-
1 standard for the exchange of product definition data
standard for the exchange of product definition data Standard m zum Austausch produktdefinierter Daten (zwischen unterschiedlichen CA-Systemen)English-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > standard for the exchange of product definition data
-
2 STEP
English-German dictionary of Electrical Engineering and Electronics > STEP
-
3 размерность физической величины
- Größendimension, f
- Dimension, f
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension einer GroBe
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:
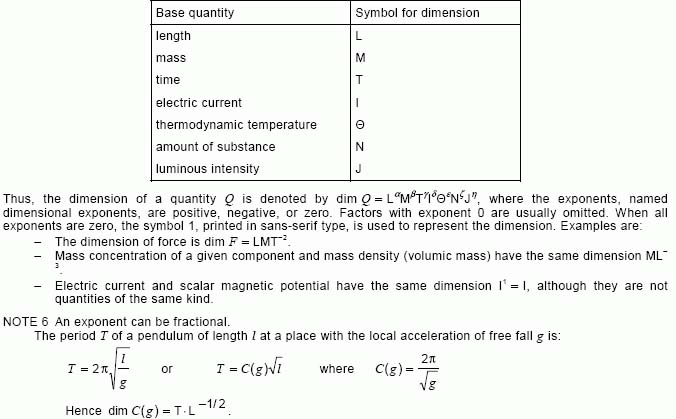
[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
2.9. Размерность физической величины
Размерность величины Нрк. Формула размерности
D. Dimension einer GroBe
E. Dimensions of a quantity
F. Dimension d’une grandeur
Выражение, отражающее связь величины с основными величинами системы, в котором коэффициент пропорциональности принят равным 1.
Примечания:
1. Размерность величины представляет собой произведение основных величин, возведенных в соответствующие степени.
2. Размерность производной величины отражает, во сколько раз изменяется ее размер при изменении размеров основных величин, например, если размерность величины х равна LaM^Tv и длина изменяется от / до /', масса — от m до т' и время — от t до то новый размер величины будет больше прежнего в (/'//)а
(/'//)v раз.
Источник: ГОСТ 16263-70: Государственная система обеспечения единства измерений. Метрология. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > размерность физической величины
-
4 width
nounwhat is the width of...? — wie breit/weit ist...?
be half a metre in width — einen halben Meter breit/weit sein
3) (piece of material) Bahn, die* * *[widƟ]1) (size from side to side: What is the width of this material?; This fabric comes in three different widths.) die Breite2) (the state of being wide.) die Weite* * *[wɪtθ]nthe corridor runs the \width of the building der Flur ist so breit wie das Gebäudeto come in different \widths unterschiedlich breit seinto swim two \widths zweimal quer durch das Becken schwimmenthere is a surprising \width of support for the proposal der Vorschlag findet eine überraschend große Unterstützung* * *[wɪdɵ]n2) (= piece of material) Breite fthree widths of cloth — drei mal die Breite
* * *width [wıdθ] s1. Breite f, Weite f:6 feet in width 6 Fuß breit;what is its width? wie breit ist es?2. (Stoff-, Tapeten-, Rock) Bahn f3. ARCHa) Spannweite f (eines Bogens, einer Brücke etc)b) lichte Weite4. GEOL Mächtigkeit f5. fig Weite f, Größe f:width of mind geistiger Horizontw. abk1. weight2. wide3. width4. wife5. with* * *nounwhat is the width of...? — wie breit/weit ist...?
be half a metre in width — einen halben Meter breit/weit sein
3) (piece of material) Bahn, die* * *(printing) n.Schriftbreite f. n.Breite -en f.Weite -n f. -
5 НКУ распределения и управления
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления (НКУ)
Низковольтные коммутационные аппараты и устройства управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования, собранные совместно, со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями и конструктивными элементами.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439-1-2012]
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления
Комбинация низковольтных коммутационных аппаратов с устройствами управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования и т. п., полностью смонтированных изготовителем НКУ (под его ответственность на единой конструктивной основе) со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями с соответствующими конструктивными элементами
Примечания
1. В настоящем стандарте сокращение НКУ используют для обозначения низковольтных комплектных устройств распределения и управления.
2. Аппараты, входящие в состав НКУ, могут быть электромеханическими или электронными.
3. По различным причинам, например по условиям транспортирования или изготовления, некоторые операции сборки могут быть выполнены на месте установки, вне предприятия-изготовителя.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]EN
power switchgear and controlgear assembly (PSC-assembly)
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly used to distribute and control energy for all types of loads, intended for industrial, commercial and similar applications where operation by ordinary persons is not intended
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
combination of one or more low-voltage switching devices together with associated control, measuring, signalling, protective, regulation equipment, etc., completely assembled under the responsibility of the manufacturer with all the internal electrical and mechanical interconnections and structural parts.
