-
21 line
1) линия; кривая2) линия, производственная линия; участок3) серия, гамма (напр. станков)4) строка; кадр УП ( станка с ЧПУ)5) магистраль; трубопровод; канал6) облицовка; футеровка || облицовывать; футеровать7) устанавливать соосно; выставлять по одной линии•- adaptive manufacturing lineline per minute — строк в минуту, число строк в минуту (единица скорости работы, напр. печатающего устройства)
- addendum line
- adiabatic line
- air line
- arithmetical mean line of the profile
- assembling line
- assembly line
- asynchronized line
- automated grinding line
- automated line
- automated machine assembly line
- automatic rotary line
- base line
- basic line
- belt pitch line
- block and head line
- blurred line
- boring line
- branch line
- broach line
- broaching line
- broken line
- build line
- calibration line
- carousel buffer line
- catenary line
- center line of blade profile
- center line of fluid flow
- center line of mass
- center line of root
- center line of rotation
- center line of spindle
- center line
- central reference line
- checked line
- CNC cell line
- CNC transfer line
- code line
- coding line
- coil line
- coiled line
- command line
- concurrent lines
- constant-pressure line
- construction lines
- contact line
- continuous line of shafting
- continuous line
- control line
- conveyor line
- conveyorized line
- coolant line
- cooling lines
- crane clearance line
- curve line
- curved line
- cutting plane line
- dash line
- dash-and-dot line
- datum line
- dedendum line
- dedicated line
- delay line
- delivery line
- desired line of cut
- die line
- digital line
- dimension line
- discharge line
- DNC line
- dot-and-dash line
- dotted line
- double-belt assembly line
- drain line
- drilling line
- driven-roller line
- earthed line
- echo line
- effective line of action
- elastic line
- equiclearance contour line
- exhaust line
- extension line
- extraheavy line
- face line of tooth
- faint grid lines
- feed line
- final assembly line
- finish line
- flank line
- flexible flow line
- flexible transfer line
- flow line
- FMS line
- free-form line
- fuel line
- full line
- generating line
- generator line
- ghost lines
- graduation line
- grinding line
- grounded line
- guide line
- hair line
- hard automation line
- heavy line
- helical line
- helix line
- hidden line
- high-volume laser production line
- housing line
- hydraulic line
- hyperboloid generating line
- in line with
- index line
- indexing line
- influence line
- initial straight line of reference
- inlet line
- instantaneous line of contact
- instruction main line
- intake line
- intermediate language line
- isobaric line
- isochoric line
- isomancost line
- isothermal line
- junction line
- killed line
- knuckle line
- large prismatic machining line
- layout line
- lead line
- leader line
- less robotized line
- level line
- line of action
- line of contact
- line of debris
- line of engagement
- line of fluid flow
- line of machines
- line of profile peaks
- line of profile valleys
- line of slide
- lines of NC code
- live line
- load line
- local line
- lubrication line
- machine-tool product line
- machining center line
- machining center-based line
- machining line
- manufacturing line
- margin line
- match line
- mean line
- metalforming machines line
- metalforming machines transfer line
- milling line
- mismatch contour line
- mixed line
- multiple lines of reasoning
- multiple product line
- multiproduct flow line
- multirobot machining line
- multistation line
- Nagare line
- nonsynchronous transfer line
- numerically controlled line of machines
- oil line
- outlet line
- output limit line
- overlapped scan lines
- paced assembly line
- paint line
- pallet line
- pallet table line
- pallet transfer line
- pallet transporter line
- palletized transfer line
- parameter line
- part manual line
- parting line
- perpendicular line
- phantom line
- pilot line
- piston manufacturing line
- pitch line
- plumb line
- power line
- pre-filled line
- press line
- pressure line
- pressure lubrication line
- pressure purge line
- pressure relief line
- primary contact line
- prismatic machining line
- prismatic parts FMS line
- product line
- production line
- pump line
- pumping line
- purge line
- quasi-synchronous line
- recirculated line
- reference line
- reference rack pitch line
- representative line
- return lubrication line
- robot welding line
- robotized line
- robot-manned line
- root line
- rotary transfer line
- rotational parts FMS line
- rotational parts line
- sampling line
- sawing line
- scale line
- scanning lines
- scavenging line
- screw line
- scribe line
- scribed line
- secondary contact line
- secondary pumping line
- semiautomated line
- sequential production line
- service line
- shaft line
- shear line
- shearing line
- sheet line
- side line
- signal main line
- simulated production line
- single-component transfer line
- skew lines
- sky line
- slanting line
- slide line
- small prismatic machining line
- solid line
- special boring line
- spiral line
- split lines
- spot-welding line
- steel fabrication line
- straight line
- suction line
- suction lubrication line
- superimposed line
- supply line
- synchronized line
- synchronized transfer line
- synchronous line
- synchronous transfer line
- tank return line
- tape line
- thin line
- tip line
- to line out
- to line up
- tooth bearing contour line
- tooth center line
- top line
- tow line
- transfer line
- transfer machining line
- transmission line
- transporter line
- transverse line of action
- trunk line
- turning line
- unbalanced production line
- unit line
- utility line
- vacuum line
- vehicle conveyor line
- vortex line
- walking-beam transfer line
- way-type line
- wear distribution line
- weld line
- welding assembly line
- working hydraulic line
- working line
- zero lineEnglish-Russian dictionary of mechanical engineering and automation > line
-
22 service
[̈ɪˈsə:vɪs]account solicitation service бюро рассмотрения ходатайств о предоставлении кредитов advisory service консультативная служба (например, по вопросам трудоустройства, профессиональной ориентации и т. д.) aftersales service послепродажное обслуживание ambulance service служба "Скорой помощи"; "Скорая помощь" as a service в качестве услуги service услуга, одолжение; at your service к вашим услугам; to be of service быть полезным auxiliary service вспомогательная служба, дополнительная (побочная) служба bank transfer service банковские переводы bathing service банная служба service услуга, одолжение; at your service к вашим услугам; to be of service быть полезным bus service автобусное сообщение car hire service служба проката автомобилей care attendant services услуги по уходу за больными central care service центральная служба по уходу civic service служба общественных работ; участие (безработных) в общественных работах и в общественных службах civil alternative service альтернативная воинская служба на объектах общественного характер cleaning service служба по очистке территорий и удалению мусора client service обслуживание клиентов client service обслуживание клиентуры combined service смешанные перевозки community service государственная служба community service общинная служба community service социальное обеспечение complimentary limousine service бесплатное обслуживание автомобильным транспортом compulsory military service воинская повинность; обязательная воинская служба в течение установленного законом срока consultative service консультативная служба consumer service обслуживание потребителей courier service услуги курьера customer service