-
1 compatible current sinking logic
прил.выч. совместимая токовая логика; совместимые логические схемы с потреблением токаФранцузско-русский универсальный словарь > compatible current sinking logic
-
2 complementary constant current logic
неизм.выч. комплементарные логические схемы с переключением сигналов в виде постоянных токовФранцузско-русский универсальный словарь > complementary constant current logic
-
3 courant admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant admissible, m
-
4 courant permanent admissible, m
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant permanent admissible, m
-
5 courant d'intersection
ток координации
Токовая координата точки пересечения время-токовых характеристик двух устройств для защиты от сверхтоков.
МЭК 60050(441-17-16).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
ток координации (Iв)
Координата точки пересечения время-токовых характеристик наибольшей отключающей способности двух аппаратов защиты от сверхтоков.
Примечания
1 Ток координации — предельное значение тока, выше которого при наличии двух последовательно соединенных аппаратов защиты от сверхтоков защитный аппарат, расположенный со стороны питания, как правило, но не обязательно обеспечивает резервную защиту второго защитного аппарата
2 Вместо время-токовых характеристик можно использовать характеристики I2t
[ ГОСТ Р 50345-99( МЭК 60898-95)]EN
take-over current
the current co-ordinate of the intersection between the time-current characteristics of two over-current protective devices
[IEV number 441-17-16]FR
courant d'intersection
valeur du courant correspondant à l'intersection des caractéristiques temps-courant de deux dispositifs de protection à maximum de courant
[IEV number 441-17-16]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
ток пересечения
-
[IEV number 442-05-61]EN
take-over current
the current co-ordinate of the intersection between the maximum break time-current characteristics of two overcurrent protective devices
Source: 441-17-16 MOD
[IEV number 442-05-61]FR
courant d'intersection
coordonnées du courant de l'intersection entre les caractéristiques de durée maximale de coupure temps-courant de deux dispositifs de protection à maximum de courant
Source: 441-17-16 MOD
[IEV number 442-05-61]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
ток пересечения IB
-
[IEV number 442-05-61]EN
take-over current
the current co-ordinate of the intersection between the maximum break time-current characteristics of two overcurrent protective devices
[IEV number 442-05-61]FR
courant d'intersection
coordonnées du courant de l'intersection entre les caractéristiques de durée maximale de coupure temps-courant de deux dispositifs de protection à maximum de courant
[IEV number 442-05-61]Тематики
Синонимы
- IB
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant d'intersection
-
6 disjoncteur limiteur de courant
токоограничивающий автоматический выключатель
Выключатель с чрезвычайно малым временем отключения, в течение которого ток короткого замыкания не успевает достичь своего максимального значения.
[МЭК 60947-1]En
current-limiting circuit breaker
Circuit-breaker with a break-time short enough to prevent the short-circuit current reaching its otherwise attainable peak value.
[< size="2">IEC 60077-3, ed. 1.0 (2001-12)]
Circuit-breaker that, within a specified range of current, prevents the let-through current reaching the prospective peak value and which limits the let-through energy (I2t) to a value less than the let-through energy of a half-cycle wave of the symmetrical prospective current
NOTE 1 - Reference may be made to either the symmetrical or asymmetrical prospective peak value of let-through current.
NOTE 2 - The let-through current is also referred to as the cut-off current (see IEV 441-17-12).
NOTE 3 - Templates for the graphical representation of the cut-off current characteristic and the let-through energy characteristic are given in Figures K.2 to K.5 and examples of the use of the templates in Figures K.6 and K.7.
[IEC 60947-2, ed. 4.0, amd. 1 (2009-01)]Fr
disjoncteur limiteur de courant
Disjoncteur dont la durée de coupure est particulièrement brève en vue d’obtenir que le courant de court-circuit ne puisse atteindre son amplitude maximale
[< size="2">IEC 60077-3, ed. 1.0 (2001-12)]
Disjoncteur qui, à l'intérieur d'un domaine de courant spécifié, empêche le courant coupé limité d'atteindre la valeur crête présumée et qui limite l'énergie limitée (I2t) à une valeur inférieure à l'énergie limitée d'une demi-période du courant présumé symétrique
NOTE 1 Il peut être fait référence à la valeur crête présumée symétrique ou assymétrique du courant coupé limité.
