-
61 adventure training
HRactivities undertaken out of doors and away from the everyday work environment with a view to developing the skills and abilities of participants. Adventure training often takes place at a residential outdoor activity center and may include physically challenging activities such as climbing and rappelling or group exercises and games. The activities are designed to promote experiential learning in areas such as interpersonal communication, problem solving, decision making, and teamwork, and to develop self-confidence and leadership skills. Adventure training has its origins in the work of Kurt Hahn, the founder of Gordonstoun School in Scotland, who developed the Outward Bound program of outdoor activities during World War II. Adventure training programs for organizational personnel became popular during the late 1970s and 1980s, although some have doubted their value and effectiveness. -
62 de Havilland, Sir Geoffrey
SUBJECT AREA: Aerospace[br]b. 27 July 1882 High Wycombe, Buckinghamshire, Englandd. 21 May 1965 Stanmore, Middlesex, England[br]English designer of some eighty aircraft from 1909 onwards.[br]Geoffrey de Havilland started experimenting with aircraft and engines of his own design in 1908. In the following year, with the help of his friend Frank Hearle, he built and flew his first aircraft; it crashed on its first flight. The second aircraft used the same engine and made its first flight on 10 September 1910, and enabled de Havilland to teach himself to fly. From 1910 to 1914 he was employed at Farnborough, where in 1912 the Royal Aircraft Factory was established. As Chief Designer and Chief Test Pilot he was responsible for the BE 2, which was the first British military aircraft to land in France in 1914.In May 1914 de Havilland went to work for George Holt Thomas, whose Aircraft Manufacturing Company Ltd (Airco) of Hendon was expanding to design and build aircraft of its own design. However, because de Havilland was a member of the Royal Flying Corps Reserve, he had to report for duty when war broke out in August. His value as a designer was recognized and he was transferred back to Airco, where he designed eight aircraft in four years. Of these, the DH 2, DH 4, DH 5, DH 6 and DH 9 were produced in large numbers, and a modified DH 4A operated the first British cross- Channel air service in 1919.On 25 September 1920 de Havilland founded his own company, the De Havilland Aircraft Company Ltd, at Stag Lane near Edgware, London. During the 1920s and 1930s de Havilland concentrated on civil aircraft and produced the very successful Moth series of small biplanes and monoplanes, as well as the Dragon, Dragon Rapide, Albatross and Flamingo airliners. In 1930 a new site was acquired at Hatfield, Hertfordshire, and by 1934 a modern factory with a large airfield had been established. His Comet racer won the England-Australia air race in 1934 using de Havilland engines. By this time the company had established very successful engine and propeller divisions. The Comet used a wooden stressed-skin construction which de Havilland developed and used for one of the outstanding aircraft of the Second World War: the Mosquito. The de Havilland Engine Company started work on jet engines in 1941 and their Goblin engine powered the Vampire jet fighter first flown by Geoffrey de Havilland Jr in 1943. Unfortunately, Geoffrey Jr and his brother John were both killed in flying accidents. The Comet jet airliner first flew in 1949 and the Trident in 1962, although by 1959 the De Havilland Company had been absorbed into Hawker Siddeley Aviation.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsKnight Bachelor 1944. Order of Merit 1962. CBE 1934. Air Force Cross 1919. (A full list is contained in R.M.Clarkson's paper (see below)).Bibliography1961, Sky Fever, London; repub. 1979, Shrewsbury (autobiography).Further ReadingR.M.Clarkson, 1967, "Geoffrey de Havilland 1882–1965", Journal of the Royal Aeronautical Society (February) (a concise account of de Havilland, his achievements and honours).C.M.Sharp, 1960, D.H.—An Outline of de Havilland History, London (mostly a history of the company).A.J.Jackson, 1962, De Havilland Aircraft since 1915, London.JDSBiographical history of technology > de Havilland, Sir Geoffrey
-
63 Essen, Louis
SUBJECT AREA: Horology[br]b. 6 September 1908 Nottingham, England[br]English physicist who produced the first practical caesium atomic clock, which was later used to define the second.[br]Louis Essen joined the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) at Teddington in 1927 after graduating from London University. He spent his whole working life at the NPL and retired in 1972; his research there was recognized by the award of a DSc in 1948. At NPL he joined a team working on the development of frequency standards using quartz crystals and he designed a very successful quartz oscillator, which became known as the "Essen ring". He was also involved with radio frequency oscillators. His expertise in these fields was to play a crucial role in the development of the caesium clock. The idea of an atomic clock had been proposed by I.I.Rabbi in 1945, and an instrument was constructed shortly afterwards at the National Bureau of Standards in the USA. However, this device never realized the full potential of the concept, and after seeing it on a visit to the USA Essen was convinced that a more successful instrument could be built at Teddington. Assisted by J.V.L.Parry, he commenced work in the spring of 1953 and by June 1955 the clock was working reliably, with an accuracy that was equivalent to one second in three hundred years. This was significantly more accurate than the astronomical observations that were used at that time to determine the second: in 1967 the second was redefined in terms of the value for the frequency of vibration of caesium atoms that had been obtained with this clock.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsFRS 1960. Clockmakers' Company Tompion Gold Medal 1957. Physical Society C.V.Boys Prize 1957. USSR Academy of Science Popov Gold Medal 1959.Bibliography1957, with J.V.L.Parry, "The caesium resonator as a standard of frequency and time", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society (Series A) 25:45–69 (the first comprehensive description of the caesium clock).Further ReadingP.Forman, 1985, "Atomichron: the atomic clock from concept to commercial product", Proceedings of the IEEE 75:1,181–204 (an authoritative critical review of the development of the atomic clock).N.Cessons (ed.), 1992, The Making of the Modern World, London: Science Museum, pp.190–1 (contains a short account).See also: Marrison, Warren AlvinDV -
64 Goodyear, Charles