вчт. обслуживание клиентов customer service обслуживание покупателя customer service предоставление услуг покупателю datel service вчт. система передачи по телефону кодированой информации dealing service обслуживание биржевых операций delayed service вчт. обслуживание с ожиданием diffusion service служба распространения direct debiting service банковские услуги по оформлению безналичных платежей divine service богослужение drop-in service служба помощи без предварительной записи (оказывает помощь алкоголикам, наркоманам, бездомным) educational service служба обучения (воспитания, переподготовки, переквалификации) elapsed service вчт. обслуживание выполненное до прерывания emergency call service телефонная служба скорой помощи employment service служба занятости employment service служба занятости; служба трудоустройства employment service служба по трудоустройству employment service служба трудоустройства environmental service экологическая служба escort service служба сопровождения; караульная служба exempt from military service освобожденный от военной службы extention service служба распространения знаний farm relief service служба содействия фермерским хозяйствам ferry service паромное сообщение ferry service служба морских перевозок financial service финансовая консультационная фирма financial service финансовое обслуживание free service бесплатная услуга freight service грузовые перевозки freight service предоставление транспортных услуг friendly visiting services бесплатные услуги на дому (оказываемые благотворительными организациями или отдельными лицами) goods service доставка товаров government service государственная служба gratuitions service бесплатная служба home-help service служба помощи по дому hourly service транс. почасовое обслуживание 24 hours social services круглосуточные социальные службы housing service жилищная служба information service вчт. информационная служба information service служба информации interpreter service служба перевода; служба переводчиков investment management service служба управления портфелем ценных бумаг investment service обслуживание инвестирования joint service совместное обслуживание limousine service прокат автомобиля с водителем line service рейсовое плавание mail service почтовая связь maximum debt service максимальная сумма процентов по долгу minimum debt service минимальное обслуживание долга municipal health service муниципальная служба здравоохранения national health service государственная служба здравоохранения news service служба новостей night service ночная служба non-military service невоенная служба, альтернативная гражданская служба non-military service невоенная служба nonpreemptive service вчт. обслуживание без прерывания nonpreferential service вчт. обслуживание без приоритета order booking service приказ об обслуживании ordered service вчт. обслуживание в порядке поступления ordinary service обычная услуга ordinary service обычное обслуживание out-patient service амбулаторное обслуживание outside service обслуживание силами посторонней организации parcel bulk service перевозка мелкой партии бестарного груза personal service личное вручение судебного приказа pharmaceutical service фармацевтмческая служба; фармацевтическое ослуживание phase service вчт. многофазное обслуживание phase-type service вчт. многофазное обслуживание placement service биржа труда placement service бюро трудоустройства placement service служба занятости police service полицейская служба postal service почтовая связь postal service почтовая служба preemptive service вчт. обслуживание с прерыванием premium service услуга, предоставляемая за дополнительную плату priority service вчт. обслуживание с приоритетом probationary service служба, исполняющая приговор о направлении на "испытание" property service услуги по управлению имуществом provide a service обеспечивать обслуживание provide a service оказывать услугу public employment service государственная служба занятости purchased service оплаченная услуга put into service вводить в эксплуатацию put into service включать в работу quantum service вчт. обслуживание порциями referral service справочная служба regular service регулярное сообщение regular service регулярные рейсы salvage service услуги по спасанию service церк. служба; to say a service отправлять богослужение security service служба безопасности selection for service выбор на обслуживание self-drive car-hire service прокат легкового автомобиля без водителя service attr. служебный; service record послужной список service by letter судебное извещение путем направления письма service by post судебное извещение по почте service in batches вчт. групповое обслуживание service in bulk групповое обслуживание service in cyclic order обслуживание в циклическом порядке service in random order обслуживание в случайном порядке service loss coefficient коэффициент простоя вследствие обслуживания service of court notice to pay debt вручение уведомления суда об уплате долга service of notice вручение извещения service of process повестка service of process процессуальное извещение, повестка service of process процессуальное извещение service of public lands эксплуатация государственных земель service of summons извещение, повестка о вызове в суд service on loan погашение долга service on loan уплата долга service attr. служебный; service record послужной список service time expectation математическое ожидание времени обслуживания service with privileged interruptions вчт. обслуживание с прерыванием service with waiting вчт. обслуживание с ожиданием service without interruption вчт. обслуживание без прерывания service = service-tree service-tree: service-tree бот. рябина домашняя service воен. род войск; the (fighting) services армия, флот и военная авиация services: services обслуживающие отрасли экономики service сфера услуг service услуги shuttle service движение туда и обратно (поездов, автобусов и т. п.), маятниковое движение single service вчт. обслуживание одиночных требований sitting service служба по присмотру за детьми на время отсутствия дома родителей social service социальная служба; социальное обслуживание social service социальная услуга social services социальные службы (например, службы здравоохранения, профилактики заболеванй и предотвращения несчастных случаев) services: social service общественные учреждения social service социальные услуги substituted service субститут личного вручения судебного приказа service служба; to take into one's service нанимать; to take service (with smb.) поступать на службу (к кому-л.) service служба; to take into one's service нанимать; to take service (with smb.) поступать на службу (к кому-л.) training service служба профподготовки transport service транспортная линия transport service транспортное обслуживание unarmed service альтернативная служба (вместо военной) useful service вчт. срок полезного использования videotex service служба видеотексной связи voluntary service добровольная служба, добровольное оказание услуг warranty service вчт. гарантийная наработка welfare service служба социального обеспечения -
23 line conductor
линейный проводник
Проводник, находящийся под напряжением в нормальном режиме работы электроустановки, используемый для передачи и распределения электрической энергии, но не являющийся нулевым рабочим проводником или средним проводником.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
линейный проводник (L)
Проводник, находящийся под напряжением при нормальном оперировании и используемый для передачи и распределения электрической энергии, но не нейтральный проводник или средний проводник.