NOTE 2 Le courant coupé limité (let-through current) est aussi nommé "cut-off current" (voir VEI 441-17-12).
NOTE 3 Les modèles de représentation graphique des caractéristiques de courant coupé limité et d'énergie limitée sont illustrés dans les Figures K.2 à K.5 et les exemples d'utilisation des modèles dans les Figures K.6 et K.7.
[IEC 60947-2, ed. 4.0, amd. 1 (2009-01)]Токоограничивающий автоматический выключатель имеет чрезвычайно малое время отключения, в течение которого ток КЗ не успевает достичь максимального значения.
Токоограничивающие автоматические выключатели ограничивают ток КЗ с помощью быстрого введения в цепь дополнительного сопротивления электрической дуги (в первый же полупериод, до того, как ток КЗ значительно возрастет) и последующего быстрого отключения КЗ, при этом ток КЗ не достигает ожидаемого расчетного максимального значения. Токоограничение начинается с некоторого значения тока, определяемого характеристикой токоогранияения.
В токоограничивающих автоматических выключателях при больших ожидаемых токах КЗ контакты, сразу же отбрасываются электродинамическими силами, вводя в цепь сопротивление дуги, и затем уже не соприкасаются, так как своевременно срабатывает электромагнитный расцепитель.
При малых токах КЗ контакты не отбрасываются, а отключение производится электромагнитным расцепителем.
[А.В.Беляев. Выбор аппаратуры, защит и кабелей в сетях 0,4 кВ. - Л.: Энергоатомиздат. 1988.]Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
EN
- current limiting circuitbreaker
- current-limiting circuit breaker
- current-limiting circuit-breaker
- limiting circuit breaker
- limiting circuit-breaker
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > disjoncteur limiteur de courant
-
7 courant assigné
номинальный ток
Ток, указанный изготовителем на приборе
Примечание.
Если ток для прибора не указан, то номинальный ток равен:- для нагревательных приборов – току, рассчитанному по номинальной потребляемой мощности и номинальному напряжению;
- для электромеханических и комбинированных приборов – току, измеренному в период работы прибора в условиях нормальной работы при номинальном напряжении.
EN
rated current
current assigned to the appliance by the manufacturer
NOTE - If no current is assigned to the appliance, the rated current is
– for heating appliances, the current calculated from the rated power input and the rated voltage;
– for motor-operated appliances and combined appliances, the current measured when the appliance is supplied at rated voltage and operated under normal operation.
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]FR
courant assigné
courant attribué à l'appareil par le fabricant
NOTE - Si aucun courant n'est attribué à l'appareil, le courant assigné est
– pour les appareils chauffants, le courant calculé à partir de la puissance assignée et de la tension assignée;
– pour les appareils à moteur et les appareils combinés, le courant mesuré lorsque l'appareil est alimenté sous la tension assignée et mis en fonctionnement dans les conditions de fonctionnement normal.
[IEC 60335-1, ed. 4.0 (2001-05)]2
номинальный ток
значение тока, являющееся исходным при установлении требований настоящего стандарта к счетчику.
[ ГОСТ 6570-96]Тематики
EN
FR
паспортный ток
-
[IEV number 314-07-02]EN
rated current
value of current in accordance with which the relevant performance of a transformer operated meter is fixed
[IEV number 314-07-02]FR
courant assigné
valeur du courant en fonction de laquelle certaines des caractéristiques d’un compteur alimenté par transformateur(s) sont fixées
[IEV number 314-07-02]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant assigné
-
8 surintensité
сверхток
Любой ток, превышающий номинальный
МЭК 60050(441-11-06).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]
[ ГОСТ Р 50345-99( МЭК 60898-95)]
сверхток
Электрический ток, превышающий номинальный электрический ток.
Сверхток представляет собой любой электрический ток, величина которого превышает номинальный ток какого-либо элемента электроустановки здания или используемого в ней электрооборудования, например: номинальный ток электрической цепи, допустимый длительный ток проводника, номинальный ток автоматического выключателя и т. д. В нормативной и правовой документации различают два основных вида сверхтока – ток перегрузки и ток короткого замыкания.
