-
81 Nervi, Pier Luigi
[br]b. 21 June 1891 Sondrio, Italyd. 9 January 1979 (?), Italy[br]Italian engineer who played a vital role in the use and adaptation of reinforced concrete as a structural material from the 1930s to the 1970s.[br]Nervi early established a reputation in the use of reinforced concrete with his stadium in Florence (1930–2). This elegant concrete structure combines graceful curves with functional solidity and is capable of seating some 35,000 spectators. The stadium was followed by the aircraft hangars built for the Italian Air Force at Orvieto and Ortebello, in which he spanned the vast roofs of the hangars with thin-shelled vaults supported by precast concrete beams and steel-reinforced ribs. The structural strength and subtle curves of these ribbed roofs set the pattern for Nervi's techniques, which he subsequently varied and elaborated on to solve problems that arose in further commissions.Immediately after the Second World War Italy was short of supplies of steel for structural purposes so, in contrast to the USA, Britain and Germany, did not for some years construct any quantity of steel-framed rectangular buildinngs used for offices, housing or industrial use. It was Nervi who led the way to a ferroconcrete approach, using a new type of structure based on these materials in the form of a fine steel mesh sprayed with cement mortar and used to roof all kinds of structures. It was a method that resulted in expressionist curves instead of rectangular blocks, and the first of his great exhibition halls at Turin (1949), with a vault span of 240 ft (73 m), was an early example of this technique. Nervi continued to create original and beautiful ferroconcrete structures of infinite variety: for example, the hall at the Lido di Roma, Ostia; the terme at Chianciano; and the three buildings that he designed for the Rome Olympics in 1960. The Palazzetto dello Sport is probably the most famous of these, for which he co-operated with the architect Annibale Vitellozzi to construct a small sports palace seating 5,000 spectators under a concrete "big top" of 194 ft (59 m) diameter, its enclosing walls supported by thirtysix guy ropes of concrete; inside, the elegant roof displays a floral quality. In 1960 Nervi returned to Turin to build his imaginative Palace of Labour for the centenary celebrations of Garibaldi and Victor Emmanuel in the city. This vast hall, like the Crystal Palace in England a century earlier (see Paxton), had to be built quickly and be suitable for later adaptation. It was therefore constructed partly in steel, and the metal supporting columns rose to palm-leaf capitals reminiscent of those in ancient Nile palaces.Nervi's aim was always to create functional buildings that simultaneously act by their aesthetic qualities as an effective educational influence. Functionalism for Nervi never became "brutalism". In consequence, his work is admired by the lay public as well as by architects. He collaborated with many of the outstanding architects of the day: with Gio Ponti on the Pirelli Building in Milan (1955–9); with Zehrfuss and Breuer on the Y-plan UNESCO Building in Paris (1953–7); and with Marcello Piacentini on the 16,000-seat Palazzo dello Sport in Rome. Nervi found time to write a number of books on building construction and design, lectured in the Universities of Rio de Janiero and Buenos Aires, and was for many years Professor of Technology and Technique of Construction in the Faculty of Architecture at the University of Rome. He continued to design new structures until well into the 1970s.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsRIBA Royal Gold Medal 1960. Royal Institute of Structural Engineers Gold Medal 1968. Honorary Degree Edinburgh University, Warsaw University, Munich University, London University, Harvard University. Member International Institute of Arts and Letters, Zurich; American Academy of Arts and Sciences; Royal Academy of Fine Arts, Stockholm.Bibliography1956, Structures, New York: Dodge.1945, Scienza o Arte del Costruire?, Rome: Bussola.Further ReadingP.Desideri et al., 1979, Pier Luigi Nervi, Bologna: Zanichelli.A.L.Huxtable, 1960, Masters of World Architecture; Pier Luigi Nervi, New York: Braziller.DY -
82 Poelzig, Hans
SUBJECT AREA: Architecture and building[br]b. 1869 Berlin, Germanyd. June 1936 Berlin, Germany[br]German teacher and practising architect, the most notable individualistic exponent of the German Expressionist movement in the modern school.[br]In the last decade of the nineteenth century and in the first of the twentieth, Poelzig did not, like most of his colleagues in Germany and Austria, follow the Jugendstil theme or the eclectic or fundamentalist lines: he set a path to individualism. In 1898 he began a teaching career at the Breslau (now Wroclaw, Poland) Academy of Arts and Crafts, remaining there until 1916. He early introduced workshop practice into the curriculum, presaging Gropius's Bauhaus ideas by many years; the school's workshop produced much of the artisan needs for a number of his buildings. From Breslau Poelzig moved to Dresden, where he was appointed City Architect. It was there that he launched his Expressionist line: which was particularly evident in the town hall and concert hall in the city. The structure for which Poelzig is best known and with which his name will always be associated is the Großes Schauspielhaus in Berlin; he had returned to his native city after the First World War and this great theatre was his first commission there. Using modern materials, he created a fabulous interior to seat 5,000 spectators. It was in the form of a vast amphitheatre with projecting stage and with the curving area roofed by a cavernous, stalactited dome, the Arabic-style stalactites of which were utilized by Poelzig for acoustic purposes. In the 1920s Poelzig went on to design cinemas, a field for which Expressionism was especially suited; these included the Capitol Cinema in Berlin and the Deli in Breslau. For his later industrial commissions—for example, the administrative building for the chemical firm I.G.Far ben in Frankfurt—he had perforce to design in more traditional modern manner.Poelzig died in 1936, which spared him, unlike many of his contemporaries, the choice of emigrating or working for National Socialism.[br]Further ReadingDennis Sharp, 1966, Modern Architecture and Expressionism, Longmans.Theodor Heuss, 1966, Hans Poelzig: Lebensbild eines Baumeister, Tübingen, Germany: Wunderlich.DY -