В электрических цепях переменного тока линейные проводники используют совместно с нейтральными проводниками и PEN-проводниками, а в электрических цепях постоянного тока – совместно со средними проводниками и PEM-проводниками для обеспечения электроэнергией электрооборудования переменного и постоянного тока, применяемого в электроустановках зданий. Линейные проводники относят к токоведущим частям. В нормальном режиме электроустановки здания они, как правило, находятся под напряжением, которое может представлять серьёзную опасность для человека и животных.
В электроустановках зданий напряжение линейного проводника относительно нейтрального проводника, PEN-проводника и земли обычно равно 230 В. Напряжение между линейными проводниками разных фаз в трёхфазных электрических цепях равно 400 В.
В трёхпроводных электрических цепях постоянного тока напряжение линейного проводника относительно среднего проводника, PEM-проводника и земли обычно равно 220 В, а напряжение между линейными проводниками разных полюсов равно 440 В. В двухпроводных электрических цепях постоянного тока напряжение между линейными проводниками обычно равно 220 В.
Линейные проводники, применяемые в электрических цепях сверхнизкого напряжения, обычно не представляют опасности для человека и животных.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CB/view/29/]EN
line conductor
conductor which is energized in normal operation and capable of contributing to the transmission or distribution of electric energy but which is not a neutral or mid-point conductor
Source: 601-03-09 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-08]FR
conducteur de ligne
conducteur sous tension en service normal et capable de participer au transport ou à la distribution de l'énergie électrique, mais qui n'est ni un conducteur de neutre ni un conducteur de point milieu
Source: 601-03-09 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-08]
L1, L2, L3 - линейные проводники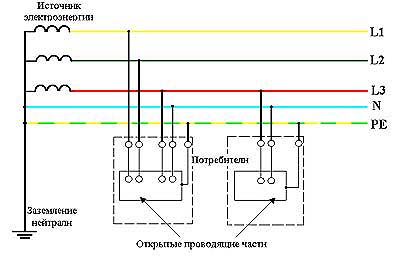
[http://bgd.alpud.ru/images/tn_s.htm]
N - нулевой рабочий проводник
PE - защитный проводникНедопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- line conductor
- line wire
- phase conductor (in AC systems) (deprecated)
- pole conductor (in DC systems) (deprecated)
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > line conductor
-
24 line wire
линейный проводник
Проводник, находящийся под напряжением в нормальном режиме работы электроустановки, используемый для передачи и распределения электрической энергии, но не являющийся нулевым рабочим проводником или средним проводником.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
линейный проводник (L)
Проводник, находящийся под напряжением при нормальном оперировании и используемый для передачи и распределения электрической энергии, но не нейтральный проводник или средний проводник.
В электрических цепях переменного тока линейные проводники используют совместно с нейтральными проводниками и PEN-проводниками, а в электрических цепях постоянного тока – совместно со средними проводниками и PEM-проводниками для обеспечения электроэнергией электрооборудования переменного и постоянного тока, применяемого в электроустановках зданий. Линейные проводники относят к токоведущим частям. В нормальном режиме электроустановки здания они, как правило, находятся под напряжением, которое может представлять серьёзную опасность для человека и животных.
В электроустановках зданий напряжение линейного проводника относительно нейтрального проводника, PEN-проводника и земли обычно равно 230 В. Напряжение между линейными проводниками разных фаз в трёхфазных электрических цепях равно 400 В.
В трёхпроводных электрических цепях постоянного тока напряжение линейного проводника относительно среднего проводника, PEM-проводника и земли обычно равно 220 В, а напряжение между линейными проводниками разных полюсов равно 440 В. В двухпроводных электрических цепях постоянного тока напряжение между линейными проводниками обычно равно 220 В.
Линейные проводники, применяемые в электрических цепях сверхнизкого напряжения, обычно не представляют опасности для человека и животных.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%CB/view/29/]EN
line conductor
conductor which is energized in normal operation and capable of contributing to the transmission or distribution of electric energy but which is not a neutral or mid-point conductor
Source: 601-03-09 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-08]FR
conducteur de ligne
conducteur sous tension en service normal et capable de participer au transport ou à la distribution de l'énergie électrique, mais qui n'est ni un conducteur de neutre ni un conducteur de point milieu
Source: 601-03-09 MOD
[IEV number 195-02-08]
L1, L2, L3 - линейные проводники
[http://bgd.alpud.ru/images/tn_s.htm]
N - нулевой рабочий проводник
PE - защитный проводникНедопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- line conductor
- line wire
- phase conductor (in AC systems) (deprecated)
- pole conductor (in DC systems) (deprecated)
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > line wire
-
25 service road
1. подъездная дорога2. временная дорога -
26 The Value Line OTC Special Situation Service
Биржевой термин: Уровень цен ОТС службы особых положений (издание)Универсальный англо-русский словарь > The Value Line OTC Special Situation Service
-
27 public broadcasting service
1) СМИ., гос. упр. общественное вещание (вещание некоммерческих СМИ на средства, собранные со слушателей и телезрителей)2) СМИ, гос. упр. = !"может быть, просто ""public broadcasting"", а не ""public broadcasting service""?"!"The Public Broadcasting Service ( PBS) is a non-profit public broadcasting television service with 354 member TV stations in the United States, with some member stations available over the air and by cable in Canada. While the term ""broadcasting"" encompasses both radio and television, PBS only covers TV; public radio in the United States is served by National Public Radio, as well as content providers American Public Media, and Public Radio International."PBS was founded on November 3, 1969,[1\] at which time it took over many of the functions of its predecessor, National Educational Television (NET) (which merged with station WNDT Newark, New Jersey to form WNET). It commenced broadcasting on Monday, October 5, 1970. In 1973, it merged with Educational Television Stations.PBS is a non-profit, private corporation which is owned collectively by its member stations.