuclear reactionреа́кция я́дерного си́нтеза — thermonuclear reactionреа́кция я́коря эл. — armature reaction -
7 ход
course, ( доменной печи) drive, driving, excursion, computation line геод., line, ( механизма) move, movement, ( шагающих балок) pitch метал., run, process, route, running, stroke, (напр. поршня) throw, trace, tracing, traverse, way* * *ход м.1. ( движение) motion, move, movementво вре́мя хо́да су́дна — while the ship is underwayна ходу́ (напр. регулировать) — (e. g., adjust) on the goсвои́м хо́дом (о судне, автомобиле и т. п.) — under its own power3. (работа, эксплуатация) operation, service, actionпуска́ть в ход — put into operation, put into service, put into actionрабо́тать на холосто́м ходу́ — idle, run idle, run without loadсодержа́ть на ходу́ (напр. машины и т. п.) — keep (e. g., machines, etc.) in operation [in service, on the go]4. ( в теплообменном устройстве) pass5. (развитие чего-л.) progress, course6. ( скорость) rate, speed7. (место, через которое проходят) passage; ( вход) entrance, entry8. (изменение или характер изменения какой-л. физической величины, как правило, в зависимости от другой) behaviour, change, dependence, variation9. геод., топ. computation course, computation line, route, traverse10. (вид движения в транспортных средствах; существует только в сочетаниях с определяющими словами):на гу́сеничном ходу́ — on tracks, tracked, track-layingна колё́сном ходу́ — on wheels, wheeledазимута́льный ход — azimuth(al) motionход амортиза́тора — travelпри хо́де растяже́ния амортиза́тора — during extension …при хо́де сжа́тия амортиза́тора — during contraction …ход бата́на текст. — path of lay, stroke of latheход без толчко́в — smooth motionбесшу́мный ход — silent [noiseless] runningход вверх — upstroke, upward [ascending] strokeход вниз — downstroke, downward [inward, descending] strokeход впу́ска двс. — suction [admission, intake, charging] strokeвременно́й ход — time dependence, time variation, variation (of smth.) with timeход вса́сывания двс. — suction [admission, charging, intake] strokeход вы́пуска