-
1 воздействие производства энергии на окружающую среду
воздействие производства энергии на окружающую среду
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
environmental impact of energy
Energy and environmental problems are closely related, since it is nearly impossible to produce, transport, or consume energy without significant environmental impact. The environmental problems directly related to energy production and consumption include air pollution, water pollution, thermal pollution, and solid waste disposal. The emission of air pollutants from fossil fuel combustion is the major cause of urban air pollution. Diverse water pollution problems are associated with energy usage. One major problem is oil spills. In all petroleum-handling operations, there is a finite probability of spilling oil either on the earth or in a body of water. Coal mining can also pollute water. Changes in groundwater flow produced by mining operations often bring otherwise unpolluted waters into contact with certain mineral materials which are leached from the soil and produce an acid mine drainage. Solid waste is also a by-product of some forms of energy usage. Coal mining requires the removal of large quantities of earth as well as coal. In general, environmental problems increase with energy use and this combined with the limited energy resource base is the crux of the energy crisis. An energy impact assessment should compare these costs with the benefits to be derived from energy use. (Source: RAU)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > воздействие производства энергии на окружающую среду
-
2 компенсация реактивной мощности
компенсация реактивной мощности
-EN
reactive power compensation
an action to optimize the transmission of reactive power in the network as a whole
[МЭС 603-04-28]FR
compensation de l'énergie réactive
action dont le but est d'optimiser globalement le transport d'énergie réactive dans le réseau
[МЭС 603-04-28]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Reactive energy management
In electrical networks, reactive energy results in increased line currents for a given active energy transmitted to loads.
The main consequences are:
• Need for oversizing of transmission and distribution networks by utilities,
• Increased voltage drops and sags along the distribution lines,
• Additional power losses.
This results in increased electricity bills for industrial customers because of:• Penalties applied by most utilities on reactive energy,
• Increased overall kVA demand,
• Increased energy consumption within the installations.
Reactive energy management aims to optimize your electrical installation by reducing energy consumption, and to improve power availability.
Total CO2 emissions are also reduced.
Utility power bills are typically reduced by 5 % to 10 %.
[Schneider Electric]Компенсация реактивной мощности
Передача по электрической сети реактивной энергии приводит к увеличению линейных токов (по сравнению токами, протекающими при передаче нагрузкам только активной энергии).
Основные последствия этого явления:
● необходимость увеличения сечения проводников в сетях передачи и распределения электроэнергии;
● повышенное падение и провалы напряжения в распределительных линиях;
● дополнительные потери электроэнергии;
Для промышленных потребителей такие потери приводят к возрастанию расходов на оплату электроэнергии, что вызвано:● штрафами, накладываемыми поставщиками электроэнергии за избыточную реактивную мощность;
● увеличением потребления полной мощности (измеряемой в кВА);
● повышенным энергопотреблением электроустановок.Цель компенсации реактивной мощности (КРМ) – оптимизация работы электроустановки за счет сокращения потребления энергии и увеличения надежности электроснабжения. Кроме того, КРМ позволяет уменьшить выбросы CO2 и сократить расходы на электроэнергию в среднем на 5-10 %.
[Перевод Интент]Наиболее эффективным способом снижения потребляемой из сети реактивной мощности является применение установок компенсации реактивной мощности (конденсаторных установок).
Использование конденсаторных установок позволяет:- разгрузить питающие линии электропередачи, трансформаторы и распределительные устройства;
- снизить расходы на оплату электроэнергии;
- при использовании определенного типа установок снизить уровень высших гармоник;
- подавить сетевые помехи, снизить несимметрию фаз;
- увеличить надежность и экономичность распределительных сетей.
На практике коэффициент мощности после компенсации находится в пределах от 0,93 до 0,99.
Наибольший экономический эффект достигается при размещении компенсирующих устройств вблизи электроприемников, потребляющих реактивную мощность.
Различают следующие виды компенсации:-
индивидуальная (нерегулируемая) компенсация
Целесообразна, если мощность электроприемника больше 20 кВт и потребляемая мощность постоянна в течение длительного времени.
Компенсирующая нерегулируемая установка подключается непосредственно у потребителя. Как правило, применяется для компенсации реактивной мощности таких потребителей, как мощные компрессоры, вентиляторы и насосы, силовые трансформаторы. - групповая (нерегулируемая) компенсация
- централизованная компенсация
Для ламп типа ДРЛ, ДРИ, ДРИЗ, ДНаТ может применяться как групповая, так и индивидуальная компенсация реактивной мощности
[ПУЭ]Тематики
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
- конденсатор компенсации реактивной мощности
- конденсаторная батарея компенсации реактивной мощности
- контроллер компенсации реактивной мощности
- недостаточная компенсация реактивной мощности
- перекомпенсация реактивной мощности
- потребляемая реактивная мощность
- ступень компенсации реактивной мощности
- установка КРМ
- устройства динамической компенсации реактивной мощности
EN
- energy compensation
- management of reactive energy
- power factor compensation
- reactive energy management
- reactive power compensation
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > компенсация реактивной мощности
-
3 оперирование контактного коммутационного аппарата за счет запасенной энергии
оперирование контактного коммутационного аппарата за счет запасенной энергии
Управление путем приложения энергии, накопленной в самом механизме до завершения оперирования и достаточной для доведения его до конца в заданных условиях.