[2\] However, its operations are largely funded by the Corporation for Public Broadcasting. Its headquarters are in Arlington, Virginia.Unlike the commercial television broadcast model of American networks such as ABC, CBS, FOX, NBC, The CW and MyNetworkTV, in which affiliates give up portions of their local advertising airtime in exchange for network programming, PBS member stations pay substantial fees for the shows acquired and distributed by the national organization."This relationship means that PBS member stations have greater latitude in local scheduling than their commercial counterparts. Scheduling of PBS-distributed series may vary greatly from market to market. This can be a source of tension as stations seek to preserve their localism and PBS strives to market a consistent national line-up. However, PBS has a policy of ""common carriage"" requiring most stations to clear the national prime time programs on a common schedule, so that they can be more effectively marketed on a national basis. This setup is in many ways similar to the pre-2002 British ITV system of having some ""networked"" programs shown nationwide on all network contractors, and the remainder of scheduling being up to individual affiliates." "Unlike its radio counterpart, National Public Radio, PBS has no central program production arm or news department. All of the programming carried by PBS, whether news, documentary, or entertainment, is created by (or in most cases produced under contract with) other parties, such as individual member stations. WGBH in Boston is one of the largest producers of educational programming. News programs are produced by WETA-TV in Washington, D.C., WNET in New York and WPBT in Miami. The Charlie Rose interview show, Secrets of the Dead, NOW, Nature, Cyberchase, and The NewsHour with Jim Lehrer come from or through WNET in New York. Once a program is offered to and accepted by PBS for distribution, PBS (and not the member station that supplied the program) retains exclusive rights for rebroadcasts during the period for which such rights were granted; the suppliers do maintain the right to sell the program in non-broadcast media such as DVDs, books, and sometimes PBS licensed merchandise (but sometimes grant such ancillary rights as well to PBS)." "PBS stations are commonly operated by non-profit organizations, state agencies, local authorities (e.g., municipal boards of education), or universities in their community of license. In some states, PBS stations throughout the entire state may be organized into a single regional ""subnetwork"" (e.g., Alabama Public Television). Unlike Canada's CBC/SRC, PBS does not own any of the stations that broadcast its programming. This is partly due to the origins of the PBS stations themselves, and partly due to historical license issues."In the modern broadcast marketplace, this organizational structure is considered outmoded by some media critics. A common restructuring proposal is to reorganize the network so that each state would have one PBS affiliate which would broadcast state-wide. However, this proposal is controversial, as it would reduce local community input into PBS programming, especially considering how PBS stations are significantly more community-oriented, according to the argument, than their commercial counterparts.* * *Англо-русский экономический словарь > public broadcasting service
-
28 trunk-line service
1. магистральное движение2. междугородная связь -
29 main-line service
English-Russian big polytechnic dictionary > main-line service
-
30 freight service
English-Russian big polytechnic dictionary > freight service
-
31 second-line support
вторая линия поддержки
(ITIL Service Operation)
Второй уровень в иерархии групп поддержки, вовлеченных в разрешение инцидентов и исследование проблем. На каждом следующем уровне специалисты обладают большим опытом, либо им предоставляется больше времени или других ресурсов.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]EN
second-line support
(ITIL Service Operation)
The second level in a hierarchy of support groups involved in the resolution of incidents and investigation of problems. Each level contains more specialist skills, or has more time or other resources.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > second-line support
-
32 first line support
первая линия поддержки
(ITIL Service Operation)
Первый уровень в иерархии групп поддержки, вовлеченных в разрешение инцидентов. Каждый последующий уровень включает в себя более высокую квалификацию специалистов, либо большее количество времени или прочих ресурсов.
См. тж. эскалация.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]EN
first-line support
(ITIL Service Operation)
The first level in a hierarchy of support groups involved in the resolution of incidents. Each level contains more specialist skills, or has more time or other resources.
See also escalation.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > first line support
-
33 third-line support
третья линия поддержки
(ITIL Service Operation)
Третий уровень в иерархии групп поддержки, вовлеченных в разрешение инцидентов и исследование проблем. На каждом следующем уровне специалисты обладают большим опытом, либо им предоставляется больше времени или других ресурсов.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]EN
third-line support
(ITIL Service Operation)
The third level in a hierarchy of support groups involved in the resolution of incidents and investigation of problems. Each level contains more specialist skills, or has more time or other resources.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > third-line support
-
34 AC line
фазный проводник
L
Линейный проводник, используемый в электрической цепи переменного тока.
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]
фазный проводник
L
Линейный проводник, используемый в электрической цепи переменного тока.
Термин «фазный проводник» признан недопустимым Международным электротехническим словарем (МЭС). Вместо него МЭС предписывает применять термин «линейный проводник». Однако рассматриваемый термин целесообразно использовать в национальной нормативной и правовой документации.
Фазный проводник представляет собой частный случай линейного проводника, применяемого в электрической цепи переменного тока. Фазные проводники совместно с нейтральными проводниками и PEN-проводниками используют в электроустановках зданий для обеспечения электроэнергией применяемого в них электрооборудования переменного тока.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%D4/view/87/]EN
line conductor
phase conductor (in AC systems) (deprecated)
pole conductor (in DC systems) (deprecated)
conductor which is energized in normal operation and capable of contributing to the transmission or distribution of electric energy but which is not a neutral or mid-point conductor
[IEV number 195-02-08]FR
conducteur de ligne
conducteur de phase (déconseillé)
conducteur sous tension en service normal et capable de participer au transport ou à la distribution de l'énergie électrique, mais qui n'est ni un conducteur de neutre ni un conducteur de point milieu
[IEV number 195-02-08]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Ensure in the installation that the Neutral will never be disconnected before the supplying AC lines.
[Delta Energy Systems]Электроустановка должна быть устроена таким образом, чтобы отключение нулевого рабочего проводника происходило только после того, как будут отключены фазные проводники.
[Перевод Интент]If the phase currents are connected correctly...
[Schneider Electric]Если фазные проводники подключены правильно...
[Перевод Интент]Phases must at least be marked L1, L2, L3, at the end and at connection points.
[Schneider Electric]Фазные проводники должны иметь маркировку L1, L2, L3 по крайней мере на концах и в точках присоединения.