Появление сверхтока в каком-либо элементе электроустановки здания может привести к его перегреву, возгоранию и, как следствие, к возникновению пожара в здании. Поэтому в электроустановках зданий выполняют защиту от сверхтока.
[ http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%D1/view/59/]
сверхток
сверхток в электротехническом изделии
Ток, значение которого превосходит наибольшее рабочее значение тока электротехнического изделия (устройства).
[ ГОСТ 18311-80]
сверхток
Электрический ток, превышающий номинальный электрический ток.
Примечание - Для проводников номинальный ток считается равным длительному допустимому току.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Сверхток может оказывать или может не оказывать вредные воздействия в зависимости от его величины и продолжительности. Сверхтоки могут возникать в результате перегрузок в электроприемниках или при повреждениях, таких как короткие замыкания или замыканиях на землю
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]
сверхток
Любой ток, превышающий номинальное значение. Для проводов номинальным значением является допустимый ток.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]EN
overcurrent
electric current exceeding the rated electric current
NOTE – For conductors, the rated current is considered as equal to the current-carrying capacity
[IEV number 826-11-14]
over-current
<>current exceeding the rated current
<>[IEC 61095, ed. 2.0 (2009-02)]
over-current
electric current the value of which exceeds a specified limiting value
[IEV number 151-15-28]
[IEV number 442-01-20]FR
surintensité, f
courant électrique supérieur au courant électrique assigné
NOTE – Pour des conducteurs, on considère que le courant assigné est égal au courant admissible.
[IEV number 826-11-14]
surintensité
courant supérieur au courant assigné
[IEC 61095, ed. 2.0 (2009-02)]
[IEV number 442-01-20]
surintensité, f
courant électrique dont la valeur dépasse une valeur limite spécifiée
[IEV number 151-15-28]Параллельные тексты EN-RU The design of LV installations leads to basic protection devices being fitted for three types of faults:
-
overloads
-
short-circuits
-
insulation faults
Низковольтные электроустановки должны быть оснащены устройствами защиты трех типов:
-
от перегрузки;
-
от короткого замыкания;
- от токов утечки.
[Перевод Интент]
Примечание.
Слово fault в данном случае пришлось опустить, поскольку:
- его нельзя перевести как "неисправность", т. к. возникновение перегрузки ( overload) не является неисправностью;
- его нельзя перевести как "сверхток", т. к. ток утечки не является сверхтоком.The chosen switchgear must withstand and eliminate faults at optimised cost with respect to the necessary performance.
[Schneider Electric]Выбранная аппаратура распределения должна иметь такие характеристики, чтобы рентабельно выдерживать и ограничивать сверхтоки.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > surintensité
-
overloads
-
9 courant coupé (d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible)
ток отключения
Принятое значение ожидаемого тока в цепи, отключенной аппаратом, в заданный момент времени.
[ ГОСТ 17703-72]
ток отключения
Ток в полюсе выключателя в момент возникновения дуги при отключении
[ ГОСТ Р 50345-99( МЭК 60898-95)]
ток отключения
Iоткл, А
Номинальный ток, отключаемый разъединителем (заземлителем).
[ ГОСТ Р 52726-2007]
ток отключения (коммутационного аппарата или плавкого предохранителя)
Ток в одном полюсе коммутационного аппарата или в плавком предохранителе в момент возникновения дуги в процессе отключения.
МЭК 60050(441-17-07).
Примечание. Для переменного тока это симметричное действующее значение периодической составляющей.
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
breaking current (of a switching device or a fuse)
the current in a pole of a switching device or in a fuse at the instant of initiation of the arc during a breaking process
[IEV number 441-17-07]FR
courant coupé (d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible)
courant dans un pôle d'un appareil de connexion ou dans un fusible évalué à l'instant de l'amorçage de l'arc au cours d'une coupure
[IEV number 441-17-07]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
Current flow monitoring
This function is used to detect a break in current flow safely, immediately and pole selectively.