двс. — outstroke, exhaust strokeвысо́тный ход физ. — altitude curve, height dependence, altitudinal variationsдвойно́й ход — double strokeход до́менной пе́чи — run [operation] of a blast furnaceход зави́симости — variation, dependenceход зави́симости, напр. x от y — plot of x as a function of y, behaviour of x with (variations in) y, variations in x with yза́дний ход — reverse movement; reverse [backward] running; ж.-д. moving back, return motion; (поршня, ползуна) back strokeза́мкнутый ход геод. — closed circuitзо́льный ход кож. — line roundход иглы́ ( распылителя в топливной аппаратуре дизелей) — needle liftход каре́тки1. вчт. carriage movement2. текст. pitch of the coilход конта́ктов — contact travelход криво́й — ( имеется в виду кривая как таковая) trend [shape, run] of a curve; (имеется в виду какая-л. физическая величина, представленная кривой):ход криво́й ано́дного то́ка в зави́симости от се́точного напряже́ния пока́зывает, что … — a plot of anode current against grid voltage shows that …, the manner in which anode current varies with grid voltage shows that …, the behaviour of anode current with (variations in) grid voltage shows that …лесоспла́вный ход — floating routeли́тниковый ход — sprueход луча́ опт. — ray path (length)стро́ить ход луча́ — set up [trace] a rayмагистра́льный ход геод. — main [primary, principal] traverseма́лый ход мор. — low [slow] speedход маши́ны — machine runningмё́ртвый ход ( зазор в механизме) — backlash, lost motion, play, free travel, slackход нагнета́ния двс. — pressure strokeнеравноме́рный ход — irregular [discontinuous, uneven] runningнивели́рный ход — line of levels, level(ling) lineобра́тный ход — reverse [return] motion; reverse [backward] running; back strokeодина́рный ход — single strokeход педа́ли авто — pedal stroke, pedal travelход педа́ли сцепле́ния, свобо́дный — clutch pedal clearance, free travel of the clutch pedalпере́дний ход — forward motion; forward running; мор. advancing, aheadingперекидно́й ход ( коксовой печи) — cross-over flueход пе́чи — run [operation, working] of a furnaceрасстро́ить ход пе́чи — disturb [upset] the operation of a furnaceход пе́чи, горя́чий — hot run of a furnaceход пе́чи, неро́вный — erratic [irregular] operation of a furnaceход пе́чи, расстро́енный — disturbed operation of a furnaceход пе́чи, ро́вный — smooth [regular] operation of a furnaceход пе́чи, сты́лый — cold working of a furnaceход пе́чи, ти́хий — slow run [slow operation] of a furnaceход пе́чи, холо́дный — cold run of a furnaceход пилообра́зного напряже́ния элк. — stroke of a sawtooth voltageход пилообра́зного напряже́ния, обра́тный элк. — return stroke of a sawtooth voltageход пилообра́зного напряже́ния, прямо́й элк. — forward stroke of a sawtooth voltageход пилообра́зного напряже́ния, рабо́чий элк. — working stroke of a sawtooth voltageход пла́вки — progress of a heatпла́вный ход — smooth runningход плу́га — plough travel, plough draughtход подве́ски — suspension movementполигонометри́ческий ход — traverse, polygon(al) [polygonometric] traverse, polygonal courseпо́лный ход мор. — full speedрабо́чий ход двс. — working [power] strokeход развё́ртки (осциллоскопа, индикатора и т. п) — sweep motionход (развё́ртки), обра́тный — retrace (motion) of the sweep, flybackход (развё́ртки), прямо́й — forward motion of the sweep, active phase of the sweep scanход расшире́ния — двс. expansion [working, combustion, firing] stroke; ( амортизатора) extensionса́мый ма́лый ход мор. — dead slow speedса́мый по́лный ход мор. — flank speedсвобо́дный ход — free (easy) running, free travel; free wheelingход сжа́тия — compression [pressure] stroke; ( рессоры или пружины) bump stroke; ( амортизатора) contractionспоко́йный ход — smooth [quiet] runningсре́дний ход мор. — half [moderate] speedсу́точный ход — day [diurnal] variationсу́точный ход магни́тного склоне́ния — diurnal changes in magnetic variaticsтеодоли́тный ход — field [theodolite] traverseто́почный ход — (furnace) flueхолосто́й ход — idle [free, light, loose, no-load] running, idle [no-load] strokeпри холосто́м хо́де эл. — at no-loadход часо́в — daily rate (of a time niece)ход часо́в, отрица́тельный — rate of losingход