МЭК 60050(441-16-15).
Примечание. Такое управление можно характеризовать:
1) способом накопления энергии (применению пружины, груза и т. п.);
2) происхождением энергии (ручной, электрической и т. п.);
3) способом высвобождения этой энергии (ручному, электрическому и т. п.).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
stored energy operation (of a mechanical switching device)
an operation by means of energy stored in the mechanism itself prior to the completion of the operation and sufficient to complete it under predetermined conditions
NOTE – This kind of operation may be subdivided according to:
1. The manner of storing the energy (spring, weight, etc.);
2. The origin of the energy (manual, electric, etc.);
3. The manner of releasing the energy (manual, electric, etc.).
[IEV number 441-16-15 ]FR
manoeuvre à accumulation d'énergie (d'un appareil mécanique de connexion)
manoeuvre effectuée au moyen d'énergie emmagasinée dans le mécanisme lui-même avant l'achèvement de la manoeuvre et suffisante pour achever la manoeuvre dans des conditions prédéterminées
NOTE – Ce type de manoeuvre peut être subdivisé suivant:
1. le mode d'accumulation de l'énergie (ressort, poids, etc.);
2. la provenance de l'énergie (manuelle, électrique, etc.);
3. le mode de libération de l'énergie (manuel, électrique, etc.).
[IEV number 441-16-15 ]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > оперирование контактного коммутационного аппарата за счет запасенной энергии
-
4 геотермальная энергия
геотермальная энергия
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
geothermal energy
An energy produced by tapping the earth's internal heat. At present, the only available technologies to do this are those that extract heat from hydrothermal convection systems, where water or steam transfer the heat from the deeper part of the earth to the areas where the energy can be tapped. The amount of pollutants found in geothermal vary from area to area but may contain arsenic, boron, selenium, lead, cadmium, and fluorides. They also may contain hydrogen sulphide, mercury, ammonia, radon, carbon dioxide, and methane. (Source: KOREN)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > геотермальная энергия
-
5 технология использования солнечной энергии
технология использования солнечной энергии
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
solar energy technology
Solar energy can be converted to useful work or heat by using a collector to absorb solar radiation, allowing much of the sun's radiant energy to be converted to heat. This heat can be used directly in residential, industrial, and agricultural operations; converted to mechanical or electrical power; or applied in chemical reactions for production of fuels and chemicals. (Source: PARCOR)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > технология использования солнечной энергии
-
6 распределительный шкаф
распределительный шкаф
Комплектное устройство шкафного типа для стационарной наружной установки, предназначенное для распределения электрической энергии посредством кабеля для другого оборудования. Это другое оборудование не предназначено для потребления электрической энергии (см. рисунок 1).
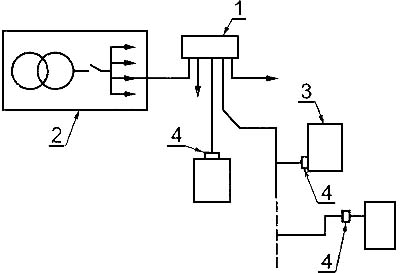
Рисунок 1 - Типовая распределительная сеть
1 - распределительный шкаф;
2 - подстанция (высокое напряжение/низкое напряжение);
3 - потребители;
4 - точки соединений
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 5-99 ( МЭК 60439-5-98)]EN
cable distribution cabinet
CDC
cubicle-type assembly for outdoor installation which in use receives electrical energy via cables from one or more substation cable distribution boards (SCDBs), and distributes that energy through one or more cables to other equipment
NOTE This other equipment is not intended to consume electrical energy.
[IEC 60439-5, ed. 2.0 (2006-06)]FR
ensemble d'appareillage pour réseau de distribution
ERD
ensemble en armoire pour installation extérieure qui, lors de son utilisation, reçoit de l’énergie électrique via des câbles d’un ou plusieurs tableaux de distribution par câbles pour poste (SCDB) et, distribue cette énergie par un ou plusieurs câbles à d’autres matériels
NOTE Ces autres matériels ne sont pas conçus pour consommer de l'énergie électrique.
[IEC 60439-5, ed. 2.0 (2006-06)]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > распределительный шкаф
-
7 входной
- entréed', qualificatif
входной
-
[IEV number 151-15-13]EN
input, adj
qualifies a port or a device through which a signal, an energy, a power or information is received by a device or an equipment, or by extension this signal, energy, power or information, or any associated quantity
NOTE – The term "input" is also used as a noun to designate an input port, an input signal, etc.
[IEV number 151-15-13]FR
entréed', qualificatif
qualifie un accès ou un dispositif par l'intermédiaire duquel un signal est appliqué, une énergie ou une puissance est fournie, ou des informations sont fournies, à un dispositif ou à un équipement; par extension, qualifie ce signal, cette énergie ou puissance, ces informations, ou toute grandeur associée
NOTE – Le terme "entrée" est aussi employé comme nom pour désigner un accès d’entrée, un signal d’entrée, etc.