83 καί
καί conjunction (Hom.+), found most frequently by far of all Gk. particles in the NT; since it is not only used much more commonly here than in other Gk. lit. but oft. in a different sense, or rather in different circumstances, it contributes greatly to some of the distinctive coloring of the NT style.—HMcArthur, ΚΑΙ Frequency in Greek Letters, NTS 15, ’68/69, 339–49. The vivacious versatility of κ. (for earlier Gk. s. Denniston 289–327) can easily be depressed by the tr. ‘and’, whose repetition in a brief area of text lacks the support of arresting aspects of Gk. syntax.① marker of connections, andⓐ single wordsα. gener. Ἰάκωβος καὶ Ἰωσὴφ καὶ Σίμων καὶ Ἰούδας Mt 13:55. χρυσὸν καὶ λίβανον καὶ σμύρναν 2:11. ἡ ἐντολὴ ἁγία καὶ δικαία καὶ ἀγαθή Ro 7:12. πολυμερῶς κ. πολυτρόπως Hb 1:1. ὁ θεὸς κ. πατήρ God, who is also the Father 1 Cor 15:24; cp. 2 Cor 1:3; 11:31; Eph 1:3; Js 1:27; 3:9 al.—Connects two occurrences of the same word for emphasis (OGI 90, 19 [196 B.C.] Ἑρμῆς ὁ μέγας κ. μέγας; pap in Mayser II/1, 54) μείζων κ. μείζων greater and greater Hv 4, 1, 6. ἔτι κ. ἔτι again and again B 21:4; Hs 2, 6 (B-D-F §493, 1; 2; s. Rob. 1200).β. w. numerals, w. the larger number first δέκα καὶ ὁκτώ Lk 13:16. τεσσεράκοντα κ. ἕξ J 2:20. τετρακόσιοι κ. πεντήκοντα Ac 13:20.—The καί in 2 Cor 13:1 ἐπὶ στόματος δύο μαρτύρων καὶ τριῶν σταθήσεται πᾶν ῥῆμα=‘or’ ([v.l. ἢ τριῶν for καὶ τριῶν as it reads Mt 18:16]; cp. Js 4:13 v.l. σήμερον καὶ αὔριον=‘today or tomorrow’, but s. above all Thu. 1, 82, 2; Pla., Phd. 63e; X., De Re Equ. 4, 4 ἁμάξας τέτταρας καὶ πέντε; Heraclides, Pol. 58 τρεῖς καὶ τέσσαρας; Polyb. 3, 51, 12 ἐπὶ δυεῖν καὶ τρισὶν ἡμέραις; 5, 90, 6; Diod S 34 + 35 Fgm. 2, 28 εἷς καὶ δύο=one or two; schol. on Apollon. Rhod. 4, 1091 p. 305, 22 W. τριέτης καὶ τετραέτης) by the statement of two or three witnesses every charge must be sustained, as explained by Dt 19:15.γ. adding the whole to the part and in general (Aristoph., Nub. 1239 τὸν Δία καὶ τοὺς θεούς; Thu. 1, 116, 3; 7, 65, 1) Πέτρος καὶ οἱ ἀπόστολοι Peter and the rest of the apostles Ac 5:29. οἱ ἀρχιερεῖς κ. τὸ συνέδριον ὅλον the high priest and all the rest of the council Mt 26:59. Vice versa, adding a (specially important) part to the whole and especially (πᾶς Ἰουδὰ καὶ Ἰερουσαλήμ 2 Ch 35:24; cp. 32, 33; 1 Macc 2:6) τοῖς μαθηταῖς κ. τῷ Πέτρῳ Mk 16:7. σὺν γυναιξὶ κ. Μαριάμ Ac 1:14.δ. The expr. connected by καί can be united in the form of a hendiadys (Alcaeus 117, 9f D.2 χρόνος καὶ καρπός=time of fruit; Soph., Aj. 144; 749; Polyb. 6, 9, 4; 6, 57, 5 ὑπεροχὴ καὶ δυναστεία=1, 2, 7; 5, 45, 1 ὑπεροχὴ τῆς δυναστείας; Diod S 5, 67, 3 πρὸς ἀνανέωσιν καὶ μνήμην=renewal of remembrance; 15, 63, 2 ἀνάγκη καὶ τύχη=compulsion of fate; 16, 93, 2 ἐπιβουλὴ κ. θάνατος=a fatal plot; Jos., Ant. 12, 98 μετὰ χαρᾶς κ. βοῆς=w. a joyful cry; 17, 82 ἀκρίβεια κ. φυλακή) ἐξίσταντο ἐπὶ τῇ συνέσει καὶ ταῖς ἀποκρίσεσιν αὐτοῦ they were amazed at his intelligent answers Lk 2:47. δώσω ὑμῖν στόμα κ. σοφίαν I will give you wise utterance 21:15. τροφὴ κ. εὐφροσύνη joy concerning (your) food Ac 14:17. ἐλπὶς κ. ἀνάστασις hope of a resurrection 23:6 (2 Macc 3:29 ἐλπὶς καὶ σωτηρία; s. OLagercrantz, ZNW 31, ’32, 86f; GBjörck, ConNeot 4, ’40, 1–4).ε. A colloquial feature is the coordination of two verbs, one of which should be a ptc. (s. B-D-F §471; Rob. 1135f) ἀποτολμᾷ κ. λέγει = ἀποτολμῶν λέγει he is so bold as to say Ro 10:20. ἔσκαψεν κ. ἐβάθυνεν (=βαθύνας) Lk 6:48. ἐκρύβη κ. ἐξῆλθεν (=ἐξελθών) J 8:59. Sim. χαίρων κ. βλέπων I am glad to see Col 2:5. Linking of subordinate clause and ptc. Μαριὰμ ὡς ἦλθεν … καὶ ἰδοῦσα J 11:32 v.l. Cp. παραλαβών … καὶ ἀνέβη Lk 9:28 v.l.ⓑ clauses and sentencesα. gener.: ἐν γαστρὶ ἕξει κ. τέξεται υἱόν Mt 1:23 (Is 7:14). εἰσῆλθον … κ. ἐδίδασκον Ac 5:21. διακαθαριεῖ τὴν ἅλωνα αὐτοῦ κ. συνάξει τὸν σῖτον Mt 3:12. κεκένωται ἡ πίστις καὶ κατήργηται ἡ ἐπαγγελία Ro 4:14 and very oft. Connecting two questions Mt 21:23, or quotations (e.g. Ac 1:20), and dialogue (Lk 21:8), or alternate possibilities (13:18).β. Another common feature is the practice, drawn fr. Hebrew or fr. the speech of everyday life, of using κ. as a connective where more discriminating usage would call for other particles: καὶ εἶδον καὶ (for ὅτι) σεισμὸς ἐγένετο Rv 6:12. καὶ ἤκουσεν ὁ βασιλεὺς … καὶ (for ὅτι) ἔλεγον and the king learned that they were saying Mk 6:14 (s. HLjungvik, ZNW 33, ’34, 90–92; on this JBlinzler, Philol. 96, ’43/44, 119–31). τέξεται υἱὸν καὶ καλέσεις τὸ ὄνομα αὐτοῦ (for οὗ τὸ ὄνομα καλ.) Mt 1:21; cp. Lk 6:6; 11:44. καλόν ἐστιν ἡμᾶς ὧδε εἶναι καὶ ποιήσωμεν σκηνάς Mk 9:5. Esp. freq. is the formula in historical narrative καὶ ἐγένετο … καὶ (like וַ … וַיְהִי) and it happened or came about … that Mt 9:10; Mk 2:15; Lk 5:1 v.l. (for ἐγένετο δὲ … καὶ; so also the text of 6:12), 12, 17; 14:1; 17:11 al. (Gen 7:10 al.; JosAs 11:1; 22:1). S. MJohannessohn, Das bibl. Καὶ ἐγένετο u. seine Geschichte, 1926 (fr. ZVS 35, 1925, 161–212); KBeyer, Semitische Syntax im NT I, 1 ’62, 29–62; Mlt-Turner 334f; ÉDelebecque, Études Grecques sur L’Évangile de Luc ’76, 123–65; JVoelz, The Language of the NT: ANRW II/25/2, 893–977, esp. 959–64.