часо́в, положи́тельный — rate of gainingчасто́тный ход (какой-л. физической величины) — variations with frequencyперепа́д мо́щности определя́ется часто́тным хо́дом перехо́дного ослабле́ния ответви́теля — the change in power is determined by variations in the dynamic attenuation of the coupler with frequencyчасто́тный ход оши́бки — the difference in error between the limiting frequenciesчасто́тный ход усиле́ния — plot of gain as a function of frequency, frequency dependence of gain, variations in gain with frequencyшу́мный ход — noisy runningход электро́нного луча́, обра́тный — flyback, return trace, retraceгаси́ть обра́тный ход электро́нного луча́ — eliminate [suppress, blank] the flyback [return trace, retrace]ход электро́нного луча́, обра́тный по вертика́ли — vertical flybackход электро́нного луча́, обра́тный по горизонта́ли — horizontal flybackход электро́нного луча́, обра́тный по ка́дру — frame flybackход электро́нного луча́, обра́тный по строке́ — line flybackход я́коря — armature travel -
8 polarizovana svtlost
• polarized armature light -
9 лист
mлист боковой стены, облицовочный
—FRA panneau m de paroi latéraleENG body side panelITA lamiera f della parete longitudinaleRUS лист m боковой стены, облицовочныйсм. поз. 859 на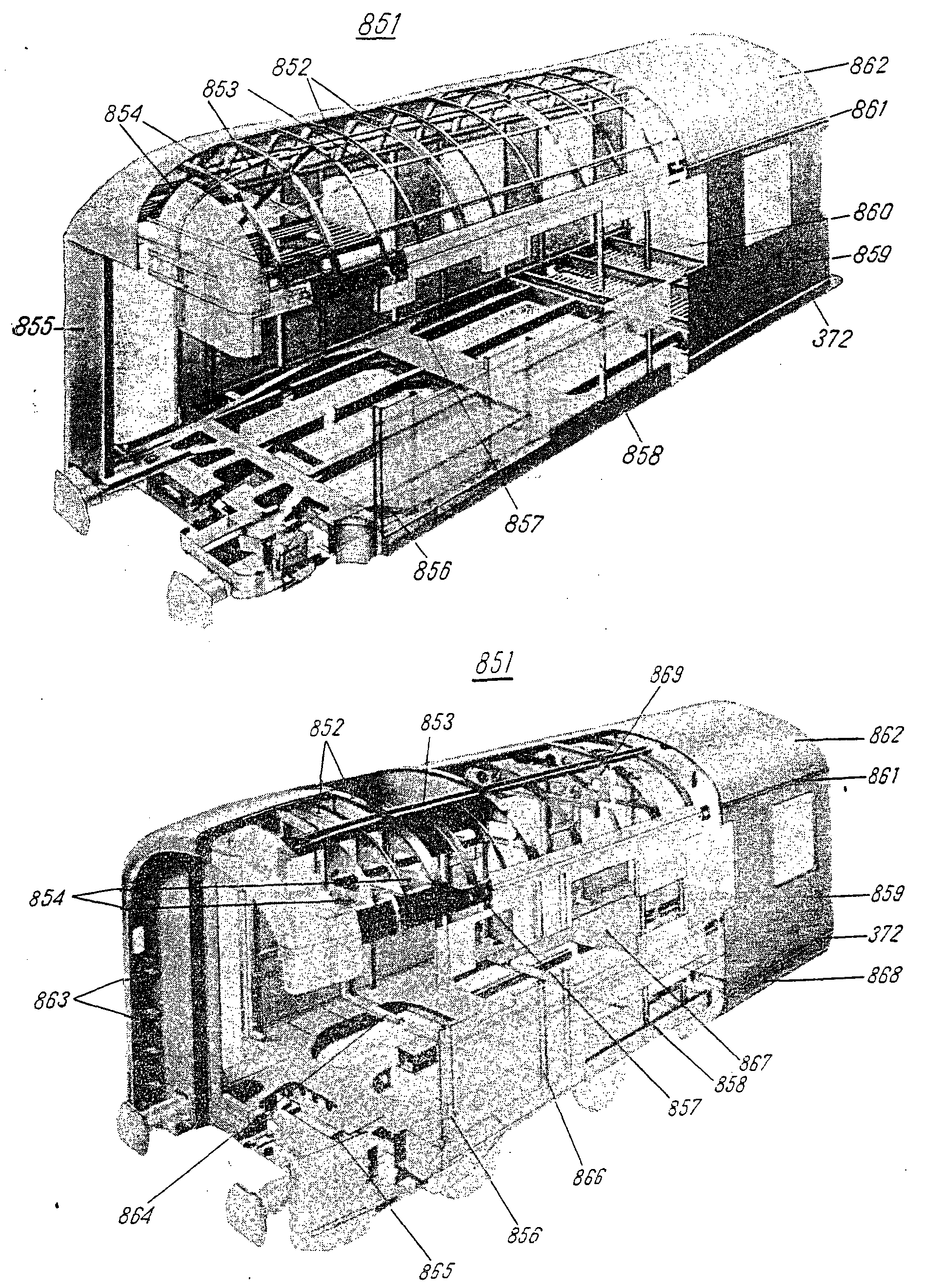 ,
,  —FRA couvre-joint m de riveITA coprigiunto m di estremitàPLN skrajnik m dachuRUS лист m карниза крышисм. поз. 999 на
—FRA couvre-joint m de riveITA coprigiunto m di estremitàPLN skrajnik m dachuRUS лист m карниза крышисм. поз. 999 на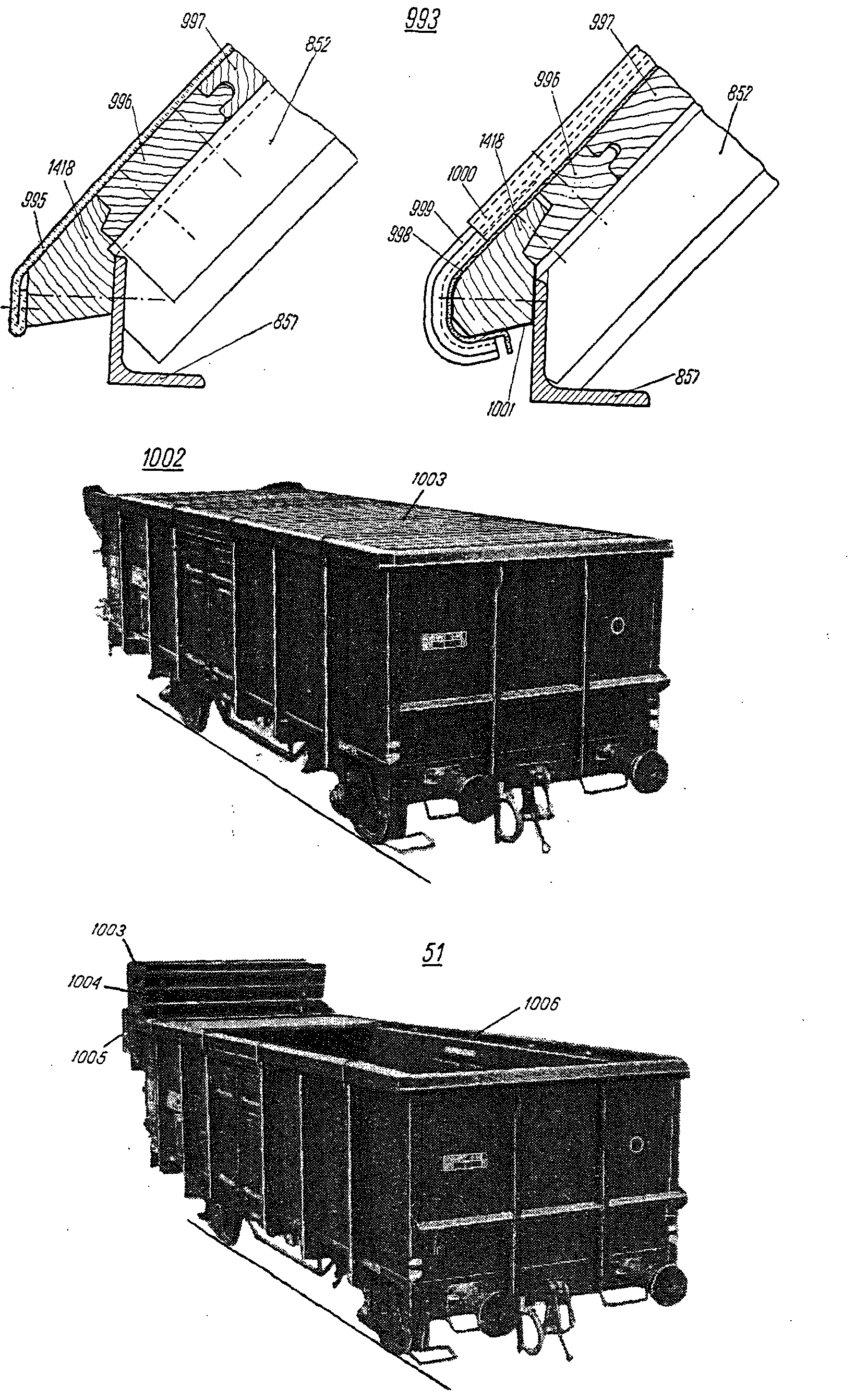 —FRA revêtement m de toitureDEU Dachdecke fENG roof coveringITA rivestimento m dell'imperialePLN pokrycie n dachuRUS лист m крышисм. поз. 995 на
—FRA revêtement m de toitureDEU Dachdecke fENG roof coveringITA rivestimento m dell'imperialePLN pokrycie n dachuRUS лист m крышисм. поз. 995 на
лист крыши, алюминиевый
—FRA revêtement f de toiture (alliage léger)ITA rivestimento m dell'imperiale (lega leggera)PLN blacha f dachowa (alummiowa)RUS лист m крыши, алюминиевыйсм. поз. 998 на —FRA tôle f de cloison transversaleITA lamiera f di parete trasversalePLN blacha f ścianki działowejRUS лист m перегородкисм. поз. 883 на
