-
41 Perkins, Jacob
[br]b. 9 July 1766 Newburyport, Massachusetts, USAd. 30 July 1849 London, England[br]American inventor of a nail-making machine and a method of printing banknotes, investigator of the use of steam at very high pressures.[br]Perkins's occupation was that of a gold-and silversmith; while he does not seem to have followed this after 1800, however, it gave him the skills in working metals which he would continue to employ in his inventions. He had been working in America for four years before he patented his nail-making machine in 1796. At the time there was a great shortage of nails because only hand-forged ones were available. By 1800, other people had followed his example and produced automatic nail-making machines, but in 1811 Perkins' improved machines were introduced to England by J.C. Dyer. Eventually Perkins had twenty-one American patents for a range of inventions in his name.In 1799 Perkins invented a system of engraving steel plates for printing banknotes, which became the foundation of modern siderographic work. It discouraged forging and was adopted by many banking houses, including the Federal Government when the Second United States Bank was inaugurated in 1816. This led Perkins to move to Philadelphia. In the intervening years, Perkins had improved his nail-making machine, invented a machine for graining morocco leather in 1809, a fire-engine in 1812, a letter-lock for bank vaults and improved methods of rolling out spoons in 1813, and improved armament and equipment for naval ships from 1812 to 1815.It was in Philadelphia that Perkins became interested in the steam engine, when he met Oliver Evans, who had pioneered the use of high-pressure steam. He became a member of the American Philosophical Society and conducted experiments on the compressibility of water before a committee of that society. Perkins claimed to have liquified air during his experiments in 1822 and, if so, was the real discoverer of the liquification of gases. In 1819 he came to England to demonstrate his forgery-proof system of printing banknotes, but the Bank of England was the only one which did not adopt his system.While in London, Perkins began to experiment with the highest steam pressures used up to that time and in 1822 took out his first of nineteen British patents. This was followed by another in 1823 for a 10 hp (7.5 kW) engine with only 2 in. (51 mm) bore, 12 in. (305 mm) stroke but a pressure of 500 psi (35 kg/cm2), for which he claimed exceptional economy. After 1826, Perkins abandoned his drum boiler for iron tubes and steam pressures of 1,500 psi (105 kg/cm2), but the materials would not withstand such pressures or temperatures for long. It was in that same year that he patented a form of uniflow cylinder that was later taken up by L.J. Todd. One of his engines ran for five days, continuously pumping water at St Katherine's docks, but Perkins could not raise more finance to continue his experiments.In 1823 one his high-pressure hot-water systems was installed to heat the Duke of Wellington's house at Stratfield Saye and it acquired a considerable vogue, being used by Sir John Soane, among others. In 1834 Perkins patented a compression ice-making apparatus, but it did not succeed commercially because ice was imported more cheaply from Norway as ballast for sailing ships. Perkins was often dubbed "the American inventor" because his inquisitive personality allied to his inventive ingenuity enabled him to solve so many mechanical challenges.[br]Further ReadingHistorical Society of Pennsylvania, 1943, biography which appeared previously as a shortened version in the Transactions of the Newcomen Society 24.D.Bathe and G.Bathe, 1943–5, "The contribution of Jacob Perkins to science and engineering", Transactions of the Newcomen Society 24.D.S.L.Cardwell, 1971, From Watt to Clausius. The Rise of Thermodynamics in the Early Industrial Age, London: Heinemann (includes comments on the importance of Perkins's steam engine).A.F.Dufton, 1940–1, "Early application of engineering to warming of buildings", Transactions of the Newcomen Society 21 (includes a note on Perkins's application of a high-pressure hot-water heating system).RLH -