[Schneider Electric]Контроль тока
Данная функция используется для безопасного мгновенного обнаружения тока отключения, протекающего через каждый полюс выключателя.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
- выключатель автоматический
- выключатель, переключатель
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
- предохранитель
- релейная защита
Синонимы
EN
- break in current
- breaking current
- breaking current (of a switching device or a fuse)
- interrupted current
- interrupting current
- opening current
- tripping current
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant coupé (d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible)
-
10 caractéristique courant-tension
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость электрического напряжения на выводах элемента электрической цепи от электрического тока в нем.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость тока от приложенного к элементу электрич. цепи напряжения или зависимость падения напряжения на элементе электрич. цепи от протекающего через него тока. Если сопротивление элемента не зависит от тока, то В.-а. х.—прямая линия, проходящая через начало координат. В.-а. х. нелинейных элементов электрич. цепи (электровакуумные, газоразрядные и твёрдотельные приборы) имеют нелинейные участки и разнообразную форму (N-образные В.-а. х., S-образные и т. п.).
[Физический энциклопедический словарь. М.: «Советская энциклопедия», 1984]
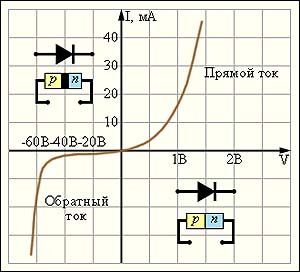
Вольт-амперная характеристика диода
[http://fizika.ayp.ru/4/4_14.html]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
- current versus voltage curve
- current-voltage characteristic
- current-voltage curve
- current-voltage diagram
- current/voltage diagram
- CVD
- E-I characteristic
- natural characteristic
- VI characteristic
- volt-ampere characteristic
- volt-amps diagram
- volt-current plot|voltage-current plot
- volt-current relationship
- voltage-current characteristic
- voltage-current relationship
DE
- I-U-Charakteristik
- I-U-Kennlinie
- Spannungs-Strom-Charakteristik
- Strom-Spannungs-Kennlinie
- Strom-Spannungs-Verhalten
- Stromspannungskennlinie
- U-I-Kennlinie
- Voltamperecharakteristik
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > caractéristique courant-tension
-
11 caractéristique intensité-tension
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость электрического напряжения на выводах элемента электрической цепи от электрического тока в нем.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость тока от приложенного к элементу электрич. цепи напряжения или зависимость падения напряжения на элементе электрич. цепи от протекающего через него тока. Если сопротивление элемента не зависит от тока, то В.-а. х.—прямая линия, проходящая через начало координат. В.-а. х. нелинейных элементов электрич. цепи (электровакуумные, газоразрядные и твёрдотельные приборы) имеют нелинейные участки и разнообразную форму (N-образные В.-а. х., S-образные и т. п.).
[Физический энциклопедический словарь. М.: «Советская энциклопедия», 1984]

Вольт-амперная характеристика диода
[http://fizika.ayp.ru/4/4_14.html]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
- current versus voltage curve
- current-voltage characteristic
- current-voltage curve
- current-voltage diagram
- current/voltage diagram
- CVD
- E-I characteristic
- natural characteristic
- VI characteristic
- volt-ampere characteristic
- volt-amps diagram
- volt-current plot|voltage-current plot
- volt-current relationship
- voltage-current characteristic
- voltage-current relationship
DE
- I-U-Charakteristik
- I-U-Kennlinie
- Spannungs-Strom-Charakteristik
- Strom-Spannungs-Kennlinie
- Strom-Spannungs-Verhalten
- Stromspannungskennlinie
- U-I-Kennlinie
- Voltamperecharakteristik
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > caractéristique intensité-tension
-
12 caractéristique tension-courant
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость электрического напряжения на выводах элемента электрической цепи от электрического тока в нем.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость тока от приложенного к элементу электрич. цепи напряжения или зависимость падения напряжения на элементе электрич. цепи от протекающего через него тока. Если сопротивление элемента не зависит от тока, то В.-а. х.—прямая линия, проходящая через начало координат. В.-а. х. нелинейных элементов электрич. цепи (электровакуумные, газоразрядные и твёрдотельные приборы) имеют нелинейные участки и разнообразную форму (N-образные В.-а. х., S-образные и т. п.).