—FRA tôle f de cloison transversaleITA lamiera f di parete trasversalePLN blacha f ścianki działowejRUS лист m перегородкисм. поз. 883 на —FRA tôle-marchepied fDEU Trittblech nENG tread plateITA lamiera-pedana fPLN blacha f progowaRUS лист m подпоркисм. поз. 367 на
—FRA tôle-marchepied fDEU Trittblech nENG tread plateITA lamiera-pedana fPLN blacha f progowaRUS лист m подпоркисм. поз. 367 на —FRA lame f de ressortDEU Federblatt nITA foglia f di molla a balestraPLN pióro ń sprężynyRUS лист m рессорныйсм. поз. 231 на
—FRA lame f de ressortDEU Federblatt nITA foglia f di molla a balestraPLN pióro ń sprężynyRUS лист m рессорныйсм. поз. 231 на
лист торцевой стены, облицовочный
—FRA panneau m de paroi de boutDEU Stirnwandblech nENG body end panelITA lamiera f della parete di testaRUS лист m торцевой стены, облицовочныйсм. поз. 855 на
лист, армировочный
—FRA armature fDEU Bewehrung fENG cover plateITA armatura fRUS лист m, армировочныйсм. поз. 1604 на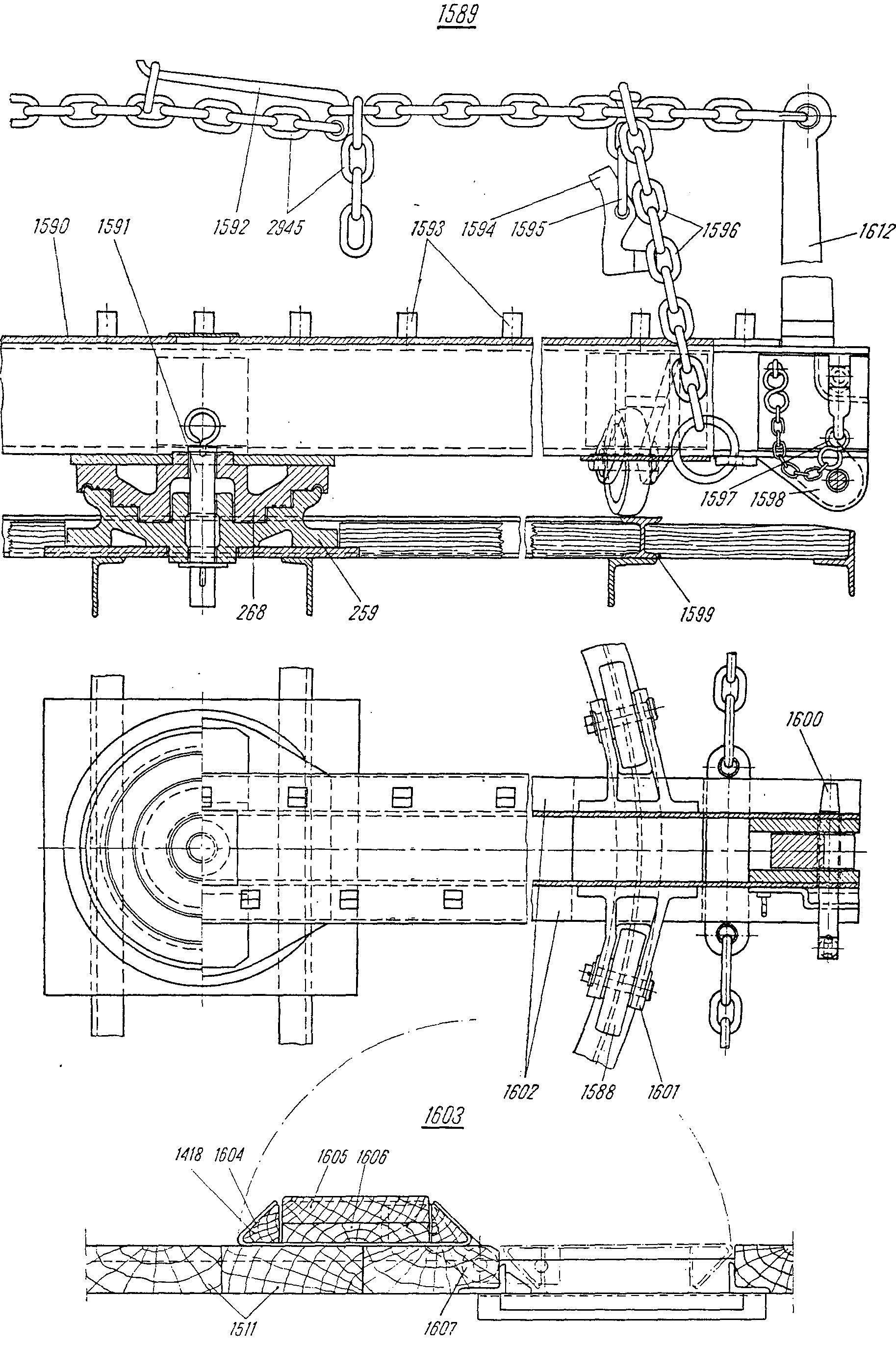
лист, коренной рессорный
—FRA lame f maîtresse de ressortITA foglia f maestra di - molla a balestraRUS лист m, коренной рессорныйсм. поз. 233 на
лист, кровельный
—FRA tôle f de toitureDEU Dachblech nITA lamiera f dell'imperialePLN blacha f poszyciowa dachuRUS лист m, кровельныйсм. поз. 862 на ,
, 
лист, несущий
—FRA tôle-support fDEU Tragblech nENG stiffening plateITA lamiera f di supportoPLN blachownica fRUS лист m, несущийсм. поз. 364 на
лист, опорный
—FRA plaque f d’assemblageDEU Verbindungsplatte fENG bearing plateITA piastra f di collegamentoPLN płyta f górnaRUS лист m, опорныйсм. поз. 1590 на
лист, предохранительный
—FRA tôle f pare-étincellesDEU Schutzblech nENG spark arresterITA lamiera f parascintillePLN blacha f ochronnaRUS лист m, предохранительныйсм. поз. 354 на
-
10 ток
current
движение элеронов по проводнику. измеряется в амперах и обозначается буквой i. — the movement of electrons through а conductor. measured in amperes,and ist symbol is i.
