-
1 Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
-
2 Strombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Strombelastbarkeit, f
-
3 Kabeltrog
лоток
Лотком называется открытая конструкция, предназначенная для прокладки на ней проводов и кабелей.
Лоток не является защитой от внешних механических повреждений проложенных на нем проводов и кабелей. Лотки должны изготовляться из несгораемых материалов. Они могут быть сплошными, перфорированными или решетчатыми. Лотки могут применяться в помещениях и наружных установках
[ПУЭ. Раздел 2]
кабельный лоток
Опорная конструкция для кабелей, состоящая из протяженного основания с вертикальными бортами и не имеющая крышки.
Примечание - Кабельный лоток может быть перфорированным или сетчатым
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
лоток для прокладки кабеля(или полка)
Опорная конструкция в виденепрерывногопротяженного основания сребордамибортами и без крышки.
Примечание
Кабельный лоток может иметь или не иметь перфорацию.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
лоток электротехнический
Открытый жёлоб на специальных подставках, применяемый для размещения в нём кабелей при надземной их прокладке на местности
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
cable tray
cable support consisting of a continuous base with raised edges but no covering
NOTE – A cable tray may be perforated or mesh.
[IEV number 826-15-08]
cable tray
cable support consisting of a continuous base and raised edges and no covering
NOTE A cable tray may be perforated or non-perforated.
[IEV 826-15-08]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
chemin de câbles, m
tablette, f
support de câbles constitué d'une base continue avec de rebords, mais ne comportant pas de couvercle
NOTE – Un chemin de câbles peut être perforé ou en treillis.
[IEV number 826-15-08]
Кабельный лоток неперфорированный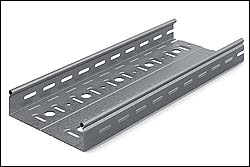
Кабельный лоток перфорированный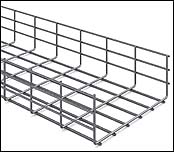
Кабельный лоток проволочный (сетчатый)[ http://www.szpk-nw.ru/catalog_p.html?cid=5]

[ http://www.elsyst.ru/photo/catalog/6l.jpg]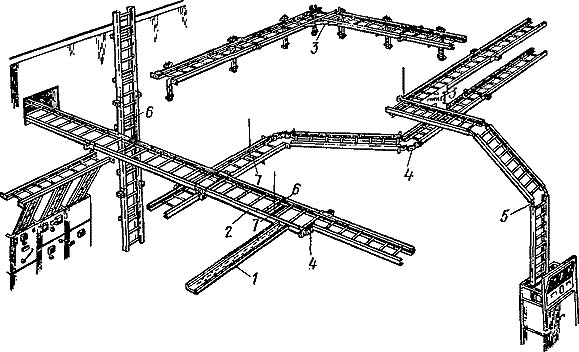
Рис. 33. Кабельный лоток лестничного типа:
1, 2- прямые секции,
3 — угловая секция.
4, 5 — переходные секции и шарнирные соединители,
6 — прижимы,
7 — подвескиКабельные лотки применяют для прокладки силовых и контрольных кабелей и проводов напряжением до 1000 В и изготовляют из перфорированного гнутого металлического листа. Ширина лотка 50, 100, 200 и 400 мм, длина 2 м. В номенклатуру лотков входят готовые для сборки элементы, обеспечивающие создание трассы с необходимыми поворотами и разветвлениями в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях.
Соединение лотков выполняют болтами, благодаря этому обеспечивается надежная электрическая цепь, необходимая для сети заземления. Крепят лотки на кронштейнах, подвесках и сборных кабельных конструкциях. Лотки, установленные на опорных конструкциях, крепят так, чтобы была исключена возможность сползания, опрокидывания и падения их.
При пересечении лотков с другими коммуникациями лотки прокладывают с отступом от стен, если это невозможно, выполняют обходы.[ http://forca.ru/knigi/oborudovanie/montazh-i-ekpluataciya-kabelei_8.html]

Кабельный лоток
[ http://www.solan.ru/data/lotok_dstr.gif]Тематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Kabeltrog
- Kabelwanne, f
FR
- canal électrotechnique
- chemin de câbles, m
- tablette, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Kabeltrog
-
4 Kabelwanne, f
лоток
Лотком называется открытая конструкция, предназначенная для прокладки на ней проводов и кабелей.
