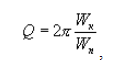-
1 fréquence maximum de bobine
максимальная частота катушки индуктивности
максимальная частота
Частота, при которой катушка еще может использоваться в качестве индуктивности.
[ ГОСТ 20718-75]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
FR
63. Максимальная частота катушки индуктивности
Максимальная частота
Е. Maximum frequency of coil
F. Fréquence maximum de bobine
Источник: ГОСТ 20718-75: Катушки индуктивности аппаратуры связи. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > fréquence maximum de bobine
-
2 fréquence maximale d'oscillation
максимальная частота генерации биполярного транзистора
Наибольшая частота, при которой транзистор способен генерировать в схеме автогенератора.
Обозначение
fmax
fmax
[ ГОСТ 20003-74]Тематики
EN
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > fréquence maximale d'oscillation
-
3 Fréquence maximale d’oscillation
31. Максимальная частота генерации биполярного транзистора
E. Maximum frequency of oscillation
F. Fréquence maximale d’oscillation
fmax
Наибольшая частота, при которой транзистор способен генерировать в схеме автогенератора
Источник: ГОСТ 20003-74: Транзисторы биполярные. Термины, определения и буквенные обозначения параметров оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Fréquence maximale d’oscillation
-
4 caractéristique de tenue d'un parafoudre sous tension à fréquence industrielle en fonction du temps
- характеристика «напряжение-время»
характеристика «напряжение-время»
Выдерживаемое напряжение промышленной частоты в зависимости от времени его приложения к ОПН. Показывает максимальный промежуток времени, в течение которого к ОПН может быть приложено напряжение промышленной частоты, превышающее Uнр, не вызывая повреждения или термической неустойчивости.
[ ГОСТ Р 52725-2007]EN
power-frequency withstand voltage versus time characteristic of an arrester
power-frequency withstand voltage versus time characteristic shows the maximum time durations for which corresponding power-frequency voltages may be applied to arresters without causing damage or thermal instability, under specified conditions in accordance with 6.10.
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]FR
caractéristique de tenue d'un parafoudre sous tension à fréquence industrielle en fonction du temps
durées maximales pendant lesquelles les tensions à fréquence industrielle correspondantes peuvent être appliquées aux parafoudres sans entraîner de détérioration ou d'instabilité thermique, dans des conditions spécifiées selon 6.10
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]Тематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
- power-frequency withstand voltage versus time characteristic of an arrester
FR
- caractéristique de tenue d'un parafoudre sous tension à fréquence industrielle en fonction du temps
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > caractéristique de tenue d'un parafoudre sous tension à fréquence industrielle en fonction du temps
-
5 tension assignée d'un parafoudre
номинальное напряжение
Uн
Действующее значение напряжения промышленной частоты, которое ограничитель может выдерживать в течение 10 с в процессе рабочих испытаний. Номинальное напряжение должно быть не менее 1,25 наибольшего длительно допустимого рабочего напряжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 52725-2007]EN
rated voltage of an arrester
Ur
maximum permissible r.m.s. value of power-frequency voltage between its terminals at which it is designed to operate correctly under temporary overvoltage conditions as established in the operating duty tests
NOTE 1 The rated voltage is used as a reference parameter for the specification of operating characteristics.
NOTE 2 The rated voltage as defined in this standard is the 10 s power-frequency voltage used in the operating duty test after high-current or long-duration impulses. Tests used to establish the voltage rating in IEC 60099-1, as well as some national standards, involve the application of repetitive impulses at nominal current with power-frequency voltage applied. Attention is drawn to the fact that these two methods used to established rating do not necessarily produce equivalent values (a resolution to this discrepancy is under consideration).
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]FR
tension assignée d'un parafoudre
Ur
valeur maximale de la tension efficace à fréquence industrielle admissible entre ses bornes pour laquelle le parafoudre est prévu pour fonctionner correctement dans des conditions de surtension temporaires comme il est défini dans les essais de fonctionnement
NOTE 1 La tension assignée est utilisée comme paramètre de référence pour la spécification des caractéristiques de fonctionnement.