[IEV number 151-15-13]EN
- input, adj
DE
- Eingangs... (in Zusammensetzungen)
FR
- entréed', qualificatif
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > входной
-
8 выходной
- de sortie, qualificatif
выходной
-
[IEV number 151-15-14]EN
output, adj
qualifies a port or a device through which a device or an equipment delivers a signal, an energy, a power or information, or by extension this signal, energy, power or information, or any associated quantity
NOTE – The term "output" is also used as a noun to designate an output port, an output signal, etc.
[IEV number 151-15-14]FR
de sortie, qualificatif
qualifie un accès ou un dispositif par l'intermédiaire duquel un dispositif ou un équipement fournit un signal, une énergie, une puissance, ou des informations; par extension, qualifie ce signal, cette énergie ou puissance, ces informations, ou toute grandeur associée
NOTE – Le terme "sortie" est aussi employé comme nom pour désigner un accès de sortie, un signal de sortie, etc.
[IEV number 151-15-14]EN
- output, adj
DE
- Ausgangs... (in Zusammensetzungen)
FR
- de sortie, qualificatif
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > выходной
-
9 граница между воздухом и поверхностью океана
граница между воздухом и поверхностью океана
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
ocean-air interface
The sea and the atmosphere are fluids in contact with one another, but in different energy states - the liquid and the gaseous. The free surface boundary between them inhibits, but by no means totally prevents, exchange of mass and energy between the two. Almost all interchanges across this boundary occur most effectively when turbulent conditions prevail. A roughened sea surface, large differences in properties between the water and the air, or an unstable air column that facilitates the transport of air volumes from sea surface to high in the atmosphere. Both heat and water (vapor) tend to migrate across the boundary in the direction from sea to air. Heat is exchanged by three processes: radiation, conduction, and evaporation. The largest net exchange is through evaporation, the process of transferring water from sea to air by vaporization of the water. (Source: PARCOR)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > граница между воздухом и поверхностью океана
-
10 испытательное выходное устройство (для счетчика энергии)
- dispositif (de sortie) d’essai (d'un compteur d'énergie)
испытательное выходное устройство (для счетчика энергии)
-
[IEV number 314-07-12]EN
te st output device (of an energy meter)
device which can be used for determining the meter error
NOTE – This device can be, for electromechanical induction meters, a mark on the disk, where the passage of the mark is detected by an external photoelectric device, or, for static meters, an internal electronic pulse emitting device.
[IEV number 314-07-12]FR
dispositif (de sortie) d’essai (d'un compteur d'énergie)
dispositif qui peut être utilisé pour la détermination de l’erreur du compteur
NOTE – Ce dispositif peut consister, pour un compteur à induction électromécanique, en une marque sur le disque, marque dont le passage est détecté par un dispositif photoélectrique extérieur, ou, pour un compteur statique, en un dispositif électronique interne émetteur d’impulsions.
[IEV number 314-07-12]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
- счетчик электроэнергии
EN
DE
FR
- dispositif (de sortie) d’essai (d'un compteur d'énergie)
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > испытательное выходное устройство (для счетчика энергии)
-
11 НКУ распределения и управления
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления (НКУ)
Низковольтные коммутационные аппараты и устройства управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования, собранные совместно, со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями и конструктивными элементами.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439-1-2012]
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления
Комбинация низковольтных коммутационных аппаратов с устройствами управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования и т. п., полностью смонтированных изготовителем НКУ (под его ответственность на единой конструктивной основе) со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями с соответствующими конструктивными элементами
Примечания
1. В настоящем стандарте сокращение НКУ используют для обозначения низковольтных комплектных устройств распределения и управления.
2. Аппараты, входящие в состав НКУ, могут быть электромеханическими или электронными.
3. По различным причинам, например по условиям транспортирования или изготовления, некоторые операции сборки могут быть выполнены на месте установки, вне предприятия-изготовителя.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]EN
power switchgear and controlgear assembly (PSC-assembly)
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly used to distribute and control energy for all types of loads, intended for industrial, commercial and similar applications where operation by ordinary persons is not intended
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
combination of one or more low-voltage switching devices together with associated control, measuring, signalling, protective, regulation equipment, etc., completely assembled under the responsibility of the manufacturer with all the internal electrical and mechanical interconnections and structural parts.
[IEC 61892-3, ed. 2.0 (2007-11)]
switchgear and controlgear
a general term covering switching devices and their combination with associated control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment, also assemblies of such devices and equipment with associated interconnections, accessories, enclosures and supporting structures
[IEV number 441-11-01]
switchgear and controlgear
electric equipment intended to be connected to an electric circuit for the purpose of carrying out one or more of the following functions: protection, control, isolation, switching
NOTE – The French and English terms can be considered as equivalent in most cases. However, the French term has a broader meaning than the English term and includes for example connecting devices, plugs and socket-outlets, etc. In English, these latter devices are known as accessories.
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
switchboard
A large single electric control panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted (either on the back or on the face, or both) switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and usually instruments; not intended for installation in a cabinet but may be completely enclosed in metal; usually is accessible from both the front and rear.
[ McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture & Construction]
switchboard
One or more panels accommodating control switches, indicators, and other apparatus for operating electric circuits
[ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language]FR
ensemble d'appareillage de puissance (ensemble PSC)
ensemble d'appareillage à basse tension utilisé pour répartir et commander l'énergie pour tous les types de charges et prévu pour des applications industrielles, commerciales et analogues dans lesquelles l'exploitation par des personnes ordinaires n'est pas prévue
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
appareillage, m
matériel électrique destiné à être relié à un circuit électrique en vue d'assurer une ou plusieurs des fonctions suivantes: protection, commande, sectionnement, connexion
NOTE – Les termes français et anglais peuvent être considérés comme équivalents dans la plupart des cas. Toutefois, le terme français couvre un domaine plus étendu que le terme anglais, et comprend notamment les dispositifs de connexion, les prises de courant, etc. En anglais, ces derniers sont dénommés "accessories".
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
appareillage
terme général applicable aux appareils de connexion et à leur combinaison avec des appareils de commande, de mesure, de protection et de réglage qui leur sont associés, ainsi qu'aux ensembles de tels appareils avec les connexions, les accessoires, les enveloppes et les charpentes correspondantes
[IEV number 441-11-01]
A switchboard as defined in the National Electrical Code is a large single panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted, on the face or back or both switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and, usually, instruments.
Switchboards are generally accessible from the rear as well as from the front and are not intended to be installed in cabinets.
The types of switchboards, classified by basic features of construction, are as follows:
1. Live-front vertical panels
2. Dead-front boards
3. Safety enclosed boards( metal-clad)
[American electricians’ handbook]
The switchboard plays an essential role in the availability of electric power, while meeting the needs of personal and property safety.
Its definition, design and installation are based on precise rules; there is no place for improvisation.
The IEC 61439 standard aims to better define " low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies", ensuring that the specified performances are reached.
It specifies in particular:
> the responsibilities of each player, distinguishing those of the original equipment manufacturer - the organization that performed the original design and associated verification of an assembly in accordance with the standard, and of the assembly manufacturer - the organization taking responsibility for the finished assembly;
> the design and verification rules, constituting a benchmark for product certification.
All the component parts of the electrical switchboard are concerned by the IEC 61439 standard.
Equipment produced in accordance with the requirements of this switchboard standard ensures the safety and reliability of the installation.
A switchboard must comply with the requirements of standard IEC 61439-1 and 2 to guarantee the safety and reliability of the installation.
Managers of installations, fully aware of the professional and legal liabilities weighing on their company and on themselves, demand a high level of safety for the electrical installation.
What is more, the serious economic consequences of prolonged halts in production mean that the electrical switchboard must provide excellent continuity of service, whatever the operating conditions.
[Schneider Electric]НКУ играет главную роль в обеспечении электроэнергией, удовлетворяя при этом всем требованиям по безопасности людей и сохранности имущества.
Выбор конструкции, проектирование и монтаж основаны на чётких правилах, не допускающих никакой импровизации.
Требования к низковольтным комплектным устройствам распределения и управления сформулированы в стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000).
В частности, он определяет:
> распределение ответственности между изготовителем НКУ - организацией, разработавшей конструкцию НКУ и проверившей его на соответствие требованиям стандарта, и сборщиком – организацией, выполнившей сборку НКУ;
> конструкцию, технические характеристики, виды и методы испытаний НКУ.
В стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000) описываются все компоненты НКУ.
Оборудование, изготовленное в соответствии с требованиями этого стандарта, обеспечивает безопасность и надежность электроустановки.
Для того чтобы гарантировать безопасность эксплуатации и надежность работы электроустановки, распределительный щит должен соответствовать требованиям стандарта МЭК 61439-1 и 2.
Лица, ответственные за электроустановки, должны быть полностью осведомлены о профессиональной и юридической ответственности, возложенной на их компанию и на них лично, за обеспечение высокого уровня безопасности эксплуатации этих электроустановок.
Кроме того, поскольку длительные перерывы производства приводят к серьезным экономическим последствиям, электрический распределительный щит должен обеспечивать надежную и бесперебойную работу независимо от условий эксплуатации.
[Перевод Интент]LV switchgear assemblies are undoubtedly the components of the electric installation more subject to the direct intervention of personnel (operations, maintenance, etc.) and for this reason users demand from them higher and higher safety requirements.
The compliance of an assembly with the state of the art and therefore, presumptively, with the relevant technical Standard, cannot be based only on the fact that the components which constitute it comply with the state of the art and therefore, at least presumptively, with the relevant technical standards.
In other words, the whole assembly must be designed, built and tested in compliance with the state of the art.
Since the assemblies under consideration are low voltage equipment, their rated voltage shall not exceed 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c. As regards currents, neither upper nor lower limits are provided in the application field of this Standard.
The Standard IEC 60439-1 states the construction, safety and maintenance requirements for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, without dealing with the functional aspects which remain a competence of the designer of the plant for which the assembly is intended.
[ABB]Низковольтные комплектные устройства (НКУ), вне всякого сомнения, являются частями электроустановок, которые наиболее подвержены непосредственному вмешательству оперативного, обслуживающего и т. п. персонала. Вот почему требования потребителей к безопасности НКУ становятся все выше и выше.
Соответствие НКУ современному положению дел и вследствие этого, гипотетически, соответствующим техническим стандартам, не может основываться только на том факте, что составляющие НКУ компоненты соответствуют современному состоянию дел и поэтому, по крайней мере, гипотетически, - соответствующим техническим стандартам
Другими словами, НКУ должно быть разработано, изготовлено и испытано в соответствии с современными требованиями.