[Физический энциклопедический словарь. М.: «Советская энциклопедия», 1984]

Вольт-амперная характеристика диода
[http://fizika.ayp.ru/4/4_14.html]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
- current versus voltage curve
- current-voltage characteristic
- current-voltage curve
- current-voltage diagram
- current/voltage diagram
- CVD
- E-I characteristic
- natural characteristic
- VI characteristic
- volt-ampere characteristic
- volt-amps diagram
- volt-current plot|voltage-current plot
- volt-current relationship
- voltage-current characteristic
- voltage-current relationship
DE
- I-U-Charakteristik
- I-U-Kennlinie
- Spannungs-Strom-Charakteristik
- Strom-Spannungs-Kennlinie
- Strom-Spannungs-Verhalten
- Stromspannungskennlinie
- U-I-Kennlinie
- Voltamperecharakteristik
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > caractéristique tension-courant
-
13 caractéristique voltampère
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость электрического напряжения на выводах элемента электрической цепи от электрического тока в нем.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость тока от приложенного к элементу электрич. цепи напряжения или зависимость падения напряжения на элементе электрич. цепи от протекающего через него тока. Если сопротивление элемента не зависит от тока, то В.-а. х.—прямая линия, проходящая через начало координат. В.-а. х. нелинейных элементов электрич. цепи (электровакуумные, газоразрядные и твёрдотельные приборы) имеют нелинейные участки и разнообразную форму (N-образные В.-а. х., S-образные и т. п.).
[Физический энциклопедический словарь. М.: «Советская энциклопедия», 1984]

Вольт-амперная характеристика диода
[http://fizika.ayp.ru/4/4_14.html]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
- current versus voltage curve
- current-voltage characteristic
- current-voltage curve
- current-voltage diagram
- current/voltage diagram
- CVD
- E-I characteristic
- natural characteristic
- VI characteristic
- volt-ampere characteristic
- volt-amps diagram
- volt-current plot|voltage-current plot
- volt-current relationship
- voltage-current characteristic
- voltage-current relationship
DE
- I-U-Charakteristik
- I-U-Kennlinie
- Spannungs-Strom-Charakteristik
- Strom-Spannungs-Kennlinie
- Strom-Spannungs-Verhalten
- Stromspannungskennlinie
- U-I-Kennlinie
- Voltamperecharakteristik
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > caractéristique voltampère
-
14 fonction tension-courant
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость электрического напряжения на выводах элемента электрической цепи от электрического тока в нем.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
[ОАО РАО "ЕЭС России" СТО 17330282.27.010.001-2008]
вольт-амперная характеристика
Зависимость тока от приложенного к элементу электрич. цепи напряжения или зависимость падения напряжения на элементе электрич. цепи от протекающего через него тока. Если сопротивление элемента не зависит от тока, то В.-а. х.—прямая линия, проходящая через начало координат. В.-а. х. нелинейных элементов электрич. цепи (электровакуумные, газоразрядные и твёрдотельные приборы) имеют нелинейные участки и разнообразную форму (N-образные В.-а. х., S-образные и т. п.).
[Физический энциклопедический словарь. М.: «Советская энциклопедия», 1984]

Вольт-амперная характеристика диода
[http://fizika.ayp.ru/4/4_14.html]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
- current versus voltage curve
- current-voltage characteristic
- current-voltage curve
- current-voltage diagram
- current/voltage diagram
- CVD
- E-I characteristic
- natural characteristic
- VI characteristic
- volt-ampere characteristic
- volt-amps diagram
- volt-current plot|voltage-current plot
- volt-current relationship
- voltage-current characteristic
- voltage-current relationship
DE
- I-U-Charakteristik
- I-U-Kennlinie
- Spannungs-Strom-Charakteristik
- Strom-Spannungs-Kennlinie
- Strom-Spannungs-Verhalten
- Stromspannungskennlinie
- U-I-Kennlinie
- Voltamperecharakteristik
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > fonction tension-courant
-
15 courant de charge
зарядный ток конденсатора
Ток, проходящий через конденсатор при его зарядке.