Лоток не является защитой от внешних механических повреждений проложенных на нем проводов и кабелей. Лотки должны изготовляться из несгораемых материалов. Они могут быть сплошными, перфорированными или решетчатыми. Лотки могут применяться в помещениях и наружных установках
[ПУЭ. Раздел 2]
кабельный лоток
Опорная конструкция для кабелей, состоящая из протяженного основания с вертикальными бортами и не имеющая крышки.
Примечание - Кабельный лоток может быть перфорированным или сетчатым
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
лоток для прокладки кабеля(или полка)
Опорная конструкция в виденепрерывногопротяженного основания сребордамибортами и без крышки.
Примечание
Кабельный лоток может иметь или не иметь перфорацию.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]
лоток электротехнический
Открытый жёлоб на специальных подставках, применяемый для размещения в нём кабелей при надземной их прокладке на местности
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
cable tray
cable support consisting of a continuous base with raised edges but no covering
NOTE – A cable tray may be perforated or mesh.
[IEV number 826-15-08]
cable tray
cable support consisting of a continuous base and raised edges and no covering
NOTE A cable tray may be perforated or non-perforated.
[IEV 826-15-08]
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
chemin de câbles, m
tablette, f
support de câbles constitué d'une base continue avec de rebords, mais ne comportant pas de couvercle
NOTE – Un chemin de câbles peut être perforé ou en treillis.
[IEV number 826-15-08]
Кабельный лоток неперфорированный
Кабельный лоток перфорированный
Кабельный лоток проволочный (сетчатый)[ http://www.szpk-nw.ru/catalog_p.html?cid=5]

[ http://www.elsyst.ru/photo/catalog/6l.jpg]
Рис. 33. Кабельный лоток лестничного типа:
1, 2- прямые секции,
3 — угловая секция.
4, 5 — переходные секции и шарнирные соединители,
6 — прижимы,
7 — подвескиКабельные лотки применяют для прокладки силовых и контрольных кабелей и проводов напряжением до 1000 В и изготовляют из перфорированного гнутого металлического листа. Ширина лотка 50, 100, 200 и 400 мм, длина 2 м. В номенклатуру лотков входят готовые для сборки элементы, обеспечивающие создание трассы с необходимыми поворотами и разветвлениями в горизонтальной и вертикальной плоскостях.
Соединение лотков выполняют болтами, благодаря этому обеспечивается надежная электрическая цепь, необходимая для сети заземления. Крепят лотки на кронштейнах, подвесках и сборных кабельных конструкциях. Лотки, установленные на опорных конструкциях, крепят так, чтобы была исключена возможность сползания, опрокидывания и падения их.
При пересечении лотков с другими коммуникациями лотки прокладывают с отступом от стен, если это невозможно, выполняют обходы.[ http://forca.ru/knigi/oborudovanie/montazh-i-ekpluataciya-kabelei_8.html]

Кабельный лоток
[ http://www.solan.ru/data/lotok_dstr.gif]Тематики
- изделие электромонтажное
- электропроводка, электромонтаж
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Kabeltrog
- Kabelwanne, f
FR
- canal électrotechnique
- chemin de câbles, m
- tablette, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Kabelwanne, f
-
5 Umhüllung
1
оболочка
Кожух, обеспечивающий тип и степень защиты, необходимые для данного применения.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
оболочка
Корпус (кожух), обеспечивающий тип и степень защиты, соответствующие определенным условиям применения.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
оболочка
Элемент, обеспечивающий защиту оборудования от определенных внешних воздействий, а также защиту со всех сторон от прямых контактов.
Примечание - Определение, взятое из МЭС, требует следующих пояснений относительно области применения настоящего стандарта:
а) оболочки обеспечивают защиту людей или домашних животных и скота от доступа к опасным частям;
б) барьеры, решетки или любые другие средства, либо присоединенные к оболочке, либо размещенные под ней и приспособленные для предотвращения или ограничения проникновения специальных испытательных датчиков, рассматривают как части оболочки, кроме случаев, когда они могут быть демонтированы без применения ключа или другого инструмента.