Мы рассматриваем низковольтные комплектные устройства и это означает, что их номинальное напряжение не превышает 1000 В переменного тока или 1500 В постоянного тока. Что касается тока, то ни верхнее, ни нижнее значение стандартами, относящимися к данной области, не оговариваются
Стандарт МЭК 60439-1 устанавливает требования к конструкции, безопасности и техническому обслуживанию низковольтных комплектных устройств без учета их функций, полагая, что функции НКУ являются компетенцией проектировщиков электроустановки, частью которых эти НКУ являются.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
Классификация
>>>Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- assembly
- electrical switchboard
- low voltage controlgear and assembly
- low voltage switchboard
- low voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear assembly
- panel
- power switchgear and controlgear assembly
- PSC-assembly
- switchboard
- switchgear and controlgear
- switchgear/controlgear
DE
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > НКУ распределения и управления
-
12 электричество
электричество (1)
-
[IEV number 151-11-01]EN
electricity (1)
set of phenomena associated with electric charges and electric currents
NOTE 1 – Examples of usage of this concept: static electricity, biological effects of electricity.
NOTE 2 – In English, the term "electricity" is also used to denote electric energy. In French, the usage of the term "électricité" in this sense is deprecated. For example, the expression "distribution of electricity" is used in English, but "distribution d'énergie électrique" is used in French.
Source: 121-11-76 MOD
[IEV number 151-11-01]FR
électricité (1), f
ensemble de phénomènes associés à des charges électriques et à des courants électriques
NOTE 1 – Exemples d’emploi de ce concept: électricité statique, effets biologiques de l’électricité.
NOTE 2 – En anglais, le terme "electricity" est aussi utilisé au sens d'énergie électrique. En français, l'emploi du terme "électricité" est déconseillé dans ce sens. Par exemple, l'expression "distribution of electricity", employée en anglais, correspond en français à "distribution d'énergie électrique".
Source: 121-11-76 MOD
[IEV number 151-11-01]электричество (2)
-
[IEV number 151-11-02]EN
electricity (2)
branch of science dealing with electric phenomena
NOTE – Examples of usage of this concept: handbook of electricity, school of electricity.
[IEV number 151-11-02]FR
électricité (2), f
branche de la science traitant des phénomènes électriques
NOTE – Exemples d’emploi de ce concept: manuel d’électricité, école d’électricité.
[IEV number 151-11-02]EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электричество
-
13 элемент питания (техн.)
элемент питания (техн.)
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
cell (energy)
The basic building block of a battery. It is an electrochemical device consisting of an anode and a cathode in a common electrolyte kept apart with a separator. This assembly may be used in its own container as a single cell battery or be combined and interconnected with other cells in a container to form a multicelled battery. (Source: LEE)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > элемент питания (техн.)
-
14 циркуляция морской воды
циркуляция морской воды
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
sea circulation
Large-scale horizontal water motion within an ocean. The way energy from the sun, stored in the sea, is transported around the world. The currents explain, for example, why the UK has ice-free ports in winter, while St. Petersburg, at the same latitude as the Shetland Islands, needs ice breakers. Evidence is growing that the world's ocean circulation was very different during the last ice age and has changed several times in the distant past, with dramatic effects on climate. The oceans are vital as storehouses, as they absorb more than half the sun's heat reaching the earth. This heat, which is primarily absorbed near the equator is carried around the world and released elsewhere, creating currents which last up to 1.000 years. As the Earth rotates and the wind acts upon the surface, currents carry warm tropical water to the cooler parts of the world. The strength and direction of the currents are affected by landmasses, bottlenecks through narrow straits, and even the shape of the sea-bed. When the warm water reaches polar regions its heat evaporates into the atmosphere, reducing its temperature and increasing its density. When sea-water freezes it leaves salt behind in the unfrozen water and this cold water sinks into the ocean and begins to flow back to the tropics. Eventually it is heated and begins the cycle all over again. (Source: MGH / WRIGHT)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > циркуляция морской воды
-
15 вращающаяся электрическая машина
вращающаяся электрическая машина
Электротехническое устройство, предназначенное для преобразования энергии на основе электромагнитной индукции и взаимодействия магнитного поля с электрическим током, содержащее, по крайней мере, две части, участвующие в основном процессе преобразования и имеющие возможность вращаться или поворачиваться относительно друг друга.
[ ГОСТ 27471-87]
электрическая машина
Электрическая машина, служит для преобразования механической энергии в электрическую и электрической в механическую, а также электрической энергии в электрическую же, отличающуюся по напряжению, роду тока, частоте и другим параметрам. Действие Э. м. основано на использовании явления электромагнитной индукции и законов, определяющих взаимодействие электрических токов и магнитных полей.
Для преобразования механической энергии в электрическую служат генераторы электромашинные, электрической энергии в механическую — двигатели электрические. Каждая из этих машин (в соответствии с Ленца правилом) энергетически обратима, т. е. может работать как в генераторном, так и в двигательном режиме; однако выпускаемые промышленностью Э. м. обычно предназначены для выполнения определённой работы (см. также Переменного тока машина, Постоянного тока машина, Асинхронная электрическая машина, Синхронная машина, Коллекторная машина).
