-
61 ariga
face, cheek;ariga ora, (lit. "living face") keepsake, memento, memory, souvenir (of someone). This used to be the name given the moai (stone statues) carved as memories of the dead; -
62 вид компенсации реактивной мощности
вид компенсации реактивной мощности
-См. также компенсация реактивной мощности
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
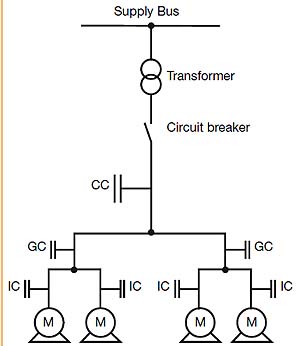
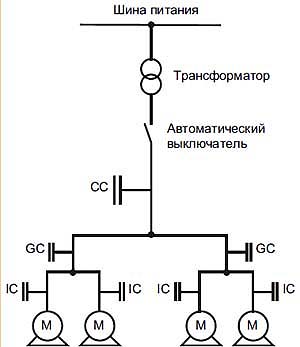
CC: Central Compensation
GC: Group Compensation
IC: Individual Compensation
M: Motor LoadCC: Централизованная компенсация
GC: Групповая компенсация
IC: Индивидуальная компенсация
M: Нагрузка (электродвигатель)The location of low-voltage capacitors in an installation constitutes the mode of compensation, which may be central (one location for the entire installation), by sector (section-by-section), at load level, or some combination of the latter two.
In principle, the ideal compensation is applied at a point of consumption and at the level required at any moment in time.
In practice, technical and economic factors govern the choice.
The location for connection of capacitor banks in the electrical network is determined by:
• the overall objective (avoid penalties on reactive energy relieve transformer or cables, avoid voltage drops and sags)
• the operating mode (stable or fluctuating loads)
• the foreseeable influence of capacitors on the network characteristics
• the installation cost.
[Schneider Electric]Вид компенсации определяется расположением конденсаторов низкого напряжения в электроустановке. Различают следующие виды компенсации: централизованная (одна конденсаторная батарея на всю электроустановку), групповая (по батарее на группу нагрузок), инидивидуальная или комбинированная - сочетание двух последних видов компенсации.
Теоретически, идеальной является компенсация, выполняемая в любой момент времени в требуемой точке электроустановки в требуемом количестве.
На практике выбор определяется техническими и экономическими соображениями.
Место подключения конденсаторных батарей к электрической сети определяется:
● общей задачей (избежать штрафов за потребление реактивной энергии, разгрузить силовой трансформатор и кабели, предотвратить падение и провалы напряжения);
● режимом работы (постоянные и переменные нагрузки);
● предполагаемым влиянием конденсаторов на характеристики электросети;
● стоимостью установки.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > вид компенсации реактивной мощности
-
63 входная воздействующая величина измерительного электрического реле
входная воздействующая величина измерительного электрического реле
Воздействующая величина электрического реле, которая сама представляет характеристическую величину или необходима для ее образования
[ ГОСТ 16022-83]EN
input energizing quantity
for a measuring relay: that energizing quantity which either by itself constitutes the characteristic quantity or helps to constitute it
[IEV number 446-12-02]FR
grandeur d'alimentation d'entrée
pour un relais de mesure: grandeur d'alimentation qui constitue par elle-même la grandeur caractéristique ou qui est nécessaire à sa constitution
[IEV number 446-12-02]Тематики
Классификация
>>>EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > входная воздействующая величина измерительного электрического реле
-
64 Европейский Суд
Европейский Суд
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
European Court of Justice
The supreme court of The European Union which oversees the application of the EU treaties, decides upon the validity and the meaning of Community legislation and determines whether any act or omission by the European Commission, the Council of Minister or any member state constitutes a breach of Community law. (Source: EUEN / DICLAW)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Европейский Суд
-
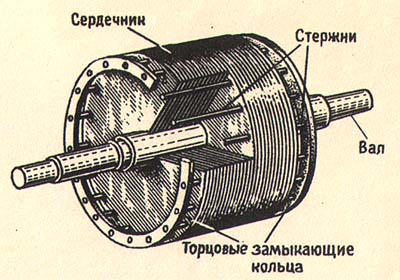
65 короткозамкнутый ротор
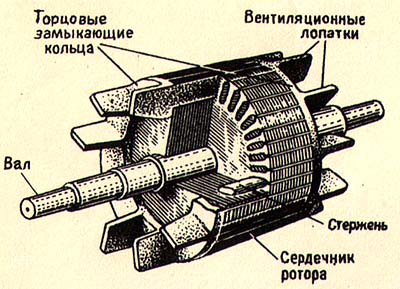
Короткозамкнутый ротор с алюминиевой литой клеткойПараллельные тексты EN-RU
The second element is the rotor, which is positioned inside the stator and constitutes the induced circuit of the motor. The rotor is constituted by a system of bars (in copper or aluminum), which are coaxial to the rotation axis and directly die-cast in the slots made along the external periphery of the ferromagnetic; they are closed in short-circuit by two rings located on the extremities and constituting also a mechanical fixing.