[br]b. 29 December 1800 New Haven, Connecticut, USAd. 1 July 1860 New York, USA[br]American inventor of the vulcanization of rubber.[br]Goodyear entered his father's country hardware business before setting up his own concern in Philadelphia. While visiting New York, he noticed in the window of the Roxburgh India Rubber Company a rubber life-preserver. Goodyear offered to improve its inflating valve, but the manager, impressed with Goodyear's inventiveness, persuaded him to tackle a more urgent problem, that of seeking a means of preventing rubber from becoming tacky and from melting or decomposing when heated. Goodyear tried treatments with one substance after another, without success. In 1838 he started using Nathaniel M.Hayward's process of spreading sulphur on rubber. He accidentally dropped a mass of rubber and sulphur on to a hot stove and noted that the mixture did not melt: Goodyear had discovered the vulcanization of rubber. More experiments were needed to establish the correct proportions for a uniform mix, and eventually he was granted his celebrated patent no. 3633 of 15 June 1844. Goodyear's researches had been conducted against a background of crippling financial difficulties and he was forced to dispose of licences to vulcanize rubber at less than their real value, in order to pay off his most pressing debts.Goodyear travelled to Europe in 1851 to extend his patents. To promote his process, he designed a spectacular exhibit for London, consisting of furniture, floor covering, jewellery and other items made of rubber. A similar exhibit in Paris in 1855 won him the Grande Médaille d'honneur and the Croix de la Légion d'honneur from Napoleon III. Patents were granted to him in all countries except England. The improved properties of vulcanized rubber and its stability over a much wider range of temperatures greatly increased its applications; output rose from a meagre 31.5 tonnes a year in 1827 to over 28,000 tonnes by 1900. Even so, Goodyear profited little from his invention, and he bequeathed to his family debts amounting to over $200,000.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsGrande Médaille d'honneur 1855. Croix de la Légion d'honneur 1855.Bibliography15 June 1844, US patent no. 3633 (vulcanization of rubber).1853, Gum Elastic and Its Varieties (includes some biographical material).Further ReadingB.K.Pierce, 1866, Trials of an Inventor: Life and Discoveries of Charles Goodyear.H.Allen, 1989, Charles Goodyear: An Intimate Biographical Sketch, Akron, Ohio: Goodyear Tire \& Rubber Company.LRD -
65 Morris, William Richard, Viscount Nuffield
[br]b. 10 October 1877 Worcester, Englandd. 22 August 1963 Nuffield Place, England[br]English industrialist, car manufacturer and philanthropist.[br]Morris was the son of Frederick Morris, then a draper. He was the eldest of a family of seven, all of whom, except for one sister, died in childhood. When he was 3 years old, his father moved to Cowley, near Oxford, where he attended the village school. After a short time with a local bicycle firm he set up on his own at the age of 16 with a capital of £4. He manufactured pedal cycles and by 1902 he had designed a motor cycle and was doing car-repair work. By 1912, at the Motor Show, he was able to announce his first car, the 8.9 hp, two-seater Morris Oxford with its characteristic "bull-nose". It could perform at up to 50 mph (80 km/h) and 50 mpg (5.65 1/100 km). It cost £165.Though untrained, Morris was a born engineer as well as a natural judge of character. This enabled him to build up a reliable team of assistants in his growing business, with an order for four hundred cars at the Motor Show in 1912. Much of his business was built up in the assembly of components manufactured by outside suppliers. In he moved out of his initial premises by New College in Longwall and bought land at Cowley, where he brought out his second model, the 11.9hp Morris Oxford. This was after the First World War, during which car production was reduced to allow the manufacture of tanks and munitions. He was awarded the OBE in 1917 for his war work. Morris Motors Ltd was incorporated in 1919, and within fifteen months sales of cars had reached over 3,000 a year. By 1923 he was producing 20,000 cars a year, and in 1926 50,000, equivalent to about one-third of Britain's output. With the slump, a substantial overdraft, and a large stock of unsold cars, Morris took the bold decision to cut the prices of cars in stock, which then sold out within three weeks. Other makers followed suit, but Morris was ahead of them.Morris was part-founder of the Pressed Steel Company, set up to produce car bodies at Cowley. A clever operation with the shareholding of the Morris Motors Company allowed Morris a substantial overall profit to provide expansion capital. By 1931 his "empire" comprised, in addition to Morris Motors, the MG Car Company, the Wolseley Company, the SU Carburettor Company and Morris Commercial Cars. In 1936, the value of Morris's financial interest in the business was put at some £16 million.William Morris was a frugal man and uncomplicated, having little use for all the money he made except to channel it to charitable purposes. It is said that in all he gave away some £30 million during his lifetime, much of it invested by the recipients to provide long-term benefits. He married Elizabeth Anstey in 1904 and lived for thirty years at Nuffield Place. He lived modestly, and even after retirement, when Honorary President of the British Motor Corporation, the result of a merger between Morris Motors and the Austin Motor Company, he drove himself to work in a modest 10 hp Wolseley. His generosity benefited many hospitals in London, Oxford, Birmingham and elsewhere. Oxford Colleges were another class of beneficiary from his largesse.[br]Principal Honours and DistinctionsViscount 1938; Baron (Lord Nuffield) 1934; Baronet 1929; OBE 1917; GBE 1941; CH 1958. FRS 1939. He was a doctor of seven universities and an honorary freeman of seven towns.Further ReadingR.Jackson, 1964, The Nuffield Story.P.W.S.Andrews and E.Brunner, The Life of Lord Nuffield.IMcNBiographical history of technology > Morris, William Richard, Viscount Nuffield
-
66 проектный
цели проектирования; проектные параметры — design objective
ошибка проектирования; проектная недоработка — design fault
Бизнес, юриспруденция. Русско-английский словарь > проектный
-
67 Philosophy
And what I believe to be more important here is that I find in myself an infinity of ideas of certain things which cannot be assumed to be pure nothingness, even though they may have perhaps no existence outside of my thought. These things are not figments of my imagination, even though it is within my power to think of them or not to think of them; on the contrary, they have their own true and immutable natures. Thus, for example, when I imagine a triangle, even though there may perhaps be no such figure anywhere in the world outside of my thought, nor ever have been, nevertheless the figure cannot help having a certain determinate nature... or essence, which is immutable and eternal, which I have not invented and which does not in any way depend upon my mind. (Descartes, 1951, p. 61)Let us console ourselves for not knowing the possible connections between a spider and the rings of Saturn, and continue to examine what is within our reach. (Voltaire, 1961, p. 144)As modern physics started with the Newtonian revolution, so modern philosophy starts with what one might call the Cartesian Catastrophe. The catastrophe consisted in the splitting up of the world into the realms of matter and mind, and the identification of "mind" with conscious thinking. The result of this identification