42 Staite, William Edwards
[br]b. 19 April 1809 Bristol, Englandd. 26 September 1854 Caen, France[br]English inventor who did much to popularize electric lighting in early Victorian England and demonstrated the first self-regulating arc lamp.[br]Before devoting the whole of his attention to the electric light, Staite was a partner in a business of iron merchants and patented a method of obtaining extracts and essences. From 1834 he attempted to produce a continuous light by electricity. The first public exhibition of Staite's arc lamp incorporating a fixed-rate clockwork mechanism was given in 1847 to the Sunderland Literary and Philosophical Society. He also demonstrated an incandescent lamp with an iridioplatinum filament. Sir Joseph Wilson Swan recorded that it was attending lectures by Staite in Sunderland, Newcastle and Carlisle that started him on the quest which many years later was to lead to his incandescent lamp.In association with William Petrie (1821–1904), Staite made an important advance in the development of arc lamps by introducing automatic regulation of the carbon rods by way of an electromagnet. This was the first of many self-regulating arc lamps that were invented during the nineteenth century employing this principle. A contributory factor in the success of Staite's lamp was the semi enclosure of the arc in a transparent vessel that reduced the consumption of carbons, a feature not used again until the 1890s. His patents included processes for preparing carbons and the construction of primary cells for arc lighting. An improved lamp used by Staite in a theatrical production at Her Majesty's Theatre, London, in April 1849 may be considered the first commercial success of the electric light in England. In spite of the limitations imposed by the use of primary cells as the only available source of power, serious interest in this system of electric lighting was shown by railway companies and dock authorities. However, after he had developed a satisfactory arc lamp, an end to these early experiments was brought about by Staite's death.[br]BibliographyJuly 1847, British patent no. 1,1783 (electromagnetic regulation of an arc lamp).His manuscript "History of electric light" is in the Institution of Electrical Engineers archives.Further ReadingJ.J.Fahie, 1902, "Staite and Petrie's electric light 1846–1853", Electrical Engineer 30:297–301, 337–40, 374–6 (a detailed reliable account).G.Woodward, 1989, "Staite and Petrie: pioneers of electric lighting", Proceedings of the Institution of Electrical Engineers 136 (Part A): 290–6 GWBiographical history of technology > Staite, William Edwards
-
43 метод испытания в бомбе
Русско-английский военно-политический словарь > метод испытания в бомбе
-
44 определение
блок автоматического определения дальностиautomatic range unitбортовая система определения массы и центровкиonboard weight and balance systemвизир для определения сносаdrift sight(в полете) визуальное определение местоположенияvisual fixingзамер с целью определения положенияspot measurementконтрольная точка для определения местоположенияmetering fixметод определения положенияfixing methodопределение дальностиrangingопределение дальности радиолокационным методомradar rangingопределение местонахождения воздушного судна по звездамastrofixопределение местоположения1. fixing2. position fixing определение местоположения по наземным ориентирамvisual ground fixingопределение местоположения по пеленгу одной станцииone-station fixingопределение местоположения по пройденному пути и курсуrange-bearing fixingопределение местоположения с помощью радиосредстваradio fixingопределение положения1. position-finding2. position indication определение положения счислением путиreckoningошибка при визуальном определении местоположенияobservation errorрадиолокационный метод определения параметров ветраrawinсветовое устройство для определения цветоощущенияcolor perception lanternсредства определения траекторииtrack-defining aidsточное определение положенияspotting(в процессе полета) точность определения местоположенияposition accuracy -