[ABB]Второй частью электродвигателя является ротор. Он расположен внутри статора и представляет собой ту часть электродвигателя, в которой возникает индукционный ток. Ротор состоит из медных или алюминиевых стержней, отлитых под давлением в пазах внешней части ферромагнитного сердечника, расположенных параллельно оси вращения ротора. С торцов эти стержни замыкаются механически и электрически двумя торцевыми кольцами.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > короткозамкнутый ротор
-
66 МОК в роли клиента
МОК в роли клиента
МОК сам по себе представляет собой клиента и ожидает предоставления услуг от организаторов (включая транспорт, размещение, аккредитацию), в соответствии с согласованными сервисными уровнями, в частности, во время Игр.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]EN
IOC as client
IOC constitutes a client in its own right, and expects delivery of services from the organizers (including transport, accommodation, accreditation) in accordance with agreed service levels, particularly at the Games time.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]Тематики
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > МОК в роли клиента
-
67 международный водный путь
международный водный путь
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
international watercourse
Portions of a geographical area which constitutes a hydrogeological unit as the catchment area for a single river which are under the jurisdiction of two or more countries. (Source: WPRa)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > международный водный путь
-
68 многостороннее соглашение
многостороннее соглашение
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
multilateral agreement
Multilateralism stands for a long-held but rarely achieved ideal, namely the voluntary co-operation of nations for peace and development. Multilateral initiatives are undermined or diluted by ultra-nationalist, bilateral and regional initiatives. Multilateralism may be undercut by the uncoordinated decisions of those contributing to it. Multilateralism constitutes the democracy of international society. An enlightened multilateralism enhances the specific interests of states while advancing their common cause. (Source: WPR)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > многостороннее соглашение
-
69 Олимпийская идентификационная и аккредитационная карточка (ОИАК)
Олимпийская идентификационная и аккредитационная карточка (ОИАК)
Олимпийская идентификационная и аккредитационная карточка, выдаваемая сотрудникам СМИ, может использоваться в качестве въездной (выездной) визы, а также в качестве разрешения на работу в течение определенного времени до и после Игр, и позволяет владельцу карты выполнять профессиональные обязанности в связи с Играми.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]EN
Olympic identity and accreditation card (OIAC)
Olympic identity and accreditation card issued to media personnel constitutes an entry/exit visa and a work permit for a certain period of time before and after the Games allowing the holder to carry out professional duties in the context of the Games.
[Департамент лингвистических услуг Оргкомитета «Сочи 2014». Глоссарий терминов]Тематики
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Олимпийская идентификационная и аккредитационная карточка (ОИАК)
-
70 явление электрической дуги
явление электрической дуги
-
[Интент]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Electric arc phenomenon
The electric arc is a phenomenon which takes place as a consequence of a discharge which occurs when the voltage between two points exceeds the insulating strength limit of the interposed gas; then, in the presence of suitable conditions, a plasma is generated which carries the electric current till the opening of the protective device on the supply side.
