-
121 Memory
To what extent can we lump together what goes on when you try to recall: (1) your name; (2) how you kick a football; and (3) the present location of your car keys? If we use introspective evidence as a guide, the first seems an immediate automatic response. The second may require constructive internal replay prior to our being able to produce a verbal description. The third... quite likely involves complex operational responses under the control of some general strategy system. Is any unitary search process, with a single set of characteristics and inputoutput relations, likely to cover all these cases? (Reitman, 1970, p. 485)[Semantic memory] Is a mental thesaurus, organized knowledge a person possesses about words and other verbal symbols, their meanings and referents, about relations among them, and about rules, formulas, and algorithms for the manipulation of these symbols, concepts, and relations. Semantic memory does not register perceptible properties of inputs, but rather cognitive referents of input signals. (Tulving, 1972, p. 386)The mnemonic code, far from being fixed and unchangeable, is structured and restructured along with general development. Such a restructuring of the code takes place in close dependence on the schemes of intelligence. The clearest indication of this is the observation of different types of memory organisation in accordance with the age level of a child so that a longer interval of retention without any new presentation, far from causing a deterioration of memory, may actually improve it. (Piaget & Inhelder, 1973, p. 36)4) The Logic of Some Memory Theorization Is of Dubious Worth in the History of PsychologyIf a cue was effective in memory retrieval, then one could infer it was encoded; if a cue was not effective, then it was not encoded. The logic of this theorization is "heads I win, tails you lose" and is of dubious worth in the history of psychology. We might ask how long scientists will puzzle over questions with no answers. (Solso, 1974, p. 28)We have iconic, echoic, active, working, acoustic, articulatory, primary, secondary, episodic, semantic, short-term, intermediate-term, and longterm memories, and these memories contain tags, traces, images, attributes, markers, concepts, cognitive maps, natural-language mediators, kernel sentences, relational rules, nodes, associations, propositions, higher-order memory units, and features. (Eysenck, 1977, p. 4)The problem with the memory metaphor is that storage and retrieval of traces only deals [ sic] with old, previously articulated information. Memory traces can perhaps provide a basis for dealing with the "sameness" of the present experience with previous experiences, but the memory metaphor has no mechanisms for dealing with novel information. (Bransford, McCarrell, Franks & Nitsch, 1977, p. 434)7) The Results of a Hundred Years of the Psychological Study of Memory Are Somewhat DiscouragingThe results of a hundred years of the psychological study of memory are somewhat discouraging. We have established firm empirical generalisations, but most of them are so obvious that every ten-year-old knows them anyway. We have made discoveries, but they are only marginally about memory; in many cases we don't know what to do with them, and wear them out with endless experimental variations. We have an intellectually impressive group of theories, but history offers little confidence that they will provide any meaningful insight into natural behavior. (Neisser, 1978, pp. 12-13)A schema, then is a data structure for representing the generic concepts stored in memory. There are schemata representing our knowledge about all concepts; those underlying objects, situations, events, sequences of events, actions and sequences of actions. A schema contains, as part of its specification, the network of interrelations that is believed to normally hold among the constituents of the concept in question. A schema theory embodies a prototype theory of meaning. That is, inasmuch as a schema underlying a concept stored in memory corresponds to the mean ing of that concept, meanings are encoded in terms of the typical or normal situations or events that instantiate that concept. (Rumelhart, 1980, p. 34)Memory appears to be constrained by a structure, a "syntax," perhaps at quite a low level, but it is free to be variable, deviant, even erratic at a higher level....Like the information system of language, memory can be explained in part by the abstract rules which underlie it, but only in part. The rules provide a basic competence, but they do not fully determine performance. (Campbell, 1982, pp. 228, 229)When people think about the mind, they often liken it to a physical space, with memories and ideas as objects contained within that space. Thus, we speak of ideas being in the dark corners or dim recesses of our minds, and of holding ideas in mind. Ideas may be in the front or back of our minds, or they may be difficult to grasp. With respect to the processes involved in memory, we talk about storing memories, of searching or looking for lost memories, and sometimes of finding them. An examination of common parlance, therefore, suggests that there is general adherence to what might be called the spatial metaphor. The basic assumptions of this metaphor are that memories are treated as objects stored in specific locations within the mind, and the retrieval process