was the shallow rationalism of l'esprit Cartesien, and an impoverishment of psychology which it took three centuries to remedy even in part. (Koestler, 1964, p. 148)It has been made of late a reproach against natural philosophy that it has struck out on a path of its own, and has separated itself more and more widely from the other sciences which are united by common philological and historical studies. The opposition has, in fact, been long apparent, and seems to me to have grown up mainly under the influence of the Hegelian philosophy, or, at any rate, to have been brought out into more distinct relief by that philosophy.... The sole object of Kant's "Critical Philosophy" was to test the sources and the authority of our knowledge, and to fix a definite scope and standard for the researches of philosophy, as compared with other sciences.... [But Hegel's] "Philosophy of Identity" was bolder. It started with the hypothesis that not only spiritual phenomena, but even the actual world-nature, that is, and man-were the result of an act of thought on the part of a creative mind, similar, it was supposed, in kind to the human mind.... The philosophers accused the scientific men of narrowness; the scientific men retorted that the philosophers were crazy. And so it came about that men of science began to lay some stress on the banishment of all philosophic influences from their work; while some of them, including men of the greatest acuteness, went so far as to condemn philosophy altogether, not merely as useless, but as mischievous dreaming. Thus, it must be confessed, not only were the illegitimate pretensions of the Hegelian system to subordinate to itself all other studies rejected, but no regard was paid to the rightful claims of philosophy, that is, the criticism of the sources of cognition, and the definition of the functions of the intellect. (Helmholz, quoted in Dampier, 1966, pp. 291-292)Philosophy remains true to its classical tradition by renouncing it. (Habermas, 1972, p. 317)I have not attempted... to put forward any grand view of the nature of philosophy; nor do I have any such grand view to put forth if I would. It will be obvious that I do not agree with those who see philosophy as the history of "howlers" and progress in philosophy as the debunking of howlers. It will also be obvious that I do not agree with those who see philosophy as the enterprise of putting forward a priori truths about the world.... I see philosophy as a field which has certain central questions, for example, the relation between thought and reality.... It seems obvious that in dealing with these questions philosophers have formulated rival research programs, that they have put forward general hypotheses, and that philosophers within each major research program have modified their hypotheses by trial and error, even if they sometimes refuse to admit that that is what they are doing. To that extent philosophy is a "science." To argue about whether philosophy is a science in any more serious sense seems to me to be hardly a useful occupation.... It does not seem to me important to decide whether science is philosophy or philosophy is science as long as one has a conception of both that makes both essential to a responsible view of the world and of man's place in it. (Putnam, 1975, p. xvii)What can philosophy contribute to solving the problem of the relation [of] mind to body? Twenty years ago, many English-speaking philosophers would have answered: "Nothing beyond an analysis of the various mental concepts." If we seek knowledge of things, they thought, it is to science that we must turn. Philosophy can only cast light upon our concepts of those things.This retreat from things to concepts was not undertaken lightly. Ever since the seventeenth century, the great intellectual fact of our culture has been the incredible expansion of knowledge both in the natural and in the rational sciences (mathematics, logic).The success of science created a crisis in philosophy. What was there for philosophy to do? Hume had already perceived the problem in some degree, and so surely did Kant, but it was not until the twentieth century, with the Vienna Circle and with Wittgenstein, that the difficulty began to weigh heavily. Wittgenstein took the view that philosophy could do no more than strive to undo the intellectual knots it itself had tied, so achieving intellectual release, and even a certain illumination, but no knowledge. A little later, and more optimistically, Ryle saw a positive, if reduced role, for philosophy in mapping the "logical geography" of our concepts: how they stood to each other and how they were to be analyzed....Since that time, however, philosophers in the "analytic" tradition have swung back from Wittgensteinian and even Rylean pessimism to a more traditional conception of the proper role and tasks of philosophy. Many analytic philosophers now would accept the view that the central task of philosophy is to give an account, or at least play a part in giving an account, of the most general nature of things and of man. (Armstrong, 1990, pp. 37-38)8) Philosophy's Evolving Engagement with Artificial Intelligence and Cognitive ScienceIn the beginning, the nature of philosophy's engagement with artificial intelligence and cognitive science was clear enough. The new sciences of the mind were to provide the long-awaited vindication of the most potent dreams of naturalism and materialism. Mind would at last be located firmly within the natural order. We would see in detail how the most perplexing features of the mental realm could be supported by the operations of solely physical laws upon solely physical stuff. Mental causation (the power of, e.g., a belief to cause an action) would emerge as just another species of physical causation. Reasoning would be understood as a kind of automated theorem proving. And the key to both was to be the depiction of the brain as the implementation of multiple higher level programs whose task was to manipulate and transform symbols or representations: inner items with one foot in the physical (they were realized as brain states) and one in the mental (they were bearers of contents, and their physical gymnastics were cleverly designed to respect semantic relationships such as truth preservation). (A. Clark, 1996, p. 1)Socrates of Athens famously declared that "the unexamined life is not worth living," and his motto aptly explains the impulse to philosophize. Taking nothing for granted, philosophy probes and questions the fundamental presuppositions of every area of human inquiry.... [P]art of the job of the philosopher is to keep at a certain critical distance from current doctrines, whether in the sciences or the arts, and to examine instead how the various elements in our world-view clash, or fit together. Some philosophers have tried to incorporate the results of these inquiries into a grand synoptic view of the nature of reality and our human relationship to it. Others have mistrusted system-building, and seen their primary role as one of clarifications, or the removal of obstacles along the road to truth. But all have shared the Socratic vision of using the human intellect to challenge comfortable