Преобразования рода тока, частоты, числа фаз, напряжения осуществляют электромашинными преобразователями(см. Преобразовательная техника), электромашинными усилителями, трансформаторами электрическими.
К Э. м. относят также машины специального назначения, например тахогенератор, тяговый электродвигатель.
[БСЭ]EN
(electrical) rotating machine
an electrical apparatus depending on electromagnetic induction for its operation and having components capable of relative rotary movement and intended for converting energy
NOTE – This term also applies to electrical apparatus operating on the same principle and similar in construction and intended for other purposes, e.g. regulation, supplying or absorbing reactive power. It is not intended to cover electrostatic machines.
[IEV number 411-31-01]FR
machine (électrique) tournante
appareil électrique utilisant l'induction magnétique pour son fonctionnement, constitué d'éléments pouvant effectuer un mouvement relatif de rotation et destiné à la transformation de l'énergie
NOTE – Ce terme s'applique également aux appareils électriques fonctionnant suivant le même principe, de construction analogue et utilisés à d'autres fins, par exemple à des fins de régulation, de fourniture et d'absorption de puissance réactive. Il ne s'étend pas aux machines électrostatiques.
[IEV number 411-31-01]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- electrical rotating machine
- electrical machine
- electrical rotating machinery
- rotating electrical machine
- rotating machine
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > вращающаяся электрическая машина
-
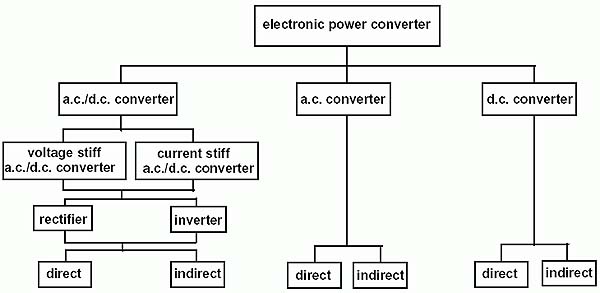
16 полупроводниковый инвертор
полупроводниковый инвертор
инвертор
Полупроводниковый преобразователь электроэнергии, предназначенный для преобразования постоянного тока в переменный.
[ ГОСТ 23414-84]
инвертор
обратный преобразователь
-
[IEV number 151-13-46]EN
inverter
electric energy converter that changes direct electric current to single-phase or polyphase alternating currents
[IEV number 151-13-46]
inverter
invertor
an a.c./d.c. converter for inversion
NOTE – In English, the two spellings "invertor" and "inverter" are in use, and both are correct. In this document, the spelling "inverter" is used in order to avoid duplications.
[IEV number 551-12-10]
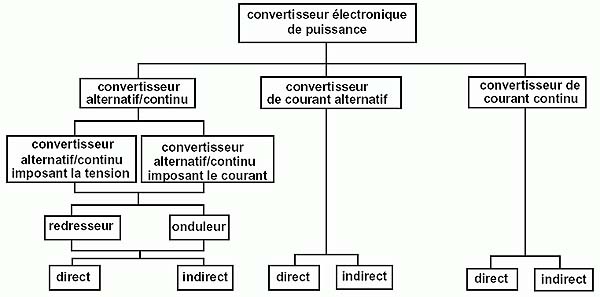
FR
onduleur, m
convertisseur d'énergie électrique qui transforme un courant électrique continu en courants alternatifs monophasés ou polyphasés
[IEV number 151-13-46]
onduleur
convertisseur alternatif/continu assurant un fonctionnement onduleur
NOTE – En anglais, on utilise les deux orthographes "invertor" et "inverter", qui sont toutes les deux correctes. Dans le présent document on utilise l'orthographe "inverter" pour éviter les duplications.
[IEV number 551-12-10]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > полупроводниковый инвертор
-
17 постоянная (счетчика)
постоянная (счетчика)
-
[IEV number 314-07-08]EN
(meter) constant
value expressing the relation between the active energy registered by a meter and the corresponding value of the test output.
NOTE – If this value is a number of pulses, the constant should be either pulses per kilowatt-hour (imp/kWh) or watt-hours per pulse (Wh/imp)
[IEV number 314-07-08]FR
co nstante (du compteur)
valeur exprimant la relation entre l’énergie enregistrée par un compteur et la valeur correspondante donnée par le dispositif de sortie d’essai
NOTE – Si cette valeur est un nombre d’impulsions, la constante doit être soit le nombre d’impulsions par kilowattheure (imp/kWh), soit le nombre de wattheures par impulsion (Wh/imp)
[IEV number 314-07-08]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
- счетчик электроэнергии
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > постоянная (счетчика)
-
18 распределительный щит
- tableau de répartition, m
- tableau de distribution
распределительный щит
Комплектное устройство, содержащее различную коммутационную аппаратуру, соединенное с одной или более отходящими электрическими цепями, питающееся от одной или более входящих цепей, вместе с зажимами для присоединения нейтральных и защитных проводников.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
щит распределительный
Электротехническое устройство, объединяющее коммутационную, регулирующую и защитную аппаратуру, а также контрольно-измерительные и сигнальные приборы
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
распределительный щит
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]EN
distribution board
assembly containing different types of switchgear and controlgear associated with one or more outgoing electric circuits fed from one or more incoming electric circuits, together with terminals for the neutral and protective conductors.