[ ГОСТ 21415-75]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
ток нагрузки
-EN
load current
current flowing through the line conductor/s
[IEC 61557-13, ed. 1.0 (2011-07)]
load current
the r.m.s. value of the current in any winding under service conditions
[IEC 60076-1, ed. 3.0 (2011-04)]
load current
current to which the devices are subjected to produce power loss P
[IEC 60749-34, ed. 2.0 (2010-10)]FR
courant de charge
courant circulant à travers le (les) conducteur(s) de ligne
[IEC 61557-13, ed. 1.0 (2011-07)]
courant de charge
<>la valeur efficace vraie (r.m.s.) du courant dans tout enroulement en conditions de service
[IEC 60076-1, ed. 3.0 (2011-04)]
courant de charge
courant auquel sont soumis les dispositifs pour produire la perte de puissance P
[IEC 60749-34, ed. 2.0 (2010-10)]Параллельные тексты EN-RU
If it is left ON or OFF for a long time, it is recommended to switch load current on a regular basis.
[LS Industrial Systems]Если (автоматический выключатель) продолжительное время находится во включенном или отключенном состоянии, то рекомендуется периодически коммутировать этим выключателем ток нагрузки.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
FR
D. Ladestrom
E. Charging current
F. Courant de charge
Ток, проходящий через конденсатор при его зарядке
Источник: ГОСТ 21415-75: Конденсаторы. Термины и определения оригинал документа
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant de charge
-
16 courant de défaut à la terre
ток замыкания на землю
Ток повреждения, проходящий в землю через место замыкания.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]
ток замыкания на землю
Электрический ток, протекающий в Землю, открытую и стороннюю проводящие части и защитный проводник при повреждении изоляции токоведущей части.
Примечание – В Международном электротехническом словаре используют термин «ток повреждения на землю».
При повреждении изоляции токоведущей части резко уменьшается сопротивление между этой токоведущей частью, с одной стороны, и Землёй, открытыми, сторонними проводящими частями и защитными проводниками, с другой стороны. В результате этого резко увеличивается величина электрического тока, стекающего с токоведущей части в Землю, а также в проводящие части, соединённые защитными проводниками с заземляющим устройством электроустановки здания и с заземлённой токоведущей частью источника питания. Подобный электрический ток аварийного режима электроустановки здания в нормативной и правовой документации называют током замыкания на землю.
Путь, по которому может протекать ток замыкания на землю, зависит от типа заземления системы. Если произошло повреждение основной изоляции опасной токоведущей части электрооборудования класса I и возникло её замыкание на открытую проводящую часть, то в электроустановке здания, соответствующей типам заземления системы TT и IT, ток замыкания на землю через повреждённую изоляцию протекает из токоведущей части в открытую проводящую часть. Далее из открытой проводящей части по защитному проводнику, главной заземляющей шине, заземляющим проводникам и заземлителю электрический ток протекает в локальную землю. Если электроустановка здания соответствует типам заземления системы TN, преобладающая часть тока замыкания на землю протекает не в локальную землю, а по защитным проводникам и по PEN-проводникам электроустановки здания и низковольтной распределительной электрической сети протекает к заземлённой токоведущей части источника питания.
[] http://www.volt-m.ru/glossary/letter/%D2/view/81/EN
earth fault current
current flowing to earth due to an insulation fault
[IEV number 442-01-23]FR
courant de défaut à la terre
courant qui s'écoule à la terre lors d'un défaut d'isolement
[IEV number 442-01-23]Параллельные тексты EN-RU The earth fault current starts as a localized arc at the point where the insulation has failed; this arc is characterized by a rather modest current level of the order of tens of milliamps. Subsequently, the fault evolves, more or less rapidly, to become a true earth-phase fault. If not rapidly interrupted by protection devices, this fault may end up affecting all the phases, creating a three-phase shortcircuit with earth contact.
[ABB]Ток замыкания на землю возникает в зоне повреждения изоляции в виде локальной дуги. Эта дуга характеризуется относительно небольшим значением тока порядка десятков миллиампер. Со временем зона повреждения изоляции постепенно увеличивается, и образуется однофазное замыкание на землю. Если ток не будет своевременно отключен устройством защиты, то эта неисправность в итоге может затронуть все фазные проводники и привести к трехфазному короткому замыканию на землю.