Gases, which are good insulating means under normal conditions, may become current conductors in consequence of a change in their chemical-physical properties due to a temperature rise or to other external factors.
To understand how an electrical arc originates, reference can be made to what happens when a circuit opens or closes.
During the opening phase of an electric circuit the contacts of the protective device start to separate thus offering to the current a gradually decreasing section; therefore the current meets growing resistance with a consequent rise in the temperature.
As soon as the contacts start to separate, the voltage applied to the circuit exceeds the dielectric strength of the air, causing its perforation through a discharge.
The high temperature causes the ionization of the surrounding air which keeps the current circulating in the form of electrical arc. Besides thermal ionization, there is also an electron emission from the cathode due to the thermionic effect; the ions formed in the gas due to the very high temperature are accelerated by the electric field, strike the cathode, release energy in the collision thus causing a localized heating which generates electron emission.
The electrical arc lasts till the voltage at its ends supplies the energy sufficient to compensate for the quantity of heat dissipated and to maintain the suitable conditions of temperature. If the arc is elongated and cooled, the conditions necessary for its maintenance lack and it extinguishes.
Analogously, an arc can originate also as a consequence of a short-circuit between phases. A short-circuit is a low impedance connection between two conductors at different voltages.
The conducting element which constitutes the low impedance connection (e.g. a metallic tool forgotten on the busbars inside the enclosure, a wrong wiring or a body of an animal entered inside the enclosure), subject to the difference of potential is passed through by a current of generally high value, depending on the characteristics of the circuit.
The flow of the high fault current causes the overheating of the cables or of the circuit busbars, up to the melting of the conductors of lower section; as soon as the conductor melts, analogous conditions to those present during the circuit opening arise. At that point an arc starts which lasts either till the protective devices intervene or till the conditions necessary for its stability subsist.
The electric arc is characterized by an intense ionization of the gaseous means, by reduced drops of the anodic and cathodic voltage (10 V and 40 V respectively), by high or very high current density in the middle of the column (of the order of 102-103 up to 107 A/cm2), by very high temperatures (thousands of °C) always in the middle of the current column and – in low voltage - by a distance between the ends variable from some microns to some centimeters.
[ABB]Явление электрической дуги
Электрическая дуга между двумя электродами в газе представляет собой физическое явление, возникающее в тот момент, когда напряжения между двумя электродами превышает значение электрической прочности изоляции данного газа.
При наличии подходящих условий образуется плазма, по которой протекает электрический ток. Ток будет протекать до тех пор, пока на стороне электропитания не сработает защитное устройство.
Газы, являющиеся хорошим изолятором, при нормальных условиях, могут стать проводником в результате изменения их физико-химических свойств, которые могут произойти вследствие увеличения температуры или в результате воздействия каких-либо иных внешних факторов.
Для того чтобы понять механизм возникновения электрической дуги, следует рассмотреть, что происходит при размыкании или замыкании электрической цепи.
При размыкании электрической цепи контакты защитного устройства начинают расходиться, в результате чего постепенно уменьшается сечение контактной поверхности, через которую протекает ток.
Сопротивление электрической цепи возрастает, что приводит к увеличению температуры.
Как только контакты начнут отходить один от другого, приложенное напряжение превысит электрическую прочность воздуха, что вызовет электрический пробой.
Высокая температура приведет к ионизации воздуха, которая обеспечит протекание электрического тока по проводнику, представляющему собой электрическую дугу. Кроме термической ионизации молекул воздуха происходит также эмиссия электронов с катода, вызванная термоэлектронным эффектом. Образующиеся под воздействием очень высокой температуры ионы ускоряются в электрическом поле и бомбардируют катод. Высвобождающаяся, в результате столкновения энергия, вызывает локальный нагрев, который, в свою очередь, приводит к эмиссии электронов.
Электрическая дуга длится до тех пор, пока напряжение на ее концах обеспечивает поступление энергии, достаточной для компенсации выделяющегося тепла и для сохранения условий поддержания высокой температуры. Если дуга вытягивается и охлаждается, то условия, необходимые для ее поддержания, исчезают и дуга гаснет.