[Перевод Интент]6.6.28. В трех- или двухпроводных однофазных линиях сетей с заземленной нейтралью могут использоваться однополюсные выключатели, которые должны устанавливаться в цепи фазного провода, или двухполюсные, при этом должна исключаться возможность отключения одного нулевого рабочего проводника без отключения фазного.
[ПУЭ]
ОПН (или РВ) на ВЛИ должны быть присоединены к фазному проводу посредством прокалывающих зажимов
[Методические указания по защите распределительных электрических сетей]
2.4.19. На опорах допускается любое расположение фазных проводов независимо от района климатических условий. Нулевой провод, как правило, следует располагать ниже фазных проводов. Провода наружного освещения, прокладываемые на опорах совместно с проводами ВЛ, должны располагаться, как правило, над нулевым проводом.
[ПУЭ]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
- электроустановки
Синонимы
EN
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > AC line
-
35 supplying AC line
фазный проводник
L
Линейный проводник, используемый в электрической цепи переменного тока.
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]
фазный проводник
L
Линейный проводник, используемый в электрической цепи переменного тока.
Термин «фазный проводник» признан недопустимым Международным электротехническим словарем (МЭС). Вместо него МЭС предписывает применять термин «линейный проводник». Однако рассматриваемый термин целесообразно использовать в национальной нормативной и правовой документации.
Фазный проводник представляет собой частный случай линейного проводника, применяемого в электрической цепи переменного тока. Фазные проводники совместно с нейтральными проводниками и PEN-проводниками используют в электроустановках зданий для обеспечения электроэнергией применяемого в них электрооборудования переменного тока.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%D4/view/87/]EN
line conductor
phase conductor (in AC systems) (deprecated)
pole conductor (in DC systems) (deprecated)
conductor which is energized in normal operation and capable of contributing to the transmission or distribution of electric energy but which is not a neutral or mid-point conductor
[IEV number 195-02-08]FR
conducteur de ligne
conducteur de phase (déconseillé)
conducteur sous tension en service normal et capable de participer au transport ou à la distribution de l'énergie électrique, mais qui n'est ni un conducteur de neutre ni un conducteur de point milieu
[IEV number 195-02-08]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Ensure in the installation that the Neutral will never be disconnected before the supplying AC lines.
[Delta Energy Systems]Электроустановка должна быть устроена таким образом, чтобы отключение нулевого рабочего проводника происходило только после того, как будут отключены фазные проводники.
[Перевод Интент]If the phase currents are connected correctly...
[Schneider Electric]Если фазные проводники подключены правильно...
[Перевод Интент]Phases must at least be marked L1, L2, L3, at the end and at connection points.
[Schneider Electric]Фазные проводники должны иметь маркировку L1, L2, L3 по крайней мере на концах и в точках присоединения.
[Перевод Интент]6.6.28. В трех- или двухпроводных однофазных линиях сетей с заземленной нейтралью могут использоваться однополюсные выключатели, которые должны устанавливаться в цепи фазного провода, или двухполюсные, при этом должна исключаться возможность отключения одного нулевого рабочего проводника без отключения фазного.
[ПУЭ]
ОПН (или РВ) на ВЛИ должны быть присоединены к фазному проводу посредством прокалывающих зажимов
[Методические указания по защите распределительных электрических сетей]
2.4.19. На опорах допускается любое расположение фазных проводов независимо от района климатических условий. Нулевой провод, как правило, следует располагать ниже фазных проводов. Провода наружного освещения, прокладываемые на опорах совместно с проводами ВЛ, должны располагаться, как правило, над нулевым проводом.
[ПУЭ]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
- электроустановки
Синонимы
EN
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > supplying AC line
-
36 special service
1. воен. служба специального назначения; десантно-диверсионные части «командос»2. воен. амер. служба организации досуга войск3. воен. амер. нестроевая служба -
37 engineer service
-
38 front-line
прил.марк. работающий с клиентами, обслуживающий клиентов (о работнике, подразделении или процессе, которые связаны с обслуживанием клиентов и)front-line employees — персонал, работающий с клиентами
We will provide our front-line sales team with the absolute best in compensation. — Наши менеджеры по продажам, работающие с клиентами, получают самое высокое вознаграждение.
Front-line functions (including sales, installation, customer service, technical support) are each managed separately and optimized locally, and are therefore disjointed and not integrated.
-
39 dial-up line
обычная коммутируемая телефонная линия, используемая для подключения к Internet."Netcom had local dial-up lines in 51 cities around the country" (Т. Shimomura). — У Netcom было множество локальных коммутируемых линий в 51 городе по всей стране.