NOTE 2 La tension assignée comme définie dans la présente norme est la tension à fréquence industrielle de 10 s, utilisée pour vérifier la stabilité après application des chocs de courant de grande amplitude ou de longue durée lors de l'essai de fonctionnement. Les essais utilisés pour définir la tension assignée dans la CEI 60099-1, ainsi que dans certaines normes nationales, impliquent l'application de chocs répétés au courant nominal pendant que la tension à fréquence industrielle est appliquée. On attire l'attention sur le fait que ces deux méthodes utilisées pour définir les valeurs assignées ne produisent pas nécessairement des valeurs équivalentes (une résolution de cette différence est à l'étude).
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]Тематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > tension assignée d'un parafoudre
-
6 courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant admissible, m
-
7 courant permanent admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant permanent admissible, m
-
8 concentration maximale d'immission
максимальная концентрация иммиссии
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
maximum immission concentration
The maximum concentration of air polluting substances in the free environment whose impact when of specified duration and frequency is not objectionable to man, fauna and flora. (Source: ECHO2)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > concentration maximale d'immission
-
9 facteur de qualité
добротность
1. Количественная характеристика потерь колебательной системы при резонансе, равная
где Wк - полный запас энергии колебаний при резонансе;
Wп - потери энергии за период
[ Физический энциклопедический словарь]
2. Количественная мера потерь колебательной системы. Показывает, во сколько раз амплитуда вынужденных колебаний при резонансе превышает амплитуду на частоте, много меньшей резонансной при одинаковой внешней силе
3. Отношение резонансной частоты спектра колебаний к его ширине на уровне 0,707 от максимального значения амплитуды спектра
Примечание
Определения 2 и 3 являются достаточно точными для систем с высокой добротностью (Q >(5-10)), определение 1 пригодно во всех случаях
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
добротность (1)
коэффициент добротности (1)
-
[IEV number 151-15-45]
добротность (2)
коэффициент добротности (2)
-
[IEV number 151-15-46]EN
quality factor (1)
Q factor (1)
for a capacitor or inductor under periodic conditions, ratio of the absolute value of the reactive power to the active power
NOTE 1 – The quality factor is a measure of the losses, usually unwanted, in a capacitor or an inductor.
NOTE 2 – The quality factor depends generally on frequency and voltage.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
quality factor (2)
Q factor (2)
for a resonant circuit at the resonance frequency, 2π times the ratio of the maximum stored energy to the energy dissipated during one period
NOTE – The quality factor is a measure of sharpness of the resonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]FR
facteur de qualité (1), m
facteur de surtension (1), m
pour un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance en régime périodique, rapport de la valeur absolue de la puissance réactive à la puissance active
NOTE 1 – Le facteur de qualité caractérise les pertes, généralement non désirées, dans un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance.
NOTE 2 – Le facteur de qualité dépend généralement de la fréquence et de la tension.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
facteur de qualité (2), m
facteur de surtension (2), m
pour un circuit résonant fonctionnant à la fréquence de résonance, 2π fois le rapport de l'énergie maximale emmagasinée dans le circuit à l'énergie dissipée pendant une période
NOTE – Le facteur de qualité caractérise l'acuité de la résonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
добротность конденсатора
Отношение реактивной мощности конденсатора к его активной мощности при синусоидальном напряжении определенной частоты.
[ ГОСТ 21415-75]
добротность конденсатора
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
D. Gütefaktor
E. Quality factor
F. Facteur de qualité
Отношение реактивной мощности конденсатора к его активной мощности при синусоидальном напряжении определенной частоты
Источник: ГОСТ 21415-75: Конденсаторы. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > facteur de qualité
-
10 facteur de surtension
добротность
1. Количественная характеристика потерь колебательной системы при резонансе, равная
где Wк - полный запас энергии колебаний при резонансе;
Wп - потери энергии за период
[ Физический энциклопедический словарь]
2. Количественная мера потерь колебательной системы. Показывает, во сколько раз амплитуда вынужденных колебаний при резонансе превышает амплитуду на частоте, много меньшей резонансной при одинаковой внешней силе
3. Отношение резонансной частоты спектра колебаний к его ширине на уровне 0,707 от максимального значения амплитуды спектра
Примечание
Определения 2 и 3 являются достаточно точными для систем с высокой добротностью (Q >(5-10)), определение 1 пригодно во всех случаях
[Система неразрушающего контроля. Виды (методы) и технология неразрушающего контроля. Термины и определения (справочное пособие). Москва 2003 г.]