involves a search through the mind in order to find specific memories....However, while the spatial metaphor has shown extraordinary longevity, there have been some interesting changes over time in the precise form of analogy used. In particular, technological advances have influenced theoretical conceptualisations.... The original Greek analogies were based on wax tablets and aviaries; these were superseded by analogies involving switchboards, gramophones, tape recorders, libraries, conveyor belts, and underground maps. Most recently, the workings of human memory have been compared to computer functioning... and it has been suggested that the various memory stores found in computers have their counterparts in the human memory system. (Eysenck, 1984, pp. 79-80)Primary memory [as proposed by William James] relates to information that remains in consciousness after it has been perceived, and thus forms part of the psychological present, whereas secondary memory contains information about events that have left consciousness, and are therefore part of the psychological past. (Eysenck, 1984, p. 86)Once psychologists began to study long-term memory per se, they realized it may be divided into two main categories.... Semantic memories have to do with our general knowledge about the working of the world. We know what cars do, what stoves do, what the laws of gravity are, and so on. Episodic memories are largely events that took place at a time and place in our personal history. Remembering specific events about our own actions, about our family, and about our individual past falls into this category. With amnesia or in aging, what dims... is our personal episodic memories, save for those that are especially dear or painful to us. Our knowledge of how the world works remains pretty much intact. (Gazzaniga, 1988, p. 42)The nature of memory... provides a natural starting point for an analysis of thinking. Memory is the repository of many of the beliefs and representations that enter into thinking, and the retrievability of these representations can limit the quality of our thought. (Smith, 1990, p. 1)Historical dictionary of quotations in cognitive science > Memory
-
122 насос сплинкерной системы пожаротушения
насос сплинкерной системы пожаротушения
жокей-насос
-Принцип работы насосной установки спринклерной системы пожаротушения, в состав которой входит жокей-насос
В случае падения давления воды в спринклерной системе, первым включается жокей-насос. Если расход воды небольшой и жокей-насос справляется с восполнением утечки, то через некоторое время после достижения верхнего предела заданного давления он выключится. Если же это не протечка, а открылось несколько спринклеров и расход воды значительный, то даже при работающем жокей-насосе давление продолжает падать. В этом случае, по сигналу второго реле давления, включается пожарный насос. Резервный агрегат включается в случае невыхода основного на рабочий режим. Независимо от того, потушен пожар или нет, пожарные насосы сами не отключаются, их можно выключить только вручную со шкафа управления.
[ http://www.airweek.ru/pr_news_137.html]
Jockey Pump
A jockey pump is a small pump connected to a fire sprinkler system and is intended to maintain pressure in a fire protection piping system to an artificially high level so that the operation of a single fire sprinkler will cause an appreciable pressure drop which will be easily sensed by the fire pump automatic controller, causing the fire pump to start. The jockey pump is essentially a portion of the fire pump's control system.
In the U.S.
The application of a jockey pump in a fire protection system is covered by documents produced by the NFPA (National Fire Protection Association,) known as NFPA 20 "Fire Pumps" Standard and NFPA 13 "Design and Installation of Fire Sprinkler Systems". These must be inspected as with any other part of the system per NFPA 25 "Inspection and Testing of Water-Based Fire Protection Systems".Fire protection systems are governed in most states by statute, building code, and/or fire code.
In India
This jockey pump is also a must while designing the Fire Hydrants Pumps skid for Industrial installations.While the logic followed for the effective operation of the fire fighting pumps may depend upon or vary as per the regulations in a particular country, in India, the pump manufacturers like Mather-Platt with standard Fire Pumps generally adhere to the TAC guidelines (Tariff Advisory Committee guidelines).
Although India's premier manufacturer Kirloskar Brothers Limited, with approvals from UL and FM Global, LPCB, ASIB: follows TAC guidelines (Tariff Advisory Committee guidelines), or FM GLobal and UL standards depending on the clients needs.
If one is following the TAC guidelines, follow this approach
*Once the complete fire fighting circuit is under pressure by operating the pumps for sufficient time provided all the fire hydrant valves (Single yard hydrants, Fire escape hydrants, etc)are closed, the main pump stops.
*Due to some leakages somewhere in the fire fighting piping circuit, when there is a loss of system pressure which will be constantly monitored by the Pressure sensors in the circuit, the jockey pumps receives a signal to start from the automatic control panel, and will run to augment this loss of pressure by pumping more water into the circuit. Once the pressure is maintained as per the set point, it stops.