—As in popular speech, κ. is used in rapid succession Mt 14:9ff; Mk 1:12ff; Lk 18:32ff; J 2:13ff; 1 Cor 12:5f; Rv 6:12ff; 9:1ff. On this kind of colloquial speech, which joins independent clauses rather than subordinating one to the other (parataxis rather than hypotaxis) s. B-D-F §458; Rdm.2 p. 222; Rob. 426; Dssm., LO 105ff (LAE 129ff), w. many references and parallels fr. secular sources. This is a favorite, e.g., in Polyaenus 2, 3, 2–4; 2, 4, 3; 3, 9, 10; 3, 10, 2; 4, 6, 1; 7, 36 al.γ. It is also coordination rather than subordination when κ. connects an expr. of time with that which occurs in the time (Od. 5, 362; Hdt. 7, 217; Thu. 1, 50, 5; Pla., Symp. 220c; Aeschin. 3, 71 νὺξ ἐν μέσῳ καὶ παρῆμεν; s. B-D-F §442, 4; KBrugmann4-AThumb, Griechische Gramm. 1913, 640*): ἤγγικεν ἡ ὥρα κ. παραδίδοται the time has come when he is to be given up Mt 26:45. κ. ἐσταύρωσαν αὐτόν when they crucified him Mk 15:25. κ. ἀνέβη εἰς Ἰεροσόλυμα when he went up to Jerusalem J 2:13. κ. συντελέσω when I will make Hb 8:8 (Jer 38:31); cp. J 4:35; 7:33; Lk 19:43; 23:44; Ac 5:7.δ. καί introducing an apodosis is really due to Hebr./LXX infl. (B-D-F §442, 7; Abel §78a, 6 p. 341; Mlt-H. 422; KBeyer, Semitische Syntax im NT I, 1 ’62, 66–72; but not offensive to ears trained in good Gk.: s. Il. 1, 478; Hdt. 1, 79, 2; sim.Thu. 2, 93, 4 ὡς ἔδοξεν αὐτοῖς, καὶ ἐχώρουν εὐθύς; 8, 27, 5; Herm. Wr. 13, 1 …, καὶ ἔφης; Delebecque [s. above in β] 130–32) καὶ ὅτε ἐπλήσθησαν ἡμέραι ὀκτὼ …, κ. ἐκλήθη τὸ ὄνομα αὐτοῦ Lk 2:21; cp. Rv 3:20. Also κ. ἰδού in an apodosis Lk 7:12; Ac 1:10.ε. connecting negative and affirmative clauses Lk 3:14. οὔτε ἄντλημα ἔχεις κ. τὸ φρέαρ ἐστὶ βαθύ you have no bucket, and the well is deep J 4:11; cp. 3J 10 (οὔτε … καί Eur., Iph. Taur. 591f; Longus, Past. 1, 17; 4, 28; Aelian, NA 1, 57; 11, 9; Lucian, Dial. Meretr. 2, 4 οὔτε πάντα ἡ Λεσβία, Δωρί, πρὸς σὲ ἐψεύσατο καὶ σὺ τἀληθῆ ἀπήγγελκας Μυρτίῳ ‘It wasn’t all lies that Lesbia told you, Doris; and you certainly reported the truth to Myrtium’). After a negative clause, which influences the clause beginning w. καί: μήποτε καταπατήσουσιν … κ. στραφέντες ῥήξωσιν ὑμᾶς Mt 7:6; cp. 5:25; 10:38; 13:15 (Is 6:10); 27:64; Lk 12:58; 21:34; J 6:53; 12:40 (Is 6:10); Ac 28:27 (Is 6:10); 1 Th 3:5; Hb 12:15; Rv 16:15.ζ. to introduce a result that comes fr. what precedes: and then, and so Mt 5:15; 23:32; Mk 8:34; 2 Cor 11:9; Hb 3:19; 1J 3:19. καὶ ἔχομεν and so we have 2 Pt 1:19. Esp. after the impv., or expr. of an imperatival nature (Soph., Oed. Col. 1410ff θέσθε … καὶ … οἴσει, El. 1207; Sir 2:6; 3:17) δεῦτε ὀπίσω μου καὶ ποιήσω and then I will make Mt 4:19. εἰπὲ λόγῳ, κ. ἰαθήσεται ὁ παῖς μου speak the word, and then my servant will be cured Mt 8:8; Lk 7:7; cp. Mt 7:7; Mk 6:22; Lk 10:28; J 14:16; Js 4:7, 10; Rv 4:1.—καί introduces a short clause that confirms the existence of someth. that ought to be: ἵνα τέκνα θεοῦ κληθῶμεν, καὶ ἐσμέν that we should be called children of God; and so we really are (καλέω 1d) 1J 3:1 (Appian, Bell. Civ. 2, 40 §161 they were to conquer Sardinia, καὶ κατέλαβον=and they really took it; 4, 127 §531 one day would decide [κρίνειν] the fate of Rome, καὶ ἐκρίθη).η. emphasizing a fact as surprising or unexpected or noteworthy: and yet, and in spite of that, nevertheless (Eur., Herc. Fur. 509; Philostrat., Her. 11 [II 184, 29 Kayser] ῥητορικώτατον καὶ δεινόν; Longus, Past. 4, 17 βουκόλος ἦν Ἀγχίσης καὶ ἔσχεν αὐτὸν Ἀφροδίτη) κ. σὺ ἔρχῃ πρὸς μέ; and yet you come to me? Mt 3:14; cp. 6:26; 10:29; Mk 12:12; J 1:5, 10; 3:11, 32; 5:40; 6:70; 7:28; 1 Cor 5:2; 2 Cor 6:9; Hb 3:9 (Ps 94:9); Rv 3:1. So also, connecting what is unexpected or otherw. noteworthy with an attempt of some kind (JBlomqvist, Das sogennante και adversativum ’79): but ζητεῖ κ. οὐχ εὑρίσκει but he finds none (no resting place) Mt 12:43. ἐπεθύμησαν ἰδεῖν κ. οὐχ εἶδαν but did not see (it) 13:17; cp. 26:60; Lk 13:7; 1 Th 2:18. Cp. GJs 18:3 (not pap). Perhaps Mk 5:20. Introducing a contrasting response καὶ ἀποδώσεις μοι Hv 2, 1, 3.θ. to introduce an abrupt question, which may often express wonder, ill-will, incredulity, etc. (B-D-F §442, 8. For older lit. exx. of this usage s. Kühner-G. II p. 247f; for later times EColwell, The Gk. of the Fourth Gospel ’31, 87f): κ. πόθεν μοι τοῦτο; how have I deserved this? Lk 1:43. κ. τίς; who then? Mk 10:26; Lk 10:29; J 9:36. καὶ τί γέγονεν ὅτι … ; how does it happen that … ? 14:22. καὶ πῶς σὺ λέγεις … ; how is it, then, that you say … J 14:9 v.l. W. a protasis εἰ γὰρ ἐγὼ λυπῶ ὑμᾶς, κ. τίς ὁ εὐφραίνων με; for if I make you sad, who then will cheer me up? 2 Cor 2:2 (cp. Ps.-Clem., Hom. 2, 43; 44 εἰ [ὁ θεὸς] ψεύδεται, καὶ τίς ἀληθεύει;). Thus Phil 1:22 is prob. to be punctuated as follows (s. ADebrunner, GGA 1926, 151): εἰ δὲ τὸ ζῆν ἐν σαρκί, τοῦτο μοι καρπὸς ἔργου, καὶ τί αἱρήσομαι; οὐ γνωρίζω but if living on here means further productive work, then which shall I choose? I really don’t know. καὶ πῶς αὐτοῦ υἱός ἐστιν; how, then, is he his son? Lk 20:44 (cp. Gen 39:9).ι. to introduce a parenthesis (Eur., Orest. 4, Hel. 393; X., Equ. 11, 2.—B-D-F §465, 1; Rob. 1182) κ. ἐκωλύθην ἄρχι τοῦ δεῦρο but so far I have been prevented Ro 1:13.ⓒ oft. explicative; i.e., a word or clause is connected by means of καί w. another word or clause, for the purpose of explaining what goes before it and so, that is, namely (PPetr II, 18 [1], 9 πληγὰς … καὶ πλείους=blows … indeed many of them.—Kühner-G. II 247; B-D-F §442, 9; Rob. 1181; Mlt-Turner 335) χάριν κ. ἀποστολήν grace, that is, the office of an apostle Ro 1:5. ἀπήγγειλαν πάντα καὶ τὰ τ. δαιμονιζομένων they told everything, namely what had happened to those who were possessed Mt 8:33. καὶ χάριν ἀντὶ χάριτος that is, grace upon grace J 1:16. Cp. 1 Cor 3:5; 15:38.—Mt 21:5.—Other explicative uses are καὶ οὗτος, καὶ τοῦτο, καὶ ταῦτα (the first and last are in earlier Gk.: Hdt., X. et al.; s. Kühner-G. I 647; II 247) and, also ascensive and indeed, and at that Ἰ. Χρ., καὶ τοῦτον ἐσταυρωμένον J. Chr., (and) indeed him on the cross 1 Cor 2:2. καὶ τοῦτο Ro 13:11; 1 Cor 6:6, 8; Eph 2:8. καὶ ταῦτα w. ptc. and to be sure Hb 11:12. See B-D-F §290, 5; 425, 1; 442, 9.