preconceptions, insisting that every aspect of human theory and practice be subjected to continuing critical scrutiny....Philosophy is, of course, part of a continuing tradition, and there is much to be gained from seeing how that tradition originated and developed. But the principal object of studying the materials in this book is not to pay homage to past genius, but to enrich one's understanding of central problems that are as pressing today as they have always been-problems about knowledge, truth and reality, the nature of the mind, the basis of right action, and the best way to live. These questions help to mark out the territory of philosophy as an academic discipline, but in a wider sense they define the human predicament itself; they will surely continue to be with us for as long as humanity endures. (Cottingham, 1996, pp. xxi-xxii)10) The Distinction between Dionysian Man and Apollonian Man, between Art and Creativity and Reason and Self- ControlIn his study of ancient Greek culture, The Birth of Tragedy, Nietzsche drew what would become a famous distinction, between the Dionysian spirit, the untamed spirit of art and creativity, and the Apollonian, that of reason and self-control. The story of Greek civilization, and all civilizations, Nietzsche implied, was the gradual victory of Apollonian man, with his desire for control over nature and himself, over Dionysian man, who survives only in myth, poetry, music, and drama. Socrates and Plato had attacked the illusions of art as unreal, and had overturned the delicate cultural balance by valuing only man's critical, rational, and controlling consciousness while denigrating his vital life instincts as irrational and base. The result of this division is "Alexandrian man," the civilized and accomplished Greek citizen of the later ancient world, who is "equipped with the greatest forces of knowledge" but in whom the wellsprings of creativity have dried up. (Herman, 1997, pp. 95-96)Historical dictionary of quotations in cognitive science > Philosophy
-
68 автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
- residual current-operated circuit-breaker
- residual current-operated circuit breaker
- residual current circuit-breaker
- residual current circuit breaker
- RCCB
- ELCB
- earth leakage circuit breaker
- circuit-breaker with integrated residual current protection
- circuit-breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit breaker incorporating residual current protection
- CBR
автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, предназначенный для включения, проведения и отключения токов при нормальных условиях электрической цепи, а также отключения электрической цепи в случае, когда значение дифференциального тока достигает заданной величины в определенных условиях.
[Перевод Интент]EN
residual current-operated circuit-breaker
mechanical switching device designed to make, carry and break currents under normal service conditions and to cause the opening of the contacts when the residual current attains a given value under specified conditions.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]FR
interrupteur à courant différentiel résiduel
appareil mécanique de connexion destiné à établir, supporter et couper des courants dans les conditions de service normales et à provoquer l'ouverture des contacts quand le courant différentiel atteint, dans des conditions spécifiées, une valeur donnée.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
- автоматический выключатель остаточных токов
- автоматический выключатель с функцией защиты от тока утечки
- автоматический выключатель, управляемый остаточным током
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
- CBR
- circuit breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker with integrated residual current protection
- earth leakage circuit breaker
- ELCB
- RCCB
- residual current circuit breaker
- residual current circuit-breaker
- residual current-operated circuit breaker
- residual current-operated circuit-breaker
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
-
69 аппарат защиты от сверхтока
аппарат защиты от сверхтока
-EN
overcurrent protection device
device, such as a fuse or circuit-breaker, designed to interrupt the circuit when the current flow exceeds a predetermined value for a predetermined time
[IEC 60092-507, ed. 2.0 (2008-01)]FR
dispositif de protection contre les surintensités
dispositif, fusible ou disjoncteur, conçu pour interrompre le circuit lorsque le flux de courant dépasse une valeur prédéterminée pendant une durée prédéterminée
[IEC 60092-507, ed. 2.0 (2008-01)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
Синонимы
EN
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > аппарат защиты от сверхтока
-
70 включающая и отключающая способность при коротком замыкании
включающая и отключающая способность при коротком замыкании
-
[IEV number 442-05-48]EN
short-circuit (making and breaking) capacity
the alternating component of the prospective current, expressed by its rms value, which the circuit-breaker is designed to make, to carry for its opening time and to break under specified conditions
[IEV number 442-05-48]FR
pouvoir de coupure (et de fermeture) en court-circuit
composante alternative du courant présumé, exprimée en valeur efficace, que le disjoncteur, par conception, peut établir, peut supporter pendant son temps d'ouverture et peut interrompre dans des conditions spécifiées
[IEV number 442-05-48]EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > включающая и отключающая способность при коротком замыкании
-
71 линейно-интерактивный источник бесперебойного питания
линейно-интерактивный источник бесперебойного питания
источник бесперебойного питания с линейно-интерактивным режимом работы
-EN
line interactive UPS
A system, which energizes the load from the utility mains providing conditioned power by filtering and stabilizing mains voltage (VI class per IEC 62040-3).
Upon mains outage the load is energized from batteries via the Inverter.
[ http://www.upsonnet.com/UPS-Glossary/]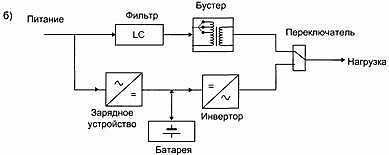
Структурная схема линейно-интерактивного ИБП
[ http://www.tcs.ru/reviews/?id=345]Исчезновение напряжения в питающей сети - явление довольно редкое.
Гораздо чаще происходят провалы или всплески напряжения, вызывающие не менее серьезные последствия в нагрузке (электроприемнике). Именно это обстоятельство послужило причиной для разработки ИБП, способных регулировать напряжение сети. Такие ИПБ получили название линейно-интерактивных.
Нетрудно заметить, что по схемотехнике линейно-интерактивные ИБП похожи на off-line ИБП. Принципиальным отличием между ними, обусловившим выделение line-interactive ИБП в отдельную группу, является наличие специального устройства (бустера), предназначенного для ступенчатой стабилизации выходного напряжения, осуществляемого путем автоматического переключения отводов трансформатора.
Линейно-интерактивные ИБП являются удачным сочетанием простоты и надежности off-line ИПБ и быстродействия on-line ИБП. Существенным отличием указанных ИБП является форма выходного напряжения в автономном (аккумуляторном) режиме работы: у off-line ИПБ - ступенчатая, а у линейно-интерактивного ИБП - синусоидальная.