[Перевод Интент]Therefore, the first consequence of the earth fault current is the damage caused to the plant, whether due to the modest initial arc currents which, because of the difficulty in detection by the overcurrent releases may continue for long periods of time and start a fire, or due to the shortcircuit that develops after the integrity of the entire plant has been jeopardized.
[ABB]Таким образом, ток замыкания на землю может повредить электроустановку. Сначала возникает электрическая дуга с небольшим током, который максимальный расцепитель тока обнаружить не в состоянии, вследствие чего этот ток может протекать длительное время и привести к пожару. Кроме того, может возникнуть короткое замыкание, способное полностью вывести электроустановку из строя.
[Перевод Интент]Another important consequence of the earth fault current involves the danger to persons caused by indirect contact, i.e. following the contact with exposed-conductive-parts that have been energized accidentally due to a decay in the insulation.
[ABB]Другим последствием тока замыкания на землю является опасность косвенного прикосновения, т. е. прикосновения человека к открытым проводящим частям, оказавшимся вследствие повреждения изоляции под напряжением.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant de défaut à la terre
-
17 disjoncteur à protection par courant différentiel résiduel incorporée
- автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, предназначенный для включения, проведения и отключения токов при нормальных условиях электрической цепи, а также отключения электрической цепи в случае, когда значение дифференциального тока достигает заданной величины в определенных условиях.
[Перевод Интент]EN
residual current-operated circuit-breaker
mechanical switching device designed to make, carry and break currents under normal service conditions and to cause the opening of the contacts when the residual current attains a given value under specified conditions.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]FR
interrupteur à courant différentiel résiduel
appareil mécanique de connexion destiné à établir, supporter et couper des courants dans les conditions de service normales et à provoquer l'ouverture des contacts quand le courant différentiel atteint, dans des conditions spécifiées, une valeur donnée.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
- автоматический выключатель остаточных токов
- автоматический выключатель с функцией защиты от тока утечки
- автоматический выключатель, управляемый остаточным током
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
- CBR
- circuit breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker with integrated residual current protection
- earth leakage circuit breaker
- ELCB
- RCCB
- residual current circuit breaker
- residual current circuit-breaker
- residual current-operated circuit breaker
- residual current-operated circuit-breaker
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > disjoncteur à protection par courant différentiel résiduel incorporée
-
18 DPR
- автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, предназначенный для включения, проведения и отключения токов при нормальных условиях электрической цепи, а также отключения электрической цепи в случае, когда значение дифференциального тока достигает заданной величины в определенных условиях.
[Перевод Интент]EN
residual current-operated circuit-breaker
mechanical switching device designed to make, carry and break currents under normal service conditions and to cause the opening of the contacts when the residual current attains a given value under specified conditions.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]FR
interrupteur à courant différentiel résiduel
appareil mécanique de connexion destiné à établir, supporter et couper des courants dans les conditions de service normales et à provoquer l'ouverture des contacts quand le courant différentiel atteint, dans des conditions spécifiées, une valeur donnée.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
- автоматический выключатель остаточных токов
- автоматический выключатель с функцией защиты от тока утечки
- автоматический выключатель, управляемый остаточным током
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
- CBR
- circuit breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker with integrated residual current protection
- earth leakage circuit breaker
- ELCB
- RCCB
- residual current circuit breaker
- residual current circuit-breaker
- residual current-operated circuit breaker
- residual current-operated circuit-breaker
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > DPR
-
19 interrupteur à courant différentiel résiduel
- автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
автоматический выключатель, управляемый дифференциальным током
Контактный коммутационный аппарат, предназначенный для включения, проведения и отключения токов при нормальных условиях электрической цепи, а также отключения электрической цепи в случае, когда значение дифференциального тока достигает заданной величины в определенных условиях.
[Перевод Интент]EN
residual current-operated circuit-breaker
mechanical switching device designed to make, carry and break currents under normal service conditions and to cause the opening of the contacts when the residual current attains a given value under specified conditions.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]FR
interrupteur à courant différentiel résiduel
appareil mécanique de connexion destiné à établir, supporter et couper des courants dans les conditions de service normales et à provoquer l'ouverture des contacts quand le courant différentiel atteint, dans des conditions spécifiées, une valeur donnée.