[IEC 61892-3, ed. 2.0 (2007-11)]
switchgear and controlgear
a general term covering switching devices and their combination with associated control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment, also assemblies of such devices and equipment with associated interconnections, accessories, enclosures and supporting structures
[IEV number 441-11-01]
switchgear and controlgear
electric equipment intended to be connected to an electric circuit for the purpose of carrying out one or more of the following functions: protection, control, isolation, switching
NOTE – The French and English terms can be considered as equivalent in most cases. However, the French term has a broader meaning than the English term and includes for example connecting devices, plugs and socket-outlets, etc. In English, these latter devices are known as accessories.
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
switchboard
A large single electric control panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted (either on the back or on the face, or both) switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and usually instruments; not intended for installation in a cabinet but may be completely enclosed in metal; usually is accessible from both the front and rear.
[ McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture & Construction]
switchboard
One or more panels accommodating control switches, indicators, and other apparatus for operating electric circuits
[ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language]FR
ensemble d'appareillage de puissance (ensemble PSC)
ensemble d'appareillage à basse tension utilisé pour répartir et commander l'énergie pour tous les types de charges et prévu pour des applications industrielles, commerciales et analogues dans lesquelles l'exploitation par des personnes ordinaires n'est pas prévue
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
appareillage, m
matériel électrique destiné à être relié à un circuit électrique en vue d'assurer une ou plusieurs des fonctions suivantes: protection, commande, sectionnement, connexion
NOTE – Les termes français et anglais peuvent être considérés comme équivalents dans la plupart des cas. Toutefois, le terme français couvre un domaine plus étendu que le terme anglais, et comprend notamment les dispositifs de connexion, les prises de courant, etc. En anglais, ces derniers sont dénommés "accessories".
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
appareillage
terme général applicable aux appareils de connexion et à leur combinaison avec des appareils de commande, de mesure, de protection et de réglage qui leur sont associés, ainsi qu'aux ensembles de tels appareils avec les connexions, les accessoires, les enveloppes et les charpentes correspondantes
[IEV number 441-11-01]
A switchboard as defined in the National Electrical Code is a large single panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted, on the face or back or both switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and, usually, instruments.
Switchboards are generally accessible from the rear as well as from the front and are not intended to be installed in cabinets.
The types of switchboards, classified by basic features of construction, are as follows:
1. Live-front vertical panels
2. Dead-front boards
3. Safety enclosed boards( metal-clad)
[American electricians’ handbook]
The switchboard plays an essential role in the availability of electric power, while meeting the needs of personal and property safety.
Its definition, design and installation are based on precise rules; there is no place for improvisation.
The IEC 61439 standard aims to better define " low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies", ensuring that the specified performances are reached.
It specifies in particular:
> the responsibilities of each player, distinguishing those of the original equipment manufacturer - the organization that performed the original design and associated verification of an assembly in accordance with the standard, and of the assembly manufacturer - the organization taking responsibility for the finished assembly;
> the design and verification rules, constituting a benchmark for product certification.
All the component parts of the electrical switchboard are concerned by the IEC 61439 standard.
Equipment produced in accordance with the requirements of this switchboard standard ensures the safety and reliability of the installation.
A switchboard must comply with the requirements of standard IEC 61439-1 and 2 to guarantee the safety and reliability of the installation.
Managers of installations, fully aware of the professional and legal liabilities weighing on their company and on themselves, demand a high level of safety for the electrical installation.
What is more, the serious economic consequences of prolonged halts in production mean that the electrical switchboard must provide excellent continuity of service, whatever the operating conditions.
[Schneider Electric]НКУ играет главную роль в обеспечении электроэнергией, удовлетворяя при этом всем требованиям по безопасности людей и сохранности имущества.
Выбор конструкции, проектирование и монтаж основаны на чётких правилах, не допускающих никакой импровизации.
Требования к низковольтным комплектным устройствам распределения и управления сформулированы в стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000).
В частности, он определяет:
> распределение ответственности между изготовителем НКУ - организацией, разработавшей конструкцию НКУ и проверившей его на соответствие требованиям стандарта, и сборщиком – организацией, выполнившей сборку НКУ;
> конструкцию, технические характеристики, виды и методы испытаний НКУ.
В стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000) описываются все компоненты НКУ.
Оборудование, изготовленное в соответствии с требованиями этого стандарта, обеспечивает безопасность и надежность электроустановки.