Линейно-интерактивные ИБП часто используются для защиты офисной техники и серверов масштаба одного отдела.Достоинства:
- компактность,
- экономичность,
- синусоидальная форма выходного напряжения,
- ступенчатая стабилизация выходного напряжения.
Недостатки:
- отсутствие гальванической развязки нагрузки (электропотребителя) от питающей сети,
- отсутствие стабилизации частоты выходного напряжения,
- недостаточный уровень стабилизация выходного напряжения относительно номинального значения (5-7%).
[ http://www.tcs.ru/reviews/?id=345 с изменениями]
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
The Agilon VX line-interactive UPS is a best value product designed for PCs, laptops, and POS equipment used in home offices and small businesses.
[Delta Electronics]Линейно-интерактивный ИПБ Agilon VX600 является одним из лучших источников для бесперебойного питания персональных компьютеров и терминалов розничной торговли в домашних офисах и малом бизнесе.
[Перевод Интент]
Is it important that UPS include a Voltage Regulator?
Definitively. When the AC Line voltage is not suitable for your PC the UPS uses internal batteries to supply appropriate power to your PC. If the UPS does not include a Voltage Regulator this range is rather narrow but when UPS includes Voltage Regulator this range can be quite wide because most of the variations can be managed by the stabilization system and consequently the use of the batteries is less frequent. Evidently the less the UPS uses the batteries the longer life they will have.
Batteries Life Expectancy in an UPS including Voltage Regulator (Called Interactive UPS or In-Line UPS) is about 3 years, while batteries in an UPS not including Voltage Regulator (Off Line UPS) usually do not last longer than a year. Nevertheless end users rarely realize their batteries are loosing properties since the back up time can only be measured during actual blackouts and then it could be too late.
[ http://www.integra-ups.com/am/en/soporte/preguntas.htm]
Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > линейно-интерактивный источник бесперебойного питания
-
72 номинальное напряжение ОПН
номинальное напряжение
Uн
Действующее значение напряжения промышленной частоты, которое ограничитель может выдерживать в течение 10 с в процессе рабочих испытаний. Номинальное напряжение должно быть не менее 1,25 наибольшего длительно допустимого рабочего напряжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 52725-2007]EN
rated voltage of an arrester
Ur
maximum permissible r.m.s. value of power-frequency voltage between its terminals at which it is designed to operate correctly under temporary overvoltage conditions as established in the operating duty tests
NOTE 1 The rated voltage is used as a reference parameter for the specification of operating characteristics.
NOTE 2 The rated voltage as defined in this standard is the 10 s power-frequency voltage used in the operating duty test after high-current or long-duration impulses. Tests used to establish the voltage rating in IEC 60099-1, as well as some national standards, involve the application of repetitive impulses at nominal current with power-frequency voltage applied. Attention is drawn to the fact that these two methods used to established rating do not necessarily produce equivalent values (a resolution to this discrepancy is under consideration).
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]FR
tension assignée d'un parafoudre
Ur
valeur maximale de la tension efficace à fréquence industrielle admissible entre ses bornes pour laquelle le parafoudre est prévu pour fonctionner correctement dans des conditions de surtension temporaires comme il est défini dans les essais de fonctionnement
NOTE 1 La tension assignée est utilisée comme paramètre de référence pour la spécification des caractéristiques de fonctionnement.
NOTE 2 La tension assignée comme définie dans la présente norme est la tension à fréquence industrielle de 10 s, utilisée pour vérifier la stabilité après application des chocs de courant de grande amplitude ou de longue durée lors de l'essai de fonctionnement. Les essais utilisés pour définir la tension assignée dans la CEI 60099-1, ainsi que dans certaines normes nationales, impliquent l'application de chocs répétés au courant nominal pendant que la tension à fréquence industrielle est appliquée. On attire l'attention sur le fait que ces deux méthodes utilisées pour définir les valeurs assignées ne produisent pas nécessairement des valeurs équivalentes (une résolution de cette différence est à l'étude).
[IEC 60099-4, ed. 2.0 (2004-05)]Тематики
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > номинальное напряжение ОПН
-
73 плавкий предохранитель
- thermal fuse
- SF
- safety plug
- safety fuse
- safety cutoff
- protective fuse
- plug fuse
- fusible switch
- fusible plug
- fusible cutout
- fuse switch
- fuse
- fu
- electric fuse
- cutoff
плавкий предохранитель
Коммутационный аппарат, который посредством плавления одного или нескольких своих специально спроектированных и калиброванных элементов размыкает цепь, в которую он включен, и отключает ток, когда он превышает заданную величину в течение достаточного времени. Плавкий предохранитель содержит все части, образующие укомплектованный аппарат.
МЭК 60050(441-18-01).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
плавкий предохранитель
Аппарат, который вследствие расплавления одного или нескольких специально спроектированных и рассчитанных элементов размыкает цепь, в которую он включен, отключая ток, превышающий заданное значение в течение достаточно продолжительного времени. В состав плавкого предохранителя входят все части, образующие аппарат в комплекте
[ ГОСТ Р 50339. 0-2003 ( МЭК 60269-1-98)]
предохранитель
Коммутационный электрический аппарат, предназначенный для отключения защищаемой цепи посредством разрушения специально предусмотренных для этого токоведущих частей под действием тока, превышающего определенную величину.
[ ГОСТ 17703-72]
предохранитель
Устройство для разрыва электрических цепей при силе тока, превышающей допустимое значение
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
fuse
a device that by the fusing of one or more of its specially designed and proportioned components, opens the circuit in which it is inserted by breaking the current when this exceeds a given value for a sufficient time. The fuse comprises all the parts that form the complete device
[IEV number 441-18-01 ]FR
fusible
coupe-circuit à fusibles
appareil dont la fonction est d'ouvrir par la fusion d'un ou de plusieurs de ses éléments conçus et calibrés à cet effet le circuit dans lequel il est inséré en coupant le courant lorsque celui-ci dépasse pendant un temps suffisant une valeur donnée. Le fusible comprend toutes les parties qui constituent l'appareil complet
[IEV number 441-18-01 ]Настоящий стандарт распространяется на плавкие предохранители на номинальный ток от 2 до 2500 А, номинальное напряжение переменного тока до 1000 В и постоянного тока до 1200 В, устанавливаемые в комплектные устройства и предназначенные для защиты при перегрузках и коротких замыканиях силовых и вспомогательных цепей электроустановок промышленных предприятий, общественных и жилых зданий, изготовляемые для нужд народного хозяйства и экспорта и номинальное напряжение до 3000 В для защиты полупроводниковых устройств.