добротность (1)
коэффициент добротности (1)
-
[IEV number 151-15-45]
добротность (2)
коэффициент добротности (2)
-
[IEV number 151-15-46]EN
quality factor (1)
Q factor (1)
for a capacitor or inductor under periodic conditions, ratio of the absolute value of the reactive power to the active power
NOTE 1 – The quality factor is a measure of the losses, usually unwanted, in a capacitor or an inductor.
NOTE 2 – The quality factor depends generally on frequency and voltage.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
quality factor (2)
Q factor (2)
for a resonant circuit at the resonance frequency, 2π times the ratio of the maximum stored energy to the energy dissipated during one period
NOTE – The quality factor is a measure of sharpness of the resonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]FR
facteur de qualité (1), m
facteur de surtension (1), m
pour un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance en régime périodique, rapport de la valeur absolue de la puissance réactive à la puissance active
NOTE 1 – Le facteur de qualité caractérise les pertes, généralement non désirées, dans un condensateur ou une bobine d'inductance.
NOTE 2 – Le facteur de qualité dépend généralement de la fréquence et de la tension.
[IEV number 151-15-45]
facteur de qualité (2), m
facteur de surtension (2), m
pour un circuit résonant fonctionnant à la fréquence de résonance, 2π fois le rapport de l'énergie maximale emmagasinée dans le circuit à l'énergie dissipée pendant une période
NOTE – Le facteur de qualité caractérise l'acuité de la résonance.
Source: 801-24-12 MOD
[IEV number 151-15-46]Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
добротность пьезоэлектрического резонатора
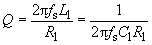
Отношение реактивного сопротивления пьезоэлектрического резонатора на частоте последовательного резонанса к его динамическому сопротивлению.
[ ГОСТ 18669-73]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > facteur de surtension
-
11 transport quotidien en heures creuses
внепиковая маятниковая миграция
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
off-peak commuting
Traveling back and forth regularly over some distance, outside of the hours of maximum traffic frequency. (Source: RHW)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > transport quotidien en heures creuses
-
12 courant initial de démarrage
начальный пусковой ток
Наибольшее действующее значение тока, потребляемого заторможенным электродвигателем переменного тока с короткозамкнутым ротором или магнитом переменного тока, у которого якорь установлен так, что создается максимальный воздушный зазор при номинальных напряжении и частоте.
Обозначение
символ IA
Примечание
Переходные процессы не принимают во внимание.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-426-2006]EN
initial starting current
Symbol IA
highest r.m.s. value of current absorbed by an a.c. motor when at rest or by an a.c. magnet with its armature clamped in the position of maximum air gap when supplied at rated voltage and rated frequency
NOTE – Transient phenomena are ignored.
[IEV number 426-08-04]FR
courant initial de démarrage
valeur efficace la plus élevée du courant absorbé par un moteur à courant alternatif au repos ou par un électro-aimant à courant alternatif dont l’armature est bloquée dans la position donnant l’entrefer maximal lorsqu’il est alimenté à sa tension et à sa fréquence assignées
NOTE – Les phénomènes transitoires ne sont pas pris en compte.
[IEV number 426-08-04]
Тематики
EN
DE
- Anzugstrom, m
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant initial de démarrage
-
13 démarrage direct
прямой пуск вращающегося электродвигателя
Пуск вращающегося электродвигателя путем непосредственного подключения его к питающей сети.
