-
1 kritischer Strom (einer Stromrichterschaltung)
критический ток
Значение тока отключения менее значения номинального тока отключения, при котором время дуги значительно возрастает.
[ ГОСТ Р 52565-2006]
критический ток
[IEV number 551-17-20]EN
transition current
the mean direct current of a converter connection when the direct current(s) of the commutation group(s) become(s) intermittent when decreasing the current
[IEV number 551-17-20]FR
courant critique
valeur moyenne du courant continu d'un montage convertisseur au-dessous de laquelle le courant continu des groupes commutants devient intermittent, lorsqu'on fait décroître le courant
[IEV number 551-17-20]Тематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > kritischer Strom (einer Stromrichterschaltung)
-
2 Schaltanlage
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
36. Электрическое распределительное устройство
Распределительное устройство
D. Schaltanlage
E. Switch-gear
По ГОСТ 24291
Источник: ГОСТ 20375-83: Электроагрегаты и передвижные электростанции с двигателями внутреннего сгорания. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Schaltanlage
-
по назначению:
-
3 Schaltstation
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
3 (электрическое) распределительное устройство; РУ
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы, обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд
605-01-02**
de Schaltstation
en switching substation
fr poste de sectionnement, poste de coupure
Источник: ГОСТ 24291-90: Электрическая часть электростанции и электрической сети. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Schaltstation
-
по назначению:
-
4 elektrischer Messumformer
(электроизмерительный) преобразователь
-
[IEV number 313-03-01]EN
(electrical measuring) transducer
device for converting an alternating measurand to a direct current, a direct voltage or a digital signal for measurement purposes
[IEV number 313-03-01]FR
transducteur (de mesure électrique)
appareil destiné à convertir, à des fins de mesure, un mesurande électrique alternatif en courant continu, tension continue ou signal numérique
[IEV number 313-03-01]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > elektrischer Messumformer
-
5 bistabiles Relais
двустабильное электрическое реле
Электрическое реле, которое, изменив свое состояние под воздействием входной воздействующей или характеристической величины, после устранения воздействия не изменяет своего состояния до приложения другого необходимого воздействия
[ ГОСТ 16022-83]EN
bistable relay
electrical relay which, having responded to an energizing quantity and having changed its condition, remains in that condition after the quantity has been removed; a further appropriate energization is required to make it change its condition
[IEV number 444-01-08]FR
relais bistable, m
relais électrique qui, ayant changé d'état sous l'action d'une grandeur d'alimentation d'entrée, reste dans le même état lorsqu'on supprime cette grandeur ; une autre action appropriée est nécessaire pour le faire changer d'état
[IEV number 444-01-08]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
In a bistable relay with one winding, the opposite energizing is created by a voltage with opposite polarity being applied to the same winding.
In a bistable relay with two windings, the opposing energizing is created by a voltage being applied to the second winding with opposite winding sense.
[Tyco Electronics]В двустабильном реле с одной обмоткой изменение коммутационного положения осуществляется подачей напряжения противоположной полярности на эту же самую обмотку.
В двустабильном реле с двумя обмотками изменение коммутационного положения осуществляется подачей напряжения на другую обмотку (т. е. на обмотку, действие которой противоположно действию предыдущей обмотки).
[Перевод Интент]A remanent, bistable relay which adopts a particular switching position following an energizing direct current in any direction and is then held in this position by the remanence in the magnetic circuit, i.e. through the magnetization of parts of the magnetic circuit. The contacts return to their original position following a small energizing current of limited amplitude of the opposite polarity. This demagnetises the magnetic circuit.
[Tyco Electronics]Двустабильное реле с остаточной намагниченностью переходит в определенное коммутационное положение при подаче постоянного тока любой полярности и затем удерживается в этом положении за счет остаточной намагниченности частей магнитопровода. Контакты реле возвращаются в исходное положение после воздействия небольшого тока обратной полярности. При этом происходит размагничивание магнитопровода.