3.2.14. Предохранители должны быть сконструированы таким образом, чтобы отключать электрическую цепь при токах отключения в пределах: от условного тока плавления — для предохранителей с плавкими вставками типов g и gR или от наименьшего тока отключения, установленного в стандартах или технических условиях на предохранители конкретных серий и типов, для предохранителей с плавкими вставками типов а и aR — до наибольшего тока отключения
[ ГОСТ 17242-86]... токи, при которых проводят испытания, предназначенные для проверки способности данного плавкого предохранителя срабатывать удовлетворительно в диапазоне малых сверхтоков.
[ ГОСТ Р 50339.0-2003]... Если неисправность заканчивается срабатыванием плавкого предохранителя или если плавкий предохранитель не срабатывает примерно в течение 1 с, то...
[ ГОСТ Р 52319-2005]ЭЛЕКТРИЧЕСКИЕ ПАРАМЕТРЫ И ХАРАКТЕНИСТИКИ ПРЕДОХРАНИТЕЛЕЙ
(взято из ГОСТ 17242-86)-
Для держателя (или основания) предохранителя:
- номинальное напряжение;
- номинальный ток;
- род тока и номинальная частота для переменного тока;
- допустимые потери мощности;
- число полюсов, если их более одного.
-
Для плавкой вставки:
- номинальное напряжение;
- номинальный ток;
- род тока и номинальная частота для переменного тока;
- потери мощности;
- время-токовые характеристики с указанием коэффициентов K1 и K2 для плавких вставок типа а;
- перегрузочная способность;
- диапазон токов отключения;
- наибольшая отключающая способность;
- наименьший ток отключения для плавких вставок типа а;
- характеристика пропускаемого тока;
- характеристики интегралов Джоуля;
- перенапряжение и характеристика перенапряжения для плавких вставок типов aR и gR;
- условия селективности (при необходимости);
- электрическое сопротивление плавкой вставки в холодном состоянии (допускается указать в рабочих чертежах, утвержденных в установленном порядке).
-
Для предохранителя:
- степень защиты по ГОСТ 14255—69;
- номинальное напряжение, номинальный ток и коммутационная способность свободных контактов (при их наличии).
Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Check to make sure that fuse F1 on power supply module V is not fused.
If the fuse is defective, it should not be replaced without determining the cause of failure.
If a fuse is replaced without eliminating the problem, there is the danger that the damage will spread.
[Schneider Electric]Убедитесь в исправности предохранителя F1 в модуле питания V.
Если предохранитель оказался неисправным, то прежде чем заменить его необходимо установить причину возникновения неисправности.
Замена предохранителя без выяснения причины его срабатывания может привести к повторению срабатывания.
[Перевод Интент]High voltage system may embrace a fuse.
Note that a fuse may not be manually adjusted as the circuit breaker relay does so the fuse choice for the appropriate purpose/circuit adaptation is deemed most important.
[LS Industrial Systems]Высоковольтная система < электропитания> может содержать предохранители.
Обратите внимание! Предохранитель нельзя настроить, как это можно сделать с расцепителем автоматического выключателя. Поэтому предохранитель необходимо выбрать так, чтобы он как можно точнее соотвествовал конкретным условиям защиты аппарата или участка цепи.
[Перевод Интент]
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Действия
- защищать при перегрузках и коротких замыканиях
- отключать электрическую цепь
- срабатывание предохранителя
Синонимы
EN
- cutoff
- electric fuse
- fu
- fuse
- fuse switch
- fusible cutout
- fusible plug
- fusible switch
- plug fuse
- protective fuse
- safety cutoff
- safety fuse
- safety plug
- SF
- thermal fuse
DE
FR
3.1 плавкий предохранитель (fuse): Устройство, которое за счет расплавления одной или нескольких его деталей, имеющих определенную конструкцию и размеры, размыкает цепь, в которую оно включено, прерывая ток, если он превышает заданное значение в течение определенного времени. Предохранитель включает в себя все детали, образующие готовые изделия.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60127-1-2005: Миниатюрные плавкие предохранители. Часть 1. Терминология для миниатюрных плавких предохранителей и общие требования к миниатюрным плавким вставкам оригинал документа
3.1.3 плавкий предохранитель (fuse): Коммутационный аппарат, который вследствие расплавления одного или более специально спроектированных и калиброванных элементов размыкает цепь, в которую он включен, и отключает ток, когда тот превышает заданную величину в течение достаточного времени.
[МЭС 441-18-01]
Источник: ГОСТ Р 50345-2010: Аппаратура малогабаритная электрическая. Автоматические выключатели для защиты от сверхтоков бытового и аналогичного назначения. Часть 1. Автоматические выключатели для переменного тока оригинал документа
3.3.3 плавкий предохранитель (fuse): Коммутационный аппарат, который посредством плавления одного или нескольких своих специально спроектированных и калиброванных элементов размыкает цепь, в которую он включен, и отключает ток, когда тот превышает заданное значение в течение определенного времени. Плавкий предохранитель содержит все части, образующие укомплектованный аппарат.
[МЭС 441-18-01] [1]
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51327.1-2010: Выключатели автоматические, управляемые дифференциальным током, бытового и аналогичного назначения со встроенной защитой от сверхтоков. Часть 1. Общие требования и методы испытаний оригинал документа
3.2.4 плавкий предохранитель (fuse): Коммутационный аппарат, размыкающий цепь (посредством плавления одного или нескольких своих специально спроектированных и калиброванных элементов), в которую он включен, и отключает ток, когда он превышает заданную величину в течение достаточного времени. Плавкий предохранитель содержит все части, образующие укомплектованный аппарат.