[IEC 62335, ed. 1.0 (2008-07)]Недопустимые, нерекомендуемые
- автоматический выключатель остаточных токов
- автоматический выключатель с функцией защиты от тока утечки
- автоматический выключатель, управляемый остаточным током
Тематики
Классификация
>>>Обобщающие термины
Синонимы
EN
- CBR
- circuit breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker incorporating residual current protection
- circuit-breaker with integrated residual current protection
- earth leakage circuit breaker
- ELCB
- RCCB
- residual current circuit breaker
- residual current circuit-breaker
- residual current-operated circuit breaker
- residual current-operated circuit-breaker
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > interrupteur à courant différentiel résiduel
-
20 courant présumé
ожидаемый ток
Ток, который будет в цепи, если коммутационный аппарат зашунтироватъ проводником с пренебрежимо малым сопротивлением.
[ ГОСТ 17703-72]EN
prospective current
the current that would flow in the circuit, if each main current path of the switching device and of the overcurrent protective device, if any, were replaced by a conductor of negligible impedance
NOTE – The prospective current can be qualified in the same manner as an actual current, for example: prospective breaking current, prospective peak current, prospective residual current, etc.
[IEV number 442-01-47]FR
courant présumé
courant qui circulerait dans le circuit, si chaque voie principale de courant du dispositif de coupure et du dispositif éventuel de protection contre les surintensités était remplacée par un conducteur d'impédance négligeable
NOTE – Le courant présumé peut être qualifié de la même façon qu'un courant réel, par exemple courant de coupure présumé, courant de crête présumé, courant différentiel présumé, etc.
[IEV number 442-01-47]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > courant présumé
См. также в других словарях:
Current TV — s official logo Launched August 1, 2005 Owned by Current Media, Inc. Slogan Your World. View. Headquarters San Francisco, California Website … Wikipedia
Current 93 — 2007 г. Основная информация … Википедия
Current — may refer to: Contents 1 Ongoing events 2 Science and Mathematics 3 Business 4 Ships 5 Media … Wikipedia
Current 93 — in 2007 Background information Origin Britain Genres Apo … Wikipedia
Current 93 — bei einem Auftritt am 19. Mai 2007 Current 93 ist ein britisches Musikprojekt, das 1982 von David Tibet (Geburtsname: David Michael Bunting) gegründet wurde. Den Namen „Tibet“ erhielt er von seinem damaligen Weggefährten Genesis P Orridge… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Current 93 — en 2007 Current 93 est un groupe britannique de musique expérimentale formé en 1982 par David Tibet (né David Michael Bunting, rebaptisé Tibet par Genesis P Orridge peu avant la création du groupe) Sommaire … Wikipédia en Français
current — I adjective being done, belonging to the time, concurrent, contemporaneous, contemporary, customary, existent, existing, hie, immediate, in fashion, in style, in the fad, in vogue, instant, latest, latter day, new, occurring, of the moment, of… … Law dictionary
Current 93 — Saltar a navegación, búsqueda Current 93 Información personal Origen Londres, Reino Unido … Wikipedia Español
Current — Cur rent (k?r rent), a. [OE. currant, OF. curant, corant, p. pr. of curre, corre, F. courre, courir, to run, from L. currere; perh. akin to E. horse. Cf. {Course}, {Concur}, {Courant}, {Coranto}.] 1. Running or moving rapidly. [Archaic] [1913… … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English
Current — TV Current TV est une chaîne télévisée américaine fondée par l ancien vice président américain Al Gore, l avocat Joel Hyatt et une équipe d industriels et de jeunes impliqués dans le monde des médias. Depuis le 12 mars 2007, les abonnés … Wikipédia en Français
current — cur‧rent [ˈkʌrənt ǁ ˈkɜːr ] adjective [only before a noun] happening, existing, or true now: • the current world price for crude oil • the budget for the current year * * * Ⅰ. current UK US /ˈkʌrənt/ adjective [usually before noun] ► happening or … Financial and business terms