—The ascensive force of καί is also plain in Ῥωμαῖον καὶ ἀκατάκριτον a Roman citizen, and uncondemned at that Ac 22:25. ἔρχεται ὥρα καὶ νῦν ἐστιν an hour is coming, indeed it is already here J 5:25. προσέθηκεν καὶ τοῦτο ἐπὶ πᾶσιν καὶ κατέκλεισεν τὸν Ἰωάννην ἐν φυλακῇ added this on top of everything else, namely to put John in prison Lk 3:20.ⓓ After πολύς and before a second adj. καί is pleonastic fr. the viewpoint of modern lang. (earlier Gk.: Hom. et al. [Kühner-G. II 252, 1]; cp. Cebes 1, 1 πολλὰ καὶ ἄλλα ἀναθήματα; 2, 3; B-D-F §442, 11) πολλὰ … κ. ἄλλα σημεῖα many other signs J 20:30 (cp. Jos., Ant. 3, 318). πολλὰ κ. βαρέα αἰτιώματα many severe charges Ac 25:7. πολλὰ … καὶ ἕτερα Lk 3:18 (cp. Himerius, Or. 40 [=Or. 6], 6 πολλὰ καὶ ἄλλα). πολλοὶ καὶ ἀνυπότακτοι Tit 1:10.ⓔ introducing someth. new, w. loose connection: Mt 4:23; 8:14, 23, 28; 9:1, 9, 27, 35; 10:1; 12:27; Mk 5:1, 21; Lk 8:26; J 1:19 and oft.ⓕ καί … καί both … and, not only …, but also (Synes., Dreams 10 p. 141b καὶ ἀπιστεῖν ἔξεστι καὶ πιστεύειν.—B-D-F §444, 3; Rob. 1182; Mlt-Turner 335) connecting single expressions Mt 10:28; Mk 4:41; Ro 11:33; Phil 2:13; 4:12. κ. ἐν ὀλίγῳ κ. ἐν μεγάλῳ Ac 26:29. κ. ἅπαξ κ. δίς (s. ἅπαξ 1) Phil 4:16; 1 Th 2:18. Connecting whole clauses or sentences: Mk 9:13; J 7:28; 9:37; 12:28; 1 Cor 1:22. Introducing contrasts: although … yet (Anthol. VII, 676 Δοῦλος Ἐπίκτητος γενόμην καὶ σῶμʼ ἀνάπηρος καὶ πενίην ῏Ιρος καὶ φίλος ἀθανάτοις ‘I was Epictetus, a slave; crippled in body and an Iros [a beggar in Hom., Od.] in poverty, but dear to the Immortals’) J 15:24; Ac 23:3. καὶ … κ. οὐ Lk 5:36; J 6:36. καὶ οὐ … καί 17:25; κ. … κ. now … now Mk 9:22. On τὲ … καί s. τέ 2c. Somet. w. ἤ q.v. 1aβ.—HCadbury, Superfluous καί in the Lord’s Prayer (i.e. Mt 6:12) and Elsewhere: Munera Studiosa (=WHatch Festschr.) ’46.② marker to indicate an additive relation that is not coordinate to connect clauses and sentences, also, likewise, funct. as an adv.ⓐ simply κ. τὴν ἄλλην the other one also Mt 5:39; cp. vs. 40; 6:21; 12:45; Mk 1:38; 2:26; 8:7 and oft. Freq. used w. pronouns κἀγώ (q.v.). καὶ σύ Mt 26:73. κ. ὑμεῖς 20:4, 7; Lk 21:31; J 7:47 and oft. κ. αὐτός (s. αὐτός 1f).ⓑ intensive: even Mt 5:46f; 10:30; Mk 1:27; Lk 10:17; J 14:9 v.l.; Ac 5:39; 22:28; Ro 9:24 (ἀλλὰ καί); 1 Cor 2:10; 2 Cor 1:8; Gal 2:17; Eph 5:12; Phlm 21; Hb 7:25; 1 Pt 4:19 (but s. d below); Jd 23; Hs 5, 2, 10; 7:1; ἔτι καὶ νῦν Dg 2:3. CBlackman, JBL 87, ’68, 203f would transl. Ro 3:26b: … even in the act of declaring righteous (cp. the gen. abs. Polemon Soph. B 14 Reader καὶ Δάτιδος ἀποπλέοντος=even though Datis was sailing away). In formulas expressing a wish: ὄφελον καί if only, would that Gal 5:12. In connection w. a comparative: κ. περισσότερον προφήτου one who is even more than a prophet Mt 11:9. κ. μείζονα ποιήσει J 14:12.ⓒ In sentences denoting a contrast καί appears in var. ways, somet. in both members of the comparison, and oft. pleonastically, to our way of thinking καθάπερ …, οὕτως καί as …, thus also 2 Cor 8:11. ὥσπερ …, οὕτως καί (Hyperid. 1, 2, 5–8) Ro 5:19; 11:30f; 1 Cor 11:12; 15:22; Gal 4:29. ὡς …, οὕτως καί Ro 5:15, 18. ὸ̔ν τρόπον …, οὕτως καί 2 Ti 3:8.—οὕτως καί thus also Ro 6:11. ὡσαύτως καί in the same way also 1 Cor 11:25. ὁμοίως καί (Jos., Bell. 2, 575) J 6:11; Jd 8. ὡς καί Ac 11:17; 1 Cor 7:7; 9:5. καθὼς καί Ro 15:7; 1 Cor 13:12; 2 Cor 1:14; Eph 4:17. καθάπερ καί Ro 4:6; 2 Cor 1:14.—καί can also stand alone in the second member w. the mng. so also, so. ὡς … καί Mt 6:10; Ac 7:51; Gal 1:9; Phil 1:20. καθὼς … καί Lk 6:31 v.l.; J 6:57; 13:15; 1 Cor 15:49.—οἷος …, τοιοῦτος καί 1 Cor 15:48. After a comp. ὅσῳ καί by so much also Hb 8:6. καί is found in both members of the comparison (s. Kühner-G. II 256; 2 Macc 2:10; 6:14) Ro 1:13; 1 Th 2:14. καθὼς καὶ … οὕτως καί Col 3:13 (cp. Hyperid. 1, 40, 20–25 ὥσπερ καὶ … οὕτω καί; 3, 38).ⓓ w. expressions that introduce cause or result, here also pleonastic to a considerable degree διὰ τοῦτο καί for this reason (also) Lk 11:49; J 12:18. διὸ καί Lk 1:35; Ac 10:29; Ro 4:22; Hb 13:12. εἰς τοῦτο καί 2 Cor 2:9. ὥστε καί 1 Pt 4:19 (but this pass. may well fit in b). ὅθεν καί Hb 7:25; 11:19.ⓔ after an interrogative (as Thu., X., et al.; s. Kühner-G. II 255. S. also B-D-F §442, 14) at all, still ἱνατί καὶ τ. γῆν καταργεῖ; Lk 13:7. τί καί; (Hyperid. 3, 14 τί καὶ ἀδικεῖ; what kind of wrong, then, is he committing?) τί καὶ ἐλπίζει; why does he still (need to) hope? Ro 8:24. v.l. τί καὶ βαπτίζονται; why are they baptized (at all)? 1 Cor 15:29; cp. vs. 30.ⓕ used w. a relative, it oft. gives greater independence to the foll. relative clause: Mk 3:14; Lk 10:30; J 11:2 v.l.; Ac 1:3, 11; 7:45; 10:39; 11:30; 12:4; 13:22; 28:10; Ro 9:24; 1 Cor 11:23; Gal 2:10; Col 1:29 al.ⓖ used pleonastically w. prep.α. μετά (BGU 412, 6 μετὰ καὶ τ. υἱοῦ) Phil 4:3.β. σύν (ins in PASA III 612; PFay 108; BGU 179, 19; 515, 17) 1 Cl 65:1.—Dssm., NB 93 (BS 265f).ⓗ w. double names ὁ καί who is also called … (the earliest ex. in a fragment of Ctesias: 688 Fgm. 15, 51 p. 469, 23 Jac. ῏Ωχος καὶ Δαρειαῖος [s. Hatch 141]; OGI 565; 574; 583; 589; 603; 604; 620; 623; 636; POxy 45; 46; 54; 101; 485; 1279; PFay 30; BGU 22, 25; 36, 4; Jos., Ant. 1, 240; 5, 85; 12, 285; 13, 320; 18, 35. Further material in WSchmid, Der Atticismus III 1893, 338; Dssm., B 181ff [BS 313–17]. Lit. in B-D-F §268, 1) Σαῦλος, ὁ καὶ Παῦλος Ac 13:9. Ἰγνάτιος, ὁ καὶ Θεοφόρος ins of all the letters of Ign.ⓘ with other particlesα. καὶ γάρ for (s. γάρ 1b).—καὶ γὰρ … ἀλλά (or granted that … but) 2 Cor 13:4; Phil 2:27.—καὶ γὰρ οὐ(κ): neither 1 Cor 11:9; for even … not 2 Cor 3:10.β. καί γε (without intervening word [opp. earlier Gk, e.g. Pla., Phd. 58d; Rep. 7, 531a]: Hippocr., Septim. 