[Перевод Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
- бистабильное реле
- реле с механической блокировкой
- реле с самоудерживанием
- реле самозамыкающее
- реле самоудерживающее
Тематики
Классификация
>>>EN
DE
FR
14. Двустабильное электрическое реле
D. Bistabiles Relais
Е. Bistable relay
F. Relais bistable
Электрическое реле, которое, изменив свое состояние под воздействием входной воздействующей или характеристической величины, после устранения воздействия не изменяет своего состояния до приложения другого необходимого воздействия
Источник: ГОСТ 16022-83: Реле электрические. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > bistabiles Relais
-
6 Umrichterstation
преобразовательная подстанция
Электрическая подстанция, предназначенная для преобразования рода тока или его частоты.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]EN
converter substation
a substation including converters and the main function of which is to convert alternating current into direct current or vice versa
[IEV number 605-01-07]FR
poste de conversion
station de conversion (déconseillé)
poste comprenant des convertisseurs et dont la fonction principale consiste à convertir le courant alternatif en courant continu ou le courant continu en courant alternatif
[IEV number 605-01-07]
Тематики
EN
DE
FR
27 преобразовательная подстанция
Электрическая подстанция, предназначенная для преобразования рода тока или его частоты
605-01-07**
de Umrichterstation
en converter substation
fr poste de conversion, station de conversion (déconseille)
Источник: ГОСТ 24291-90: Электрическая часть электростанции и электрической сети. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Umrichterstation
-
7 DCEL
(англ. Direct Current Electroluminiscense Display) индикация посредством электролюминесцентных приборов постоянного токаDeutsch-russische wörterbuch der automobil-und automotive service > DCEL
-
8 Serientaktspannung
напряжение помехи последовательного вида
-
[IEV number 312-01-04]EN
series mode voltage
unwanted part of the input voltage which is superimposed on the voltage due to the measurand
NOTE – Typical examples of a series mode voltage are induced voltages, for example a ripple on a direct current signal, or thermopotentials.
[IEV number 312-01-04]FR
tension de mode série
partie indésirable de la tension d'entrée qui est superposée à la tension causée par le mesurande
NOTE – Des exemples typiques de tension de mode série sont les tensions induites, par exemple une ondulation sur une tension continue, ou les tensions d'origine thermoélectrique.
[IEV number 312-01-04]EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Serientaktspannung
-
9 polarisiertes Relais
поляризованное электрическое реле
Электрическое реле постоянного тока, изменение состояния которого зависит от полярности его входной воздействующей величины
[ ГОСТ 16022-83]EN
polarized relay (d.c.)
a direct current relay, the change of condition of which depends upon the polarity of its input energizing quantity(ies)
[IEV number 446-11-14]FR
relais polarisé (à courant continu)
relais à courant continu dont le changement d'état dépend de la polarité de sa ou ses grandeurs d'alimentation d'entrée
[IEV number 446-11-14]Тематики
EN
DE
- polarisiertes Relais
- Relais, polarisiertes
FR
15. Поляризованное электрическое реле
D. Polarisiertes Relais
E. Polarized relay
F. Relais polarisé
Электрическое реле постоянного тока, изменение состояния которого зависит от полярности его входной воздействующей величины
Источник: ГОСТ 16022-83: Реле электрические. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > polarisiertes Relais
-
10 Relais, polarisiertes
поляризованное электрическое реле
Электрическое реле постоянного тока, изменение состояния которого зависит от полярности его входной воздействующей величины
[ ГОСТ 16022-83]EN
polarized relay (d.c.)
a direct current relay, the change of condition of which depends upon the polarity of its input energizing quantity(ies)
[IEV number 446-11-14]FR
relais polarisé (à courant continu)
relais à courant continu dont le changement d'état dépend de la polarité de sa ou ses grandeurs d'alimentation d'entrée
[IEV number 446-11-14]Тематики
EN
DE
- polarisiertes Relais
- Relais, polarisiertes
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Relais, polarisiertes
-
11 Gleichstromantrieb
электропривод постоянного [переменного] тока
Электропривод, содержащий электродвигатель постоянного [переменного] тока.
[ ГОСТ Р 50369-92]Тематики
EN
DE
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Gleichstromantrieb
-
12 Anlauf mit direktem Einschalten
прямой пуск вращающегося электродвигателя
Пуск вращающегося электродвигателя путем непосредственного подключения его к питающей сети.
[ ГОСТ 27471-87]EN
direct-on-line starting
across-the-line starting (US)
the process of starting a motor by connecting it directly to the supply at rated voltage
[IEV number 411-52-15]FR
démarrage direct
mode de démarrage d'un moteur, consistant à lui appliquer directement sa pleine tension assignée
[IEV number 411-52-15]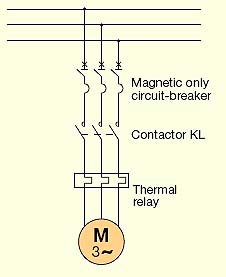
Рис. ABB
Схема прямого пуска электродвигателяMagnetic only circuit-breaker - Автоматический выключатель с электромагнитным расцепителем
Contactor KL - Контактор KL
Thermal relay - Тепловое реле
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Direct-on-line starting
Direct-on-line starting, which is often abbreviated as DOL, is perhaps the most traditional system and consists in connecting the motor directly to the supply network, thus carrying out starting at full voltage.Direct-on-line starting represents the simplest and the most economical system to start a squirrel-cage asynchronous motor and it is the most used.