МЭК 60050(441-18-01)]
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51731-2010: Контакторы электромеханические бытового и аналогичного назначения оригинал документа
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > плавкий предохранитель
-
74 плавкий элемент
плавкий элемент
Часть плавкой вставки, рассчитанная на расплавление под воздействием тока на протяжении определенного периода времени, превышающего определенное значение.
МЭК 60050(441-18-08).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
плавкий элемент
Часть плавкой вставки, предназначенная для расплавления при срабатывании плавкого предохранителя. В плавкой вставке может быть несколько параллельных плавких элементов.
[ ГОСТ Р 50339. 0-2003 ( МЭК 60269-1-98)]
плавкий элемент предохранителя
плавкий элемент
Часть плавкой вставки, предназначенная для расплавления при срабатывании предохранителя.
[ ГОСТ 17242-86]EN
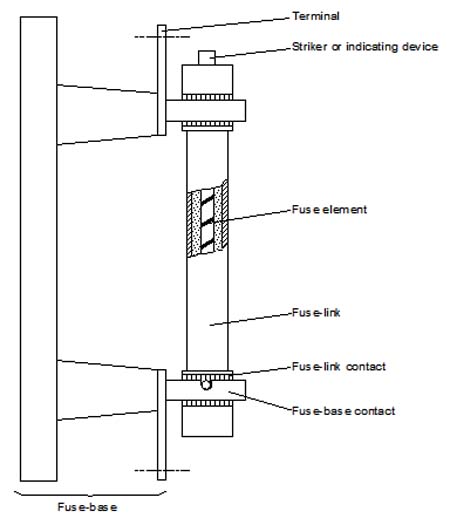
fuse-element
a part of the fuse-link designed to melt under the action of current exceeding some definite value for a definite period of time
[IEV number 441-18-08]
[IEC 60282-1, ed. 7.0 (2009-10)FR
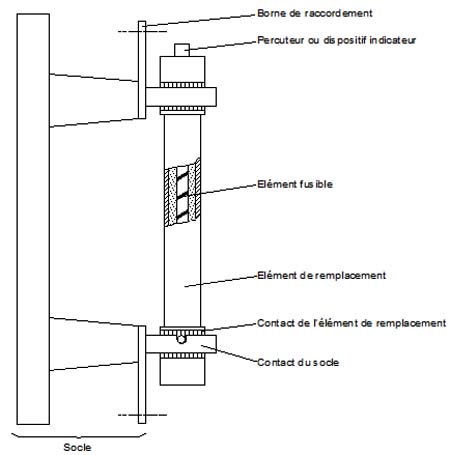
élément fusible
partie de l'élément de remplacement destiné à fondre sous l'action d'un courant dépassant une valeur déterminée pendant une durée déterminée
[IEV number 441-18-08]
[IEC 60282-1, ed. 7.0 (2009-10)]Тематики
Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
3.14 плавкий элемент (fuse-element): Деталь плавкой вставки, предназначенная для расплавления при срабатывании плавкого предохранителя.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60127-1-2005: Миниатюрные плавкие предохранители. Часть 1. Терминология для миниатюрных плавких предохранителей и общие требования к миниатюрным плавким вставкам оригинал документа
2.1.5 плавкий элемент (fuse-element): Часть плавкой вставки, предназначенная для расплавления при срабатывании плавкого предохранителя.
[МЭС 441-18-08]
Примечание - В плавкой вставке может быть несколько параллельных плавких элементов.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60269-1-2010: Предохранители низковольтные плавкие. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > плавкий элемент
-
75 полупроводниковое коммутационное устройство
полупроводниковое коммутационное устройство
-
[IEV number 442-04-19]EN
semiconductor switching device
a switching device designed to make or break the current in an electric circuit by means of the controlled conductivity of a semiconductor in that circuit
NOTE – In a circuit where the current passes through zero (periodically or otherwise) the effect of "not making" the current following such a zero value is equivalent to breaking the current.
[IEV number 442-04-19]FR
dispositif de coupure à semiconducteur
dispositif de coupure conçu pour établir ou couper le courant dans un circuit électrique au moyen de la conductivité contrôlée d'un semiconducteur dans ce circuit
NOTE – Dans un circuit où le courant passe par zéro (périodiquement ou autrement), le fait de ne pas rétablir le courant après un tel passage à zéro est équivalent à la coupure du courant.
[IEV number 442-04-19]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
DE
FR
3.2.3 полупроводниковое коммутационное устройство (semiconductor switching device): Коммутационное устройство, созданное для включения и/или отключения тока в электрической цепи в результате воздействия на регулируемую проводимость полупроводника.
Примечание - Определение отличается от МЭК 60050(441-14-03) тем, что полупроводниковый прибор, использованный в полупроводниковом коммутационном устройстве, рассчитан также на отключение тока.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51731-2010: Контакторы электромеханические бытового и аналогичного назначения оригинал документа
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > полупроводниковое коммутационное устройство
-
76 преобразователь среднеквадратичных значений
преобразователь среднеквадратичных значений
-
[IEV number 313-03-09]EN
rms-sensing transducer
transducer specifically designed to respond to the rms value of the input and which is characterized by the manufacturer for use on a specified range of waveforms
[IEV number 313-03-09]FR
transducteur de valeur efficace
transducteur spécifiquement conçu pour répondre à la valeur efficace de l’entrée et qui est caractérisé par le constructeur pour utilisation avec une plage de formes d’onde spécifiée
[IEV number 313-03-09]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > преобразователь среднеквадратичных значений
-
77 природный парк
природный парк
—
[ http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]EN
natural park
A designation of project lands which preserves natural resources for their scientific, scenic, cultural and/or educational value by limiting development and management practices. Land managed to protect rare and endangered species of flora and fauna will be designed as natural areas. (Source: LANDY)
[http://www.eionet.europa.eu/gemet/alphabetic?langcode=en]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > природный парк
-
78 "дуговая" неисправность
"дуговая" неисправность
Неисправность, приводящая к возникновению дуги.
