-
1 многожильный кабель
- Mehrleiterkabel, n
- mehradriges Kabel, n
многожильный кабель
многожильный провод
многожильный шнур
Кабель (провод, шнур), в котором число жил более трех.
[ ГОСТ 15845-80]EN
multicore cable
cable having more than one core
Note – The French term «câble multipolaire» is more specifically used to designate the cable constituting the phases of a multiphase system (example: three-core cable).
[EV ref 461-06-04]
multiconductor cable
cable having more than one conductor, some of which may be uninsulated
[IEV ref 461-06-03]FR
câble multiconducteur
câble multipolaire
câble comprenant plus d'un conducteur isolé
Note – Le terme câble multipolaire est plus particulièrement utilisé pour désigner le câble constituant les phases d'un système polyphasé (exemple: câble tripolaire).
[EV ref 461-06-04]
câble multiconducteur
câble multipolaire
câble comprenant plus d'une âme, dont éventuellement certaines non isolées
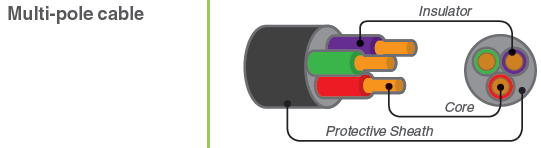
[IEV ref 461-06-03]Core - (токопроводящая) жила;
Insulator - изоляция жилы;
Protective Sheath - оболочка кабеля.Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Примечание(1) Мнение автора карточкиТематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
- bundled cable
- multi-pole cable
- multiconductor cable
- multicore cable
- multiple cable
- multiple-conductor cable
- multiple-core cable
- multistrand cable
- N-conductor cable
- polycore cable
DE
- mehradriges Kabel, n
- Mehrleiterkabel, n
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > многожильный кабель
-
2 длительный допустимый ток
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > длительный допустимый ток
-
3 управление землями различного хозяйственного назначения
управление землями различного хозяйственного назначения
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
multiple use management area
1) Coordinated management for the most judicious and harmonious use of the land on a long term basis under the concept of combining two or more uses and/or purposes with attention to sustainability and nonimpairment of the natural resources and land area. 2) Use of land for more than one purpose; e.g. grazing of livestock, watershed and wildlife protection, recreation, and timber production. (Source: UNUN / EPAGLO)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-немецкий словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > управление землями различного хозяйственного назначения
См. также в других словарях:
Multiple sclerosis — Classification and external resources Demyelination by MS. The CD68 colored tissue shows several macrophages in the area of the lesion. Original scale 1:100 ICD … Wikipedia
Multiple chemical sensitivity — Classification and external resources MeSH D018777 Multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) is a chronic medical condition characterized by symptoms the affected person attributes to exposure to low levels of chemicals. Commonly suspected substances… … Wikipedia
Multiple endocrine neoplasia — Classification and external resources Micrograph of a medullary thyroid carcinoma, as may be seen in MEN 2A and MEN 2B. H E stain … Wikipedia
Multiple Single-Level — or Multi Security Level (MSL) is a method of separating different levels of data by using separate PCs or virtual machines for each level. It aims to give some of the benefits of Multilevel security without needing special changes to the OS or… … Wikipedia
Multiple system atrophy — Classification and external resources ICD 10 G90.3 ICD 9 333.0 … Wikipedia
Multiple trace theory — (MTT) is a memory consolidation model advanced as an alternative model to strength theory. It posits that each time some information is presented to a person, it is neurally encoded in a unique memory trace composed of a combination of its… … Wikipedia
Multiple abnormalities — Classification and external resources ICD 10 Q87 ICD 9 759.7 … Wikipedia
Multiple myeloma — Classification and external resources Micrograph of a plasmacytoma, the histologic correlate of multiple myeloma. H E stain ICD … Wikipedia
Multiple organ dysfunction syndrome — Classification and external resources ICD 9 995.92 eMedicine med/3372 … Wikipedia
Term limits in Oregon — Term limits legislation – term limits for state and federal office holders – has been a recurring political issue in the U.S. state of Oregon since 1992. In that year s general election, Oregon voters approved Ballot Measure 3, an initiative that … Wikipedia
Multiple-complex Developmental Disorder — (McDD) represents a distinct group within the autism spectrum based on symptomatology.Ever since autism was first recognized, its continuity with schizophrenia has been a matter of debate. In fact, until the late 1970s, children with autism were… … Wikipedia