As represented in Figure 5, it provides the direct connection to the supply network and therefore starting is carried out at full voltage and with constant frequency, developing a high starting torque with very reduced acceleration times.
The typical applications are relevant to small power motors also with full load starting.
These advantages are linked to some problems such as, for example, the high inrush current, which - in the first instants - can reach values of about 10 to 12 times the rated current, then can decrease to about 6 to 8 times the rated current and can persist to reach the maximum torque speed.The effects of such currents can be identified with the high electro-dynamical stresses on the motor connection cables and could affect also the windings of the motor itself; besides, the high inrush torques can cause violent accelerations which stress the transmission components (belts and joints) generating distribution problems with a reduction in the mechanical life of these elements.
Finally, also the possible electrical problems due to voltage drops on the supply line of the motor or of the connected equipment must be taken into consideration.
[ABB]Прямой пуск
Прямой пуск, который по-английски часто сокращенно обозначают как DOL, является, пожалуй наиболее распространенным способом пуска. Он заключается в непосредственном (т. е. прямом) подключении двигателя к питающей сети. Это означает, что пуск двигателя осуществляется при полном напряжении.Схема прямого пуска является наиболее простым, экономичным и чаще всего применяемым решением для электродвигателей с короткозамкнутым ротором.
Схема прямого подключения к сети представлена на рисунке 5. Пуск осуществляется при полном напряжении и постоянной частоте сети. Электродвигатель развивает высокий пусковой момент при коротком времени разгона.
Типичные области применения – маломощные электродвигатели, в том числе с пуском при полной нагрузке.
Однако, наряду с преимуществами имеются и определенные недостатки, например, бросок пускового тока, достигающий в первоначальный момент 10…12-кратного значения от номинального тока электродвигателя. Затем ток двигателя уменьшается примерно до 6…8-кратного значения номинального тока и будет держаться на этом уровне до тех пор, пока скорость двигателя не достигнет максимального значения.
Такое изменение тока оказывает значительное электродинамическое воздействие на кабель, подключенный к двигателю. Кроме того пусковой ток воздействует на обмотки двигателя. Высокий начальный пусковой момент может привести к значительному ускорению и следовательно к значительной нагрузке элементов привода (ремней, крепления узлов), что вызывает сокращение их срока службы.
И, наконец, следует принять во внимание возможное возникновение проблем, связанных с падением напряжения в линии питания двигателя и подключенного к этой линии оборудования.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- across-the-line starting (US)
- direct line starting
- direct operation of a motor
- direct starting
- direct-on-line starting
- DOL
- full voltage starter application
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Anlauf mit direktem Einschalten
-
13 Primärstromauslöser
максимальный расцепитель тока прямого действия
Максимальный расцепитель тока, срабатывающий непосредственно от тока главной цепи коммутационного аппарата.
[Интент]EN
direct over-current release
an over-current release directly energized by the current in the main circuit of a mechanical switching device.
[IEV number 441-16-36]
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]FR
déclencheur direct à maximum de courant
déclencheur à maximum de courant alimenté directement par le courant dans le circuit principal d’un appareil mécanique de connexion.
[IEV number 441-16-36]
[IEC 62271-100, ed. 2.0 (2008-04)]
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- выключатель автоматический
- расцепитель, тепловое реле
Классификация
>>>EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Primärstromauslöser
-
14 Synchron-Längsreaktanz
синхронное реактивное сопротивление по продольной оси
-EN
direct-axis synchronous reactance
the quotient of the sustained value of that fundamental a.c. component of armature voltage, which is produced by the total direct-axis primary flux due to direct-axis armature current, and the value of the fundamental a.c. component of this current, the machine running at rated speed
[IEV ref 411-50-07]FR
réactance synchrone longitudinale
quotient de la valeur, en régime établi, du terme fondamental de la composante de la tension d'induit produite par le flux longitudinal total dû au courant d'induit longitudinal, par la valeur du terme fondamental de ce courant, la machine tournant à sa vitesse assignée
[IEV ref 411-50-07]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Synchron-Längsreaktanz
-
15 Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
-
16 Strombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Strombelastbarkeit, f
-
17 Basisstrom(stärke) (eines Zählers)
базовый ток
-
[IEV number 314-07-01]EN
basic current
value of current in accordance with which the relevant performance of a direct connected meter is fixed
[IEV number 314-07-01]FR
courant de base
valeur du courant en fonction de laquelle certaines des caractéristiques d’un compteur à branchement direct sont fixées
[IEV number 314-07-01]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Basisstrom(stärke) (eines Zählers)
-
18 Spitzendurchlassstrom der Diode
импульсный прямой ток диода
Iпр.и
IFM
Наибольшее мгновенное значение прямого тока диода, исключая повторяющиеся и неповторяющиеся переходные токи.