*If any hydrant valve is opened due to some fire and water is consumed, then the jockey pump due to its small capacity compared to the main pumps (one running, one stand-by)in terms of volumetric capacity, the main pump will start and then the jockey immediately stops.This way jockey pump is important which senses the loss of pressure in the circuit first.[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jockey_pump#Jockey_Pump]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > насос сплинкерной системы пожаротушения
-
123 распределительный щиток
распределительный щиток
щиток
-
[ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001]-
по назначению
-
исполнению, относящемуся к виду установки:
-
наличию отключающего аппарата на вводе:
- с аппаратом:
- без аппарата;
-
наличию учета электроэнергии:
- со счетчиком;
- без счетчика;
-
по наличию слаботочного отсека
- количеству защитных аппаратов групповых цепей;
-
виду защитных аппаратов групповых цепей
- автоматические выключатели;
- предохранители;
-
наличию устройств защитного отключения:
- с УЗО;
- без УЗО;
-
способу защиты человека от поражения электрическим током:
- классы I и II по ГОСТ Р МЭК 536.
-
по числу фаз ввода в щиток
-
однофазный при Рр ≤ 11 кВт;
-
трехфазный при Рр ≥ 11 кВт или при наличии трехфазных токоприемников;
-
однофазный при Рр ≤ 11 кВт;
-
по наличию аппарата для защиты и отключения питающей цепи (стояка):
- с аппаратом (или предусмотренным местом для последующей его установки потребителем);
- без аппарата
Примечание. Рр - расчетная мощность на вводе квартиры.
[ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001] и [ ГОСТ Р 51628-2000]
Распределительные щитки (далее — щитки), применяемые в осветительных и силовых установках производственных, общественных, административных и других подобных зданий для приема и распределения электрической энергии при напряжении 380/220 и 660/380 В трехфазного переменного тока частотой 50 — 60 Гц, нечастого включения и отключения линий групповых цепей, а также для их защиты при перегрузках и коротких замыканиях.
Щитки могут устанавливаться в местах, доступных при эксплуатации неквалифицированному персоналу для выполнения коммутационных операций
Щитки, присоединяемые к трехфазным сетям с типами систем заземления TN-S, TN-C, TN-C-S, ТТ...
В щитках без отключающего аппарата на вводе должны быть зажимы для присоединения проводников питающей цепи
Дверцы щитков должны запираться на ключ
В щитках без дверец...
В щитках со счетчиками для исключения несанкционированного доступа к цепям учета электроэнергии (от входных зажимов вводного аппарата до ввода в счетчик) должны предусматриваться конструктивные элементы с возможностью их опломбирования
На оперативной панели щитка должна выполняться маркировка защитных аппаратов групповых цепей порядковыми номерами
В качестве аппаратов защиты групповых линий используются модульные автоматические выключатели с шириной модуля 18 мм.
На вводе и групповых линиях щитка могут быть установлены устройства защитного отключения с отключающим дифференциальным током на вводе - 30; 100; 300 мА, на групповых линиях - 10; 30 мА.
[ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001]
A panelboard as defined by the National Electrical Code is a single panel or a group of panel units designed for assembly in the form of a single panel; including buses, automatic overcurrent devices, and equipped with or without switches for the control of light, heat, or power circuits, designed to be placed in a cabinet or cutout box placed in or against a wall or partition and accessible only from the front.
Panelboards provide a compact and convenient method of grouping circuit switching and protective devices at some common point.
Panelboards may be of either the flush or the surface type (Fig. 4.125).
The flush type is used with concealed-wiring installations and has the advantage of not taking up space in the room by extending beyond the surface of the wall. Surface type boxes are used for installations employing exposed wiring.
The boxes are generally constructed of sheet steel, which must be not less than 0.053 in. (1.35 mm) in thickness.
The steel must be galvanized or be covered with some other protective coating to prevent corrosion.
Gutters are provided around the panelboards in cabinets to allow sufficient space for wiring (Figs. 4.125 and 4.126).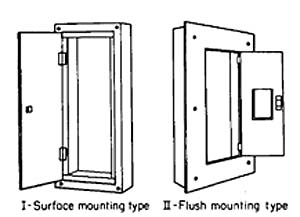
FIGURE 4.125 Panel boxes.
The Code requires that all cabinets which contain connections to more than eight conductors be provided with back or side wiring spaces. These wiring spaces must be separated from the panelboard or other devices in the cabinet by partitions so that they will be separate closed compartments, unless all wires are led from the cabinet at points directly opposite their terminal connections to the panelboard.