[ ГОСТ 27471-87]EN
direct-on-line starting
across-the-line starting (US)
the process of starting a motor by connecting it directly to the supply at rated voltage
[IEV number 411-52-15]FR
démarrage direct
mode de démarrage d'un moteur, consistant à lui appliquer directement sa pleine tension assignée
[IEV number 411-52-15]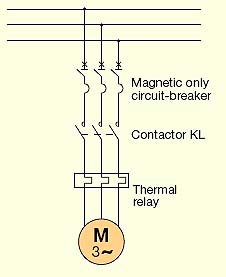
Рис. ABB
Схема прямого пуска электродвигателяMagnetic only circuit-breaker - Автоматический выключатель с электромагнитным расцепителем
Contactor KL - Контактор KL
Thermal relay - Тепловое реле
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Direct-on-line starting
Direct-on-line starting, which is often abbreviated as DOL, is perhaps the most traditional system and consists in connecting the motor directly to the supply network, thus carrying out starting at full voltage.Direct-on-line starting represents the simplest and the most economical system to start a squirrel-cage asynchronous motor and it is the most used.
As represented in Figure 5, it provides the direct connection to the supply network and therefore starting is carried out at full voltage and with constant frequency, developing a high starting torque with very reduced acceleration times.
The typical applications are relevant to small power motors also with full load starting.
These advantages are linked to some problems such as, for example, the high inrush current, which - in the first instants - can reach values of about 10 to 12 times the rated current, then can decrease to about 6 to 8 times the rated current and can persist to reach the maximum torque speed.The effects of such currents can be identified with the high electro-dynamical stresses on the motor connection cables and could affect also the windings of the motor itself; besides, the high inrush torques can cause violent accelerations which stress the transmission components (belts and joints) generating distribution problems with a reduction in the mechanical life of these elements.
Finally, also the possible electrical problems due to voltage drops on the supply line of the motor or of the connected equipment must be taken into consideration.
[ABB]Прямой пуск
Прямой пуск, который по-английски часто сокращенно обозначают как DOL, является, пожалуй наиболее распространенным способом пуска. Он заключается в непосредственном (т. е. прямом) подключении двигателя к питающей сети. Это означает, что пуск двигателя осуществляется при полном напряжении.Схема прямого пуска является наиболее простым, экономичным и чаще всего применяемым решением для электродвигателей с короткозамкнутым ротором.
Схема прямого подключения к сети представлена на рисунке 5. Пуск осуществляется при полном напряжении и постоянной частоте сети. Электродвигатель развивает высокий пусковой момент при коротком времени разгона.
Типичные области применения – маломощные электродвигатели, в том числе с пуском при полной нагрузке.
Однако, наряду с преимуществами имеются и определенные недостатки, например, бросок пускового тока, достигающий в первоначальный момент 10…12-кратного значения от номинального тока электродвигателя. Затем ток двигателя уменьшается примерно до 6…8-кратного значения номинального тока и будет держаться на этом уровне до тех пор, пока скорость двигателя не достигнет максимального значения.
Такое изменение тока оказывает значительное электродинамическое воздействие на кабель, подключенный к двигателю. Кроме того пусковой ток воздействует на обмотки двигателя. Высокий начальный пусковой момент может привести к значительному ускорению и следовательно к значительной нагрузке элементов привода (ремней, крепления узлов), что вызывает сокращение их срока службы.
И, наконец, следует принять во внимание возможное возникновение проблем, связанных с падением напряжения в линии питания двигателя и подключенного к этой линии оборудования.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- across-the-line starting (US)
- direct line starting
- direct operation of a motor
- direct starting
- direct-on-line starting
- DOL
- full voltage starter application
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > démarrage direct
-
14 fréquence de l’impédance maximale
- частота пьезоэлектрического резонатора при максимальном полном сопротивлении
частота пьезоэлектрического резонатора при максимальном полном сопротивлении
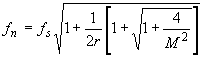
Частота, при которой абсолютное значение полного электрического сопротивления пьезоэлектрического резонатора является максимальным.