9, VII 450 Littré; Cornutus p. 40, 12; Περὶ ὕψους 13, 2; Rhetor Apsines [III A.D.] p. 332, 17 Hammer; TestReub 4:4 al.; for גָּם always in Theod. [DBarthélemy, Les devanciers d’Aquila ’63, 31ff]), weakened force: (if) only or at least Lk 19:42 v.l.; intensive: indeed (Jos. Ant 29, 19) Ac 2:18 (J 3:2 v.l.; Mel., P. 30, 207); Hm 8:5; 9:9. καί γε οὐ μακράν= and indeed God is not far Ac 17:27.—Kühner-G. II 176b; Schwyzer II 561; B-D-F §439, 2; Rdm.2 35–37.γ. καὶ … δέ and also, but also (s. δέ 5b).δ. καίτοι (Il. 13, 267 et al., ins, pap; 4 Macc 2:6; 5:18; 7:13; Ath. 8, 1 al.; Mel., P. 58, 422) particle (B-D-F §425, 1; 450, 3; Rob. 1129 and 1154) w. finite verb (Chion, Ep. 3, 1; Jos. Ant. 5, 78) yet, on the other hand Ac 14:17. W. gen. abs. foll. (BGU 850, 4 [76 A.D.] καίτοι ἐμοῦ σε πολλὰ ἐρωτήσαντος; 898, 26; Philo, Vi. Mos. 1, 20; Jos., Ant. 2, 321; Ath. 19, 2; 25, 2) Hb 4:3.—καίτοι γε or καί τοι γε (since Aristoph., Ach. 611; but esp. in later Gk. [cp. Schwyzer II 561; MMeister, De Aiocho dial., Breslau diss. 1915 p. 31, 5]; Ps.-Pla., Axioch. 364b; Jos., Bell. 1, 7, Ant. 5, 36; Epict. 3, 24, 90; Just., A II, 11, 2; D. 7, 3; Ath. 3, 1; 22, 7; SIG 685, 76 and 82 [139 B.C.]) although J 4:2; Ac 14:17 v.l.; Dg 8:3. W. part. foll. (Jos., C. Ap. 1, 230; Mel., P. 58, 422) AcPt Ox 849, 18.—Kühner-G. II 151f; B-D-F §439, 1; 450, 3.—For ἀλλὰ κ., δὲ και, ἐὰν κ., εἰ κ., ἢ κ. s. ἀλλά, δέ, ἐάν, εἰ, ἤ.—ERobson, KAI-Configurations in the Gk. NT, 3 vols. diss. Syracuse ’79. LfgrE s.v. καί col. 1273f (lit.). DELG. M-M. EDNT. -
84 Отсутствие артиклей перед существительными, которые снабжены ссылками
It follows from Theorem 1 that $x=1$Section 2 of this paper gives (contains) a concise presentation of the notation to be used belowProperty 1 is called (known as) the triangle inequalityThis assertion (statement, proposition) has been proved in part 1 (part (a)) of the (our) proofAlgorithm 1 (с большой буквы) defines elementary permutations and elementary triangle matrices of index 2Equation (1) ((the) inequality (1)) can thus be written in the (артикль обязателен) form (2)In the language of our notation, algorithm (1) (с маленькой буквы) is a stable way of computing the inner productThe only place where the algorithm can break down is in statement 3 (in Statement 3)We combine Exercises 1 and 2 to construct an algorithm for finding an approximate eigenvectorThis case is illustrated in (но не on) Figure 1The asymptotic formula (1) was proved in Example 1Corollary 1 can be used to estimate the error in the inverse of a perturbed matrixBy property 1 (by Theorem 1), this function is positive except at the zero vectorA less trivial example is given in Appendix 3Step 1 in Example 1 and steps 2 and 3 in Example 2The idea of a norm will be introduced in Chapter 4Now from statements 2 and 3 of (1), we have...All the drivers for solving linear systems are listed in Table 1 (are illustrated in Figure 1)If Algorithm 1 in four-digit arithmetic is applied to refine $x$, then we obtain...Assertion (ii) is nothing but the statement that one natural way of extending these ideas to $R^n$ is to generalize formula (1) to obtain a Euclidean length of a vectorBy property 1, this function is positive except at the zero vectorWe have seen on page 3 that set of matrices is a vector space which is essentially identical with...Equation (1) effectively gives an algorithm for using the output of Algorithm 1 to solve...Русско-английский словарь по прикладной математике и механике > Отсутствие артиклей перед существительными, которые снабжены ссылками
-
85 ó-
usually reduced to o- when unstressed a prefix "used in words describing the meeting, junction, or union of two things or persons, or of two groups thought of as units". In omentië, onóna, ónoni, q.v. WJ:367, PE17:191; in the Etymologies, stem WŌ, the prefix o-, ó- is simply defined as "together". In VT43:29 is found a table showing how pronominal endings can be added to the preposition ó-; the resulting forms are onyë or óni *"with me", ómë *"with us" also in VT43:36, where "us" is said to be exclusive, ólyë or ólë *"with you" olyë only sg. "you", whereas ólë can be either sg. or pl., ósë *"with him/her", ótë *"with them" of animates where "them" refers to non-persons, óta or shortened ót is used, though the conceptual validity of ta as a pl. pronoun is questionable, ósa or shortened ós "with it". Two additional forms, ótar and ótari, presumably mean with them of inanimate things; see VT49:56 for a possible second attestation of tar as the word for plural inanimate they. However, Tolkien's later decision to the effect that ó- refers to two parties only may throw doubt upon the conceptual validity of some of these forms, where at least three persons would be implied like ótë "with them", where one person is "with" two or more others though Tolkien indicates that two groups may also be involved where the preposition ó- is used. The explicit statement in WJ:367 that the prepostion o variant of ó did not exist independently in Quenya is however difficult to get around, so instead using the preposition ó/o with or without endings for "with", writers may rather use as, the form appearing in the last version of Tolkien's Quenya Hail Mary also attested with a pronominal suffix: aselyë "with you". -
86 бак
tank
-, вспомогательный — auxiliary tank
-, гидравлический — hydraulic tank /reservoir/
-, дополнительный (топливный) — extra fuel tank
-, дополнительный топливный (в центроплане) — (center wing) auxiliary fuel tank
-, дренажный (для сообщения с атмосферой) — vent tank
-, дренажный (в системе наддува гидробака) — vent tank
-, дренажный (сливной) — drain tank
-, дренажный (утечек из насоса-регулятора) — fuel drain can
- емкостью... литров — tank of... liter capacity
- (-) кессон, топливный (бакотсек) — integral fuel tank
бак, образованный элементами конструкции крыла (стенками лонжеронов и обшивками). — a fuel tank built within the normal contours of an aircraft and using the skin of the vehicle as a wall of the tank.