- (нагрузка) — load
- автостабилизации — autostabilization current
-, большой — high current
-, вихревой — eddy current(s)
also called foucault currents, inducted in body.
- включения (реле) — (relay) pickup current
- выключения (реле) — (relay) dropout /tripping/ current
- высокого напряжения (в оборудовании) — high-voltage current
- высокого напряжения (в системе зажигания) — high-tension (нт) current
- высокой частоты — high-frequency (hf) current
- датчиха момента акселерометра — torque current. a torque current being а measure of the restoring torque.
-, двухфазный — two-phase current
-, зарядный (аккумулятора) — (battery) charge current
monitor dc ammeter for normal charge current on battery.
-, малый (слабый) — low current
- нагрузки — load current
- нагрузки (разрядки) аккумулятора, элемента — (battery) drain. current supplied by a battery or cell.
-, обратный — reverse current
-, отпускания (реле) — dropout current
- отрыва (реле,прерывателя) — dropout current
-, переменный — alternating current (ас), (ac)
электрический ток, периодически изменяющийся по силе и направлению, т.е. достигающий макс. значения в одном направлении, затем падающий до нуля, и снова достигающий макс. значения, но в противоположном направлении. — а flow of electricity which reaches maximum in one direetion, decreases to zero, then reverses itself and reaches maximum in the opposite direction. the cycle is repeated continuously.
-, постоянный — direct current (do),(dc)
эл. ток, не изменяющийся ни по силе, ни по направлению. — an essentially constant-value current that flows in only one direction.
-, потребляемый — current drawn /consumed/
-, потребляемый (параметр в технических данных, таблице) — current, current requirements
-, потребляемый к-л. нагрузкой — current drawn /consumed, taken/ by а load
- потребляемый от источника питания — current drawn (consumed, taken from power source, power source drain
-, пусковой — starting current
-, рабочий — operating current
-, разрядный (акк.) — discharge current, drain
- расходуемый источником питания — power source drain
-, световой — light-inducted current
ток, возникающий в датчике под воздействием светового потока.
- срабатывания реле — relay operating current
- срабатывания реле (в отличие от тока отпускания) — relay pickup current
-, трехфазный — three-phase current
ток, поступающий по трем проводникам, каждый являющийся обратным проводом для двух других. — а current delivered through three wires - each wire serving as the return for the other two.
-, трогания — pickup current
ток, вызывающий срабатывание электромагнитных устройств. — the current at which a magnetically-operated device starts to operate.
- удержания (реле) — holding current
sufficient current in the relay winding to keep the relay energized.
- утечки — leakage current
-, электрический — electric current
магнитные поля, создаваемые электротоком. агрегат переменного (постаянного) тока (напр., генератор) — magnetic fields created by electric currents. ас (dc) unit, ас (dc) generator
измеритель тока (нагрузки) — loadmeter
под т. — energized
не отсоединять проводки, если цепь находится под током (напряжением) — do not disconnect wiring when the system is energized.
под током (напряжением) — alive
генератор под током, напряжением. — generator is alive.
включать т. — switch on current
при включении тока автостабилизации, якорь соленоида вызывает срабатывание клапана. — а solenoid, when the autostabilization current is switched on, pushes the central armature against a valve.
держать под т. — energize, keep energized
do not energize the solenoid for more than 10 sec.