Syn:Ant:Англо-русский толковый словарь терминов и сокращений по ВТ, Интернету и программированию. > dial-up line
-
40 near cash
!гос. фин. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.This paper provides background information on the framework for the planning and control of public expenditure in the UK which has been operated since the 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR). It sets out the different classifications of spending for budgeting purposes and why these distinctions have been adopted. It discusses how the public expenditure framework is designed to ensure both sound public finances and an outcome-focused approach to public expenditure.The UK's public spending framework is based on several key principles:"consistency with a long-term, prudent and transparent regime for managing the public finances as a whole;" "the judgement of success by policy outcomes rather than resource inputs;" "strong incentives for departments and their partners in service delivery to plan over several years and plan together where appropriate so as to deliver better public services with greater cost effectiveness; and"the proper costing and management of capital assets to provide the right incentives for public investment.The Government sets policy to meet two firm fiscal rules:"the Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending; and"the Sustainable Investment Rule states that net public debt as a proportion of GDP will be held over the economic cycle at a stable and prudent level. Other things being equal, net debt will be maintained below 40 per cent of GDP over the economic cycle.Achievement of the fiscal rules is assessed by reference to the national accounts, which are produced by the Office for National Statistics, acting as an independent agency. The Government sets its spending envelope to comply with these fiscal rules.Departmental Expenditure Limits ( DEL) and Annually Managed Expenditure (AME)"Departmental Expenditure Limit ( DEL) spending, which is planned and controlled on a three year basis in Spending Reviews; and"Annually Managed Expenditure ( AME), which is expenditure which cannot reasonably be subject to firm, multi-year limits in the same way as DEL. AME includes social security benefits, local authority self-financed expenditure, debt interest, and payments to EU institutions.More information about DEL and AME is set out below.In Spending Reviews, firm DEL plans are set for departments for three years. To ensure consistency with the Government's fiscal rules departments are set separate resource (current) and capital budgets. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.To encourage departments to plan over the medium term departments may carry forward unspent DEL provision from one year into the next and, subject to the normal tests for tautness and realism of plans, may be drawn down in future years. This end-year flexibility also removes any incentive for departments to use up their provision as the year end approaches with less regard to value for money. For the full benefits of this flexibility and of three year plans to feed through into improved public service delivery, end-year flexibility and three year budgets should be cascaded from departments to executive agencies and other budget holders.Three year budgets and end-year flexibility give those managing public services the stability to plan their operations on a sensible time scale. Further, the system means that departments cannot seek to bid up funds each year (before 1997, three year plans were set and reviewed in annual Public Expenditure Surveys). So the credibility of medium-term plans has been enhanced at both central and departmental level.Departments have certainty over the budgetary allocation over the medium term and these multi-year DEL plans are strictly enforced. Departments are expected to prioritise competing pressures and fund these within their overall annual limits, as set in Spending Reviews. So the DEL system provides a strong incentive to control costs and maximise value for money.There is a small centrally held DEL Reserve. Support from the Reserve is available only for genuinely unforeseeable contingencies which departments cannot be expected to manage within their DEL.AME typically consists of programmes which are large, volatile and demand-led, and which therefore cannot reasonably be subject to firm multi-year limits. The biggest single element is social security spending. Other items include tax credits, Local Authority Self Financed Expenditure, Scottish Executive spending financed by non-domestic rates, and spending financed from the proceeds of the National Lottery.AME is reviewed twice a year as part of the Budget and Pre-Budget Report process reflecting the close integration of the tax and benefit system, which was enhanced by the introduction of tax credits.AME is not subject to the same three year expenditure limits as DEL, but is still part of the overall envelope for public expenditure. Affordability is taken into account when policy decisions affecting AME are made. The Government has committed itself not to take policy measures which are likely to have the effect of increasing social security or other elements of AME without taking steps to ensure that the effects of those decisions can be accommodated prudently within the Government's fiscal rules.Given an overall envelope for public spending, forecasts of AME affect the level of resources available for DEL spending. Cautious estimates and the AME margin are built in to these AME forecasts and reduce the risk of overspending on AME.Together, DEL plus AME sum to Total Managed Expenditure (TME). TME is a measure drawn from national accounts. It represents the current and capital spending of the public sector. The public sector is made up of central government, local government and public corporations.Resource and Capital Budgets are set in terms of accruals information. Accruals information measures resources as they are consumed rather than when the cash is paid. So for example the Resource Budget includes a charge for depreciation, a measure of the consumption or wearing out of capital assets."Non cash charges in budgets do not impact directly on the fiscal framework. That may be because the national accounts use a different way of measuring the same thing, for example in the case of the depreciation of departmental assets. Or it may be that the national accounts measure something different: for example, resource budgets include a cost of capital charge reflecting the opportunity cost of holding capital; the national accounts include debt interest."Within the Resource Budget DEL, departments have separate controls on:"Near cash spending, the sub set of Resource Budgets which impacts directly on the Golden Rule; and"The amount of their Resource Budget DEL that departments may spend on running themselves (e.g. paying most civil servants’ salaries) is limited by Administration Budgets, which are set in Spending Reviews. Administration Budgets are used to ensure that as much money as practicable is available for front line services and programmes. These budgets also help to drive efficiency improvements in departments’ own activities. Administration Budgets exclude the costs of frontline services delivered directly by departments.The Budget preceding a Spending Review sets an overall envelope for public spending that is consistent with the fiscal rules for the period covered by the Spending Review. In the Spending Review, the Budget AME forecast for year one of the Spending Review period is updated, and AME forecasts are made for the later years of the Spending Review period.The 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review ( CSR), which was published in July 1998, was a comprehensive review of departmental aims and objectives alongside a zero-based analysis of each spending programme to determine the best way of delivering the Government's objectives. The 1998 CSR allocated substantial additional resources to the Government's key priorities, particularly education and health, for the three year period from 1999-2000 to 2001-02.Delivering better public services does not just depend on how much money the Government spends, but also on how well it spends it. Therefore the 1998 CSR introduced Public Service Agreements (PSAs). Each major government department was given its own PSA setting out clear targets for achievements in terms of public service improvements.The 1998 CSR also introduced the DEL/ AME framework for the control of public spending, and made other framework changes. Building on the investment and reforms delivered by the 1998 CSR, successive spending reviews in 2000, 2002 and 2004 have:"provided significant increase in resources for the Government’s priorities, in particular health and education, and cross-cutting themes such as raising productivity; extending opportunity; and building strong and secure communities;" "enabled the Government significantly to increase investment in public assets and address the