- (-) кессон, силовой — torsion box integral fuel tank
-, консольный (на законцовке крыла) — wingtip tank
-, концевой (крыльевой) — tip tank
-, крыльевой — wing tank
-, масляный — oil tank
резервуар для масла, входящий в масляную систему двигателя самолета. — oil reservoir incorporated in the engine oil system.
-, мягкий (топливный) — flexible fuel tank, bladder-type
бак нежесткой конструкции, изготовленный из эластичных материалов. — cell
- неправильной формы — irregularly-shaped tank
-, непротектированный — unprotected tank
-, отдельный топливный — separate fuel tank
-, основной топливный — main fuel tank
- отрицательных перегрузок (топливный) — recuperator
- (-) отсек, топливный (баккессон) — integral fuel tank /cell/
межлонжеронное пространство крыла используется в качестве топливного бакакессона. — the space between wing spars is devoted to form integral fuel tank.
- (второй, первой) очереди (топливный) — (second, first) fuel consumed tank
- очередной (перекачки топлива) — alternate fuel tank
-, перегоночный (топливный) — ferry tank
- перекачки (топливный) топливо в основные баки обычно перекачивается из баков перекачки. — alternate fuel tank the main tank is normally replenished from its alternate tank.
- подачи топлива в перевернутом полете — recuperator
-, подвесной — external tank
-, подвесной (сбрасываемый) — drop tank
-, подкрыльевой (подвесной) — under-wing tank
-, подфюзеляжный (подвесной) — ventral tank
-, полный — full tank
- правильной формы — regularly-shaped tank
-, предрасходный топливный — alternate fuel tank (alt)
топливо перекачивается из основных в предрасходные, а затем в расходные баки. — the fuel is transferred from the main to alternate and then to service tanks.
- приемный (канализационной системы) — waste tank
-, промежуточный топливный — alternate fuel tank
-, протектированный — self-sealing fuel tank
бак, имеющий защитную оболочку, предотвращающую утечку при повреждении стенки бака. — capable of covering or closing small ruptures in itself, as by means of a lining substance ·
-, пустой — empty tank
-, расходный (основной, питающий двигатель) — fuel consumed (main) tank
-, расходный (специальный) — service tank
топливный резервуар, в который топливо поступает из баков топливной системы самолета для непосредственной подачи к авиационному двигателю. — a fixed fuel tank near each power unit, into which fuel from other tanks is pumped and from which the fuel supplying the engines is drawn.
- с наддувом (поддавливанием) — pressurized tank
-, сбрасываемый — drop tank
-, сбрасываемый принудительно — jettisonable tank
-, сливной (туалетный) — waste tank
-, топливный — fuel tank
-, топливный в горизонтальном гребне (фюзеляжа) — strake fuel tank array
-, туалетный (приемный) — waste tank
- фасонной формы — irregularly-shaped tank
-, фюзеляжный — fuselage tank
вместимость б. — tank capacity
объем б. (вместимость) — capacity
объем б. (геометрический) — tank volume
перезаливка б. — tank overflow
поддавливание б. — tank pressurization
промывка б. — tank flushing
содержимое б. — tank contents
заправлять б. — fill the tank
заправлять б. маслом — fill the tank with oil
заправлять б. полностью — fill the tank to full capacity
заправлять б. топливом — fuel the tank
поддавливать б. — pressurize the tank
промывать б. — flush the tank
расходовать из б. — use fuel from the tank
сливать масло (топливо) из б. — drain oil (fuel) from the tank
сливать б. — drain the tank
тарировать б. — calibrate the tankРусско-английский сборник авиационно-технических терминов > бак
-
87 Anthemios of Tralles
SUBJECT AREA: Architecture and building[br]fl. sixth century AD Tralles, Lydia, Asia Minor[br]Greek architect, geometer, mathematician and physicist.[br]Tralles was a wealthy city in ancient Greece. Ruins of the city are situated on a plateau above the present-day Turkish city of Aydin, in Asia Minor, which is near to Ephesus. In 334 BC Tralles was used as a base by Alexander the Great and later it was occupied by the Romans. After the collapse of the western half of the Roman Empire in the fifth century AD Tralles remained a part of the Byzantine Empire until its destruction in 1282. Anthemios was one of the great sons of Tralles and was probably educated in Alexandria. He is especially famed as architect (with Isodorus of Miletos) of the great Church of Santa Sophia in Istanbul. This vast building, later a Turkish mosque and now a museum, was built for the Emperor Justinian between 532 and 537 AD. It was an early and, certainly for many centuries, the largest example of pendentive construction to support a dome. This form, using the spherical triangles of the pendentives, enabled a circular-based dome to be supported safely upon piers that stood on a square plan below. It gradually replaced the earlier squinch type of structure, though both forms of design stem from Middle Eastern origins. At Santa Sophia the dome rises to 180ft (55m) above floor level and has a diameter of over 100ft (30m). Together with Isodorus, Anthemios also worked upon the Church of the Holy Apostles in Istanbul.[br]Further ReadingG.L.Huxley, 1959, Anthemius of Tralles: A Study in Later Greek Geometry, Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press.Procopius, 1913, De Aedificiis, On the Buildings Constructed by the Emperor Justinian, Leipzig.Richard Krautheimer, 1965, Early Christian and Byzantine Architcture, Penguin.DY -
88 Coffey, Aeneas
SUBJECT AREA: Chemical technology[br]b. 1779/80 Englandd. 26 November 1852 Bromley, England[br]English inventor of the Coffey still for fractional distillation.[br]As Surveyor and Inspector General of Excise in Ireland, Coffey was responsible for the suppression of the illicit distilling of alcohol. In 1818 he published a pamphlet refuting charges of oppression and brutality brought against him by Irish revenue officers. He seems to have hunted with the hounds, for as a distiller himself in Dublin, he patented in 1831 the improved form of still that bears his name. The still was quickly adopted by the whisky industry as it accomplished in a single operation what had previously required several stages using the old pot stills. It is still used in the making of potable spirits, and consists of two adjacent columns, an analyser and a rectifier. Steam is passed through the liquor in the analyser, which removes the volatile fraction, and is then fractionally condensed in the rectifier column; almost pure alcohol could be produced by this means.[br]Further ReadingE.J.Rothery, 1968, Annals of Science 24:53.LRD -
89 γαζοφυλάκιον
γαζοφυλάκιον, ου, τό (v.l. γαζοφυλακεῖον N25 but-φυλάκιον preferred by B-D-F §13; s. DELG s.v. φύλαξ)① a place for the storing of valuables, treasure room, treasury (Diod S 9, 12, 2; Strabo 7, 6, 1; OGI 225, 16; Esth 3:9; 1 Macc 3:28). In this sense our sources of information on the Jerusalem temple speak of γαζοφ. in the pl. (2 Esdr 22: 44; Jos., Bell. 5, 200; 6, 282) and sg. (1 Macc 14:49; 2 Macc 3:6, 24, 28, 40; 4:42; 5:18; 2 Esdr 23: 5, 7; Jos., Ant. 19, 294). It can be taken in this sense J 8:20 (sing.) in (or at) the treasury (for the use of ἐν in the sense of ‘near’ [the public would of course not be permitted in the treasure room(s)] see s.v. ἐν 1c. But it is quite prob. that J may be using the term γ. loosely of the area generally known as the ‘treasury’, which would have the equivalent of a vault; the prep. would then be used in its customary locative sense).② For Mk 12:41, 43; Lk 21:1 the mng. contribution box or receptacle is attractive. Acc. to Mishnah, Shekalim 6, 5 there were in the temple 13 such receptacles in the form of trumpets. But even in these passages the general sense of ‘treasury’ is prob., for the contributions would go the treasury via the receptacles.—Billerb. II 37–46. GKaminski, JDAI 106, ’91, 63–181.—M-M.Ελληνικά-Αγγλικά παλαιοχριστιανική Λογοτεχνία > γαζοφυλάκιον
-
90 линейный регулируемый источник электропитания
линейный регулируемый источник электропитания
-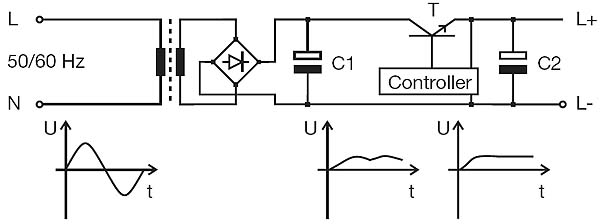
Рис. ABBThe AC mains voltage is transformed to a lower level, rectified and smoothed by capacitor C1. Then, voltage regulation is performed, typically using a power transistor. The power transistor acts as a variable resistor, controlled to keep the output voltage constant.