Оболочка может быть в виде:
- шкафа или коробки, установленного(ой) либо на машине, либо отдельно от нее;
- отсека, представляющего собой закрытое пространство и являющегося частью конструкции машины.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
кожух 1)
Часть оборудования, обеспечивающая его защиту от определенных внешних воздействий и от прямого контакта в любых направлениях.
[ ГОСТ Р 52319-2005( МЭК 61010-1: 2001)]
1) Должно быть оболочка
[Интент]EN
enclosure
housing affording the type and degree of protection suitable for the intended application
Source: 195-02-35
[IEV number 151-13-08]
enclosure
part providing protection of equipment against certain external influences and, in any direction, protection against direct contact
[IEC 61010-031, ed. 1.0 (2002-01)]FR
enveloppe, f
enceinte assurant le type et le degré de protection approprié pour l'application prévue
Source: 195-02-35
[IEV number 151-13-08]
enveloppe
partie assurant la protection d’un appareil contre certaines influences extérieures et, dans toutes les directions, la protection contre le contact direct
[IEC 61010-031, ed. 1.0 (2002-01)]2
оболочка
сплошная непрерывная трубка из металла или неметаллического материала, как правило, наложенного с помощью экструзии
Примечание. Термин «sheath» в Северной Америке используется только для металлической оболочки, в то время как для неметаллических покрытии применяется термин «jacket»
[IEV number 461-05-03]EN
sheath
jacket (North America)
uniform and continuous tubular covering of metallic or non-metallic material, generally extruded
NOTE – The term sheath is only used for metallic coverings in North America, whereas the term jacket is used for non-metallic coverings.
[IEV number 461-05-03]FR
gaine
revêtement tubulaire continu et uniforme en matériau métallique ou non métallique, généralement extrudé
NOTE – En Amérique du Nord, le terme “sheath” est utilisé uniquement pour les revêtements métalliques tandis que le terme “jacket” est utilisé pour les revêtements non métalli
[IEV number 461-05-03]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
- enveloppe, f
- gaine
оболочка
Часть НКУ, обеспечивающая степень защиты оборудования от внешних воздействий, а также от прямого доступа со всех сторон не менее IP2X
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
оболочка
Корпус, обеспечивающий тип и степень защиты оборудования, соответствующие ее назначению.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439.1-2013]
оболочка
Часть ВРУ, обеспечивающая защиту от внешних воздействий и прямого доступа к токоведущим частям со всех сторон, а также выполняющая в ВРУ шкафного исполнения функцию несущей конструкции
[ ГОСТ Р 51732-2001]
пустая оболочка
Оболочка, предназначенная для размещения внутри нее электрооборудования, внутреннее пространство которой обеспечивает надежную защиту электрооборудования от внешних воздействий, а также указанную степень защиты от прикосновения или контакта с частями, находящимися под напряжением, и от контакта с подвижными частями.
Примечание - В настоящем стандарте вместо термина «пустая оболочка» использован сокращенный вариант термина «оболочка».
[ ГОСТ Р 52796- 2007( МЭК 62208: 2002)]EN
enclosure (of an assembly)
a part of an assembly providing a specified degree of protection of equipment against external influences and a specified degree of protection against approach to or contact with live parts and against contact with moving parts
[IEV number 441-13-01]FR
enveloppe (d'un ensemble)
partie d'un ensemble procurant un degré de protection spécifié du matériel contre les influences externes et un degré de protection spécifié contre l'approche des parties actives ou le contact avec elles ou contre le contact avec des pièces en mouvement
[IEV number 441-13-01]


Оболочка шкафа
Оболочка распределительного щитка
Оболочка пульта с вертикальной надстройкой
Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
- кожух
- металлокорпус
- обшивка
- пустой шкаф (щит, пульт)
- собственно шкаф (щит, пульт)
Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
Сопутствующие термины
- металлическая оболочка
- неразборная оболочка
- пластмассовая оболочка
- сборная оболочка
- сварная оболочка
EN
DE
FR
оболочка аппарата
Часть, обеспечивающая оговоренные степени защиты аппарата от некоторых внешних воздействий и от приближения или прикосновения к частям, находящимся под напряжением, и подвижным частям.