legacy of under investment from past decades. Departmental Investment Strategies were introduced in SR2000. As a result there has been a steady increase in public sector net investment from less than ¾ of a per cent of GDP in 1997-98 to 2¼ per cent of GDP in 2005-06, providing better infrastructure across public services;" "introduced further refinements to the performance management framework. PSA targets have been reduced in number over successive spending reviews from around 300 to 110 to give greater focus to the Government’s highest priorities. The targets have become increasingly outcome-focused to deliver further improvements in key areas of public service delivery across Government. They have also been refined in line with the conclusions of the Devolving Decision Making Review to provide a framework which encourages greater devolution and local flexibility. Technical Notes were introduced in SR2000 explaining how performance against each PSA target will be measured; and"not only allocated near cash spending to departments, but also – since SR2002 - set Resource DEL plans for non cash spending.To identify what further investments and reforms are needed to equip the UK for the global challenges of the decade ahead, on 19 July 2005 the Chief Secretary to the Treasury announced that the Government intends to launch a second Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR) reporting in 2007.A decade on from the first CSR, the 2007 CSR will represent a long-term and fundamental review of government expenditure. It will cover departmental allocations for 2008-09, 2009-10 and 2010 11. Allocations for 2007-08 will be held to the agreed figures already announced by the 2004 Spending Review. To provide a rigorous analytical framework for these departmental allocations, the Government will be taking forward a programme of preparatory work over 2006 involving:"an assessment of what the sustained increases in spending and reforms to public service delivery have achieved since the first CSR. The assessment will inform the setting of new objectives for the decade ahead;" "an examination of the key long-term trends and challenges that will shape the next decade – including demographic and socio-economic change, globalisation, climate and environmental change, global insecurity and technological change – together with an assessment of how public services will need to respond;" "to release the resources needed to address these challenges, and to continue to secure maximum value for money from public spending over the CSR period, a set of zero-based reviews of departments’ baseline expenditure to assess its effectiveness in delivering the Government’s long-term objectives; together with"further development of the efficiency programme, building on the cross cutting areas identified in the Gershon Review, to embed and extend ongoing efficiency savings into departmental expenditure planning.The 2007 CSR also offers the opportunity to continue to refine the PSA framework so that it drives effective delivery and the attainment of ambitious national standards.Public Service Agreements (PSAs) were introduced in the 1998 CSR. They set out agreed targets detailing the outputs and outcomes departments are expected to deliver with the resources allocated to them. The new spending regime places a strong emphasis on outcome targets, for example in providing for better health and higher educational standards or service standards. The introduction in SR2004 of PSA ‘standards’ will ensure that high standards in priority areas are maintained.The Government monitors progress against PSA targets, and departments report in detail twice a year in their annual Departmental Reports (published in spring) and in their autumn performance reports. These reports provide Parliament and the public with regular updates on departments’ performance against their targets.Technical Notes explain how performance against each PSA target will be measured.To make the most of both new investment and existing assets, there needs to be a coherent long term strategy against which investment decisions are taken. Departmental Investment Strategies (DIS) set out each department's plans to deliver the scale and quality of capital stock needed to underpin its objectives. The DIS includes information about the department's existing capital stock and future plans for that stock, as well as plans for new investment. It also sets out the systems that the department has in place to ensure that it delivers its capital programmes effectively.This document was updated on 19 December 2005.Near-cash resource expenditure that has a related cash implication, even though the timing of the cash payment may be slightly different. For example, expenditure on gas or electricity supply is incurred as the fuel is used, though the cash payment might be made in arrears on aquarterly basis. Other examples of near-cash expenditure are: pay, rental.Net cash requirement the upper limit agreed by Parliament on the cash which a department may draw from theConsolidated Fund to finance the expenditure within the ambit of its Request forResources. It is equal to the agreed amount of net resources and net capital less non-cashitems and working capital.Non-cash cost costs where there is no cash transaction but which are included in a body’s accounts (or taken into account in charging for a service) to establish the true cost of all the resourcesused.Non-departmental a body which has a role in the processes of government, but is not a government public body, NDPBdepartment or part of one. NDPBs accordingly operate at arm’s length from governmentMinisters.Notional cost of a cost which is taken into account in setting fees and charges to improve comparability with insuranceprivate sector service providers.The charge takes account of the fact that public bodies donot generally pay an insurance premium to a commercial insurer.the independent body responsible for collecting and publishing official statistics about theUK’s society and economy. (At the time of going to print legislation was progressing tochange this body to the Statistics Board).Office of Government an office of the Treasury, with a status similar to that of an agency, which aims to maximise Commerce, OGCthe government’s purchasing power for routine items and combine professional expertiseto bear on capital projects.Office of the the government department responsible for discharging the Paymaster General’s statutoryPaymaster General,responsibilities to hold accounts and make payments for government departments and OPGother public bodies.Orange bookthe informal title for Management of Risks: Principles and Concepts, which is published by theTreasury for the guidance of public sector bodies.Office for NationalStatistics, ONS60Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————"GLOSSARYOverdraftan account with a negative balance.Parliament’s formal agreement to authorise an activity or expenditure.Prerogative powerspowers exercisable under the Royal Prerogative, ie powers which are unique to the Crown,as contrasted with common-law powers which may be available to the Crown on the samebasis as to natural persons.Primary legislationActs which have been passed by the Westminster Parliament and, where they haveappropriate powers, the Scottish Parliament and the Northern Ireland Assembly. Begin asBills until they have received Royal Assent.arrangements under which a public sector organisation contracts with a private sectorentity to construct a facility and provide associated services of a specified quality over asustained period. See annex 7.5.Proprietythe principle that patterns of resource consumption should respect Parliament’s intentions,conventions and control procedures, including any laid down by the PAC. See box 2.4.Public Accountssee Committee of Public Accounts.CommitteePublic corporationa trading body controlled by central government, local authority or other publiccorporation that has substantial day to day operating independence. See section 7.8.Public Dividend finance provided by government to public sector bodies as an equity stake; an alternative to Capital, PDCloan finance.Public Service sets out what the public can expect the government to deliver with its resources. EveryAgreement, PSAlarge government department has PSA(s) which specify deliverables as targets or aimsrelated to objectives.a structured arrangement between a public sector and a private sector organisation tosecure an outcome delivering good value for money for the public sector. It is classified tothe public or private sector according to which has more control.Rate of returnthe financial remuneration delivered by a particular project or enterprise, expressed as apercentage of the net assets employed.Regularitythe principle that resource consumption should accord with the relevant legislation, therelevant delegated authority and this document. See box 2.4.Request for the functional level into which departmental Estimates may be split. RfRs contain a number Resources, RfRof