The efficiency of linearly regulated power supplies is only approx. 50 % due to the high losses inside the power transistor. The remaining energy is emitted in the form of heat. Due to this, sufficient ventilation is required to cool the power supply. Compared with unregulated power supplies, linearly regulated power supplies have a very small residual ripple of the output voltage (in the dimension of millivolts).
Linearly regulated power supplies are used for all applications that require a very exact output voltage, e.g. for highly precise medical devices.
[ABB]Тематики
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > линейный регулируемый источник электропитания
-
91 estar seguro
v.1 to be sure, to be certain, to be clear, to know one's own mind.María está segura Mary is sure.2 to be safe.El barco está seguro The boat is safe.* * *= be sure, make + sure, set + your watch byEx. Inconsistencies are mostly merely annoying, although it can be difficult to be sure whether a group of citations which look similar all relate to the same document.Ex. DOBIS/LIBIS first checks the borrower's number to make sure that it is in the files and is valid.Ex. There are a few things you can count on; I mean really set your watch by in life.* * *estar seguro(de)(v.) = be certain (of), be confident about, feel + confidentEx: Using this in-depth search system, you can be certain you are conducting your search in the most efficient and accurate way.
Ex: Such variations make it difficult for users to be confident about the form of a heading.Ex: Most consumers felt confident that once a letter is written and posted, no one will read it either accidently or on purpose except for the intended addressee.= be sure, make + sure, set + your watch byEx: Inconsistencies are mostly merely annoying, although it can be difficult to be sure whether a group of citations which look similar all relate to the same document.
Ex: DOBIS/LIBIS first checks the borrower's number to make sure that it is in the files and is valid.Ex: There are a few things you can count on; I mean really set your watch by in life. -
92 arroba
f.1 at, \@ symbol (computing) (en dirección de correo electrónico).2 twenty five pounds.3 at sign.pres.indicat.3rd person singular (él/ella/ello) present indicative of spanish verb: arrobar.* * *1 (medida de peso) measure of weight equal to 11.502 kg, 25.3 lbs; (medida de capacidad) variable liquid measure\por arrobas heaps of, stacks of, loads of* * *SF1) (=medida de peso) 25 pounds; (=medida de líquidos) a variable liquid measuretiene talento por arrobas — he has loads of talent, he oozes talent *
2) (Internet) [en dirección electrónica] at* * *1)b) ( medida de capacidad) unit of liquid measure of between 12 and 16 liters (US 25-34 pts, Brit. 21-28 pts) according to region2) ( en dirección electrónica) at, \@* * *1)b) ( medida de capacidad) unit of liquid measure of between 12 and 16 liters (US 25-34 pts, Brit. 21-28 pts) according to region2) ( en dirección electrónica) at, \@* * *arroba(\@)= \@ (at).Nota: Símbolo utilizado antiguamente en el comercio marítimo para representar la "ánfora" (vasija de dos asas) como unidad de transporte y peso.Ex: If any of you have questions and want to send me e-mail, my address is saunders\@novelnet.org.
* * *A feminine2 (medida de capacidad) unit of liquid measure of between 12 and 16 liters (US 25-34 pts, Brit. 21-28 pts) according to regionpor arrobas: nos dieron comida/vino por arrobas they gave us large quantities of o ( colloq) loads of food/wineB (en dirección electrónica) at, \@* * *
Del verbo arrobar: ( conjugate arrobar)
arroba es:
3ª persona singular (él/ella/usted) presente indicativo2ª persona singular (tú) imperativo
Multiple Entries:
arroba
arrobar
arroba sustantivo femenino
1 ( en dirección electrónica) at, at sign
2 Hist
arroba f (medida) Spanish unit of weight and of liquid measure, varying according to region
* * *arroba nf1. [unidad de peso] = 11.5 kg;Figpor arrobas by the sackful2. [unidad de volumen] [para vino] = approx 16 litres;[para aceite] = approx 12 litres“juan, arroba mundonet, punto, es” “juan, at mundonet, dot, es”ARROBA “\@”In standard Spanish grammar, where nouns, adjectives and pronouns have masculine and feminine forms, the masculine plural form is used when referring to a group which includes men and women (cf. the now old-fashioned use of “mankind” to mean “all humanity” in English). Although this is an inheritance from Latin, it has been criticized by many who say it “makes women invisible”. However, unless one explicitly uses both forms in full (“ellos y ellas” or “alumnos y alumnas” etc), the rules of grammar dictate the choice. In recent years, however, an informal alternative has emerged using the “\@” symbol, and this has become especially popular on the Internet. Thus “hola a tod\@s” (hello everyone) can stand for “todos” and “todas”. This usage has been criticised and has yet to migrate into formal written contexts, and there is no spoken equivalent (other than the wordy “hola a todos y todas”), but it is a sign that even in a gender-inflected language like Spanish there are moves to get round gender stereotyping.* * *f INFOR at sign, \@;josé arroba … josé at …* * *arroba nf: arroba (Spanish unit of measurement) -
93 Πλειάδες
Πλειάδες, [dialect] Ep. and [dialect] Ion. [full] Πληϊάδες ([dialect] Aeol. [full] Πληΐαδες Sapph.52), αἱ,II later in sg., of the whole constellation, esp. in notes of time, at the setting of the P.,Hp.