Для того чтобы гарантировать безопасность эксплуатации и надежность работы электроустановки, распределительный щит должен соответствовать требованиям стандарта МЭК 61439-1 и 2.
Лица, ответственные за электроустановки, должны быть полностью осведомлены о профессиональной и юридической ответственности, возложенной на их компанию и на них лично, за обеспечение высокого уровня безопасности эксплуатации этих электроустановок.
Кроме того, поскольку длительные перерывы производства приводят к серьезным экономическим последствиям, электрический распределительный щит должен обеспечивать надежную и бесперебойную работу независимо от условий эксплуатации.
[Перевод Интент]LV switchgear assemblies are undoubtedly the components of the electric installation more subject to the direct intervention of personnel (operations, maintenance, etc.) and for this reason users demand from them higher and higher safety requirements.
The compliance of an assembly with the state of the art and therefore, presumptively, with the relevant technical Standard, cannot be based only on the fact that the components which constitute it comply with the state of the art and therefore, at least presumptively, with the relevant technical standards.
In other words, the whole assembly must be designed, built and tested in compliance with the state of the art.
Since the assemblies under consideration are low voltage equipment, their rated voltage shall not exceed 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c. As regards currents, neither upper nor lower limits are provided in the application field of this Standard.
The Standard IEC 60439-1 states the construction, safety and maintenance requirements for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, without dealing with the functional aspects which remain a competence of the designer of the plant for which the assembly is intended.
[ABB]Низковольтные комплектные устройства (НКУ), вне всякого сомнения, являются частями электроустановок, которые наиболее подвержены непосредственному вмешательству оперативного, обслуживающего и т. п. персонала. Вот почему требования потребителей к безопасности НКУ становятся все выше и выше.
Соответствие НКУ современному положению дел и вследствие этого, гипотетически, соответствующим техническим стандартам, не может основываться только на том факте, что составляющие НКУ компоненты соответствуют современному состоянию дел и поэтому, по крайней мере, гипотетически, - соответствующим техническим стандартам
Другими словами, НКУ должно быть разработано, изготовлено и испытано в соответствии с современными требованиями.
Мы рассматриваем низковольтные комплектные устройства и это означает, что их номинальное напряжение не превышает 1000 В переменного тока или 1500 В постоянного тока. Что касается тока, то ни верхнее, ни нижнее значение стандартами, относящимися к данной области, не оговариваются
Стандарт МЭК 60439-1 устанавливает требования к конструкции, безопасности и техническому обслуживанию низковольтных комплектных устройств без учета их функций, полагая, что функции НКУ являются компетенцией проектировщиков электроустановки, частью которых эти НКУ являются.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
Классификация
>>>Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- assembly
- electrical switchboard
- low voltage controlgear and assembly
- low voltage switchboard
- low voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear assembly
- panel
- power switchgear and controlgear assembly
- PSC-assembly
- switchboard
- switchgear and controlgear
- switchgear/controlgear
DE
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > НКУ распределения и управления
-
6 оптимизация
оптимизация
Процесс отыскания варианта, соответствующего критерию оптимальности
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
оптимизация
1. Процесс нахождения экстремума функции, т.е. выбор наилучшего варианта из множества возможных, процесс выработки оптимальных решений; 2. Процесс приведения системы в наилучшее (оптимальное) состояние. Иначе говоря, первое определение трактует термин «О.» как факт выработки и принятия оптимального решения (в широком смысле этих слов); мы выясняем, какое состояние изучаемой системы будет наилучшим с точки зрения предъявляемых к ней требований (критерия оптимальности) и рассматриваем такое состояние как цель. В этом смысле применяется также термин «субоптимизация» в случаях, когда отыскивается оптимум по какому-либо одному критерию из нескольких в векторной задаче оптимизации (см. Оптимальность по Парето, Векторная оптимизация). Второе определение имеет в виду процесс выполнения этого решения: т.е. перевод системы от существующего к искомому оптимальному состоянию. В зависимости от вида используемых критериев оптимальности (целевых функций или функционалов) и ограничений модели (множества допустимых решений) различают скалярную О., векторную О., мно¬гокритериальную О., стохастическую О (см. Стохастическое программирование), гладкую и негладкую (см. Гладкая функция), дискретную и непрерывную (см. Дискретность, Непрерывность), выпуклую и вогнутую (см. Выпуклость, вогнутость) и др. Численные методы О., т.е. методы построения алгоритмов нахождения оп¬тимальных значений целевых функций и соответствующих точек области допустимых значений — развитой отдел современной вычислительной математики. См. Оптимальная задача.