работать на переменном (постоянном) т. — be ас (dc) powered
работать на переменном т. частотой... гц и напряжением...вольт — operate at а supply of... hz,... volts ас, be powered by... hz, volt ас
работать на постоянном т. напряжением... вольт — operate at а supply of... volts dc, be powered by... volt dcРусско-английский сборник авиационно-технических терминов > ток
-
11 Ferranti, Sebastian Ziani de
[br]b. 9 April 1864 Liverpool, Englandd. 13 January 1930 Zurich, Switzerland[br]English manufacturing engineer and inventor, a pioneer and early advocate of high-voltage alternating-current electric-power systems.[br]Ferranti, who had taken an interest in electrical and mechanical devices from an early age, was educated at St Augustine's College in Ramsgate and for a short time attended evening classes at University College, London. Rather than pursue an academic career, Ferranti, who had intense practical interests, found employment in 1881 with the Siemens Company (see Werner von Siemens) in their experimental department. There he had the opportunity to superintend the installation of electric-lighting plants in various parts of the country. Becoming acquainted with Alfred Thomson, an engineer, Ferranti entered into a short-lived partnership with him to manufacture the Ferranti alternator. This generator, with a unique zig-zag armature, had an efficiency exceeding that of all its rivals. Finding that Sir William Thomson had invented a similar machine, Ferranti formed a company with him to combine the inventions and produce the Ferranti- Thomson machine. For this the Hammond Electric Light and Power Company obtained the sole selling rights.In 1885 the Grosvenor Gallery Electricity Supply Corporation was having serious problems with its Gaulard and Gibbs series distribution system. Ferranti, when consulted, reviewed the design and recommended transformers connected across constant-potential mains. In the following year, at the age of 22, he was appointed Engineer to the company and introduced the pattern of electricity supply that was eventually adopted universally. Ambitious plans by Ferranti for London envisaged the location of a generating station of unprecedented size at Deptford, about eight miles (13 km) from the city, a departure from the previous practice of placing stations within the area to be supplied. For this venture the London Electricity Supply Corporation was formed. Ferranti's bold decision to bring the supply from Deptford at the hitherto unheard-of pressure of 10,000 volts required him to design suitable cables, transformers and generators. Ferranti planned generators with 10,000 hp (7,460 kW)engines, but these were abandoned at an advanced stage of construction. Financial difficulties were caused in part when a Board of Trade enquiry in 1889 reduced the area that the company was able to supply. In spite of this adverse situation the enterprise continued on a reduced scale. Leaving the London Electricity Supply Corporation in 1892, Ferranti again started his own business, manufacturing electrical plant. He conceived the use of wax-impregnated paper-insulated cables for high voltages, which formed a landmark in the history of cable development. This method of flexible-cable manufacture was used almost exclusively until synthetic materials became available. In 1892 Ferranti obtained a patent which set out the advantages to be gained by adopting sector-shaped conductors in multi-core cables. This was to be fundamental to the future design and development of such cables.A total of 176 patents were taken out by S.Z. de Ferranti. His varied and numerous inventions included a successful mercury-motor energy meter and improvements to textile-yarn produc-tion. A transmission-line phenomenon where the open-circuit voltage at the receiving end of a long line is greater than the sending voltage was named the Ferranti Effect after him.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsFRS 1927. President, Institution of Electrical Engineers 1910 and 1911. Institution of Electrical Engineers Faraday Medal 1924.Bibliography18 July 1882, British patent no. 3,419 (Ferranti's first alternator).13 December 1892, British patent no. 22,923 (shaped conductors of multi-core cables). 1929, "Electricity in the service of man", Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers 67: 125–30.Further ReadingG.Z.de Ferranti and R. Ince, 1934, The Life and Letters of Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti, London.A.Ridding, 1964, S.Z.de Ferranti. Pioneer of Electric Power, London: Science Museum and HMSO (a concise biography).R.H.Parsons, 1939, Early Days of the Power Station Industry, Cambridge, pp. 21–41.GWBiographical history of technology > Ferranti, Sebastian Ziani de
-
12 Stratingh, Sibrandus
SUBJECT AREA: Electricity[br]b. 9 April 1785 Adorp, The Netherlandsd. 15 February 1841 Groningen, The Netherlands[br]Dutch chemist and physician, maker of early electric motors.[br]Stratingh spent five years working for a relative who was a chemist in Groningen, and studied pharmacy under Professor Driessen. Encouraged to become a medical student, he qualified as a doctor of medicine in 1809. Later becoming a professor of chemistry at Groningen, he was honoured by a personal visit from the King to his laboratory in 1837. In 1835, assisted by Christopher Becker, an instrument maker, he built a table-top model of an electrically propelled vehicle. The motor, with wound armature and field coils, was geared to a wheel of a small carriage which also carried a single voltaic cell. A full-scale road vehicle was never built, but in 1840 he succeeded in making an electrically powered boat.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsCross of the Netherlands Lion 1831.Bibliography1841, De nagedachtenis van S.Stratingh Ez.gevierd in het Genootschap: ter bevordering der natuurkundige wetenschappen te Groningen, Groningen (a memorial volume that includes a list of his works).Further ReadingB.Bowers, 1982, A History of Electric Light and Power, London, p. 45 (provides a brief account of Stratingh's electric vehicle).GW -