45 путем
путь сущwayавтомат счисления пути1. automatic dead reckoning computer2. air-mileage unit блок индикатора оставшегося путиalong track display unitблок индикатора отклонения от линии путиacross track display unitвоздушная яма на пути полетаin flight bumpвосстанавливать заданную линию путиreestablish the trackвыбирать кратчайший путьcut shortвывод на линию путиtracking guidanceдлина пути распространения звукаsound propagation distanceзаданная линия путиintended trackизменять линию путиchange the trackиндикатор отклонения от линии путиacross track displayиспытание путем имитации полетаsimulated flight testкартографирование путем радиолокационного обзора местностиlong range mappingконтроль состояния посевов по пути выполнения основного заданияassociated crop control operationлиния заданного пути1. track reference2. desired track 3. course line линия огней пути руленияsteering barлиния путиtrackлиния пути относительно координатной сеткиgrid trackлиния пути полетаflight trackлиния пути по локсодромииrhumb-line trackлиния пути по схеме с двумя спаренными разворотамиrace trackлиния пути приближенияinbound trackлиния пути при взлетеtakeoff trackлиния пути удаленияoutbound trackлиния пути установленной схемыprocedure trackмагнитная ортодромическая линия путиmagnetic great circle trackметод счисления пути1. dead reckoning method2. dead-reckoning technique навигация методом счисления путиdead-reckoning navigationопределение местоположения по пройденному пути и курсуrange-bearing fixingопределение положения счислением путиreckoningотклонение от линии путиacross-track displacementотклонение от прямого путиobliquityположение, определенное методом счисления путиdead-reckoned positionпрепятствие на пути полетаair obstacleпроизводить счисление путиdead-reckonпротивопожарное патрулирование по пути выполнения основного заданияassociated fire control operationпутем изменения курсаby altering the headingрасчетное время в путиestimated time en-routeсчисление путиdead reckoningсчисление пути полетаflight dead reckoningтормозной путьbrake-wayуказатель автомата счисления путиdead-reckoning indicatorуказатель оставшегося путиdistance-to-go indicatorуказатель пройденного путиdistance flown indicatorустанавливать кратчайший путьbeat a shorter partфактическая линия путиtrue trackхарактеристики наведения по линии путиtrack-defining characteristics -
46 путь
путь сущwayавтомат счисления пути1. automatic dead reckoning computer2. air-mileage unit блок индикатора оставшегося путиalong track display unitблок индикатора отклонения от линии путиacross track display unitвоздушная яма на пути полетаin flight bumpвосстанавливать заданную линию путиreestablish the trackвыбирать кратчайший путьcut shortвывод на линию путиtracking guidanceдлина пути распространения звукаsound propagation distanceзаданная линия путиintended trackизменять линию путиchange the trackиндикатор отклонения от линии путиacross track displayконтроль состояния посевов по пути выполнения основного заданияassociated crop control operationлиния заданного пути1. track reference2. course line 3. desired track линия огней пути руленияsteering barлиния путиtrackлиния пути относительно координатной сеткиgrid trackлиния пути полетаflight trackлиния пути по локсодромииrhumb-line trackлиния пути по схеме с двумя спаренными разворотамиrace trackлиния пути приближенияinbound trackлиния пути при взлетеtakeoff trackлиния пути удаленияoutbound trackлиния пути установленной схемыprocedure trackмагнитная ортодромическая линия путиmagnetic great circle trackметод счисления пути1. dead reckoning method2. dead-reckoning technique навигация методом счисления путиdead-reckoning navigationопределение местоположения по пройденному пути и курсуrange-bearing fixingопределение положения счислением путиreckoningотклонение от линии путиacross-track displacementотклонение от прямого путиobliquityположение, определенное методом счисления путиdead-reckoned positionпрепятствие на пути полетаair obstacleпроизводить счисление путиdead-reckonпротивопожарное патрулирование по пути выполнения основного заданияassociated fire control operationрасчетное время в путиestimated time en-routeсчисление путиdead reckoningсчисление пути полетаflight dead reckoningтормозной путьbrake-wayуказатель автомата счисления путиdead-reckoning indicatorуказатель оставшегося путиdistance-to-go indicatorуказатель пройденного путиdistance flown indicatorустанавливать кратчайший путьbeat a shorter partфактическая линия путиtrue trackхарактеристики наведения по линии путиtrack-defining characteristics -
