-
1 Krepp-Romain
сущ.текст. креп-ромэн (ткань типа креп-жоржета с переплетением "рогожка") -
2 Crêpe romain
креп-роменDeutsch-Russische Wörterbuch der Mode und des Design > Crêpe romain
-
3 Römer
'røːmər(ɪn)m (f - Römerin); RELRomain(e) m/fRömerR75a4e003ö/75a4e003mer (in) ['rø:m3f3a8ceeɐ/3f3a8cee]<-s, -> Substantiv Maskulin(Feminin)Romain(e) Maskulin(Feminin) -
4 römisch
-
5 römisch-katholisch
'røːmɪʃka'toːlɪʃadjREL. catholique romainrömisch-katholischr75a4e003ö/75a4e003misch-kathb8b49fd9o/b8b49fd9lischcatholique romain(e) -
6 Crêpe
Deutsch-Russische Wörterbuch der Mode und des Design > Crêpe
-
7 Reich
n1) empire m2) ( Königreich) royaume mReichR136e9342ei/136e9342ch [re39291efai/e39291efç] <-[e]s, -e>1 (Imperium) empire Maskulin; Beispiel: das Dritte Reich le III7af8d89cə/7af8d89c Reich; Beispiel: das Römische Reich l'Empire romain -
8 Sisyphusarbeit
SisyphusarbeitSisyphusarbeit ['zi:zyf62c8d4f5ʊ/62c8d4f5s?arbe39291efai/e39291eft]travail Maskulin de Romain -
9 griechisch-römisch
-
10 Dimension einer Grösse
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:
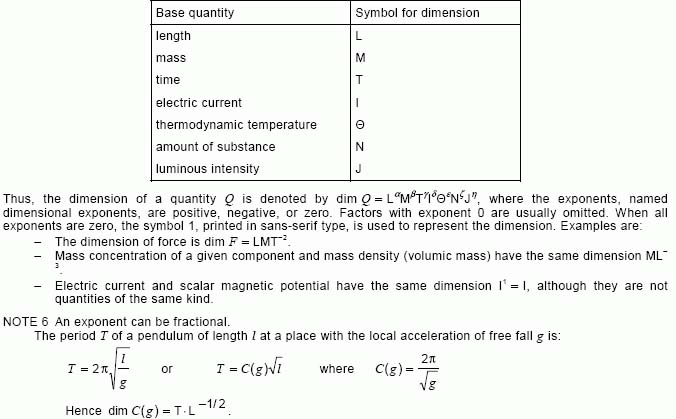
[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dimension einer Grösse
-
11 Dimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Dimension, f
-
12 Größendimension, f
размерность физической величины
размерность величины
Выражение в форме степенного одночлена, составленного из произведений символов основных физических величин в различных степенях и отражающее связь данной физической величины с физическими величинами, принятыми в данной системе величин за основные с коэффициентом пропорциональности, равным 1.
Примечания
1. Степени символов основных величин, входящих в одночлен, в зависимости от связи рассматриваемой физической величины с основными, могут быть целыми, дробными, положительными и отрицательными. Понятие размерность распространяется и на основные величины. Размерность основной величины в отношении самой себя равна единице, т.е. формула размерности основной величины совпадает с ее символом.
2. В соответствии с международным стандартом ИСО 31/0, размерность величин следует обозначать знаком dim [2]. В системе величин LMT размерность величины.x будет: dim х = LlMmTt, где L, М, Т - символы, величин, принятых за основные (соответственно длины, массы, времени).
[РМГ 29-99]EN
dimension of a quantity
quantity dimension
dimension
expression of the dependence of a quantity on the base quantities of a system of quantities as a product of powers of factors corresponding to the base quantities, omitting any numerical factor
NOTE 1 – A power of a factor is the factor raised to an exponent. Each factor is the dimension of a base quantity.
NOTE 2 – The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a base quantity is a single upper case letter in roman (upright) sans-serif type. The conventional symbolic representation of the dimension of a derived quantity is the product of powers of the dimensions of the base quantities according to the definition of the derived quantity. The dimension of a quantity Q is denoted by dim Q.
NOTE 3 – In deriving the dimension of a quantity, no account is taken of its scalar, vector or tensor character.
NOTE 4 – In a given system of quantities, – quantities of the same kind have the same dimension, – quantities of different dimensions are always of different kinds, and – quantities having the same dimension are not necessarily of the same kind. For example, in the ISQ, pressure and energy density (volumic energy) have the same dimension L–1MT–2. See also note 5.