[IEV number 826-16-08]FR
tableau de répartition, m
ensemble comportant différents types d'appareillage associés à un ou plusieurs circuits électriques de départ alimentés par un ou plusieurs circuits électriques d'arrivée, ainsi que des bornes pour les conducteurs neutre et de protection.
[IEV number 826-16-08]Distribution switchboards, including the Main LV Switchboard (MLVS), are critical to the dependability of an electrical installation. They must comply with well-defined standards governing the design and construction of LV switchgear assemblies
A distribution switchboard is the point at which an incoming-power supply divides into separate circuits, each of which is controlled and protected by the fuses or switchgear of the switchboard. A distribution switchboard is divided into a number of functional units, each comprising all the electrical and mechanical elements that contribute to the fulfilment of a given function. It represents a key link in the dependability chain.
Consequently, the type of distribution switchboard must be perfectly adapted to its application. Its design and construction must comply with applicable standards and working practises.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительные щиты, включая главный распределительный щит низкого напряжения (ГРЩ), играют решающую роль в обеспечении надежности электроустановки. Они должны отвечать требованиям соответствующих стандартов, определяющих конструкцию и порядок изготовления НКУ распределения электроэнергии.
В распределительном щите выполняется прием электроэнергии и ее распределение по отдельным цепям, каждая из которых контролируется и защищается плавкими предохранителями или автоматическими выключателями.
Распределительный щит состоит из функциональных блоков, включающих в себя все электрические и механические элементы, необходимые для выполнения требуемой функции. Распределительный щит представляет собой ключевое звено в цепи обеспечения надежности.
Тип распределительного щита должен соответствовать области применения. Конструкция и изготовление распределительного щита должны удовлетворять требованиям применимых стандартов и учитывать накопленную практику применения.
[Перевод Интент]
Рис. Schneider Electric
With Prisma Plus G you can be sure to build 100% Schneider Electric switchboards that are safe, optimised:
> All components (switchgear, distribution blocks, prefabricated connections, etc.) are perfectly rated and coordinated to work together;
> All switchboard configurations, even the most demanding ones, have been tested.
You can prove that your switchboard meets the current standards, at any time.
You can be sure to build a reliable electrical installation and give your customers full satisfaction in terms of dependability and safety for people and the installation.
Prisma Plus G with its discreet design, blends harmoniously into all tertiary and industrial buildings, including in entrance halls and passageways.
With Prisma Plus G you can build just the right switchboard for your customer, sized precisely to fit costs and needs.
With this complete, prefabricated and tested system, it's easy to upgrade your installation and still maintain the performance levels.
> The wall-mounted and floor-standing enclosures combine easily with switchboards already in service.
> Devices can be replaced or added at any time.
[Schneider Electric]С помощью оболочек Prisma Plus G можно создавать безопасные распределительные щиты, на 100 % состоящие из изделий Schneider Electric:
> все изделия (коммутационная аппаратура, распределительные блоки, готовые заводские соединения и т. д.) полностью совместимы механически и электрически;
> все варианты компоновки распределительных щитов, в том числе для наиболее ответственных применений, прошли испытания.В любое время вы можете доказать, что ваши распределительные щиты полностью соответствуют требованиям действующих стандартов.
Вы можете быть полностью уверены в том, что создаете надежные электроустановки, удовлетворяющие всем требованиям безопасности для людей и оборудования
Благодаря строгому дизайну, распределительные щиты Prisma Plus G гармонично сочетаются с интерьером любого общественного или промышленного здания. Они хорошо смотрятся и в вестибюле, и в коридоре.
Применяя оболочки Prisma Plus G можно создавать распределительные щиты, точно соответствующие требованиям заказчика как с точки зрения технических характеристик, так и стоимости.
С помощью данной испытанной системы, содержащей все необходимые компоненты заводского изготовления можно легко модернизировать существующую электроустановку и поддерживать её уровни производительности.> Навесные и напольные оболочки можно легко присоединить к уже эксплуатируемым распределительным щитам.
> Аппаратуру можно заменять или добавлять в любое время.
[Перевод Интент]The switchboard, central to the electrical installation.
Both the point of arrival of energy and a device for distribution to the site applications, the LV switchboard is the intelligence of the system, central to the electrical installation.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительный щит – «сердце» электроустановки.
Низковольтное комплектное устройство распределения является «сердцем» электроустановки, поскольку именно оно принимает электроэнергию из сети и распределяет её по территориально распределенным нагрузкам.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
EN
- branch distribution panel
- distributing board
- distributing panel
- distributing switchboard
- distribution bench
- distribution board
- distribution panel
- distribution switchboard
- gear
- keyboard
- PNL
- SB
- sw & d
- switchboard
- switchboard panel
DE
- elektrischer Verteiler, m
- Schalttafel
- Verteiler, m
FR
- tableau de distribution
- tableau de répartition, m
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > распределительный щит
-
19 электрическая опасность
EN
electrical hazard
potential source of harm when electric energy is present in an electrical installation
NOTE – The ISO/IEC Guide 51:1990 gives as French equivalent “danger” for the English term “hazard”. In the draft revision of this guide, “hazard” is rendered in French by “phénomène dangereux”.