47 сигнал
сигнал сущ1. pulse2. signal визуальный сигналvisual signalвходной сигнал1. actuating signal2. input signal выдавать сигналproduce the signalвыходной сигналoutput signalвычислитель воздушных сигналовair data computerдатчик воздушных сигналовair-data sensorзадающий сигналdrive signalзвуковой сигнал1. acoustical signal2. audible signal калибровочный сигналcalibration signalкод визуального сигнала земля - воздухground-air visual signal codeкодированный сигналcoded signalкодовый сигналcode signalкодовый сигнал "терплю бедствие"maydayложный сигналfalse signalмеждународная частота сигнала бедствияinternational distress frequencyметод подачи сигналовsignaling methodназемный аэродромный сигналaerodrome ground signalназемный визуальный сигналvisual ground signalобнаружение сигналаclock acquisitionобратный сигналanswerbackогибающая суммарного сигналаsummary signal envelopeожидание сигнала к взлетуground holdопознавание сигналаsignal determinationопознавание сигналовidentification of signalsопознавательный кодовый сигналselective identification featureослабление сигналов в атмосфереatmospheric lossответный сигналbeacon reply signalотраженный радиолокационный сигналradar echoотраженный сигналback echoпиротехнический сигналpyrotechnic signalпогрешность сигнала наведенияguidance signal errorподавать сигналsupply the signalполет по сигналам с землиdirected reference flightпредупредительный сигнал1. warning signal2. attention signal прекращать подачу сигналаcancel the signalпреобразователь сигнала по тангажуpitch transformerприводной сигналhoming signalприемник сигналов всенаправленного радиомаякаomnirange receiverпринимать сигналreceive the signalпринятый сигналlocked-on signalпродолжительность единичного звукового сигналаunit noise durationпропускать сигналpass the signalрасшифровка сигналаinterpretation of the signalсветовой сигналlight signalсветовой сигнал готовностиarming lightсветовой сигнал готовности ВППrunway clearance lightсветовой сигнал лети вышеfly-up lightсветовой сигнал лети нижеfly-down lightсглаживание сигналаsignal smoothingсглаживать сигналsmooth the signalсигнал автоматического парирования сносаautomatic decrab signalсигнал бедствияdistress signalсигнал бедствия в коде ответчикаsquawk maydayсигнал возобновления движенияgo signalсигнал входа в глиссадуon-slope signalсигнал вызоваcall signalсигнал движение разрешаюpositive go signalсигнал действий в полетеflight urgency signalсигнал запроса1. interrogation signal2. demand signal сигнал земля - воздухground-air signalсигнал исправности системыOK signalсигнал ложной тревогиfalse alarmсигнал между воздушными судами в полетеair-to-air signalсигнал обратной связиfeedback signalсигнал о местоположенииposition pulseсигнал о неисправности цепиcircuit alarmсигнал опасной высотыaltitude alert signalсигнал оповещения об опасности столкновенияcollision warning alarmсигнал опознаванияidentification signalсигнал отклонения от глиссады1. off-slope signal2. glide slope error сигнал отклонения от курсаoff-course signalсигнал отклонения от курса на маякlocalizer-error signalсигнал пожарной тревогиfire callсигнал полета по курсуon-course signalсигнал прекращения движенияstop signalсигнал рассогласованияerror signalсигнал синхронизации по времениsynchronized time signalсигнал состояния готовностиsteady state signalсигнал с применением полотнищаpaulin signalсигнал срочности1. urgency signal2. priority alarm сигнал точного времениtickсигнал тревоги1. alarm signal2. alarm сигналы готовностиstandby squawkсигналы управления движениемmarshalling signals(воздушных судов на аэродроме) синусоидальный сигналsinusoidal signalсистема сбора воздушных сигналовair data computer systemтрансформатор сигнала по кренуroll transformerтрансформатор сигнала по курсуyaw transformerуправляющий сигналcontrol signalусиливать сигналamplify the signalусилитель сигналов коррекцииslaving amplifierфиксировать сигналpick up the signalцветной дымовой сигналcolored smoke signalчастота сигнала бедствияdistress frequencyчеткость курсового сигналаcourse sharpnessчувствительность к отклонению по сигналам курсового маякаlokalizer displacement sensitivityширокополосный сигналbroadband signal -