NOTE 5 – In the International System of Quantities (ISQ), the symbols representing the dimensions of the base quantities are:

[IEV number 112-01-11]FR
dimension, f
dimension d'une grandeur, f
expression de la dépendance d’une grandeur par rapport aux grandeurs de base d'un système de grandeurs sous la forme d'un produit de puissances de facteurs correspondant aux grandeurs de base, en omettant tout facteur numérique
NOTE 1 – Une puissance d'un facteur est le facteur muni d'un exposant. Chaque facteur exprime la dimension d'une grandeur de base.
NOTE 2 – Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur de base est une lettre majuscule unique en caractère romain (droit) sans empattement. Par convention, la représentation symbolique de la dimension d'une grandeur dérivée est le produit de puissances des dimensions des grandeurs de base conformément à la définition de la grandeur dérivée. La dimension de la grandeur Q est notée dim Q.
NOTE 3 – Pour établir la dimension d'une grandeur, on ne tient pas compte du caractère scalaire, vectoriel ou tensoriel.
NOTE 4 – Dans un système de grandeurs donné, – les grandeurs de même nature ont la même dimension, – des grandeurs de dimensions différentes sont toujours de nature différente, – des grandeurs ayant la même dimension ne sont pas nécessairement de même nature. Par exemple, dans l'ISQ, la pression et l'énergie volumique ont la même dimension L–1MT–2. Voir aussi la note 5.
NOTE 5 – Dans le Système international de grandeurs (ISQ), les symboles représentant les dimensions des grandeurs de base sont:

[IEV number 112-01-11]Тематики
- метрология, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dimension einer Grösse
- Dimension, f
- Größendimension, f
FR
- dimension d'une grandeur, f
- dimension, f
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Größendimension, f
-
13 Romankalk
романцемент
Цемент на основе клинкера, получаемого обжигом не до спекания известковых и магнезиальных мергелей с суммарным содержанием кремнезёма и окиси алюминия менее 25%
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Romankalk
См. также в других словарях:
romain — romain, aine [ rɔmɛ̃, ɛn ] adj. et n. • 1080; lat. romanus 1 ♦ Qui appartient à l ancienne Rome et à son empire. ⇒ latin, 2. roman. Antiquité grecque et romaine. Empereur romain. Paix romaine. Spécialiste du droit romain (⇒ 1. romaniste) .… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Romain — may refer to:People* Jérôme Romain (born 1971), former track and field athlete * Romain Barnier (born 1976), freestyle swimmer * Romain Barras (born 1980), French decathlete * Romain Bellenger, French road racing cyclist * Romain Bussine (1830… … Wikipedia
Romain — ist: der Name mehrerer Gemeinden in Frankreich: Romain (Doubs), Gemeinde im Département Doubs Romain (Jura), Gemeinde im Département Jura Romain (Marne), Gemeinde im Département Marne Romain (Meurthe et Moselle), Gemeinde im Département Meurthe… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Romain II — Empereur byzantin Solidus représentant Constantin VII et Romain II Règne 9 … Wikipédia en Français
romain — romain, aine 1. (ro min, mè n ) adj. 1° Qui appartient à l ancienne Rome ou aux Romains. • ....Au seul aspect de la grandeur romaine, CORN. Sertor. II, 2. • Regardez moi, seigneur, comme dame romaine, CORN. ib. II, 2. • Il ne reste pas… … Dictionnaire de la Langue Française d'Émile Littré
Romain IV — Diogène Le Christ couronnant Romain et Eudoxie Romain Diogène (1032 1071) fut empereur byzantin sous le nom de Romain IV. À la mort de Constantin X, en 1067, sa femme Eudoxie devint impératrice. Elle épousa peu de temps après Romain Diogène … Wikipédia en Français
Romain — Saltar a navegación, búsqueda Romain puede referirse a: Romain, comuna francesa situada en la región de Franco Condado, departamento de Jura. Romain, comuna francesa situada en el departamento de Marne. Romain, comuna francesa situada en el… … Wikipedia Español
romain — ROMAIN, [rom]aine. adj. On ne met point ce mot comme un nom de nation, mais parce qu il a d autres usages dans la langue. On appelle, Chiffre romain, Le chiffre qui se fait avec les lettres numerales, comme C. D. I. V. X. &c. Les cadrans des… … Dictionnaire de l'Académie française
ROMAIN (J.) — ROMAIN JULES, ital. GIULIO PIPPI dit GIULIO ROMANO (1492 ou 1499 1546) Né à Rome où il se forme au contact même de la ville antique que l’on redécouvrait alors avec passion, Jules Romain est le principal collaborateur de Raphaël entre 1515 et… … Encyclopédie Universelle
Romain — (franz., spr. mäng), die französische Bezeichnung der lateinischen, geradestehenden Druckschrift, s. Antiqua … Meyers Großes Konversations-Lexikon
romain — Romain, Romanus … Thresor de la langue françoyse