Примечание. Определение аналогично формулировке МЭК 60050(441-13-01), относящейся к узлам.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
enclosure (of an assembly)
a part of an assembly providing a specified degree of protection of equipment against external influences and a specified degree of protection against approach to or contact with live parts and against contact with moving parts
[IEV number 441-13-01]FR
enveloppe (d'un ensemble)
partie d'un ensemble procurant un degré de protection spécifié du matériel contre les influences externes et un degré de protection spécifié contre l'approche des parties actives ou le contact avec elles ou contre le contact avec des pièces en mouvement
[IEV number 441-13-01]EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Umhüllung
-
6 Umwelterziehung
экологическое образование
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
environmental education
The educational process that deals with the human interrelationships with the environment and that utilizes an interdisciplinary problem-solving approach with value clarification. Concerned with education progress of knowledge, understanding, attitudes, skills, and commitment for environmental problems and considerations. The need for environmental education is continuous, because each new generation needs to learn conservation for itself. (Source: UNUN)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Umwelterziehung
-
7 Austernzucht
разведение устриц
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
oyster farming
There are two types of oyster farming: suspension culture, in which oysters are grown off bottom, in floating trays, is a labor-intensive form of cultivation that requires continuous tending and cleaning of both gear and shellfish, and bottom culture, which is similar to conventional crop farming on land; it involves selecting areas of the sea floor that provide a natural food supply, necessary currents, minimum exposure to predators, and proper temperature and then "seeding" the bottom with shellfish stock that are left to grow to market size. Then they are harvested with a bottom drag from a boat. Both suspension culture and bottom culture depend on natural food supplies for growing the shellfish being raised. (Source: MSTF)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Austernzucht
-
8 diskontinuierliches Verfahren
периодический процесс
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
batch process
A process that is not in continuous or mass production; operations are carried out with discrete quantities of material or a limited number of items. (Source: MGH)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > diskontinuierliches Verfahren
-
9 Reptilien
рептилии
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
reptile
A class of terrestrial vertebrates, characterized by the lack of hair, feathers, and mammary glands; the skin is covered with scales, they have a three chambered heart and the pleural and peritoneal cavities are continuous. (Source: MGH)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Reptilien
См. также в других словарях:
Continuous function — Topics in Calculus Fundamental theorem Limits of functions Continuity Mean value theorem Differential calculus Derivative Change of variables Implicit differentiation Taylor s theorem Related rates … Wikipedia
Continuous and progressive aspects — The continuous and progressive aspects (abbreviated cont and prog) are grammatical aspects that express incomplete action in progress at a specific time: they are non habitual, imperfective aspects. It is a verb category with two principal… … Wikipedia
Continuous stochastic process — Not to be confused with Continuous time stochastic process. In the probability theory, a continuous stochastic process is a type of stochastic process that may be said to be continuous as a function of its time or index parameter. Continuity is a … Wikipedia
Continuous function (topology) — In topology and related areas of mathematics a continuous function is a morphism between topological spaces. Intuitively, this is a function f where a set of points near f(x) always contain the image of a set of points near x . For a general… … Wikipedia
Continuous-wave radar — is a type of radar system where a known stable frequency continuous wave radio energy is transmitted and then received from any reflecting objects.[1]Continuous wave (CW) radar uses Doppler, which renders the radar immune to interference from… … Wikipedia
Continuous reactor — Continuous reactors (alternatively referred to as flow reactors) carry material as a flowing stream. Reactants are continuously fed into the reactor and emerge as continuous stream of product. Continuous reactors are used for a wide variety of… … Wikipedia
Continuous Computing — Type Private Industry Technology Founded 1998 … Wikipedia
Continuous variable valve timing — offers a unique ability to have independent control of the intake and exhaust valves in an internal combustion engine. For any engine load criteria, the timing of intake and exhaust can be independently programmed [1]. The main variations of… … Wikipedia
Continuous auditing — is the independent application of automated tools to provide assurance on financial, compliance, strategic and operational data within a company. Continuous auditing uses a set of tools to assure the internal control system is functioning to… … Wikipedia
Continuous monitoring — is the process and technology used to detect compliance and risk issues associated with an organization s financial and operational environment. The financial and operational environment consists of people, processes, and systems working together … Wikipedia
Continuous wavelet transform — of frequency breakdown signal. Used symlet with 5 vanishing moments. A continuous wavelet transform (CWT) is used to divide a continuous time function into wavelets. Unlike Fourier transform, the continuous wavelet transform possesses the ability … Wikipedia