Аналогичным образом возникает дуга в результате короткого замыкания электрической цепи. Короткое замыкание представляет собой низкоомное соединение двух проводников, находящихся под разными потенциалами.
Проводящий элемент с малым сопротивлением, например, металлический инструмент, забытый на шинах внутри комплектного устройства, ошибка в электромонтаже или тело животного, случайно попавшего в комплектное устройство, может соединить элементы, находящиеся под разными потенциалами, в результате чего через низкоомное соединение потечет электрический ток, значение которого определяется параметрами образовавшейся короткозамкнутой цепи.
Протекание большого тока короткого замыкания вызывает перегрев кабелей или шин, который может привести к расплавлению проводников с меньшим сечением. Как только проводник расплавится, возникает ситуация, аналогичная размыканию электрической цепи. Т. е. в момент размыкания возникает дуга, которая длится либо до срабатывания защитного устройства, либо до тех пор, пока существуют условия, обеспечивающие её стабильность.
Электрическая дуга характеризуется интенсивной ионизацией газов, что приводит к падению анодного и катодного напряжений (на 10 и 40 В соответственно), высокой или очень высокой плотностью тока в середине плазменного шнура (от 102-103 до 107 А/см2), очень высокой температурой (сотни градусов Цельсия) всегда в середине плазменного шнура и низкому падению напряжения при расстоянии между концами дуги от нескольких микрон до нескольких сантиметров.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > явление электрической дуги
См. также в других словарях:
constitutes — index definite Burton s Legal Thesaurus. William C. Burton. 2006 … Law dictionary
constitutes — con·sti·tute || kÉ’nstɪtjuËt v. comprise, form, make up; establish, found; appoint a person to a a particular position … English contemporary dictionary
collection management authority — Constitutes the authority to establish, prioritize, and validate theater collection requirements, establish sensor tasking guidance, and develop theater collection plans. Also called CMA. See also collection manager; collection plan; collection… … Military dictionary
Vice President of Nepal — ) constitutes the deputy head of State of the country of Nepal and was created when the Nepalese monarchy was abolished in May 2008.Under the [http://www.worldstatesmen.org/Nepal Interim Constitution2007.pdf interim constitution] adopted in… … Wikipedia
is part of — constitutes a part of, comprises a piece of … English contemporary dictionary
Laborem Exercens — was an encyclical written by Pope John Paul II in 1981, on human work. It is part of a larger body of writings known as Catholic social teaching, that trace their origin to Rerum Novarum which was issued by Pope Leo XIII in 1891.External links*… … Wikipedia
Christianity — /kris chee an i tee/, n., pl. Christianities. 1. the Christian religion, including the Catholic, Protestant, and Eastern Orthodox churches. 2. Christian beliefs or practices; Christian quality or character: Christianity mixed with pagan elements; … Universalium
Arctic Regions — ▪ 2009 The Arctic regions may be defined in physical terms (astronomical [north of the Arctic Circle, latitude 66° 30′ N], climatic [above the 10 °C (50 °F) July isotherm], or vegetational [above the northern limit of the tree line]) or in human… … Universalium
Idealism (italian) and after — Italian idealism and after Gentile, Croce and others Giacomo Rinaldi INTRODUCTION The history of twentieth century Italian philosophy is strongly influenced both by the peculiar character of its evolution in the preceding century and by… … History of philosophy
Kierkegaard’s speculative despair — Judith Butler Every movement of infinity is carried out through passion, and no reflection can produce a movement. This is the continual leap in existence that explains the movement, whereas mediation is a chimera, which in Hegel is supposed to… … History of philosophy
china — /chuy neuh/, n. 1. a translucent ceramic material, biscuit fired at a high temperature, its glaze fired at a low temperature. 2. any porcelain ware. 3. plates, cups, saucers, etc., collectively. 4. figurines made of porcelain or ceramic material … Universalium