[Интент]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
An arc fault occurs when there is a reduction in the dielectric strength of the insulating means (air, in LV switchboards) interposed between two or more conducting elements at different potential.
The arc is generated at the moment when, due to the high ionization of the air, there is a breakdown of the dielectric of the medium and the consequent flow of the current through it.
In an arc fault the highest stresses are of thermal type and proportional to RaI2 owing to the high value taken by the arc resistance Ra; this because the fault current flows in a medium which is always insulating, even if extremely ionized.
Such stresses manifest themselves essentially in the form of:
• high thermal gradients caused by the quick and intense rise in the air temperature;
• high pressure gradients in the form of pressure wave;
• high ionization of the air with consequent reduction of its insulating strength.
Generally speaking, in a LV assembly designed and tested according to the Standard IEC 60439-1 an arc fault is not very likely to occur; however, should it occur, the consequences would be extremely harmful to both the equipment as well as the personnel (see Chapters 2.2 and 2.3).
The causes of an arc fault can be both technical as well as non technical; among the latter the most frequent are the following:
• personnel errors, above all during maintenance operations;
• installation operations not sufficiently accurate;
• inadequate maintenance, above all in the case of severe environmental conditions.
Among the technical causes of an arc fault in a LV assembly the following ones are to be remembered:
• breakdown of the insulation essentially in the proximity of the supports of the busbars and of the plug-in contacts of the withdrawable units (75% of cases);
• overvoltages generating disruptive discharges between the points at minimum clearances (15% of cases);
• constructional defects of the apparatus (10% of cases).
[ABB]К «дуговой» неисправности, относится неисправность, обусловленная уменьшением электрической прочности изолирующей среды (воздуха в НКУ) между двумя или более токоведущими частями, находящимися под разными электрическими потенциалами.
Дуга образуется в тот момент, когда вследствие высокой ионизации воздуха происходит пробой изолирующей среды, вследствие чего через нее начинает протекать электрический ток.
Проявлением дуговой неисправности, является тепловое воздействие, пропорциональное RaI2 и достигающее большого значения вследствие большого сопротивления дуги Ra.
Дело в том, что ток дуги протекает через среду, которая всегда является изолирующей, пусть даже и чрезвычайно ионизированной.
Указанные воздействия очевидны сами по себе особенно в форме:
• теплового градиента температуры, вызванного быстрым и интенсивным подъемом температуры воздуха;
• высоким градиентом давления в форме волны давления;
• высокой ионизацией воздуха с последующим уменьшением электрической прочности.
Вообще говоря, в НКУ, разработанных и испытанных в соответствии с требованиями стандарта МЭК 60439-1 «дуговая» неисправность маловероятна. Однако, если дуга все таки возникнет, ее последствия буду чрезвычайно тяжелыми как для оборудования, так и для персонала (см. п. 2.2 и 2.3).
Причина дуговой неисправности может носить как технический, так и нетехнический характер. Среди последних наиболее часто возникают следующие:
• ошибки персонала, совершаемые главным образом во время технического обслуживания;
• недостаточно аккуратное выполнение монтажа;
• ненадлежащее техническое обслуживание, главным образом при эксплуатации НКУ в тяжелых условиях окружающей среды.
Среди технических причин дуговой неисправности в НКУ необходимо помнить о следующих:
• пробой изоляции, особенно вблизи опор шин и втычных контактов выдвижных частей НКУ (75 % случаев);
• перенапряжения, вызываемые разрушительными электрическими разрядами между точками с минимальными зазорами (15 % случаев);
• конструктивные дефекты аппаратуры (10 % случаев).
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > "дуговая" неисправность
См. также в других словарях:
Value Place — is a chain of hotels in the United States, based in Wichita, Kansas. It is currently one of the fastest growing hotel chains in the United States, with more than 100 locations in 23 states. It was founded by Jack DeBoer in 2001… … Wikipedia
Value of information — (VoI) in decision analysis is the amount a decision maker would be willing to pay for information prior to making a decision. imilar termsVoI is sometimes distinguished into value of perfect information, also called value of clairvoyance (VoC),… … Wikipedia
Value menu — A selection of value menu hamburgers from McDonald s, Burger King, Sonic Drive In and Wendy s. A value menu is a group of items on a fast food restaurant menu that are designed to be the least expensive items available. In the US, the items are… … Wikipedia
Value stream mapping software — is a type of software that helps prepare and/or analyze value stream maps. The software typically helps design maps through utilizing a series of symbols representing activity and information/material flow, and as a supplement to manual… … Wikipedia
Value Added Tax-free Exports from the Channel Islands — are exports of goods from the Channel Islands on which value added tax (VAT) is not levied. In recent years, companies in the United Kingdom have expressed concern at the competition thereby offered to their goods on which VAT is… … Wikipedia
value — The utility of an object in satisfying, directly or indirectly, the needs or desires of human beings, called by economists value in use, or its worth consisting in the power of purchasing other objects, called value in exchange. Joint Highway… … Black's law dictionary
Value, Daily (DV) — A new term appearing on food labels, Daily Value is a new dietary reference value designed to help consumers use food label information to plan a healthy diet. Daily Values (DVs) comprise two sets of reference values for nutrients: Daily… … Medical dictionary
Value shop — The value shop was first conceptualized by Thompson in 1967. A value shop is an organization designed to solve customer or client problems rather than creating value by producing output from an input of raw materials. Compared to Michael Porter s … Wikipedia
Designed landscape — A designed landscape is an area of land which has been modified by people for primarily aesthetic effect. The term is used by historians to denote various types of site, such as gardens, parks, cemeteries, and estates. Such sites are often… … Wikipedia
Value-added reseller — A value added reseller (VAR) is a company that adds some feature(s) to an existing product(s), then resells it (usually to end users) as an integrated product or complete turn key solution. This practice is common in the electronics industry,… … Wikipedia
Value of monogamy — The value of monogamy refers to people s views about the contributions monogamy makes, good or bad, to individual and social well being. Some cultures value monogamy as an ideal form of family organization. However, many cultures prefer other… … Wikipedia