functions being carried out by the department in pursuit of one or more of thatdepartment’s objectives.Resource accountan accruals account produced in line with the Financial Reporting Manual (FReM).Resource accountingthe system under which budgets, Estimates and accounts are constructed in a similar wayto commercial audited accounts, so that both plans and records of expenditure allow in fullfor the goods and services which are to be, or have been, consumed – ie not just the cashexpended.Resource budgetthe means by which the government plans and controls the expenditure of resources tomeet its objectives.Restitutiona legal concept which allows money and property to be returned to its rightful owner. Ittypically operates where another person can be said to have been unjustly enriched byreceiving such monies.Return on capital the ratio of profit to capital employed of an accounting entity during an identified period.employed, ROCEVarious measures of profit and of capital employed may be used in calculating the ratio.Public Privatepartnership, PPPPrivate Finance Initiative, PFIParliamentaryauthority61Managing Public Money"————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARYRoyal charterthe document setting out the powers and constitution of a corporation established underprerogative power of the monarch acting on Privy Council advice.Second readingthe second formal time that a House of Parliament may debate a bill, although in practicethe first substantive debate on its content. If successful, it is deemed to denoteParliamentary approval of the principle of the proposed legislation.Secondary legislationlaws, including orders and regulations, which are made using powers in primary legislation.Normally used to set out technical and administrative provision in greater detail thanprimary legislation, they are subject to a less intense level of scrutiny in Parliament.European legislation is,however,often implemented in secondary legislation using powers inthe European Communities Act 1972.Service-level agreement between parties, setting out in detail the level of service to be performed.agreementWhere agreements are between central government bodies, they are not legally a contractbut have a similar function.Shareholder Executive a body created to improve the government’s performance as a shareholder in businesses.Spending reviewsets out the key improvements in public services that the public can expect over a givenperiod. It includes a thorough review of departmental aims and objectives to find the bestway of delivering the government’s objectives, and sets out the spending plans for the givenperiod.State aidstate support for a domestic body or company which could distort EU competition and sois not usually allowed. See annex 4.9.Statement of Excessa formal statement detailing departments’ overspends prepared by the Comptroller andAuditor General as a result of undertaking annual audits.Statement on Internal an annual statement that Accounting Officers are required to make as part of the accounts Control, SICon a range of risk and control issues.Subheadindividual elements of departmental expenditure identifiable in Estimates as single cells, forexample cell A1 being administration costs within a particular line of departmental spending.Supplyresources voted by Parliament in response to Estimates, for expenditure by governmentdepartments.Supply Estimatesa statement of the resources the government needs in the coming financial year, and forwhat purpose(s), by which Parliamentary authority is sought for the planned level ofexpenditure and income.Target rate of returnthe rate of return required of a project or enterprise over a given period, usually at least a year.Third sectorprivate sector bodies which do not act commercially,including charities,social and voluntaryorganisations and other not-for-profit collectives. See annex 7.7.Total Managed a Treasury budgeting term which covers all current and capital spending carried out by the Expenditure,TMEpublic sector (ie not just by central departments).Trading fundan organisation (either within a government department or forming one) which is largely orwholly financed from commercial revenue generated by its activities. Its Estimate shows itsnet impact, allowing its income from receipts to be devoted entirely to its business.Treasury Minutea formal administrative document drawn up by the Treasury, which may serve a wide varietyof purposes including seeking Parliamentary approval for the use of receipts asappropriations in aid, a remission of some or all of the principal of voted loans, andresponding on behalf of the government to reports by the Public Accounts Committee(PAC).62Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARY63Managing Public MoneyValue for moneythe process under which organisation’s procurement, projects and processes aresystematically evaluated and assessed to provide confidence about suitability, effectiveness,prudence,quality,value and avoidance of error and other waste,judged for the public sectoras a whole.Virementthe process through which funds are moved between subheads such that additionalexpenditure on one is met by savings on one or more others.Votethe process by which Parliament approves funds in response to supply Estimates.Voted expenditureprovision for expenditure that has been authorised by Parliament. Parliament ‘votes’authority for public expenditure through the Supply Estimates process. Most expenditureby central government departments is authorised in this way.Wider market activity activities undertaken by central government organisations outside their statutory duties,using spare capacity and aimed at generating a commercial profit. See annex 7.6.Windfallmonies received by a department which were not anticipated in the spending review.————————————————————————————————————————
См. также в других словарях:
Caledonia class ship of the line — The Caledonia class ships of the line were a class of nine 120 gun first rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir William Rule.The armament remained the same for the first 3 ships of the class, with the exception of an increase in firepower on… … Wikipedia
Repulse class ship of the line — The Repulse class ships of the line were a class of eleven 74 gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir William Rule. The final three ships of the class were built to a lightly modified version of Rule s draught.hips *HMS|Sceptre|1802|6 … Wikipedia
Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service — The promulgation of the law in the Reichsgesetzblatt, the public law journal The Law for the Restoration of the Professional Civil Service (in German: Gesetz zur Wiederherstellung des Berufsbeamtentums or short: Berufsbeamtengesetz), also known… … Wikipedia
Essex class ship of the line — The Essex class ships of the line were a class of two 64 gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Thomas Slade.hips*HMS|Essex|1760|6:Builder: Wells and Stanton, Rotherhithe:Ordered: 31 January 1759:Launched: 28 August 1760:Fate: Sold… … Wikipedia
Exeter class ship of the line — The Exeter class ships of the line were a class of four 64 gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by William Bateley.DesignThe draught for Exeter was based upon the sclass|Richmond|frigate|3s of 1757.hips*HMS|Exeter|1763|6:Builder: Henniker … Wikipedia
Ganges class ship of the line — The Ganges class ships of the line were a class of six 74 gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Edward Hunt.hips *HMS|Ganges|1782|6:Builder: Randall, Rotherhithe:Ordered: 14 July 1779:Launched: 30 March 1782:Fate: Broken up,… … Wikipedia
Ramillies class ship of the line — The Ramillies class ships of the line were a class of nine 74 gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Thomas Slade. DesignThe draught for the Ramillies class was very similar to that of the sclass|Bellona|ship of the line|0 and… … Wikipedia
Hercules class ship of the line — The Hercules class ships of the line were a class of two 74 gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Thomas Slade.DesignThe Hercules class ships were a development on Slade s previous two designs: the sclass|Dublin|ship of the line|0,… … Wikipedia
Pompée class ship of the line — The Pompée class ships of the line were a class of two 74 gun third rates. They were built for the Royal Navy to the lines of the French ship HMS|Pompée|1793|2, a Téméraire class ship of the line which had been captured by Britain in… … Wikipedia
Arrogant class ship of the line — The Arrogant class ships of the line were a class of twelve 74 gun third rate ships designed by Sir Thomas Slade for the Royal Navy.DesignThe Arrogant class ships were designed as a development of Slade s previous Bellona class, sharing the same… … Wikipedia
Ardent class ship of the line — The Ardent class ships of the line were a class of seven 64 gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Thomas Slade.DesignSlade based the design of the Ardent class on the captured French ship… … Wikipedia