48 счисление
автомат счисления пути1. air-mileage unit2. automatic dead reckoning computer метод счисления пути1. dead-reckoning technique2. dead reckoning method навигация методом счисления путиdead-reckoning navigationопределение положения счислением путиreckoningположение, определенное методом счисления путиdead-reckoned positionпроизводить счисление путиdead-reckonпрокладчик курса методом счисленияdead-reckoning tracerсчисление путиdead reckoningсчисление пути полетаflight dead reckoningуказатель автомата счисления путиdead-reckoning indicator -
49 распределительный щиток
распределительный щиток
щиток
-
[ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001]-
по назначению
-
исполнению, относящемуся к виду установки:
-
наличию отключающего аппарата на вводе:
- с аппаратом:
- без аппарата;
-
наличию учета электроэнергии:
- со счетчиком;
- без счетчика;
-
по наличию слаботочного отсека
- количеству защитных аппаратов групповых цепей;
-
виду защитных аппаратов групповых цепей
- автоматические выключатели;
- предохранители;
-
наличию устройств защитного отключения:
- с УЗО;
- без УЗО;
-
способу защиты человека от поражения электрическим током:
- классы I и II по ГОСТ Р МЭК 536.
-
по числу фаз ввода в щиток
-
однофазный при Рр ≤ 11 кВт;
-
трехфазный при Рр ≥ 11 кВт или при наличии трехфазных токоприемников;
-
однофазный при Рр ≤ 11 кВт;
-
по наличию аппарата для защиты и отключения питающей цепи (стояка):
- с аппаратом (или предусмотренным местом для последующей его установки потребителем);
- без аппарата
Примечание. Рр - расчетная мощность на вводе квартиры.
[ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001] и [ ГОСТ Р 51628-2000]
Распределительные щитки (далее — щитки), применяемые в осветительных и силовых установках производственных, общественных, административных и других подобных зданий для приема и распределения электрической энергии при напряжении 380/220 и 660/380 В трехфазного переменного тока частотой 50 — 60 Гц, нечастого включения и отключения линий групповых цепей, а также для их защиты при перегрузках и коротких замыканиях.
Щитки могут устанавливаться в местах, доступных при эксплуатации неквалифицированному персоналу для выполнения коммутационных операций
Щитки, присоединяемые к трехфазным сетям с типами систем заземления TN-S, TN-C, TN-C-S, ТТ...
В щитках без отключающего аппарата на вводе должны быть зажимы для присоединения проводников питающей цепи
Дверцы щитков должны запираться на ключ
В щитках без дверец...
В щитках со счетчиками для исключения несанкционированного доступа к цепям учета электроэнергии (от входных зажимов вводного аппарата до ввода в счетчик) должны предусматриваться конструктивные элементы с возможностью их опломбирования
На оперативной панели щитка должна выполняться маркировка защитных аппаратов групповых цепей порядковыми номерами
В качестве аппаратов защиты групповых линий используются модульные автоматические выключатели с шириной модуля 18 мм.
На вводе и групповых линиях щитка могут быть установлены устройства защитного отключения с отключающим дифференциальным током на вводе - 30; 100; 300 мА, на групповых линиях - 10; 30 мА.
[ ГОСТ Р 51778-2001]
A panelboard as defined by the National Electrical Code is a single panel or a group of panel units designed for assembly in the form of a single panel; including buses, automatic overcurrent devices, and equipped with or without switches for the control of light, heat, or power circuits, designed to be placed in a cabinet or cutout box placed in or against a wall or partition and accessible only from the front.
Panelboards provide a compact and convenient method of grouping circuit switching and protective devices at some common point.