[ ГОСТ 25529-82]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
8. Импульсный прямой ток диода
D. Spitzendurchlassstrom der Diode
E. Peak forward current
F. Courant direct de crête
Iпр.и
Наибольшее мгновенное значение прямого тока диода, исключая повторяющиеся и неповторяющиеся переходные токи
Источник: ГОСТ 25529-82: Диоды полупроводниковые. Термины, определения и буквенные обозначения параметров оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Spitzendurchlassstrom der Diode
-
19 Kleinsignalstromverstärkung
коэффициент передачи тока биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
Отношение изменения выходного тока к вызвавшему его изменению входного тока в режиме короткого замыкания выходной цепи по переменному току.
Обозначение
h21
h21
Примечание
В схеме с общей базой или общим эмиттером добавляется индекс соответственно "б" или "э" для отечественных буквенных обозначений и "b" и "е" для международных обозначений.
[ ГОСТ 20003-74]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
- valeur du rapport de transfert direct du courant, sortie en court-circuit pour de petits signaux
16. Коэффициент передачи тока биполярного транзистора в режиме малого сигнала
D. Kleinsignalstromverstärkung
E. Small-signal value of the short-circuit forward current transfer ratio
F. Valeur du rapport de transfert direct du courant, sortie en court-circuit pour de petits signaux
h*21
Отношение изменения выходного тока к вызвавшему его изменению входного тока в режиме короткого замыкания выходной цепи по переменному току
Источник: ГОСТ 20003-74: Транзисторы биполярные. Термины, определения и буквенные обозначения параметров оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Kleinsignalstromverstärkung
-
20 Betrag der Kurzschlussstromverstärkung in Emitterschaltung bei HF
- модуль коэффициента передачи тока биполярного транзистора на высокой частоте
модуль коэффициента передачи тока биполярного транзистора на высокой частоте
Модуль коэффициента передачи тока в схеме с общим эмиттером в режиме малого сигнала на высокой частоте.
Обозначение
│h21э│
│h21e│
[ ГОСТ 20003-74]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
17. Модуль коэффициента передачи тока биполярного транзистора на высокой частоте
D. Betrag der Kurzschlussstromverstärkung in Emitterschaltung bei HF
E. Modulus of the short-circuit forward current transfer ratio
F. Module du rapport de transfert direct du courant
|h21э|
Модуль коэффициента передачи тока в схеме с общим эмиттером в режиме малого сигнала на высокой частоте
Источник: ГОСТ 20003-74: Транзисторы биполярные. Термины, определения и буквенные обозначения параметров оригинал документа
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Betrag der Kurzschlussstromverstärkung in Emitterschaltung bei HF
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
Direct current — (red curve). The horizontal axis measures time; the vertical, current or voltage. Direct current (DC) is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and… … Wikipedia
direct current — n. an electric current flowing in one direction: abbrev. DC: cf. ALTERNATING CURRENT * * * ▪ electronics abbreviation Dc, flow of electric charge that does not change direction. Direct current is produced by batteries, fuel cells,… … Universalium
Direct current — (Elec.) (a) A current flowing in one direction only; distinguished from {alternating current}. When steady and not pulsating a direct current is often called a {continuous current}. (b) {A direct induced current}, or momentary current of the same … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
direct current — direct currents N VAR A direct current is an electric current that always flows in the same direction. The abbreviation DC is also used. Some kinds of batteries can be recharged by connecting them to a source of direct current … English dictionary
direct current — n an electric current flowing in one direction only and substantially constant in value abbr. DC * * * (DC) a current that flows in one direction only; when modeled as a wave, its amplitude is constant. When used medically it is called galvanic… … Medical dictionary
direct current — ► NOUN ▪ an electric current flowing in one direction only. Compare with ALTERNATING CURRENT(Cf. ↑alternating current) … English terms dictionary
direct current. — direct current, adj. Elect. an electric current of constant direction, having a magnitude that does not vary or varies only slightly. Abbr.: dc Cf. alternating current. [1885 90] * * * … Universalium
direct current — n. an electric current flowing in one direction: abbrev. DC: cf. ALTERNATING CURRENT … English World dictionary
direct current. — direct current, adj. Elect. an electric current of constant direction, having a magnitude that does not vary or varies only slightly. Abbr.: dc Cf. alternating current. [1885 90] … Useful english dictionary
Direct Current — [engl.], Gleichstrom … Universal-Lexikon
direct current (DC) — Flow of electric charge that does not change direction. Direct current is produced by batteries, fuel cells, rectifiers, and generators with commutators. Direct current was supplanted by alternating current (AC) for common commercial power in the … Universalium