13 Wilde, Henry
SUBJECT AREA: Electricity[br]b. 1833 Manchester, Englandd. 28 March 1919 Alderley Edge, Cheshire, England[br]English inventor and pioneer manufacturer of electrical generators.[br]After completing a mechanical engineering apprenticeship Wilde commenced in business as a telegraph and lightning conductor specialist in Lancashire. Several years spent on the design of an alphabetic telegraph resulted in a number of patents. In 1864 he secured a patent for an electromagnetic generator which gave alternating current from a shuttle-wound armature, the field being excited by a small direct-current magneto. Wilde's invention was described to the Royal Society by Faraday in March 1866. When demonstrated at the Paris Exhibition of 1867, Wilde's machine produced sufficient power to maintain an arc light. The small size of the generator provided a contrast to the large and heavy magnetoelectric machines also exhibited. He discovered, by experiment, that alternators in synchronism could be connected in parallel. At about the same time John Hopkinson arrived at the same conclusions on theoretical grounds.Between 1866 and 1877 he sold ninety-four machines with commutators for electroplating purposes, a number being purchased by Elkingtons of Birmingham. He also supplied generators for the first use of electric searchlights on battleships. In his early experiments Wilde was extremely close to the discovery of true self-excitation from remnant magnetism, a principle which he was to discover in 1867 on machines intended for electroplating. His patents proved to be financially successful and he retired from business in 1884. During the remaining thirty-five years of his life he published many scientific papers, turning from experimental work to philosophical and, finally, theological matters. His record as an inventor established him as a pioneer of electrical engineering, but his lack of scientific training was to restrict his later contributions.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsFRS 1886.Bibliography1 December 1863, British patent no. 3,006 (alternator with a magneto-exciter).1866, Proceedings of the Royal Society 14:107–11 (first report on Wilde's experiments). 1900, autobiographical note, Journal of the Institution of Electrical Engineers 29:3–17.Further ReadingW.W.Haldane Gee. 1920, biography, Memoirs, Manchester Literary and Philosophical Society 63:1–16 (a comprehensive account).P.Dunsheath, 1962, A History of Electrical Engineering, London: Faber \& Faber, pp. 110–12 (a short account).GW -
14 арматура
-
15 неполяризованный
Русско-английский словарь по информационным технологиям > неполяризованный
См. также в других словарях:
History of electromagnetism — The history of electromagnetism, that is the human understanding and recorded use of electromagnetic forces, dates back over two thousand years ago, see Timeline of electromagnetism. The ancients must have been acquainted with the effects of… … Wikipedia
List of Tesla patents — Below is a list of Tesla patents. Dr. Nikola Tesla was an inventor who obtained around 300 patents [Snezana Sarbo, [http://www.tesla symp06.org/papers/Tesla Symp06 Sarboh.pdfNikola Tesla s Patents] , Sixth International Symposium Nikola Tesla,… … Wikipedia
sculpture — sculptural, adj. sculpturally, adv. /skulp cheuhr/, n., v., sculptured, sculpturing. n. 1. the art of carving, modeling, welding, or otherwise producing figurative or abstract works of art in three dimensions, as in relief, intaglio, or in the… … Universalium
Statue of Liberty — For other uses, see Statue of Liberty (disambiguation). Statue of Liberty Locat … Wikipedia
Headphones — For other uses, see Headphones (disambiguation). Sennheiser HD555 headphones, used in audio production environments … Wikipedia
Electric motor — For other kinds of motors, see motor (disambiguation). For a railroad electric engine, see electric locomotive. Various electric motors. A 9 volt PP3 transistor battery is in the center foreground for size comparison. An electric motor converts… … Wikipedia
electromagnetism — /i lek troh mag ni tiz euhm/, n. 1. the phenomena associated with electric and magnetic fields and their interactions with each other and with electric charges and currents. 2. Also, electromagnetics. the science that deals with these phenomena.… … Universalium
Magnetic lock — A magnetic lock is a simple locking device that consists of an electromagnet and armature plate. By attaching the electromagnet to the door frame and the armature plate to the door, a current passing through the electromagnet attracts the… … Wikipedia
Lurie Garden — Infobox park park = Lurie Garden image size = 250px caption = Historic Michigan Boulevard District and Randolph Street streetwalls from Lurie Garden type = Public Garden location = Millennium Park city state|Chicago|Illinois coordinates =… … Wikipedia
Alternator — s are called turbo alternators.HistoryAlternating current generating systems were known in simple forms from the discovery of the magnetic induction of electric current. The early machines were developed by pioneers such as Michael Faraday and… … Wikipedia
Brushed DC electric motor — A brushed DC motor is an internally commutated electric motor designed to be run from a direct current power source. Contents 1 Simple two pole DC motor 2 The commutating plane 2.1 Compensation for stator field distortion … Wikipedia