[American electricians’ handbook]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > распределительный щиток
-
по назначению
-
124 КП
1) General subject: сокр. Коммунистическая партия2) Naval: A.P. (кормовой перпендикуляр)3) Medicine: кожная проба4) Military: CP, action center, battle headquarters, command center, command point, command position, command post, control center, operational room, operational station, operations center, operations office, operations room, tactical headquarters5) Engineering: cf, командные пункты6) Accounting: краткосрочные пассивы (short-term liabilities)7) Abbreviation: газета "Комсомольская правда", авто коробка передач, колесная пара, контрольный пост, коммунальное предприятие8) Information technology: code receiver (кодовый приемник)10) Astronautics: launch control station, mission control station11) Sakhalin S: километровый пост12) Chemical weapons: конвейер передачи, конвейер подачи13) SAP.fin. PstKy14) oil&gas: контролируемый пункт, коэффициент пористости15) Politico-military term: командный пункт -
125 Кп
1) General subject: сокр. Коммунистическая партия2) Naval: A.P. (кормовой перпендикуляр)3) Medicine: кожная проба4) Military: CP, action center, battle headquarters, command center, command point, command position, command post, control center, operational room, operational station, operations center, operations office, operations room, tactical headquarters5) Engineering: cf, командные пункты6) Accounting: краткосрочные пассивы (short-term liabilities)7) Abbreviation: газета "Комсомольская правда", авто коробка передач, колесная пара, контрольный пост, коммунальное предприятие8) Information technology: code receiver (кодовый приемник)10) Astronautics: launch control station, mission control station11) Sakhalin S: километровый пост12) Chemical weapons: конвейер передачи, конвейер подачи13) SAP.fin. PstKy14) oil&gas: контролируемый пункт, коэффициент пористости15) Politico-military term: командный пункт -
126 бомбардировщик под кодовым наименованием Хот-Пойнт-22
Makarov: bomber code-named Hot Point 22Универсальный русско-английский словарь > бомбардировщик под кодовым наименованием Хот-Пойнт-22
-
127 возвращать индекс кодовой точки
Programming: return the index of the code pointУниверсальный русско-английский словарь > возвращать индекс кодовой точки
-
128 возвращать кодовую точку, начало и конец которой находится в указанной позиции
Универсальный русско-английский словарь > возвращать кодовую точку, начало и конец которой находится в указанной позиции
См. также в других словарях:
Point code — An SS7 point code is similar to an IP address in an IP network. It is a unique address for a node (Signaling Point, or SP), used in MTP layer 3 to identify the destination of a message signal unit (MSU). In such a message you will find an OPC… … Wikipedia
delivery point code — In mail processing, the finest depth of code to which a mailpiece can be sorted by its address. It is usually the 11 digit numeric code formed from the ZIP+4 and represented by the delivery point barcode (DPBC) … Glossary of postal terms
Пойнт-код Point Code — Поинт код (англ. Point Code) сигнальной системы 7 (SS7, ОКС 7) это уникальный (в домашней сети) адрес узла, используемый на третьем уровне MTP (маршрутизация) в телекоммуникационных ОКС 7 сетях для идентификации отправителя/получателя MSU (англ.… … Википедия
Code point — Not to be confused with Point code. In character encoding terminology, a code point or code position is any of the numerical values that make up the code space (or code page).[1] For example, ASCII comprises 128 code points in the range 0hex to… … Wikipedia
Code Correcteur — Un code correcteur est une technique de codage basée sur la redondance. Elle est destinée à corriger les erreurs de transmission d une information (plus souvent appelée message) sur une voie de communication peu fiable. La théorie des codes… … Wikipédia en Français
Code MDS — Code parfait et code MDS Un code parfait (ou code MDS, pour maximum distance séparable) est un concept de la théorie des codes et qui traite plus spécifiquement des codes correcteurs. Un code correcteur est un code permettant au récepteur de… … Wikipédia en Français
Code Parfait Et Code MDS — Un code parfait (ou code MDS, pour maximum distance séparable) est un concept de la théorie des codes et qui traite plus spécifiquement des codes correcteurs. Un code correcteur est un code permettant au récepteur de détecter ou de corriger des… … Wikipédia en Français
Code parfait — et code MDS Un code parfait (ou code MDS, pour maximum distance séparable) est un concept de la théorie des codes et qui traite plus spécifiquement des codes correcteurs. Un code correcteur est un code permettant au récepteur de détecter ou de… … Wikipédia en Français
Code parfait et code mds — Un code parfait (ou code MDS, pour maximum distance séparable) est un concept de la théorie des codes et qui traite plus spécifiquement des codes correcteurs. Un code correcteur est un code permettant au récepteur de détecter ou de corriger des… … Wikipédia en Français
Code page — is another term for character encoding. It consists of a table of values that describes the character set for a particular language. The term code page originated from IBM s EBCDIC based mainframe systems,[1] but many vendors use this term… … Wikipedia
Code Cyclique — En mathématiques et en informatique, un code cyclique est un code correcteur linéaire. Ce type de code possède non seulement la capacité de détecter les erreurs, mais aussi de les corriger sous reserve d altérations modérée. Les mathématiques… … Wikipédia en Français