[ ГОСТ 18669-73]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
- fréquence de l’impédance maximale
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > fréquence de l’impédance maximale
-
15 rigidité diélectrique
электрическая прочность изоляции
Испытательное напряжение, прикладываемое в специальных условиях, которое должна выдерживать изоляция устройства
[МЭК 50(151)-78]EN
dielectric strength
maximum voltage between all parts of the electric circuit and the sheath of the thermometer or, in the case of a thermometer with two or more sensing circuits, between two individual circuits which the thermometer can withstand without damage. The measurement conditions for d.c and a.c (with frequency) have to be specified.
[IEC 60751, ed. 2.0 (2008-07)]FR
rigidité diélectrique
tension maximale entre tous les composants du circuit électrique et la gaine du thermomètre ou, dans le cas d’un thermomètre possédant plusieurs circuits de capteurs, entre deux circuits individuels, que le thermomètre peut supporter sans dégradation. Les conditions de mesure pour les tensions continues et alternatives (ainsi que la fréquence) doivent être spécifiées
[IEC 60751, ed. 2.0 (2008-07)]If used in conditions of highly humidity, the dielectric strength or electric performance may be degraded.
[LS Industrial Systems]При эксплуатации (выключателя) в условиях повышенной влажности могут ухудшиться электрическая прочность изоляции и другие электрические характеристики.
[Перевод Интент]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
- dielectric rigidity
- dielectric strength
- dielectric withstand
- electric strength of insulation
- insulating strength
- insulator level
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > rigidité diélectrique
См. также в других словарях:
maximum frequency — didžiausiasis dažnis statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. maximum frequency vok. maximale Frequenz, f rus. максимальная частота, f pranc. fréquence maximale, f … Fizikos terminų žodynas
maximum frequency of oscillation — didžiausiasis generavimo dažnis statusas T sritis radioelektronika atitikmenys: angl. maximum frequency of oscillation vok. maximale Schwingungsfrequenz, f rus. максимальная частота генерации, f pranc. fréquence maximale d oscillation, f … Radioelektronikos terminų žodynas
maximum frequency of oscillation — didžiausias generavimo dažnis statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Virpesių generatoriaus didžiausias generuojamas dažnis. atitikmenys: angl. maximum frequency of oscillation vok. maximale Schwingungsfrequenz, f rus.… … Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
maximum frequency of amplification — didžiausias srovės stiprinimo dažnis statusas T sritis Standartizacija ir metrologija apibrėžtis Srovės stiprintuvo didžiausias stiprinamas dažnis. atitikmenys: angl. maximum frequency of amplification vok. Übergangsgrenzfrequenz, f rus.… … Penkiakalbis aiškinamasis metrologijos terminų žodynas
maximum frequency of amplification — didžiausiasis srovės stiprinimo dažnis statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. maximum frequency of amplification vok. Übergangsgrenzfrequenz, f rus. максимальная частота усиления по току, f pranc. fréquence maximale d’amplification en… … Fizikos terminų žodynas
maximum frequency of oscillation — didžiausiasis virpesių dažnis statusas T sritis fizika atitikmenys: angl. maximum frequency of oscillation vok. maximale Schwingfrequenz, f; maximale Schwingungsfrequenz, f rus. максимальная частота колебаний, f pranc. fréquence maximale… … Fizikos terminų žodynas
Frequency deviation — (Δf) is used in FM radio to describe the maximum instantaneous difference between an FM modulated frequency and the nominal carrier frequency. The term is sometimes mistakenly used as synonymous with frequency drift, which is an unintended offset … Wikipedia
Frequency-shift keying — Passband modulation v · d · e Analog modulation AM · … Wikipedia
Maximum usable frequency — (MUF) describes, in radio transmission, using reflection from the regular ionized layers of the ionosphere, the upper frequency limit that can be used for transmission between two points at a specified time, independent of transmitter power. This … Wikipedia
Frequency-hopping spread spectrum — (FHSS) is a method of transmitting radio signals by rapidly switching a carrier among many frequency channels, using a pseudorandom sequence known to both transmitter and receiver. A spread spectrum transmission offers three main advantages over… … Wikipedia
Frequency response — is the measure of any system s spectrum response at the output to a signal of varying frequency (but constant amplitude) at its input. In the audible range it is usually referred to in connection with electronic amplifiers, microphones and… … Wikipedia