Panelboards may be of either the flush or the surface type (Fig. 4.125).
The flush type is used with concealed-wiring installations and has the advantage of not taking up space in the room by extending beyond the surface of the wall. Surface type boxes are used for installations employing exposed wiring.
The boxes are generally constructed of sheet steel, which must be not less than 0.053 in. (1.35 mm) in thickness.
The steel must be galvanized or be covered with some other protective coating to prevent corrosion.
Gutters are provided around the panelboards in cabinets to allow sufficient space for wiring (Figs. 4.125 and 4.126).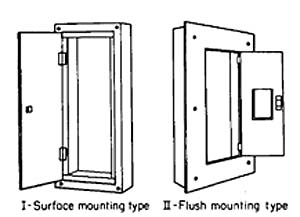
FIGURE 4.125 Panel boxes.
The Code requires that all cabinets which contain connections to more than eight conductors be provided with back or side wiring spaces. These wiring spaces must be separated from the panelboard or other devices in the cabinet by partitions so that they will be separate closed compartments, unless all wires are led from the cabinet at points directly opposite their terminal connections to the panelboard.
[American electricians’ handbook]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
Русско-английский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > распределительный щиток
-
по назначению
См. также в других словарях:
Automatic summarization — is the creation of a shortened version of a text by a computer program. The product of this procedure still contains the most important points of the original text. The phenomenon of information overload has meant that access to coherent and… … Wikipedia
Automatic link establishment — Automatic Link Establishment, commonly known as ALE, is the worldwide de facto standard for digitally initiating and sustaining HF (High Frequency) radio communications.cite web|title=Frequency Agile Systems in the MF/HF Bands |author=Telecom… … Wikipedia
Automatic Packet Reporting System — (APRS) is an amateur radio based system for real time tactical digital communications of information of immediate value in the local area. In addition, all such data is ingested into the APRS Internet system (APRS IS) and distributed globally for … Wikipedia
Automatic milking — is the milking of dairy animals without human labour.The milking processThe milking process is the collection of tasks specifically devoted to extracting milk from an animal (rather than the broader field of dairy animal husbandry). This process… … Wikipedia
Automatic image annotation — (also known as automatic image tagging) is the process by which a computer system automatically assigns metadata in the form of captioning or keywords to a digital image. This application of computer vision techniques is used in image retrieval… … Wikipedia
Automatic gain control — (AGC) is an adaptive system found in many electronic devices. The average output signal level is fed back to adjust the gain to an appropriate level for a range of input signal levels. For example, without AGC the sound emitted from an AM radio… … Wikipedia
Automatic parallelization — Automatic parallelization, also auto parallelization, autoparallelization, parallelization, or //ization (shorthand), the last two of which imply automation when used in context, refers to converting sequential code into multi threaded or… … Wikipedia
Automatic Laser Shutdown — Automatic Laser Shutdown, or ALS, is a method for assuring Laser safety in Optical Transmission Systems (Like optical SDH) registered under US Patent #6194707.ALS is a semi intelligent method which cuts the Tx line if the Rx line is inactive, and … Wikipedia
Automatic identification and data capture — (AIDC) refers to the methods of automatically identifying objects, collecting data about them, and entering that data directly into computer systems (i.e. without human involvement). Technologies typically considered as part of AIDC include bar… … Wikipedia
Automatic repeat-request — Automatic Repeat Query (ARQ) (or Automatic Repeat reQuest) is an error control method for data transmission which uses acknowledgments and timeouts to achieve reliable data transmission. An acknowledgment is a message sent by the receiver to the… … Wikipedia
Automatic frequency control — (AFC) is a method (or device) to automatically maintain a tuning of electromagnetic radiation (radio or microwave) signal to desired frequency. Assuming that a receiver is nearly tuned to the desired frequency, a circuit in the receiver develops… … Wikipedia