[ http://slovar-lopatnikov.ru/]Параллельные тексты EN-RU из ABB Review. Перевод компании Интент
The quest for the optimumВопрос оптимизацииThroughout the history of industry, there has been one factor that has spurred on progress more than any other. That factor is productivity. From the invention of the first pump to advanced computer-based optimization methods, the key to the success of new ideas was that they permitted more to be achieved with less. This meant that consumers could, over time and measured in real terms, afford to buy more with less money. Luxuries restricted to a tiny minority not much more than a generation ago are now available to almost everybody in developed countries, with many developing countries rapidly catching up.На протяжении всей истории промышленности существует один фактор, подстегивающий ее развитие сильнее всего. Он называется «производительность». Начиная с изобретения первого насоса и заканчивая передовыми методами компьютерной оптимизации, успех новых идей зависел от того, позволяют ли они добиться большего результата меньшими усилиями. На языке потребителей это значит, что они всегда хотят купить больше, а заплатить меньше. Меньше чем поколение назад, многие предметы считались роскошью и были доступны лишь немногим. Сейчас в развитых странах, число которых быстро увеличивается, подобное может позволить себе почти каждый.With industry and consumers expecting the trend towards higher productivity to continue, engineering companies are faced with the challenge of identifying and realizing further optimization potential. The solution often lies in taking a step back and looking at the bigger picture. Rather than optimizing every step individually, many modern optimization techniques look at a process as a whole, and sometimes even beyond it. They can, for example, take into account factors such as the volatility of fuel quality and price, the performance of maintenance and service practices or even improved data tracking and handling. All this would not be possible without the advanced processing capability of modern computer and control systems, able to handle numerous variables over large domains, and so solve optimization problems that would otherwise remain intractable.На фоне общей заинтересованности в дальнейшем росте производительности, машиностроительные и проектировочные компании сталкиваются с необходимостью определения и реализации возможностей по оптимизации своей деятельности. Для того чтобы найти решение, часто нужно сделать шаг назад, поскольку большое видится на расстоянии. И поэтому вместо того, чтобы оптимизировать каждый этап производства по отдельности, многие современные решения охватывают процесс целиком, а иногда и выходят за его пределы. Например, они могут учитывать такие факторы, как изменение качества и цены топлива, результативность ремонта и обслуживания, и даже возможности по сбору и обработке данных. Все это невозможно без использования мощных современных компьютеров и систем управления, способных оперировать множеством переменных, связанных с крупномасштабными объектами, и решать проблемы оптимизации, которые другим способом решить нереально.Whether through a stunning example of how to improve the rolling of metal, or in a more general overview of progress in optimization algorithms, this edition of ABB Review brings you closer to the challenges and successes of real world computer-based optimization tasks. But it is not in optimization and solving alone that information technology is making a difference: Who would have thought 10 years ago, that a technician would today be able to diagnose equipment and advise on maintenance without even visiting the factory? ABB’s Remote Service makes this possible. In another article, ABB Review shows how the company is reducing paperwork while at the same time leveraging quality control through the computer-based tracking of production. And if you believed that so-called “Internet communities” were just about fun, you will be surprised to read how a spin-off of this idea is already leveraging production efficiency in real terms. Devices are able to form “social networks” and so facilitate maintenance.Рассказывая об ошеломляющем примере того, как был усовершенствован процесс прокатки металла, или давая общий обзор развития алгоритмов оптимизации, этот выпуск АББ Ревю знакомит вас с практическими задачами и достигнутыми успехами оптимизации на основе компьютерных технологий. Но информационные технологии способны не только оптимизировать процесс производства. Кто бы мог представить 10 лет назад, что сервисный специалист может диагностировать производственное оборудование и давать рекомендации по его обслуживанию, не выходя из офиса? Это стало возможно с пакетом Remote Service от АББ. В другой статье этого номера АББ Ревю рассказывается о том, как компания смогла уменьшить бумажный документооборот и одновременно повысить качество управления с помощью компьютерного контроля производства. Если вы считаете, что так называемые «интернет-сообщества» служат только для развлечения,то очень удивитесь, узнав, что на основе этой идеи можно реально повысить производительность. Формирование «социальной сети» из автоматов значительно облегчает их обслуживание.This edition of ABB Review also features several stories of service and consulting successes, demonstrating how ABB’s expertise has helped customers achieve higher levels of productivity. In a more fundamental look at the question of what reliability is really about, a thought-provoking analysis sets out to find the definition of that term that makes the greatest difference to overall production.