[IEV number 651-01-30]FR
danger électrique
source potentielle de dommage due à la présence d'énergie électrique dans une installation électrique
NOTE – Le Guide ISO/CEI 51:1990 donne comme équivalent pour le terme anglais "hazard" le terme français "danger". Dans le projet de révision de ce guide, "hazard" est rendu en français par "phénomène dangereux".
[IEV number 651-01-30]
4.3 Электрические опасности
Электрические опасности могут приводить к ожогам, травмам или смерти от поражения электрическим током и к ожогам. Они могут быть вызваны:- соприкосновением людей с токоведущими частями, находящимися при нормальной работе под напряжением (прямой контакт);
- соприкосновением людей с частями, попадающими под напряжение при неисправностях, особенно в результате повреждения электрической изоляции (непрямой контакт);
- приближением людей к токоведущим частям, находящимся под напряжением, особенно под высоким напряжением;
- несоответствием электрической изоляции предусмотренным условиям эксплуатации машины;
- контактом человека с деталями, заряженными статическим электричеством;
- тепловым излучением;
- выбросом расплавленных частиц или химических веществ при коротком замыкании или в случае перегрузок.
Электрические опасности также могут приводить к падениям людей (или предметов на людей) в результате шока, вызванного поражением электрическим током.
[ ГОСТ Р ИСО 12100-1:2007]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электрическая опасность
-
20 электрический
- électrique (1)
- d’électricité (2)
электрический
Основанный на электрической технологии.
Примечания
1. Данный термин предназначен для того, чтобы охватить любое или все устройства, или системы, действующие на основе электричества.
2. В число электрических/электронных/программируемых электронных устройств входят:
- электромеханические устройства (электрические);
- полупроводниковые непрограммируемые электронные устройства (электроника);
- электронные устройства, основанные на компьютерных технологиях (программируемые электронные); см. 3.2.5.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61508-4-2007]
электрический (1)
-
[IEV number 151-11-03]EN
electric, adj
containing, producing, arising from, or actuated by electricity
NOTE – Examples of usage of the term "electric": electric energy, electric lamp, electric motor, electric quantity.
[IEV number 151-11-03]FR
électrique, adj
contenant, produisant, provenant de, actionné par l'électricité
NOTE – Exemples d'emploi de l'adjectif "électrique": énergie électrique, lampe électrique, moteur électrique, grandeur électrique.
[IEV number 151-11-03]электрический (2)
-
[IEV number 151-11-05]EN
electrical (2), adj
pertaining to electricity, but not having its properties or characteristics
NOTE – Examples of usage of this concept: electrical handbook.
[IEV number 151-11-05]FR
d’électricité, qualificatif
relatif à l'électricité, mais n'ayant ni ses propriétés ni ses caractéristiques
NOTE – Exemples d'emploi de ce concept: manuel d'électricité.
[IEV number 151-11-05]EN
DE
- elektrisch (1)
- Elektro... (2) (in Zusammensetzungen)
FR
- d’électricité (2)
- électrique (1)
Русско-французский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > электрический
См. также в других словарях:
Energy conservation features — This includes building shell conservation features, HVAC conservation features, lighting conservation features, any conservation features, and other conservation features incorporated by the building. However, this category does not include any … Energy terms
Energy (esotericism) — This article is about spiritual energy. For other uses, see Energy (disambiguation). Subtle energy redirects here. For the mystical concept of psychospiritual bodies overlaying the physical body, see Subtle body. Spiritual practices and ideas… … Wikipedia
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy — (EDS, EDX or EDXRF) is an analytical technique used for the elemental analysis or chemical characterization of a sample. As a type of spectroscopy, it relies on the investigation of a sample through interactions between electromagnetic radiation… … Wikipedia
Energy Policy Act of 1992 — (EPACT) A comprehensive legislative package that mandates and encourages energy efficiency standards, alternative fuel use, and the development of renewable energy technologies. Public Law 102 486, October 24th, 1992. Also authorized the… … Energy terms
Energy — The capability of doing work; different forms of energy can be converted to other forms, but the total amount of energy remains the same. This is broadly defined as the capability of doing work. In the electric power industry, energy is more… … Energy terms
Energy Efficiency — Programs that reduce consumption. *** A ratio of service provided to energy input (e.g., lumens to watts in the case of light bulbs). Services provided can include buildings sector end uses such as lighting, refrigeration, and heating:… … Energy terms
Energy Reserves — The portion of total energy resources that is known and can be recovered with presently available technology at an affordable cost. *** Estimated quantities of energy sources that are demonstrated to exist with reasonable certainty on the… … Energy terms
Energy management practices — Involvement, as a part of the building s normal operations, in energy efficiency programs that are designed to reduce the energy used by specific end use systems. This includes the following EMCS, DSM Program Participation, Energy Audit, and a… … Energy terms
Surplus energy — Energy generated that is beyond the immediate needs of the producing system. This energy may be supplied by spinning reserve and sold on an interruptible basis. U.S. Dept. of Energy, Energy Information Administration s Energy Glossary … Energy terms
energy payback time — The time required for any energy producing system or device to produce as much energy as was required in its manufacture. For solar electric panels, this is about 16 20 months. Solar Electric Glossary … Energy terms
Energy — This article is about the scalar physical quantity. For other uses, see Energy (disambiguation). Energetic redirects here. For other uses, see Energetic (disambiguation) … Wikipedia