Epid.1.1;πρὸ Πλειάδος ἐπιτολῆς Arist.HA 553b31
; ἀπὸ Πλειάδος ἀνατολῆς ib. 599b10; μετὰ Πλειάδα ib. 598b7; ἀπὸ Πλειάδος δύσεως ib. 599a28; περὶ Πλειάδος δύσιν ib. 542b22; πρὸς δύσιν Πλειάδος χειμερινήν ib. 566a21;Σείριος ἐγγὺς τῆς ἑπταπόρου Π. ᾄσσων E.IA8
(anap.), cf. Ion 1152: in sg., also a name given to the seven best Alexandrian tragic poets, Heph.9.4, Choerob. in Heph.p.236 C., Suid. s.v. Ἀλέξανδρος Αἰτωλός, al. ( Πλειάδες is perh. derived from πλέω, sail, because they rose at the beginning of the sailing-season (if so Πληϊάδες is metri gr. for Πλε (ϝ) ϊάδες).—Poets (Hes.Frr.177, 178, 179, Pi.N.2.11, A.Fr. 312), using the lengthened form Πελειάδες (Alcm.23.60, gen. sg. (lyr.)), represented them as doves flying before the hunter Orion.)Greek-English dictionary (Αγγλικά Ελληνικά-λεξικό) > Πλειάδες
-
94 μοχλός
Grammatical information: m.Meaning: `lever, bar, long, strong bar', often used to shut off doors, `crossmeam, -bar' (Od.).Other forms: μοκλός Anakr. 88Derivatives: Diminut. μοχλ-ίον ( Com. Adesp., Luc.), - ίσκος (Hp., Ar.), μοχλ-ικός `regarding the lever' (Hp., Ph. Bel.) and the verbs 1. μοχλεύω, also with ἀνα-, ἐκ-, `(re)move with a lever' (ion. poet., also late prose) with μοχλ-εία `removing with a lever, restore with a lever' (Arist., medic.), - ευσις `id.' (Hp.), - ευτής (Ar.), - ευτικός `belonging to using the lever' (medic.); 2. μοχλέω `id.' (M 259); 3. μοχλόω `shut with a bar' (Ar.).Origin: PG [a word of Pre-Greek origin]Etymology: One supposed *μογ-σλο-ς with the same instrumental suffix as e.g. in Lat. pālus `pole' \< *paḱ-slos (cf. on πάσσαλος and μύχλος). Acc. to Chantraine Form. 240 rather with λο-suffix and expressive aspiration. The basis is in any case the same word (verb?) as in μόχθος and μογέω (s. vv.). -- Schulze KZ 28, 270 n. 1 = Kl. Schr. 437 n. 1 (p. 438) identified μοχλός with a from Lat. mōlior reconsructed * mōlos `lever'; diff. on mōlior W.-Hofmann s.v. To be rejected Pisani Ist. Lomb. 73, 528: to Skt. myakṣ- `sit fast' as also in μόχθος. - The variation and the connection with μόχθος and μογέω shows that the word is Pre-Greek.Page in Frisk: 2,262Greek-English etymological dictionary (Ελληνικά-Αγγλικά ετυμολογική λεξικό) > μοχλός
-
95 Gruß
einen [schönen] \Gruß an Ihre Gattin [please] give my [best] regards to your wife;liebe Grüße auch an die Kinder give my love to the children, too;ohne \Gruß without saying hello/goodbye;zum \Gruß as a greeting;sie reichten die Hände zum \Gruß they shook hands2) ([Floskeln am] Briefschluss) regards;mit kollegialen Grüßen Yours sincerely;herzliche Grüße best wishes;\Gruß und Kuss ( fam) love [and kisses]WENDUNGEN:der Deutsche \Gruß hist the Nazi salute;der Englische \Gruß rel the Ave Maria;viele Grüße vom Getriebe, Gang kommt nach! (Gang kommt nach!) greetings from the gearbox, how about using the clutch! ( hum) -
96 в виде
( чего)1) (в форме чего-либо, наподобие чего-либо) in the form of smth.; shaped like smth.С горы видно, как между каменными корпусами завода стекают вниз к морю, к пирсам, триумфальными арками, в виде гигантской буквы Н, бетонные устои канатной дороги. (Ф. Гладков, Цемент) — One could see, between the grey buildings of the works, an overhead cable-line stretching down to the sea, upon triumphal concrete arches, each shaped like a gigantic 'H'.
2) ( в качестве чего-либо) by way of smth.; asСлово "поэзия" вам смешно, вы употребляете его в виде насмешливого упрёка. (Л. Толстой, Из записок князя Нехлюдова) — The word 'poetry' is ridiculous for you; hence your using it by way of a derisive reproach.
-
97 hot-desking
Gen Mgta flexible working practice enabling employees to occupy any vacant workspace instead of sitting at a permanent personalized desk. Organizations using a hot-desking system may have a set of standardized workspaces equipped with information and communications technologies, and employees may sit at a different desk each day. Alternatively, the majority of employees may have their own desks, but some employees, such as consultants or parttime workers, may sit at any desk that happens to be free that day. Most conventional offices are only full for a fraction of the time they are open because of sickness, vacations, or teleworking and this results in empty desks and wasted resources. Hot-desking enables expensive office space to be fully utilized and forms part of the concept of the virtual office. Although employees practicing hot-desking may have limited storage space in the form of a filing cabinet or locker, most of their work and information will be stored electronically. -
98 преобразование
transformation, transform, mapping, operator, map, conversion, processing, rearranging, changing• В результате преобразования уравнение (1) становится (= принимает вид)... - After simplification equation (1) becomes...• Очевидно, что такое преобразование производит... - Obviously, such a transformation produces...• Поразительный пример подобного преобразования возникает в связи с... - A striking example of such a transformation appears in connection with...• Преобразование градусной меры в радианную является задачей на пропорции. - The conversion of degrees to radians is just a proportion problem.• Проделав некоторые преобразования/, мы можем доказать... - After some manipulation, it can be proved that...• Путем небольшого преобразования можно показать зависимость этой формулы от... - With a little manipulation this formula can be shown to depend on...• С целью упрощения алгебраических преобразований мы будем... - In order to simplify the algebra we shall...• С этим преобразованием связаны две проблемы. - There are two problems with this arrangement.• Стандартное преобразование затем дает... - Standard manipulation then gives...• Таким образом, искомое преобразование было найдено в терминах... - Thus, the desired transformation has been found in terms of...• Такое преобразование позволяет... - Such an arrangement permits...• Теперь мы обсудим полезное преобразование... - We now discuss a useful transformation of...• Уже знакомыми преобразованиями мы... - By familiar manipulations we...• Это может быть проделано путем преобразования уравнения (1) к следующей форме... - This may be accomplished by rearranging Eq. (1) in the form...• Это преобразование можно также произвести графически, используя... - This transformation may also be performed graphically using...• Это преобразование не особо желательно, потому что... - This arrangement is not particularly desirable because... -
99 estar seguro (de)
(v.) = be certain (of), be confident about, feel + confidentEx. Using this in-depth search system, you can be certain you are conducting your search in the most efficient and accurate way.Ex. Such variations make it difficult for users to be confident about the form of a heading.Ex. Most consumers felt confident that once a letter is written and posted, no one will read it either accidently or on purpose except for the intended addressee. -
100 paint
[peɪnt]1. nouna colouring substance in the form of liquid or paste:دُهان( also adjective) a paint pot.
2. verb1) to spread paint carefully on (wood, walls etc):يَدْهَنHe is painting the kitchen.
2) to make a picture (of something or someone) using paint:يَرْسُمShe painted her mother and father.
См. также в других словарях:
The Freewheelin' Bob Dylan — Infobox Album Name = The Freewheelin Bob Dylan Type = Album Artist = Bob Dylan Released = May 27, 1963 Recorded = April 241962 – April 241963 at Columbia Studios, New York City Genre = Folk Length = 50:08 Label = Columbia Producer = John H.… … Wikipedia
The Lord of the Rings Strategy Battle Game — Players 2+ Setup time < 10 minutes Playing time ≈1 hour per 500 points of miniatures (approx.) Random chance Medium High … Wikipedia
The Culture — is a fictional interstellar anarchist, socialist, and utopian[1][2] society created by the Scottish writer Iain M. Banks which features in a number of science fiction novels and works of short fiction by him, collectively called the Culture… … Wikipedia
The Mote in God's Eye — … Wikipedia
The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen timeline — The League of Extraordinary Gentlemen is an ongoing graphic novel series written by Alan Moore and illustrated by Kevin O Neill. The primary commentator on the League of Extraordinary Gentlemen series (hereto after in this article referred to as… … Wikipedia
The Go-ongers — The nihongo|Go ongers|ゴーオンジャー|Gōonjā are the fictional eponymous protagonists of the Japanese Super Sentai series Engine Sentai Go onger . They are chosen by fictional sentient vehicles known as Engines to battle the evil Barbaric Machine Clan… … Wikipedia
The Chronicles of Amber — is group of novels that comprise a fantasy series written by Roger Zelazny. The main series consists of two story arcs, each five novels in length. Additionally, there are a number of Amber short stories and other works. The Amber stories take… … Wikipedia
The Amazing Race — sometimes referred to as TAR, is a reality television game show in which teams of two people (with one exception), who have some form of a preexisting personal relationship, race around the world in competition with other teams. Contestants stri … Wikipedia
The Cantos — by Ezra Pound is a long, incomplete poem in 120 sections, each of which is a canto . Most of it was written between 1915 and 1962, although much of the early work was abandoned and the early cantos, as finally published, date from 1922 onwards.… … Wikipedia
The Legend of Dragoon — North American box art Developer(s) SCEI Publisher(s) … Wikipedia
The World Ends with You — Left to right, Joshua, Neku, Beat (above), Shiki, and Rhyme Developer(s) Square Enix Jupiter … Wikipedia