В этом номере АББ Ревю есть несколько статей, рассказывающих об успешных решениях по организации дистанционного сервиса и консультирования. Из них видно, как опыт АББ помогает нашим заказчикам повысить производительность своих предприятий. Углубленные размышления о самой природе термина «надежность» приводят к парадоксальным выводам, способным в корне изменить представления об оптимизации производства.Robots have often been called “the extended arm of man.” They are continuously advancing productivity by meeting ever-tightening demands on precision and efficiency. This edition of ABB Review dedicates two articles to robots.Робот – это могучее «продолжение» человеческой руки. Применение роботов способствует постоянному повышению производительности, поскольку они отвечают самым строгим требованиям точности и эффективности. Две статьи в этом номере АББ Ревю посвящены роботам.Further technological breakthroughs discussed in this issue look at how ABB is keeping water clean or enabling gas to be shipped more efficiently.Говоря о других технологических достижениях, обсуждаемых на страницах журнала, следует упомянуть о том, как компания АББ обеспечивает чистоту воды, а также более эффективную перевозку сжиженного газа морским транспортом.The publication of this edition of ABB Review is timed to coincide with ABB Automation and Power World 2009, one of the company’s greatest customer events. Readers visiting this event will doubtlessly recognize many technologies and products that have been covered in this and recent editions of the journal. Among the new products ABB is launching at the event is a caliper permitting the flatness of paper to be measured optically. We are proud to carry a report on this product on the very day of its launch.Публикация этого номера АББ Ревю совпала по времени с крупнейшей конференцией для наших заказчиков «ABB Automation and Power World 2009». Читатели, посетившие ее, смогли воочию увидеть многие технологии и изделия, описанные в этом и предыдущих выпусках журнала. Среди новинок, представленных АББ на этой конференции, был датчик, позволяющий измерять толщину бумаги оптическим способом. Мы рады сообщить, что сегодня он готов к выпуску.Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > оптимизация
См. также в других словарях:
Product lifecycle management — (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its conception, through design and manufacture, to service and disposal. [cite web title = About PLM publisher = CIMdata url = http://www.cimdata.com/PLM/aboutPLM.html ] PLM… … Wikipedia
Product Structure Modeling — Product structure is a hierarchical decomposition of a product, typically know as the BOM (Bill of Materials).As business becomes more responsive to unique consumer tastes and derivative products grow to meet the unique configurations, BOM… … Wikipedia
Product integral — Product integrals are a counterpart of standard integrals of infinitesimal calculus. They were first developed by the mathematician Vito Volterra in 1887 to solve systems of linear differential equations. Since then, product integrals have found… … Wikipedia
Product Family Engineering — Product families/lines are quite common in our daily lives, but before a product family can be successfully established, an extensive process has to be followed. This process is known as product family engineering, product line engineering, and… … Wikipedia
Product liability — is the area of law in which manufacturers, distributors, suppliers, retailers, and others who make products available to the public are held responsible for the injuries those products cause. Product liability in the United StatesIn the United… … Wikipedia
Product lifecycle — or product life cycle is the course of a product s sales and profits over time. The five stages of each product lifecycle are product development, introduction, growth, maturity and decline. [cite book |last=Kotler |first=Philip |coauthors=Gary… … Wikipedia
Product Manufacturing Information — Product and Manufacturing Information, or PMI, is used in 3D computer aided design (CAD) and Collaborative Product Development systems to convey information on the design of a product’s components for manufacturing. This includes data such as… … Wikipedia
Product Lifecycle Management — Pour les articles homonymes, voir PLM. Le Product Lifecycle Management (PLM, littéralement « gestion du cycle de vie du produit ») est le nom du domaine d activité dont le but est de créer et maintenir les produits tout au long de leur… … Wikipédia en Français
Product rule — For Euler s chain rule relating partial derivatives of three independent variables, see Triple product rule. For the counting principle in combinatorics, see Rule of product. Topics in Calculus Fundamental theorem Limits of functions Continuity… … Wikipedia
Product topology — In topology and related areas of mathematics, a product space is the cartesian product of a family of topological spaces equipped with a natural topology called the product topology. This topology differs from another, perhaps more obvious,… … Wikipedia
Product (category theory) — In category theory, the product of two (or more) objects in a category is a notion designed to capture the essence behind constructions in other areas of mathematics such as the cartesian product of sets, the direct product of groups, the direct… … Wikipedia
Перевод: со всех языков на немецкий
с немецкого на все языки- С немецкого на:
- Все языки
- Со всех языков на:
- Все языки
- Английский
- Арабский
- Итальянский
- Немецкий
- Нидерландский
- Русский
- Суахили
- Украинский
- Французский
