-
21 Dimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
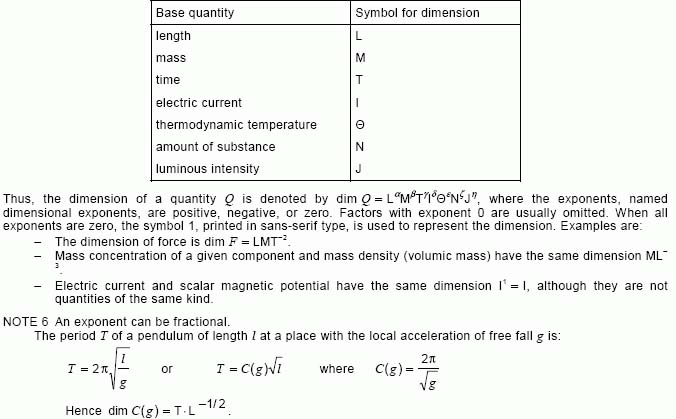
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:
[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dimension, f
-
22 Größendimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Größendimension, f
-
23 Polder-Tensorpermeabilität
тензор Полдера
Тензор магнитной проницаемости материала с намагниченностью технического насыщения вдоль одной из осей координат.
[ ГОСТ 19693-74]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Polder-Tensorpermeabilität
-
24 Trägheitstensor
тензор инерции
Симметричный тензор второго ранга, компонентами которого являются осевые и взятые с обратными знаками центробежные моменты инерции системы.
[Сборник рекомендуемых терминов. Выпуск 102. Теоретическая механика. Академия наук СССР. Комитет научно-технической терминологии. 1984 г.]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Trägheitstensor
-
25 Tensorpermeabilität
тензор магнитной проницаемости
Тензор, определяющий связь между пространственными векторами магнитной индукции и напряженности магнитного поля.
[ ГОСТ 19693-74]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Tensorpermeabilität
- 1
- 2
См. также в других словарях:
tensor — TENSÓR, tensori, s.m. Obiect matematic definit în cadrul algebrei şi geometriei, frecvent utilizat în fizică, reprezentând o generalizare a noţiunii de vector. – Din fr. tenseur, germ. Tensor. Trimis de LauraGellner, 26.06.2004. Sursa: DEX 98 … … Dicționar Român
tensor — tensor, ra adjetivo,sustantivo masculino y femenino 1. Que tensa o sirve para tensar: músculo tensor, mecanismo tensor. A este dispositivo le falta el tensor. sustantivo masculino 1. Mecanismo o dispositivo para tensar o estirar algo: el tensor… … Diccionario Salamanca de la Lengua Española
tensor — Cualquiera de los músculos corporales que tensan estructuras, tales como el tensor de la fascia lata del muslo. Diccionario Mosby Medicina, Enfermería y Ciencias de la Salud, Ediciones Hancourt, S.A. 1999 … Diccionario médico
tensor — tensor, ra (Del lat. tensor, ōris). 1. adj. Que tensa, origina tensión o está dispuesto para producirla. U. t. c. s.) 2. m. Mecanismo que se emplea para tensar algo. 3. Fís. Sistema de magnitudes, coexistentes y de igual índole, tales que se… … Diccionario de la lengua española
Tensor — Ten sor, n. [NL. See {Tension}.] 1. (Anat.) A muscle that stretches a part, or renders it tense. [1913 Webster] 2. (Geom.) The ratio of one vector to another in length, no regard being had to the direction of the two vectors; so called because… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
Tensor — (lat.), Streckmuskel … Pierer's Universal-Lexikon
tensor — muscle that stretches a part, 1704, Modern Latin agent noun of L. tendere to stretch (see TENET (Cf. tenet)) … Etymology dictionary
tensor — |ô| adj. 1. [Anatomia] Diz se dos músculos que servem para estender um membro ou um órgão qualquer. • s. m. 2. Grandeza matemática de vários componentes definidos no quadro da geometria vetorial e linear. 3. [Mecânica] Dispositivo destinado a… … Dicionário da Língua Portuguesa
tensor — [ten′sər, ten′sôr΄] n. [ModL < L tensus: see TENSE1] 1. any muscle that stretches, or tenses, some part of the body 2. Math. an abstract object representing a generalization of the vector concept and having a specified system of components… … English World dictionary
Tensor — For other uses, see Tensor (disambiguation). Note that in common usage, the term tensor is also used to refer to a tensor field. Stress, a second order tensor. The tensor s components, in a three dimensional Cartesian coordinate system, form the… … Wikipedia
Tensor — Levi Civita Symbol im Dreidimensionalen als Beispiel eines besonders einfachen dreistufigen Tensors Der Tensor ist ein mathematisches Objekt aus der Algebra und Differentialgeometrie. Der Begriff wurde ursprünglich in der Physik eingeführt und… … Deutsch Wikipedia
